TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Krafton, which filed for an IPO earlier this week, has built a gigantic gaming empire. If the firm is able to raise the target $5 billion from the IPO it will be the largest public offering in its home country, South Korea. The firm has something to celebrate elsewhere in the world, too.
On Thursday, it pulled off another feat that no other firm has been able to achieve: Its sleeper hit title, PUBG Mobile, has made a return to India, which banned the title more than nine months ago.
The world’s second-largest internet market banned over 200 apps last year citing national security concerns. All the apps New Delhi blocked in the nation had links to China. The move was seen by many as retaliation as tension between the two nuclear-armed neighboring nations escalated last year.
Every other app that has been banned by India — and pulled by Google and Apple from their respective app stores in the country in compliance with local government orders — remains in that state. ByteDance, whose TikTok app identified India as its largest market, has significantly downsized its team in the country. (ByteDance runs several businesses in India and many remain operational. Employees have been instructed to stay off the radar.)
Which is what makes PUBG Mobile’s return to India all the more interesting. The game, which has been rebranded to Battlegrounds Mobile India in the South Asia market, is available to download from the Play Store for any user in the country — provided they sign up for an early access before the imminent launch.
Even as PUBG Mobile is now using a different moniker, the game follows the same plot, and the identical home screen greets users with the familiar ecstatic background score.
Moreover, users are offered a quick and straightforward option to migrate their PUBG Mobile accounts to the new app.
Rishi Alwani, the quintessential gaming reporter in India who edits IGN India, told TechCrunch that the new game is “essentially PUBG Mobile with data compliance, green blood, and a constant reminder that you’re in a ‘virtual world’ with such messaging present as you start a game and when you’re in menus.”
The changes are likely Krafton’s attempt to assuage previous concerns from the local authorities, some of whom had expressed concerns about the game’s affect on youngsters.

Image Credits: TechCrunch / screen capture
But these on-the-surface changes raise a set of bigger questions that have been a topic of discussion among several startup founders and policy executives in India in recent months:
Neither the Indian government nor Krafton have publicly said anything on this subject. Krafton, on its part, has taken steps to assuage India’s concerns. For instance, last year the South Korean firm cut ties with its publishing partner Tencent, the only visible Chinese affiliation — if the Indian government was indeed banning just Chinese apps. Krafton also publicly announced that it will be investing $100 million in India’s gaming ecosystem.
The Indian government’s order and the communication and compliance mechanism for concerned entities have been so opaque on this subject that it is unclear on what grounds Krafton has been able to bring the game back.
One explanation — albeit admittedly full of speculation — is that it’s a new app in the sense that it has a new app ID. In this instance, it happens to have a new developer account, too. Remember, India banned apps, and not the firms themselves. Several Tencent and Alibaba apps, for instance, remain available in India.
This would also explain how BIGO has been able to launch a new app — Tiki Video — under a new developer account and plenty of effort to conceal its connection. That app, which was launched in late February, has amassed over 16 million monthly active users, according to mobile insight firm App Annie. The app’s existence and affiliation with BIGO have not been previously reported.
But the question remains, are these simple workarounds enough to escape the ban? To be sure, some apps, including Battlegrounds Mobile India, are also hosting their data in the country now, and have agreed for periodic audits. So is that enough? And if it is, why aren’t most — if not all — apps making a return to India?
Regardless, the return of PUBG Mobile India is a welcome move for tens of millions of users in the country, many of whom — about 38 million last month, according to App Annie — were using workarounds themselves to continue to play the game.
Powered by WPeMatico
Companies like Stripe and Twilio have put APIs front and center as an effective way to integrate complex functionality that may not be core to your own technology stack but is a necessary part of your wider business. Today, a company that has taken that model to create an effective way to integrate email, calendars and other tools into other apps using APIs is announcing a big round of funding to expand its business.
Nylas, which describes itself as a communications API platform — enabling more automation particularly in business apps by integrating productivity tools through a few lines of code — has raised $120 million in funding, money that it will be using to continue expanding the kinds of APIs that it offers, with a focus in particular not just on productivity apps, but AI and related tools to bring more automation into workflows.
Nylas is not disclosing its valuation, but this is a very significant step up for the company at a time when it is seeing strong traction.
This is more than double what Nylas had raised up to now ($55 million since being founded in 2015), and when it last raised — a $16 million Series B in 2018 — it said it had “thousands of developers” among its users. Now, that number has ballooned to 80,000, with Nylas processing some 1.2 billion API requests each day, working out to 20 terabytes of data, daily. It also said that revenue growth tripled in the last 12 months.
The Series C is bringing a number of interesting names to Nylas’s cap table. New investor Tiger Global Management is leading the round, with previous backers Citi Ventures, Slack Fund, 8VC and Round13 Capital also participating. Other new backers in this round include Owl Rock Capital, a division of Blue Owl; Stripe co-founders Patrick Collison and John Collison; Klarna CEO Sebastian Siemiatkowski; and Tony Fadell.
As with other companies in the so-called API economy, the gap and opportunity that Nylas has identified is that there are a lot of productivity tools that largely exist in their own silos — meaning when a person wants to use them when working in an application, they have to open a separate application to do so. At the same time, building new, say, tools, or building a bridge to integrate an existing application, can be time-consuming and complex.
