Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
French startup Ankorstore has raised a $102 million Series B funding round (€84 million). Tiger Global and Bain Capital Ventures are leading today’s funding round with existing investors Index Ventures, GFC, Alven and Aglaé also participating. This is a significant funding round, as it comes just a few months after the company raised €25 million.
If you’re not familiar with Ankorstore, the company is building a wholesale marketplace for independent shop owners. You may have noticed some highly Instagrammable shops with a selection of random items, such as household supplies, maple syrup, candles, headbands, bath salts and stationery items.
Essentially, Ankorstore helps you source those items for shop owners. It lets you buy a ton of cutesy stuff and act as a curator for your customers. Even if you’re already working with brands directly, the startup offers some advantageous terms. In addition to buying from several brands at once, Ankorstore withdraws the money from your bank account 60 days after placing an order.
On the other side of the marketplace, brands get paid upon delivery. Even if you’re just getting started, the minimum first order is €100 per brand.
And metrics have been going up and to the right. There are now 5,000 brands on Ankorstore, and 50,000 shops are buying stuff through the platform. And the best is likely ahead, as stores begin to re-open across Europe and tourism picks up again.
Ankorstore is now live across 14 different markets. The majority of the company’s revenue comes from international markets — not its home market France. The company’s co-founder Nicolas Cohen mentions the U.K., Germany, the Netherlands and Sweden as growth markets.
The total addressable market is huge, as the company has identified 800,000 independent shops across Europe that could potentially work with Ankorstore. And the success of other wholesale marketplaces, such as Faire, proves that this relatively new market is still largely untapped.
Powered by WPeMatico
Every branch of science is increasingly reliant on big data sets and analysis, which means a growing confusion of formats and platforms — more than inconvenient, this can hinder the process of peer review and replication of research. Code Ocean hopes to make it easier for scientists to collaborate by making a flexible, shareable format and platform for any and all data sets and methods, and it has raised a total of $21 million to build it out.
Certainly there’s an air of “Too many options? Try this one!” to this (and here’s the requisite relevant XKCD). But Code Ocean isn’t creating a competitor to successful tools like Jupyter or GitLab or Docker — it’s more of a small-scale container platform that lets you wrap up all the necessary components of your data and analysis in an easily shared format, whatever platform they live on natively.
The trouble appears when you need to share what you’re doing with another researcher, whether they’re on the bench next to you or at a university across the country. It’s important for replication purposes that data analysis — just like any other scientific technique — be done exactly the same way. But there’s no guarantee that your colleague will use the same structures, formats, notation, labels and so on.
That doesn’t mean it’s impossible to share your work, but it does add a lot of extra steps as would-be replicators or iterators check and double check that all the methods are the same, that the same versions of the same tools are being used in the same order, with the same settings, and so on. A tiny inconsistency can have major repercussions down the road.
Turns out this problem is similar in a way to how many cloud services are spun up. Software deployments can be as finicky as scientific experiments, and one solution to this is containers, which like tiny virtual machines include everything needed to accomplish a computing task, in a portable format compatible with many different setups. The idea is a natural one to transfer to the research world, where you can tie up all in one tidy package the data, the software used and the specific techniques and processes used to reach a given result. That, at least, is the pitch Code Ocean offers for its platform and “Compute Capsules.”
Say you’re a microbiologist looking at the effectiveness of a promising compound on certain muscle cells. You’re working in R, writing in RStudio on an Ubuntu machine, and your data are such and such collected during an in vitro observation. While you would naturally declare all this when you publish, there’s no guarantee anyone has an Ubuntu laptop with a working RStudio setup around, so even if you provide all the code, it might be for nothing.
If, however, you put it on Code Ocean, like this, it makes all the relevant code available, and capable of being inspected and run unmodified with a click, or being fiddled with if a colleague is wondering about a certain piece. It works through a single link and web app, cross platform, and can even be embedded on a webpage like a document or video. (I’m going to try to do that below, but our backend is a little finicky. The capsule itself is here.)
More than that, though, the Compute Capsule can be repurposed by others with new data and modifications. Maybe the technique you put online is a general purpose RNA sequence analysis tool that works as long as you feed it properly formatted data, and that’s something others would have had to code from scratch in order to take advantage of some platforms.
