TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Social media has served as a launchpad to success almost as long as it has been around. The stories of going viral from a self-produced YouTube video and then securing a record deal established the mythology of social media platforms. Ever since, social media has consistently gravitated away from text-based formats and toward visual mediums like video sharing.
For most people, a video on social media won’t be a ticket to stardom, but in recent months, there have been a growing number of stories of people getting hired based on videos posted to TikTok. Even LinkedIn has embraced video assets on user profiles with the recent addition of the “Cover Story” feature, which allows workers to supplement their profiles with a video about themselves.
As technology continues to evolve, is there room for a world where your primary resume is a video on TikTok? And if so, what kinds of unintended consequences and implications might this have on the workforce?
In recent months, U.S. job openings have risen to an all-time high of 10.1 million. For the first time since the pandemic began, available jobs have exceeded available workers. Employers are struggling to attract qualified candidates to fill positions, and in that light, it makes sense that many recruiters are turning to social platforms like TikTok and video resumes to find talent.
But the scarcity of workers does not negate the importance of finding the right employee for a role. Especially important for recruiters is finding candidates with the skills that align with their business’ goals and strategy. For example, as more organizations embrace a data-driven approach to operating their business, they need more people with skills in analytics and machine learning to help them make sense of the data they collect.
Recruiters have proven to be open to innovation where it helps them find these new candidates. Recruiting is no longer the manual process it used to be, with HR teams sorting through stacks of paper resumes and formal cover letters to find the right candidate. They embraced the power of online connections as LinkedIn rose to prominence and even figured out how to use third-party job sites like GlassDoor to help them draw in promising candidates. On the back end, many recruiters use advanced cloud software to sort through incoming resumes to find the candidates that best match their job descriptions. But all of these methods still rely on the traditional text-based resume or profile as the core of any application.
Videos on social media provide the ability for candidates to demonstrate soft skills that may not be immediately apparent in written documents, such as verbal communication and presentation skills. They are also a way for recruiters to learn more about the personality of the candidate to determine how they’d fit into the culture of the company. While this may be appealing for many, are we ready for the consequences?
While innovation in recruiting is a big part of the future of work, the hype around TikTok and video resumes may actually take us backward. Despite offering a new way for candidates to market themselves for opportunities, it also carries potential pitfalls that candidates, recruiters and business leaders need to be aware of.
The very element that gives video resumes their potential also presents the biggest problems. Video inescapably highlights the person behind the skills and achievements. As recruiters form their first opinions about a candidate, they will be confronted with information they do not usually see until much later in the process, including whether they belong to protected classes because of their race, disability or gender.
Diversity, equity and inclusion (DE&I) concerns have had a major surge in attention over the last couple of years amid heightened awareness and scrutiny around how employers are — or are not — prioritizing diversity in the workplace.
But evaluating candidates through video could erase any progress made by introducing more opportunities for unconscious, or even conscious, bias. This could create a dangerous situation for businesses if they do not act carefully because it could open them up to consequences such as damage to their reputation or even something as severe as discrimination lawsuits.
A company with a poor track record for diversity may have the fact that they reviewed videos from candidates used against them in court. Recruiters reviewing the videos may not even be aware of how the race or gender of candidates are impacting their decisions. For that reason, many of the businesses I have seen implement an option for video in their recruiting flow do not allow their recruiters to watch the video until late in the recruiting process.
But even if businesses address the most pressing issues of DE&I by managing bias against those protected classes, by accepting videos there are still issues of diversity in less protected classes such as neurodiversity and socioeconomic status. A candidate with exemplary skills and a strong track record may not present themselves well through a video, coming across as awkward to the recruiter watching the video. Even if that impression is irrelevant to the job, it could still influence the recruiter’s stance on hiring.
Furthermore, candidates from affluent backgrounds may have access to better equipment and software to record and edit a compelling video resume. Other candidates may not, resulting in videos that may not look as polished or professional in the eyes of the recruiter. This creates yet another barrier to the opportunities they can access.
As we sit at an important crossroads in how we handle DE&I in the workplace, it is important for employers and recruiters to find ways to reduce bias in the processes they use to find and hire employees. While innovation is key to moving our industry forward, we have to ensure top priorities are not being compromised.
Despite all of these concerns, social media platforms — especially those based on video — have created new opportunities for users to expand their personal brands and connect with potential job opportunities. There is potential to use these new systems to benefit both job seekers and employers.
The first step is to ensure that there is always a place for a traditional text-based resume or profile in the recruiting process. Even if recruiters can get all the information they need about a candidate’s capabilities from video, some people will just naturally feel more comfortable staying off camera. Hiring processes need to be about letting people put their best foot forward, whether that is in writing or on video. And that includes accepting that the best foot to put forward may not be your own.
