TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Today, both the U.S. Department of Justice and the Securities and Exchange Commission charged Manish Lachwani, co-founder of mobile app testing company HeadSpin, with fraud. The SEC says he violated antifraud provisions, and the civil penalties it’s seeking include a permanent injunction, a conduct-based injunction, and to bar him for serving as a corporate executive or board member.
The DOJ, which arrested Lachwani earlier, has accused him of one count of wire fraud and one count of securities fraud, and the associated penalties if he’s found guilty are more harsh, including, for wire fraud, a maximum sentence of 20 years in prison and a fine of $250,000. If he’s found guilty of securities fraud, he faces a maximum sentence of 20 years in prison and a fine of $5,000,000.
Both the the SEC and the DOJ say Lachwani — who led the six-year-old company as CEO until May of last year — defrauded investors out of $80 million by falsely claiming that HeadSpin had “achieved strong and consistent growth in acquiring customers and generating revenue” when he was pitching its Series C round to potential backers.
By the SEC’s telling, his fabrications were designed to help secure the round at a so-called unicorn valuation. That apparent plan worked, too, with Palo Alto-based HeadSpin attracting coverage in Forbes in February of last year after Dell Technologies Capital, Iconiq Capital and Tiger Global provided the company with $60 million in Series C funding at a $1.16 billion valuation. Forbes reported at the time that the valuation was double the valuation investors assigned HeadSpin when it closed its Series B round in October 2018.
The SEC also says that Lachwani was looking to enrich himself, saying he did so “by selling $2.5 million of his HeadSpin shares in a fundraising round during which he made misrepresentations to an existing HeadSpin investor.” (It isn’t clear from its complaint whether the SEC is referring to the Series C or an earlier round.)
The two federal complaints suggest that Lachwani’s alleged scheming to inflate HeadSpin’s valuation dates back to “at least 2018,” and the DOJ says it picked up momentum when the company was fundraising in late 2019.
More specifically, the DOJ complaint alleges that “in materials and presentations to potential investors, Lachwani reported false revenue and overstated key financial metrics of the company … he maintained control over operations, sales, and record-keeping, including invoicing, and he was the final decision-maker on what revenue was booked and included in the company’s financial records.”
In the investigation that led to the DOJ’s charges, the FBI discovered “multiple examples” of Lachwani “instructing employees to include revenue from potential customers that inquired but did not engage HeadSpin, from past customers who no longer did business with HeadSpin, and from existing customers whose business was far less than the reported revenue,” says the department.
How far off were these collective calculations? The complaint says that ultimately, Lachwani “provided investors false information that overstated HeadSpin’s annual recurring revenue … by approximately $51 million to $55 million.”
According to the complaint, Lachwani’s fraud unraveled after the company’s board of directors conducted an internal investigation and revised HeadSpin’s valuation down from $1.1 billion to $300 million. Indeed, in August of last year, The Information reported that the company was planning to lower the value of its Series C stock by nearly 80%.
The outlet reported at the time that Lachwani had already been replaced by another executive. That person, according to LinkedIn, is Rajeev Butani, who joined HeadSpin as its chief sales officer early last year.
Nikesh Arora, a former SoftBank president and the current CEO and chairman of Palo Alto Networks, helped lead the internal review as a then-director on the board of HeadSpin, said The Information.
The SEC says its investigation is continuing. The DOJ similarly notes in its announcement that “a complaint merely alleges that crimes have been committed, and all defendants are presumed innocent until proven guilty beyond a reasonable doubt.”
Either way, the outlook doesn’t look very promising right now for Lachwani, who, according to Forbes, previously sold a mobile cloud business to Google and wound up co-founding HeadSpin after Yahoo co-founder Jerry Yang introduced him to Brien Colwell, a former Palantir and Quora engineer who was working at the time on a different startup.
Colwell remains with HeadSpin as its CTO. He has not been named in either the SEC or the DOJ’s complaints relating to HeadSpin.
The company itself, which says it has been cooperating with the government’s investigation, was also not charged.
Powered by WPeMatico
Cruise, the self-driving car company under General Motors, has launched a new initiative called Farm to Fleet that will allow the company to source solar power from farms in California’s Central Valley. The San Francisco Chronicle was the first to report the news that Cruise is directly purchasing renewable energy credits from Sundale Vineyards and Moonlight Companies to help power its fleet of all-electric autonomous vehicles in San Francisco.
