TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
You’ve heard of challenger banks? Now meet the challenger energy suppliers. The U.K.’s Octopus Energy has attained a $2.06 billion valuation (£1.5 billion) after attracting a $200 million (£150 million) investment from Tokyo Gas, for a 9.7% stake, in order to launch a joint venture. Octopus will own 30% of the venture, with Tokyo Gas owning the majority. After five years of operation, Octopus is now close to the valuation of British Gas owner Centrica.
Octopus will now launch as a brand in Japan with its trademark 100% renewable electricity operation, which uses an innovative AI and data-based platform to balance loads around the grid. Its Kraken software is also licensed to Origin Energy, nPower and E.On, Good Energy and Hanwha Corporation, among others, reaching 17 million energy accounts worldwide.
“This joint venture will bring our exciting approach to renewable energy and technology to the world’s largest competitive energy market, and the investment will turbocharge our mission to revolutionize energy globally,” said chief executive Greg Jackson (pictured above) in a statement.
Australia’s Origin Energy is also set to take a stake in Octopus for $50 million (£37 million) following a larger investment in April when Origin bought a 20% stake.
Octopus says it is aiming for 100 million customers around the world by 2027, and recently launched in the U.S., Australia, Germany and New Zealand.
In the U.K., Octopus has a 5% share of the energy supply market and counts 1.8 million households in its retail portfolio, according to the company.
Tokyo Gas president Takashi Uchida said: “Through this partnership, we will contribute to the achievement of a better lifestyle for customers by realizing value creation and delivery tailored to every one of them.”
Japanese renewables lag the U.K. by 50% (renewables in Japan in 2019 accounted for 18.9% of electricity versus 37.9% in the U.K.), so the potential for growth is significant. Japanese Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga has set a target of reaching net-zero by 2050.
In the U.K., Octopus has also launched Electric Juice, an electric vehicle roaming network, and partnered with Tesla to launch Tesla Power.
Powered by WPeMatico
Lalamove will extend its network to cover more small Chinese cities after raising $515 million in Series E funding, the on-demand logistics company announced on its site. The round was led by Sequoia Capital China, with participation from Hillhouse Capital and Shunwei Capital. All three are returning investors.
According to Crunchbase data, this brings Lalamove’s total raised so far to about $976.5 million. The company’s last funding announcement was in February 2019, when it hit unicorn status with a Series D of $300 million.
Bloomberg reported last week that Lalamove was seeking at least $500 million in new funding at $8 billion valuation, or four times what it raised last year.
Founded in 2013 for on-demand deliveries within the same city, Lalamove has since grown its business to include freight services, enterprise logistics, moving and vehicle rental. In addition to 352 cities in mainland China, Lalamove also operates in Hong Kong (where it launched), Taiwan, Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines and Thailand. The company entered the United States for the first time in October, and currently claims about 480,000 monthly active drivers and 7.2 million monthly active users.
Part of its Series D had been earmarked to expand into India, but Lalamove was among 43 apps that were banned by the government, citing cybersecurity concerns.
In its announcement, Lalamove CEO Shing Chow said its Series E will be used to enter more fourth and fifth-tier Chinese cities, adding “we believe the mobile internet’s transformation of China’s logistics industry is far from over.”
Other companies that have recently raised significant funding rounds for their logistics operations in China include Manbang and YTO.
Lalamove’s (known in Chinese as Huolala) Series E announcement said the company experienced a 93% drop in shipment volume at the beginning of the year, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but has experienced a strong rebound, with order volume up 82% year-over-year even before Double 11.
Powered by WPeMatico
When we examine any year in enterprise M&A, it’s tempting to highlight the biggest, gaudiest deals — and there were plenty of those in 2020. I’ve written about 34 acquisitions so far this year. Of those, 15 were worth $1 billion or more, 12 were small enough to not require that the companies disclose the price and the remainder fell somewhere in between.
Four deals involving chip companies coming together totaled over $100 billion on their own. While nobody does eye-popping M&A quite like the chip industry, other sectors also offered their own eyebrow-raising deals, led by Salesforce buying Slack earlier this month for $27.7 billion.
