TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Welcome to 2021, a year that could extend 2020’s startup market disruptions and excesses — or change patterns that previously performed well for early-stage tech companies and their investors.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
As we turn the page, I have a number of questions worth raising as we muck into 2021.
Each relates to a 2020 change that is expected to persist, by either the general market or those bullish on startups. I want to know what would need to change to shake up what became the new normal last year. After all, it’s precisely when it feels like nothing could shake up a downturn (or a boom) that things often do.
 Today, let’s discuss seed deals, venture investing cadence, the resulting valuation pressures from rapid-fire bets, current IPO expectations and what happens to software sales when remote work begins to fade.
Today, let’s discuss seed deals, venture investing cadence, the resulting valuation pressures from rapid-fire bets, current IPO expectations and what happens to software sales when remote work begins to fade.
As 2020 came to a close, Natasha Mascarenhas and I reported on seed investing’s strong year and its especially strong second half. How long can that pace keep up?
Nearly all our questions today deal with the endurance of certain conditions, namely: how long the market can keep parts of startup land red-hot.
When it comes to seed deal-making, Q1 and Q2 2020 saw similar levels of investment in the United States. But Q3 proved explosive, with money invested into domestic seed deals rising from around $1.5 to $1.6 billion during the first two quarters to $2.2 billion in the July-September period.
Q4 numbers are yet to fully come in, but it’s clear that private investors were incredibly bullish on early-stage startups in the second half of 2020. How long can that keep up? I think the answer is for a while yet, as investors have shown scant enthusiasm for slowing down their dealmaking cadence.
While cadence remains hot generally, seed deals should stay heated as the number of investors who are willing to invest early has increased.
Which brings us to our second question:
A theme that cropped up in the second half of 2020 was the pace at which investors were conducting venture capital deals. This was for a few reasons. To start, venture capitalists have raised larger funds in recent years, meaning that they need larger returns to make the math work out. This led to many investors putting money to work in younger and younger companies, hoping to get in early on a big win. That setup led to more deal competition and faster deal-making.
How? Two things. Investors who were already on a startup’s cap table — already part-owners, in other words — led preemptive rounds, in part to get ahead of other investors who might want to poach the succeeding deal. Other investors, knowing this, seemed to do the same math and move even faster, and earlier, to get around the defense.
So how long can the trend keep up? Given that many big VC firms raised in 2020, many startups picked up some tailwinds from the COVID-19 economy and exits have been strong, forever? Until something stops things? Think of it as Newton’s First Law of startup investing.
What could be the sudden impact to shake up the current set of conditions boosting the pace at which seed and later deals occur? An asteroid strike is probably too extreme, but inertia is one hell of a drug and markets love to stay happy.
Moving along, all the competition to get money to work in hot startups now has had another effect than the mere speed of deal-making; it has also pushed prices higher.
Powered by WPeMatico
Healthcare startup Color has raised a sizable $167 million in Series D funding round, at a valuation of $1.5 billion post-money, the company announced today. This brings the total raised by Color to $278 million, with its latest large round intended to help it build on a record year of growth in 2020 with even more expansion to help put in place key health infrastructure systems across the U.S. — including those related to the “last mile” delivery of COVID-19 vaccines.
This latest investment into Color was led by General Catalyst, and by funds invested by T. Rowe Price, along with participation from Viking Global investors as well as others. Alongside the funding, the company is also bringing on a number of key senior executives, including Claire Vo (formerly of Optimizely) as chief product officer, Emily Reuter (formerly of Uber, where she played a key role in its IPO process) as VP of Strategy and Operations, and Ashley Chandler (formerly of Stripe) as VP of Marketing.
“I think with the [COVID-19] crisis, it’s really shone the light on that lack of infrastructure. We saw it multiple times, with lab testing, with antigen testing and now with vaccines,” Color CEO and co-founder Othman Laraki told me in an interview. “The model that we’ve been developing, that’s been working really well and we feel like this is the opportunity to really scale it in a very major way. I think literally what’s happening is the building of the public health infrastructure for the country that’s starting off from a technology-first model, as opposed to, what ends up happening in a lot of industries, which is you start off taking your existing logistics and assets, and add technology to them.”
Color’s 2020 was a record year for the company, thanks in part to partnerships like the one it formed with San Francisco to establish testing for healthcare workers and residents. Laraki told me they did about five-fold their prior year’s business, and while the company is already set up to grow on its own sustainably based on the revenue it pulls in from customers, its ambitions and plans for 2021 and beyond made this the right time to help it accelerate further with the addition of more capital.