Instead, candidates and businesses should consider using videos as a place for past co-workers or managers to endorse the candidate. An outside endorsement can do a lot more good for an application than simply stating your own strengths because it shows that someone else believes in your capabilities, too.
Video resumes are hot right now because they are easier to make and share than ever and because businesses are in desperate need of strong talent. But before we get caught up in the novelty of this new way of sharing our credentials, we need to make sure that we are setting ourselves up for success.
The goal of any new recruiting technology should be to make it easier for candidates to find opportunities where they can shine without creating new barriers. There are some serious kinks to work out before video resumes can achieve that, and it is important for employers to consider the repercussions before they damage the success of their DE&I efforts.
Powered by WPeMatico
Relyance AI, an early-stage startup that is helping companies stay in compliance with privacy laws at the code level, announced a $25 million Series A today. At the same time, they revealed a previously unannounced $5 million seed round.
Menlo Ventures and Unusual Ventures led the A round, while Unusual was sole lead on the seed. Serial entrepreneur Jyoti Bansal from Unusual will join the board under the terms of the deal. His partner John Vrionis had previously joined after the seed round. Matt Murphy from Menlo is coming on as a board observer. The company has now raised $30 million.
Relyance takes an unusual approach to verifying that data stays in compliance working at the code level, while ingesting contracts and existing legal requirements as code to ensure that a company is in compliance. Company co-CEO and co-founder Abhi Sharma says that code-level check is key to the solution. “For the first time, we are building the legal compliance and regulation into the source code,” Sharma told me.
He added, “Relyance is actually embedded within the DevOps pipeline of our customers’ infrastructure. So every time a new ETL pipeline is built or a machine learning model is receiving new source code, we do a compiler-like analysis of how personal sensitive data is flowing between internal microservices, data lakes and data warehouses, and then get a metadata analysis back to the privacy and compliance professionals [inside an organization].”
Leila R. Golchehreh, the other founder and co-CEO, brings a strong compliance background to the equation and has experienced the challenge of keeping companies in compliance firsthand. She said that Relyance also enables companies to define policy and contracts as code.
“Our approach is specifically to ingest contracts. We’ve actually created an algorithm around how [you] actually write a good data protection agreement. We’ve extracted those relevant provisions and we will compare that against [your] operational reality. So if there’s a disconnect, we will be able to raise that as an intelligent insight of a data misalignment,” she said.
With 32 employees, the co-founders hope to double or perhaps even triple that number in the next 12-18 months. Golchehreh and Sharma are a diverse co-founder team and they are attempting to build a company that reflects that. They believe being remote-first gives them a leg up in this regard, but they also have internal policies to drive it.
“The recruiters we work with have a mandate internally to say, ‘Hey, we really want to hire good people and diverse people.’ Relyance as a company is the genesis of two individuals from two completely different ends of the spectrum coming together. And I think hopefully, we can do our job of relaying that into the company as we scale,” Sharma said.
The two founders have been friends for several years and began talking about forming a company together in 2019 over a pizza dinner. The idea began to gel and they launched the company in February 2020. They spent some time talking to compliance pros to understand their requirements better, then in July 2020 began building the solution they have today. They released a beta in February and began quietly selling it in March.
Today they have a number of early customers working with their software, including Dialpad, Patreon, Samsara and True.
Powered by WPeMatico
Ascend on Wednesday announced a $5.5 million seed round to further its insurance payments platform that combines financing, collections and payables.
First Round Capital led the round and was joined by Susa Ventures, FirstMark Capital, Box Group and a group of angel investors, including Coalition CEO Joshua Motta, Newfront Insurance executives Spike Lipkin and Gordon Wintrob, Vouch Insurance CEO Sam Hodges, Layr Insurance CEO Phillip Naples, Anzen Insurance CEO Max Bruner, Counterpart Insurance CEO Tanner Hackett, former Bunker Insurance CEO Chad Nitschke, SageSure executive Paul VanderMarck, Instacart co-founders Max Mullen and Brandon Leonardo and Houseparty co-founder Ben Rubin.
This is the first funding for the company that is live in 20 states. It developed payments APIs to automate end-to-end insurance payments and to offer a buy now, pay later financing option for distribution of commissions and carrier payables, something co-founder and co-CEO Andrew Wynn, said was rather unique to commercial insurance.
Wynn started the company in January 2021 with his co-founder Praveen Chekuri after working together at Instacart. They originally started Sheltr, which connected customers with trained maintenance professionals and was acquired by Hippo in 2019. While working with insurance companies they recognized how fast the insurance industry was modernizing, yet insurance sellers still struggled with customer experiences due to outdated payments processes. They started Ascend to solve that payments pain point.
