TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Given the attention that TechCrunch pays to Y Combinator’s Demo Days, we also try to keep tabs on the same startups as they scale and raise more capital. Yesterday we covered YC Winter 2020 participant BuildBuddy, for example. Today we’re taking a look at Heru, a startup based in Mexico City that is announcing a $1.7 million raise after taking part in YC’s Summer 2019 session.
The pre-seed round was led by Mountain Nazca, and participated in by Magma Partners, Xtraordinary Venture Partners, Flourish Ventures, YC itself and a handful of angels. The investment was raised in two pieces: a $500,000 check in February and the other $1.2 million closing a few weeks ago.
Heru wants to provide software-based services for gig workers in Mexico, and eventually other countries. Its founders, Mateo Jaramillo and Stiven Rodríguez Sánchez, are both ex-Uber employees, which is how they wound up in Mexico from their native Colombia.
But Heru didn’t have a straightforward path to existence. The founding duo told TechCrunch their original idea, something similar to OYO, was what they went through Y Combinator and initially raised money for. But after finding OYO already in their target market, the company took three months to rethink and, keeping investors on board, pivoted to Heru.
Heru is a package of software products aimed at delivery drivers and the like, helping provide insurance, credit and tax preparation support. The tax element is key, as the company’s founders explained to TechCrunch that Mexico now expects independent workers to file taxes on a monthly basis. Folks need help with that, so Heru built them a tool to do so.
There’s competition to that element of its product, Heru said, noting that there are accountants in the market that will do the work for $25 to $30. Heru’s tax service, in contrast, costs a smaller $5 each month (100 pesos). Insurance is another $5 each month for accident-related coverage. The startup worked with an insurance provider to build what it describes as a “tailor-made” policy for gig workers who need low-cost coverage.

The founding duo, via the company.
Heru is not only targeting Uber drivers and their like, however. The company noted that it also wants to support freelancers more broadly, a population that is much larger than the three million gig workers it counts in the Mexican market.
The company’s app has been soft-launched in the market for a few weeks, with the startup now making more noise about its existence. According to its founders, around 1,200 users were accepted during its test period. Another 20,000 are in line.
Among its early user base, customers are buying on average 1.2 Heru products, a number that I’ll track as the startup scales.
Heru’s app is neat, its market large and the need it is serving material. But in the background of the software story is a brick-and-mortar tale. The startup, in addition to building its app, put together a number of so-called “Heru Casas,” places where gig workers can recharge their phones and use a bathroom. You need the app to enter a Heru Casa, helping the startup find early users.
Currently all Heru Casas are located in Mexico City. The startup is not sure about expanding that part of its efforts to more cities where its app may attract users. Why? It’s hard to scale physical build-outs, it told TechCrunch. Software is much better for quick expansion, and as that’s the name of the startup game, holding off on more physical locations could make good sense until the company can raise more capital.
Heru has big plans to double-down its product work, and eventually add more countries to its roster. The Latin American market is a ripe place for startups to shake things up. Let’s see how quickly Heru can make its mark.
Powered by WPeMatico
With a pandemic raging across many parts of the world, many companies have customer service agents spread out as well, creating a workforce management nightmare. It wasn’t easy to manage and route requests when CSAs were in one place, it’s even harder with many working from home.
To help answer that problem Salesforce is developing a new product called Service Cloud Workforce Engagement. Bill Patterson, EVP and general manager for CRM Applications at Salesforce, points out that with these workforces spread out, it’s a huge challenge for management to distribute work and keep up with customer volume, especially as customers have moved online during COVID.
“With Service Cloud Workforce Engagement, Salesforce will arm the contact center with a connected solution — all on one platform so our customers can remain resilient and agile no matter what tomorrow may bring,” Patterson said in a statement.
Like many Salesforce products, this one is made up of several key components to deliver a complete solution. For starters, there is Service Forecast for Customer 360, a tool that helps predict workforce requirements and uses AI to distribute customer service requests in a way that makes sense. This can help in planning at a time with a likely predictable uptick in service requests like Black Friday or Cyber Monday, or even those times when there is an unexpected spike.