Laraki described Color’s approach as one that is both cost-efficient for the company, and also significant cost-saving for the healthcare providers it works with. He likens their approach to the shift that happened in retail with the move to online sales — and the contribution of one industry heavyweight in particular.
“At some point, you build Amazon — a technology-first stack that’s optimized around access and scale,” Laraki said. “I think that’s literally what we’re seeing now with healthcare. What’s kind of getting catalyzed right now is we’ve been realizing it applies to the COVID crisis, but also, we started actually working on that for prevention and I think actually it’s going to be applying to a huge surface area in healthcare; basically all the aspects of health that are not acute care where you don’t need to show up in hospital.”
Ultimately, Color’s approach is to rethink healthcare delivery in order to “make it accessible at the edge directly in people’s lives,” with “low transaction costs,” in a way that’s “scalable, [and] doesn’t use a lot of clinical resourcing,” Laraki says. He notes that this is actually very possible once you reasses the problem without relying on a lot of accepted knowledge about the way things are done today, which result in a “heavy stack” versus what you actually need to deliver the desired outcomes.
Laraki doesn’t think the problem is easy to solve — on the contrary, he acknowledges that 2021 is likely to be even more difficult and challenging than 2020 in many ways for the healthcare industry, and we’ve already begun to see evidence of that in the many challenges already faced by vaccine distribution and delivery in its initial rollout. But he’s optimistic about Color’s ability to help address those challenges, and to build out a “last mile” delivery system for crucial care that expands accessibility, while also making sure things are done right.
“When you take a step back, doing COVID testing or COVID vaccinations … those are not complex procedures at all — they’re extremely simple procedures,” he said. “What’s hard is doing them massive scale and with a very low transaction cost to the individual and to the system. And that’s a very different tooling.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Slack did its best to ease the working world back into their jobs this morning by breaking, ensuring that everyone’s return to the grind would be as chaotic and unproductive as possible.
Precisely when the downtime began is not clear, though problems amongst the TechCrunch staff began a little after 10 o’clock in the morning. Slack itself posted at 10:14 a.m. Eastern Time that there was a problem:

Downtime issues are not new for the workplace chat application that went public in mid-2019, before announcing a deal to sell itself to Salesforce toward the end of 2020. TechCrunch covered the service’s uptime issues in 2020, 2019, 2018, 2017 and so forth.
The downtime is embarrassing, as Slack is in the midst of selling itself for a hefty check. For a service designed to help folks work, falling apart precisely when the users — customers! — you serve are trying to gear back up for a working year is simply awful.
I suppose we can call one another until Slack is back up.
To close, here’s the view from Redmond, with its competing Teams product:
Update: Slack sent TechCrunch a statement, saying the following:
Our teams are aware and are investigating the issue. We know how important it is for people to stay connected and we are working hard to get everyone running as normal. For the latest updates please keep an eye on @slackstatus and status.slack.com.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
This is Equity Monday, our weekly kickoff that tracks the latest private market news, talks about the coming week, digs into some recent funding rounds and mulls over a larger theme or narrative from the private markets. You can follow the show on Twitter here and myself here — and don’t forget to check out the second of our two holiday eps, the most recent looking at what we think might happen this year.
What did we get into today? A great question. Here’s the rundown:
Mostly we’re still making sure that our brains still work and that the return of work really is here. Taking a break was nice. Now the news is coming back, so we are as well. Hugs, and chat Thursday.
Powered by WPeMatico
TMYTEK recently raised a Series A+ round of about $10 million for products that make it easier to test 5G millimeter wave equipment. So far, the company’s clients include KDDI, NTT DoCoMo and research institutions. But the Taiwanese startup has aspirations to sell its own base stations, too, competing with well-established players like Nokia, Ericsson, Samsung and Huawei. TMYTEK plans to use its expertise, gleaned from helping other researchers develop 5G infrastructure, to create what its chief executive officer describes as a “complete 5G industrial chain.”
Its latest funding round was led by TMYTEK’s manufacturing partner Inventec, one of the largest OEMs in Taiwan, and brings the startup’s total funding so far to $13.3 million. Other investors included Taisic Materials, ITEQ, Tamagawa Electronics and Taiwan’s National Development Fund. TMYTEK also recently took part in SparkLabs Taipei’s accelerator program.