We are likely to see more industries consolidate the way chips did in 2020, albeit probably not quite as dramatically or expensively.
Yet in spite of the drama of these larger numbers, the most interesting targets to me were the pandemic-driven smaller deals that started popping up in May. Those small acquisitions are the ones that are so insignificant that the company doesn’t have to share the purchase price publicly. They usually involve early-stage companies being absorbed by cash-rich concerns looking for some combination of missing technology or engineering talent in a particular area like security or artificial intelligence.
It was certainly an active year in M&A, and we still might not have seen the last of it. Let’s have a look at why those minor deals were so interesting and how they compared with larger ones, while looking ahead to what 2021 M&A might look like.
It’s always hard to know exactly why an early-stage startup would give up its independence by selling to a larger entity, but we can certainly speculate on some of the reasons why this year’s rapid-fire dealing started in May. While we can never know for certain why these companies decided to exit via acquisition, we know that in April, the pandemic hit full force in the United States and the economy began to shut down.
Some startups were particularly vulnerable, especially companies low on cash in the April timeframe. Obviously companies fail when they run out of funding, and we started seeing early-stage startups being scooped up the following month.
We don’t know for sure of course if there is a direct correlation between April’s economic woes and the flurry of deals that started in May, but we can reasonably speculate that there was. For some percentage of them, I’m guessing it was a fire sale or at least a deal made under less than ideal terms. For others, maybe they simply didn’t have the wherewithal to keep going under such adverse economic conditions or the partnerships were just too good to pass up.
It’s worth noting that I didn’t cover any deals in April. But, beginning on May 7, Zoom bought Keybase for its encryption expertise; five days later Atlassian bought Halp for Slack integration; and the day after that VMware bought cloud native security startup Octarine — and we were off and running. Granted the big companies benefited from making these acquisitions, but the timing stood out.
Powered by WPeMatico
AWS, Amazon’s flourishing cloud arm, has been growing at a rapid clip for more than a decade. An early public cloud infrastructure vendor, it has taken advantage of first-to-market status to become the most successful player in the space. In fact, one could argue that many of today’s startups wouldn’t have gotten off the ground without the formation of cloud companies like AWS giving them easy access to infrastructure without having to build it themselves.
In Amazon’s most-recent earnings report, AWS generated revenues of $11.6 billion, good for a run rate of more than $46 billion. That makes the next AWS milestone a run rate of $50 billion, something that could be in reach in less than two quarters if it continues its pace of revenue growth.
The good news for competing companies is that in spite of the market size and relative maturity, there is still plenty of room to grow.
While the cloud division’s growth is slowing in percentage terms as it comes firmly up against the law of large numbers in which AWS has to grow every quarter compared to an ever-larger revenue base. The result of this dynamic is that while AWS’ year-over-year growth rate is slowing over time — from 35% in Q3 2019 to 29% in Q3 2020 — the pace at which it is adding $10 billion chunks of annual revenue run rate is accelerating.
At the AWS re:Invent customer conference this year, AWS CEO Andy Jassy talked about the pace of change over the years, saying that it took the following number of months to grow its run rate by $10 billion increments:
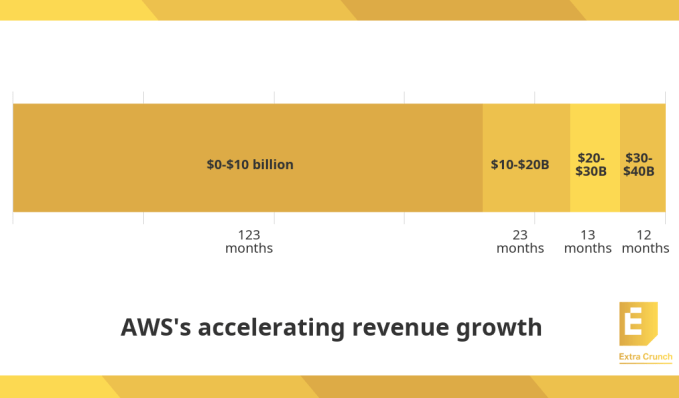
Image Credits: TechCrunch (data from AWS)
Extrapolating from the above trend, it should take AWS fewer than 12 months to scale from a run rate of $40 billion to $50 billion. Stating the obvious, Jassy said “the rate of growth in AWS continues to accelerate.” He also took the time to point out that AWS is now the fifth-largest enterprise IT company in the world, ahead of enterprise stalwarts like SAP and Oracle.