The insurance industry is largely still operating on pen-and-paper — some 600 million paper checks are processed each year, Wynn said. He referred to insurance as a “spaghetti web of money movement” where payments can take up to 100 days to get to the insurance carrier from the customer as it makes its way through intermediaries. In addition, one of the only ways insurance companies can make a profit is by taking those hundreds of millions of dollars in payments and investing it.
Home and auto insurance can be broken up into payments, but the commercial side is not as customer friendly, Wynn said. Insurance is often paid in one lump sum annually, though, paying tens of thousands of dollars in one payment is not something every business customer can manage. Ascend is offering point-of-sale financing to enable insurance brokers to break up those commercial payments into monthly installments.
“Insurance carriers continue to focus on annual payments because they don’t have a choice,” he added. “They want all of their money up front so they can invest it. Our platform not only reduces the friction with payments by enabling customers to pay how they want to pay, but also helps carriers sell more insurance.”
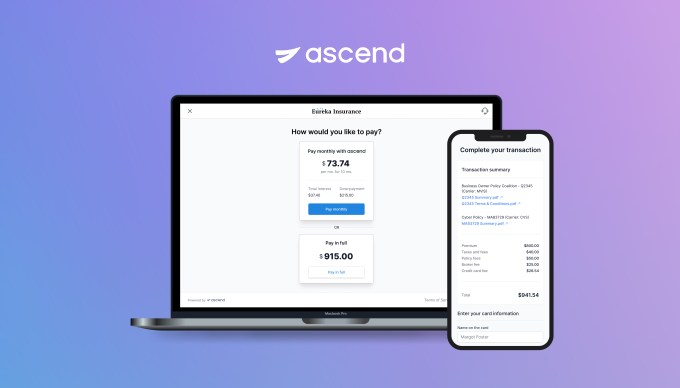
Ascend app
Startups like Ascend aiming to disrupt the insurance industry are also attracting venture capital, with recent examples including Vouch and Marshmallow, which raised close to $100 million, while Insurify raised $100 million.
Wynn sees other companies doing verticalized payment software for other industries, like healthcare insurance, which he says is a “good sign for where the market is going.” This is where Wynn believes Ascend is competing, though some incumbents are offering premium financing, but not in the digital way Ascend is.
He intends to deploy the new funds into product development, go-to-market initiatives and new hires for its locations in New York and Palo Alto. He said the raise attracted a group of angel investors in the industry, who were looking for a product like this to help them sell more insurance versus building it from scratch.
Having only been around eight months, it is a bit early for Ascend to have some growth to discuss, but Wynn said the company signed its first customer in July and six more in the past month. The customers are big digital insurance brokerages and represent, together, $2.5 billion in premiums. He also expects to get licensed to operate as a full payment in processors in all states so the company can be in all 50 states by the end of the year.
The ultimate goal of the company is not to replace brokers, but to offer them the technology to be more efficient with their operations, Wynn said.
“Brokers are here to stay,” he added. “What will happen is that brokers who are tech-enabled will be able to serve customers nationally and run their business, collect payments, finance premiums and reduce backend operation friction.”
Bill Trenchard, partner at First Round Capital, met Wynn while he was still with Sheltr. He believes insurtech and fintech are following a similar story arc where disruptive companies are going to market with lower friction and better products and, being digital-first, are able to meet customers where they are.
By moving digital payments over to insurance, Ascend and others will lead the market, which is so big that there will be many opportunities for companies to be successful. The global commercial insurance market was valued at $692.33 billion in 2020, and expected to top $1 trillion by 2028.
Like other firms, First Round looks for team, product and market when it evaluates a potential investment and Trenchard said Ascend checked off those boxes. Not only did he like how quickly the team was moving to create momentum around themselves in terms of securing early pilots with customers, but also getting well known digital-first companies on board.
“The magic is in how to automate the underwriting, how to create a data moat and be a first mover — if you can do all three, that is great,” Trenchard said. “Instant approvals and using data to do a better job than others is a key advantage and is going to change how insurance is bought and sold.”
Powered by WPeMatico
In order to support a buildout of renewable energy, which tends to over-generate electricity at certain times of day and under-generate at others, the grid is going to need a lot of batteries. While lithium-ion works fine for consumer electronics and even electric vehicles, battery startup EnerVenue says it developed a breakthrough technology to revolutionize stationary energy storage.
The technology itself — nickel-hydrogen batteries — isn’t actually new. In fact, it’s been used for decades in aerospace applications, to power everything from satellites to the International Space Station and the Hubble Telescope. Nickel-hydrogen had been too expensive to scale for terrestrial applications, until Stanford University professor (and now EnerVenue chairman) Yi Cui determined a way to adapt the materials and bring the costs way, way down.