Co-founder and chief executive officer Su-Wei Chang told TechCrunch that it plans to raise a Series B next to develop and commercialize its base stations. To get ready for its base station business, TMYTEK recently joined the O-RAN Alliance, founded by some of the world’s biggest telecoms to create more interoperable mobile networks, in a bid to encourage the development of new technology and faster deployment.
Chang said TMYTEK’s base in Taiwan gives it a strategic advantage. 5G manufacturing is an important part of Taiwan’s economy, with exports reaching record highs during the second half of 2020, thanks in part to demand for 5G-related equipment and technology for smartphones, autonomous vehicles and smart devices.
Chang studied at University of Massachusetts Amherst and when TMYTEK was founded six years ago, he was often asked why he didn’t stay in the United States, where it would have been easier to secure startup funding. But being in Taiwan puts the company closer to many important markets, including Japan, where 30% of its current business comes from, and gives TMYTEK a good foundation to expand into the U.S. and European market, he said.
It has also given the company a supply chain advantage. TMYTEK has manufacturing partners across Asia, including Inventec in Taiwan, and factories in Vietnam and Thailand, in addition to China. Chang said this means TMYTEK was not limited by the COVID-19 pandemic or the U.S.-China trade war.
Before launching TMYTEK in 2014, Chang and co-founder Ethan Lin both worked at Academia Sinica, one of the top research institutions in Taiwan, where they focused on millimeter waves even though at the time most researchers were more interested in the mid-band spectrum.
But as more devices and applications began to crowd the 4G spectrum, mmWave became less niche. With Qualcomm’s launch of next-generation 5G mmWave hardware and chips, and more carriers launching mmWave coverage, mmWave is poised to become mainstream.
Millimeter waves offer powerful signals with wide bandwidth and low latency, but drawbacks include difficulty traveling through obstacles like buildings. It also has a limited range, which is why millimeter waves need more base stations. Beamforming, which directs signals toward a specific device, and antenna array, or multiple antennas that work like a single antenna, are used to extend its coverage.
One of the main challenges for the millimeter wave market, however, is the lack of R&D tools to speed up their development and time to market, resulting in higher costs and slower deployment.
To keep up with market opportunities, TMYTEK transitioned from design and manufacturing projects for clients to offering 5G-focused solutions like the BBox, which stands for “beamforming box.” The BBox was created after a professor at National Taiwan University told Chang that his team was working on antenna design, but didn’t have the resources to work on beamforming technology, too. It lets researchers create 16 beams and control the signal’s amplitude and phase with software, so they can test how it works with antennas and other hardware more quickly. TMYTEK claims the BBox can save researchers and engineers up to 80% in time and cost.
Chang said TMYTEK realized that if researchers at NTU, one of Taiwan’s largest research universities, needed a solution, then other labs did, too. So far, it has delivered 30 sets to companies including KDDI, NTT DoCoMo, Fujitsu, several Fortune 500 companies and research institutions.
While the BBox was created for antenna designers, the company also began exploring solutions to help other designers, including algorithm developers who want to test beam tracking, communicate with base stations and collect data.
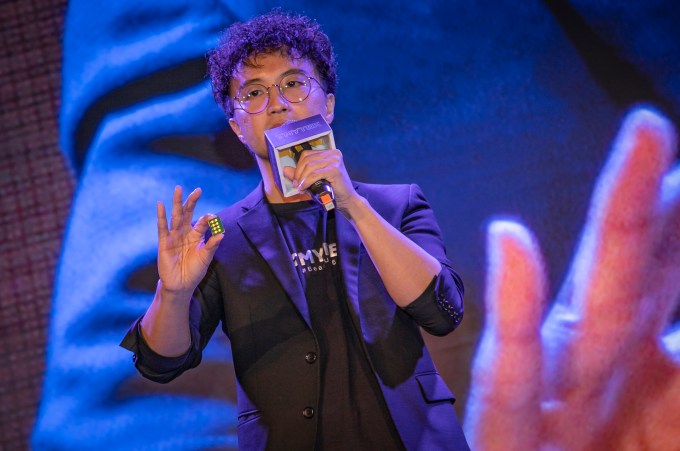

TMYTEK vice president Ethan Lin holds the antenna-in-package for its XBeam millimeter wave testing solution (Image Credits: TMYTEK)
For that scenario, TMYTEK created the XBeam, which it describes as a “total solution,” and is meant for the mass production phase, testing modules, smartphones and base stations before they are shipped. Traditional solutions to test modules rely on mechanical rotators, but Chang said this is more suited to the research and development process. The XBeam, which is based on the BBox, electronically scans beams instead. The company claims the XBeam is up to 20 times faster than other testing solutions.
