TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Payments startup Stripe has changed the landscape for how businesses can collect funds online by using a few lines of code, and today the company is announcing that it’s picked up more funding of its own. Stripe has raised $245 million, valuing the company at $20 billion.
This is a big jump on its previous round, two years ago, that valued it at $9 billion.
Led by Tiger Global Management, other new backers included DST Global and Sequoia, along with existing investors Andreessen Horowitz, Kleiner Perkins, Khosla Ventures, General Catalyst and Thrive Capital.
The company says it plans to use the funding to hire more people for what it describes as its “distributed global engineering team.” It now has hubs in San Francisco, Seattle and Dublin (its co-founders, John and Patrick Collison, hail from Ireland), and it’s also going to launch a new hub in Singapore.
Engineering has been at the heart of the company’s growth from the start, up to now. Recall the famous essay by Paul Graham about Stripe that served as a mantra of sorts for how startups should grow. Fast forward to today, and Stripe boasts that “all told, the company deployed more than 3,200 new versions of its core API over the past year.”
The funding underscores the continuing strong climate for raising money from private backers at increasingly staggering valuations. VCs and private equity firms have raised billions, and they are looking for fast-growing, promising startups where they can invest that money. A number of startups are foregoing, or delaying, going public in favor of staying private for longer, financed by them.
“We have no plans to go public,” said John Collison in an interview. “We’re fortunate to be in the position that the Stripe business is performing very well and the long-term opportunity is that we’re very optimistic to providing the richer stack to businesses. Strong businesses do not always tend to be dependent on outside funding.”
(Not all are following this route: a key competitor of Stripe’s, Adyen, had a very strong IPO debut earlier this year.)
Stripe itself is a prime target for VCs looking to park their money in fast-growing, outsized startups. The company says it now has “millions” of customers, including Google, Didi, Mindbody, Spotify and Uber. It is live in 130 markets for acceptance and 25 countries for originating the charges.
Carving a place out for itself as a faster, easier way to integrate payments infrastructure into websites and apps, by way of a few lines of code, Stripe’s pitch is that it replaces the more laborious, and often more expensive route, of working with banks and other payment providers in a complicated chain of players that includes gateway providers, credit card processors, merchant acquirers, specialized payment methods, wallets and more.
And although Amazon is one of the world’s biggest companies, and most retailers have a digital presence, e-commerce is still a relatively nascent area, with only about three percent of all transactions occurring online at a global average. That means a big opportunity for companies like Stripe, but also competitors like Adyen, PayPal and others.
“We believe in the contingency of progress,” said Stripe CEO and co-founder Patrick Collison, in a statement. “Better global payments infrastructure will increase economic output, encourage entrepreneurship and help upstarts compete with incumbents. By bringing Stripe into more markets and building out our capabilities for companies of all sizes, we hope to accelerate innovation around the world.” Stripe estimates there will be $4 trillion in online sales by 2020 globally.
While payments is Stripe’s bread and butter, the company has also been diversifying and now also includes Stripe Issuing, Stripe Terminal, fraud detection and potentially cash advances, among its various offerings. These help the company develop stronger ties with its customers, and also potentially increase its margins.
“No one else is going as deep as us on software and the technology stack as we are,” said co-founder and president John Collison.
Powered by WPeMatico
Today, a new crop of startups is launching out of the Entrepreneurs Roundtable Accelerator. This marks the 15th ERA class, with the past 14 classes comprising 165 startups with a combined market capitalization of more than $2 billion.
Thirteen companies in total are participating in the demo day today, spanning a variety of industries, including e-commerce, real estate and voice collaboration.
Here are the new startups:
Agilis is a B2B commerce platform for chemical distributors. The supply chain for chemical distribution is often complex, but Agilis aggregates supply and demand and facilitates transactions on behalf of all parties involved, from producers to distributors to buyers.
As voice interfaces continue to grow in prominence, Airbud is looking to offer developers and companies a way to add voice capabilities to their websites and apps. Airbud’s technology quickly ingests the information on a website or app to allow users to interact with that information with their voice.
Bikky looks to give restaurant owners more insight into their customers, aggregating data across online ordering channels and using SMS to get real-time feedback on orders. The customer analytics platform for restaurants hopes to help businesses increase their customer retention and better understand what is and isn’t working with their business.
Daivergent was founded by Byran Dai. Inspired by his brother, who has autism, he created Daivergent to allow businesses to hire individuals with autism who are particularly well-suited to perform complex data tasks. The platform provides training, management and workflow functions alongside making the initial connection between these highly skilled workers and companies.
Ettitude is a D2C bedding and homewares brand looking to compete with the likes of Brooklinen. Unlike most competitors, however, Ettitude uses a proprietary supply of organic bamboo lyocell fabric to make soft, cooling, hypoallergenic sheets, pillowcases, etc.