Next up is Omnichannel Capacity Planning, which helps managers distribute CSAs across channels such as phone, messaging or email wherever they are needed most based on the demand across a given channel.
Finally, there is a teaching component that helps coach customer service agents to give the correct answer in the correct way for a given situation. “To increase agent engagement and performance, companies will be able to quickly onboard and continually train agents by delivering bite-size, guided learning paths directly in the agent’s workspace during their shift,” the company explained.
The company says that Service Cloud Workforce Engagement will be available in the first half of next year.
Powered by WPeMatico
Orbit, a startup that is building tools to help organizations build communities around their proprietary and open-source products, today announced that it has raised a $4 million seed funding round led by Andreessen Horowitz’s Martin Casado. A number of angel investors, including Chris Aniszczyk, Jason Warner and Magnus Hillestad, as well as the a16z’s Cultural Leadership Fund, also participated, in addition to previous backers Heavybit and Harrison Metal.
The company describes its service as a “community experience platform.” Currently, Orbit’s focus is on Developer Relations and Community teams, as well as open-source maintainers. There’s no reason the company couldn’t branch out into other verticals as well, though, given that its overall framework is really applicable across all communities.
As Orbit co-founder Patrick Woods told me, community managers have generally had a hard time figuring out who was really contributing to their communities because those contributions can come in lots of forms and often happen across a wide variety of platforms. In addition, the sales and marketing teams also often don’t understand how a community impacts a company’s bottom line. Orbit aggregates all of these contributions across platforms.
“There is a lack of understanding around the ways in which community impacts go-to-market and business value,” Woods told me when I asked him about the genesis of the idea. “There’s a big gap in terms of the tooling associated with that. Many companies agree that community is important, but if you put $1 in the community machine today, it’s hard to know where that’s going to come out — and is it going to come out in terms of $0.50 or $100? This was a set of challenges that we noticed across companies of all sizes.”
Especially in open-source communities, there will always be community members who create a lot of value but who don’t have a commercial relationship with a company at all. That makes it even harder for companies to quantify the impact of their communities, even if they agree that community is an important way to grow their business and that, in Orbit’s words, “community is the new pre-sales.”
At the core of Orbit (the company) is Orbit the open-source community framework. The founding team of Woods (CEO) and Josh Dzielak (CTO) developed this framework to help organizations understand how to best build what the team calls a “high gravity community” to attract new members and retain existing ones — and how to evaluate them. You can read more about the concept here.
“We’re trying to reframe the discussion away from an extractive worldview that says how much value can we generate from this lead? It’s actually more about how much love can we generate from these community members,” Woods said. “Because, if you think about the culture associated with what we’re trying to do, it’s fundamentally creative and generative. And our goal is really to help people think less about value extraction and more about value creation.”
At the end of the day, though, no matter the philosophy behind your community-building efforts, there has to be a way to measure ROI and turn some of those community members into paying customers. To do that, Orbit currently pulls in data from sources like GitHub, Twitter and Discourse, with support for Slack and other tools coming soon. With that, the service makes it far easier for community managers to keep tabs on what is happening inside their community and who is participating.
In addition to the built-in dashboards, Orbit also provides an API to help integrate all of this data into third-party services as well.
“One of the key understandings that drives the Orbit vision is that a community is not a funnel and building a community is not about conversions, but making connections; cultivating dialog and engagement; being open and giving back; and creating value versus trying to capture it,” a16z’s Casado writes. “The model has proven to be very effective, and now Orbit has built a product around it. We strongly believe Orbit is a must-have product for those building developer-focused companies.”
The company is already working with just under 150 companies and its users include the likes of Postman, CircleCI, Kubernetes and Apollo GraphQL.
The company will use the new round, which closed a few weeks ago, to, among other things, build out its go-to-market efforts and develop more integrations.
