TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
With the rise of livestreaming, gaming has evolved from a toy-like consumer product to a legitimate platform and medium in its own right for entertainment and competition.
Twitch’s viewer base alone has grown from 250,000 average concurrent viewers to over 3 million since its acquisition by Amazon in 2014. Competitors like Facebook Gaming and YouTube Live are following similar trajectories.
The boom in viewership has fueled an ecosystem of supporting products as today’s professional streamers push technology to its limit to increase the production value of their content and automate repetitive aspects of the video production cycle.
The largest streamers hire teams of video editors and social media managers, but growing and part-time streamers struggle to do this themselves or come up with the money to outsource it.
The online streaming game is a grind, with full-time creators putting in eight- if not 12-hour performances on a daily basis. In a bid to capture valuable viewer attention, 24-hour marathon streams are not uncommon either.
However, these hours in front of the camera and keyboard are only half of the streaming grind. Maintaining a constant presence on social media and YouTube fuels the growth of the stream channel and attracts more viewers to catch a stream live, where they may purchase monthly subscriptions, donate and watch ads.
Distilling the most impactful five to 10 minutes of content out of eight or more hours of raw video becomes a non-trivial time commitment. At the top of the food chain, the largest streamers can hire teams of video editors and social media managers to tackle this part of the job, but growing and part-time streamers struggle to find the time to do this themselves or come up with the money to outsource it. There aren’t enough minutes in the day to carefully review all the footage on top of other life and work priorities.
An emerging solution is to use automated tools to identify key moments in a longer broadcast. Several startups compete to dominate this emerging niche. Differences in their approaches to solving this problem are what differentiate competing solutions from each other. Many of these approaches follow a classic computer science hardware-versus-software dichotomy.
Athenascope was one of the first companies to execute on this concept at scale. Backed by $2.5 million of venture capital funding and an impressive team of Silicon Valley Big Tech alumni, Athenascope developed a computer vision system to identify highlight clips within longer recordings.
In principle, it’s not so different from how self-driving cars operate, but instead of using cameras to read nearby road signs and traffic lights, the tool captures the gamer’s screen and recognizes indicators in the game’s user interface that communicate important events happening in-game: kills and deaths, goals and saves, wins and losses.
These are the same visual cues that traditionally inform the game’s player what is happening in the game. In modern game UIs, this information is high-contrast, clear and unobscured, and typically located in predictable, fixed locations on the screen at all times. This predictability and clarity lends itself extremely well to computer vision techniques such as optical character recognition (OCR) — reading text from an image.
The stakes here are lower than self-driving cars, too, since a false positive from this system produces nothing more than a less-exciting-than-average video clip — not a car crash.
Powered by WPeMatico
China is becoming a superpower in the tech industry. According to Straits Times, China is the only place in the world where it takes less than six years for a startup to become a unicorn — it takes seven years in the U.S., eight years in the U.K. and 11 years in Germany. Despite geopolitical tensions and recent amendments in CFIUS, it is hard to ignore China.
When I joined Runa Capital almost a year ago, my task was to help our portfolio companies enter the Chinese market, find the right partners and raise funding from Chinese investors. And almost on every call with our startups, colleagues from Runa or other global VCs, I heard: Is it a good idea to raise from a Chinese VC? Is it OK to co-invest with Chinese investors? I was surprised to learn that there is little research answering such questions, as there is a lack of adequate information in English about Chinese investments.
Access to the Chinese market seems to be an obvious reason to invite Chinese funds aboard, but only about 20% of Western startups with Chinese capital have operations in China.
So as a Mandarin-speaking specialist, I decided to fill this gap by conducting a study based on Chinese VC database ITjuzi (the Chinese version of Crunchbase) with the help of our powerful data science resources developed by Danil Okhlopkov.
Below, I will try to answer the following questions using statistics and a case-based approach:
After studying data from ITjuzi, we estimated that Chinese funds invested around $250 billion in 2020 (three times higher than the figure reported in Crunchbase). This figure puts Chinese VC investments only 30% lower than investments by U.S. funds, but three times that of U.K. funds and 12.5 times more than German funds.
