TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Five months after it was announced that Pal Gelsinger would be stepping down as CEO of VMware to take the top job at Intel, the virtualization giant has finally appointed a permanent successor. Raghu Raghuram — a longtime employee of the company — has been appointed the new CEO. He will be taking on the new role on June 1. Until then, CFO Zane Rowe will continue in the role in the interim.
Raghuram has been with the company for 17 years in a variety of roles, most recently COO of products and cloud services. He’s also held positions at the company overseeing areas like data centers and VMware’s server business. Putting a veteran at the helm sends a clear message that VMware has picked someone clearly dedicated to the company and its culture. No drama here.
Indeed, the move is coming at a time when there is already a lot of other change underway and speaks to the company looking for stability and continuity to lead it through that. About a month ago, Dell confirmed long-anticipated news that it would be spinning out its stake in VMware in a deal that’s expected to bring Dell at least $9 billion — putting to an end a financial partnership that initially kicked off with an eye-watering acquisition of EMC in 2016. That partnership will not end the strategic relationship, however, which is set to continue and now Raghuram will be in charge of building and leading.
For that reason, you might look at this as a deal nodded through significantly by Dell.
“I am thrilled to have Raghu step into the role of CEO at VMware. Throughout his career, he has led with integrity and conviction, playing an instrumental role in the success of VMware,” said Michael Dell, chairman of the VMware board of directors, in a statement. “Raghu is now in position to architect VMware’s future, helping customers and partners accelerate their digital businesses in this multicloud world.”
Raghuram has not only been the person overseeing some of VMware’s biggest divisions and newer areas like software-defined networking and cloud computing, but he’s had a central role in building and driving strategy for the company’s core virtualization business, been involved with M&A and, as VMware points out, “key in driving partnerships with Dell Technologies,” among other partners.
“VMware is uniquely poised to lead the multicloud computing era with an end-to-end software platform spanning clouds, the data center and the edge, helping to accelerate our customers’ digital transformations,” said Raghuram in a statement. “I am honored, humbled and excited to have been chosen to lead this company to a new phase of growth. We have enormous opportunity, we have the right solutions, the right team and we will continue to execute with focus, passion and agility.”
The company also took the moment to update on guidance for its Q1 results, which will be coming out on May 27. Revenues are expected to come in at $2.994 billion, up 9.5% versus the same quarter a year ago. Subscription and SaaS and license revenue, meanwhile, is expected to be $1.387 billion, up 12.5%. GAAP net income per diluted share is expected to be $1.01 per diluted share, and non-GAAP net income per diluted share is expected to be $1.76 per diluted share, it said.
Powered by WPeMatico
Cisco announced this morning that it intends to acquire Indianapolis-based startup Socio, which helps plan hybrid in-person and virtual events. The two companies did not share the purchase price.
Socio provides a missing hybrid event management component for the company to add to its Webex platform. The goal appears to be to combine this with the recent purchase of Slido and transform Webex from an application mostly for video meetings into a more comprehensive event platform.
“As part of Cisco Webex’s vision to deliver inclusive, engaging and intelligent meeting and event experiences, the acquisition of Socio Labs complements Cisco’s recent acquisition of Slido, an industry-leading audience engagement tool, which together will create a comprehensive, cost-effective and easy-to-use event management solution [ … ],” the company explained in a statement.
The impact of the pandemic was not lost on Cisco, and it’s clear that as we can foresee going back to live events, having the ability to combine it with a virtual experience means that you can open up your event to a much wider audience beyond those who can attend in person. That’s likely not something that’s going away, even after we get past COVID.
Jeetu Patel, SVP and GM for security and collaboration at Cisco says that the future of work is going to be hybrid, whether it’s for work meetings or larger events and Cisco is making this acquisition to expand the use cases for the Webex platform.
“Whether it’s a 1:1 call, a small team huddle, a group meeting or a large external event, we want to remove friction and help people engage with each other in an inclusive manner. Slido allows for every voice to be heard — even when you’re not talking. Socio allows for getting your voice heard by a large number of people,” Patel said.
And the company believes that Webex provides the platform to make it all happen. “It’s a really potent combination of technology to make human interactions more engaging, no matter the type of conversation,” he added.
Brent Leary, founder and principal analyst at CRM Essentials, says that it’s a smart move to take advantage of the changing events landscape and that this acquisition helps make Cisco a serious player in this space.