Powered by WPeMatico
While Salesforce made a big splash yesterday with the announcement that it’s buying Slack for $27.7 billion, it’s not the only thing going on for the CRM giant this week. In fact, Dreamforce, the company’s customer extravaganza, is also on the docket. While it is virtual this year, there are still product announcements aplenty, and today the company announced Einstein Automate, a new AI-fueled set of workflow solutions.
Sarah Franklin, EVP & GM of Platform, Trailhead and AppExchange at Salesforce, says that she is seeing companies facing a digital imperative to automate processes as things move ever more quickly online, being driven there even faster by the pandemic. “With Einstein Automate, everyone can change the speed of work and be more productive through intelligent workflow automation,” she said in a statement.
Brent Leary, principal analyst at CRM Essentials, says that combined, these tools are designed to help customers get to work more quickly. “It’s not only about identifying the insight, it’s about making it easier to leverage it at the right time. And this should make it easier for users to do it without spending more time and effort,” Leary told TechCrunch.
Einstein is the commercial name given to Salesforce’s artificial intelligence platform that touches every aspect of the company’s product line, bringing automation to many tasks and making it easier to find the most valuable information on customers, which is often buried in an avalanche of data.
Einstein Automate encompasses several products designed to improve workflows inside organizations. For starters, the company has created Flow Orchestrator, a tool that uses a low-code, drag and drop approach for building workflows, but it doesn’t stop there. It also relies on AI to provide help to suggest logical next steps to speed up workflow creation.
Salesforce is also bringing into the mix MuleSoft, the integration company it bought for $6.5 billion in 2018. Instead of processes like a mortgage approval workflow, the MuleSoft piece lets IT build complex integrations between applications across the enterprise and the Salesforce family of products more easily.
To make it easier to build these workflows, Salesforce is announcing the Einstein Automate collection page available in AppExchange, the company’s application marketplace. The collection includes more than 700 pre-built connectors so customers can grab and go as they build these workflows, and finally it’s updating the OmniStudio, their platform for generating customer experiences. As Salesforce describes it, “Included in OmniStudio is a suite of resources and no-code tools, including pre-built guided experiences, templates and more, allowing users to deploy digital-first experiences like licensing and permit applications quickly and with ease.”
Per usual with Salesforce Dreamforce announcements, the Flow Orchestrator being announced today won’t be available in beta until next summer. The MuleSoft component will be available in early 2021, but the OmniStudio updates and the Einstein connections collection are available today.
Powered by WPeMatico
Welcome, the HR software that helps organizations make and close offers to new candidates, announced the close of a $6 million seed round today, led by FirstMark Capital. Participating investors include Ludlow Ventures, Nat Turner and Zach Weinberg, and Keenan Rice and Ben Porterfield (which were existing investors), as well as a wide array of angels.
TechCrunch last covered Welcome in August, when it announced a $1.4 million funding round. That the startup was able to raise more as quickly as it has is testament to how hot the early-stage venture capital market is today, and likely an endorsement of Welcome’s economic profile and recent growth.
Past the new capital, Welcome is also launching a new product today called Total Rewards, which helps not just new candidates but also existing employees get a complete, easy-to-understand picture of their compensation, across salary, benefits, equity, etc.
But let’s back up.
Welcome was founded in 2019 by Nick Gavronsky and Rick Pereira, with a mission to help organizations close offers on candidates by providing a much clearer picture of compensation, particularly around equity. Co-founder and CEO Nick Gavronsky explained that many candidates don’t truly understand the value of the equity they’re offered, or how it works.
“A lot of recruiting teams aren’t well-equipped to use it as a selling tool and explain it effectively and showcase the value to candidates to help them think about their ownership at the company,” he added.
