Startups
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Squad Mobility’s vision of the perfect urban vehicle is a low-cost EV equipped with solar panels, swappable batteries and enough zip and range in its diminutive 6.5-foot package to meet the needs of city drivers.
The early-stage Dutch startup, which recently revealed the final design of its quadricycle, is now assembling working prototypes in Breda, the Netherlands. Squad has said the vehicle will have a base price of €5,750 ($6,790), excluding taxes. That price goes up if buyers want to add features like removable doors, air conditioning, heating and extra batteries.
Squad plans to present the prototypes this fall, Robert Hoevers, CEO and co-founder of the company, said in a recent interview. Pre-production is also expected to begin this year with a goal to start delivering the car at the end of 2022.
Squad, like so many other new entrants to the EV car scene, will need more funds to reach its target.
In June, the company raised an undisclosed amount from Bloomit Ventures. To reach its production goals, Hoevers estimates Squad will need an additional €3.5 million ($4.1 million) for its next round, and then another €8 million ($9.6 million) to be able to deliver the first Squads. The company has not yet announced a round publicly, but says it’s in talks with various interested parties.
Interested customers can go on Squad’s website and pay a €5 reserve fee, but where Squad really sees its path to market is with shared mobility companies. The startup says it is in talks with a range of micromobility and car-sharing operators that might be interested in diversifying their fleets with a compact, smart vehicle.
The Squad, which is a combination of the words “solar” and “quadricycle,” seats two, punches up to 30 miles per hour and is fueled by two swappable batteries with a capacity of around 1.6 Kwh each and a collective range of about 62 miles. This is similar to the battery capacity and range of electric mopeds.
For the average European city driver, that should be enough range. Squad also installed a 250-watt solar panel to the vehicle, which the company says adds another 12 miles per day given the amount of sun Europe tends to get.
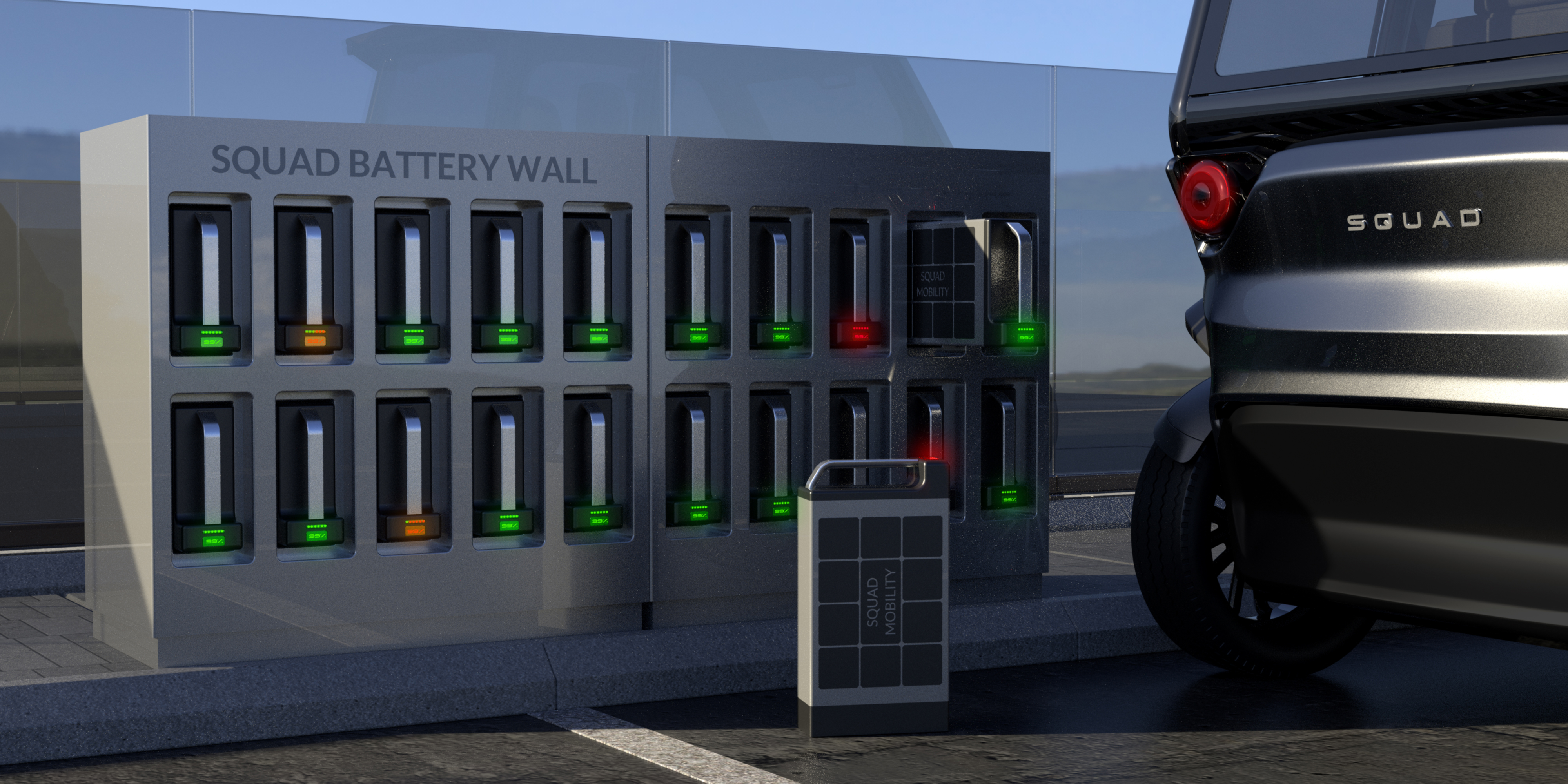

Rendering of a Squad charging station for swappable batteries that can be used by shared mobility operators. Image Credits: Squad Mobility
Squad is coming onto the scene at the intersection of new mobility categories and EV charging innovation, which could be appealing to shared mobility operators looking to solve more use cases.