Nickel-hydrogen has a number of key benefits over lithium-ion, according to EnerVenue: it can withstand super-high and super-low temperatures (so no need for air conditioners or thermal management systems); it requires very little to no maintenance; and it has a far longer lifespan.
The technology has caught the eye of two giants in the oil and gas industry, energy infrastructure company Schlumberger and Saudi Aramco’s VC arm, which together with Stanford University have raised $100 million in Series A funding. The investment comes around a year after EnerVenue raised a $12 million seed. The company is planning on using the funds to scale its nickel-hydrogen battery production, including a Gigafactory in the U.S., and has entered a manufacturing and distribution agreement with Schlumberger for international markets.
“I spent almost three and a half years prior to EnerVenue looking for a battery storage technology that I thought could compete with lithium-ion,” CEO Jorg Heinemann told TechCrunch in a recent interview. “I had essentially given up.” Then he met with Cui, who had managed through his research to bring the cost down from around $20,000 per kilowatt hour to $100 per kilowatt hour within line of sight — a jaw-dropping decrease that puts it on-par with existing energy storage technology today.

EnerVenue CEO Jorg Heinemann Image Credits: EnerVenue (opens in a new window)
Think of a nickel-hydrogen battery as a kind of battery-fuel cell hybrid. It charges by building up hydrogen inside a pressure vessel, and when it discharges, that hydrogen gets reabsorbed in water, Heinemann explained. One of the key differences between the batteries in space and the one’s EnerVenue is developing on Earth is the materials. The nickel-hydrogen batteries in orbit use a platinum electrode, which Heinemann said accounts for as much as 70% of the cost of the battery. The legacy technology also uses a ceramic separator, another high cost. EnerVenue’s key innovation is finding new, low-cost and Earth-abundant materials (though the exact materials they aren’t sharing).
Heinemann also hinted that an advanced team within the company is working on a separate technology breakthrough that could bring the cost down even further, to the range of around $30 per kilowatt hour or less.
Those aren’t the only benefits. EnerVenue’s batteries can charge and discharge at different speeds depending on a customer’s needs. It can go from a 10-minute charge or discharge to as slow as a 10-20 hour charge-discharge cycle, though the company is optimizing for a roughly two-hour charge and four- to eight-hour discharge. EnerVenue’s batteries are also designed for 30,000 cycles without experiencing a decline in performance.
“As renewables get cheaper and cheaper, there’s lots of time of the day where you’ve got, say, a one- to four-hour window of close to free power that can be used to charge something, and then it has to be dispatched fast or slow depending on when the grid needs it,” he said. “And our battery does that really well.”
It’s notable that this round was funded by two companies that loom large in the oil and gas industry. “I think nearly 100% of the oil and gas industry is now pivoting to renewables in a huge way,” Heinemann added. “They all see the future as, the energy mix is shifting. We’re going to be 75% renewable by mid-century, most think it’s going to happen quicker, and those are based on studies that the oil and gas industry did. They see that and they know they need a new play.”

Image Credits: EnerVenue
Don’t expect nickel-hydrogen to start appearing in your iPhone anytime soon. The technology is big and heavy — even scaled down as much as possible, a nickel-hydrogen battery is still around the size of a two-liter water flask, so lithium-ion will definitely still play a major role in the future.
Stationary energy storage may have a different future. EnerVenue is currently in “late-stage” discussions on the site and partner for a United States factory to produce up to one gigawatt-hour of batteries annually, with the goal of eventually scaling even beyond that. Heinemann estimates that the tooling cap-ex per megawatt hour should be just 20% that of lithium ion. Under the partnership with Schlumberger, the infrastructure company will also be separately manufacturing batteries and selling them in Europe and the Middle East.
“It’s a technology that works today,” Heinemann said. “We’re not waiting on a technology breakthrough, there’s no science project in our future that we have to go achieve in order to prove out something. We know it works.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Cross-border commerce company Zonos raised $69 million in a Series A, led by Silversmith Capital Partners, to continue building its APIs that auto classify goods and calculate an accurate total landed cost on international transactions.
St. George, Utah-based Zonos is classifying the round as a minority investment that also included individual investors Eric Rea, CEO of Podium, and Aaron Skonnard, co-founder and CEO of Pluralsight. The Series A is the first outside capital Zonos has raised since it was founded in 2009, Clint Reid, founder and CEO, told TechCrunch.
As Reid explained it, “total landed cost” refers to the duties, taxes, import and shipping fees someone from another country might pay when purchasing items from the U.S. However, it is often difficult for businesses to figure out the exact cost of those fees.
Global cross-border e-commerce was estimated to be over $400 billion in 2018, but is growing at twice the rate of domestic e-commerce. This is where Zonos comes in: The company’s APIs, apps and plugins simplify cross-border sales by providing an accurate final price a consumer pays for an item on an international purchase. Businesses can choose which one or multiple shipping carriers they want to work with and even enable customers to choose at the time of purchase.