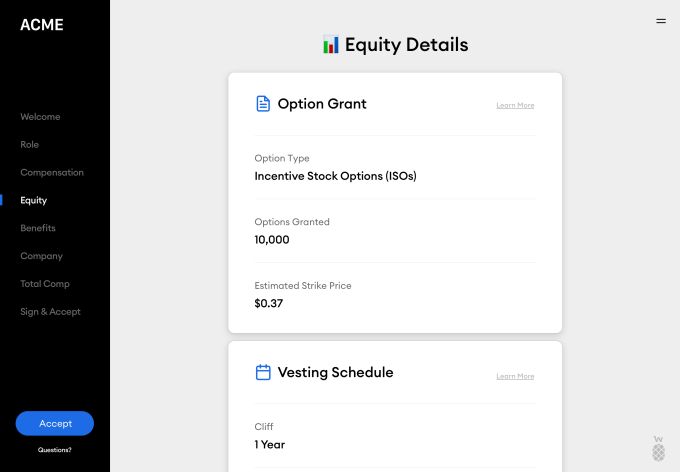
Image Credits: Welcome
Welcome allows companies to organize their compensation offers based on level and position, and deliver that information digitally to candidates in a way that makes sense.
The startup integrates with a variety of other software providers, including Slack, Lever, Greenhouse, ADP and Justworks to name a few, simplifying onboarding for Welcome clients and bringing a broad array of information into one place.
Offers sent through Welcome show a description of the role, equity details, total compensation and even include a welcome note and video. This is in stark contrast to the black and white legal PDF often sent to candidates.
Image Credits: Welcome
The next phase for the company comes in the form of the launch of Total Rewards, which is meant to help retain existing employees, helping them understand their compensation value and their potential at the company.
“Painting a better picture becomes a pre-retention tool,” said Gavronsky. “An employee will sometimes leave thousands of dollars on the table because they don’t understand what they’re walking away from. A lot of times companies will wait until that person is going to resign. Let me now bring up all the things that are great about our company and talk through your stock options. But the decision’s already made. So we wanted something that we can kind of put in with performance reviews.”
Welcome also has plans to offer a third product pillar in the form of real-time accurate industry-wide compensation data, helping companies understand where they fit into the larger ecosystem with regards to compensation.
Thus far, Welcome has 40 companies on the platform, including Uncork and Betterment, with hundreds on the waitlist, according to the co-founders. The company plans to use the funding to build out the team and the product.
Powered by WPeMatico
Jitsu, a graduate of the Y Combinator Summer 2020 cohort, is developing an open-source data integration platform that helps developers send data to a data warehouse. Today, the startup announced a $2 million seed investment.
Costanoa Ventures led the round with participation from Y Combintaor, The House Fund and SignalFire.
In addition to the open-source version of the software, the company has developed a hosted version that companies can pay to use, which shares the same name as the company. Peter Wysinski, Jitsu’s co-founder and CEO, says a good way to think about his company is an open-source Segment, the customer data integration company that was recently sold to Twilio for $3.2 billion.
But, he says, it goes beyond what Segment provides by allowing you to move all kinds of data, whether customer data, connected device data or other types. “If you look at the space in general, companies want more granularity. So let’s say for example, a couple years ago you wanted to sync just your transactions from QuickBooks to your data warehouse, now you want to capture every single sale at the point of sale. What Jitsu lets you do is capture essentially all of those events, all of those streams, and send them to your data warehouse,” Wysinski explained.
Among the data warehouses it currently supports are Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, PostGres and Snowflake.
The founders built the open-source project called EventNative to help solve problems they themselves were having moving data around at their previous jobs. After putting the open-source version on GitHub a few months ago, they quickly attained 1,000 stars, proving that they had delivered something that solved a common problem for data teams. They then built the hosted version, Jitsu, which went live a couple of weeks ago.
For now, the company is just the two co-founders, Wysinski and CTO Vladimir Klimontovich and couple of contract engineers, but they intend to do some preliminary hiring over the next year to grow the company, most likely adding engineers. As they begin to build out the startup, Wysinski says that being open source will help drive diversity and inclusion in their hiring.
“The goal is essentially to go after that open-source community and hire people from anywhere because engineers aren’t just […] one color or one race, they’re everywhere, and being open source, and especially being in a remote world, makes it so, so much simpler [to build a diverse workforce], and a lot of companies I feel are going down that road,” he said.
He says along that line, the plan is to be a fully remote company, even after the pandemic ends, as they hire from anywhere. The goal is to have quarterly offsite meetings to check in with employees, but do the majority of the work remotely.