LVRG is a vendor relationship management platform for the enterprise, allowing decision-makers within organizations to make collaborative, informed purchasing decisions with the help of an AI algorithm.
Maivino reinvents the idea of boxed wine by letting users subscribe to receive premium wine in a pouch. Unlike a box or a bottle, Maivino’s pouch keeps wine fresh for 32 days after opening, letting users have control of their own pace.
ProdPerfect wants to make quality assurance regression tests for web applications easier and more effective. By analyzing live user traffic to build test cases from behavior patterns, the company gives engineering teams QA testing coverage that continuously and automatically updates as they add new features.
Rocket Cloud is looking to be the Angie’s List for industrial suppliers. The company has created a marketplace that connects electrical, plumbing and HVAC equipment manufacturers and suppliers to online customers.
Rubik is a data platform for real estate investors, providing up-to-date financial data on 70 million single family homes in the U.S., letting investors search based on their own investment criteria.
Threshing Floor Security collects, aggregates and analyzes internet background noise, network scans, web scrapers and authentication attempts to let security teams find alerts that matter to them. The company integrates its technology with the most popular enterprise security products out there.
Triyo is a secure project collaboration platform for highly regulated industries, particularly financial services. As teams work together on a project, they can use Triyo to collaborate on documents, presentations and spreadsheets efficiently without duplicating work, all within the bounds of internal compliance and regulatory rules.
Woveon is a CRM tool that aggregates data from all channels, including phone calls, email, social media and CRM, so that companies can get a bird’s-eye view of their customer relations. The platform is powered by AI, allowing Woveon to point out the most relevant information for resolving customer inquiries.
Powered by WPeMatico
There’s a secret Facebook app called Blink. Built for employees only, it’s how the company tests new video formats it’s hoping will become the next Boomerang or SuperZoom. They range from artsy Blur effects to a way even old Android phones can use Slo-Mo. One exciting format in development offers audio beat detection that syncs visual embellishments to songs playing in the background or added via the Music feature for adding licensed songs as soundtracks that is coming to Facebook Stories after debuting on Instagram.
“When we first formed the team . . . we brought in film makers and cinematographers to help the broader team understand the tropes around storytelling and film making,” says Dantley Davis, Facebook Stories’ director of design. He knows those tropes himself, having spent seven years at Netflix leading the design of its apps and absorbing creative tricks from countless movies. He wants to democratize those effects once trapped inside expensive desktop editing software. “We’re working on formats to enable people to take the video they have and turn it into something special.”
For all the jabs about Facebook stealing Stories from Snapchat, it’s working hard to differentiate. That’s in part because there’s not much left to copy, and because it’s largely succeeded in conquering the prodigal startup that refused to be acquired. Snapchat’s user count shrank last quarter to 188 million daily users.
Meanwhile, Facebook’s versions continue to grow. The Messenger Day brand was retired a year ago and now Stories posts to either the chat app or Facebook sync to both. After announcing in May that Facebook Stories had 150 million users, with Messenger citing 70 million last September, today the company revealed they have a combined 300 million daily users. The Middle East, Central Latin America and Southeast Asia, where people already use Facebook and Messenger most, are driving that rapid growth.

With the success of any product comes the mandate to monetize it. That push ended up pushing out the founders of Facebook acquisition WhatsApp, and encroachment on product decision-making did the same to Instagram’s founders who this week announced they were resigning.
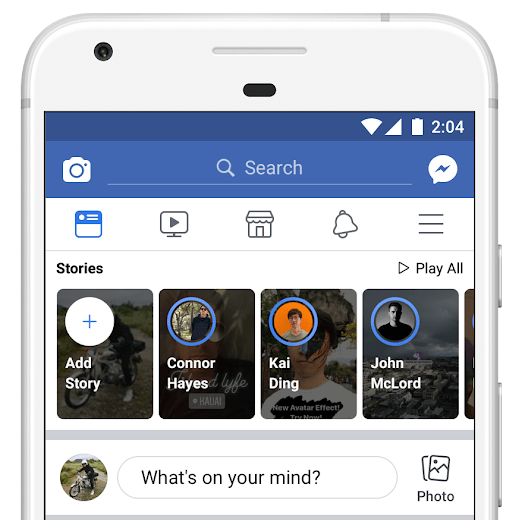
Now the mandate has reached Facebook Stories, which today opened up to advertisers globally, and also started syndicating those ads into Stories within Messenger. Facebook is even running “Stories School” programs to teach ad execs the visual language of ephemerality since all four of its family of apps will monetize Stories with ads. WhatsApp will start to show ads in its Status version of Stories starting next year now that its founders that hated ads have left.
As sharing to Stories is predicted to surpass feed sharing in 2019, Facebook is counting on the ephemeral slideshows to sustain its ad revenue. Fears they wouldn’t lopped $120 billion off Facebook’s market cap this summer.