Cruise recently secured a permit to shuttle passengers in its test vehicles in San Francisco without a human safety operator behind the wheel. The company is also ramping up its march to commercialization with a recent $5 billion line of credit from GM Financial to pay for hundreds of electric and autonomous Origin vehicles. While this partnership with California farmers is undoubtedly a boon to the state’s work in progressing renewable energies while also providing jobs and financial opportunities to local businesses, Cruise isn’t running a charity here.
The California Independent System Operator has been soliciting power producers across the western United States to sell more megawatts to the state this summer in anticipation of heat waves that will boost electricity demand and potentially cause blackouts. Power supplies are lower than expected already due to droughts, outages and delays in bringing new energy generation sources to the grid, causing reduced hydroelectric generation. To ensure California’s grid can handle the massive increase in fleet size Cruise is planning, it seems that the company has no choice but to find creative ways to bolster the grid. Cruise, however, is holding firm that it’s got loftier goals than securing the energy from whatever sources are available.
“This is entirely about us doing the right thing for our cities and communities and fundamentally transforming transportation for the better,” Ray Wert, a Cruise spokesperson, told TechCrunch.
With droughts continuing to plague California farmers, converting farmland to solar farms is a potential way to help the state meet its climate change targets, according to a report from environmental nonprofit Nature Conservancy. Which is why Cruise saw the logic in approaching Central Valley farmers now.
“Farm to Fleet is a vehicle to rapidly reduce urban transportation emissions while generating new revenue for California’s farmers leading in renewable energy,” said Rob Grant, Cruise’s vice president of social affairs and global impact, in a blog post.
Cruise is paying negotiated contract rates with the farms through its clean energy partner, BTR Energy. The company isn’t disclosing costs, but says it’s paying no more or less than what it would pay for using other forms of renewable energy credits (RECs). RECs are produced when a renewable energy source generates one megawatt-hour of electricity and passes it on to the grid. According to Cruise, Sundale has installed 2 megawatts of solar capacity to power their 200,000 square footage of cold storage, and Moonlight has installed a combined 3.9 MW of solar arrays and two-battery storage system for its sorting and storage facilities. So when Cruise buys credits from these farms, it’s able to say that a specific amount of its electricity use came from a renewable source. RECs are unique and tracked, so it’s clear where they came from, what kind of energy they used and where they went. Cruise did not share how many RECs it plans to purchase from the farms, but says it will be enough to power its San Francisco fleet.
“While the solar power still flows through the same grid, Cruise purchases and then ultimately ‘retires’ the renewable energy credits generated by the solar panels at the farms,” said Wert. “Through data that we submit to the California Air Resources Board quarterly, we retire a number of RECs equivalent to the amount of electricity we used to charge our vehicles.”
Cruise is also working with BTR Energy to finalize a supply of RECs for its operations in Arizona, including its delivery pilot with Walmart.
Wert says using fully renewable power is actually profitable for Cruise in California due to the Low Carbon Fuel Standard, which is designed to decrease the carbon intensity of transportation fuels in the state and provide more low-carbon alternatives. Cruise owns and operates all of its own EV charging ports, so it’s able to generate credits based on the carbon intensity score of the electricity and amount of energy delivered. Cruise can then sell its credits to other companies seeking to reduce their footprints and comply with regulations.
Aside from practicalities, Cruise is aiming to set a standard for the industry and create demand for renewable energy, thus incentivizing more people and businesses to create it.
Aram Shumavon, CEO of grid analytics startup Kevala, says Cruise should be applauded for this partnership.
“What Cruise seems to be trying to acknowledge is that there is carbon intensity associated with the electricity that they’re consuming, and they’re offsetting that in some way,” Shumavon told TechCrunch. “There’s a whole category of carbon accounting, that’s referred to as Scope 3, which is trying to understand how much carbon the supply chain that you use to provide your service actually involves, and Cruise is probably, as a very deliberate decision, getting out in front of their Scope 3 requirements.”
Shumavon said that by quantifying the total carbon intensity of commercial activity, companies become more accountable to it and can then drive change by asking providers for their supply to source from renewables. For example, an automaker might ask their aluminum provider to source only from an area with hydroelectric power instead of coal power, which would ultimately bring the automaker’s carbon intensity down.
“Transportation is responsible for over 40% of greenhouse gas emissions, which is why we announced our Clean Mile Challenge in February, where we challenged the rest of the AV industry to report how many miles they’re driving on renewable energy every year,” said Wert. “We’re hoping that others follow our lead.”
This article has been updated to reflect new information provided by Cruise, as well as expert commentary from Aram Shumavon, CEO of Kevala.
Powered by WPeMatico
If you haven’t noticed yet, the hiring market is a hot one — and getting more complicated as enterprise talent acquisition leaders face technology gaps while assessing candidates. This leads to difficulty in determining compensation.
