TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Young startups need to be great at design, not just for their products, but for their brands. The pandemic made that all harder — but lessons are being learned. We caught up with Scott Tong, a startup design expert who advises early-stage companies, to learn more.
The office may still be the best place to hash out big multiteam decisions, he says, but new best practices and modern tools are making remote collaboration easier and easier.
Brand design seems to only be getting trickier, however. “To users,” he explains, “brand and product are lumped together and they each represent the other.”
Today, many users have spent lots of time at home online, often thinking harder about world events and how they are living their lives. They’re scrutinizing what they can observe about a startup to see if its values line up with theirs before they make a decision to sign up (or quit).
The solution, in Tong’s view, is to create a unifying plan where design decisions can address problems before they emerge.
More details are in the interview below. For a full conversation, check out Tong’s talk about design strategy coming up at our TC Early Stage 2021 – Marketing & Fundraising conference on July 8.
The pandemic affected us all. How has it affected user-focused brand design?
The pandemic drove people to consume even more media than before. News about science, politics, race and the economy were unavoidable. Brands have had to navigate a very complex landscape of topics that can be divisive. People increasingly identify with brands that are aligned with their values. But in order to understand a brand’s values, someone has to sift through competing signals — some from the brand itself, and others from vocal supporters and critics. Say the wrong thing and a brand can risk alienating large portions of their audience (including their own employees). If a brand says nothing, their silence can be interpreted as complicity. And if brand messaging comes across as unauthentic, it could spell disaster. It’s a difficult needle to thread. It’s not uncommon for companies to run surveys to gather signals about how their brand is perceived by customers and noncustomers alike.
What new things about users should startups consider when working on designing their identities? What are you advising startups now about designing their brands, versus what you said circa December 2020?
Identities are only one part of a much larger constellation of touch points that make up a user’s perception of a brand. User expectations are extremely high and will continue to rise. Even with their free products, users have gotten accustomed to highly polished experiences. While “high quality” is table stakes for users, the challenge for a company is to pinpoint the handful of dimensions that matter most. That’s why constantly seeking to understand users is so important. Deeply understanding what they care about will help isolate those critical dimensions so teams can focus on areas that will drive the most meaningful impact.
Founders, help TechCrunch find the best growth marketers for startups.
Provide a recommendation in this quick survey and we’ll share the results with everybody.
What do startups continue to get wrong?
One recurring observation is that brand teams and product teams often sit in different parts of a company’s org structure. While there are reasons for this, it’s important to remember that users don’t care about your org structure. To users, brand and product are lumped together and they each represent the other.
Internally, how are companies handling internal challenges like collaborative designing in a more remote world? In-person communication has been vital historically to get all parts of a company thinking in the same way. What is helping those who have gone remote-first succeed (tools, approaches to meeting and documentation, etc.)?
Collaboration tools have never been more abundant. But while tools are plenty, norms around their usage can vary significantly from group to group, even within the same company. Where can I find the project brief? How many back-to-back meetings is too many? How are brainstorms run in a virtual environment? When do I use Slack versus email? Establishing those norms requires conversation and experimentation.
Along with norms around tools, it’s helpful to establish a cadence/rhythm that allows team members to get and stay in sync. Depending on the team, that cadence may be daily, weekly, biweekly, monthly or quarterly, etc., but find the appropriate cadence for each audience.
Alternatively, do you think the demands of good design work will motivate more early-stage startups back into in-person office work?
There are varying opinions on whether being in-person spurs innovation or productivity. The pandemic has forced us all to adapt, and design is no exception. It’s been encouraging to see good design happen in remote work environments, and a lot of that has been enabled by tools and the norms around their usage. While I personally would prefer being in-person, especially at the early stages of company building, I think it’s entirely possible to establish a high-functioning team in a remote environment. Of course there are cases — like hardware or soft goods — where tactile feedback is important and hard to replicate remotely. But even then I’ve seen some successful workarounds (for example, sending the same material sample to every team member). Given that this is all still very new, there will inevitably be hiccups along the way. But a team of willing participants with the right mix of tools and norms can make it work.
Overall, with more teams remote and distributed, it may be even more natural than before to work with a third-party brand design expert. When do you advise startups to bring in an outside consultant today, and how should they work with them?
This depends largely on how design is valued within an organization — as a service or as a partner.
If design is viewed as a partner, then the relationship is ongoing and iterative. This means design is a function that builds, measures and learns alongside their product and engineering counterparts and the benefits of institutional knowledge compound over time.
If design is viewed as a service, third parties make sense, because in a service relationship there is usually a defined beginning and end to an engagement. Clear scope, timeline and deliverables will set this kind of service relationship up for success.
Powered by WPeMatico
Foursquare co-founder Dennis Crowley has announced that he is stepping back from his full-time role at the company. During the first seven years of the company, he was the startup’s Chief Executive Officer. In 2016, Crowley moved to an executive chairman position. He’s also been running the Foursquare Labs R&D group since then.
Going forward, Crowley won’t be working full-time at the company. He’ll remain on the board of directors as co-chair with Factual founder Gil Elbaz.
In 2009, Foursquare was better known for its location-based social network. People would check in to locations to share what they’ve been up to with their friends. Users would earn badges and mayorships.
Over the years, the most active users had amassed thousands of checkins. Foursquare became a great app to keep track of places you like. You could also use it to discover your friends’ favorite places.
That’s why the company decided to split its main app into two separate apps — the Foursquare City Guide and Swarm. At the same time, the company started working on developer APIs and SDKs so that other companies could take advantage of Foursquare’s location data.
That business in particular has been quite lucrative. With the company’s Pilgrim SDK, developers can build location-aware apps. For instance, an advertiser can send a personalized notification based on where you are. Foursquare tries to be as accurate as possible and can sometimes even figure out when you enter or exit a venue.
That SDK enables many different possibilities. It’s easy to track the impact of an advertising campaign on online sales, but what about offline interest?
Foursquare’s SDK can help advertisers and brands see whether an advertising campaign has an impact on foot traffic. Of course, you can also combine that data with other customer data.
The company has become an important advertising and marketing platform focused on location. Overall, the company has generated more than $100 million in revenue in 2020. And it plans to grow in 2021 and beat that number.
Crowley mentions two reasons why he’s leaving now. According to him, the company is doing well, and he’s been working on the same thing for 12 years already.