“As we get closer to a post-pandemic world, the need to create hybrid event experiences is going to quickly accelerate as people start venturing out to attend physical events. So having an event stack that combines local event support/participation with tools to integrate a broader virtual audience will be the future of event management,” Leary told me.
Socio was founded in 2016 and raised around $7 million in investment capital, according to Crunchbase data. It has a prestigious list of enterprise customers that includes Microsoft, Google, Jet Blue, Greenpeace, PepsiCo and Hyundai.
The deal is expected to close in Q4 of FY2021. When it does close, Socio’s 135 employees will be joining Cisco. The plan is to incorporate Socio’s tooling into the Webex platform while allowing it to continue as a stand-alone product, according to a Cisco spokesperson.
Powered by WPeMatico
Low-code and no-code tools abound these days, as the industry attempts to give nontechnical end users the ability to create applications without code (or very little anyway). Salesforce has been a big proponent of this approach to help reduce the complexity of working on its platform, and today the CRM giant announced a new wrinkle: drag and drop interactive components.
These new components allow users to create more sophisticated kinds of interactions, says Ryan Ellis, SVP for product management and platform at Salesforce. “We’re introducing this new feature called Dynamic Interactions and prior to their existence you had to have developers if you wanted to be able to build essentially truly interactive applications,” Ellis said.
What he means by this is if you have an application made up of multiple components such as a list of companies, a map and information about the company. You can click a company name and its location instantly appears on the map, and information about the company appears alongside it.
Salesforce will be providing about 150 such interactions like maps, lists, Einstein next best action and so forth. Developers can also create these for users as reusable building blocks that make sense to your organization or make them available in the AppExchange for others to use. Finally, you might have a systems integrator or consultant help build them for you.
“With dynamic interactions, we’re really dramatically simplifying the process of building apps with components that communicate with each other, pass data back and forth and react to user actions. It’s an entirely no-code tool so that developers write the code once for their component, and then that component can be reused by people who don’t have technical skills by dragging and dropping them onto the page, then configuring what should happen when a user takes an action,” Ellis explained.
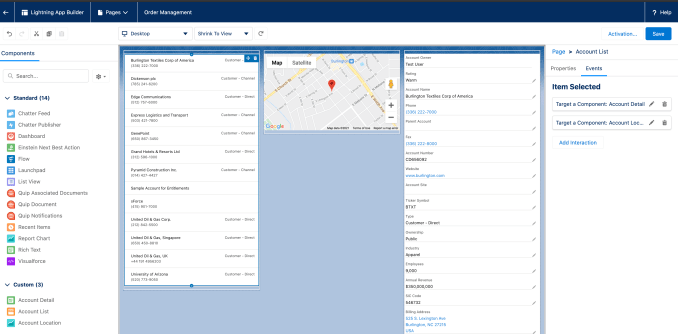
Image Credits: Salesforce
He says that this is part of a larger trend of digital transformation happening across the industry, one that was accelerated by the pandemic, something we hear frequently from tech companies like Salesforce.
“There’s really this big push to go digital faster than ever before, and this was happening for years as we were seeing businesses having to pivot much more rapidly as new business models were coming about. […] But then in this last year COVID really changed the game, and people just had to put on full gas in terms of actually being able to deliver those digital transformations in some instances overnight,” he said.
When you combine that with a shortage of developers, it makes sense that Salesforce and many other companies in the industry are developing these low-code tools that allow nontechnical business users to build some applications themselves, while freeing developers to concentrate on more sophisticated organizational requirements.
Dynamic Interactions will be available starting today from Salesforce (in beta). The product is expected to be generally available around Dreamforce in the fall.
Powered by WPeMatico
Charity Dean has been in the national spotlight lately because she was among a group of doctors, scientists and tech entrepreneurs who sounded the pandemic alarm early last year and who are featured in a new book by Michael Lewis about the U.S. response, called The Premonition.
It’s no wonder the press — and, seemingly moviemakers, too — are interested in Dean. Surgery is her first love, but she also studied tropical diseases and not only applied what she knows about outbreaks on the front lines last year, but also came to appreciate an opportunity that only someone in her position could see. Indeed, after the pandemic laid bare just how few tools were available to help the U.S. government to track how the virus was moving and mutating, she helped develop a model that has since been turned into subscription software to (hopefully) prevent, detect, and contain costly disease outbreaks in the future.