What’s amazing is that AWS achieved its scale so fast, not even existing until 2006. That growth rate makes us ask a question: Can anyone hope to stop AWS’ momentum?
The short answer is that it doesn’t appear likely.
A good place to start is surveying the cloud infrastructure competitive landscape to see if there are any cloud companies that could catch the market leader. According to Synergy Research, AWS remains firmly in front, and it doesn’t look like any competitor could catch AWS anytime soon unless some market dynamic caused a drastic change.
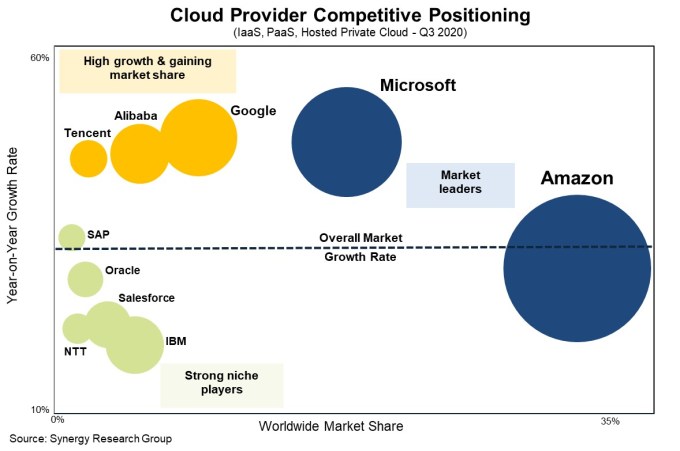
Image Credits: Synergy Research
With around a third of the market, AWS is the clear front-runner. Its closest and fiercest rival Microsoft has around 20%. To put that into perspective a bit, last quarter AWS had $11.6 billion in revenue compared to Microsoft’s $5.2 billion Azure result. While Microsoft’s equivalent cloud number is growing faster at 47%, like AWS, that number has begun to drop steadily while it gains market share and higher revenue and it falls victim to that same law of large numbers.
Powered by WPeMatico
Even in a non-hell year, running a successful startup is a tremendous lift. After the events of 2020, however, no doubt many already lean businesses are hanging on by the skin of their teeth. For every company that saw increased interest in their offerings during the pandemic, there were several that simply couldn’t make it through the finish line.
We’ve put this list together for several years now. It’s not a fun task, but it seems worthwhile to commemorate the startups that have closed up shop over the past 12 months. (Some of them were acquired by larger companies before shutting down, but all of them began their life as startups, and it still felt worthwhile to mark the end of their stories.) It also offers an opportunity to examine those issues from a bit of distance to see if there are any broader takeaways for the community at large.
This year’s list is among the most diverse we’ve done, ranging from standard smaller-name closures to big blockbuster crashes like Quibi and Essential . For some, the pandemic was the final nail in the coffin, but in many cases, cracks in business models were already starting to surface well before COVID-19 ground the global economy to a screeching halt.
Total Raised: $75 million

Atrium, a 100-person legal tech startup founded by Justin Kan, shut down in March after failing to find an efficient way to replace the arduous systems of law firms. The startup even returned some of its $75.5 million in funding to its investors, including Andreessen Horowitz.
The shutdown comes after the platform had pivoted just months earlier, laying off in-house lawyers and turning into a clearer SaaS play. Ultimately, Atrium’s failure shows how difficult and unprofitable it could be to disrupt a traditional and complicated system.
The closure came just three years after it launched with the goal to build software for startups to navigate fundraising, hiring, acquisition deals and collaboration with their legal team.