Facebook Stories ads open to all advertisers today
But to run ads you need viewers, and that will require responses to questions that have dogged Facebook Stories since its debut in early 2017: “Why do I need Stories here too when I already have Instagram Stories and WhatsApp Status?” Many find it annoying that Stories have infected every one of Facebook’s products.

Facebook user experience research manager Liz Keneski
The answer may be creativity. However, Facebook is taking a scientific approach to determining which creative tools to build. Liz Keneski is a user experience research manager at Facebook. She leads the investigative trips, internal testing and focus groups that shape Facebook’s products. Keneski laid out the different types of research Facebook employs to go from vague idea to polished launch:
Last year Facebook went on a foundational research expedition to India. Devanshi Bhandari, who works on the globalization, discovered that even in emerging markets where Snapchat never got popular, people already knew how to use Stories. “We’ve been kind of surprised to learn . . . Ephemeral sharing wasn’t as new to some people as we expected,” she tells me. It turns out there are regional Stories copycats around the globe.
As Bhandari dug deeper, she found that people wanted more creative tools, but not at the cost of speed. So Facebook began caching the Stories tray from your last visit so it’d still appear when you open Facebook Lite without having to wait for it to load. This week, Facebook will start offering creative tools like filters inside Facebook Lite Stories by enabling them server-side so users can do more than just upload unedited videos.
That trip to India ended up spawning whole new products. Bhandari noticed some users, especially women, weren’t comfortable showing their face in Stories. “People would sometimes put their thumb over the video camera but share the audio content,” she tells me. That led Facebook to build Audio Stories.
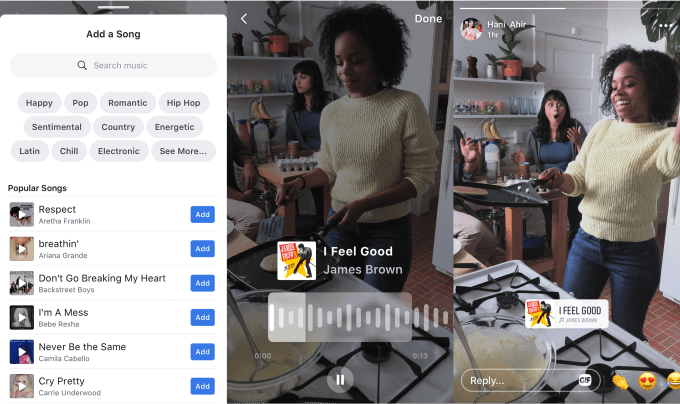
Facebook now lets U.S. users add music to Stories just like Instagram

Dantley Davis, Facebook Stories’ director of design
Back at Facebook headquarters in California, the design team runs exercises to distill their own visions of creative. “We have a phase of our design cycle where we ask the designers . . . to bring in their inspiration,” says Davis. That means everything from apps to movie clips to physical objects. Facebook determined that users needed better ways to express emotion through text. While it offers different fonts, from billboard to typewriter motifs, they couldn’t convey if someone is happy or sad. So now Davis reveals Facebook is building “kinetic text.” Users can select if they want to convey if text is supposed to be funny or happy or sad, and their words will appear stylized with movement to get that concept across.
But to make Stories truly Facebook-y, the team had to build them into all its products while solving problems rather than creating them. For example, birthday wall posts are one of the longest running emerging behaviors on the social network. But most people just post a thin, generic “happy birthday!” or “HBD” post, which can feel impersonal, even dystopic. So after announcing the idea in May, Facebook is now running Birthday Stories that encourage friends to submit a short video clip of well wishes instead of bland text.
Facebook recently launched Group and Event Stories, where members can collaborate by all contributing clips that show up in the Stories tray atop the News Feed. Now Facebook is going to start building its own version of Snapchat’s Our Stories. Facebook is now testing holiday-based collaborative Stories, starting with the Mid-Autumn Festival in Vietnam. Users can opt to post to this themed Story, and friends (but not the public) will see those clips combined.
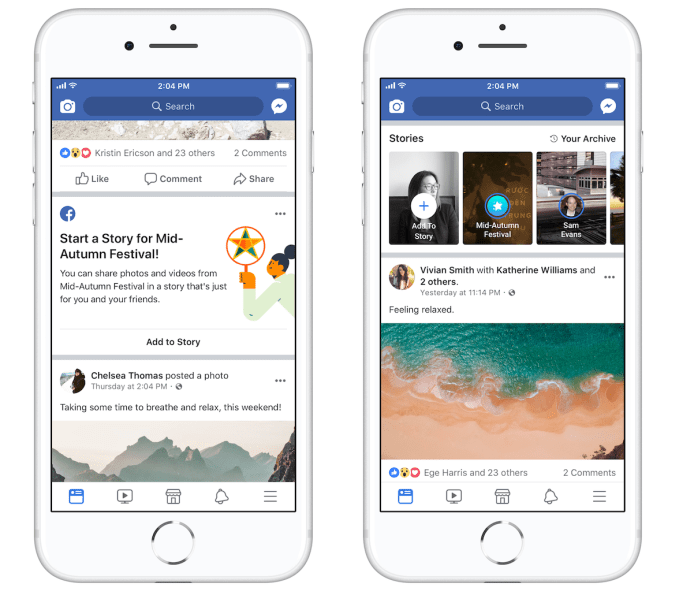
This is the final step of Facebook’s three-part plan to get people hooked on Stories, according to Facebook’s head of Stories, Rushabh Doshi. The idea is that first, Facebook has to get people a taste of Stories by spotlighting them atop the app as well as amidst the feed. Then it makes it easy for people to post their own Stories by offering simple creative tools. And finally, it wants to “Build Stories for what people expect out of Facebook.” That encompasses all the integrations of Stories across the product.