Well, they can just clone your capsule, run it with their own data and get their own results in addition to verifying your own. This can be done via the Code Ocean website or just by downloading a zip file of the whole thing and getting it running on their own computer, if they happen to have a compatible setup. A few more example capsules can be found here.
This sort of cross-pollination of research techniques is as old as science, but modern data-heavy experimentation often ends up siloed because it can’t easily be shared and verified even though the code is technically available. That means other researchers move on, build their own thing and further reinforce the silo system.
Right now there are about 2,000 public compute capsules on Code Ocean, most of which are associated with a published paper. Most have also been used by others, either to replicate or try something new, and some, like ultra-specific open source code libraries, have been used by thousands.
Naturally there are security concerns when working with proprietary or medically sensitive data, and the enterprise product allows the whole system to run on a private cloud platform. That way it would be more of an internal tool, and at major research institutions that in itself could be quite useful.
Code Ocean hopes that by being as inclusive as possible in terms of codebases, platforms, compute services and so on will make for a more collaborative environment at the cutting edge.
Clearly that ambition is shared by others, as the the company has raised $21 million so far, $6 million of which was in previously undisclosed investments and $15 million in an A round announced today. The A round was led by Battery Ventures, with Digitalis Ventures, EBSCO and Vaal Partners participating as well as numerous others.
The money will allow the company to further develop, scale and promote its platform. With luck they’ll soon find themselves among the rarefied air often breathed by this sort of savvy SaaS — necessary, deeply integrated and profitable.
Powered by WPeMatico
At long last, the Monday.com crew dropped an F-1 filing to go public in the United States. TechCrunch has long known that the company, which sells corporate productivity and communications software, has scaled north of $100 million in annual recurring revenue (ARR).
The countdown to its IPO filing — an F-1, because the company is based in Israel, rather than the S-1s filed by domestic companies — has been ticking for several quarters, so seeing Monday.com drop the document on this Monday morning was just good fun.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on Extra Crunch or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
The Exchange has been riffling through the document since it came out, and we’ve picked up on a few things to explore. We’ll start by looking at the company’s revenue growth on a historical basis to see if it has accelerated in recent quarters thanks to the pandemic. Then, we’ll turn to profitability, cash burn, share-based compensation expenses and product vision.
 We’ll wrap at the end with a summary of what we’ve learned and also make sure to check out the company’s marketing spend, because I’m sure you’ve seen its digital ads.
We’ll wrap at the end with a summary of what we’ve learned and also make sure to check out the company’s marketing spend, because I’m sure you’ve seen its digital ads.
It’s a lot to chew through, so no more dilly-dallying. Into the numbers!
As always, we’re starting with revenue growth because it’s still the single most important thing about any venture-backed company.
This is great news for the startup, its employees and its investors. From 2019 to 2020, Monday.com grew its revenues from $78.1 million to $161.1 million, or 106%.
From Q1 2020 to Q1 2021, the company’s revenues grew from $31.9 million to $59 million. That’s about 85% growth. So, by what measure do we mean that the company’s revenue growth is accelerating? Its sequential-quarter revenue growth is picking up. Observe the following:
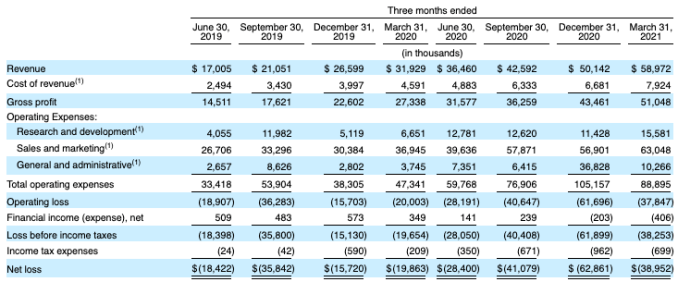
Image Credits: Monday.com F-1 filing
From Q2 2019 to Q3 2019, the company added around $4 million in revenue. From Q2 2020 to Q3 2020, that number was $6.1 million. More recently, the company’s revenue added $7.6 million from Q3 2020 to Q4 2020, which accelerated to $8.8 million from the final quarter of 2020 to the first quarter of 2021. Of course, from an ever-larger base, the company’s growth rate may decline. But the super clean and obvious expanding sequential revenue gains at the company are solid.