Total Raised: $330 million

Image Credits: Darrell Etherington
Big plans, big names and a boatload of money should have been enough to buy Essential a lengthy runway. Sure, Essential was entering a mature and oversaturated market, but the Playground-backed startup was doing so with $330 million in funding, a team of top industry executives and some genuinely innovative ideas.
When I spoke to the company at launch, an executive outlined a 10-year plan to become a major player in both the mobile and smart home categories. Ultimately, the company was able to eke out just under three years of life after coming out of stealth. And while it did give the world a promising handset, its connected home hub never arrived.
Timing, broader marketing issues and troubling allegations of sexual misconduct were all contributing factors that stopped Essential’s big plans dead in their tracks.
Total Raised: $11.4 million

Image Credits: HubHaus
HubHaus, founded by Shruti Merchant, was a long-term housing rental platform rooted in the belief that adult dormitories would take off. The startup targeted working professionals in cities, and raised only around $11 million in known venture capital. When it came to raising a Series B, Merchant says the company struggled to close and lost investor interest due to WeWork’s failed IPO.
After then pivoting to a self-funded company, HubHaus was just finding footing when the coronavirus pandemic arrived in the United States, drastically hurting the rental market (as shown by Airbnb’s public struggles, as well). The housing company eventually decided to close down in September, leaving landlords, members and vendors in limbo and bringing on a fresh sweep of critique and controversy.
Affordable housing continues to be an issue in the Bay Area, and HubHaus’s departure from the scene underscores this truth.
Total Raised: $55 million

Image Credits: Hipmunk
Hipmunk, founded by Adam J. Goldstein and Reddit co-founder Steve Huffman, was one of the first travel aggregation platforms on the market. The company put together information on flights, hotels and car rental all into one place so consumers could compare and contrast prices with ease.
The focus was enough for the platform to get acquired by Concur, but now after four years, the travel startup shut down. Notably, the travel startup’s closure wasn’t necessarily tied to the coronavirus pandemic. The site officially went dark on January 23, months before lockdowns came to the United States.
Total Raised: $51.4 million

Photo: Thomas Barwick/Getty Images
IfOnly had created a marketplaces of exclusive events — such as “goat yoga” — a business that faced obvious challenges during the pandemic. The startup was actually acquired by one of its investors, Mastercard, late last year, but the acquisition wasn’t announced until IfOnly revealed over the summer that it was shutting down.
Mastercard also said IfOnly’s team and technology are still part of its Priceless experience marketplace: “The IfOnly platform will continue to help advance our Priceless strategy and our combined team will be even better positioned and equipped to deliver exclusive experiences for cardholders globally.”
Mixer/Beam Interactive (2014-2020)
Total Raised: $520,000
Image Credits: Microsoft
Microsoft shut down its Twitch competitor Mixer this year, handing off its partnerships to Facebook Gaming. The service had its roots in the software giant’s acquisition of Beam Interactive shortly after the startup won TechCrunch’s Startup Battlefield in 2016.
Before giving up, Microsoft made some big investments in Mixer’s success, most notably signing streaming superstars Ninja and Shroud to exclusive deals. (They became free agents after the shutdown.) However, Microsoft’s gaming chief Phil Spencer said the company suffered from starting out “pretty far behind” the biggest players in the streaming market.
Total Raised: $10.2 million

Image Credits: The Outline
Despite a busy year of innovation and venture for news media platforms, The Outline, which branded itself as “the next generation version of the New Yorker” was shut down. The media site was started by Josh Topolsky and had an explicit focus on serving millennials with a digital-first news media brand.
The shutdown was part of a broader layoffs at Bustle Digital Group, which acquired the publication in 2019. Pre-acquisition, The Outline had already scaled back its editorial staff and refocused on freelance articles. (Input — a tech site that Topolsky founded for BDG — continues to publish.)

Periscope went out with more of a whimper than a bang. The startup was acquired by Twitter before it had even launched a product. With Meerkat bursting on the scene that year at SXSW, Twitter went on the offensive, buying the startup to build out its own live video offering.