It’s tech that companies with global operations might want to understand better. It has also attracted $8 million in seed funding Venrock, Alphabet’s Verily unit, and Sweat Equity Ventures. We talked late last week with Dean about her now 20-person outfit, called The Public Health Company, and why she thinks disease-focused risk management will be as crucial for companies going forward as cybersecurity software. Our chat has been edited for length; you can also listen to our longer conversation here.
TC: You went to medical school but you also have a master’s degree in public health and tropical medicine. Why was the latter an area of interest for you?
CD: Neither of my parents had college degrees. I grew up in a very modest setting in rural Oregon. We were poor and by the grace of a full ride scholarship to college I got to be premed. When I was a little girl some missionaries came to our church and talked about disease outbreaks in Africa. I was seven years old, and driving home that evening with my parents, I said, ‘I’m going to be a doctor, and I’m going to study disease.’ It was outrageous because I didn’t know a single person with a college degree. But . . my heart was set on that, and it never deviated from it.
TC: How did you wind up at the Santa Barbara County Public Health Department, instead of in private practice?
CD: It’s funny, when I was finishing up my residency — which I started doing general surgery, then I pivoted into internal medicine — I had a number of different doctors’ private practices come to me and try to recruit me because of the shortage of women physicians.
[At the same time] the medical director from the county public health department came and found me and he said, ‘Hey, I hear you have a master’s in tropical medicine.’ And he said, ‘Would you consider coming to work as the deputy health officer, and communicable disease controller, and tuberculosis controller, and [oversee the] HIV clinic and homeless clinic?’ And . . . it was, for me, a fairly easy choice.
TC: Because there was so little attention being paid to all of these other issues?
CD: What caught my attention is when he said communicable disease controller and tuberculosis controller. I had lived in Africa [for a time] and learned a lot about HIV, AIDS, tuberculosis, vaccine-preventable diseases — things you don’t see in the United States. [And the job] was so in lockstep with who I was because it’s the safety net. [These afflicted individuals] don’t have health insurance. Many are undocumented. Many have nowhere else to go for health care, and the county clinic truly serves the communities that I cared about, and that’s where I wanted to be.
TC: In that role — and later at the California Department of Public Health — you developed expertise in multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis. Was your understanding of how it is transmitted — and how the symptoms present differently — what made you attuned to what was headed for the U.S. early last year?
CD: It was probably the single biggest contributor to my thinking. When we have a novel pathogen as a doctor, or as a communicable disease controller, our minds think in terms of buckets of pathogen: some are airborne, some are spread on surfaces, some are spread through fecal material or through water. In January [of last year], as I was watching the news reports emerge out of China, it became clear to me that this was potentially a perfect pathogen. What does that mean? It would mean it had some of the attributes of things like tuberculosis or measles or influenza — that it had the ability to spread from person to person, likely through the air, that it made people sick enough that China was standing up hospitals in two weeks, and that it moved fast enough through the population to grow exponentially.
TC: You are credited with helping to convince California Governor Gavin Newsom to issue lock-down orders when he did.
CD: Everything I’ve done is as part of a team. In March, some amazing heroes parachuted in from the private sector, including [former U.S Chief Technology Officer] Todd Park, [famed data scientist] DJ Patil, [and Venrock’s] Bob Kocher, to help the state of California develop a modeling effort that would actually show, through computer-generated models, in what direction the pandemic was headed.
TC: How did those efforts and thinking lead you to form The Public Health Company last August?
CD: What we are doing at The Public Health Company is incorporating the genomic variant analysis — or the fingerprint of the virus of COVID virus as it mutates and as it moves through a population — with epidemiology investigations and [porting these with] the kind of traditional data you might have from a local public health officer into a platform to make those tools readily available and easy to use to inform decision makers. You don’t have to have a mathematician and a data scientist and an infectious disease doctor standing next to you to make a decision; we make those tools automated and readily available.
TC: Who are your customers? The U.S. government? Foreign governments?
CD: Are the tools that we are developing useful for government? Absolutely. We’re engaged in a number of different partnerships where this is of incredible service to governments. But they are as useful, if not even more useful, to the private sector because they haven’t had these tools. They don’t have a disease control capability at their fingertips and many of them have had to essentially stand up their own internal public health department, and figure it out on the fly, and the feedback that we’re seeing from private sector businesses has been incredible.