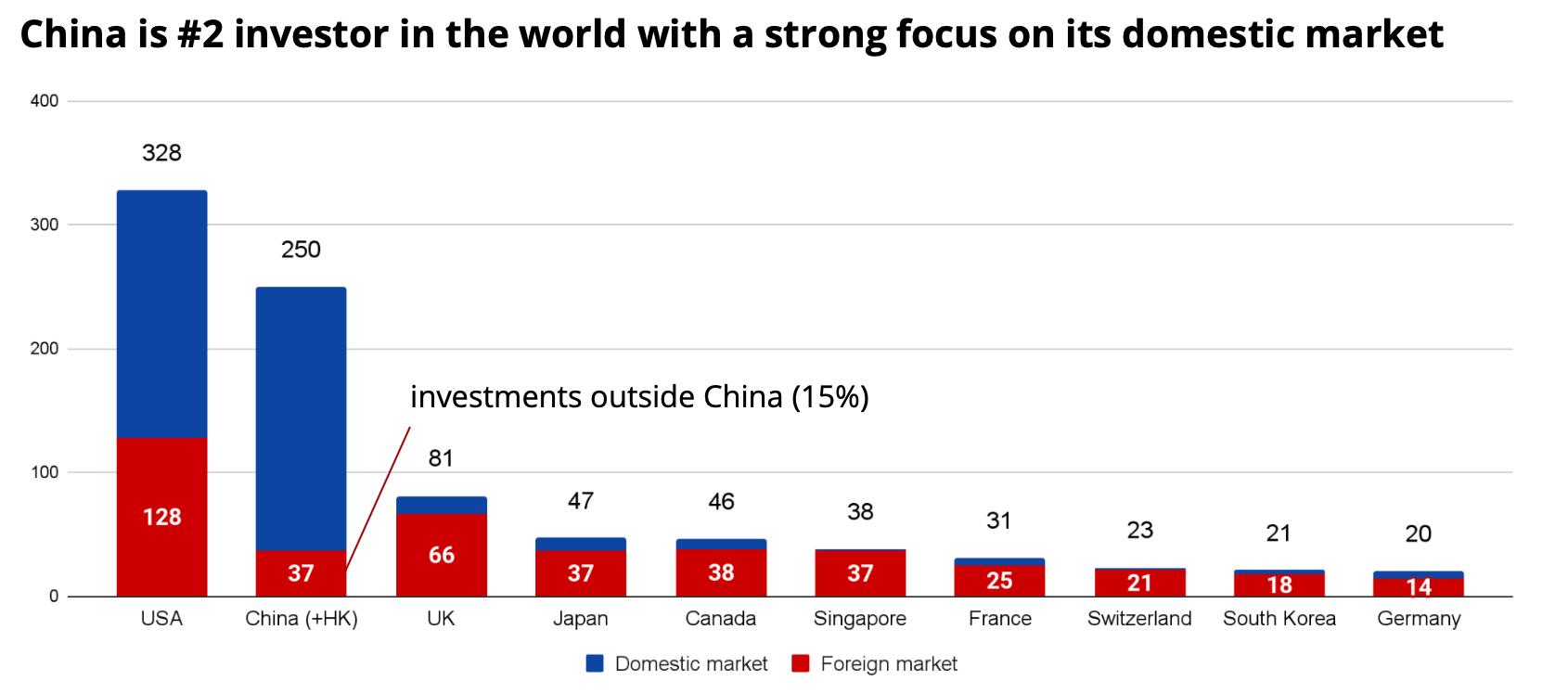
Fig. 1 — Comparison of investment from different countries in 2020, $bn. Source: Crunchbase, ITjuzi. Image Credits: Denis Kalinin
However, only 15% of investments in 2020 and 17% of investments in the first half of 2021 were in companies outside China, significantly lower than in 2019. This appears to be because during COVID, China’s economy recovered much faster than other countries’, so many Chinese investors preferred to redirect their capital flows to the domestic market.
On the other hand, there is great potential for overseas investments to rebound as soon as the borders reopen and the global economy starts to recover.
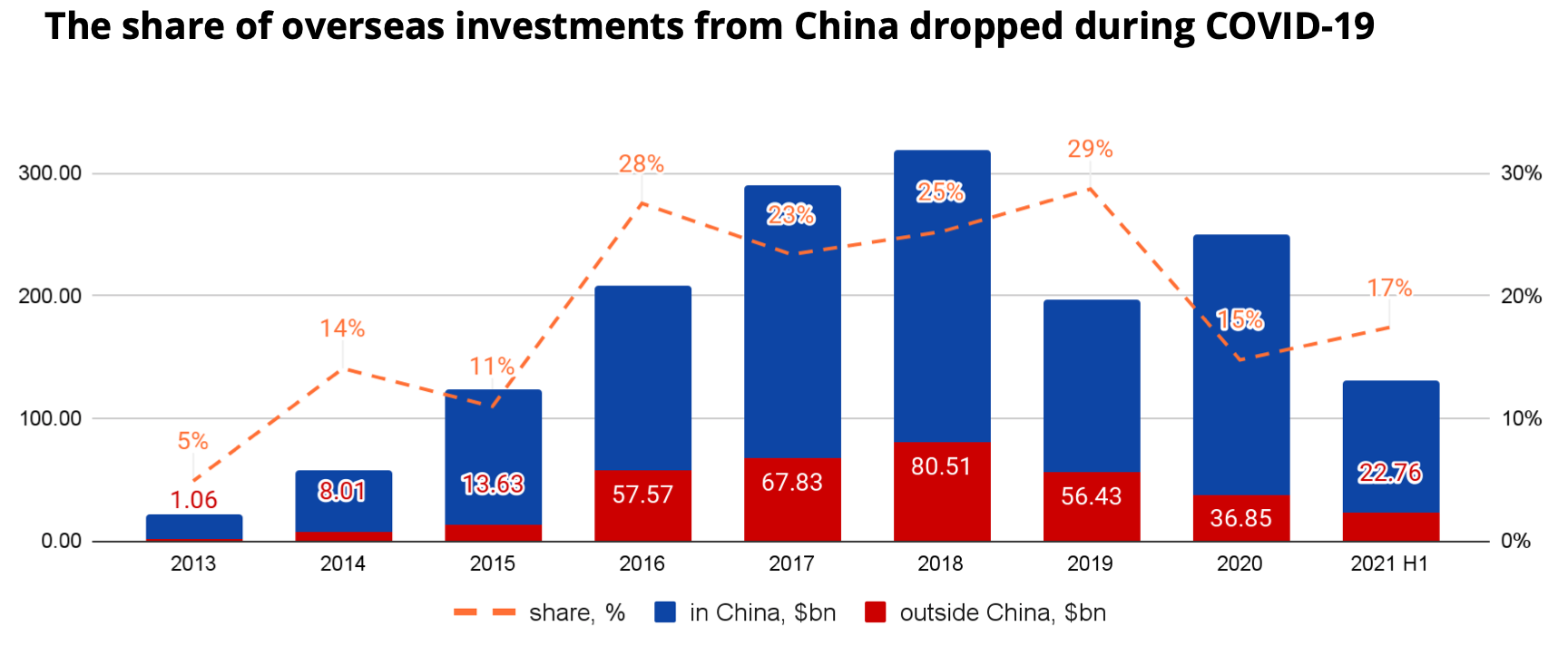
Fig. 2 — Dynamics of Chinese investments. $bn. Source: Crunchbase, ITjuzi. Image Credits: Denis Kalinin
We can also see that Chinese investors are eyeing European startups favorably, which is related to U.S.-China geopolitical tensions as well as the fact that the European VC market is becoming mature.