Rushabh Doshi, Facebook’s head of Stories
Still, the toughest nut to crack won’t be helping users figure out what to share but who to share to. Facebook Stories’ biggest disadvantage is that it’s built around an extremely broad social graph that includes not only friends but family, work colleagues and distant acquaintances. That can apply a chilling effect to sharing as people don’t feel comfortable posting silly, off-the-cuff or vulnerable Stories to such a wide audience.
Facebook has struggled with this problem in News Feed for over a decade. It ended up killing off its Friend List Feeds that let people select a subset of their friends and view a feed of just their posts because so few people were using them. Yet the problem remains rampant, and the invasion of parents and bosses has pushed users to Instagram, Snapchat and other younger apps. Unfortunately for now, Doshi says there are no Friend Lists or specific ways to keep Facebook Stories more private amongst friends. “To help people keep up with smaller groups, we’re focused on ways people are already connecting on Facebook, such as Group Stories and Event Stories” Doshi tells me. At least he says “We’re also looking at new ways people could share their stories with select groups of people.”
At 300 million daily users, Facebook Stories doesn’t deserve the “ghost town” label any more. People who were already accustomed to Stories elsewhere still see the feature as intrusive, interruptive and somewhat desperate. But with 2.2 billion total Facebookers, the company can be forced to focus on one-size-fits-all solutions. Yet if Facebook’s Blink testing app can produce must-use filters and effects, and collaborative Stories can unlock new forms of sharing, Facebook Stories could find its purpose.
Powered by WPeMatico
Sometimes $10 billion isn’t as much as you think.
It’s true that when you look at the bottom line number of the $10 billion Joint Enterprise Defense Infrastructure (JEDI) cloud contract, it’s easy to get lost in the sheer size of it, and the fact that it’s a one-vendor deal. The key thing to remember as you think about this deal is that while it’s obviously a really big number, it’s spread out over a long period of time and involves a huge and growing market.
It’s also important to remember that the Pentagon has given itself lots of out clauses in the way the contract is structured. This could be important for those who are worried about one vendor having too much power in a deal like this. “This is a two-year contract, with three option periods: one for three years, another for three years, and a final one for two years,” Heather Babb, Pentagon spokeswoman told TechCrunch.
The contract itself has been set up to define the department’s cloud strategy for the next decade. The thinking is that by establishing a relationship with a single vendor, it will improve security and simplify overall management of the system. It’s also part of a broader view of setting technology policy for the next decade and preparing the military for more modern requirements like Internet of Things and artificial intelligence applications.
Many vendors have publicly expressed unhappiness at the winner-take-all, single vendor approach, which they believe might be unfairly tilted toward market leader Amazon. Still, the DOD, which has stated that the process is open and fair, seems determined to take this path, much to the chagrin of most vendors, who believe that a multi-vendor strategy makes more sense.
John Dinsdale, chief analyst at Synergy Research Group, a firm that keeps close tabs on the cloud market, says it’s also important to keep the figure in perspective compared to the potential size of the overall market.
“The current worldwide market run rate is equivalent to approximately $60 billion per year and that will double in less than three years. So in very short order you’re going to see a market that is valued at greater than $100 billion per year – and is continuing to grow rapidly,” he said.
Put in those terms, $10 billion over a decade, while surely a significant figure, isn’t quite market altering if the market size numbers are right. “If the contract is truly worth $10 billion that is clearly a very big number. It would presumably be spread over many years which then puts it at only a very small share of the total market,” he said.
He also acknowledges that it would be a big feather in the cap of whichever company wins the business, and it could open the door for other business in the government and private sector. After all, if you can handle the DOD, chances are you can handle just about any business where a high level of security and governance would be required.
Final RFPs are now due on October 12th with a projected award date of April 2019, but even at $10 billion, an astronomical sum of money to be sure, it ultimately might not shift the market in the way you think.
Powered by WPeMatico
A future dominated by autonomous vehicles (AVs) is, for many experts, a foregone conclusion. Declarations that the automobile will become the next living room are almost as common — but, they are imprecise. In our inevitable driverless future, the more apt comparison is to the mobile device. As with smartphones, operating systems will go a long way toward determining what autonomous vehicles are and what they could be. For mobile app companies trying to seize on the coming AV opportunity, their future depends on how the OS landscape shapes up.