“Foursquare hasn’t just found its way … it leads the way. I used to say that my goal was to make the name ‘Foursquare’ synonymous with ‘innovation in contextual aware computing’ … And, here in 2021, we’ve built the tools and frameworks that can make that so,” Crowley writes in a blog post.
“Also, 12 years is a lot of time. I have lots of things I still want to build — many of which don’t fit neatly into the Foursquare of 2021 (and, hey fellow founder, it’s fine to feel this way!),” he adds. He’s also going to spend some well-deserved time with his family.
Crowley has been an iconic startup founder during the Web 2.0 era. He managed to attract tens of millions of users. It’s clear that he’s been a great product CEO during the early years of the company. And now, the company is also generating revenue. So it’s going to be interesting to see what he builds next.
Powered by WPeMatico
As the second quarter races to a close, we’re down to the wire for IPOs looking to get out before June ends. One such company is SentinelOne, a cybersecurity startup backed by Insight Venture Partners, Redpoint, Tiger Global Management, Data Collective and Anchorage Capital, among others.
SentinelOne raised an ocean of capital while private, including nearly $500 million across two rounds in 2020. Its debut is therefore a huge liquidity event for a host of investing groups. And today, the cybersecurity unicorn had good news in the form of an upgrade to its IPO price range.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
Last week, The Exchange wrote that the company’s IPO would be a “good heat check for the IPO market” given its rapid growth and pace of losses. How investors valued it would help explain the public market’s current appetite for loss-making startups. Today’s news implies healthy appetites.
 SentinelOne raised its IPO price range this morning from $26 to $29 per share to $31 to $32 per share, a sizable lift to its valuation and IPO raise.
SentinelOne raised its IPO price range this morning from $26 to $29 per share to $31 to $32 per share, a sizable lift to its valuation and IPO raise.
This morning, we’re unpacking the company’s new valuation range, thinking about SentinelOne’s growth and revenue results compared to similar public companies, and working to understand if the company is inexpensive, neutrally priced or expensive compared to current comps. Sound fun? It will be!
Recall that when SentinelOne last raised capital it was valued at $2.7 billion on a pre-money basis. The company was therefore worth just under $3 billion after the $267 million round. The unicorn is going to yeet that figure into space in its IPO, barring something catastrophic.
Its new IPO price range of $31 to $32 per share values the company on a much richer basis. With an anticipated simple share count of 253,530,006 after its IPO, inclusive of a private placement, the company would be worth $7.86 billion to $8.11 billion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Shopify changed the e-commerce landscape by making it easier for merchants to set up their websites both quickly and affordably. A startup called Tapcart is now doing the same for mobile commerce.
The company, which has referred to itself as the “Shopify for mobile apps,” today powers the shopping apps for top brands, including Fashion Nova, Pier One Imports, The Hundreds, Patta, Culture Kings, and thousands more. Following a year of 3x revenue growth, in part driven by the pandemic, Tapcart is today announcing the close of a $50 million round of Series B funding, led by Left Lane Capital. Having clearly taken notice of Tapcart’s traction with its own merchant base, Shopify is among the round’s participants.
Other investors in the round include SignalFire, Greycroft, Act One Ventures and Amplify LA.
Tapcart’s co-founders, Sina Mobasser and Eric Netsch, have worked in the mobile app industry for years. Mobasser’s previous company, TestMax, offered one of the first test prep courses on iOS, while Netsch had more recently worked on the agency side to create mobile and digital experiences for brands. Together, the two realized the potential in helping online merchants bring their businesses to mobile, as easily as they were able to go online with Shopify.

Tapcart’s founders Sina Mobasser and Eric Netsch at their Santa Monica HQ. Image Credits: Tapcart
“Now, you can launch an app on our platform in a matter of weeks, where historically it would take up to a year if you wanted to custom build an app,” explains Mobasser. “And you can do it for a low monthly fee.”
Tapcart’s platform itself offers a simple drag-and-drop builder that allows anyone to create a mobile app for their existing Shopify store using tools to design their layout, customize the product detail pages, integrate checkout options, include product reviews, and even optionally add other branded content, like blogs, lookbooks, videos (including live video) and more. Everything is synced directly from Shopify to the app in real-time, so the merchant’s inventory, products and collections are all kept up-to-date. That’s a big differentiator from some rivals, which require duplicate sets of data and data transformation.
Tapcart, meanwhile, leverages all of Shopify’s APIs and SDKs to create a native application that works with Shopify’s existing data structures.
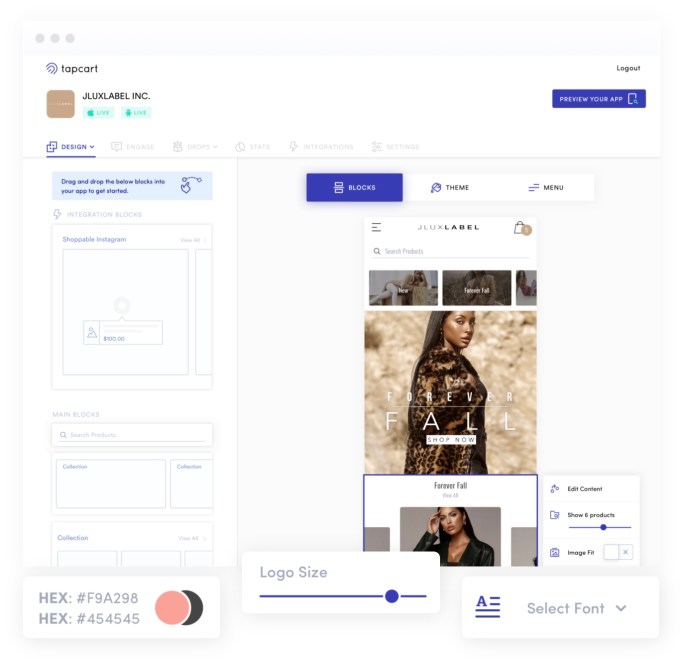
Image Credits: Tapcart
This tight integration with Shopify helps Tapcart because it doesn’t have to focus on the e-commerce infrastructure, as the way things are structured around inventory and collections are roughly 90% the same across brands. Instead, Tapcart focuses on the 10% that makes brands stand out from one another, which includes things like branding, content and design. Its CMS allows merchants to create exclusive content, change the colors and fonts, add videos and more to make the app look and feel fully customized.