Powered by WPeMatico
Both as a term and as a financial product, “buy now, pay later” has become mainstream in the past few years. BNPL has evolved to assume various forms today, from small-ticket offerings by fintechs on consumer checkout platforms and marketplaces, to closed-loop products offered on marketplaces such as Amazon Pay Later (which they are now extending for outside use as well). You can also see some variants offered by companies that want to expand the scope of consumption and consumer credit.
Globally, BNPL has seen the most growth in the consumer segment and has driven retail consumption and lending over the past few years. Consumer BNPL offerings are a good alternative to credit cards, especially for people who do not have a credit history and can’t get credit from banks. That said, a specific vertical of BNPL products is gaining traction — one targeted toward small and medium enterprises (SMEs). This new vertical is known as “SME BNPL.”
BNPL can be particularly useful when flow-based underwriting or transaction-based underwriting is used to offer credit to small businesses.
E-commerce has seen tremendous growth in India over the past decade. Skyrocketing smartphone and internet penetration led to rapid growth in e-commerce across large cities and smaller towns alike. Consumer credit has also taken off in parallel as credit cards and digital lending spurred credit-based consumption across offline and online stores.
However, the large B2B supply chain enabling the burgeoning retail market was plagued by bottlenecks and inefficiencies because it involved a plethora of intermediaries and streamlining became a big problem. A number of tech players responded by organizing the previously disorganized B2B commerce market at various touch points, inserting convenience, pricing and easier product access through tech-enabled logistics and a modern supply chain.
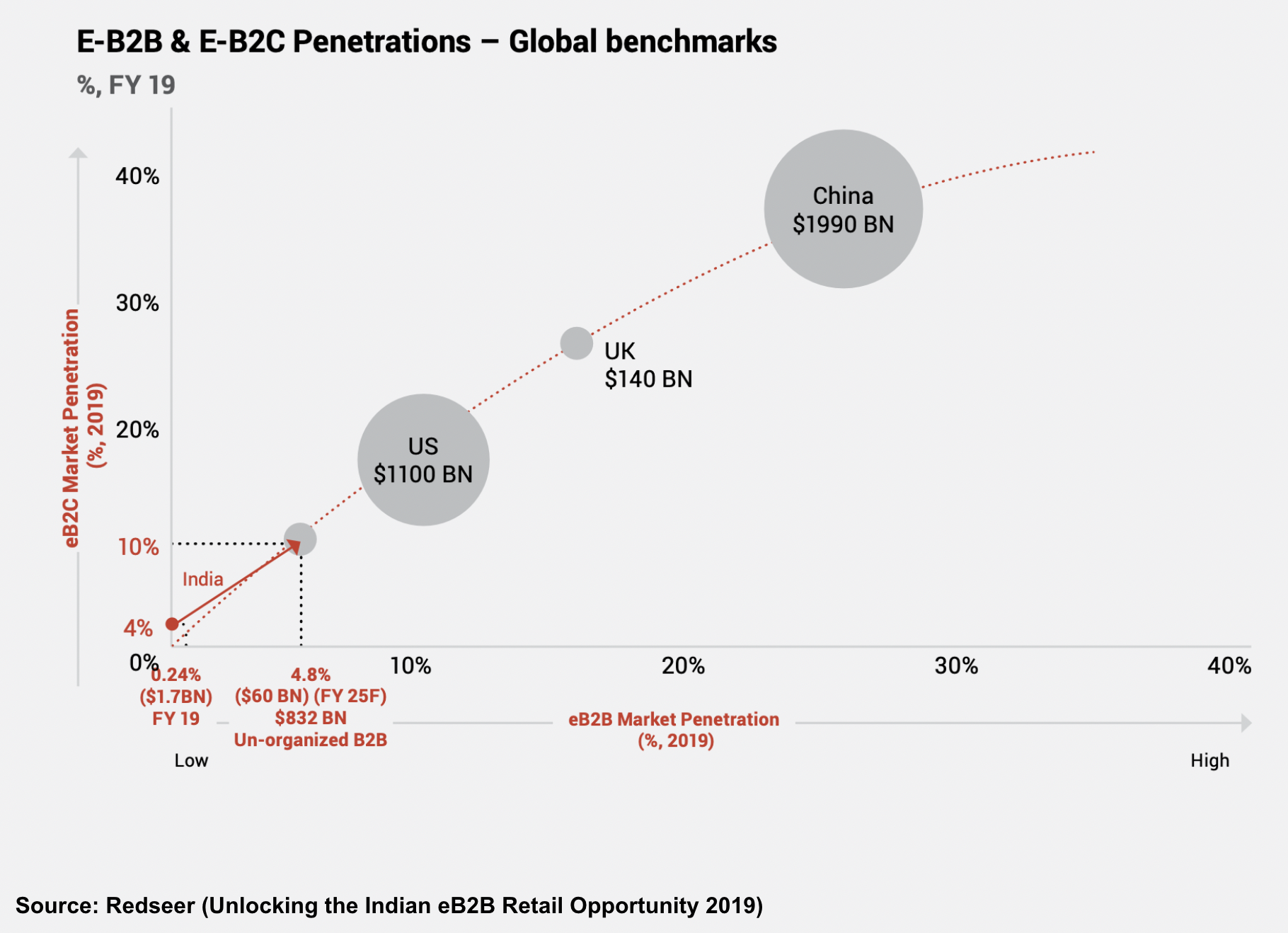
Image Credits: Redseer
India’s B2B e-commerce space has developed rapidly since 2020. Small businesses have moved from using paper to smartphone apps for running a significant part of their day-to-day business, leading to widespread disruption in how businesses transact today. The COVID-19 pandemic also forced small businesses, which were earlier using physical means to procure goods and services, to try new and online models to conduct their affairs.