TC: I could see hedge funds and insurance companies gravitating quickly to this. What are some customers or types of customers that might surprise readers?
CD: One bucket that might not occur to people is in the risk management space of a large enterprise that has global operations like a warehouse or a factory in different places. The risk management of COVID-19 is going to look very different in each one of those locations based on: how the virus is mutating in that location, the demographics of their employees, the type of activities they’re doing, [and] the ventilation system in their facility. Trying to grapple with all of those different factors . . .is something that we can do for them through a combination of our tech-enabled service, the expertise we have, the modeling, and the genetic analysis.
I don’t know that risk management in terms of disease control has been a big part of private sector conversations, [but] we think of it similar to cyber security in that after a number of high-profile cyber security attacks, it became clear to every insurance agency or private sector business that risk management had to include cyber security they had to stand up. We very much believe that disease control in risk management for continuity of operations is going to be incredibly important moving forward in a way that I couldn’t have explained before COVID. They see it now and they understand it’s an existential threat.
Powered by WPeMatico
Panaseer, which takes a data science approach to cybersecurity, has raised $26.5 million in a Series B funding led by AllegisCyber Capital. Existing investors, including Evolution Equity Partners, Notion Capital, AlbionVC, Cisco Investments and Paladin Capital Group, as well as new investor National Grid Partners, also participated. Panaseer has now raised $43 million to date.
Panaseer’s special sauce and sales pitch amount to what it calls “Continuous Controls Monitoring” (CCM). In plainer English that means correlating a great deal of data from all available security tools to check assets, control gaps, you name it.
As a result, the company says it can identify zero-day and other exposures faster, or exposure to, say, FireEye or SolarWinds vulnerabilities.
Jonathan Gill, CEO, Panaseer said: “Most enterprises have the tools and capability to theoretically prevent a breach from occurring. However, one of the key reasons that breaches occur is that there is no technology to monitor and react to failed controls. CCM continuously validates and measures levels of protection and provides notifications of failures. Ultimately, CCM enables these failures to be fixed before they become security incidents.”
Speaking to me on a call he added: “The investment, allows us to scale our organization to meet those demands of customers with a team of people to implement the platform and help them get tremendous value and to evolve the product. To add more and more capability to that technology to support more and more use cases. So they’re the two main directions, and there’s a market we think of tens of thousands of organizations of a certain size, who are regulated or they have assets worth protecting and a level of complexity that makes it difficult to solve the problem themselves. And our Advisory Board and the customers I’ve spoken with think maybe there are barely 20 companies in the world who can solve this problem. And everybody else gets stuck on the fact that it’s a really difficult data science problem to solve. So we want to scale that and take that to more organizations.”
And why did they pick these investors: “I think we picked them and they picked us, we’ve been on that journey together. It takes months to find the best combination. The dollars are all the same when it comes to investors, but I think they can help improve as an organization and grow just like the existing investors do. They give us access and reach into parts of the market and help make us better as organizations as well.”
Bob Ackerman, founder and managing director of AllegisCyber Capital, and co-founder of DataTribe said: “The emergence of Continuous Controls Monitoring as a new cybersecurity category demonstrates a ‘coming of age’ for cybersecurity. Cyber is the existential threat to the global digital economy. All levels of the enterprise, from the CISO, to Chief Risk Officer, to the Board of Directors are demanding comprehensive visibility, transparency and hard metrics to assess cyber situational awareness.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Jamf, the enterprise Apple device management company, announced that it was acquiring Wandera, a zero trust security startup, for $400 million at the market close today. Today’s purchase is the largest in the company’s history.
Using a set of management services for Apple devices, Jamf provides IT at large organizations. It is the leader in the market, and snagging Wandera provides a missing modern security layer for the platform.
Jamf CEO Dean Hager says that Wandera’s zero trust approach fills in an important piece in the Jamf platform tool set. “The combination of Wandera and Jamf will provide our customers a single source platform that handles deployment, application lifecycle management, policies, filtering and security capabilities across all Apple devices while delivering zero trust network access for all mobile workers,” Hager said in a statement.