The fact that it added so much top line in recent quarters also helps explain why Monday.com is going public now. Sure, the markets are still near record highs and the pandemic is fading, but just look at that consistent growth! It’s investor catnip.
Powered by WPeMatico
After years in the backwaters of venture capital, edtech had a booming 2020. Not only did its products become must-haves after schools around the globe went remote, but investors also poured capital into leading projects. There was even some exit activity, with well-known edtech players like Coursera going public earlier this year.
But despite a rush of private capital — which has continued into this year, as we’ll demonstrate — edtech stocks have taken a hammering in recent weeks. So while venture capitalists and other startup investors are pumping more capital into the space in hopes of future outsize returns, the stock market is signaling that things might be heading in the other direction.
Who’s right? One investor that The Exchange spoke to noted that market turbulence is just that, and that he’s tuning into activity but not yet changing his investment strategy. At the same time, the recent volatility is worth tracking in case it’s a preview of edtech’s slowdown.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on Extra Crunch or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
Let’s look at the changing value of edtech stocks in recent months, parse some preliminary data via PitchBook that provides a good feel for the directional momentum of edtech venture capital, and try to see if there’s irrational exuberance among private investors.
You could argue that it’s public investors who are suffering from irrational pessimism and that private-market investors have the right of it. But since public markets price private markets, we tend to listen to them. Let’s go!
We’re sure that you want to get into the private-market data, so we’ll be brief in describing the public-market carnage. What follows is a digest of edtech stocks and their declines from recent highs:
Powered by WPeMatico
Cisco has been busy on the acquisition front this week, and today the company announced it was buying threat assessment platform Kenna Security, the third company it has purchased this week. The two companies did not disclose the purchase price.
With Kenna, Cisco gets a startup that uses machine learning to sort through the massive pile of threat data that comes into a security system on a daily basis and prioritizes the threats most likely to do the most damage. That could be a very useful tool these days when threats abound and it’s not always easy to know where to put your limited security resources. Cisco plans to take that technology and integrate into its SecureX platform.
Gee Rittenhouse, senior vice president and general manager of Cisco’s Security Business Group, wrote in a blog post announcing the deal with Kenna that his company is getting a product that brings together Cisco’s existing threat management capabilities with Kenna’s risk-based vulnerability management skills.
“That is why we are pleased to announce our intent to acquire Kenna Security, Inc., a recognized leader in risk-based vulnerability prioritization with over 14 million assets protected and over 12.7 billion managed vulnerabilities. Using data science and real-world threat intelligence, it has a proven ability to bring data in from a multi-vendor environment and provide a comprehensive view of IT vulnerability risk,” Rittenhouse wrote in the blog post.
The security sphere has been complex for a long time, but with employees moving to work from home because of COVID, it became even more pronounced in the last year. In a world where the threat landscape changes quickly, having a tool that prioritizes what to look at first in its arsenal could be very useful.
Kenna Security CEO Karim Toubba gave a typical executive argument for being acquired: it gives him a much bigger market under Cisco than his company could have built alone.
“Now is our opportunity to change the industry: once the acquisition is complete, we will be one step closer to delivering Kenna’s pioneering Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) platform to the more than 7,000 customers using Cisco SecureX today. This single action exponentially increases the impact Kenna’s technology will have on the way the world secures networks, endpoints and infrastructures,” he wrote in the company blog.
The company, which launched in 2010, claims to be the pioneer in the RBVM space. It raised over $98 million on a $320 million post-money valuation, according to PitchBook data. Customers include HSBC, Royal Bank of Canada, Mattel and Quest Diagnostics.
For those customers, the product will cease to be standalone at some point as the companies work together to integrate Kenna technology into the SecureX platform. When that is complete, the standalone customers will have to purchase the Cisco solution to continue using the Kenna tech.
Cisco has had a busy week on the acquisition front. It announced its intent to acquire Sedona Systems on Tuesday, Socio Labs on Wednesday and this announcement today. That’s a lot of activity for any company in a single week. The deal is expected to close in Cisco Q4 FY 2021. Kenna’s 170 employees will be joining the Security Business Group led by Rittenhouse.