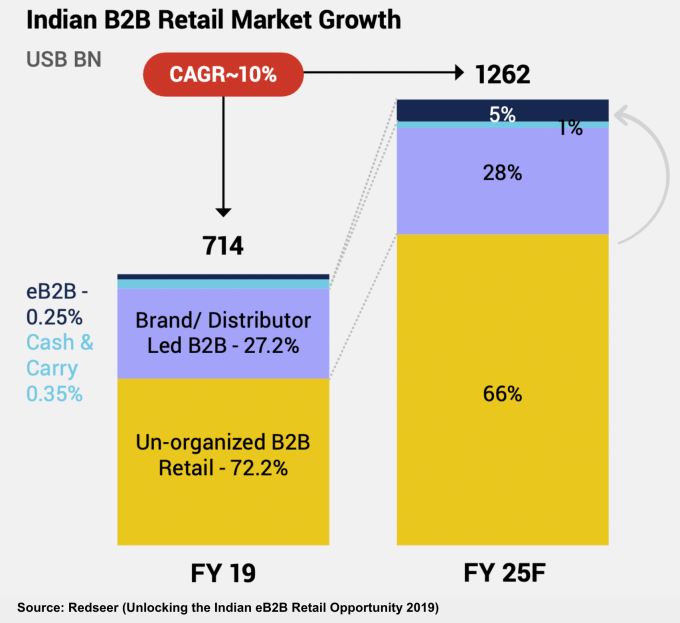
Image Credits: Redseer
Moreover, the Indian government’s widespread promotion of an instant payments system in the form of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has changed how people send money to each other or pay merchants for their goods and services. The next step for solving the digital B2B puzzle is to embed credit inside every transaction and invoice.
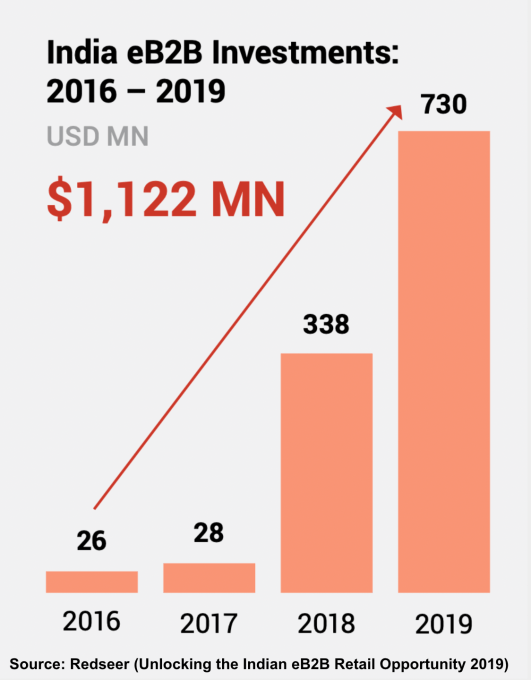
Image Credits: Redseer
If we compare online B2B transactions to the offline world, there is only one missing link: The terms offered to small businesses by their supplier/distributor or vendor. Businesses, unlike consumers, must buy goods and services to eventually trade them, or add value and sell to consumers or others down the value chain. This process is not immediate and has a certain time cycle attached.
The longer sales cycle means many small businesses require credit payment terms when buying inventory. As B2B commerce scales and grows through digital means, a BNPL product that caters to the needs of SMEs can support their growth and alleviate the burden on their cash flows.
An SME BNPL product is a purchase financing product for small businesses transacting with suppliers, distributors, aggregator platforms or B2B marketplaces.
Powered by WPeMatico
China’s first data privacy laws go into effect on November 1, 2021. Will your company be in compliance?
Modeled after the EU’s GDPR, the new regulations “[introduce] perhaps the most stringent set of requirements and protections for data privacy in the world,” writes Scott W. Pink, special counsel in O’Melveny’s Data Security & Privacy practice.
In a comprehensive overview, he explains its key requirements and compliance steps for U.S.-based firms that service Chinese consumers.