Enter Compa. The offer management platform provides “deal desk” software for recruiters to more easily manage their compensation strategies to create and communicate offers that are easy to understand and are unbiased.
Charlie Franklin, co-founder and CEO of Compa, told TechCrunch it was frustrating to lose a candidate at the compensation stage, so the company created its software to reduce the challenge of relying on crowdsourcing data or surveys to compare pay.
“Recruiters often lack the data and tools to figure out how much to pay people and communicate that effectively,” Franklin told TechCrunch. “We see talent acquisitions teams like a sales team. If you think of it from that perspective, they need to close a candidate, but to ask the recruiter to operate off of a spreadsheet slows that process down.”

Compa co-founders, from left, Charlie Franklin, Joe Malandruccolo and Taylor Cone. Image Credits: Compa
With Compa, recruiters can input pay expectations and compare recent offers and collaborate with other team members and hiring managers to reach pay consensus quicker. The software automates all of the market intelligence in real time and provides insights about compensation across similar industries and organizations.
The company, based in both California and Massachusetts, emerged from stealth Thursday with $3.9 million in seed funding led by Base10 Partners. Participation in the round also came from Crosscut Ventures and Acadian Ventures, as well as a group of strategic angel investors including 2.12 Angels, Oyster HR CEO Tony Jamous and Scout RFP co-founders Stan Garber and Alex Yakubovich.
Jamison Hill, partner at Base10 Partners, said via email his firm was doing research in the ESG “megatrend,” particularly looking for startups focused on compensation management, when it came across Compa.
He was attracted to the founders’ “clarity and conviction” on the company’s vision, their understanding of the pay gap in the market, how Compa’s solution would “create a new wave of smarter, more-data driven recruiting teams” and how it was enabling employers to use compensation and a positive offer management approach to differentiate itself from competitors.
“They deeply understand the nuances that come with enterprise-level HR teams and bring that expertise to every aspect of Compa’s product offering, which is why we believe Compa can emerge as a leader in this trend and chose to partner with this very special team,” Hill added.
Franklin, who previously led human resources M&A at Workday, founded Compa last year with Joe Malandruccolo, who was on the engineering side at Facebook and Oculus, and Taylor Cone, who has done innovation consulting for organizations like Stanford University.
The company was bootstrapped prior to going after the seed round and will use the capital to expand the team and create additional products that fit into its mission of “making compensation fair and competitive for everyone,” Franklin said.
Going forward, he adds that job offers and compensation need to catch up to how quickly the world is changing. As more people work remotely and companies want to attract a diverse workforce, compensation will be an important factor.
“This is a long-term trend we are seeing in HR — compensation becoming more transparent — not just a spreadsheet shared internally, but a transition from secretive to open and accountable, Franklin said. “Technology is catching up to that, and we have the ability to produce outcomes that drive differences in pay.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Finding the right learning platform can be difficult, especially as companies look to upskill and reskill their talent to meet demand for certain technological capabilities, like data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence roles.
Workera.ai’s approach is to personalize learning plans with targeted resources — both technical and nontechnical roles — based on the current level of a person’s proficiency, thereby closing the skills gap.
The Palo Alto-based company secured $16 million in Series A funding, led by New Enterprise Associates, and including existing investors Owl Ventures and AI Fund, as well as individual investors in the AI field like Richard Socher, Pieter Abbeel, Lake Dai and Mehran Sahami.
Kian Katanforoosh, Workera’s co-founder and CEO, says not every team is structured or feels supported in their learning journey, so the company comes at the solution from several angles with an assessment on technical skills, where the employee wants to go in their career and what skills they need for that, and then Workera will connect those dots from where the employee is in their skillset to where they want to go. Its library has more than 3,000 micro-skills and personalized learning plans.
“It is what we call precision upskilling,” he told TechCrunch. “The skills data then can go to the organization to determine who are the people that can work together best and have a complementary skill set.”
Workera was founded in 2020 by Katanforoosh and James Lee, COO, after working with Andrew Ng, Coursera co-founder and Workera’s chairman. When Lee first connected with Katanforoosh, he knew the company would be able to solve the problem around content and basic fundamentals of upskilling.
It raised a $5 million seed round last October to give the company a total of $21 million raised to date. This latest round was driven by the company’s go-to-market strategy and customer traction after having acquired over 30 customers in 12 countries.
Over the past few quarters, the company began working with Fortune 500 companies, including Siemens Energy, across industries like professional services, medical devices and energy, Lee said. As spending on AI skills is expected to exceed $79 billion by 2022, he says Workera will assist in closing the gap.