Powered by WPeMatico
Orbital imagery is in demand, and if you think having daily images of everywhere on Earth is going to be enough in a few years, you need a lesson in ambition. Alba Orbital is here to provide it with its intention to provide Earth observation at intervals of 15 minutes rather than hours or days — and it just raised $3.4 million to get its next set of satellites into orbit.
Alba attracted our attention at Y Combinator’s latest demo day; I was impressed with the startup’s accomplishment of already having six satellites in orbit, which is more than most companies with space ambition ever get. But it’s only the start for the company, which will need hundreds more to begin to offer its planned high-frequency imagery.
The Scottish company has spent the last few years in prep and R&D, pursuing the goal, which some must have thought laughable, of creating a solar-powered Earth observation satellite that weighs in at less than one kilogram. The joke’s on the skeptics, however — Alba has launched a proof of concept and is ready to send the real thing up as well.
Little more than a flying camera with a minimum of storage, communication, power and movement, the sub-kilogram Unicorn-2 is about the size of a soda can, with paperback-size solar panel wings, and costs in the neighborhood of $10,000. It should be able to capture up to 10-meter resolution, good enough to see things like buildings, ships, crops, even planes.
“People thought we were idiots. Now they’re taking it seriously,” said Tom Walkinshaw, founder and CEO of Alba. “They can see it for what it is: a unique platform for capturing data sets.”
Indeed, although the idea of daily orbital imagery like Planet’s once seemed excessive, in some situations it’s quite clearly not enough.
“The California case is probably wildfires,” said Walkinshaw (and it always helps to have a California case). “Having an image once a day of a wildfire is a bit like having a chocolate teapot… not very useful. And natural disasters like hurricanes, flooding is a big one, transportation as well.”
Walkinshaw noted that they company was bootstrapped and profitable before taking on the task of launching dozens more satellites, something the seed round will enable.
“It gets these birds in the air, gets them finished and shipped out,” he said. “Then we just need to crank up the production rate.”
When I talked to Walkinshaw via video call, 10 or so completed satellites in their launch shells were sitting on a rack behind him in the clean room, and more are in the process of assembly. Aiding in the scaling effort is new investor James Park, founder and CEO of Fitbit — definitely someone who knows a little bit about bringing hardware to market.
Interestingly, the next batch to go to orbit (perhaps as soon as in a month or two, depending on the machinations of the launch provider) will be focusing on nighttime imagery, an area Walkinshaw suggested was undervalued. But as orbital thermal imaging startup Satellite Vu has shown, there’s immense appetite for things like energy and activity monitoring, and nighttime observation is a big part of that.
The seed round will get the next few rounds of satellites into space, and after that Alba will be working on scaling manufacturing to produce hundreds more. Once those start going up it can demonstrate the high-cadence imaging it is aiming to produce — for now it’s impossible to do so, though Alba already has customers lined up to buy the imagery it does get.
The round was led by Metaplanet Holdings, with participation by Y Combinator, Liquid2, Soma, Uncommon Denominator, Zillionize and numerous angels.
As for competition, Walkinshaw welcomes it, but feels secure that he and his company have more time and work invested in this class of satellite than anyone in the world — a major obstacle for anyone who wants to do battle. It’s more likely companies will, as Alba has done, pursue a distinct product complementary to those already or in the process of being offered.
“Space is a good place to be right now,” he concluded.
Powered by WPeMatico
U.K.-based startup Sylvera is using satellite, radar and lidar data-fuelled machine learning to bolster transparency around carbon offsetting projects in a bid to boost accountability and credibility — applying independent ratings to carbon offsetting projects.
The ratings are based on proprietary data sets it’s developed in conjunction with scientists from research organisations including UCLA, the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory and University College London.
It’s just grabbed $5.8 million in seed funding led by VC firm Index Ventures. All its existing institutional investors also participated — namely: Seedcamp, Speedinvest and Revent. It also has backing from leading angels, including the existing and former CEOs of NYSE, Thomson Reuters, Citibank and IHS Markit. (It confirms it has committed not to receive any investment from traditional carbon-intensive companies.) And it’s just snagged a $2 million research contract from Innovate UK.
The problem it’s targeting is that the carbon offsetting market suffers from a lack of transparency.