Zero trust, as the name implies, is an approach to security where you don’t trust anybody regardless of whether they are inside or outside your network. It requires that you force everyone to provide multiple forms of authentication to prove their identity before they can access company resources.
The need for a zero trust approach became even more acute during the pandemic when employees have often been working from home and have needed access to applications and other company resources from wherever they happened to be, a trend that was happening even prior to COVID, and is likely to continue after it ends.
Wandera, which is based in London, was founded in 2012 by brothers Roy and Eldar Tuvey, who had previously co-founded another security startup called ScanSafe. Cisco acquired that company, which helped protect web gateways as a service, for $183 million back in 2009. The brothers raised over $53 million along the way for Wandera. Investors included Bessemer Venture Partners, 83North and Sapphire Ventures.
Sapphire co-founder and managing director Andreas Weiskam had this to say about the company: “I’ve had the pleasure of working with co-founders (and brothers) Eldar Tuvey and Roy Tuvey for the last several years now and I can honestly say they’re great entrepreneurs and leaders, having built a real company of consequence.”
He added, “They’ve created a unique security product which addresses mobile threats by leveraging the increasingly important zero trust network. By joining the Jamf family, the two will help shape the future of the zero trust cloud. And it goes without saying that this is a big win for the customers, especially for those in the Apple ecosystem.”
Under the terms of the deal, Jamf is paying Wandera $350 million in cash, then paying them two $25 million payments on October 1, 2021 and December 15, 2021. The deal is expected to close in the third quarter, assuming it passes regulatory scrutiny.
Powered by WPeMatico
For Subaru diehards holding out for an electric vehicle, the wait is almost over. The Japanese automaker just announced new details about its first-ever EV, which is set to hit the streets in 2022.
Subaru will call its first EV the Solterra, a fitting name for a brand synonymous with outdoor adventures and you know, the sun and the Earth. Also fittingly, Subaru’s first full-fledged EV will be an SUV that ships with the manufacturer’s well-regarded all-wheel-drive capabilities.
The Solterra is built on a new platform the company is developing in partnership with Toyota, which the latter company will use for its impossibly named bZ4X crossover (bZ stands for “beyond zero,” apparently).
Subaru has only released two teaser images so far, but given that the new SUV will share DNA with the Toyota bZ4X, Subaru’s offering will likely look like a toned-down, less aggressively styled version of Toyota’s forthcoming futuristic electric crossover.
Other than that, we don’t know a whole lot. If the Solterra winds up looking a lot like the BZ4X, you can expect a sort of squashed RAV4, maybe somewhere between a Crosstrek and a Forester in size.
Subaru’s first proper EV will join the plug-in hybrid Crosstrek, which the company began selling in 2014 — currently its only option for climate-conscious drivers. The Solterra will go on sale next year in the U.S., Canada, China, Europe and Japan.
Powered by WPeMatico
As vice president of Innovation at National Grid Partners, I’m responsible for developing initiatives that not only benefit National Grid’s current business but also have the potential to become stand-alone businesses. So I obviously have strong views about the future of the energy industry.
But I don’t have a crystal ball; no one does. To be a good steward of our innovation portfolio, my job isn’t to guess what the right “basket” is for our “eggs.” It’s to optimally allocate our finite eggs across multiple baskets with the greatest collective upside.
Put another way, global and regional trends make it clear that the Next Big Thing isn’t any single thing at all. Instead, the future is about open innovation and integration of elements across the entire energy supply chain. Only with such an open energy ecosystem can we adapt to the highly volatile — some might even say unpredictable — market conditions we face in the energy industry.
Just as the digital internet rewards innovation wherever it serves the market — whether you build a better app or design a cooler smartphone — so too will the energy internet offer greater opportunities across the energy supply chain.
I like to think of this open, innovation-enabling approach as the “energy internet,” and I believe it represents the most important opportunity in the energy sector today.
Here’s why I find the concept of the energy internet helpful. Before the digital internet (a term I’m using here to encompass all the hardware, software and standards that comprise it), we had multiple silos of technology such as mainframes, PCs, databases, desktop applications and private networks.
As the digital internet evolved, however, the walls between these silos disappeared. You can now utilize any platform on the back end of your digital services, including mainframes, commodity server hardware and virtual machines in the cloud.
You can transport digital payloads across networks that connect to any customer, supplier or partner on the planet with whatever combination of speed, security, capacity and cost you deem most appropriate. That payload can be data, sound or video, and your endpoint can be a desktop browser, smartphone, IoT sensor, security camera or retail kiosk.