“We are seeing a need to measure skills,” he added. “The size of the engagements are a sign as is the interest for tech and non-tech teams to develop AI literacy, which is a more pressing need.”
As a result, it was time to increase the engineering and science teams, Katanforoosh said. He plans to use the new funding to invest in more talent in those areas and to build out new products. In addition, there are a lot of natural language processes going on behind the scenes, and he wants the company to better understand it at a granular level so that the company can assess people more precisely.
Carmen Chang, general partner and head of Asia at NEA, said she is a limited partner in Ng’s AI fund and in Coursera, and has looked at a lot of his companies.
She said she is “very excited” to lead the round and about Workera’s concept. The company has a good understanding of the employee skill set, and with the tailored learning program, will be able to grow with company needs, Chang added.
“You can go out and hire anyone, but investing in the people that you have, educating and training them, will give you a look at the totality of your employees,” Chang said. “Workera is able to go in and test with AI and machine learning and map out the skill sets within a company so they will be able to know what they have, and that is valuable, especially in this environment.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Tuna is on a mission to “fine tune” the payments space in Latin America and has raised two seed rounds totaling $3 million, led by Canary and by Atlantico.
Alex Tabor, Paul Ascher and Juan Pascual met each other on the engineering team of Peixe Urbano, a company Tabor co-founded and he referred to as a “Groupon for Brazil.” While there, they came up with a way to use A/B testing to create a way of dealing with payments in different markets.
They eventually left Peixe Urbano and started Tuna in 2019 to make their own payment product that enables merchants to use A/B testing of credit card processors and anti-fraud providers to optimize their payments processing with one integration and a no-code interface.
Tabor explained that the e-commerce landscape in Latin America was consolidated, meaning few banks controlled more of the market. The address verification system merchants use to verify a purchaser is who they say they are, involves sending information to a bank that is returned to the merchant with a score of whether that match is legitimate.
“In the U.S., that score is used to determine if the purchaser is legit, but they didn’t implement that in Latin America,” he added. “Instead, merchants in LatAm have to tap into other organizations that have that data.”
That process involves manual analysis and constant adjusting due to fraud. Instead, Tuna’s A/B tests between processors and anti-fraud providers in real time and provides a guarantee that a decision to swap providers is based on objective data that considers all components of performance, like approval rates, and not just fees.
Over the past year, the company added 12 customers and saw its revenue increase 15%. It boasts a customer list that includes the large Brazilian fashion chain Riachuelo, and its platform integrates with others including VTEX, Magento and WooCommerce.
The share of e-commerce in overall retail is less than 10% in Latin America. Marcos Toledo, Canary’s managing partner, said via email that e-commerce in LatAm is currently at an inflexion point: not only has the global pandemic driven more online purchases, but also fintech innovation that has occurred in recent years.
In Brazil alone, e-commerce sales grew 73.88% in 2020, but Toledo said there was much room for improvement. What Tuna is building will help companies navigate the situation and make it easier for more customers to buy online.
Toledo met the Tuna team from his partner, Julio Vasconcellos, who was one of the co-founders of Peixe Urbano. When the firm heard that the other Tuna co-founders were starting a business that was applying some of the optimization methods they had created at Peixe Urbano, but for every company, they saw it as an opportunity to get involved.
“The vast tech expertise that Alex, Paul and Juan bring to a very technical business is something that we really admire, as well as their vision to create a solution that can impact companies throughout Latin America,” Toledo said. “The no-code solution that Tuna is building is exciting because it is scalable and can help companies not only get better margins, but also drive their developers to other efforts — and developers have been a very scarce workforce in the region.”
To meet demand for an e-commerce industry that surpassed $200 billion in 2020, Tuna plans to use the new funding to build out its team and grow outbound customer success and R&D, Tabor said.
Up next, he wants to be able to show traction in payments optimization and facilitators in Brazil before moving on to other countries. He has identified Mexico, Colombia and Argentina as potential new markets.
Powered by WPeMatico
Wildfires are burning in countries all around the world. California is dealing with some of the worst wildfires in its history (a superlative that I use essentially every year now) with the Caldor fire and others blazing in the state’s north. Meanwhile, Greece and other Mediterranean nations have been fighting fires for weeks to bring a number of massive blazes under control.
With the climate increasingly warming, millions of homes just in the United States alone are sitting in zones at high risk for wildfires. Insurance companies and governments are putting acute pressure on homeowners to invest more in defending their homes in what is typically dubbed “hardening,” or ensuring that if fires do arrive, a home has the best chance to survive and not spread the disaster further.