This fuels concerns that many offsetting projects aren’t living up to their claims of a net reduction in carbon emissions — and that “creative” carbon accountancy is rather being used to generate a lot of hot air: In the form of positive-sounding PR, which sums to meaningless greenwashing and more pollution as polluters get to keep on pumping out climate changing emissions.
Nonetheless, the carbon offset markets are poised for huge growth — of at least 15x by 2030 — as large corporates accelerate their net zero commitments. And Sylvera’s bet is that that will drive demand for reliable, independent data — to stand up the claimed impact.
How exactly is Sylvera benchmarking carbon offsets? Co-founder Sam Gill says its technology platform draws on multiple layers of satellite data to capture project performance data at scale and at a high frequency.
It applies machine learning to analyze and visualize the data, while also conducting what it bills as “deep analytical work to assess the underlying project quality”. Via that process it creates a standardised rating for a project, so that market participants are able to transact according to their preferences.
It makes its ratings and analysis data available to its customers via a web application and an API (for which it charges a subscription).
“We assess two critical areas of a project — its carbon performance, and its ‘quality’,” Gill tells TechCrunch. “We score a project against these criteria, and give them ratings — much like a Moody’s rating on a bond.”
Carbon performance is assessed by gathering “multi-layered data” from multiple sources to understand what is going on on the ground of these projects — such as via multiple satellite sources such as multispectral image, radar, and lidar data.
“We collate this data over time, ingest it into our proprietary machine learning algorithms, and analyse how the project has performed against its stated aims,” Gill explains.
Quality is assessed by considering the technical aspects of the project. This includes what Gill calls “additionality”; aka “does the project have a strong claim to delivering a better outcome than would have occurred but for the existence of the offset revenue?”.
There is a known problem with some carbon offsets claimed against forests where the landowner had no intention of logging, for example. So if there wasn’t going to be any deforestation the carbon credit is essentially bogus.
He also says it looks at factors like permanence (“how long will the project’s impacts last?”); co-benefits (“how well has the project incorporated the UN’s Sustainability Development Goals?); and risks (“how well is the project mitigating risks, in particular those from humans and those from natural causes?”).
Clearly it’s not an exact science — and Gill acknowledges risks, for example, are often interlinked.
“It is critical to assess these performance and quality in tandem,” he tells TechCrunch. “It’s not enough to simply say a project is achieving the carbon goals set out in its plan.
“If the additionality of a project is low (e.g. it was actually unlikely the project would have been deforested without the project) then the achievement of the carbon goals set out in the project does not generate the anticipated carbon goals, and the underlying offsets are therefore weaker than appreciated.”
Commenting on the seed funding in a statement, Carlos Gonzalez-Cadenas, partner at Index Ventures, said: “This is a phenomenally strong team with the vision to build the first carbon offset rating benchmark, providing comprehensive insights around the quality of offsets, enabling purchase decisions as well as post-purchase monitoring and reporting. Sylvera is putting in place the building blocks that will be required to address climate change.”
Powered by WPeMatico
More money for the now very buzzy business of reshaping how people work: Worksome is announcing it recently closed a $13 million Series A funding round for its “freelance talent platform” — after racking up 10x growth in revenue since January 2020, just before the COVID-19 pandemic sparked a remote working boom.
The 2017 founded startup, which has a couple of ex-Googlers in its leadership team, has built a platform to connect freelancers looking for professional roles with employers needing tools to find and manage freelancer talent.
It says it’s seeing traction with large enterprise customers that have traditionally used Managed Service Providers (MSPs) to manage and pay external workforces — and views employment agency giants like Randstad, Adecco and Manpower as ripe targets for disruption.
“Most multinational enterprises manage flexible workers using legacy MSPs,” says CEO and co-founder Morten Petersen (one of the Xooglers). “These largely analogue businesses manage complex compliance and processes around hiring and managing freelance workforces with handheld processes and outdated technology that is not built for managing fluid workforces. Worksome tackles this industry head on with a better, faster and simpler solution to manage large freelancer and contractor workforces.”
Worksome focuses on helping medium/large companies — who are working with at least 20+ freelancers at a time — fill vacancies within teams rather than helping companies outsource projects, per Petersen, who suggests the latter is the focus for the majority of freelancer platforms.