Periscope’s run was decent as far as these things go, and its technology will live on as part of Twitter’s video offerings, even after the app is officially discontinued next March. But in the end, Periscope was a shell of its former self. In fact, this is a rare instance where the pandemic may have actually delayed its shutdown.
The company notes, “We probably would have made this decision sooner if it weren’t for all of the projects we reprioritized due to the events of 2020.”
Total Raised: $15.1 million

Image Credits: PicoBrew
The company made beer-brewing machines that used coffee pod-style PicoPaks, then expanded into other categories like coffee and tea, but never quite attracted enough customers to make the business viable. It sold its assets earlier this year to PB Funding Group — a group of lenders recruited by then-CEO Bill Mitchell in 2018 to keep it afloat.
It’s possible that PicoBrew will live on in some form, as PB Funding Group says it’s seeking buyers for the company’s patents and other intellectual property, and that it will keep the website running in the short term so that the machines don’t stop working.
Total Raised: $1.75 billion

Quibi CEO Meg Whitman speaks about the short-form video streaming service for mobile Quibi during a keynote address January 8, 2020 at the 2020 Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas, Nevada. (Photo by ROBYN BECK/AFP via Getty Images)
More so than any tech company in recent memory (with the possible exception of Theranos), Quibi’s existence feels like a fever dream. $1.75 billion in funding later and what do we have to show for it? “Fierce Queens,” a nature documentary about female animals. The HGTV-style program, “Murder House Flip.” And, of course, “The Shape of Pasta.” A show about pasta.
Early reports of the service’s demise seemed premature — if only because there was seemingly no way a company could burn through that much capital that quickly. By late-October, however, it was over. “All that is left now is to offer a profound apology for disappointing you and, ultimately, for letting you down,” founders Jeffrey Katzenberg and Meg Whitman wrote in an open letter.
Sometimes startup failures are bad timing. Sometimes it’s just plain bad luck. With Quibi, the diagnoses of what went wrong can be summed up in one word: everything.
Total Raised: $15 million
Image Credits: Rubica
Rubica spun out of security company Concentric Advisors with the aim of offering tools that were more advanced than antivirus software, while still remaining accessible to individuals and small businesses. CEO and co-founder Frances Dewing said that when customers cut back on spending during the pandemic, the company tried to shift its focus to larger enterprise, but it failed to convince investors there was a business there.
“We were all really surprised given how relevant and needed this is right now,” she said. “Investors didn’t agree with that or see it in the same way.”
Total Raised: $104 million

Businessman’s hands with calculator and cost at the office and Financial data analyzing counting on wood desk. Image Credits: Sarinya Pinngam/EyeEm / Getty Images
ScaleFactor was a startup claiming to offer artificial intelligence tools that could replace accountants for small businesses; it blamed the pandemic for cutting its revenue in half and forcing the company to shut down. However, former employees and customers told Forbes a different story — that ScaleFactor actually relied on human accountants (including an outsourced team in the Philippines) to do the work.
While it’s hardly unprecedented for a startup to fudge the truth about their level of automation versus human labor, this reportedly resulted in error-filled accounting for ScaleFactor clients. (Responding to a fact-checking email, former CEO Kurt Rathmann said the email was “filled with numerous factual inaccuracies and misrepresentation” and declined to comment further.)
Total Raised: $20 million

Self-driving trucks startup Starksy Robotics began with this first, and problematic truck. Image Credits: Starsky Robotics
“In 2019, our truck became the first fully-unmanned truck to drive on a live highway,” Starsky Robotics co-founder and CEO Stefan Seltz-Axmacher wrote in a Medium post in March. “And in 2020, we’re shutting down.” After five years and $20 million in funding, the autonomous trucking company shut its doors that month. It wasn’t for lack of ambition or demand — it seems safe to assume there’s still a bright future for self-driving trucks.
Ultimately, however, Starsky won’t be along for that ride — a fact Seltz-Axmacher blames largely on timing. A crowded market is certainly at play, as well, with countless companies currently pushing to bring autonomous technology to the road.