Beyond the mobile app creation aspect to its business, Tapcart also helps merchants automate their marketing. Through the Tapcart platform, merchants can communicate with their customers in real-time using push notifications that can alert them to new sales, to encourage them to return to abandoned carts, or any other promotions. The marketing campaigns can be automated, as well, which helps merchants schedule their upcoming launches and product drops ahead of time. The company claims these push notifications deliver click-through rates that are 72% higher than a traditional email or SMS text because of their interactivity and branding.
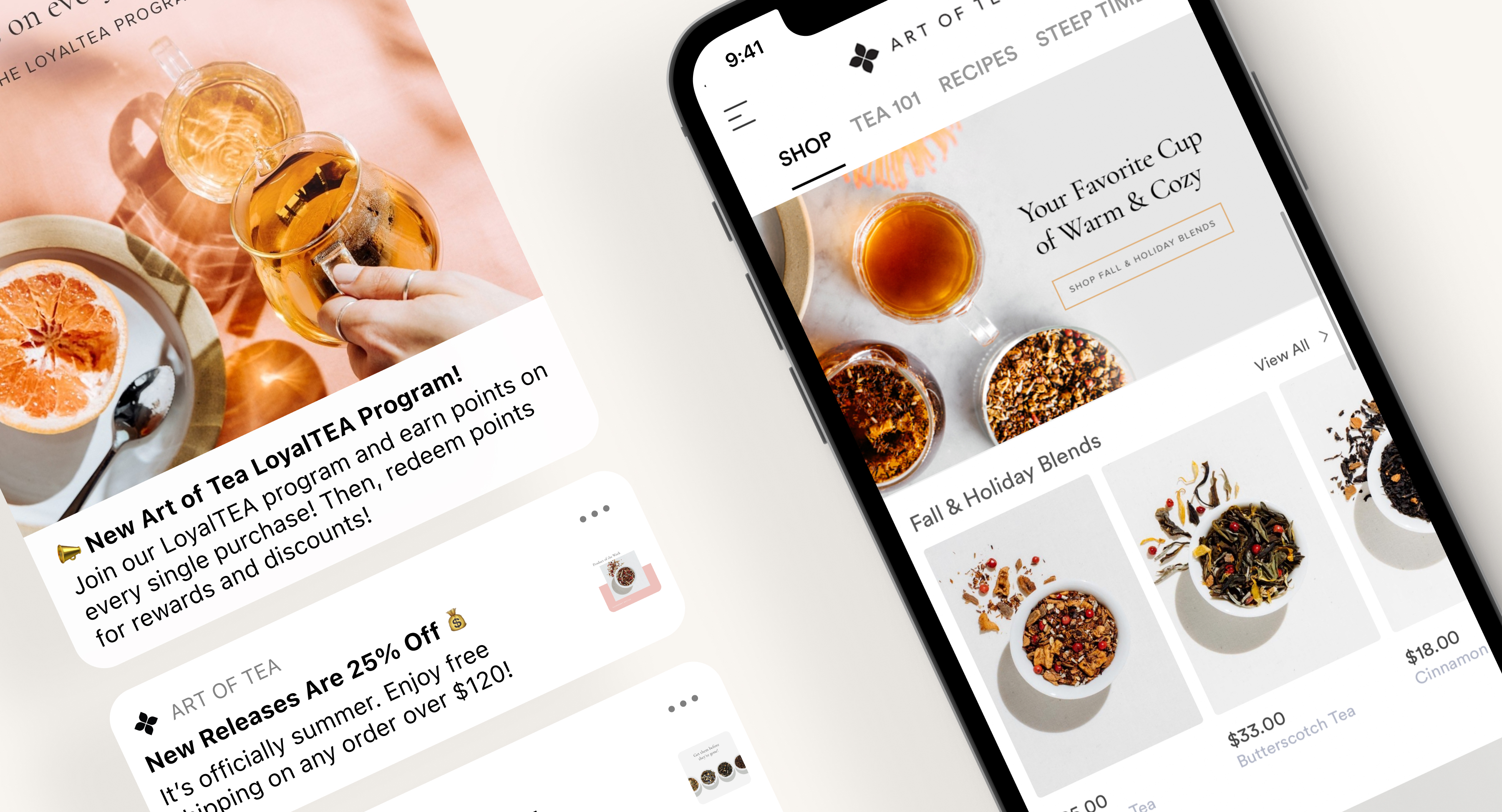
Image Credits: Tapcart
The platform has quickly found traction with SMB to mid-market enterprise customers who have reached the stage of their business where it makes sense for them to double down on customer retention and conversion and optimize their mobile workflow.
“Our sweet spot is when you have maybe a couple hundred customers in your database,” notes Netsch. “That’s a perfect time to now focus less on the paid acquisition portion of your business and more on how to retain and engage those existing customers, [so they’ll] shop more and have a better experience,” he says.
During the past 12 months, over $1.2 billion in merchant sales have flowed through Tapcart’s platform. And in 2020, Tapcart’s recurring revenue increased by 3x, as mobile apps grew even faster during the pandemic, which had increased consumer mobile screen time by 20% year-over-year from 2019. Mobile commerce spending also grew 55% year-over-year, topping $53 billion globally during the holiday shopping season, the company says. Tapcart’s own merchants saw mobile app orders at a rate of more than once-per-second during this time, and it believes these trends will continue even as the pandemic comes to an end.
Today, Tapcart generates revenue by charging a flat SaaS (software-as-a-service) fee, which differentiates it from a number of competitors who charge a percent of the merchant’s total sales.

Image Credits: Tapcart
With the additional funding, Tapcart plans to focus on its goal of becoming a vertically integrated mobile commerce suite of tools, which more recently includes support for iOS App Clips. It will also soon release an upgraded version of its insights analytics platform and will offer scripts that merchants can install on their mobile websites to compare what works on the site versus what works in the app.
Later this year, Tapcart plans to launch a full marketing automation product that will allow brands to automate and personalize their notifications even further. And it plans to invest in market expansions to make its product better designed for mobile, global commerce.
The funding will allow Santa Monica-based Tapcart to hire another 200 people over the next 24 months, up from the 70 it has currently. These will include new additions across time zones and even in markets like Australia and Europe as it moves toward global expansion.