“Worksome helps [companies] onboard people who will provide necessary skills and will be integral to longer-term business operations. It makes matches between companies and skilled freelancers, which the businesses go on to trust, form relationships with and come back to time and time again,” he goes on.
“When companies hire dozens or hundreds of freelancers at one time, processes can get very complicated,” he adds, arguing that on compliance and payments Worksome “takes on a much greater responsibility than other freelancing platforms to make big hires easier”.
The startup also says it’s concerned with looking out for (and looking after) its freelancer talent pool — saying it wants to create “a world of meaningful work” on its platform, and ensure freelancers are paid fairly and competitively. (And also that they are paid faster than they otherwise might be, given it takes care of their payroll so they don’t have to chase payments from employers.)
The business started life in Copenhagen — and its Series A has a distinctly Nordic flavor, with investment coming from the Danish business angel and investor on the local version of the Dragons’ Den TV program Løvens Hule; the former Minister for Higher Education and Science, Tommy Ahlers; and family home manufacturer Lind & Risør.
It had raised just under $6M prior to thus round, per Crunchbase, and also counts some (unnamed) Google executives among its earlier investors.
Freelancer platforms (and marketplaces) aren’t new, of course. There are also an increasing number of players in this space — buoyed by a new flush of VC dollars chasing the ‘future of work’, whatever hybrid home-office flexible shape that might take. So Worksome is by no means alone in offering tech tools to streamline the interface between freelancers and businesses.
A few others that spring to mind include Lystable (now Kalo), Malt, Fiverr — or, for techie job matching specifically, the likes of HackerRank — plus, on the blue collar work side, Jobandtalent. There’s also a growing number of startups focusing on helping freelancer teams specifically (e.g. Collective), so there’s a trend towards increasing specialism.
Worksome says it differentiates vs other players (legacy and startups) by combining services like tax compliance, background and ID checks and handling payroll and other admin with an AI powered platform that matches talent to projects.
Although it’s not the only startup offering to do the back-office admin/payroll piece, either, nor the only one using AI to match skilled professionals to projects. But it claims it’s going further than rival ‘freelancer-as-a-service’ platforms — saying it wants to “address the entire value chain” (aka: “everything from the hiring of freelance talent to onboarding and payment”).
Worksome has 550 active clients (i.e. employers in the market for freelancer talent) at this stage; and has accepted 30,000 freelancers into its marketplace so far.
Its current talent pool can take on work across 12 categories, and collectively offers more than 39,000 unique skills, per Petersen.
The biggest categories of freelancer talent on the platform are in Software and IT; Design and Creative Work; Finance and Management Consulting; plus “a long tail of niche skills” within engineering and pharmaceuticals.
While its largest customers are found in the creative industries, tech and IT, pharma and consumer goods. And its biggest markets are the U.K. and U.S.
“We are currently trailing at +20,000 yearly placements,” says Petersen, adding: “The average yearly spend per client is $300,000.”
Worksome says the Series A funding will go on stoking growth by investing in marketing. It also plans to spend on product dev and on building out its team globally (it also has offices in London and New York).
Over the past 12 months the startup doubled the size of its team to 50 — and wants to do so again within 12 months so it can ramp up its enterprise client base in the U.S., U.K. and euro-zone.
“Yes, there are a lot of freelancer platforms out there but a lot of these don’t appreciate that hiring is only the tip of the iceberg when it comes to reducing the friction in working with freelancers,” argues Petersen. “Of the time that goes into hiring, managing and paying freelancers, 75% is currently spent on admin such as timesheet approvals, invoicing and compliance checks, leaving only a tiny fraction of time to actually finding talent.”
Worksome woos employers with a “one-click-hire” offer — touting its ability to find and hire freelancers “within seconds”.
If hiring a stranger in seconds sounds ill-advised, Worksome greases this external employment transaction by taking care of vetting the freelancers itself (including carrying out background checks; and using proprietary technology to asses freelancers’ skills and suitability for its marketplace).
“We have a two-step vetting process to ensure that we only allow the best freelance talent onto the Worksome platform,” Petersen tells TechCrunch. “For step one, an inhouse-built robot assesses our freelancer applicants. It analyses their skillset, social media profiles, profile completeness and hourly or daily rate, as well as their CV and work history, to decide whether each person is a good fit for Worksome.