Nylas first identified this issue with email. An integration to make it easier to use email and the data housed in it — which works with emails from major providers like Microsoft and Google, as well as other services built with the IMAP protocol — in other apps picked up a lot of followers, leading the company to expand into other areas that today include scheduling and calendaring, a neural API to build in tools like sentiment analysis or productivity or workflow automation; and security integrations to streamline the Google OAuth security review process (used for example in an app geared at developers).
“The fundamental shift towards digital communications and connectivity has resulted in companies across all industries increasingly leaning on developers to solve critical business challenges and build unique and engaging products and experiences. As a result, APIs have become core to modern software development and digital transformation,” Gleb Polyakov, co-founder and CEO of Nylas, said in statement.
“Through our suite of powerful APIs, we’re arming developers with the tools and applications needed to meet customer and market needs faster, create competitive differentiation through powerful and customized user experiences, and generate operational ROI through more productive and intelligently automated processes and development cycles. We’re thrilled to continue advancing our mission to make the world more productive and are honored to have the backing of distinguished investors and entrepreneurs.”
Indeed, the rise of Nylas and the function it fulfills is part of a bigger shift we’ve seen in businesses overall: as organizations become more digitized and use more cloud-based apps to get work done, developers have emerged as key mechanics to help that machine run. A bigger emphasis on APIs to integrate services together is part of their much-used toolkit, one of the defining reasons for investors backing Nylas today.
“Companies are rapidly adopting APIs as a way to automate productivity and find new and innovative ways to support modern work and collaboration,” said John Curtius, a partner at Tiger, in a statement. “This trend has become critical to creating frictionless and meaningful data-driven communications that power digital transformation. We believe Nylas is uniquely positioned to lead the future of the API economy.” Curtius is joining the board with this round.
Corrected to note that Blue Owl is not connected to State Farm.
Powered by WPeMatico
As the insurance industry adjusts to life in the 21st century (heh), an AI startup that has built computer vision tools to enable remote damage appraisals is announcing a significant round of growth funding.
Tractable, which works with automotive insurance companies to let users take and submit photos of damaged cars that are then “read” to make appraisals, has raised $60 million, a Series D that values Tractable at $1 billion, the company said.
Tractable says it works with more than 20 of the top 100 auto insurers in the world, and it has seen sales grow 600% in the last 24 months, which CEO Alex Dalyac told me translates as “well into eight figures of annual revenue.” He also told me that “we would have grown even faster if it weren’t for COVID.” People staying at home meant far fewer people on the roads, and fewer accidents.
Its business today is based mostly around car accident recovery — where users can take pictures using ordinary smartphone cameras, uploading pictures via a mobile web site (not typically an app).
But Tractable’s plan is to use some of the funding to expand deeper into areas adjacent to that: natural disaster recovery (specifically for appraising property damage), and used car appraisals. It will also use the investment to continue building out its technology, specifically to help build out better, AI-based techniques of processing and parsing pictures that are taken on smartphones — by their nature small in size.
Insight Partners and Georgian Partners co-led the round and it brings the total raised by the company to $115 million.
Dalyac, a deep learning researcher by training who co-founded the company with Razvan Ranca and Adrien Cohen, said that the “opportunity” (if you could call an accident that) Tractable has identified and built to fix is that it’s generally time-consuming and stressful to deal with an insurance company when you are also coping with a problem with your car.
And while a new generation of “insurtech” startups have emerged in recent years that are bringing more modern processes into the equation, typically the incumbent major insurance companies — the ones that Tractable targets — have lacked the technology to improve that process.
It’s not unlike the tension between fintech-fuelled neobanks and the incumbent banks, which are now scrambling to invest in more technology to catch up with the times.
“Getting into an accident can be anything from a hassle to trauma,” Dalyac said. “It can be devastating, and then the process for recovery is pretty damn slow. You’re dealing with so many touch points with your insurance, so many people that need to come and check things out again. It’s hard to keep track and know when things will truly be back to normal. Our belief is that that whole process can be 10 times faster, thanks to the breakthroughs in image classification.”
That process currently also extends not just to taking pictures for claims, but also to help figure out when a car is beyond repair, in which case which parts can be recycled and reused elsewhere, also using Tractable’s computer vision technology. Dalyac noted that this was a popular enough service in the last year that the company helped recycle as many cars “as Tesla sold in 2019.”
Customers that have integrated with Tractable to date include Geico in the U.S., as well as a large swathe of insurers in Japan, specifically Tokio Marine Nichido, Mitsui Sumitomo, Aioi Nissay Dowa and Sompo. Covéa, the largest auto insurer in France, is also a customer, as is Admiral Seguros, the Spanish entity of U.K.’s Admiral Group, as well as Ageas, a top U.K. insurer.
Japan is the company’s biggest market today Dalyac said — the reason being that it has an aging population, but one that is also very strong on mobile usage: combining those two, “automation is more than a value add; it’s a must have,” Dalyac said. He also added that he thinks the U.S. will overtake Japan as Tractable’s biggest market soon.
The new directions into property and other car applications will also open the door to a wider set of use cases beyond working with insurance providers over time. It will also bring Tractable potentially into new competitive environments. There are other companies that have also identified this opportunity.