By most measures, the mobile app economy is still growing, yet the time people spend using their apps is actually starting to dip. A recent study reported that overall app session activity grew only 6 percent in 2017, down from the 11 percent growth it reported in 2016. This trend suggests users are reaching a saturation point in terms of how much time they can devote to apps. The AV industry could reverse that. But just how mobile apps will penetrate this market and who will hold the keys in this new era of mobility is still very much in doubt.
When it comes to a driverless future, multiple factors are now converging. Over the last few years, while app usage showed signs of stagnation, the push for driverless vehicles has only intensified. More cities are live-testing driverless software than ever, and investments in autonomous vehicle technology and software by tech giants like Google and Uber (measured in the billions) are starting to mature. And, after some reluctance, automakers have now embraced this idea of a driverless future. Expectations from all sides point to a “passenger economy” of mobility-as-a-service, which, by some estimates, may be worth as much as $7 trillion by 2050.
For mobile app companies this suggests several interesting questions: Will smart cars, like smartphones before them, be forced to go “exclusive” with a single OS of record (Google, Apple, Microsoft, Amazon/AGL), or will they be able to offer multiple OS/platforms of record based on app maturity or functionality? Or, will automakers simply step in to create their own closed loop operating systems, fragmenting the market completely?
Automakers and tech companies clearly recognize the importance of “connected mobility.”
Complicating the picture even further is the potential significance of an OS’s ability to support multiple Digital Assistants of Record (independent of the OS), as we see with Google Assistant now working on iOS. Obviously, voice NLP/U will be even more critical for smart car applications as compared to smart speakers and phones. Even in those established arenas the battle for OS dominance is only just beginning. Opening a new front in driverless vehicles could have a fascinating impact. Either way, the implications for mobile app companies are significant.
Looking at the driverless landscape today there are several indications as to which direction the OSes in AVs will ultimately go. For example, after some initial inroads developing their own fleet of autonomous vehicles, Google has now focused almost all its efforts on autonomous driving software while striking numerous partnership deals with traditional automakers. Some automakers, however, are moving forward developing their own OSes. Volkswagen, for instance, announced that vw.OS will be introduced in VW brand electric cars from 2020 onward, with an eye toward autonomous driving functions. (VW also plans to launch a fleet of autonomous cars in 2019 to rival Uber.) Tesla, a leader in AV, is building its own unified hardware-software stack. Companies like Udacity, however, are building an “open-source” self-driving car tech. Mobileye and Baidu have a partnership in place to provide software for automobile manufacturers.
Clearly, most smartphone apps would benefit from native integration, but there are several categories beyond music, voice and navigation that require significant hardware investment to natively integrate. Will automakers be interested in the Tesla model? If not, how will smart cars and apps (independent of OS/voice assistant) partner up? Given the hardware requirements necessary to enable native app functionality and optimal user experience, how will this force smart car manufacturers to work more seamlessly with platforms like AGL to ensure competitive advantage and differentiation? And, will this commoditize the OS dominance we see in smartphones today?
It’s clearly still early days and — at least in the near term — multiple OS solutions will likely be employed until preferred solutions rise to the top. Regardless, automakers and tech companies clearly recognize the importance of “connected mobility.” Connectivity and vehicular mobility will very likely replace traditional auto values like speed, comfort and power. The combination of Wi-Fi hotspot and autonomous vehicles (let alone consumer/business choice of on-demand vehicles) will propel instant conversion/personalization of smart car environments to passenger preferences. And, while questions remain around the how and the who in this new era in mobile, it’s not hard to see the why.
Americans already spend an average of 293 hours per year inside a car, and the average commute time has jumped around 20 percent since 1980. In a recent survey (conducted by Ipsos/GenPop) researchers found that in a driverless future people would spend roughly a third of the time communicating with friends and family or for business and online shopping. By 2030, it’s estimated the autonomous cars “will free up a mind-blowing 1.9 trillion minutes for passengers.” Another analysis suggested that even with just 10 percent adoption, driverless cars could account for $250 billion in driver productivity alone.
Productivity in this sense extends well beyond personal entertainment and commerce and into the realm of business productivity. Use of integrated display (screen and heads-up) and voice will enable business multi-tasking from video conferencing, search, messaging, scheduling, travel booking, e-commerce and navigation. First-mover advantage goes to the mobile app companies that first bundle into a single compelling package information density, content access and mobility. An app company that can claim 10 to 15 percent of this market will be a significant player.