“American firms doing business in China or with companies inside China will need to immediately start assessing how this new law will impact their activities,” he advises.
Now that the world has embraced remote work, are visas as critical for startup founders who want to succeed in the United States?
On Tuesday, September 14, at 2 p.m PT/5 p.m. ET, Managing Editor Danny Crichton and immigration law attorney Sophie Alcorn will discuss the matter on Twitter Spaces.
Join @DannyCrichton on Tuesday, September, 14 at 2 p.m. PT/5 p.m. ET as he discusses if remote work will make H-1B visas redundant with @Sophie_Alcorn https://t.co/SCMUiqUj8J
— TechCrunch (@TechCrunch) September 10, 2021
They’ll take questions from the audience, so mark your calendar and follow @techcrunch on Twitter to get a reminder before the chat.
Thanks very much for reading Extra Crunch; I hope you have a great weekend.
Walter Thompson
Senior Editor, TechCrunch
@yourprotagonist

Image Credits: hauged (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Whether or not he actually said it, “buy land, they ain’t making any more of it,” is one of Mark Twain’s best quotes on capitalism.
Past recessions and the ongoing pandemic have created real uncertainty about the future of commercial and residential real estate, but farmland is “historically stable,” says Artem Milinchuk, founder and CEO of FarmTogether.

Image Credits: mikroman6 (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Online mortgage company Better.com isn’t waiting to complete its SPAC merger before making big moves: Ryan Lawler reported that it purchased Property Partners, a U.K.-based startup that offers fractional property ownership.
It’s the second company Better bought in recent months: In July, it snapped up digital mortgage brokerage Trussle.
“We aren’t so easily categorized,” said Better CEO Vishal Garg, who told Ryan that the company plans to soon expand into traditional financial services like auto loans and insurance.
Said CFO Kevin Ryan, “a lot of people have their niches in the way they’re attacking this, but we feel like we’re on a path to being full stack where everything’s embedded in the same flow.”

Image Credits: JoKMedia (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
If you don’t have a good story to share, it doesn’t matter how big your marketing budget is.
“Paid marketing can be a useful tool in your toolkit to accelerate an already humming flywheel. Just don’t let it be the only one,” suggests Brian Rothenberg, a two-time founder who’s now a partner at Defy.
Drawing from his time as VP of growth for Eventbrite, he shares five critical factors for kick-starting, maintaining and measuring growth over the long term.

Image Credits: Peter Dazeley (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Many potential founders are well-versed in startup economics — and many are completely green.
When it comes to raising funds, understanding the relative benefits (and limitations) of debt and equity financing is required knowledge, however.
Founders who are less willing to dilute their control may be willing to use debt financing to fund their capital expenditures, “but it doesn’t make sense for everyone,” says six-time entrepreneur David Friend.

Image Credits: Getty Images
Last year, startups based in Southeast Asia raised more than $8.2 billion, a 4x increase from 2015.
In the first half of 2021, regional M&A has increased 83% to a record $124.8 billion.
It’s not just venture capitalists and Big Tech who are beefing up their presence in the region.
“Over 229 family offices have been registered in Singapore since 2020, with total assets under management of an estimated $20 billion,” writes Amit Anand, a founding partner of Jungle Ventures.

Image Credits: Bryce Durbin / TechCrunch
Natasha Mascarenhas examined the parallels between edtech and the creator economy, both of which boomed amid the pandemic — and blurred amid the rise of cohort-based classes.
“Edtech and the creator economy certainly differ in the problems they try to solve: Finding a VR solution to make online STEM classes more realistic is a different nut to crack than streamlining all of a creator’s different monetization strategies into one platform. Still, the two sectors have found common ground in the past year.”

Image Credits: Liyao Xie (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Were the shoes, jacket and makeup that looked so good on Instagram (and in your shopping cart) disappointing when you put them on for the first time?
Due to buyer’s remorse, it’s not uncommon for apparel or beauty products to languish in the back of a drawer or end up as gifts, but there are also serious consequences.
“The beauty industry produces over 120 billion units of packaging every year, little of which is recycled. Globally, an estimated 92 million tons of textile waste ends up in landfills,” Sindhya Valloppillil, founder and CEO of Skin Dossier, notes in a guest column.
The answer to bringing sustainability to the industry, she says, is using tech to personalize the retail experience:

Image Credits: Bryce Durbin / TechCrunch
Twenty million people live in Lagos, Nigeria, and each day, 14 million of them use the city’s transit system.
Travelers rely on overcrowded public buses that navigate congested routes: What should be a 30-minute trip is often a three-hour journey, but Treepz CEO and co-founder Onyeka Akumah “has big plans to ameliorate the public transport infrastructure in Africa and beyond,” writes Rebecca Bellan.
“We wanted to give people a better way to commute with predictability, where they can know when the bus will get here, the certainty that they will have a seat in a vehicle, that it’s a decent vehicle and a safe one where you can bring your laptop,” said Akumah.
“Those are the things we said we wanted to change.”
Image Credits: Bryce Durbin/TechCrunch
Dear Sophie,
My husband just accepted a job in Silicon Valley. His new employer will be sponsoring him for an E-3 visa.
I would like to continue working after we move to the United States. I understand I can get a work permit with the E-3 visa for spouses.
How soon can I apply for my U.S. work permit?