SF-based Firemaps has a bold vision for rapidly scaling up and solving the problem of home hardening by making a complicated and time-consuming process as simple as possible.
The company, which was founded just a few months ago (in March), sends out a crew with a drone to survey a homeowner’s house and property if it is in a high-risk fire zone. Within 20 minutes, the team will have generated a high-resolution 3D model of the property down to the centimeter. From there, hardening options are identified and bids are sent out to trade contractors to perform the work on the company’s marketplace.

Once the drone scans a house, Firemaps can create a full CAD model of the structure and the nearby property. Image Credits: Firemaps.
While early, it’s already gotten traction. In addition to hundreds of homeowners who have signed up on its website and a few dozen that have been scanned, Andrew Chen of a16z has led a $5.5 million seed round into the business (the Form D places the round sometime around April). Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi and Addition’s Lee Fixel also participated.
Firemaps is led by Jahan Khanna, who co-founded it along with his brother, who has a long-time background in civil engineering, and Rob Moran. Khanna was co-founder and CTO of early ridesharing startup Sidecar, where Moran joined as one of the company’s first employees. The trio spent cycles exploring how to work on climate problems, while staying focused on helping people in the here and now. “We have crossed certain thresholds [with the climate] and we need to get this problem under control,” Khanna said. “We are one part of the solution.”
Over the past few years Khanna and his brother explored opening a solar farm or a solar-powered home in California. “What was wild, whenever we talked to someone, is they said you cannot build anything in California since it will burn down,” Khanna said. “What is kind of the endgame of this?” As they explored fire hardening, they realized that millions of homeowners needed faster and cheaper options, and they needed them sooner rather than later.
While there are dozens of options to harden a home to fire, some popular options include constructing an ember-free zone within a few feet of a home, often by placing gravel made of granite on the ground, as well as ensuring that attic vents, gutters and siding are fireproof and can withstand high temperatures. These options can vary widely in cost, although some local and state governments have created reimbursement programs to allow homeowners to recoup at least some of the expenses of these improvements.
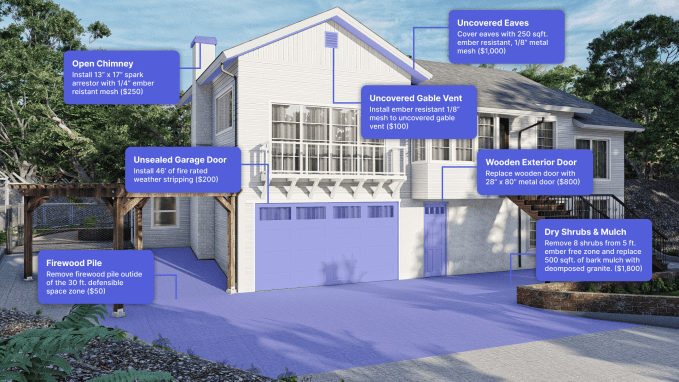
A Firemaps house in 3D model form with typical hardening options and associated prices. Image Credits: Firemaps.
The company’s business model is simple: vetted contractors pay Firemaps to be listed as an option on its platform. Khanna believes that because its drone offers a comprehensive model of a home, contractors will be able to bid for contracts without doing their own site visits. “These contractors are getting these shovel-ready projects, and their acquisition costs are basically zero,” Khanna said.
Long-term, “our operating hypothesis is that building a platform and building these models of homes is inherently valuable,” Khanna said. Right now, the company is launched in California, and the goal for the next year is to “get this model repeatable and scalable and that means doing hundreds of homes per week,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico
Jolla, the Finnish startup behind the Sailfish OS, which formed almost a decade ago when a band of Nokia staffers left to keep the torch burning for a mobile Linux-based alternative to Google’s Android, announced today it’s hitting profitability.
The mobile OS licensing startup describes 2020 as a “turning point” for the business — reporting revenues that grew 53% YoY, and EBITDA (which provides a snapshot of operational efficiency) standing at 34%.
It has a new iron in the fire too now — having recently started offering a new licensing product (called AppSupport for Linux Platforms) which, as the name suggests, can provide Linux platforms with standalone compatibility with general Android applications — without a customer needing to licence the full Sailfish OS (the latter has of course baked-in Android app compatibility since 2013).
Jolla says AppSupport has had some “strong” early interest from automotive companies looking for solutions to develop their in-house infotainment systems — as it offers a way for embedded Linux-compatible platforms the capability to run Android apps without needing to opt for Google’s automotive offerings. And while plenty of car makers have opted for Android, there are still players Jolla could net for its “Google-free” alternative.