This mix-and-match internet created an open digital supply chain that has driven an epochal boom in online innovation. Entrepreneurs and inventors can focus on specific value propositions anywhere across that supply chain rather than having to continually reinvent the supply chain itself.
The energy sector must move in the same direction. We need to be able to treat our various generation modalities like server platforms. We need our transmission grids to be as accessible as our data networks, and we need to be able to deliver energy to any consumption endpoint just as flexibly. We need to encourage innovation at those endpoints, too — just as the tech sector did.
Just as the digital internet rewards innovation wherever it serves the market — whether you build a better app or design a cooler smartphone — so too will the energy internet offer greater opportunities across the energy supply chain.
So what is the energy internet? As a foundation, let’s start with a model that takes the existing industry talk of digitalization, decentralization and decarbonization a few steps further:
Digitalization: Innovation depends on information about demand, supply, efficiency, trends and events. That data must be accurate, complete, timely and sharable. Digitalization efforts such as IoE, open energy, and what many refer to as the “smart grid” are instrumental because they ensure innovators have the insights they need to continuously improve the physics, logistics and economics of energy delivery.
Decentralization: The internet changed the world in part because it took the power of computing out of a few centralized data centers and distributed it wherever it made sense. The energy internet will do likewise. Digitalization supports decentralization by letting assets be integrated into an open energy supply chain. But decentralization is much more than just the integration of existing assets — it’s the proliferation of new assets wherever they’re needed.
Decarbonization: Decarbonization is, of course, the whole point of the exercise. We must move to greener supply chains built on decentralized infrastructure that leverage energy supply everywhere to meet energy demand anywhere. The market is demanding it and regulators are requiring it. The energy internet is therefore more than just an investment opportunity — it’s an existential imperative.
Democratization: Much of the innovation associated with the internet arose from the fact that, in addition to decentralizing technology physically, it also democratized technology demographically. Democratization is about putting power (literally, in this case) into the hands of the people. Vastly increasing the number of minds and hands tackling the energy industry’s challenges will also accelerate innovation and enhance our ability to respond to market dynamics.
Diversity: As I asserted above, no one has a crystal ball. So anyone investing in innovation at scale should diversify — not just to mitigate risk and optimize returns, but as an enablement strategy. After all, if we truly believe the energy internet (or Grid 2.0, if you prefer that term) will require that all the elements of the energy supply chain work together, we must diversify our innovation initiatives across those elements to promote interoperability and integration.
That’s how the digital internet was built. Standards bodies played an important role, but those standards and their implementations were driven by industry players like Microsoft and Cisco — as well as top VCs — who ensured the ecosystem’s success by driving integration across the supply chain.
We must take the same approach with the energy internet. Those with the power and influence to do so must help ensure we aggressively advance integration across the energy supply chain as a whole, even as we improve the individual elements. To this end, National Grid last year kicked off a new industry group called the NextGrid Alliance, which includes senior executives from more than 60 utilities across the world.
Finally, we believe it’s essential to diversify thinking within the energy ecosystem as well. National Grid has sounded alarms about the serious underrepresentation of women in the energy industry and of female undergraduates in STEM programs. On the flip side, research by Deloitte has found diverse teams are 20% more innovative. More than 60% of my own team at NGP are women, and that breadth of perspective has helped National Grid capture powerful insights into companywide innovation efforts.
The concept of the energy internet isn’t some abstract future ideal. We’re already seeing specific examples of how it will transform the market:
Green transnationalism: The energy internet is on its way to becoming as global as the digital internet. The U.K., for instance, is now receiving wind-generated power from Norway and Denmark. This ability to leverage decentralized energy supply across borders will have significant benefits for national economies and create new opportunities for energy arbitrage.
EV charging models: Pumping electricity isn’t like pumping gas, nor should it be. With the right combination of innovation in smart metering and fast-charging end-point design, the energy internet will create new opportunities at office buildings, residential complexes and other places where cars plus convenience can equal cash.
Disaster mitigation: Recent events in Texas have highlighted the negative consequences of not having an energy internet. Responsible utilities and government agencies must embrace digitization and interoperability to more effectively troubleshoot infrastructure and better safeguard communities.