For example, Hover, which has built a way to create 3D imagery of homes using ordinary smartphone cameras, is also eyeing ways of selling its tech (originally developed to help make estimates on home repairs) to insurance companies.
For now, however, it sounds like the opportunity is a big enough one that the race is more to meet demand than it is to beat competitors to do so.
“Tractable’s accelerating growth at scale is a testament to the power and differentiation of their applied machine learning system, which continues to improve as more businesses adopt it,” said Lonne Jaffe, MD at Insight Partners and Tractable board member, in a statement. “We’re excited to double down on our partnership with Tractable as they work to help the world recover faster from accidents and disasters that affect hundreds of millions of lives.”
Emily Walsh, partner at Georgian Partners added: “Tractable’s industry-leading computer vision capabilities are continuing to fuel incredible customer ROI and growth for the firm. We’re excited to continue to partner with Tractable as they apply their artificial intelligence capabilities to new, multi-billion dollar market opportunities in the used vehicle and natural disaster recovery industries.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Growth leaders used to build key relationships across a company while working together in a real-life office. Those relationships could carry over through the pandemic, but let’s say you’re a new company and you’re remote-first.
How do you build this complex collaboration from scratch?
Growth marketer and investor Susan Su tells us that the solution is not just more software tools. In the interview below, she says that after the pandemic, startup founders will need to develop a mentality that places growth at the center of company strategy.
Consultants and agencies can be great additions to this effort, especially if they have previously solved the types of problems you face. (In fact, TechCrunch is asking founders who have worked with growth marketers to share a recommendation in this survey. We’ll use your answers to find more experts to interview.)
Su is currently the head of portfolio strategy for Sound Ventures, previously a growth leader at Stripe and the first hire at Reforge. She also shared a few thoughts on market opportunities after the pandemic in the full interview below. E-commerce is mainstream for good, she says, even as we all try to step away from screens more often. However, many social and mobile sectors are mature, and it’s going to be even harder for startups to compete as real-world activities absorb more time.
Don’t forget: Susan Su will also appear at our Early Stage virtual event on July 8 (and answer questions directly).
How are you seeing startups manage changes in user engagement as more people exit pandemic lockdowns and adjust their daily lives?
As we exit the pandemic, I expect that we’ll see a natural and obvious spike in some consumer activity that will roll up to midsized businesses and enterprises. Just like with the onset of the pandemic, we’ll see uneven results across sectors:
E-commerce boomed during the pandemic but was really an augmentation of an already-accelerating trend toward digital commerce and streamlined logistics. I don’t think we backtrack from e-commerce because habit formation around online shopping has been building for years; we would be backtracking to an age long before 2020, and that’s not going to happen.
New social-mobile experiences also boomed during the pandemic, but there’s still a valid question around whether 15 months or so is enough time to become part of the ingrained infrastructure of daily life. We are living in an age of mature platforms, so every new service is stealing time away from an existing service. As with pre-pandemic growth, their success rests upon fast-accumulating network effects and great, sticky core product experience. Now that we have parks, friends and dinners out calling to us again, it’s a real test of how compelling some of these new value propositions really are, and whether they can continue to demonstrate their relevance in a more hybridized online-offline world.
That said, the pandemic was an enormous constraint on human society and [the] economy, and these kinds of constraints often breed innovation that doesn’t go away. We will evolve, but we can never go back. It sounds cheesy but it’s true.
Some aspects of the pandemic, like remote work, appear to have radically changed certain industries. How will these societal changes impact how the typical startup thinks about growth?
Growth will always be growth — that is, a process of iterative experimentation to identify and solve customer problems, and then scale those solutions in order to reach and convert bigger and bigger audiences. Platform changes like iOS 14 or Facebook’s periodic algorithm adjustments will have a bigger impact in the near term on the technical functioning of growth, and these aren’t specifically pandemic-related.
One area to watch is how growth teams are built and operated. Growth is a horizontal function that touches many different parts of the org, including product, engineering, marketing, comms and design. Many startup teams have already been working with collaboration tools even while they sat in the same office, but growth is about more than just using tools. The most effective growth leaders succeed by building relationships across the organization; it’s like the fable of Stone Soup — you’re creating this meal that will feed everyone, but you also need each person to bring a pinch of salt, or a dash of pepper, or one carrot, and that requires socialization and relationship-building. I’ll be very interested to see how new growth leaders onboard remote-only teams and what approaches they take to this “networking” need within the function.
From the days of growth hacking on social platforms, growth marketing is now an established part of the world. But it’s not necessarily the main expertise of a startup founder, even if it needs to be. So, how should they think about addressing growth marketing in 2021? What are the essentials they should do in their roles?
Every founder needs to have a growth mentality. They don’t need to memorize all the right buttons to push in an ads dashboard, but they need to be familiar and comfortable with the core work of gap-finding. That said, founders are by definition entrepreneurial — their company exists because they saw an opportunity that no one else did, and this is the fundamental work of growth as well.