For now, investors are throwing lots of money at possible winners in the autonomous automotive race, who, in turn, are beginning to define the shape of the mobile app landscape in a driverless future. In fact, what we’re seeing now looks a lot like the early days of smartphones with companies like Tesla, for example, applying an Apple -esque strategy for smart car versus smartphone. Will these OS/app marketplaces be dominated by a Tesla — or Google (for that matter) — and command a 30 percent revenue share from apps, or will auto manufacturers with proprietary platforms capitalize on this opportunity? Questions like these — while at the same time wondering just who the winners and losers in AV will be — mean investment and entrepreneurship in the mobile app sector is an extremely lucrative but risky gamble.
Powered by WPeMatico
When Salesforce bought MuleSoft last spring for the tidy sum of $6.5 billion, it looked like money well spent for the CRM giant. After all, it was providing a bridge between the cloud and the on-prem data center and that was a huge missing link for a company with big ambitions like Salesforce.
When you want to rule the enterprise, you can’t be limited by where data lives and you need to be able to share information across disparate systems. Partly that’s a simple story of enterprise integration, but on another level it’s purely about data. Salesforce introduced its intelligence layer, dubbed Einstein, at Dreamforce in 2016.
With MuleSoft in the fold, it’s got access to data cross systems wherever it lives, in the cloud or on-prem. Data is the fuel of artificial intelligence, and Salesforce has been trying desperately to get more data for Einstein since its inception.
It lost out on LinkedIn to Microsoft, which flexed its financial muscles and reeled in the business social network for $26.5 billion a couple of years ago. It’s undoubtedly a rich source of data that the company longed for. Next, it set its sights on Twitter (although Twitter was ultimately never sold, of course). After board and stockholder concerns, the company walked away.
Each of these forays was all about the data; frustrated, Salesforce went back to the drawing board. While MuleSoft did not supply the direct cache of data that a social network would have, it did provide a neat way for them to get at backend data sources — the very type of data that matters most to its enterprise customers.
Today, they have extended that notion beyond pure data access to a graph. You can probably see where this is going. The idea of a graph, the connections between say a buyer and the things they tend to buy or a person on a social network and people they tend to interact with, can be extended even to the network/API level, and that is precisely the story that Salesforce is trying to tell this week at the Dreamforce customer conference in San Francisco.
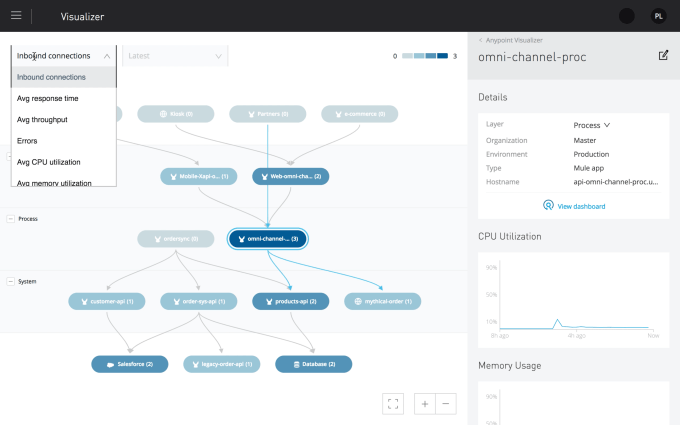
Visualizing connections in a data integration network in MuleSoft. Screenshot: Salesforce/MuleSoft
Maureen Fleming, program vice president for integration and process automation research at IDC, says that it is imperative that organizations view data as a strategic asset and act accordingly. “Very few companies are getting all the value from their data as they should be, as it is locked up in various applications and systems that aren’t designed to talk to each other. Companies who are truly digitally capable will be able to connect these disparate data sources, pull critical business-level data from these connections, and make informed business decisions in a way that delivers competitive advantage,” Fleming explained in a statement.

Configuring data connections on MuleSoft Anypoint Platform. Gif: Salesforce/MuleSoft
It’s hard to underestimate the value of this type of data is to Salesforce, which has already put MuleSoft to work internally to help build the new Customer 360 product announced today. It can point to how it’s providing this very type of data integration to which Fleming is referring on its own product set.
Bret Taylor, president and chief product officer at Salesforce, says that for his company all of this is ultimately about enhancing the customer experience. You need to be able to stitch together these different computing environments and data silos to make that happen.
“In the short term, [customer] infrastructure is often fragmented. They often have some legacy applications on premise, they’ll have some cloud applications like Salesforce, but some infrastructure in on Amazon or Google and Azure, and to actually transform the customer experience, they need to bring all this data together. And so it’s a really a unique time for integration technologies, like MuleSoft because it enables you to create a seamless customer experience, no matter where that data lives, and that means you don’t need to wait for infrastructure to be perfect before you can transform your customer experience.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Bleximo, a startup that aims to build “quantum accelerators” — basically quantum-based, application-specific integrated circuits — today announced it has raised a $1.5 million seed round led by Eniac Ventures. Other investors in this round include Boost VC, Creative Ventures, KEC Ventures and Gyan Kapur.