Shopify’s investment will open up a number of new opportunities as well, including on product, engineering, business strategy and partnerships. It will also help to get Tapcart in front of Shopify’s 1.7 million global merchants.
“There’s still quite a lot of merchants that need better mobile experiences, but have yet to really double down on the mobile effort and get something like a native app,” notes Netsch. “There’s a lot of different ways and methods that merchants are experimenting with mobile growth, and we’re trying to offer all of the best parts of that in a single platform. So there’s tons of expansion for Tapcart to do just that with the existing target addressable market,” he says.
“We believe brands must be where their customers are, and today that means being on their phones,” said Satish Kanwar, VP of product acceleration at Shopify, in a statement. “Tapcart helps merchants create mobile-first shopping experiences that customers love, reinforcing Shopify’s mission to make commerce better for everyone. We look forward to seeing Tapcart expand its success on Shopify with the more than 1.7 million merchants on our platform today.”
Powered by WPeMatico
The U.K. is gaining in popularity as a great place to start a tech firm. The country is quickly catching up to China on the tech investment front, with VC investments reaching a record of $15 billion in 2020, according to TechNation. A global health crisis notwithstanding, London remained a favorite for investors. U.K. cities made up a fifth of the top 20 European cities, with names such as Oxford, Dublin, Edinburgh and Cambridge rising to the fore in 2020.
Bristol proved especially popular among tech investors last year — local businesses raked in an impressive $414 million in 2020, making it the third-largest U.K. city for tech investment. The city also has the most fintech startups per head in the U.K. outside London, according to Whitecap’s 2019-2020 Ecosystem Report.
Efforts by the city’s private and public sectors to modernize the city have helped it rank among the top smart cities in the U.K., attracting a bevy of tech entrepreneurs. Its proximity to London has meant that it is a good alternative for founders looking for a more affordable stay while letting them tap the capital’s financial resources. The University of Bristol also has the largest robotics department in Europe.
Use discount code HARBOURSIDE to save 25% off an annual or two-year Extra Crunch membership.
This offer is only available to readers in the U.K. and Europe, and expires on August 31, 2021.
Bristol is also home to an important startup accelerator, SETsquared. A collaborative effort by the five universities of Bath, Bristol, Exeter, Southampton and Surrey, the accelerator has supported over 4,000 entrepreneurs and helped their startups raise a total of £1.8 billion. Other startup support players include the new Science Creates VC fund, set up by entrepreneur Harry Destecroix, and TechSPARK Engine Shed.
Key emerging startups from Bristol include Graphcore, Open Bionics, Ultraleap, Immersive Labs and Five AI.
To get a better idea of the state of the tech ecosystem and the investor outlook for this city, we surveyed founders, leaders and executives involved in nurturing Bristol’s startup ecosystem.
The survey revealed that the city has a robust renewable, zero-carbon and fintech startup landscape. Robotics, VR, bio, quantum, digital and deep tech are also areas showing promise. As for the investing scene, although Bristol has a healthy angel network, the city lacks institutional VC, but with London only a drive or train ride away, this has not proved a significant problem.
We surveyed:
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What are you most excited by? What does it lack?
Bristol is strong in renewable and zero-carbon innovation, fintech and robotics. It’s weak in industry 4.0.
Which are the most interesting startups in Bristol?
Graphcore, LettUs Grow, Open Bionics, Ultraleap and YellowDog.
What are the tech investors like in Bristol? What’s their focus?
A lot of focus on fintech, I think.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
Bristol is a great middle ground between a large dynamic city (plus it’s not far from London) and access to nice countryside area. With remote working we can expect it will attract new residents in the next few years.
Who are the key startup people in the city (e.g., investors, founders, lawyers, designers)?
Aimee Skinner, Abigail Frear and Stuart Harrison.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
Second major city in U.K. innovation.
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What are you most excited by? What does it lack?
Bristol is strong in media/animation, edtech, social impact, health and science. I’m most excited by edtech and the possibility to reach and positively impact millions of students via online learning. It’s weaker in hardware and fintech.
Which are the most interesting startups in Bristol?
Kaedim, Persona Education and One Big Circle.
What are the tech investors like in Bristol? What’s their focus?
There are several very active tech investment networks coming from several angles, e.g., university-led, groups of private angels and tech incubators. The great thing is they all collaborate and share resources, ideas and expertise in initiatives such as The Engine Shed and Silicon Gorge.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
More people are moving in, as Bristol has a great urban lifestyle with easy access to the countryside and Southwest/Wales holiday spots, and an international airport 20 minutes from the center.
Who are the key startup people in the city (e.g., investors, founders, lawyers, designers)?
Jerry Barnes at Bristol PE Club; Abby Frear at TechSPARK; Briony Phillips at Rocketmakers; Jack Jordan-Connelly at SETsquared.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
It’s developing rapidly with lots of support, so it will be bigger, attracting more investment and definitely more on the international scene five years from now.
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What are you most excited by? What does it lack?
Our tech ecosystem is strong in the aerospace and defense sector. We are excited by the scope and scale of digital transformation opportunities with AI available in this sector. The main weakness in this sector is the slow pace of transformation, especially now due to the pandemic.
Which are the most interesting startups in Bristol?
Graphcore and YellowDog.
What are the tech investors like in Bristol? What’s their focus?
Compared to the U.K. tech sector average, Bristol has a very low proportion of established companies (4% versus 8%), a higher proportion of seed stage companies (42% versus 37%), and a higher death rate (21% versus 17%). It’s a particularly young ecosystem.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
It is possible that people moving out of London will come into Bristol due to the transport links, strong ecosystem and beautiful nature of the city.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
I wouldn’t be surprised if Bristol turns out to be San Francisco of Europe!
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What does it lack?
Bristol is strong in the medtech, veterinary, industrial sectors.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
Others have moved in.
Who are the key startup people in the city (e.g., investors, founders, lawyers, designers)?
SETsquared.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
We will see massive growth in five years.
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What are you most excited by? What does it lack?
Our sector is weak in entrepreneurial ambition among researchers, and so suffers from low rates of deep tech spinout activity from leading universities. We are most excited by the step change in activity we have seen in the past two years and culture shift towards innovation.
Which are the most interesting startups in Bristol?
Rosa Biotech, Albotherm and CytoSeek.
What are the tech investors like in Bristol? What’s their focus?
Medium strength in shallow tech; currently weak in deep tech.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
People are moving in.