Total Raised: $10 million

Image Credits: Bryce Durbin
Founded in 2018 by ex-Googlers, Stockwell AI shut down after being unable to find business for its in-building smart vending machines that stocked everything from condoms to La Croix. The company blamed the “current landscape” (also known as the global pandemic we are experiencing) for its closure.
Stockwell AI, formerly known as Bodega, was well-funded and well-known, with more than $45 million in funding from investors that included NEA, GV, DCM Ventures, Forerunner, First Round and Homebrew. Still, even venture capital couldn’t make vending machines work well enough.
Total Raised: $2.5 million

Image Credits: Trover
Another travel-focused startup bites the dust as the coronavirus limits the chance to safely explore the world (let alone your neighborhood). Trover, a photo-sharing hub for travelers acquired by Expedia, shut down in August. The startup was founded by Rich Barton and Jason Karas and was meant to connect people travelling to the same places. The startup had quite the life: it began out of the remains of TravelPost, a travel review site, and got scooped up by its parent company when it only had $2.5 million in funding. Unfortunately, its nine-year journey is over for now.
Powered by WPeMatico
Being “underbanked” doesn’t mean that someone lacks access to financial services. Instead, it often means they don’t have traditional bank accounts or credit cards. But in markets like Indonesia, many still use digital wallets or e-commerce platforms, creating alternative sources of user data that can help them secure working capital and other financial tools. Finantier, a Singapore-based open finance startup, wants to streamline that data with a single API that gives financial services access to user data, with their consent. It also includes machine-learning-based analytics to enable credit scoring and KYC verifications.
Currently in beta mode with more than 20 clients, Finantier is busy getting ready to officially launch. It announced today that it has been accepted into Y Combinator’s Winter 2021 startup batch. The startup also recently raised an undisclosed amount of pre-seed funding led by East Ventures, with participation from AC Ventures, Genesia Ventures, Two Culture Capital and other investors.
Finantier was founded earlier this year by Diego Rojas, Keng Low and Edwin Kusuma, all of whom have experience building products for fintech companies, with the mission of enabling open finance in emerging markets.
Open finance grew out of open banking, the same framework that Plaid and Tink are built on. Meant to give people more control over their financial data instead of keeping it siloed within banks and other institutions, users can decide to grant apps or websites secure access to information from their online accounts, including bank accounts, credit cards and digital wallets. Open banking refers mainly to payment accounts, while open finance, Finantier’s specialty, covers a larger gamut of services, including business lending, mortgages and insurance underwriting.
While Finantier is focusing first on Singapore and Indonesia, it plans to expand into other countries and become a global fintech company like Plaid. It’s already eyeing Vietnam and the Philippines.
Before launching Finantier, Rojas worked on products for peer-to-peer lending platforms Lending Club and Dianrong, and served as chief technology officer for several fintech startups in Southeast Asia. He realized that many companies struggled to integrate with other platforms and fetch data from banks, or purchase data from different providers.
“People are discussing open banking, embedded finance and so on,” Rojas, Finantier’s chief executive officer, told TechCrunch. “But those are the building blocks of something bigger, which is open finance. Particularly in a region like Southeast Asia, where about 60% to 70% of adults are unbanked or underbanked, we believe in helping consumers and businesses leverage the data that they have in multiple platforms. It definitely doesn’t need to be a bank account, it could be in a digital wallet, e-commerce platform or other service providers.”
What this means for consumers is that even if someone doesn’t have a credit card, they can still establish creditworthiness: For example, by sharing data from completed transactions on e-commerce platforms. Gig economy workers can access more financial services and deals by giving data about their daily rides or other types of work they do through different apps.
Other open-banking startups focused on Southeast Asia include Brankas and Brick. Rojas said Finantier differentiates by specializing on open finance and creating infrastructure for financial institutions to build more services for end users.
The benefit of open finance for financial institutions is that they can create products for more consumers and find more opportunities for revenue sharing models. In Southeast Asia, this also means reaching more people who are underbanked or otherwise lack access to financial services.
While taking part in Y Combinator’s accelerator program, Finantier will also be participating in the Indonesia Financial Service Authority’s regulatory sandbox. Once it completes the program, it will be able to partner with more fintech companies in Indonesia, including bigger institutions.