Founders will fail if they adopt a mentality that someone else can or should do it for them. The founder’s job is to supply ambition and opinions, and then magnetize high-quality talent to come and pull the levers and bring their creative vision to life. There are many people who can do growth marketing — that is, they know how the platforms work, they understand the rules and the playbooks. But there are very few who can come up with truly visionary strategies that change the game altogether — those people become founders, and those companies become household names. So for a founder, I’d say the most important growth work is to continue to know your market and customer better than anyone else in the whole world, have an opinion about what’s missing, and work to bring the best talent to come in alongside you and be a thought partner, not just a button pusher.
Have you worked with a talented individual or agency who helped you find and keep more users?
Respond to our survey and help us find the best startup growth marketers!
With limited resources, how should early-stage companies think about what to focus on?
This is going to depend on the goals of your company. Are you planning to raise money and need to demonstrate certain KPIs? Are you bootstrapping and need to keep the lights on? Resources should always be allocated to the most strategic purposes, with the longest-term view you can afford. For some companies, this could mean forgoing revenue to focus on viral or word-of-mouth-driven user acquisition to demonstrate to future investors that there’s something special here. For other companies, perhaps in lower volume categories like enterprise, it’s about bringing a few strategic logos into the family as a signal to later customers and other stakeholders, including future employees and investors.
One thing that early-stage companies should always be focused on is building a top-shelf employer brand. You will only ever be as good as the talent you attract to your company, and interestingly growth can actually play a role in this. The best designers, engineers and product people are often flowing toward the companies that have the best growth. In that way, it’s a highly strategic role and function.
What do startups continue to get wrong?
You can’t truly outsource growth or any other core function; you can’t tack on customer acquisition after product development. At the end of the day, if you really think about it, all a company is, is a customer-acquisition engine. This needs to be core; wake up every day and think about growth, not just to hit revenue or user KPIs, but to build the company that the best people are clamoring to work at. It’s not about finding someone sufficient to solve your near-term problems; it’s about framing problems in a way that’s so compelling to the most creative, hardest-working people so that they can’t get it out of their heads. Go for talent moonshots, and figure out how to close them. The rest will fall in line from there.
When should a founder feel comfortable getting help from an outside expert or agency?
Anytime. Agencies are great. They are an extension of your talent, and the best agencies aren’t selling you — they have to be sold on your problem because they have their pick of companies just like yours. That’s the agency or outside expert you want to work with, because they’ll have a priceless perspective from the other best-in-class founders and teams they’ve worked with that they can bring to your challenge. Any agency can run Facebook ads (it’s not rocket science), but you want to find the team that’s solved the gnarliest problems for your hero companies. Then you’ll get not just an ads manager, but a teacher.
Powered by WPeMatico
Joining us onstage as a judge for TechCrunch Disrupt 2021‘s Startup Battlefield will be Yasmin Razavi, general partner at Spark Capital. Her engineering background and fintech chops should make for incisive questions for the founders presenting.
Razavi invests in growth-stage enterprise, fintech and developer companies, but her background is until fairly recently an engineering-focused one. She grew up in Tehran, studied engineering at the University of Toronto and got her MBA at Harvard Business School.
A stint at McKinsey eventually led to being a product manager at Snap, where she built the tech behind the app’s monetization stack. In 2017 she joined Spark, and since then has led investments in Marqueta, Deel, Rapyd, Niantic, Capitolis and Earnin.
We recently had Razavi at Disrupt as a panelist, and of course if you’re an Extra Crunch subscriber you can watch the whole thing here.
“Ultimately anyone who wants to be a shareholder or investor in your business wants to understand the unit economics of your business,” she said during the panel. “For me, there’s all sorts of fancy metrics being thrown around; ultimately they all come down to what is the unit economics, and what is the payback I can expect when I invest in growth?”
Razavi’s philosophy is go to market and out-execute the competition, then capitalize on that success. Why anyone would want to do the opposite is hard to say, but the point is to move quickly and decisively as early as possible so that making money later is a natural consequence rather than a scramble.
Catch her on the Disrupt stage and grab your ticket to Disrupt 2021 now!
Powered by WPeMatico
By its nature, sales is one of the most social faces of a business, so it’s no surprise that there are tools being built for sales teams that are tapping into some of the most interesting dynamics of the world of social networking, and that the startups that are doing this most successfully are making a killing.
In the latest example, a startup out of Canada called Introhive — which has built an AI engine that ingests huge amounts of data from across disparate applications to help companies (and specifically anyone in their organization that is selling to someone) to build better “relationship graphs” for target organizations — is announcing $100 million in funding.
Growth equity firm PSG is leading the round, with The Business Development Bank of Canada (BDC), Evergreen Capital and Mavan Capital Partners also participating.
The company is not disclosing valuation but CEO and co-founder Jody Glidden tells me the company is doing well. It has raised about $150 million to date and is doubling revenues every year for the last several with a platform used by large enterprises — PwC, Colliers International, Wilson Sonsini Goodrich & Rosati, Plante Moran and Clark Nexsen are a few of them. Typical deployments range between 10,000 and 100,000 seats — it’s not just people with “sales” in their job titles using Introhive — and customer retention is currently at 95%.
The idea for Introhive came as many do to enterprise startup founders: they identify something that doesn’t quite work as they want it to, and then start a new company to try to fix it. In the case of Glidden, he and Stewart Walchli were at RIM (the old parent of BlackBerry), which had acquired a previous startup of theirs called Chalk Media.