Who are the key startup people in the city (e.g., investors, founders, lawyers, designers)?
Spin Up Science, Science Creates and Science Angel Syndicate.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
Very strong in deep tech with an invested local community of entrepreneurs, incubators and investors.
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What are you most excited by? What does it lack?
Bristol is strong in wireless (5G, 60 GHz, etc.), semiconductors (especially processors, AI/ML and parallel architectures), robotics and other hard tech/deep tech.
Which are the most interesting startups in Bristol?
Graphcore, Ultraleap, Blu Wireless and Five AI.
What are the tech investors like in Bristol? What’s their focus?
It’s limited. There are some angels, but few locally focused funds.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
Much the same: People choose to live in Bristol/Bath for quality of life. Much of the work is already external — commuting to London.
Who are the key startup people in the city (e.g., investors, founders, lawyers, designers)?
Nigel Toon, Simon Knowles, Stan Boland, David May and Nick Sturge.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
Much stronger, with more processor and hardware activity.
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What are you most excited by? What does it lack?
Bristol has a strong robotics, aerospace and renewables scene. I’m most excited to see how the legacy in aerospace in Bristol will translate to future industry-defining companies. The ecosystem is weak on the investor side, though London VCs are less than a two-hour train journey away.
Which are the most interesting startups in Bristol?
Graphcore, Ultraleap and Open Bionics.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
I believe Bristol will become more attractive.
Who are the key startup people in the city (e.g., investors, founders, lawyers, designers)?
Tom Carter at Ultraleap, and Joel Gibbard at Open Bionics.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
Getting closer to London and Cambridge.
Which sectors is Bristol’s tech ecosystem strong in? What are you most excited by? What does it lack?
Bristol has a strong biotech, quantum, digital, science-based/deep tech ecosystem. I’m excited by this eclectic city with exciting people that think differently.
Which are the most interesting startups in Bristol?
Any QTEC, SETsquared, or UnitDX members and alumni.
What are the tech investors like in Bristol? What’s their focus?
Very early/nascent, mostly angels.
With the shift to remote working, do you think people will stay in Bristol or will they move out? Will others move in?
Probably move in! Beautiful green spaces around, lots of interesting, independent shops. And (just about) commutable from London.
Who are the key startup people in the city (e.g., investors, founders, lawyers, designers)?
The incubators — QTEC, QTIC, SETsquared and UnitDX; Bristol Private Equity Club; Harry Destecroix.
Where do you think the city’s tech scene will be in five years?
Buzzing. More great startups and VCs moving in.
Powered by WPeMatico
Meetings should have a clear purpose, but instead, they’ve become a way to measure status and reinforce what is colloquially referred to as CYA culture.
There’s a kernel of truth in every joke, so whenever someone quips, “This meeting could have been an email!” you can bet that some small part of them meant it sincerely.
Few people know how to run meetings effectively and keep conversations on track. Making matters worse, attendees often don’t bother to prepare, which makes a boring session even less productive.
And then there’s the complication of workplace politics: How secure do you feel declining an invitation from a co-worker — or a manager?
“Every time a recurring meeting is added to a calendar, a kitten dies,” says Chuck Phillips, co-founder of MeetWell. “Very few employees decline meetings, even when it’s obvious that the meeting is going to be a doozy.”
Full Extra Crunch articles are only available to members.
Use discount code ECFriday to save 20% off a one- or two-year subscription.
Changing your meeting culture is difficult, but given that 26% of workers plan to look for a new job when the pandemic ends, startups need to do all they can to retain talent.
Aimed at managers, this post offers several testable strategies that will help you boost productivity and say goodbye to poorly run, lazily planned meetings.
“Declining a bad meeting should never be taboo, and you should reiterate your trust in the team and challenge them to spend their and others’ time with more intention,” Phillips says. “Help them feel empowered to decline a bad meeting.”
Thanks very much for reading Extra Crunch, and have a great weekend.
Walter Thompson
Senior Editor, TechCrunch
@yourprotagonist

Image Credits: Shein
In the last year, online apparel shopping app Shein grew active daily users by 130%, reports Apptopia.
Each day, thousands of new products arrive on the app’s virtual shelves. Items are rapidly designed and prototyped before Shein’s contractors put them into production in Guangzhou factories — two weeks later, those SKUs arrive in fulfillment centers around the globe.
TechCrunch reporter Rita Liao examined how the company’s agile supply chain has become hot talk among e-commerce experts, but beyond a strong logistics game and data-driven product development, Shein’s close relationships with suppliers are integral to its success.
She also tried to answer a question many are asking: Is Shein a Chinese company?
“It’s hard to pin down where Shein is from,” answered Richard Xu from Grand View Capital, a Chinese venture capital firm.
“It’s a company with operations and supply chains in China targeting the global market, with nearly no business in China.”

Image Credits: Chevrolet
GM Vice President of Innovation Pam Fletcher is in charge of the company’s startups that tackle “electrification, connectivity and even insurance — all part of the automaker’s aim to find value (and profits) beyond its traditional business of making, selling and financing vehicles,” Kirsten Korosec writes.
Fletcher joined TechCrunch at a virtual TC Sessions: Mobility 2021 event to discuss what it’s like to launch a slew of startups under the umbrella of a 113-year-old automaker.

Image Credits: MaC Venture Capital / Wonderschool
MaC Venture Capital founding managing partner Marlon Nichols and Wonderschool CEO Chris Bennett joined Extra Crunch Live to tear down the company’s early deck.
“The first thing that jumped out at all of us was just how bare-bones the presentation is: white text on a blue background, largely made up of bullet points,” Brian Heater writes before noting the CEO admitted that “not much changed aesthetically between that first pitch and the Series A deck.”
“It aligned with what we were valuing at the time,” Bennett says. “We were really focused on getting the product-market fit and really trying to understand what our customers needed. And we’re really focused on building the team.”
Image Credits: Bryce Durbin/TechCrunch
Dear Sophie,
I’ve been working on an H-1B in the U.S. for nearly two years.
While I’m grateful to have made it through the H-1B lottery and to be working, I’m feeling unhappy and frustrated with my job.
I really want to start something of my own and work on my own terms in the United States. Are there any immigration options that would allow me to do that?
— Seeking Satisfaction
Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
Alex Wilhelm calls SentinelOne’s looming debut “fascinating.”