— Adaptive Aussie
Powered by WPeMatico
Quizlet, a flashcard tool turned artificial intelligence-powered tutoring platform, is planning an initial public offering nearly a year after it was valued at $1 billion. According to people familiar with the matter, Quizlet is considerably far along in the process to go public. A recent job filing shows that it is hiring for senior roles to “help build the financial systems and processes as we move towards an IPO.”
In an email to TechCrunch, the San Francisco-based edtech startup declined to comment. Quizlet hasn’t said much about its revenue specifics or if it’s profitable. Last year, the still-private startup claimed it was growing revenue 100% annually. On its website, Quizlet says that it has 60 million monthly learners, up 10 million learners compared to its 2018 totals.
Quizlet has built a large-scale business around simple to share and simple to use products. Its free flashcard maker helps students spin up study guides on topics to prepare for exams. Those insights fuel Quizlet Plus, the startup’s subscription product that charges $47.88 a year for access to more features, including tutoring services.
Quizlet’s tutoring arm, also known as Quizlet Learn, is the company’s most popular offering, per CEO Matthew Glotzbach. As a student goes through the system, Quizlet Learn consistently assesses students to see where they are making mistakes — and where they are making progress.
“It obviously doesn’t yet replace and can’t come anywhere close to replacing a human, but it can provide that guidance and point you in the right direction and help you spend your time in the right places,” he said. “Just even helping you set goals is such a critical step in learning.”
Most recently, Quizlet announced the launch of explanations, a feature that offers a step-by-step solution guide for problem sets from popular textbooks. The feature is “written and verified by experts” and is aimed to help “students better understand the reasoning and thought process behind study questions so they can practice and apply their learnings on their own,” it said in a statement. It also reclaimed the Q from its less fortunate predecessor, amid an entire rebrand.
Quizlet’s quiet march toward the public markets has been slow yet steady. The startup was founded in 2005 by a 15-year-old, Andrew Sutherland. It was fully bootstrapped until 2015. Glotzbach, who was previously an executive at YouTube, then joined in 2016. The startup still doesn’t appear to have a CFO, which is rare for companies that are going public.
Quizlet has raised a majority of its $62 million in venture capital under Glotzbach. Now, investors in the company include General Atlantic, Owl Ventures, Union Square Ventures, Costanoa Ventures and Altos Ventures.
Quizlet’s pursuit of the public markets comes as other edtech companies are proving the market’s reception to the sector. Duolingo, for example, is another consumer-focused education company, albeit one that focuses on one vertical versus Quizlet’s choice to stay broad. Duolingo went public in July, and is currently trading above its open price at $169.75 per share.
Powered by WPeMatico
The desire to achieve something as simple as keeping shared electric scooters off sidewalks has driven the development of some advanced technology in the micromobility industry. Once the province of geofencing, scooter companies are so eager to get a leg up on the competition that they’re now implementing technology similar to advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) usually found in cars.
Operators like Spin, Voi, Zipp, Bird and Superpedestrian are investing in camera-based or location-based tech that can detect and even correct poor rider behavior, sometimes going to the extent of slowing scooters to a stop if they’re riding on a sidewalk.
People riding or parking scooters on sidewalks is a big problem for cities and forms one of the main complaints from NIMBYist residents who dislike change all the more when it becomes a tripping hazard. Companies are trying to solve this problem with tech that effectively puts the onus of rider behavior on operators, which may result in cities requiring scooter operators to have this sort of ADAS tech.
Scooter ADAS is probably the most doable and cost-effective method that cities can use to prevent unwanted rider behavior. And, it’s far cheaper than trying to police rider behavior themselves, or, address the lack of protected cycling infrastructure.
“This technology comes from a need for protected bike lanes,” said Dmitry Shevelenko, co-founder and president of Tortoise, an automated vehicle positioning service for micromobility companies. “It exists in this world where riders kind of have to do things that aren’t that great for others, because they have nowhere else to go. And so that’s the true driver of the need for this.”
Cities can solve this problem for the long term by building bike lanes or creating scooter parking bays, but until that happens, operators need to reassure local administrations that micromobility is safe, compliant and a good thing for cities.
“Until cities have dedicated infrastructure for whatever new modality comes to play, you have to figure out a way to use technology to make sure things don’t mix poorly,” said Alex Nesic, co-founder and chief business officer of Drover AI, a computer vision startup that provides camera-based scooter ADAS. “That’s really what we’re after. We want to enable this kind of maturation of the industry.”
Drover AI works with Spin, while Luna, another computer vision company, works with Voi and Zipp to attach cameras, sensors and a microprocessor to scooters to detect lanes, sidewalks, pedestrians and other environmental surroundings.
Powered by WPeMatico
Just about every company is sitting on vast amounts of data, which they can use to their advantage if they can just learn how to harness it. Data is actually the fuel for machine learning models, and with the proper tools, businesses can learn to process this data and build models to help them compete in a rapidly changing marketplace, to react more quickly to shifting customer requirements and to find insights faster than any human ever possibly could.
Boston-based DataRobot, a late-stage startup that has built a platform to help companies navigate the machine learning model lifecycle, has been raising money by the bushel over the last several years, including $206 million in September 2019 and another $300 million in July. DataRobot CEO Dan Wright will be joining us on a panel to discuss the role of data in business at TC Sessions: SaaS on October 27th.