Although they had just joined a much bigger company (it was 2008, and BlackBerry was still far from being completely killed off by Google and Apple) Glidden said he was surprised to see how hard it was to tap its vast troves of information to find prospective sales leads.
“We realized there were a whole lot of problems with sales people at RIM not able to hit their revenue numbers,” he recalled, and so they started asking themselves some questions. “Are they bringing in right lead data? Are they able to be as intelligent as they can be?” It took some years — four, exactly — and perhaps the rise of Facebook and its focus on the “social graph,” for them to land on how to articulate the problem. They needed to “unlock relationship graph in CRM,” Glidden said.
And Introhive was the company that they formed in 2012 to address that. The company not only provides a way to better leverage CRM-related data to find the best targets for particular products or services, but it also provides analytics to the team to measure how people are doing, and over time also helps predict “winnability”.
But that was not immediate: It took several years to build out its AI platform, Glidden said, with a lot of trial and error to ensure that the data that Introhive ingested was structured correctly to match up with other information to yield productive information.
“We ran into big problems in the first years because there were so many potential systems to tap into, homegrown or otherwise, for certain info. We effectively spent a lot of time building our own version of MuleSoft to fix that,” he said with a laugh. “But since it’s also something we use for our customers we ended up employing hundreds of engineers to build this underpinning layer to understand it all.”
As a result, it took between four and five years for Introhive to make its own first sale, and in the process the whole company almost went under, he recalled. “It took a long time to get that engine running because if you are automating data that is wrong 35% of the time, you won’t keep your customers.”
The machine is more well-oiled today, of course, and is on a roll to bring in more functions to work off the data trove that it has built.
There is something about the service that reminds me a bit of LinkedIn or ZoomInfo — which you may use in your own work, or come across when Googling someone online for some reason (hey — I’m not asking why here) — for providing some kind of data base/org chart of people connected to a business. But to be very clear, the data that Introhive builds for a customer stays with that customer, and doesn’t go anywhere else.
Glidden says that there are no plans to build any kind of “freemium” version of the service, or one that anyone can tap as a SaaS, but rather to remain focused on helping larger enterprises make better sense of their data and how it can better inform the wider concept of sales.
That in itself raises an interesting point about Introhive and business in general. When you consider a company like PwC, there are likely many people who specifically might hold a job title with the word “sales” in it, but just as many whose jobs are predicated on closing deals, consultants and partners for example, who do not, but might just as easily benefit from having better visibility of a “relationship graph” of people connected to buying products at a business they are working with, or want to work with. Sales is more than just about salespeople for many organizations.
And for that reason, you can guess that one interesting aspect of Introhive is if it might evolve these tools over time to tackle other parts of an organization and how it works. Similar to the social graphs of social media, which map out how people can be connected to one another, relationship graphs in the workplace potentially resonate well beyond signing a deal, too. Business intelligence and marketing automation are already in the mix for the company.
“Introhive is on the forefront of helping grow sales and customers through its visionary, AI-powered revenue acceleration platform built for companies of all sizes and complexity. It seamlessly improves business operations across multiple departments by helping teams reduce time on manual inputs and giving them advanced insights on where they can generate more revenue, build more relationships and easily identify what great sales reps are doing that average reps aren’t,” said PSG managing director, Rick Essex. “The team’s acumen and highly capital-efficient model has set the company on a clear path for growth, and we’re proud to partner with them on this journey.”
Powered by WPeMatico
How big is the market in India for a neobank aimed at teenagers? Scores of high-profile investors are backing a startup to find out.
Bangalore-based FamPay said on Wednesday it has raised $38 million in its Series A round led by Elevation Capital. General Catalyst, Rocketship VC, Greenoaks Capital and existing investors Sequoia Capital India, Y Combinator, Global Founders Capital and Venture Highway also participated in the new round, which brings FamPay’s to-date raise to $42.7 million.
TechCrunch reported early this month that FamPay was in talks with Elevation Capital to raise a new round.
Founded by Sambhav Jain and Kush Taneja (pictured above) — both of whom graduated from Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee in 2019 — FamPay enables teenagers to make online and offline payments.
The thesis behind the startup, said Jain in an interview with TechCrunch, is to provide financial literacy to teenagers, who additionally have limited options to open a bank account in India at a young age. Through gamification, the startup said it’s making lessons about money fun for youngsters.
Unlike in the U.S., where it’s common for teenagers to get jobs at restaurants and other places and understand how to handle money at a young age, a similar tradition doesn’t exist in India.
After gathering the consent from parents, FamPay provides teenagers with an app to make online purchases, as well as plastic cards — the only numberless card of its kind in the country — for offline transactions. Parents credit money to their children’s FamPay accounts and get to keep track of high-ticket spendings.
In other markets, including the U.S., a number of startups including Greenlight, Step and Till Financial are chasing to serve the teenagers, but in India, there currently is no startup looking to solve the financial access problem for teenagers, said Mridul Arora, a partner at Elevation Capital, in an interview with TechCrunch.
It could prove to be a good issue to solve — India has the largest adolescent population in the world.
“If you’re able to serve them at a young age, over a course of time, you stand to become their go-to product for a lot of things,” Arora said. “FamPay is serving a population that is very attractive and at the same time underserved.”