Instead of building a general-purpose quantum computer like IBM, Rigetti and others, Bleximo, which was founded by Cyclotron Road fellow and quantum physicist Alexei Marchenkov, wants to focus on building quantum processors that focus on very specific applications. Before founding Bleximo, Marchenkov worked at Rigetti Computing, where we worked on developing that company’s technology for general-purpose quantum computers.
“At Eniac, we believe general quantum computing is still far away, but Bleximo’s approach of building vertical quantum computing architecture will bring this nascent technology to the mainstream in a more practical way — much like vertical AI is here today before general AI,” said Vic Singh, founding general partner at Eniac Ventures. “We are excited to support founder Alexei Marchenkov, a recognized expert in quantum computing, and the Bleximo team to help build this reality.”
Right now, Bleximo is mostly looking at speeding up simulations of new materials and molecules for drug development. Quantum computing lends itself to solving these kinds of problems, though the company argues that its technology is just as applicable to solving problems in energy, finance, manufacturing and security.
Not everybody seems to agree that general quantum computing is all that far away, though, so it remains to be seen whether a real market for this kind of specialized quantum co-processors (Bleximo calls it a “qASIC”) will really develop, especially given that a quantum computer will also be some form of hybrid machine that combines classical and quantum computing. If it does, though, Bleximo seems well-positioned to capitalize on it, especially given that its technology will be a bit simpler (as far as one can say that about anything quantum computing) and won’t need the large amount of qubits with long coherence times that a general-purpose quantum computer would need.
Powered by WPeMatico
This past Saturday, something pretty weird happened in Pokémon GO: Immediately after the monthly “Community Day” event came to a close, a strange, new, never-before-seen Pokémon showed up. And by “showed up,” I mean it was everywhere. Around the globe, this thing was spawning every few feet. A grey blob with a hex nut for a head; it wasn’t like anything that anyone had seen in-game before.
It looked like this:
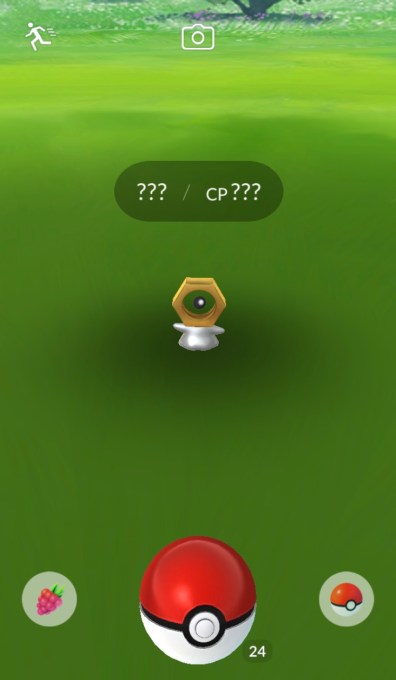
Weirder yet: No one could actually catch it. If you managed to get it to stay in a Pokéball, it would always turn into something else (in most cases, it turned into a Ditto). Just a few hours later, it was mostly gone.
Was it just a glitch? Many players assumed that Niantic put this thing in as a placeholder and a glitch brought it into public view. Or did they really just drop an entirely new Pokémon into the game out of nowhere?
Three days later, we’ve got an answer: It’s not a glitch.
This video just popped up on the official Pokémon YouTube channel, shining a bit of light on what’s going on:
In short: Its name is Meltan, and it’s an upcoming Mythical Pokémon. It all seems to be a big publicity tie-in with the upcoming Let’s Go, Pikachu! and Let’s Go, Eevee! titles that’ll launch on the Switch next month. Based on the limited info we have so far, it seems like to get a Meltan in the new games, you’ll have to catch him in Pokémon GO.
This whole stunt was pretty damned clever. Thanks to special, limited-time spawns, Pokémon GO’s Community Day events are when just about anyone who still plays the game will be actively looking at their screen. By sneaking Meltan in there for a bit at the end, they pretty much guaranteed a wave of “WTF?” would roll around the world. All for a little grey blob with a nut on his head.
As for how to catch an actual Meltan rather than a Ditto-lookalike: that’s still a mystery. Catching Mythical Pokémon in GO thus far has involved “Special Research” quests — a series of tasks that take a few days or weeks of play to complete. We might be looking at another one of those here.
Powered by WPeMatico
Airbnb, Uber, Lyft, Warby Parker and a long list of other startups of the 21st century have appointed C-level employees to roles focused exclusively on data science.
These digital-age companies have established “data cultures,” which provide employees broad access to high-quality data, advocate for data literacy and have data-driven decision-making processes, according to Carl Anderson, who previously led data analytics and data science at Warby Parker and WeWork.
Fortune 500 companies are still a long way from this ideal. Data.world, a sort of social networking site for data projects and teams, wants to give them the tools to get there. Its collaborative data community gives employees at large businesses a place to upload, exchange and catalog data sets, then discuss their findings with other employees.