Powered by WPeMatico
Today after the bell, Salesforce reported its third-quarter earnings for its fiscal 2021, a period that ended October 31, 2020. The CRM giant reported top-line revenue of $5.42 billion, up 20% from the year-ago period. Salesforce also had net income of $1.08 billion and earnings per share of $1.15.
Analysts had expected the company to earn $0.75 per share off revenues of $5.25 billion, according to Yahoo Finance.
Shares of Salesforce were off after-hours, falling around 3.6% at the time of writing. It was not clear if the company’s share price performance was due to its Q3 results, or its raised Q4 guidance, or its new fiscal 2022 expectations, or the newly announced Slack deal.
As TechCrunch reported moments ago, Salesforce will buy Slack for $27.7 billion in a cash and stock deal that was fully priced into shares of the smaller company, which dropped a little over a point on the news, having risen by nearly 50% since the deal’s existence first leaked.
Holders of Slack will be rewarded for their patience. Now it’s up to Salesforce leadership to prove that the huge buy will help boost the company’s growth.
Salesforce told investors today that it anticipates Q4 fiscal 2021 revenues of $5.665 billion to $5.675 billion, which works out to growth of around 17% from the year-ago period. The company also anticipates that it will grow around 17% in Q1 of its fiscal 2022.
But Salesforce expects to grow 21% in all of its fiscal 2022. How does it intend to accelerate? Its projections include Slack:
Full Year FY22 revenue guidance includes contributions from Slack Technologies, Inc. of approximately $600 million, net of purchase accounting, and assumes a closing date in late Q2 and Acumen Solutions, Inc. of approximately $150 million, net of purchase accounting, and assumes a closing date within Q2.
So, Salesforce investors, after two anticipated quarters of 17% growth coming up, your company will accelerate up to 21% growth for the next fiscal year. Is that worth $27.7 billion?
Powered by WPeMatico
Salesforce, the CRM powerhouse that recently surpassed $20 billion in annual revenue, announced today it is wading deeper into enterprise social by acquiring Slack in a $27.7 billion megadeal. Rumors of a pending deal surfaced last week, causing Slack’s stock price to spike.
Salesforce co-founder and CEO Marc Benioff didn’t mince words on his latest purchase. “This is a match made in heaven. Together, Salesforce and Slack will shape the future of enterprise software and transform the way everyone works in the all-digital, work-from-anywhere world,” Benioff said in a statement.
Slack CEO Stewart Butterfield was no less effusive than his future boss. “As software plays a more and more critical role in the performance of every organization, we share a vision of reduced complexity, increased power and flexibility, and ultimately a greater degree of alignment and organizational agility. Personally, I believe this is the most strategic combination in the history of software, and I can’t wait to get going,” Butterfield said in a statement.
Every worker at every company needs to communicate, something that Slack can ably empower. What’s more, it also facilitates external communication with customers and partners, something that should be quite useful for a company like Salesforce and its family of offerings.
Ultimately, Slack was ripe for the taking. Entering 2020 it had lost around 40% of its value since it went public. Consider that after its most recent earnings report, the company lost 16% of its value, and before the Salesforce deal leaked, the company was worth only a few dollars per share more than its direct listing reference price. Toss in net losses of $147.6 million during the two quarters ending July 31, 2020, Slack’s uninspiring public valuation and its winding path to profitability and it was a sitting target for a takeover like this one. The only surprise here is the price.
Slack’s current valuation, according to both Yahoo and Google Finance, is just over $25 billion, which, given its very modest price change after-hours means that the market priced the company somewhat effectively. Slack is up around 48% from its valuation that preceded the deal becoming known.
The new deal also puts Salesforce more on par — and in competition — with its arch rival and sometime friend Microsoft, whose Teams product has been directly challenging Slack in the market. Microsoft, which passed on buying Slack in the past for a fraction of what Salesforce is paying today, has made Teams a key priority in recent quarters, loathe to cede any portion of the enterprise software market to another company.