“Why? Because the company sports a combination of rapid growth and expanding losses that make it a good heat check for the IPO market,” he writes. “Its debut will allow us to answer whether public investors still value growth above all else.”
Alex delves into an early dataset from SentinelOne and why public market investors still appear to value growth above anything else.
Image Credits: Jenny Dettrick (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Guest columnist Rob Hudock, a litigator who focuses on helping companies recruit the best talent available while avoiding distracting workplace issues or lawsuits, lays out the importance of putting out any employment-related fires before an exit.
“Inattention to employment issues can have a significant impact on deals — from preventing closings and reducing the deal value to altering the deal terms or significantly limiting the pool of potential buyers,” he writes.
“Fortunately, such issues typically can be resolved well in advance with a little forethought and legal guidance.”

Image Credits: John M Lund Photography Inc (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Building an excellent product and a standout company culture require the same process, Heap CEO Ken Fine writes in a guest column.
“At Heap, the analytics solution provider I lead, a defining principle is that good ideas should not be lost to top-down dictates and overrigid hierarchies,” he writes. “The best results come when you approach leadership like you would create a great product — you hypothesize, you test and iterate, and once you get it right, you grow it.”
Here, he lays out his method that argues in favor of iterative change, not “one-and-done decrees.”
Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
The big news on Thursday was the announcement of Andreessen Horowitz’s new cryptocurrency-focused fund. Most focused on the eye-popping $2.2 billion figure, but Alex Wilhelm dug a bit deeper into the announcement to note that a16z isn’t just pumping a ton of money into the crypto space, it’s putting on gloves to fight for it.
Alex writes that “a16z intends to run defense for crypto in the American, and perhaps global, market. Crypto-focused startups are likely unable to tackle the regulation of their market on their own because they’re more focused on product work in a particular region of the larger crypto economy. The wealthy and connected investment firm that backs them will take on the task for its chosen champions.”

Image Credits: Nicholas Kamm / AFP / Getty Images
Alex Wilhelm dives headfirst into BuzzFeed’s announcement that it plans to go public via a blank check company.
He looked at its historical and anticipated revenue growth (the latter is very sunny, which is not atypical for SPAC presentations), what makes up that revenue (more “commerce” as time goes on), its long-term profitability projections, as well as fun stuff, like the Pulitzer Prize-winning BuzzFeed News.
Admit it. You’re curious.

Image Credits: SaskiaAcht (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Moving from a pay-as-you-go model to a subscription service is more than just putting a monthly or yearly price tag on a product, CloudBlue’s Jess Warrington writes in a guest column.
“Executives cannot just layer a subscription model on top of an existing business,” Warrington writes. “They need to change the entire operation process, onboard all stakeholders, recalibrate their strategy and create a subscription culture.”
Warrington says that in his role at CloudBlue, companies often approach him for “help with solving technology challenges while shifting to a subscription business model, only to realize that they have not taken crucial organizational steps necessary to ensure a successful transition.”
Here’s how to avoid that situation.
Image Credits: Bryce Durbin
Rebecca Bellan interviewed Veo CEO Candice Xie about the micromobility startup’s “old-fashioned way” of doing business.
“I understand people are eager to prove their unit economics, their scalability and also improve their matrix to the VC to raise another round,” Xie says. “I would say that’s OK in the consumer industry, like consumer electronics or SaaS.
“But we are in transportation. It is a different business, and transportation takes years of collaboration and building between private and public partners. … So I don’t see it happening from day one, turning over a billion-dollar company, while simultaneously having it all make sense for the cities and users.”

Image Credits: jayk7 (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
All companies want more or less the same thing: growth. But how do you accomplish it?
Ideally, don’t start from scratch.
The race to grow faster is more pressing than ever before. … “[F]orward-thinking entrepreneurs and growth marketers simply must make time to study their competition, learn best practices and apply them to their own business growth,” Mark Spera, the head of growth marketing at Minted, writes in a guest column.
“Of course, you should still run your own experiments, but it’s just more capital-efficient to emulate than to trial-and-error from scratch. Here are five companies with growth strategies worth emulating — including the most important lessons you can begin applying to your business today.”
Image Credits: ChrisChrisW (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
With more than 50 million Americans suffering from chronic pain and musculoskeletal (MSK) medical problems, a number of startups are offering patients new products “that don’t resemble the cookie-cutter status quo,” reports Natasha Mascarenhas.
Startups hoping to enter this space have an uphill climb. Setting aside regulations that cover aspects like product packaging and marketing, they must compete with well-entrenched competition from Big Pharma as they try to partner with health insurance companies.
Natasha profiles three companies that are each taking a different approach to personalized health: Clear, Hinge Health and PeerWell.

Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
In the second part of an Exchange series looking at the global early-stage venture capital market, Alex Wilhelm and Anna Heim unpacked the scene in Latin America, discovering it looked a lot like the situation in the United States: slow Series A rounds, fast B rounds.
“Mega-rounds are no longer an exception in Latin America; in fact, they have become a trend, with ever-larger rounds being announced over the last few months,” they write.
Despite that, the funds aren’t being equitably distributed, and the region still lags behind its peers: Brazil has the most $1 billion startups in Latin America, with 12. The U.S., meanwhile, has 369, and China has 159.
But the Latin American market remains hot, if not quite as scorching as the U.S. and China.
Powered by WPeMatico
As the pandemic unevenly roars on, Emily Melton, founder and managing partner of Threshold VC, is reflecting on a previous public health crisis: the Spanish flu.
She says the response just over a century ago prompted the rise of interventional medicine — treating illness through surgery or medicine only after symptoms manifest. Today, interventional medicine is the dominant mindset in Western healthcare. And, Melton, a lead investor in health tech startups including Livongo, Tia and Calibrate, says the care pathway ages well.
Personalized medicine — the buzzy yet powerful framing growing in popularity among Silicon Valley startups — is a delivery system in which patients receive more holistic care that takes into account multiple symptoms or comorbidities.
“What’s happening in our society? Chronic diseases, chronic pain, diabetes and obesity,” she said. “That doesn’t require a magic pill and there’s not just a surgery. Oftentimes, there’s therapeutic components, behavior changes and movable touch points.”