Embedded Linux systems also run in plenty of other places, too, so it’s hopeful of wider demand. The software could be used to enable an IoT device to run a particularly popular app, for example, as a value-add for customers.
“Jolla is doing fine,” says CEO and co-founder Sami Pienimäki. “I’m happy to see the company turning profitable last year officially.
“In general it’s the overall maturity of the asset and the company that we start to have customers here and there — and it’s been honestly a while that we’ve been pushing this,” he goes, fleshing out the reasons behind the positive numbers with trademark understatement. “The company is turning 10 years [old] in October so it’s been a long journey. And because of that we’ve been steadily improving our efficiency and our revenue.
“Our revenue grew over 50% since 2019 to 2020 and we made €5.4 million revenue. At the same time the cost base of the operation has stabilized quite well so the sum of those resulted to nice profitability.”
While the consumer mobile OS market has — for years — been almost entirely sewn up by Google’s Android and Apple’s iOS, Jolla licenses its open source Sailfish OS to governments and business as an alternative platform they can shape to their needs — without requiring any involvement of Google.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, Russia was one of the early markets that tapped in.
The case for digital sovereignty in general — and an independent (non-U.S.-based) mobile OS platform provider, specifically — has been strengthened in recent years as geopolitical tensions have played out via the medium of tech platforms; leading to, in some cases, infamous bans on foreign companies being able to access U.S.-based technologies.
In a related development this summer, China’s Huawei launched its own Android alternative for smartphones, which it’s called HarmonyOS.
Pienimäki is welcoming of that specific development — couching it as a validation of the market in which Sailfish plays.
“I wouldn’t necessarily see Huawei coming out with the HarmonyOS value proposition and the technology as a competitor to us — I think it’s more proving the point that there is appetite in the market for something else than Android itself,” he says when we ask whether HarmonyOS risks eating Sailfish’s lunch.
“They are tapping into that market and we are tapping into that market. And I think both of our strategies and messages support each other very firmly.”
Jolla has been working on selling Sailfish into the Chinese market for several years — and that sought-for business remains a work in progress at this stage. But, again, Pienimäki says Jolla doesn’t see Huawei’s move as any kind of blocker to its ambitions of licensing its Android alternative in the Far East.
“The way we see the Chinese market in general is that it’s been always open to healthy competition and there is always competing solutions — actually heavily competing solutions — in the Chinese market. And Huawei’s offering one and we are happy to offer Sailfish OS for this very big, challenging market as well.”
“We do have good relationships there and we are building a case together with our local partners also to access the China market,” he adds. “I think in general it’s also very good that big corporations like Huawei really recognize this opportunity in general — and this shapes the overall industry so that you don’t need to, by default, opt into Android always. There are other alternatives around.”
On AppSupport, Jolla says the automative sector is “actively looking for such solutions,” noting that the “digital cockpit is a key differentiator for car markers — and arguing that makes it a strategically important piece for them to own and control.
“There’s been a lot of, let’s say, positive vibes in that sector in the past few years — newcomers on the block like Tesla have really shaken the industry so that the traditional vendors need to think differently about how and what kind of user experience they provide in the cockpit,” he suggests.
“That’s been heavily invested and rapidly developing in the past years but I’m going to emphasize that at the same time, with our limited resources, we’re just learning where the opportunities for this technology are. Automotive seems to have a lot of appetite but then [we also see potential in] other sectors — IoT … heavy industry as well … we are openly exploring opportunities … but as we know automotive is very hot at the moment.”
“There is plenty of general Linux OS base in the world for which we are offering a good additional piece of technology so that those operating solutions can actually also tap into — for example — selected applications. You can think of like running the likes of Spotify or Netflix or some communications solutions specific for a certain sector,” he goes on.
“Most of those applications are naturally available both for iOS and Android platforms. And those applications as they simply exist … the capability to run those applications independently on top of a Linux platform — that creates a lot of interest.”
In another development, Jolla is in the process of raising a new growth financing round — it’s targeting €20 million — to support its push to market AppSupport and also to put toward further growing its Sailfish licensing business.
It sees growth potential for Sailfish in Europe, which remains the biggest market for licensing the mobile OS. Pienimäki also says it’s seeing “good development” in certain parts of Africa. Nor has it given up on its ambitions to crack into China.
The growth round was opened to investors in the summer and hasn’t yet closed — but Jolla is confident of nailing the raise.
“We are really turning a next chapter in the Jolla story so exploring new emerging opportunities — that requires capital and that’s what are looking for. There’s plenty of money available these days, in the investor front, and we are seeing good traction there together with the investment bank with whom we are working,” says Pienimäki.