There are 139 million adults in Indonesia who are underbanked or unbanked, said East Ventures co-founder and managing partner Willson Cuaca.
The investment firm, which focuses on Indonesia, conducts an annual survey called the East Ventures Digital Competitiveness Index and found that financial exclusion was where one of the largest divides existed. There are significant gaps in between the number of financial services available in heavily populated islands like Java, where Jakarta is located, and other islands in the archipelago.
To promote financial inclusion and alleviate the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has set a goal for 10 million micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) to go digital by the end of the year. There are currently about eight million Indonesian MSMEs that sell online, representing just 13% of MSMEs in the country.
“Providing equal access to financial services will create multiplier effects to the Indonesian economy,” Cuaca told TechCrunch about East Ventures’ decision to back Finantier. “Currently, hundreds of companies work with their own unique solutions to bring financial services to more people. We believe Finantier will help them offer more products and services to this underserved section of the population.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Indianapolis-based Boardable, a provider of board management software tools for nonprofits, has raised $8 million in a new round of financing, the company said.
The investment came from Base10 Partners with participation from the company’s seed-stage backer, the Indianapolis-based enterprise investment firm High Alpha.
Boardable provides organizational tools to help nonprofits better manage their board meetings and offers management solutions for nonprofit operations.
Software and services developers catering to the nonprofit sector are seeing more interest from investors as they look for new verticals that have been underserved by technology companies in the past. Earlier this year, Resilia, a New Orleans-based startup, raised $8 million for its own spin on services for nonprofits and charity organizations.
In a statement, Boardable said that it would use the financing to grow its team and develop new tools to become more of a one-stop shop for nonprofit operations.
“Most nonprofits manage their board members with ‘digital duct tape’—endless email threads and file sharing services. It’s a terrible experience that drains the board members and staff. Boardable is purpose-built by nonprofit founders to solve this problem, increasing efficiency and engagement,” said Jeb Banner, Boardable’s chief executive, in a statement.
Organizations including the YMCA, The Salvation Army, Big Brothers Big Sisters of America, the Girl Scouts of Indiana and more have turned to the company to use its paperless approach for board management.
Powered by WPeMatico
ReturnSafe, a symptom checking and contact tracing employee health management toolkit for businesses, has raised $3.25 million in financing from investors including Fifty Years and Active Capital.
With companies looking to reopen operations and have their employees return to work safely, management toolkits that track employee health are piling into the market offering all sorts of strategies to maintain a safe work environment.
These include offerings from companies like WorkSafe; or the ProtectWell tool from Microsoft and UnitedHealth; or NSpace, which has similar features and a scheduling tool for booking office space safely.
For its part, ReturnSafe is boasting six-figure monthly recurring revenue and is working with 50 organizations since its launch six months ago.
The pitch to investors and customers is that the need to manage employees and ensure that workspaces are free from health risks is only going to grow in a post-COVID-19 world.
Of course, the best way for employers to ensure the safety and security of their employees is to provide adequate leave and time off if employees are sick, and to ensure that everyone has access to adequate testing at regular intervals should they not be able to work remotely.
Like other companies in the market, ReturnSafe offers a symptoms screener, a testing dashboard, a case management dashboard and a new vaccine management service. In addition to those software tools, ReturnSafe pitches a set of wearable devices with built-in social distancing alarms to ensure that employees maintain safe distances.
Powered by WPeMatico
As we head toward the exits of 2020, we have one more name to add to our roll call of private companies that have reached the $100 million annual recurring revenue (ARR) milestone. Well, one and a half.
But before we get into Nexthink and give Coalition a honorable mention, let’s talk about the startups we’re looking for in 2021.
 The $100 million ARR list came together by accident, a quirk of a news cycle that happened to have a few companies reach the threshold when I was in transition back to working at TechCrunch. So, when I got back into our WordPress install, the group of companies that had each recently reached nine-figure revenues was top of mind.