The company covers the gamut of the machine learning lifecycle, including preparing data, operationalizing it and finally building APIs to make it useful for the organization as it attempts to build a soup-to-nuts platform. DataRobot’s broad platform approach has appealed to investors.
As we wrote at the time of the $206 million round:
The company has been catching the attention of these investors by offering a machine learning platform aimed at analysts, developers and data scientists to help build predictive models much more quickly than it typically takes using traditional methodologies. Once built, the company provides a way to deliver the model in the form of an API, simplifying deployment.
DataRobot has raised a total of $1 billion on $6.3 billion post valuation, according to PitchBook data, and it’s been putting that money to work to add to its platform of services. Most recently the company acquired Algorithmia, which helps manage machine learning models.
As the pandemic has pushed more business online, companies are always looking for an edge, and one way to achieve that is by taking advantage of AI and machine learning. Wright will be joined on the data panel by Monte Carlo co-founder and CEO Barr Moses and AgentSync co-founder and CTO Jenn Knight to discuss the growing role of data in business operations
In addition to our discussion with Wright, the conference will also include Microsoft’s Jared Spataro, Amplitude’s Olivia Rose, as well as investors Kobie Fuller and Laela Sturdy, among others. We hope you’ll join us. It’s going to be a thought-provoking lineup.
Buy your pass now to save up to $100. We can’t wait to see you in October!
Powered by WPeMatico
When Anik Khan graduated from college, his first job was working on credit cards and business expenses at Accenture. There, he found that someone could bring in a couple of thousand dollars just by having the right credit cards and following the rewards and promotions.
It was back in 2017 when he and David Gao got the idea for his company MaxRewards, a digital wallet app that manages credit cards and automatically activates benefits like rewards, cashback offers and monthly credits. It also makes recommendations at the point of purchase on which card would yield the best reward for that purchase.
Going after the some 83% of Americans that have a credit card, the app version was officially launched in 2019, and now the Atlanta-based company is announcing a $3 million seed round co-led by Dundee Venture Capital and Calano Ventures. Also backing the company are Techstars, Fintech Ventures Fund, Service Provider Capital and Fleetcor president Nick Izquierdo.
Tracking his own credit cards manually prior to MaxRewards, Khan recalled in one year, getting $16,000 in rewards. However, utilizing those benefits was time-consuming and difficult, because the rewards and savings aren’t always made evident by the credit card companies.
“Other companies have tried to do something similar, but the issue is you don’t have the reward information or the offers,” Khan told TechCrunch. “If you were to aggregate this information, you still would have to activate all of these things and use them before they expired.”
Users connect their accounts and when they make a purchase, their location is cross-referenced with the merchant and an algorithm is applied to tell the user which card to use. The average app user has six credit cards.
MaxRewards is free to download and use, and the majority of the app’s functionalities are free. Users who want additional features, like the auto activation or rewards, can join MaxRewards Gold and are given the opportunity to choose their own monthly price — the average is over $25 per month — based on the value they expect to gain, Khan said.
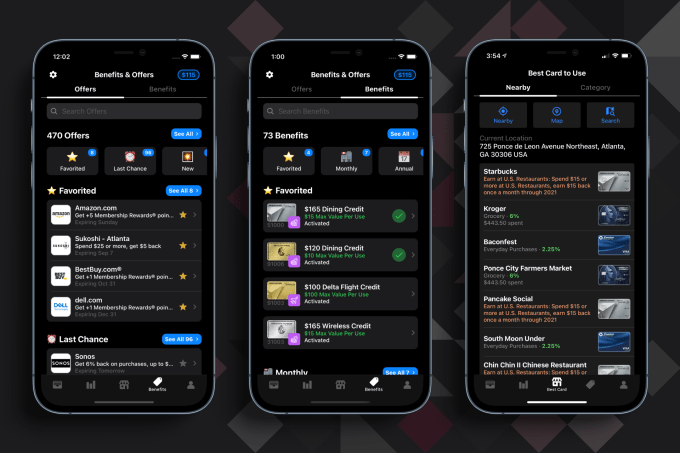
MaxRewards offers and benefits. Image Credits: MaxRewards
Ron Watson, partner at Dundee, said his firm invests in seed-stage companies between the coasts and is interested in consumer and e-commerce companies. Watson said he was impressed with what MaxRewards has been able to do with a team of three. He also relates to the company’s mission, having grown up in a lower, middle-class family that did not frequently go on vacations.
When he got his first job and was suddenly flying everywhere, he recalls building up so many rewards to the point where he was able to go on a vacation to Hawaii and only spend maybe $100, he said.
“I used to put my points into a spreadsheet, but as I got older and had kids, I realized how hard it was for the average person to do that and how important it is to have automation,” Watson said. “I downloaded the app, and on the first day, saved $20.”
The company is often compared to NerdWallet or Mint, but in terms of functionality, Khan said he feels MaxRewards is unique due to its credit card system connectors. Rather than rely on third-party aggregators to discover the rewards, MaxRewards leverages its own proprietary connectors to card systems.
There are hundreds of thousands of offers to be discovered, and consumers are asking for even more features, so Khan decided it was time to go after seed funding. He had raised a small seed, about $200,000, from his time at Techstars, but the new funding will enable him to add to his team of three people. He expects to be at 20 by the end of the year. Khan also wants to accelerate its user acquisition, product improvement and compliance.
Next up, the company is going to automate rewards and savings across additional platforms like debit cards, payment apps and cashback apps, as well as create browser extensions and a web app. Khan also wants to do more on the education side with regard to using credit cards in a smart manner.