“Businesses can’t know all of a country’s laws,” Reid added. “Our mission is to create trust in global trade. If you are transparent, you bring trust. This was traditionally thought to be a shipping problem, but it is really a technology problem.”
As part of the investment Todd MacLean, managing partner at Silversmith Capital Partners, joined the Zonos board of directors. One of the things that attracted MacLean to the company was that Reid was building a company outside of Silicon Valley and disrupting global trade far from any port.
He says while looking into international commerce, he found people wound up being charged additional fees after they have already purchased the item, leading to bad customer experiences, especially when a merchant is trying to build brand loyalty.
Even if someone chooses not to purchase the item due to the fees being too high, MacLean believes the purchasing experience will be different because the pricing and shipping information was provided up front.
“Our diligence said Zonos is the only player to take the data that exists out there and make sense of it,” MacLean said. “Customers love it — we got the most impressive customer references because this demand is already out there, and they are seeing more revenue and their customers have more loyalty because it just works.”
In fact, it is common for companies to see 25% to 30% year over year increase in sales, Reid added. He went on to say that due to fees associated with shipping, it doesn’t always mean an increase in revenue for companies. There may be a small decrease, but a longer lifetime value with customers.
Going after venture capital at this time was important to Reid, who saw global trade becoming more complex as countries added new tax laws and stopped using other trade regulations. However, it was not just about getting the funding, but finding the right partner that recognizes that this problem won’t be solved in the next five years, but will need to be in it for the long haul, which Reid said he saw in Silversmith.
The new investment provides fuel for Zonos to grow in product development and go-to-market while also expanding its worldwide team into Europe and Asia Pacific. Eighteen months ago, the company had 30 employees, and now there are over 100. It also has more than 1,500 customers around the world and provides them with millions of landed cost quotes every day.
“Right now, we are the leader for APIs in cross-border e-commerce, but we need to also be the technology leader regardless of the industry,” Reid added. “We can’t just accept that we are good enough, we need to be better at doing this. We are looking at expanding into additional markets because it is more than just servicing U.S. companies, but need to be where our customers are.”
Powered by WPeMatico
2021 has been a good year to be an adtech investor. Valuations are surging, Wall Street is happy and exits are frequent and satisfying. It’s the perfect time to double down and invest in an area that has been largely ignored but is poised for major upside in the next few years: Digital creative ad technology.
Think about it. When was the last time we saw a major adtech funding round that was directed at the actual ads themselves — the messages people actually see everyday? I’d argue that now is the perfect time.
The adtech startups that can figure out how to adapt ads that can interact with the remote control, a synced smartphone or voice commands — maybe even make them shoppable — can theoretically produce a game-changer.
Here are five reasons why VCs should consider ratcheting up their investment into adtech startups building the next generation of creative tools:
Consider how much has been spent over the 15 years on digital advertising mechanics such as targeting, serving, measuring and verification. Not to mention the trillions that have gone toward helping brands keep track of customer data and interactions — the marketing clouds, DMPs and CDPs.
Yet you can count the number of creative-centric adtech companies on one hand. This means there is a lot of room for innovation and early leaders. VideoAmp, which helps brands make ads for various social platforms, pulled in $75 million earlier this year. Given how fast platforms like TikTok and Snap are growing, it won’t be the last.
Ads need to do more work today. Between regulation, cookies going away and Apple locking down data collection, we’ve seen a renewed interest in contextual advertising, including funding for the likes of GumGum, as well as identity resolution firms like InfoSum.
But the digital ad ecosystem can’t get by only using broader data-crunching techniques to replace “retargeting.” The medium is practically crying out for a creative revival that can only be sparked by scalable tech. The recent funding for creative testing startup Marpipe is a start, but more focus is needed on actual tech-driven ideation and automation.
Powered by WPeMatico
At first blush, the $12 billion Intuit-Mailchimp deal might not make a heck of a lot of sense. But people tend to pigeonhole companies, and in this case they might see Intuit as purely a financial software company and Mailchimp as an email marketing firm and nothing more. If that’s as far as your perspective goes, the deal is confusing. From a wider lens, however, there’s more to both companies than you might think.
Let’s start with Intuit. If you go to the company website and scan the product set, it’s clearly all about managing finances for consumer and small businesses alike. The latter category appears to be what the company wants to exploit and expand upon with this deal.
Prior to yesterday’s news, Intuit’s biggest acquisition had been on the consumer side buying Credit Karma for $7.1 billion last year. That deal gave the company’s customers a way to access their credit scores outside of the big three reporting companies: Experian, Equifax and TransUnion. Apparently not content with only that transaction, it set its sights on Mailchimp to throw some money at the business side of the house.