“There’s definitely an appetite for this and that will definitely put us in a better position to invest further — both to Sailfish OS and the AppSupport technology. And in particular the go-to market operation — to make this technology available for more people out there in the market.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Here’s another edition of “Dear Sophie,” the advice column that answers immigration-related questions about working at technology companies.
“Your questions are vital to the spread of knowledge that allows people all over the world to rise above borders and pursue their dreams,” says Sophie Alcorn, a Silicon Valley immigration attorney. “Whether you’re in people ops, a founder or seeking a job in Silicon Valley, I would love to answer your questions in my next column.”
Extra Crunch members receive access to weekly “Dear Sophie” columns; use promo code ALCORN to purchase a one- or two-year subscription for 50% off.
Dear Sophie,
I received a conditional green card after my wife and I got married in 2019. Recently, we have made the difficult decision to end our marriage. I want to continue living and working in the United States.
Is it still possible for me to complete my green card based on my marriage through the I-751 process or do I need to do something else, like ask my employer to sponsor me for a work visa?
— Better to Have Loved and Lost
Dear Better,
I’m sorry to hear your marriage didn’t work out. Rest assured, you can still proceed with getting a full-fledged green card even though you and your wife are divorcing. Listen to my recent podcast with Anita Koumriqian, my law partner, in which we discuss the removal of conditions on permanent residence for people who got two-year green cards through marriage.
As you know, since you were married for less than two years when you applied for your green card through marriage, you were issued a conditional green card that is only valid for two years rather than a 10-year green card. The purpose of the I-751 is to show that the couple entered into a genuine, good faith marriage. Usually, couples must file an I-751 petition together. However, an individual may file a petition without a spouse if any of the following apply:
If your divorce is not yet finalized and you don’t have a family law attorney yet, I do recommend that you work with a family law attorney, who is necessary to help streamline the process. I also recommend consulting an immigration attorney as soon as possible to prepare the I-751 filing since it can get tricky for an individual in divorce proceedings. Both need to work together and in parallel to ensure that everything goes smoothly for you with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services.

Image Credits: Joanna Buniak / Sophie Alcorn (opens in a new window)
The I-751 should be filed within the 90-day period before your conditional green card is set to expire. I recommend filing as soon as you can within that window. Keep in mind that, if you file your I-751 petition too early, it may be returned to you. And if you file it after your conditional green card expires, you not only face having to leave the U.S., but USCIS could also deny your petition if you fail to provide a compelling reason. If you are in this situation, definitely let your immigration attorney know.
Powered by WPeMatico
At a time when remote work, cybersecurity attacks and increased privacy and compliance requirements threaten a company’s data, more companies are collecting and storing their observability data, but are being locked in with vendors or have difficulty accessing the data.
Enter Cribl. The San Francisco-based company is developing an “open ecosystem of data” for enterprises that utilizes unified data pipelines, called “observability pipelines,” to parse and route any type of data that flows through a corporate IT system. Users can then choose their own analytics tools and storage destinations like Splunk, Datadog and Exabeam, but without becoming dependent on a vendor.
The company announced Wednesday a $200 million round of Series C funding to value Cribl at $1.5 billion, according to a source close to the company. Greylock and Redpoint Ventures co-led the round and were joined by new investor IVP, existing investors Sequoia and CRV and strategic investment from Citi Ventures and CrowdStrike. The new capital infusion gives Cribl a total of $254 million in funding since the company was started in 2017, Cribl co-founder and CEO Clint Sharp told TechCrunch.
Sharp did not discuss the valuation; however, he believes that the round is “validation that the observability pipeline category is legit.” Data is growing at a compound annual growth rate of 25%, and organizations are collecting five times more data today than they did 10 years ago, he explained.
“Ultimately, they want to ask and answer questions, especially for IT and security people,” Sharp added. “When Zoom sends data on who started a phone call, that might be data I need to know so I know who is on the call from a security perspective and who they are communicating with. Also, who is sending files to whom and what machines are communicating together in case there is a malicious actor. We can also find out who is having a bad experience with the system and what resources they can access to try and troubleshoot the problem.”
Cribl also enables users to choose how they want to store their data, which is different from competitors that often lock companies into using only their products. Instead, customers can buy the best products from different categories and they will all talk to each other through Cribl, Sharp said.
Though Cribl is developing a pipeline for data, Sharp sees it more as an “observability lake,” as more companies have differing data storage needs. He explains that the lake is where all of the data will go that doesn’t need to go into an existing storage solution. The pipelines will send the data to specific tools and then collect the data, and what doesn’t fit will go back into the lake so companies have it to go back to later. Companies can keep the data for longer and more cost effectively.