“For step two, our team of talent specialists manually review and decline or approve the freelancers that pass through step one with a score of 85% or more. We have just approved our 30,000th freelancer and will be able to both scale and improve our vetting procedure as we grow.”
A majority of freelancer applicants fail Worksome’s proprietary vetting processes. This is clear because it says it has received 80,000 applicants so far — but only approved 30,000.
That raises interesting questions about how it’s making decisions on who is (and isn’t) an ‘appropriate fit’ for its talent marketplace.
It says its candidate assessing “robot” looks at “whether freelancers can demonstrate the skillset, matching work history, industry experience and profile depth” deemed necessary to meet its quality criteria — giving the example that it would not accept a freelancer who says they can lead complex IT infrastructure projects if they do not have evidence of relevant work, education and skills.
On the AI freelancer-to-project matching side, Worksome says its technology aims to match freelancers “who have the highest likelihood of completing a job with high satisfaction, based on their work-history, and performance and skills used on previous jobs”.
“This creates a feedback loop that… ensure that both clients and freelancers are matched with great people and great work,” is its circular suggestion when we ask about this.
But it also emphasizes that its AI is not making hiring decisions on its own — and is only ever supporting humans in making a choice. (An interesting caveat since existing EU data protection rules, under Article 22 of the GDPR, provide for a right for individuals to object to automated decision making if significant decisions are being taken without meaningful human interaction.)
Using automation technologies (like AI) to make assessments that determine whether a person gains access to employment opportunities or doesn’t can certainly risk scaled discrimination. So the devil really is in the detail of how these algorithmic assessments are done.
That’s why such uses of technology are set to face close regulatory scrutiny in the European Union — under incoming rules on ‘high risk’ users of artificial intelligence — including the use of AI to match candidates to jobs.
The EU’s current legislative proposals in this area specifically categorize “employment, workers management and access to self-employment” as a high risk use of AI, meaning applications like Worksome are likely to face some of the highest levels of regulatory supervision in the future.
Nonetheless, Worksome is bullish when we ask about the risks associated with using AI as an intermediary for employment opportunities.
“We utilise fairly advanced matching algorithms to very effectively shortlist candidates for a role based solely on objective criteria, rinsed from human bias,” claims Petersen. “Our algorithms don’t take into account gender, ethnicity, name of educational institutions or other aspects that are usually connected to human bias.”
“AI has immense potential in solving major industry challenges such as recruitment bias, low worker mobility and low access to digital skills among small to medium sized businesses. We are firm believers that technology should be utilized to remove human bias’ from any hiring process,” he goes on, adding: “Our tech was built to this very purpose from the beginning, and the new proposed legislation has the potential to serve as a validator for the hard work we’ve put into this.
“The obvious potential downside would be if new legislation would limit innovation by making it harder for startups to experiment with new technologies. As always, legislation like this will impact the Davids more than the Goliaths, even though the intentions may have been the opposite.”
Zooming back out to consider the pandemic-fuelled remote working boom, Worksome confirms that most of the projects for which it supplied freelancers last year were conducted remotely.
“We are currently seeing a slow shift back towards a combination of remote and onsite work and expect this combination to stick amongst most of our clients,” Petersen goes on. “Whenever we are in uncertain economic times, we see a rise in the number of freelancers that companies are using. However, this trend is dwarfed by a much larger overall trend towards flexible work, which drives the real shift in the market. This shift has been accelerated by COVID-19 but has been underway for many years.
“While remote work has unlocked an enormous potential for accessing talent everywhere, 70% of the executives expect to use more temporary workers and contractors onsite than they did before COVID-19, according to a recent McKinsey study. This shows that businesses really value the flexibility in using an on-demand workforce of highly skilled specialists that can interact directly with their own teams.”
Asked whether it’s expecting growth in freelancing to sustain even after we (hopefully) move beyond the pandemic — including if there’s a return to physical offices — Petersen suggests the underlying trend is for businesses to need increased flexibility, regardless of the exact blend of full-time and freelancer staff. So platforms like Worksome are confidently poised to keep growing.