Powered by WPeMatico
Gaming in general is moving toward accessibility, but that’s not as much the case in esports, which like other sports are competitive and by nature somewhat exclusive. Xbox and the Special Olympics are working together on a new event that combines competition with inclusion, and it’s going on right now.
This week, Special Olympics athletes will be competing against each other in tournaments of Rocket League, Madden NFL 22 and Forza Motorsport 7. The prize, other than prestige and pride, is playing with one of the Special Olympics’ celebrity supporters: “NBA superstar Jayson Tatum, NFL legend Jamaal Charles, and WNBA superstar Jewell Loyd, and WWE Superstars Dominik Mysterio and Ember Moon.” So many superstars!
“This tournament is a meaningful and important step in making esports more accessible and it empowers Special Olympics athletes with a new way to compete,” said Jenn Panattoni, head of Xbox Social Impact. “Xbox has invested in numerous accessibility features and products, like the Xbox Adaptive Controller and features like copilot or speech to text. The purpose of all this continued work is to ensure that players feel welcome and that they belong on the Xbox platform.”
The tournaments are being recorded right now, and will be broadcast over the rest of the week, along with the “celebrity showcase” coming Saturday with recaps. You can check out a schedule at the bottom of this post, but generally just keep an eye on the Xbox Twitch channel and Special Olympics YouTube channel.
I like to highlight these events because accessibility has been on the back burner for so long in the gaming world, and now we’re seeing big moves by developers, publishers and partners to make things better. Microsoft’s XAC is a great example, as is the panoply of visual, audio and difficulty options in the latest Ratchet & Clank game. Esports is definitely one of the areas that needs more diversity, though, and the participating players were glad to take part. I asked Special Olympics athletes Jose Moreno and Colton Rice for their thoughts on the matter.
Do you think competitive gaming is getting more accessible?
Rice: Competitive gaming is definitely getting more accessible. Not only are the games becoming more accessible, accessibility allows people with disabilities to become more competitive players. People with intellectual disabilities are always trying to compete at their best. We want to do what everyone else is doing, and sometimes just need a little help to make that happen.
Moreno: I do think that competitive gaming is getting more accessible because Microsoft has started bringing out video game controllers that are accessible for people with intellectual disabilities, physical disabilities — accessible to everybody. I’m a lifelong gamer, and accessibility in esports has been game-changing. Accessible gaming wasn’t available when I was growing up. Today, it’s so much more fun to play when you can play with friends of all abilities and everybody can participate.
How are you experiencing that change?
Moreno: In my opinion, the more the video games industry include people with intellectual disabilities, the better the video game community is going to get to know how we love playing video games just like everybody else. And through events like Gaming for Inclusion, I’m not just able to compete — I’m included as a part of a community of gamers where I am welcomed and included.
Rice: People with intellectual disabilities have skills and pay attention to details; when we set our minds to do something, we practice until we are the best we can be, especially when we enjoy doing it — and that includes gaming. People with disabilities just need more time to learn, but when you’re dedicated to something that you’re passionate about, you won’t stop until you succeed.
What’s something you’d like to see more of, from developers, publishers, etc.?
Moreno: I would like to see more from developers or makers or publishers of video games in general or computer games to include more people with intellectual disabilities in the video game workforce. People with intellectual disabilities can play a variety of roles and provide unique perspectives on how to improve the gaming experience. Publishers and developers can get a different perspective from people with disabilities; whether that’s featuring people with intellectual disabilities represented in their storylines or seeing them in the games themselves. We’re eager to be a part of this process, and there are lots of passionate gamers with intellectual disabilities who would like to participate in focus groups or in actual jobs as creators within the industry.
Rice: The companies who make these games are trying to make high-quality games that are enjoyable for everybody. There is still a lot that can be done to make games more accessible. For example, it can be frustrating when gamers with intellectual disabilities are learning a new game with instructions that are hard to read. It can take hours to learn how to play the new version of a game you’ve played for years. That doesn’t mean people with intellectual disabilities aren’t capable of playing or competing — it just means we need better accessibility tools to help us learn.
If gaming companies want to create accessible, inclusive games, they could benefit from including gamers with intellectual disabilities in the creative process to help make or test “easy read” or beginner’s instructions, or find ways to simplify navigation between different levels of a game. Gaming can build a community and reach people who feel left out. Accessibility allows everybody to have fun.
This competition and other events in online gaming have been essential to keeping the Special Olympics community connected and active over a difficult couple years.