What really has set Slack apart from the pack, at least initially, was its ability to integrate with other enterprise software. When you combined that with bots, those intelligent digital helpers, the company could potentially provide Salesforce customers with a central place to work without changing focus because everything they need to do can be done in Slack.
Today’s deal comes after Salesforce’s purchase of Quip in 2016 for $750 million. Quip brought to the SaaS giant a way of socially sharing documents, and when paired with the Slack acquisition gives Salesforce a much more robust social story to tell than its internal option Chatter, an early attempt at enterprise social that never really caught on.
It’s worth noting that Salesforce was interested in Twitter in 2016, the same year that Microsoft was reportedly interested in Slack, but eventually walked away from that deal when shareholders objected, not wanting to deal with the controversial side of the social platform.
Slack was founded in 2013, but its origins go back to an online multiplayer game company called Glitch that was founded in 2009. While the game was ultimately a failure, the startup developed an internal messaging system in the process of building that company that later evolved into Slack.
The company’s historic growth helped Slack raise more than $1 billion while private, earning an impressive $7 billion valuation before going public last year. But while the Glitch-to-unicorn story appears simple, Slack has always faced entrenched competition from the likes of not only Microsoft, but also Cisco, Facebook, Google and even Asana and Monday.com.
For Slack, the path to the public markets was fraught with hype and outsized expectation. The company was famous, or as famous as an enterprise software company can be. At the time it felt like its debut was the start of a long tenure as an indie company. Instead, that public life has been cut short by a huge check. Such is the dog-eat-dog world of tech.
Powered by WPeMatico
Voi, the Stockholm-headquartered micro mobility company known for its e-scooter rentals, has raised $160 million in new funding. The round, about two thirds equity and one third debt, is led by The Raine Group.
Others participating include VNV Global, Balderton, Creandum, Project A, Inbox, and “sustainability-focused investor” Stena Sessan, along with individual backers with links to tech companies such as Delivery Hero, Klarna, iZettle, Zillow, Kry/Livi and Amazon.
Voi co-founder and CEO Fredrik Hjelm says the company — which competes with the likes of Bird, Tier, Bolt and Lime — has secured an “asset-backed” debt facility tied to the scooters and e-bikes it will have on its books in 2021.
The idea is that, having proven its model can be sustained, capital funnelled into the expense of purchasing the vehicles needed to expand the service, can be secured against those assets, even if they will depreciate relatively quickly over time.
“I think, going forward, we will increase the debt ratio to equity,” he tells me. “What you wanna avoid, of course, as a startup, is dilution. We want as much debt as possible because we want cash to grow because we think we can have good ROI in capital. But the debt market is usually closed for startups, until they get to a very proven business model”.
Hjelm says, as the unit economics improved, which Voi has shown by becoming operationally profitable for a few months this year on a group level, it puts the company in a position where, coupled with enough historical data, it can understand “the payback” time on vehicles. This means a financing model similar to rental car companies, or other companies with assets that have a proven value, becomes more of a possibility.
Once it’s proven to work, he says in 6-9 months from now Voi hopes to be able to increase the debt facility. “Probably you will never write about Voi raising equity again,” Hjelm teases, likely in reference to my scooping one of the company’s earlier funding rounds.
By thinking about and funding the vehicles and the operations as two separate parts of the business, it also points to where the Voi founder believes the industry and his company in particular, is heading. “I think the direction we’re going is, we’re becoming more and more of a tech enabled infrastructure company,” he says, comparing it to a telco or other infrastructure plays.
This makes more sense when you consider that many cities around the world are holding tendering processes and only licensing two or three and sometimes only a single provider. And it’s here where Voi has also made good transaction over the last year — sped by the Coronavirus pandemic which has forced cities to open up micro mobility services faster in order to offer an alternative to packed trains and busses.
“With major new markets, including the U.K. opening up to e-scooter mobility solutions, Voi has become Europe’s preferred operator, winning over 2/3 of city license tenders across Europe, including recent wins in Birmingham, Liverpool, Bern and Cambridge,” says Voi.