These are just a few of the myriad ways in which an open, any-to-any energy internet will promote innovation, stimulate competition and generate big wins. No one can predict exactly what those big wins will be, but there will surely be many, and they will accrue to the benefit of all.
That’s why even without a crystal ball, we should all commit ourselves to digitalization, decentralization, decarbonization, democratization and diversity. In so doing, we’ll build the energy internet together, and enable a fair, affordable and clean energy future.
Powered by WPeMatico
It’s the golden age of collectibles and legacy institutions are looking to move beyond trading cards, embracing new tech that brings the fandom together online. Sequoia Games, a new game studio launching out of stealth, is aiming for a hit with its tabletop AR game that’s looking to find an audience in a post-Top Shot world.
With a game that seems to be trading cards meets Catan meets NFTs meets augmented reality, Flex NBA is aiming to capture some of the magic that Dapper Labs did with NBA Top Shot, albeit with a title reliant on physical collectibles and a tabletop game.
Collectibles are incredibly hot right now and while there’s been a lot of attention on digital-only collectibles, Sequoia Games’ hybrid approach is probably one that will likely find some new audience segments. The game is centered around these hexagonal discs that function like trading cards but can be tracked inside its mobile app with 3D animations of the players superimposed on top of them. With mechanics similar to other popular trading card games, users can augment those tiles with power-up tiles.
Users get a handful of tiles that vary depending on the tier of their Kickstarter pledge, but going forward, the startup is planning to sell the tiles in randomized packs as well.

Image via Sequoia Games
Users register these tiles inside their app, where the ownership of individual tiles is tracked across the network using something that sounds an awful lot like a blockchain — though that’s a word the team was very careful to avoid using. What’s interesting is that once the tiles are registered, users can play the game in-person or online. The company is working on a first-party marketplace for the tiles, though buyers will have to actually purchase and ship the physical tiles even if they are only playing on mobile.
Like Top Shot, Sequoia Games boasts an official partnership with the NBA and national players’ association. Unlike Dapper Labs, they’re not currently sitting on hundreds of millions of dollars of venture money. The startup’s founder says they’ve raised a modest seed round and are in the process of closing a more sizable Series A.
Also unlike Top Shot, which can — and has been able to — rapidly adjust supply of new moments to meet demand, Sequoia Games is stuck in the physical world and is thus a little more supply-confined — one of the reasons they’ve chosen to do a Kickstarter to gauge interest from potential users early-on.
Prices for the tiers of Kickstarter tiers vary pretty wildly, with a $35 basic pack that includes the most common tiles and a $699 “Supreme Flex Domination Pack” that boasts rarer items like MVP-level player tiles. The startup plans to start shipping out packs in July.
Powered by WPeMatico
The tabletop gaming industry has exploded over the last few years as millions discovered or rediscovered its joys, but it too is evolving — and The Last Gameboard hopes to be the venue for that evolution. The digital tabletop platform has progressed from crowdfunding to $4 million seed round, and having partnered with some of the biggest names in the industry, plans to ship by the end of the year.
As the company’s CEO and co-founder Shail Mehta explained in a TC Early Stage pitch-off earlier this year, The Last Gameboard is a 16-inch square touchscreen device with a custom OS and a sophisticated method of tracking game pieces and hand movements. The idea is to provide a digital alternative to physical games where that’s practical, and do so with the maximum benefit and minimum compromise.
If the pitch sounds familiar… it’s been attempted once or twice before. I distinctly remember being impressed by the possibilities of D&D on an original Microsoft Surface… back in 2009. And I played with another at PAX many years ago. Mehta said that until very recently there simply wasn’t the technology and the market wasn’t ready.
“People tried this before, but it was either way too expensive or they didn’t have the audience. And the tech just wasn’t there; they were missing that interaction piece,” she explained, and certainly any player will recognize that the, say, iPad version of a game definitely lacks physicality. The advance her company has achieved is in making the touchscreen able to detect not just taps and drags, but game pieces, gestures and movements above the screen, and more.
“What Gameboard does, no other existing touchscreen or tablet on the market can do — it’s not even close,” Mehta said. “We have unlimited touch, game pieces, passive and active… you can use your chess set at home, lift up and put down the pieces, we track it the whole time. We can do unique identifiers with tags and custom shapes. It’s the next step in how interactive surfaces can be.”