Enter personalized medicine. The buzzy yet powerful framing is growing in popularity among Silicon Valley startups. It’s a delivery system in which patients receive more holistic care that takes into account multiple symptoms or comorbidities. In hormonal health, for example, personalized medicine could add more data and specificity to which birth control someone takes, instead of the usual process of trial and error. Essentially, it’s the opposite of interventional medicine.
“We’re not just an arm or a leg, we’re not just obese or a diabetic or a pain sufferer,” Melton said. “How do we treat you as a whole person?”
A number of companies are using this approach to reinvent care for patients with musculoskeletal (MSK) medical conditions and chronic pain. These conditions are commonly treated with addictive opioids, a major public health concern. As an estimated 50 million Americans suffer from chronic pain, entrepreneurs are working on solutions that don’t resemble the cookie-cutter status quo. And the money market is certainly there: In 2017, the global MSK medical market was valued at $57.4 billion; the market for chronic pain, which overlaps with MSK medicine, is expected to hit $151.7 billion in value by 2030.
“Oftentimes it’s not new ideas, it’s conflating a number of factors that come together at one moment in time that allow exponential change that makes a startup work,” Melton said, of the boom and recent activity in MSK medicine. Today, we’ll focus on three startups taking different approaches to help people suffering from chronic pain and MSK-related conditions: Clearing, PeerWell and Hinge Health.
Avi Dorfman says going direct to consumers is the most effective way to treat chronic pain, so he founded Clearing. The digital health startup worked with a medical advisory board of physicians and researchers from Harvard, Johns Hopkins and NYC’s Hospital for Special Surgery to create an opioid-free solution for people struggling with pain.
Last month, Clearing raised a $20 million seed round led by Bessemer and Founders Fund. Melton also invested in the round on behalf of Threshold.
Clearing offers four products: prescription compound cream that includes FDA-approved ingredients, CBD cream for topical discomfort, nutraceuticals to supplement joint health, and a directory of prerecorded, at-home exercises. It currently is available to patients in California, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee and Texas.
Powered by WPeMatico
Seattle-based Edge Delta, a startup that is building a modern distributed monitoring stack that is competing directly with industry heavyweights like Splunk, New Relic and Datadog, today announced that it has raised a $15 million Series A funding round led by Menlo Ventures and Tim Tully, the former CTO of Splunk. Previous investors MaC Venture Capital and Amity Ventures also participated in this round, which brings the company’s total funding to date to $18 million.
“Our thesis is that there’s no way that enterprises today can continue to analyze all their data in real time,” said Edge Delta co-founder and CEO Ozan Unlu, who has worked in the observability space for about 15 years already (including at Microsoft and Sumo Logic). “The way that it was traditionally done with these primitive, centralized models — there’s just too much data. It worked 10 years ago, but gigabytes turned into terabytes and now terabytes are turning into petabytes. That whole model is breaking down.”
He acknowledges that traditional big data warehousing works quite well for business intelligence and analytics use cases. But that’s not real-time and also involves moving a lot of data from where it’s generated to a centralized warehouse. The promise of Edge Delta is that it can offer all of the capabilities of this centralized model by allowing enterprises to start to analyze their logs, metrics, traces and other telemetry right at the source. This, in turn, also allows them to get visibility into all of the data that’s generated there, instead of many of today’s systems, which only provide insights into a small slice of this information.
While competing services tend to have agents that run on a customer’s machine, but typically only compress the data, encrypt it and then send it on to its final destination, Edge Delta’s agent starts analyzing the data right at the local level. With that, if you want to, for example, graph error rates from your Kubernetes cluster, you wouldn’t have to gather all of this data and send it off to your data warehouse where it has to be indexed before it can be analyzed and graphed.
With Edge Delta, you could instead have every single node draw its own graph, which Edge Delta can then combine later on. With this, Edge Delta argues, its agent is able to offer significant performance benefits, often by orders of magnitude. This also allows businesses to run their machine learning models at the edge, as well.
“What I saw before I was leaving Splunk was that people were sort of being choosy about where they put workloads for a variety of reasons, including cost control,” said Menlo Ventures’ Tim Tully, who joined the firm only a couple of months ago. “So this idea that you can move some of the compute down to the edge and lower latency and do machine learning at the edge in a distributed way was incredibly fascinating to me.”
Edge Delta is able to offer a significantly cheaper service, in large part because it doesn’t have to run a lot of compute and manage huge storage pools itself since a lot of that is handled at the edge. And while the customers obviously still incur some overhead to provision this compute power, it’s still significantly less than what they would be paying for a comparable service. The company argues that it typically sees about a 90 percent improvement in total cost of ownership compared to traditional centralized services.
Edge Delta charges based on volume and it is not shy to compare its prices with Splunk’s and does so right on its pricing calculator. Indeed, in talking to Tully and Unlu, Splunk was clearly on everybody’s mind.
“There’s kind of this concept of unbundling of Splunk,” Unlu said. “You have Snowflake and the data warehouse solutions coming in from one side, and they’re saying, ‘hey, if you don’t care about real time, go use us.’ And then we’re the other half of the equation, which is: actually there’s a lot of real-time operational use cases and this model is actually better for those massive stream processing datasets that you required to analyze in real time.”
But despite this competition, Edge Delta can still integrate with Splunk and similar services. Users can still take their data, ingest it through Edge Delta and then pass it on to the likes of Sumo Logic, Splunk, AWS’s S3 and other solutions.
“If you follow the trajectory of Splunk, we had this whole idea of building this business around IoT and Splunk at the Edge — and we never really quite got there,” Tully said. “I think what we’re winding up seeing collectively is the edge actually means something a little bit different. […] The advances in distributed computing and sophistication of hardware at the edge allows these types of problems to be solved at a lower cost and lower latency.”
The Edge Delta team plans to use the new funding to expand its team and support all of the new customers that have shown interest in the product. For that, it is building out its go-to-market and marketing teams, as well as its customer success and support teams.
Powered by WPeMatico
Regularly testing waterways and reservoirs is a never-ending responsibility for utility companies and municipal safety authorities, and generally — as you might expect — involves either a boat or at least a pair of waders. Nixie does the job with a drone instead, making the process faster, cheaper, and a lot less wet.
The most common methods of testing water quality haven’t changed in a long time, partly because they’re effective and straightforward, and partly because really, what else are you going to do? No software or web platform out there is going to reach into the middle of the river and pull out a liter of water.