“Special Olympics has a long-standing partnership with Microsoft that has been incredibly valuable for the athletes and families of the Special Olympics movement,” said the organization’s chief information and technology officer, Prianka Nandy. “With the COVID-19 pandemic, our main concern has been the safety and health of our athletes, who are amongst the most vulnerable population to have an adverse or catastrophic outcome from the virus. This led to the cancellation and postponement of thousands of annual in-person events and competitions — which meant our athletes have missed out on the connections and opportunities to experience the joy of being with their teammates, coaches and friends. At this time, our goals remain to raise awareness of the Special Olympics movement and the accomplishments, hopes and dreams of our incredible athletes, and to change attitudes towards people with intellectual disabilities within the gaming community, all while remembering that gaming can be fun and inclusive for all.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Canva is now valued at $40 billion following a fresh capital injection of $200 million (USD) in a round led by T. Rowe Price. New and existing investors participated in the round, including Franklin Templeton, Sequoia Capital Global Equities, Bessemer Venture Partners, Greenoaks Capital, Dragoneer Investments, Blackbird, Felicis and AirTree Ventures.
This round solidifies Canva as one of the most valuable private software companies out there, and it also propels the Australian tech scene forward.
Co-founder and CEO Melanie Perkins and her team started working on Canva in 2012, and launched the product in 2013. The premise behind it was relatively simple, but the technology itself… not so much.
Canva allows anyone to design. Presentations, t-shirts, brochures, flyers… you name it. The first step in this is creating a truly simple user interface, where folks can simply drag and drop components into their designs, complete with hundreds of thousands of templates, without doing a lot of fine tuning. The second step is creating a massive library of content, from fonts to templates to imagery, gifs and videos. The third step is to make that product accessible to everyone, whether it’s a platform or device or language or price.
Going after everyone, instead of just designers, has proved incredibly fruitful for the company. To be clear, designers still use Canva to lay out components they’ve designed in other products, such as Figma and Sketch, and Canva actually plays nicely with a variety of design software products. But Canva has no intention of going head to head with Figma, Adobe or Sketch.
Perkins described it with the example of a business card. Designers will create the components of a business card in their design platform of choice, and then lay out the template for business cards in Canva, sharing that template with the entire organization. That way, when someone gets a title change or a new employee comes on, they can actually edit the card themselves without the help of a designer and send it to print.
TechCrunch asked Perkins why Canva hasn’t extended the platform more aggressively into the workflow of professional designers.
“We would like to replace PDF,” said Perkins. “Rather than people sending PDFs backwards and forwards between the designer and the client, designers can just create a template for organization use. It’s less important for us to absolutely excel at things like vector design because there are amazing programs on the market that may be there. We really want to focus on that collaboration piece.”
Though a bottoms-up enterprise strategy is relatively popular these days, Canva was an early master of the model. Canva launched as a free product, and over time the company introduced enterprise layers into the mix.
As of now, Canva has more than 60 million monthly active users across 190 countries, with big-name companies on the enterprise plan. This includes Salesforce, Marriott International, PayPal and American Airlines. Canva expects to exceed $1 billion in annualized revenue by the end of 2021. More than 500,000 teams are paying for the product in some capacity.
With a 2,000-person team, Canva will use the fresh funding to double its workforce in the next year.
Canva also shared its DEI numbers, with females representing 42% of the workforce. The company did not share any stats around people of color on the team.
Perkins explained to TechCrunch that a huge part of the company’s growth has to do with an obsession over creating a highly valuable free product.
“We intentionally make our free product extremely generous for a number of reasons,” said Perkins. “It’s critical both for our marketing and towards our mission of empowering people to design. But, as part of our marketing, it means that people are able to love the product, share it with their friends and family, and promote it on social media. And then that virality really rapidly fuels our growth.”
Alongside growing the team, Canva also has plans to further build out the product in the next year, launching website design soon. This will allow users to turn existing and new presentations and designs into a website, and even search for and buy a domain for that site.
Canva is also working on a new video editor and an offline mode.
Perkins says that Canva has two goals, and that each fuels the other. The first is to become one of the world’s most valuable companies, and the other is to do the most good that it can do.
The company has already joined the 1% pledge and has several efforts around being a force for good, including giving the premium product to more than 130,000 nonprofits, allocating more than 45,000 volunteering hours each year and launching Print One, Plant One, which is a project that plants a tree for every single print order placed through Canva.
With today’s funding announcement, cofounders Perkins and Cliff Obrecht are committing the vast majority of their own equity in the company (around 30%) to doing good in the world, with plans to do this through the Canva Foundation.
Perkins will be joining us at Disrupt to talk about the new funding, valuation, what’s in store for Canva, and share her broader thoughts on design as a category.
Powered by WPeMatico
Are founders in fundraising mode short-sighted when it comes to working with Chinese venture funds?
Runa Capital’s Asia business development manager Denis Kalinin studied data from iTjuzi, a database of Chinese venture capitalists, and found:
“…Chinese funds invested around $250 billion in 2020 (three times higher than the figure reported in Crunchbase). This figure puts Chinese VC investments only 30% lower than investments by U.S. funds, but three times that of U.K. funds and 12.5 times more than German funds.”