The $100 million ARR list came together by accident, a quirk of a news cycle that happened to have a few companies reach the threshold when I was in transition back to working at TechCrunch. So, when I got back into our WordPress install, the group of companies that had each recently reached nine-figure revenues was top of mind.
But looking at $100 million ARR companies proved less useful than we might have hoped. Mostly what we managed was to collect a bucket of companies that were about to go public.
That was always a risk. As we wrote at the time:
Perhaps the startup market would do well to celebrate the $50 million ARR mark even more loudly. At $50 million ARR, a startup is scaling to IPO size. That’s the goal, after all.
This is our aim for 2021.
If your startup is approaching the $50 million ARR mark, or the $50 million annual run rate threshold, I want to hear from you. Drop a line if your startup has an annualized run rate between $35 million and $60 million, is privately held, and you are willing to chat about how quickly it is growing. (The Exchange first raised this idea in November.)
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
But that’s next year. Today, let’s chat about Nexthink, what the hell “digital employee experience” is and what’s good with cyber insurance and why it’s helping Coalition grow rapidly.
Nexthink is a venture-backed software company with headquarters in Lausanne, Switzerland and Boston. According to PitchBook, Nexthink raised external capital in modest amounts from 2006 until 2014, when the startup picked up a $14.5 million Series D. That round was its first worth more than $10 million.
From there, Nexthink was a venture capital success story, presumably scaling quickly as it raised two larger rounds in 2016 and 2018 worth an estimated $40 million and $85 million, respectively. Nexthink was valued at a little over $558 million (post-money) following its 2018 round.
How did it attract so much external funding? By building digital experience monitoring software. Which, after doing a bit of research this morning, appears to be software aimed at tracking what corporate end users are doing with devices and how well software running on those devices perform.
Powered by WPeMatico
StepZen, a new startup from the crew who gave you Apigee (which was sold to Google in 2016 for $625 million) had a different vision for their latest company. They are building a single API that pulls data from disparate sources to help developers deliver more complex customer experiences online.
Today, the startup emerged from stealth and announced an $8 million seed investment from Neotribe Ventures and Wing Venture Capital .
With years of experience working with APIs, the founders wanted to take that a step further, says CEO and co-founder Anant Jhingran. “StepZen is a product that lets front end developers easily create and consume one API for all the data they need from the back end,” he explained.
This is all in the service of providing a smoother, more consistent customer experience. That means whether you are on an e-commerce site accessing your order history or a banking app grabbing your current balance, these scenarios require pulling data from various back-end data resources. Connecting to those resources is a time-consuming task, and StepZen wants to simplify that for developers.
“Developers spend an enormous amount of time deploying and managing code that accesses the back end, and what StepZen wants to do is to give them that time back,” he said.
Instead of manually writing code to pull this data, StepZen enables developers to simply provide configuration information and credentials to connect to these back-end data sources, and then it builds a single API that handles all of the heavy lifting of pulling that data and presenting it when needed.
Jhingran uses the example of presenting a list of open orders for a customer. It sounds simple enough, but once you consider that the data could live in several places, including the CRM system, the order system or with your courier, that means accessing at least three separate and highly disparate systems. StepZen will help pull this all together via its API and present it smoothly to the user.
Today the company has 11 employees, including the three founders, with plans to add another eight or so in 2021. As they do that, CBO and co-founder Helen Whelan says they are working to build a diverse and inclusive company. While the founding team is itself diverse, they want to hire employees with diverse backgrounds and ways of thinking to build the most complete product and company.
“For the first 10 or so employees, we tapped into the networks of the people who we’ve worked with, people who you know can do a great job. Then I think it’s about deliberately expanding from there and deliberately taking the time that you need to explore and expand your pipeline of candidates,” she said.
The company is just nine months old and has been spending most of this year building the solution and working with pre-alpha users. Today the product is in alpha, with plans to release it as a software service early next year.
As the company emerges from stealth, it’s looking to continue building the product and looking for ways to remove as much complexity as possible. “We know how to do the hard things on the back end. We’ve got the database technologies and the API technologies down, and it’s now about finding how to make all of that simple on the outside and easy for developers to use, ” Whelan said.
Powered by WPeMatico