But with the advent of drones powerful and reliable enough to deploy in professional and industrial circumstances, the situation has changed. Nixie is a solution by the drone specialists at Reign Maker, involving either a custom-built sample collection arm or an in-situ sensor arm.
The sample collector is basically a long vertical arm with a locking cage for a sample container. You put the empty container in there, fly the drone out to the location, then submerge the arm. When it flies back, the filled container can be taken out while the drone hovers and a fresh one put in its place to bring to the next spot. (This switch can be done safely in winds up to 18 MPH and sampling in currents up to 5 knots, the company said.)
This allows for quick sampling at multiple locations — the drone’s battery will last about 20 minutes, enough for two to four samples depending on the weather and distance. Swap the battery out and drive to the next location and do it all again.
For comparison, Reign Maker pointed to New York’s water authority, which collects 30 samples per day from boats and other methods, at an approximate cost (including labor, boat fuel, etc) of $100 per sample. Workers using Nixie were able to collect an average of 120 samples per day, for around $10 each. Sure, New York is probably among the higher cost locales for this (like everything else) but the deltas are pretty huge. (The dipper attachment itself costs $850, but doesn’t come with a drone.)
It should be mentioned that the drone is not operating autonomously; it has a pilot who will be flying with line of sight (which simplifies regulations and requirements). But even so, that means a team of two, with a handful of spare batteries, can cover the same space that would normally take a boat crew and more than a little fuel. Currently the system works with the M600 and M300 RTK drones from DJI.
The drone method has the added benefits of having precise GPS locations for each sample and of not disturbing the water when it dips in. No matter how carefully you step or pilot a boat, you’re going to be pushing the water all over the place, potentially affecting the contents of the sample, but that’s not the case if you’re hovering overhead.
In development is a smarter version of the sampler that includes a set of sensors that can do on-site testing for all the most common factors: temperature, pH, troubling organisms, various chemicals. Skipping the step of bringing the water back to a lab for testing streamlines the process immensely, as you might expect.
Right now Reign Maker is working with New York’s Department of Environmental Protection and in talks with other agencies. While the system would take some initial investment, training, and getting used to, it’s probably hard not to be tempted by the possibility of faster and cheaper testing.
Ultimately the company hopes to offer (in keeping with the zeitgeist) a more traditional SaaS offering involving water quality maps updating in real time with new testing. That too is still in the drawing-board phase, but once a few customers sign up it starts looking a lot more attractive.
Powered by WPeMatico
Happs, an app that lets creators stream live video simultaneously across social platforms, has raised $4.7 million in a post-seed round. The product originally began as a platform for independent journalists, but expanded its mission last year to offer tools to all online creators while connecting them through a new social network.
The funding was led by Bullpen Capital and Crosslink, Goodwater, Corazon, Rob Hayes of First Round Capital and Bangaly Kaba, previously at Instagram and Sequoia, also participated.
What sets Happs apart from some established competitors in the space is the team’s desire to not only build tools that help video creators produce professional-looking online streams, but to cultivate a kind of meta-community that brings people together from across other social media sites.
“We kind of view this as the essence of what the creator economy is all about,” Happs CEO Mark Goldman told TechCrunch. “The idea of locking creators into an individual platform is a very traditional way of thinking about content creation.”

Like Goldman, the other co-founders, David Neuman and Drew Shepard, come from the media world. Goldman was the founding COO of Current TV, an experimental TV channel that dabbled in user-generated content and eventually sold to Al Jazeera in 2013.
“The whole idea was to democratize media and open it up,” Goldman said of his time working on Current TV, which he connects directly to his interest in building Happs. “[We] loved the creativity unleashed by that.”
Online creators tend to be siloed within the app where they’ve built the biggest community, but Happs wants to empower them to reach as many followers as possible in a platform-agnostic way. For creators, the appeal with multistreaming is maximizing reach while making content efficiently. There’s a risk of alienating YouTube followers at the expense of your Twitch community if you don’t play your cards right, but some savvy content creators have turned toward the model to grow their audiences.
Happs connects people across platforms in a few ways. For one, Happs users can broadcast live to Facebook, YouTube, Twitter and Twitch simultaneously. The app also collects live comments from all supported social media sites and beams them into its own interface where they appear in a continuous cross-platform stream.
The integrated comment feature is nice built-in option for anyone who’s straddled comments across multiple devices simultaneously while livestreaming, which is no easy feat. When you’re streaming live you can feature a comment so that followers can see it on the screen no matter what platform they’re watching on.
Other companies in the space like OBS, Streamlabs and Restream are focused on the tools part of the equation, offering power users a useful backend for pushing out multi-streamed live video. Streamyard also offers multistreaming to Facebook, YouTube, Twitter and other platforms through a simple browser interface.
Unlike those services, Happs feels more like a social network, with familiar features like user profile photos, follower counts and a feed next to a “go live” button. Anyone can use the multi-streaming platform through its iOS or Android apps or a web interface, whether they’re a creator signing up for the tools or a fan looking to support the content they love.
Happs lacks some of its competitors’ bells and whistles, stuff like fancy customized graphics and lower-thirds, but has a few interesting tricks of its own. While streaming live on Happs, you can invite someone else on the app to join your feed for a real-time collaboration. The social networking elements are meant to encourage cross-platform creativity, so a YouTuber and a Twitch personality could hang out together and boost both of their reaches, all while streaming to a bunch of other apps.
Happs also offers users monetization tools from the get-go, with no requirements before they can start making money. That speaks to the app’s appeal for creators who might be less established or just starting out. Happs could be a much harder sell for a popular creator deeply invested in a platform like Twitch, which has rules against multi-streaming for most accounts that are allowed to monetize.
There are a few different ways to monetize. One lets anyone on Happs sponsor a broadcaster through regular monthly payments. The other is a one-off option that lets you chip in an award for any livestream, or to the VOD (video on demand) after the fact. The in-app currency is a virtual coin that users can buy or earn through doing stuff on the app. There are no plans for ads (yet, anyway).
The company will take 30% cut of subscription earnings, though according to Goldman they’ll be waiving those fees for an unspecified period of time to attract people to the platform.
“We raised this round to really build up product and tech team [and] to make the platform much more stable and reliable,” Goldman said. The company is looking forward to leveraging the new resources to “really go out now and get in front of creators so they know Happs exists.”
Powered by WPeMatico