The current offerings of FamPay are just the beginning, said Jain. Eventually the startup wishes to provide a range of services and serve as a neobank for youngsters to retain them with the platform forever, he said, though he didn’t wish to share currently what those services might be.

Image Credits: FamPay
Teens represent the “most tech-savvy generation, as they haven’t seen a world without the internet,” he said. “They adapt to technology faster than any other target audience and their first exposure with the internet comes from the likes of Instagram and Netflix. This leads to higher expectations from the products that they prefer to use. We are unique in approaching banking from a whole new lens with our recipe of community and gamification to match the Gen Z vibe.”
“I don’t look at FamPay just as a payments service. If the team is able to execute this, FamPay can become a very powerful gateway product to teenagers in India and their financial life. It can become a neobank, and it also has the opportunity to do something around social, community and commerce,” said Arora.
During their college life, Jain and Taneja collaborated and built an app and worked at a number of startups, including social network ShareChat, logistics firm Rivigo and video streaming service Hotstar. Jain said their work with startups in the early days paved the idea to explore a future in this ecosystem.
Prior to arriving at FamPay, Jain said the duo had thought about several more ideas for a startup. The early days of FamPay were uniquely challenging to the founders, who had to convince their parents about their decision to do a startup rather than joining firms or startups as had most of their peers from college. Until being selected by Y Combinator, Jain said he didn’t even fully understand a cap table and dilutions.
He credited entrepreneurs such as Kunal Shah (founder of CRED) and Amrish Rau (CEO of Pine Labs) for being generous with their time and guidance. They also wrote some of the earliest checks to the startup.
The startup, which has amassed over 2 million registered users, plans to deploy the fresh capital to expand its user base and product offerings, and hire engineers. It is also looking for people to join its leadership team, said Jain.
Powered by WPeMatico
ApplyBoard, a startup that helps international students find opportunities to study abroad, announced today that it has nearly doubled its valuation in a little over a year. The Ontario-based company is now worth around $3.2 billion after raising a $300 million Series D round led by the Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan Board.
Startups that help students navigate institutional bureaucracy so they can get more value out of their educational experience may become a growing focus for investors as consumer demand for virtual personalized learning increases.
ApplyBoard makes money from revenue-sharing agreements with colleges and universities. If a student attends a college after using their services, ApplyBoard receives a cut of the tuition. Meanwhile, the service, which helps students search and apply to schools, is free to use.
Co-founder and CEO Martin Basiri did not share specifics on revenue, but he confirmed that his company is growing its sales at a 400% year-over-year rate in 2021. For context, sales in 2019 hit $300 million, meaning that ApplyBoard is making at least $1.2 billion in sales this year.
These figures violate the prevailing edtech narrative from last year: Higher ed is dead! Students don’t want to attend college anymore. Bring back the gap year, but make it permanent!
Instead, this company is proving that the university tech stack is more lucrative than many assumed, especially if you look beyond content offerings and into back-end marketing support.
My take: Startups that help students navigate institutional bureaucracy so they can get more value out of their educational experience may become a growing focus for investors as consumer demand for virtual personalized learning increases.
ApplyBoard’s recent fundraising efforts shed a light on its strategy to become, effectively, a tech-savvy guidance counselor for the approximately 200,000 students that it has served to date.
The company raised a $55 million extension round in September to bring on a partner, Education Testing Services (ETS) Strategy Capital, the venture arm of the world’s largest nonprofit education testing and assessment organization. ETS helps administer the TOEFL English-language proficiency test and the GRE graduate admissions test.
The synergies there led ApplyBoard to launch ApplyProof, a service that helps admissions and immigrant officers verify documents that international students need to apply to colleges around the world. Today’s financing event similarly brings in a strategic investor, Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan.
“The demand remains high post-pandemic and we continue to see a strong, pent-up demand from students wishing to study abroad,” Basiri said. “Students want a seamless and pain-free application process and be able to have all the information they need to make an informed decision.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Location-based services may have had their day as a salient category for hot apps or innovative tech leveraging the arrival of smartphones, but that’s largely because they are now part of the unspoken fabric of how we interact with digital services every day: We rely on location-specific information when we are on search engines, when we are using maps or weather apps, when we are taking and posting photos and more.
Still, there remain a lot of gaps in how location information links up with accurate information, and so today a company that’s made it its business to address that is announcing some funding as it scales up its service.
Uberall, which works with retailers and other brick-and-mortar operators to help them update and provide more accurate information about themselves across the plethora of apps and other services that consumers use to discover them, is announcing $115 million in funding. Alongside that, the Berlin startup is making an acquisition: it’s buying MomentFeed, a location marketing company based out of Los Angeles, to continue scaling its business.
The funding is being led by London-based investor Bregal Milestone, with Level Equity, United Internet and Uberall management also participating. From what we understand from sources, the funding values Uberall at around $500 million, and the deal for MomentFeed was made for between $50 million and $60 million.
The business combination is building way more scale into the platform: Uberall said that together they will manage the online presence for 1.35 million business locations, making the company the biggest in the field, with customers including the gas station operator BP, KFC, clothes and food chain Marks and Spencer, McDonald’s and Pizza Hut.