TMYTEK created the XBeam’s prototype in 2019 and launched the commercialized version in November 2020.
The BBox and XBeam will help TMYTEK build its own base station business in two ways, Chang said. First, having its own solutions will allow TMYTEK to test base stations and bring them to market faster. Second, the startup hopes building a reputation on effective research and development tools will help it market its base stations to private and public networks. This is especially important to TMYTEK’s ambitions since their base stations will be up against products from major players like Nokia, Ericsson, Samsung and Huawei.
“Our advantage at TMYTEK is that we’re doing the design and we have good partners for manufacturing. Inventec, our investor, is a top five manufacturer in Taiwan,” he said. “And TMYTEK also builds our own testing solution, so our value is that we can provide a total solution to our customers.”
Powered by WPeMatico
As 2020 comes to a long-awaited end, a series of filings indicate that venture capitalists are ending the year with fresh money. According to SEC paperwork, Learn Capital and USV have filed paperwork that shows the firms have raised new, multimillion-dollar funds.
If you’ve been paying attention to news this past year, it’s clear that much of venture capital isn’t just surviving 2020 – it’s flourishing through it. Zoom investing, it seems, is working just fine for cash-rich firms looking to double down on bets in categories from edtech to climate.
First up, New York-based USV submitted a pair of filings on late Thursday. The first filing shows that the firm has closed $151 million for USV Climate 2021, which one can assume is focused on climate-tech investments. As my colleague Jonathan Shieber has pointed out, climate tech.
The other, more nebulous filing, is the firm’s $22.4 million investment vehicle titled USV Bundled. It’s unclear what this is focused on, but a recent blog post suggests that the firm will continue to double down on its education investments.
Speaking of edtech, Learn Capital, an education-focused venture capital fund, filed paperwork indicating that it has closed $132 million in capital. It plans to raise a total of $250 million for this fund, which will be the firm’s fourth investment vehicle to date. The edtech category has obviously been booming with interest, which also fueled Owl Ventures to close $585 million in new capital in September.
Finally, I’ll give an honorable mention to Lattice CEO Jack Altman’s New Years Eve filing, which shows that the executive plans to raise $20 million for a new fund. It’s unclear if this filing indicates Apollo’s next step, a venture fund started by the Altman brothers. The trio, beyond Jack, includes Max and Sam, the former president of Y Combinator who currently serves as the CEO of OpenAI.
Powered by WPeMatico
When Salesforce acquired Quip in 2016 for $750 million, it gained CEO and co-founder Bret Taylor as part of the deal. Taylor has since risen quickly through the ranks of the software giant to become president and COO, second in command behind CEO Marc Benioff. Taylor’s experience shows that startup founders can sometimes play a key role in the companies that acquire them.
Benioff, 56, has been running Salesforce since its founding more than 20 years ago. While he hasn’t given any public hints that he intends to leave anytime soon, if he wanted to step back from the day-to-day running of the company or even job share the role, he has a deep bench of executive talent including many experienced CEOs, who like Taylor came to the company via acquisition.
One way to step back from the enormous responsibility of running Salesforce would be by sharing the role.
He and his wife Lynne have been active in charitable giving and in 2016 signed The Giving Pledge, an initiative from the The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, to give a majority of their wealth to philanthropy. One could see him wanting to put more time into pursuing these charitable endeavors just as Gates did 20 years ago. As a means of comparison, Gates founded Microsoft in 1975 and stayed for 25 years until he left in 2000 to run his charitable foundation full time.
Even if this remains purely speculative for the moment, there is a group of people behind him with deep industry experience, who could be well-suited to take over should the time ever come.
One way to step back from the enormous responsibility of running Salesforce would be by sharing the role. In fact, for more than a year starting in 2018, Benioff actually shared the top job with Keith Block until his departure last year. When they worked together, the arrangement seemed to work out just fine with Block dealing with many larger customers and helping the software giant reach its $20 billion revenue goal.
Before Block became co-CEO, he had a myriad other high-level titles including co-chairman, president and COO — two of which, by the way, Taylor has today. That was a lot of responsibility for one person inside a company the size of Salesforce, but promoting him to co-CEO from COO gave the company a way to reward his hard work and help keep him from jumping ship (he eventually did anyway).