A decision on which operators are awarded London’s tender is expected on December 14th. Up to three operators will be selected to operate trials, which are due to start in Spring 2021.
Voi says the new funding will be used to invest in technology platform development, fuel growth in current Voi markets and bring Voi’s latest e-scooter model — Voiager 4 — to more cities. In addition, Voi will use funds to further enhance the safety infrastructure of its platform, “the company’s number one priority,” says the company.
Powered by WPeMatico
Video has worked the same way for a long, long time. And because of its unique qualities, video has been largely immune to the machine learning explosion upending industry after industry. WaveOne hopes to change that by taking the decades-old paradigm of video codecs and making them AI-powered — while somehow avoiding the pitfalls that would-be codec revolutionizers and “AI-powered” startups often fall into.
The startup has until recently limited itself to showing its results in papers and presentations, but with a recently raised $6.5M seed round, they are ready to move towards testing and deploying their actual product. It’s no niche: video compression may seem a bit in the weeds to some, but there’s no doubt it’s become one of the most important processes of the modern internet.
Here’s how it’s worked pretty much since the old days when digital video first became possible. Developers create a standard algorithm for compressing and decompressing video, a codec, which can easily be distributed and run on common computing platforms. This is stuff like MPEG-2, H.264, and that sort of thing. The hard work of compressing a video can be done by content providers and servers, while the comparatively lighter work of decompressing is done on the end user’s machines.
This approach is quite effective, and improvements to codecs (which allow more efficient compression) have led to the possibility of sites like YouTube. If videos were 10 times bigger, YouTube would never have been able to launch when it did. The other major change was beginning to rely on hardware acceleration of said codecs — your computer or GPU might have an actual chip in it with the codec baked in, ready to perform decompression tasks with far greater speed than an ordinary general-purpose CPU in a phone. Just one problem: when you get a new codec, you need new hardware.
But consider this: many new phones ship with a chip designed for running machine learning models, which like codecs can be accelerated, but unlike them the hardware is not bespoke for the model. So why aren’t we using this ML-optimized chip for video? Well, that’s exactly what WaveOne intends to do.
I should say that I initially spoke with WaveOne’s cofounders, CEO Lubomir Bourdev and CTO Oren Rippel, from a position of significant skepticism despite their impressive backgrounds. We’ve seen codec companies come and go, but the tech industry has coalesced around a handful of formats and standards that are revised in a painfully slow fashion. H.265, for instance, was introduced in 2013, but years afterwards its predecessor, H.264, was only beginning to achieve ubiquity. It’s more like the 3G, 4G, 5G system than version 7, version 7.1, etc. So smaller options, even superior ones that are free and open source, tend to get ground beneath the wheels of the industry-spanning standards.
This track record for codecs, plus the fact that startups like to describe practically everything is “AI-powered,” had me expecting something at best misguided, at worst scammy. But I was more than pleasantly surprised: In fact WaveOne is the kind of thing that seems obvious in retrospect and appears to have a first-mover advantage.
The first thing Rippel and Bourdev made clear was that AI actually has a role to play here. While codecs like H.265 aren’t dumb — they’re very advanced in many ways — they aren’t exactly smart, either. They can tell where to put more bits into encoding color or detail in a general sense, but they can’t, for instance, tell where there’s a face in the shot that should be getting extra love, or a sign or trees that can be done in a special way to save time.
But face and scene detection are practically solved problems in computer vision. Why shouldn’t a video codec understand that there is a face, then dedicate a proportionate amount of resources to it? It’s a perfectly good question. The answer is that the codecs aren’t flexible enough. They don’t take that kind of input. Maybe they will in H.266, whenever that comes out, and a couple years later it’ll be supported on high-end devices.
So how would you do it now? Well, by writing a video compression and decompression algorithm that runs on AI accelerators many phones and computers have or will have very soon, and integrating scene and object detection in it from the get-go. Like Krisp.ai understanding what a voice is and isolating it without hyper-complex spectrum analysis, AI can make determinations like that with visual data incredibly fast and pass that on to the actual video compression part.