Florian Hübner, the CEO and co-founder of Uberall, noted in an interview that the companies have quite a lot of overlap, and in fact prior to the deal being made the companies worked together closely in the U.S. market, but all the same, MomentFeed has built some specific technology that will enrich the wider platform, such as a particularly strong tool for measuring sentiment analysis.
“Managing the online presence” is not a company’s website, nor is it its apps, but may nevertheless be its most common digital touchpoints when it comes to actually engaging with consumers online. It includes how those companies appear on local listings services like Yelp or TripAdvisor, or mapping apps like Google’s — which provide not just listings information like addresses and opening hours but also customer reviews — or social apps or location-based advertising. Altogether, when you are considering a company with multiple locations and the multiple touchpoints a consumer might use, it ends up being a complicated mess of places that need to be managed and kept up to date.
“We are the catalyst for this huge ecosystem where we enable the brands to use everything that the other tech platforms are offering in the best possible way,” Hübner told me. The tech platforms, meanwhile, are willing to work with middleware companies like Uberall to make the information on their services more accurate and complete by connecting with businesses when they have not managed to do so directly on their own. (And if you’ve ever been caught out by the wrong opening times on a Google Maps entry, or any other entry or piece of information elsewhere, you know this is an issue.)
And of course expecting any company with potentially hundreds of locations to provide the right details without a tool is also a nonstarter. “Casually updating 100,000 profiles is super hard,” Hübner said.
It also provides services to update information about vaccine and COVID-19 testing clinics, as well as other essential services that also have to contend with the same variations in location, opening hours and customer feedback as any other business on a site like Google Maps.
Altogether, Uberall has built out a platform that essentially connects up all of those end points, so that an Uberall customer can use a dashboard to provide updates that populate automatically everywhere, and also to read and respond to reviews.
Conversely, Uberall also can look out for instances where a company is being unofficially represented, or misrepresented, and locks those down. Alongside those, it has built a location-based marketing service that also serves ads for its customers. It is somewhat akin to social media management tools, which let you manage social media accounts and social media marketing campaigns, except that it’s covering a much more fragmented and disparate set of places where a company might appear online.
The bigger picture here is that just as location-based marketing is a fragmented business, so is the business of providing services to manage it. This move reduces down that field a little more and improves the efficiency of scaling such services.
“As we saw the market trending towards consolidation, we considered several potential companies to merge with. Uberall was by far our most preferred,” said MomentFeed CEO Nick Hedges in a statement. “This combination makes enormous strategic sense for our customers, who represent the who’s-who of leading U.S. omni channel brands. It helps accelerate our already rapid pace of innovation, giving customers an even greater edge in the hyper-competitive world of ’Near Me’ Marketing.” After the deal closes, Hedges will become Uberall’s chief strategy officer and EVP for North America.
“We are thrilled to partner with the Uberall team for this next phase of growth. Our strategic investment will significantly accelerate Uberall’s ambition to become the leading ‘Near Me’ Customer Experience platform worldwide. Uberall’s differentiated full-suite solution is unsurpassed by competition in terms of integration and functionality, providing customers with a real edge to reach, interact with, and convert online customers. We look forward to supporting Florian, Nick and their talented team to deliver on their exciting innovation and expansion roadmap,” said Cyrus Shey, managing partner of Bregal Milestone, in a statement.
Powered by WPeMatico
In April, Facebook announced a slew of new audio products, including its Clubhouse clone, called Live Audio Rooms, which will be available across both Facebook and Messenger. Since May, Facebook has been publicly testing the audio rooms feature in Taiwan with public figures, but today the company hosted its first public test of Live Audio Rooms in the U.S. The event itself was hosted by Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg, who chatted with fellow execs and creators.
Joining Zuckerberg were Facebook VP and Head of Facebook Reality Labs Andrew “Boz” Bosworth, Head of Facebook App Fidji Simo and three Facebook Gaming creators, including StoneMountain64, QueenEliminator and TheFierceDivaQueen.
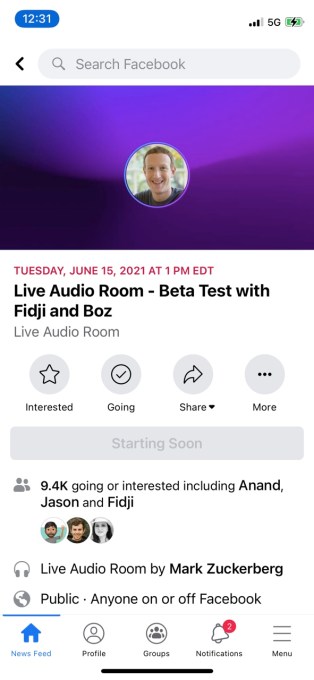
Image Credits: Facebook screenshot
The creators used their time in the Audio Room to talk more about their gaming journeys on Facebook, what kind of games they were streaming and other gaming-related matters. Zuckerberg also briefly teased new gaming features, including a new type of post, coming soon, called “Looking for Players.” This post type will help creators find others in the community to play games with while they’re streaming.
In addition, badges that are earned from livestreams will now carry over to fan groups, Zuckerberg said, adding that it was a highly requested feature by creators and fans alike.
Fan groups will also now become available to all partnered creators on Facebook Gaming, starting today, and will roll out to others in the coming weeks.