“When you ask business leaders, 90% believe that shifting their talent model to a blend of full-time and freelancers can give a future competitive advantage (Source: BCG),” he says. “We see two major trends driving this sentiment; access to talent, and building an agile and flexible organization. This has become all the more true during the pandemic — a high degree of flexibility is allowing organisations to better navigate both the initial phase of the pandemic as well the current pick up of business activity.
“With the amount of change that we’re currently seeing in the world, and with businesses are constantly re-inventing themselves, the access to highly skilled and flexible talent is absolutely essential — now, in the next 5 years, and beyond.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Scooter unicorn Bird is going public, per an agreement to merge with a special purpose acquisition company, or SPAC. After rumors and reports circulated for months about an imminent deal, it has finally arrived.
First, a quick overview of the agreement and the players involved: Bird is merging with Switchback II at an implied valuation of $2.3 billion. Fidelity Management & Research Company will lead the deal’s $160 million in private investment in public equity, or PIPE. Apollo Investment Corp. and MidCap Financial Trust provided an additional $40 million in asset financing. (Disclosure: Apollo is buying TechCrunch’s parent company.)
Historically — and based on what we’re seeing in this fantastical filing — Bird proved to be a simply awful business. Its results from 2019 and 2020 describe a company with a huge cost structure and unprofitable revenue, per filings. After posting negative gross profit in both of the most recent full-year periods, Bird’s initial model appears to have been defeated by the market.
What drove the company’s hugely unprofitable revenues and resulting net losses? Unit economics that were nearly comically destructive.
Some of the numbers Bird shared in its investor deck show a business that is growing, in terms of users and geographic footprint. Bird is in 200 cities globally and reports more than 95 million rides to date, and 3 million new riders added during the pandemic. The investor deck also touts year-round positive economics during the COVID-19 era. That all looks positive. But looking into the line-item financials, a different story emerges.
The scooter shop managed to convert a $135.7 million gross loss in 2019 to a smaller gross deficit of $23.5 million in 2020, but it did not manage to shake up its upside-down economics during its full fiscal 2020.
Update: Bird provided a response to questions about its newer fleet management business and how it expects to stem losses. Their response:
Bird’s history to date has been one of milestones. First was securing product market fit and delivering an eco-friendly way for people to travel in their communities and access opportunities – education, health and economic. The second milestone focused on unit economics and laying the foundation for a sustainable business. Then came the pandemic, which served as a catalyst for us to identify how to scale in a way that allowed us to be profitable at a ride level. As a result, in H2 2020 our ride profit (after vehicle depreciation) was positive and people are continuing to embrace naturally social distanced eco-friendly options.
Powered by WPeMatico

Planck co-founders (from left to right): David Schapiro, CEO Elad Tsur and CTO Amir Cohen. Image Credits: Planck
Planck, the AI-based data platform for commercial insurance underwriting, announced today it has raised a $20 million growth round. The funding came from 3L Capital and Greenfield Partners, along with returning investors Team8, Viola Fintech, Arbor Ventures and Eight Roads.
This brings the New York-based startup’s total raised to $48 million, including a $16 million Series B it announced in June 2020. Planck said it currently works with “dozens of commercial insurance companies in the U.S.,” including more than half of the top-30 insurers. It will use its new funding to build its U.S. team, expand into global markets and add products for new business segments. Ernie Feirer has also joined Planck as its head of U.S. business. He previously held leadership roles at LexisNexis Risk Solutions, building data analytics solutions for property and casualty insurance carriers.
Planck’s database, which includes online images, text, videos, reviews and public records, allows it to give insurance providers real-time information that helps them determine premiums, process claims and give SMEs faster quotes. It covers more than 50 business segments, including restaurants, construction, retail and manufacturing, and can deliver analytics by simply entering a business’ name and address.
For example, if a healthcare business is seeking to buy or renew an insurance policy, Planck can give underwriters information such as the type of equipment used, what kind of drugs it prescribes and the type of surgeries it performs.
In a statement, 3L Capital principal Paige Thacher said, “Commercial carriers and brokers can no longer afford to rely upon traditional data sources as they prospect, assess risk and monitor a small business insured’s changing exposure during the policy life cycle. The new imperative is to leverage AI and machine learning technologies to dynamically harvest business insights from the insured’s digital footprint.”
Powered by WPeMatico