Cribl said it is seven times more efficient at processing event data and boasts a customer list that includes Whole Foods, Vodafone, FINRA, Fannie Mae and Cox Automotive.
Sharp went after additional funding after seeing huge traction in its existing customer base, saying that “when you see that kind of traction, you want to keep doubling down.” His aim is to have a presence in every North American city and in Europe, to continue launching new products and growing the engineering team.
Up next, the company is focusing on go-to-market and engineering growth. Its headcount is 150 currently, and Sharp expects to grow that to 250 by the end of the year.
Over the last fiscal year, Cribl grew its revenue 293%, and Sharp expects that same trajectory for this year. The company is now at a growth stage, and with the new investment, he believes Cribl is the “future leader in observability.”
“This is a great investment for us, and every dollar, we believe, is going to create an outsized return as we are the only commercial company in this space,” he added.
Scott Raney, managing director at Redpoint Ventures, said his firm is a big enterprise investor in software, particularly in companies that help organizations leverage data to protect themselves, a sweet spot that Cribl falls into.
He feels Sharp is leading a team, having come from Splunk, that has accomplished a lot, has a vision and a handle on the business and knows the market well. Where Splunk is capturing the machine data and using its systems to extract the data, Cribl is doing something similar in directing the data where it needs to go, while also enabling companies to utilize multiple vendors and build apps to sit on top of its infrastructure.
“Cribl is adding opportunity by enriching the data flowing through, and the benefits are going to be meaningful in cost reduction,” Raney said. “The attitude out there is to put data in cheaper places, and afford more flexibility to extract data. Step one is to make that transition, and step two is how to drive the data sitting there. Cribl is doing something that will go from being a big business to a legacy company 30 years from now.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Bodo.ai, a parallel compute platform for data workloads, is developing a compiler to make Python portable and efficient across multiple hardware platforms. It announced Wednesday a $14 million Series A funding round led by Dell Technologies Capital.
Python is one of the top programming languages used among artificial intelligence and machine learning developers and data scientists, but as Behzad Nasre, co-founder and CEO of Bodo.ai, points out, it is challenging to use when handling large-scale data.
Bodo.ai, headquartered in San Francisco, was founded in 2019 by Nasre and Ehsan Totoni, CTO, to make Python higher performing and production ready. Nasre, who had a long career at Intel before starting Bodo, met Totoni and learned about the project that he was working on to democratize machine learning and enable parallel learning for everyone. Parallelization is the only way to extend Moore’s Law, Nasre told TechCrunch.
Bodo does this via a compiler technology that automates the parallelization so that data and ML developers don’t have to use new libraries, APIs or rewrite Python into other programming languages or graphics processing unit code to achieve scalability. Its technology is being used to make data analytics tools in real time and is being used across industries like financial, telecommunications, retail and manufacturing.
“For the AI revolution to happen, developers have to be able to write code in simple Python, and that high-performance capability will open new doors,” Totoni said. “Right now, they rely on specialists to rewrite them, and that is not efficient.”
Joining Dell in the round were Uncorrelated Ventures, Fusion Fund and Candou Ventures. Including the new funding, Bodo has raised $14 million in total. The company went after Series A dollars after its product had matured and there was good traction with customers, prompting Bodo to want to scale quicker, Nasre said.
Nasre feels Dell Technologies Capital was “uniquely positioned to help us in terms of reserves and the role they play in the enterprise at large, which is to have the most effective salesforce in enterprise.”
Though he was already familiar with Nasre, Daniel Docter, managing director at Dell Technologies, heard about Bodo from a data scientist friend who told Docter that Bodo’s preliminary results “were amazing.”
Much of Dell’s investments are in the early-stage and in deep tech founders that understand the problem. Docter puts Totoni and Nasre in that category.
“Ehsan fits this perfectly, he has super deep technology knowledge and went out specifically to solve the problem,” he added. “Behzad, being from Intel, saw and lived with the problem, especially seeing Hadoop fail and Spark take its place.”
Meanwhile, with the new funding, Nasre intends to triple the size of the team and invest in R&D to build and scale the company. It will also be developing a marketing and sales team.
The company is now shifting from financing to customer- and revenue-focused as it aims to drive up adoption by the Python community.
“Our technology can translate simple code into the fast code that the experts will try,” Totoni said. “I joined Intel Labs to work on the problem, and we think we have the first solution that will democratize machine learning for developers and data scientists. Now, they have to hand over Python code to specialists who rewrite it for tools. Bodo is a new type of compiler technology that democratizes AI.”
Powered by WPeMatico