It’s accomplished via a not particularly exotic method, which saves the Gameboard from the fate of the Surface and its successors, which cost several thousand dollars due to their unique and expensive makeups. Mehta explained that they work strictly with ordinary capacitive touch data, albeit at a higher framerate than is commonly used, and then use machine learning to characterize and track object outlines. “We haven’t created a completely new mechanism, we’re just optimizing what’s available today,” she said.
At $699 for the Gameboard it’s not exactly an impulse buy, either, but the fact of the matter is people spend a lot of money on gaming, with some titles running into multiple hundreds of dollars for all the expansions and pieces. Tabletop is now a more than $20 billion industry. If the experience is as good as they hope to make it, this is an investment many a player will not hesitate (much, anyway) to make.
Of course, the most robust set of gestures and features won’t matter if all they had on the platform were bargain-bin titles and grandpa’s-parlor favorites like “Parcheesi.” Fortunately, The Last Gameboard has managed to stack up some of the most popular tabletop companies out there, and aims to have the definitive digital edition for their games.
Asmodee Digital is probably the biggest catch, having adapted many of today’s biggest hits, from modern classics “Catan” and “Carcassonne” to crowdfunded breakout hit “Scythe” and immense dungeon-crawler “Gloomhaven.” The full list of partners right now includes Dire Wolf Digital, Nomad Games, Auroch Digital, Restoration Games, Steve Jackson Games, Knights of Unity, Skyship Studios, EncounterPlus, PlannarAlly and Sugar Gamers, as well as individual creators and developers.
These games may be best played in person, but have successfully transitioned to digital versions, and one imagines that a larger screen and inclusion of real pieces could make for an improved hybrid experience. There will be options both to purchase games individually, like you might on mobile or Steam, or to subscribe to an unlimited access model (pricing to be determined on both).
It would also be something that the many gaming shops and playing venues might want to have a couple of on hand. Testing out a game in-store and then buying a few to stock, or convincing consumers to do the same, could be a great sales tactic for all involved.
In addition to providing a unique and superior digital version of a game, the device can connect with others to trade moves, send game invites and all that sort of thing. The whole OS, Mehta said, “is alive and real. If we didn’t own it and create it, this wouldn’t work.” This is more than a skin on top of Android with a built-in store, but there’s enough shared that Android-based ports will be able to be brought over with little fuss.
Head of content Lee Allentuck suggested that the last couple years (including the pandemic) have started to change game developers’ and publishers’ minds about the readiness of the industry for what’s next. “They see the digital crossover is going to happen — people are playing online board games now. If you can be part of that new trend at the very beginning, it gives you a big opportunity,” he said.

CEO Shail Mehta (center) plays Stop Thief on the Gameboard with others on the team. Image Credits: The Last Gameboard
Allentuck, who previously worked at Hasbro, said there’s widespread interest in the toy and tabletop industry to be more tech-forward, but there’s been a “chicken and egg scenario,” where there’s no market because no one innovates, and no one innovates because there’s no market. Fortunately things have progressed to the point where a company like The Last Gameboard can raise $4 million to help cover the cost of creating that market.
The round was led by TheVentureCity, with participation from SOSV, Riot Games, Conscience VC, Corner3 VC and others. While the company didn’t go to HAX’s Shenzhen program as planned, they are still HAX-affiliated. SOSV partner Garrett Winther gave a glowing recommendation of its approach: “They are the first to effectively tie collaborative physical and digital gameplay together while not losing the community, storytelling or competitive foundations that we all look for in gaming.”
Mehta noted that the pandemic nearly cooked the company by derailing their funding, which was originally supposed to come through around this time last year when everything went pear-shaped. “We had our functioning prototype, we had filed for a patent, we got the traction, we were gonna raise, everything was great… and then COVID hit,” she recalled. “But we got a lot of time to do R&D, which was actually kind of a blessing. Our team was super small so we didn’t have to lay anyone off — we just went into survival mode for like six months and optimized, developed the platform. 2020 was rough for everyone, but we were able to focus on the core product.”
Now the company is poised to start its beta program over the summer and (following feedback from that) ship its first production units before the holiday season when purchases like this one seem to make a lot of sense.
(This article originally referred to this raise as The Last Gameboard’s round A — it’s actually the seed. This has been updated.)
Powered by WPeMatico