As Holger Mueller, an analyst at Constellation Research points out, the co-CEO concept has worked out well at major enterprise companies that have tried it in the past, and it helped with continuity. “Salesforce, SAP and Oracle all didn’t miss a beat really with the co-CEO departures,” he said.
If Benioff wanted to go back to the shared responsibility model and take some work off his plate, making Taylor (or someone else) co-CEO would be one way to achieve that. Certainly, Brent Leary, lead analyst at CRM Essentials sees Taylor gaining increasing responsibility as time goes along, giving credence to the idea.
“Ever since Quip was acquired Taylor seemed to be on the fast track, becoming president and chief product officer less than a year-and-a-half after the acquisition, and then two years later being promoted to chief operating officer,” Leary said.
While Taylor isn’t the only person who could step into Benioff’s shoes, he looks like he has the best shot at the moment, especially in light of the $27.7 billion Slack deal he helped deliver earlier this month.
“Taylor being publicly praised by Benioff for playing a significant role in the Slack acquisition, Salesforce’s largest acquisition to date, shows how much he has solidified his place at the highest levels of influence and decision-making in the organization,” Leary pointed out.
But Mueller posits that his rapid promotions could also show something might be lacking with internal options, especially around product. “Taylor is a great, smart guy, but his rise shows more the product organization bench depth challenges that Salesforce has,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico
This has been the year of the social organization. As the COVID-19 pandemic swept across the world and the United States, governments and a patchwork of nonprofits and volunteer organizations sprang into action, offering everything from food and medical supplies to children’s books and clothing to individuals and families struggling in the virus’s wake.
Perhaps the biggest divide though to getting people help has been digital — non-profits need to connect with their beneficiaries over the internet just as much as any retailer today. Unfortunately, tech talent is expensive and hard to find, particularly for often cash-strapped nonprofits.
That was part of the impetus for two Stanford seniors, Mary Zhu and Amay Aggarwal, to co-found Develop for Good, a matching service designed to connect motivated and ambitious undergrads in computer science, design and economics to nonprofits with specific projects that require expertise. They launched the network in March as the pandemic started spreading rapidly, and since then, the organization has itself started growing exponentially as well.
Develop for Good “was in response to [the pandemic], but at the same time, a lot of our peers were having their internships canceled, [and] a lot of companies were having hiring freezes,” Zhu explained. “People were also seeking opportunities to be able to develop their professional skills and develop their project experience.” This coincidence of needs among both students and nonprofits helped accelerate the matching that Develop for Good offers.
So far, the 501(c)(3) non-profit has coordinated more than 25,000 volunteer hours across groups like the Ronald McDonald House, UNICEF, the Native American Rights Fund (NARF), Easterseals, The Nature Conservancy, Save the Children, AARP and more. The program, which in its first batch focused on Zhu and Aggarwal’s network at Stanford, has since expanded to more than a dozen schools across the United States. The two first reached out to nonprofits through Stanford’s alumni network, although as the program’s reputation has grown, they have started getting inbound interest as well.
Volunteers take on a project for 5-10 hours per week for 10 weeks, typically in teams. Each team meets their nonprofit client at least weekly to ensure the project matches expectations. Typical projects include application development, data visualization, and web design. Most projects conclude at the end of the batch, although the founders note that some in-depth projects like product development can cross over into future batches. As the program has expanded, Zhu and Aggarwal have added a more formal mentorship component to the program to help guide students through their work.
Applications for the next batch starting in January are currently open for students (they’re due January 2nd, so get them in quick!). The founders told me that they are expecting 800 applications, and are likely going to be able to match about 200 volunteers to 32 projects. Applications are mostly about matching interests with potential programs for the best fit, rather than a purely competitive exercise. So far, the program has worked on 50 projects to date.
For this next batch, Amazon Web Services will sponsor a stipend for first-generation and low-income students to help defray the financial impact of volunteer work for some students. “Over the past cycle, a few people had to drop out because they said, ‘they’re unable to work for free because they’re having a lot of financial stress for their families’,” Aggarwal said. The new stipend is meant to help these students continue to volunteer while alleviating some of that financial burden.
Aggarwal said that two-thirds of the program’s volunteer developers and designers are female, and one-third are first-generation or low-income.
Powered by WPeMatico
There’s no denying that 2020 has been the year of the special purpose acquisition company.
Since the beginning of the year, 219 SPACs have raised $73 billion, according to widely reported market research from Goldman Sachs. That’s a 462% jump from 2019 and more than traditional public offerings raised by about $6 billion. By some counts, roughly one quarter of the SPACs that have been announced will target climate-related businesses.