Arron Solano, managing partner at Calano, met Khan through Techstars and said he is an advocate for using credit cards in the right way. His firm was looking for a company like MaxRewards.
“During our first call, I remember telling my partner that Anik was a bulldog who knew what he was talking about, especially at that stage,” Solano added. “He had strong team members, his vision lined up well and that checked off a massive box for us. He energized us and showed he could find a market with insanely high ‘super users.’ ”
Powered by WPeMatico
Media technology company Amagi announced Friday $100 million to further develop its cloud-based SaaS technology for broadcast and connected televisions.
Accel, Avataar Ventures and Norwest Venture Partners joined existing investor Premji Invest in the funding round, which included buying out stakes held by Emerald Media and Mayfield Fund. Nadathur Holdings continues as an existing investor. The latest round gives Amagi total funding raised to date of $150 million, Baskar Subramanian, co-founder and CEO of Amagi, told TechCrunch.
Bangalore-based Amagi provides cloud broadcast and targeted advertising software so that customers can create content that can be created and monetized to be distributed via broadcast TV and streaming TV platforms like The Roku Channel, Samsung TV Plus and Pluto TV. The company already supports more than 2,000 channels on its platform across over 40 countries.
“Video is a complex technology to manage — there are large files and a lot of computing,” Subramanian said. “What Amagi does is enable a content owner with zero technology knowledge to simplify that complex workflow and scalable infrastructure. We want to make it easy to plug in and start targeting and monetizing advertising.”
As a result, Amagi customers see operational cost savings on average of up to 40% compared to traditional delivery models and their ad impressions grow between five and 10 times.
The new funding comes at a time when the company is experiencing rapid growth. For example, Amagi grew 30 times in the United States alone over the past few years, Subramanian said. Amagi commands an audience of over 2 billion people, and the U.S. is its largest market. The company also sees growth potential in both Latin America and Europe.
In addition, in the last year, revenue grew 136%, while new customer year over year growth was 44%, including NBCUniversal — Subramanian said the Tokyo Olympics were run on Amagi’s platform for NBC, USA Today and ABS-CBN.
As more of a shift happens with video content being developed for connected television experiences, which he said is a $50 billion market, the company plans to use the new funding for sales expansion, R&D to invest in the company’s product pipeline and potential M&A opportunities. The company has not made any acquisitions yet, Subramanian added.
In addition to the broadcast operations in New Delhi, Amagi also has an innovation center in Bangalore and offices in New York, Los Angeles and London.
“Consumer behavior and infrastructure needs have reached a critical mass and new companies are bringing in the next generation of media, and we are a large part of that growth,” Subramanian said. “Sports will come on quicker, while live news and events are going to be one of the biggest growth areas.”
Shekhar Kirani, partner at Accel, said Amagi is taking a unique approach to enterprise SaaS due to that $50 billion industry shift happening in video content, where he sees half of the spend moving to connected television platforms quickly.
Some of the legacy players like Viacom and NBCUniversal created their own streaming platforms, where Netflix and Amazon have also been leading, but not many SaaS companies are enabling the transition, he said.
When Kirani met Subramanian five years ago, Amagi was already well funded, but Kirani was excited about the platform and wanted to help the company scale. He believes the company has a long tailwind because it is saving people time and enabling new content providers to move faster to get their content distributed.
“Amagi is creating a new category and will grow fast,” Kirani added. “They are already growing and doubling each year with phenomenal SaaS metrics because they are helping content providers to connect to any audience.
Powered by WPeMatico
Epic Games has asked Apple to rejoin its Fortnite developer account in South Korea as the U.S. game maker plans to re-release Fortnite on iOS in South Korea, offering both Epic and Apple payments side-by-side, it said in a tweet.
Epic has asked Apple to restore our Fortnite developer account. Epic intends to re-release Fortnite on iOS in Korea offering both Epic payment and Apple payment side-by-side in compliance with the new Korean law.
— Fortnite (@FortniteGame) September 9, 2021
This request comes after South Korea passed a bill, the updated Telecommunications Business Act, in late August that will force Apple and other tech giants to let developers use their third-party payment systems.
“Epic intends to re-release Fortnite on iOS in Korea offering both Epic payment and Apple payment side-by-side in compliance with the new Korea law,” according to the official Fortnite Twitter account.
“As we’ve said all along, we would welcome Epic’s return to the App Store if they agree to play by the same rules as everyone else. Epic has admitted to breach of contract and as of now, there’s no legitimate basis for the reinstatement of their developer account,” Apple said in its statement.
Epic would also have to agree to comply with Apple’s App Store Review Guidelines regarding all apps, but Epic has not consistently abided by the Guidelines, and their request of Apple does not indicate any change in Epic’s position, added Apple’s statement.
Even if the South Korean legislation, which is not yet effective, were to become law in the country, it would impose no obligation on Apple to approve any developer program account application, based on Apple’s statement.
In August 2020, Apple kicked Fortnite off the App Store after Epic introduced a direct payment system in Fortnite that violated Apple’s in-app purchase requirement. The two companies have been embroiled in a legal dispute over the Apple Store’s payment system.
Apple is changing its app policy to allow developers to link to external websites and it also has reached a settlement with Japan for allowing developers of “reader” apps to link to their own websites.
An Epic Games spokesperson did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Powered by WPeMatico