Variable and intelligent allocation of data means the compression process can be very efficient without sacrificing image quality. WaveOne claims to reduce the size of files by as much as half, with better gains in more complex scenes. When you’re serving videos hundreds of millions of times (or to a million people at once), even fractions of a percent add up, let alone gains of this size. Bandwidth doesn’t cost as much as it used to, but it still isn’t free.
Understanding the image (or being told) also lets the codec see what kind of content it is; a video call should prioritize faces if possible, of course, but a game streamer may want to prioritize small details, while animation requires yet another approach to minimize artifacts in its large single-color regions. This can all be done on the fly with an AI-powered compression scheme.
There are implications beyond consumer tech as well: A self-driving car, sending video between components or to a central server, could save time and improve video quality by focusing on what the autonomous system designates important — vehicles, pedestrians, animals — and not wasting time and bits on a featureless sky, trees in the distance, and so on.
Content-aware encoding and decoding is probably the most versatile and easy to grasp advantage WaveOne claims to offer, but Bourdev also noted that the method is much more resistant to disruption from bandwidth issues. It’s one of the other failings of traditional video codecs that missing a few bits can throw off the whole operation — that’s why you get frozen frames and glitches. But ML-based decoding can easily make a “best guess” based on whatever bits it has, so when your bandwidth is suddenly restricted you don’t freeze, just get a bit less detailed for the duration.
These benefits sound great, but as before the question is not “can we improve on the status quo?” (obviously we can) but “can we scale those improvements?”
“The road is littered with failed attempts to create cool new codecs,” admitted Bourdev. “Part of the reason for that is hardware acceleration; even if you came up with the best codec in the world, good luck if you don’t have a hardware accelerator that runs it. You don’t just need better algorithms, you need to be able to run them in a scalable way across a large variety of devices, on the edge and in the cloud.”
That’s why the special AI cores on the latest generation of devices is so important. This is hardware acceleration that can be adapted in milliseconds to a new purpose. And WaveOne happens to have been working for years on video-focused machine learning that will run on those cores, doing the work that H.26X accelerators have been doing for years, but faster and with far more flexibility.
Of course, there’s still the question of “standards.” Is it very likely that anyone is going to sign on to a single company’s proprietary video compression methods? Well, someone’s got to do it! After all, standards don’t come etched on stone tablets. And as Bourdev and Rippel explained, they actually are using standards — just not the way we’ve come to think of them.
Before, a “standard” in video meant adhering to a rigidly defined software method so that your app or device could work with standards-compatible video efficiently and correctly. But that’s not the only kind of standard. Instead of being a soup-to-nuts method, WaveOne is an implementation that adheres to standards on the ML and deployment side.
They’re building the platform to be compatible with all the major ML distribution and development publishers like TensorFlow, ONNX, Apple’s CoreML, and others. Meanwhile the models actually developed for encoding and decoding video will run just like any other accelerated software on edge or cloud devices: deploy it on AWS or Azure, run it locally with ARM or Intel compute modules, and so on.
It feels like WaveOne may be onto something that ticks all the boxes of a major b2b event: it invisibly improves things for customers, runs on existing or upcoming hardware without modification, saves costs immediately (potentially, anyhow) but can be invested in to add value.
Perhaps that’s why they managed to attract such a large seed round: $6.5 million, led by Khosla Ventures, with $1M each from Vela Partners and Incubate Fund, plus $650K from Omega Venture Partners and $350K from Blue Ivy.
Right now WaveOne is sort of in a pre-alpha stage, having demonstrated the technology satisfactorily but not built a full-scale product. The seed round, Rippel said, was to de-risk the technology, and while there’s still lots of R&D yet to be done, they’ve proven that the core offering works — building the infrastructure and API layers comes next and amounts to a totally different phase for the company. Even so, he said, they hope to get testing done and line up a few customers before they raise more money.
The future of the video industry may not look a lot like the last couple decades, and that could be a very good thing. No doubt we’ll be hearing more from WaveOne as it migrates from lab to product.
Powered by WPeMatico