Since the beginning of the year, 219 SPACs have raised $73 billion.
Already, of the 78 deals that have either completed or announced a merger since 2018, just over one-third have been climate-related, as tallied by Climate Tech VC. And these SPACs have outperformed the broader technology market, with the 10 climate tech companies that have completed mergers averaging a 131% return on investment versus the 50% return of the total SPAC market (assuming average offering prices of $10 per share).
Clearly this has been a banner year for companies that are tackling the climate crisis across a number of verticals, but can it last?
There are a few reasons to think that it can — led chiefly by the demand for these kinds of public offerings from institutional investors, including the pension funds, mutual funds and asset managers handling trillions of investment dollars.
“[The] current wave [of SPACs] is because over the past 24 months the institutional investor universe has come fully into believing that climate solutions are going to be a major growth area in the 2020s and beyond, but they weren’t seeing options available to them for investing into,” wrote longtime clean technology investor, Rob Day, in a DM.
“The available publicly traded ‘green’ companies were already getting really bought up, and the private equity options were underwhelming as well (smallish in the case of VC, low returns in the case of large-format projects). Throw in a Robinhood market of retail investors with a lot of enthusiasm for EVs and such, and you have a nice recipe for this to happen.”
Powered by WPeMatico
CommonGround, a startup developing technology for what its founders describe as “4D collaboration,” is announcing that it has raised $19 million in funding.
This isn’t the first time Amir Bassan-Eskenazi and Ran Oz have launched a startup together — they also founded video networking company BigBand Networks, which won two technology-related Emmy Awards, went public in 2007 and was acquired by Arris Group in 2011. Before that, they worked together at digital compression company Optibase, which Oz co-founded and where Bassan-Eskenazi served as COO.
Although CommonGround is still in stealth mode and doesn’t plan to fully unveil its first product until next year, Bassan-Eskenazi and Oz outlined their vision for me. They acknowledged that video conferencing has improved significantly, but said it still can’t match face-to-face communication.
“Some things you just cannot achieve through a flat video-conferencing-type solution,” Bassan-Eskenazi said. “Those got better over the years, but they never managed to achieve that thing where you walk into a bar … and there’s a group of people talking and you know immediately who is a little taken aback, who is excited, who is kind of ‘eh.’”
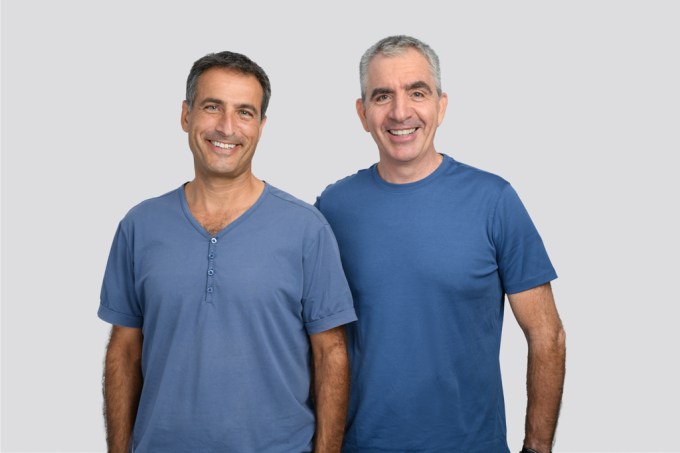

CommonGround founders Amir Bassan-Eskenazi and Ran Oz. Image Credits: CommonGround
That, essentially, is what Bassan-Eskenazi, Oz and their team are trying to build — online collaboration software that more fully captures the nuances of in-person communication, and actually improves on face-to-face conversations in some ways (hence the 4D moniker). Asked whether this involves combining video conferencing with other collaboration tools, Oz replied, “Think of it as beyond video,” using technology like computer vision and graphics.
Bassan-Eskenazi added that they’ve been working on CommonGround for more than year, so this isn’t just a response to our current stay-at-home environment. And the opportunity should still be massive as offices reopen next year.
“When we started this, it was a problem we thought some of the workforce would understand,” he said. “Now my mother understands it, because it’s how she reads to the grandkids.”
As for the funding, the round was led by Matrix Partners, with participation from Grove Ventures and StageOne Ventures.
“Amir and Ran have a bold vision to reinvent communications,” said Matrix General Partner Patrick Malatack in a statement. “Their technical expertise, combined with a history of successful exits, made for an easy investment decision.”
Powered by WPeMatico