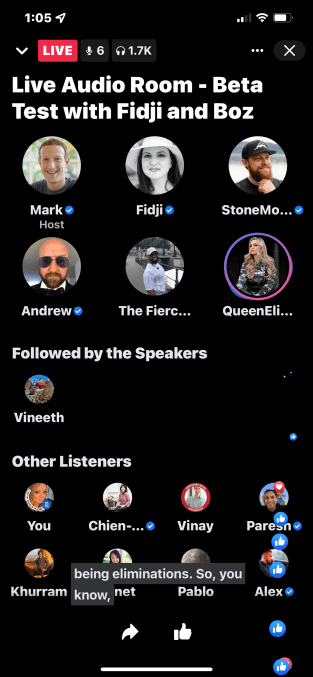
Image Credits: Facebook screenshot
The experience of using the Live Audio Room is very much like what you’d expect on another platform, like Clubhouse or Twitter Spaces. The event’s hosts appear in rounded profile icons at the top of the screen, while the listeners appear in the bottom half of the screen, as smaller icons. In between is a section that includes people followed by the speakers.
The active speaker is indicated with a glowing ring in shades of Facebook blue, purple and pink. If verified, a blue check appears next to their name.
Listeners can “Like” or otherwise react to the content as it streams live using the “Thumbs Up” button at the bottom of the screen. And they can choose to share the Audio Room either in a Facebook post, in a Group, with a friend directly or through other apps.
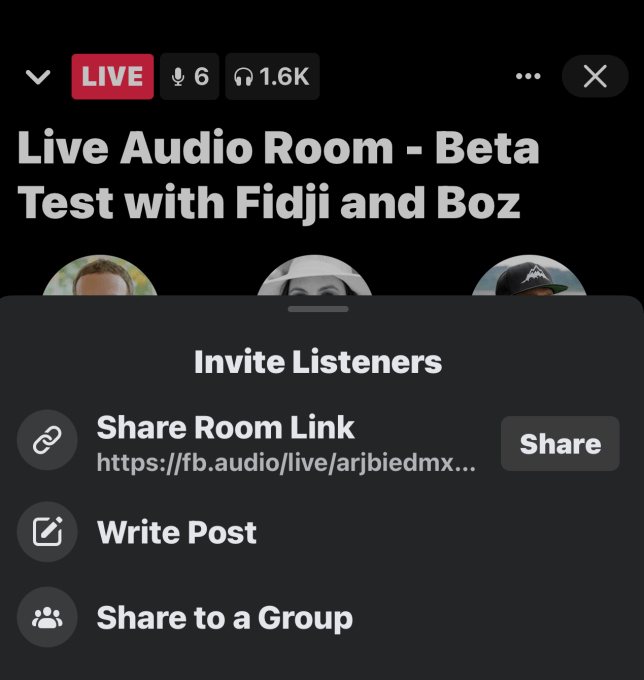
Image Credits: Facebook screenshot
A toggle switch under the room’s three-dot “more” menu lets you turn on or off auto-generated captions, for accessibility. From here, you can also report users or any issues or bugs you encountered.
The Live Audio Room today did not offer any option for raising your hand or joining the speakers on stage — it was more of a “few-to-many” broadcast experience.
Before today, TechCrunch received a couple of tips from users who reported seeing the Audio Rooms option appear for them in the Facebook app. However, the company told us it had only tested Live Audio Rooms in the U.S. with employees.
During the test period, Live Audio Rooms are only available on iOS and Android, we’re told.
Zuckerberg also used today’s event to talk more broadly about Facebook’s plans for the creator economy going forward.
“I think a good vision for the future is one where a lot more people get to do creative work and work that they enjoy, and fewer people have to do work that they just find a chore. And, in order to do that, a lot of what we need to do is basically build out a bunch of these different monetization tools,” explained Zuckerberg. “Not all creators are going to have the same business model. So having the ability to basically use a lot of different tools like Fiji [Simo] was talking about — for some people it might be, Stars or ad revenue share or subscriptions or selling things or different kinds of things like that — that will be important and part of making this all add up.”
He noted also that the tools Facebook is building go beyond gaming, saying that Facebook intends to support journalists, writers and others — likely a reference to the company’s upcoming Substack clone, Bulletin, expected to launch later this month.
Zuckerberg additionally spoke about how the company won’t immediately take a cut of the revenue generated from creators’ content.
“Having this period where we’re not taking a cut and more people can get into these kinds of roles, I think is going to be a good thing to do — especially given how hard hit a lot of parts of the economy have been with COVID and the pandemic,” he said.
More realistically, of course, Facebook’s decision to not take an immediate cut of some creator revenue is a decision it’s making in order to help attract more creators to its service, in the face of so much competition across the industry.
Clubhouse, for example, is currently wooing creators with a payments feature, where creators keep 100% of their revenue. And it’s funding some creators’ shows. Twitter, meanwhile, is tying its audio product Spaces to its broader set of creator tools, which now include newsletters, tips and, soon, a subscription platform dubbed Super Follow.
Zuckerberg didn’t say during today’s event when Live Audio Rooms would be available to the public, but said the experience would roll out to “a lot more people soon.”
Powered by WPeMatico