“There is a huge data divide that has occurred between these big traditional companies that were built from the ground up from atoms and these digital-age companies that were built from the ground up from bits,” data.world chief executive officer Brett Hurt told TechCrunch.
Today, Austin-based data.world is announcing a $12 million investment led by Workday Ventures, with participation from The Associated Press (AP) and OurCrowd. The round brings the company’s total raised since its 2016 launch to $45.3 million, including an $18.7 million Series B in February 2017.
Data.world will use the capital to continue building out its enterprise offering, which it rolled out recently. The enterprise product, which counts AP as a customer, connects with Tableau, Microsoft Excel and Power BI, IBM SPSS, MicroStrategy, Google Data Studio and more.
Hurt, who previously founded the now-public customer reviews and social commerce platform BazaarVoice, says GitHub was a big inspiration for data.world.
“They’ve done an incredible job of democratizing access to code,” he said. “They made every programmer in the world better by giving them access to the world’s code, and data is one of those things that’s very liberating if you have access to [it].”
The data.world platform is also widely used by journalists, hence the investment from the AP. Using data.world, journalists can access complex data sets quickly and efficiently. Hurt says it’s “changed the game for data journalism.”
“AP was born back in 1846 as a cooperative of newspaper publishers sharing access to a fast horse to get news updates from the war in Mexico,” said Jim Kennedy, AP’s senior vice president for strategy and enterprise development in a statement. “The data.world platform is like that fast horse, enabling us to open important new territory for newsgathering in the 21st century.”
Other backers of data.world include Chicago Ventures, Shasta Ventures, Fyrfly Venture Partners, Hunt Technology Ventures LP, LiveOak Venture Partners and Sherpa Asset Management AG.
Powered by WPeMatico
LinkedIn may be best known as a place where people and organizations keep public pages of their professional profiles, using that as a starting point for networking, recruitment and more — a service that today that has racked up more than 575 million users, 20 million companies and 15 million active job listings. But now under the ownership of Microsoft, the company has increasingly started to build a number of other services; today sees the latest of these, the launch of a new feature called Talent Insights.
Talent Insights is significant in part because it is LinkedIn’s first foray into business intelligence, that branch of enterprise analytics aimed at helping execs and other corporate end users make more informed business decisions.
Talent Insights is also notable because it’s part of a trend, where LinkedIn has been launching a number of other services that take it beyond being a straight social network, and more of an IT productivity tool. They have included a way for users to look at and plan commutes to potential jobs (or other businesses); several integrations with Microsoft software including resume building in Word and Outlook integrations; and adding in more CRM tools to its Sales Navigator product.
Interestingly, it has been nearly a year between LinkedIn first announcing Talent Insights and actually launching it today. The company says part of the reason for the gap is because it has been tinkering with it to get the product right: it’s been testing it with a number of customers — there are now 100 using Talent Insights — with employees in departments like human resources, recruitment and marketing using it.
The product that’s launching today is largely similar to what the company previewed a year ago: there are two parts to it, one focused on people at a company, called “Talent Pool,” and another focused on data about a company, “Company Report.”
The first of these will let businesses run searches across the LinkedIn database to discover talent with characteristics similar to those what a business might already be hiring, and figure out where they are at the moment (in terms of location and company affiliation), and where they are moving, what skills they might have in common, and how to better spot those who might be on the way up based on all of this.
The second set of data tools (Company Report) provides a similar analytics profile but about your organisation and those that you would like to compare against it in areas like relative education levels and schools of the respective workforces; which skills employees have or don’t have; and so on.
Dan Francis, a senior product manager running Talent Insights, said in an interview that for now the majority of the data that’s being used to power Talent Insights is primarily coming from LinkedIn itself, although there are other data sources also added into it, such as material from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. (And indeed, even some of LinkedIn’s other data troves, for example in its recruitment listings, or even in its news/content play, the material that populates both comes from third parties.)
He also added that letting companies feed in their own data to use that in number crunching — either for their own reports or those of other companies — “is on our roadmap,” an indication that LinkedIn sees some mileage in this product.
Adding in more data sources could also help the company appear more impartial and accurate: although LinkedIn is huge and the biggest repository of information of its kind when it comes to professional profiles, it’s not always accurate and in some cases can be completely out of date or intentionally misleading.
(Related: LinkedIn has yet to launch any “verified”-style profiles for people, such as you get on Facebook or Twitter, to prove they are who they say they are, that they work where they claim to work, and that their backgrounds are what they claim them to be. My guess as to why that has not been rolled out is that it would be very hard, if not impossible, to verify everything in a clear way, and so LinkedIn relies on the power of public scrutiny to keep people mostly honest.)
“We’re pretty transparent about this,” said Francis. “We don’t position this as a product as comprehensive, but as a representative sample. Ensuring data quality is good is something that we are careful about. We know sometimes data is not perfect. In some cases it is directional.”
Powered by WPeMatico