The pandemic, geopolitical tensions and other factors led many Chinese venture funds to pare back their international investments, but that’s largely “because during COVID, China’s economy recovered much faster than other countries’,” writes Kalinin.
His analysis covers multiple angles: Chinese investments in Europe are catching up with those in Asia and the United States, half of China’s top cross-border investors are CVCs, and investors are particularly interested in fintech, deep tech and digital health at the moment.
“Chinese investors can bring value to foreign startups, but you need to study their expertise and how it can be useful for you.”
Full Extra Crunch articles are only available to members
Use discount code ECFriday to save 20% off a one- or two-year subscription
Today at 2 p.m. PT/5 p.m. ET on Twitter Spaces, Managing Editor Danny Crichton and immigration law attorney Sophie Alcorn will discuss whether remote work is making H-1B visas less critical for international founders.
It’s a provocative question: If remote teams are becoming the norm, tech hubs are decentralizing and investors are comfortable cutting checks after a Zoom call, how important is it to do business as a startup inside the U.S?
It’s sure to be an interesting conversation; to get a reminder, please follow @TechCrunch on Twitter.
Thanks very much for reading Extra Crunch this week!
Walter Thompson
Senior Editor, TechCrunch
@yourprotagonist
Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
Toast released an early IPO price range of $30 to $33 per share on Monday, and Alex Wilhelm digs into the S-1/A filing to “better understand how to value vertical SaaS startups that are pursuing a payments-and-SaaS business approach.”
Is the restaurant software startup worth the $18 billion valuation it’s aiming for?

Image Credits: Peter Dazeley (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Every founder who launches an enterprise software startup has to figure out the “right” pricing model for their products.
It’s a consequential decision: Per-seat licenses are easy to manage, but what if customers prefer a concurrent licensing model?
“Early pricing discussions should center around the buyer’s perspective and the value the product creates for them,” says Ridge Ventures partner Yousuf Khan, who previously worked as a CIO.
“Of course,” he notes, “self-evaluation is hard, especially when you’re asking someone else to pay you for something you’ve created.”

Image Credits: jayk7 / Getty Images
India’s mom-and-pop businesses are experiencing a digital transformation that’s creating new e-commerce opportunities; smartphones have replaced paper records, and a new government-backed instant payments system is disrupting how value is exchanged.
But instead of importing legacy credit systems, buy now, pay later systems are the “next step for solving the digital B2B puzzle,” writes Anubhav Jain, co-founder and CEO of Rupifi.

Image Credits: scyther5 / Getty Images
Freshworks, which develops and offers a variety of business software tools, set an IPO price range of $28 to $32 per share on Monday, meaning its valuation could reach nearly $10 billion, Alex Wilhelm writes.
“It appears that the Freshworks IPO is pretty reasonably priced as is, though a boost to its price range is not out of the question if public market investors decide that they are bullish on its future growth prospects. We just don’t see dramatic upside.”
ish on its future growth prospects. We just don’t see dramatic upside.”

Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
The multibillion-dollar exits of Japanese startup Paidy (to PayPal) and Australian buy now, pay later company Afterpay (to Square) “provided hard market proof that what BNPL startups are building has value beyond simple operating results,” Alex Wilhelm writes in The Exchange.
He breaks down the value of Afterpay, Paidy and Klarna using a simple metric: What would you pay for $1 of BNPL GMV?

Image Credits: mikkelwilliam (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Video game livestreaming is booming.
Twitch has an average of almost 3 million concurrent viewers; by comparison, on the night of the 2020 U.S. presidential election, CNN’s livestream averaged 1.1 million.
The most successful streamers use their ad revenue and sponsorship money to hire video editors and social media teams to make them look good, but new automated tools are giving part-time streamers the ability to spotlight their best moments as well.

Image Credits: Boris Zhitkov (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
A data breach costs a company an average of $3.8 million, Marc Ellenbogen, Foursquare’s general counsel, notes in a guest post, adding up to a “concrete financial incentive to having The Privacy Talk.”
What is it?
“It’s the conversation that goes beyond the written, publicly posted privacy policy and dives deep into a customer, vendor, supplier or partner’s approach to ethics,” he writes.
If you think the talk doesn’t apply to you, think again.

Image Credits: Alexander Spatari (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
In an effort to “reassure local administrations that micromobility is safe, compliant and a good thing for cities,” scooter operators are “implementing technology similar to advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) usually found in cars,” Rebecca Bellan writes.
She breaks down how the tech could help prevent unwanted behavior and explores the cost for scooter operators and opportunities for startups.
Powered by WPeMatico