Shared micromobility companies are beginning to add electric mopeds to their fleets of e-scooters and e-bikes. The Squad could appeal to operators that want to appeal to a broader demographic, and one specifically more comfortable in a four-wheeled vehicle.
The potential savings from harnessing the power of the sun could attract operators as well. In the micromobility world, the labor costs associated with swapping batteries or charging vehicles represent a roadblock to profitability. A vehicle that’s constantly on a bit of a charge, at least during the daylight hours, might help alleviate that pain point.
“The idea is not to drive directly on solar,” Hoevers told TechCrunch. “The idea is to buffer the batteries with solar and then drive on the batteries. The sun is more or less drip charging the battery throughout the day, which is actually a very healthy way of charging. You don’t want to top off your batteries to 100%. You want to keep them at around 50% to 60% all the time for a longer battery life.”
Hoevers said Squad has been in talks with shared micromobility providers to pitch the quadricycle, and has found that most dockless vehicles see about four to five rides per day and drive about 36 to 38 miles per day, numbers that TechCrunch confirmed with a few micromobility operators and that are well within the range of the Squad car.
Squad also intends to equip its vehicles with cameras, sensors and other smart features like remote diagnostics and maintenance, which will make the company more attractive to shared operators looking for a fleet that can be integrated into its management platforms. Hoevers also says he and his co-founder, Chris Klok, have used their collective 40 years of experience in mobility and shared past at long range solar EV company Lightyear to develop a strong CAN bus and drivetrain upon which new features can be added.
Whether Squad ends up selling fleets to micromobility platforms or car-sharing platforms might depend on the category in which the vehicle ends up. With its current speed and weight, the Squad car will be in the L6e category for light four-wheeled vehicles.
“There are interesting cost and tax benefits in this segment,” said Hoevers. “For example, there is no congestion charge, no road tax, no parking fees, low insurance fees and no car driving license needed in most markets.”
Hoevers said the company is also considering producing a more powerful L7 that can go top speeds of around 45 miles per hour, which might be better for cities with more hills.
Squad isn’t the only company that has added solar panels to its electric vehicles. Germany-based startup Sono Motors told TechCrunch that it’s on track to begin deliveries of its electric Sion vehicle by 2023. The vehicle’s exterior is composed of hundreds of solar cells that have been integrated into polymer instead of glass and can add up to nearly 22 miles of extra battery life per day.
Although the Sion has not yet been released, the Sono app is already inviting owners of the vehicle to engage in a sort of car sharing that’s reminiscent of Airbnb for Sions in order to make use of vehicles that otherwise sit parked and useless for most of the day. As of Thursday, Sono is expanding this vision to allow any car to be shared via the Sono app.
Aptera Motors, a California company that has promised to roll out the “first mass-produced solar car” this year, raised $4 million in a Series A this February that it is using to pay for fiberglass, carbon fiber and batteries for its spaceship-looking tricycle. Aptera says its vehicle, which is available for pre-order and could cost anywhere between $25,900 and $46,900, will be built with 34 square feet of solar cells that can add an additional 40 miles of battery capacity on a clear day.
Each of the players in the solar-powered EV space have differences in tech, path to market and style, but they’re all potentially finding ways to ease the strain on the electrical grid.
In the Netherlands, new electric cars make up 25% of total market share, and that number will only increase. It might not be feasible in the long run for all of those vehicles to each plug into the grid to power up, especially when industries across sectors are beginning to electrify.
While it’s clear that the technology isn’t there yet for vehicles to run purely on solar, Squad and other companies like it are laying the groundwork for future solar technology.
Powered by WPeMatico
Southeast Asian tech companies are drawing the attention of investors around the world. In 2020, startups in the region raised over $8.2 billion, about four times more than they did in 2015. This trend continued in 2021, with regional M&A hitting a record high of $124.8 billion in the first half of 2021, up 83% from a year earlier.
This begs the question: Who exactly is investing in Southeast Asia?
Let’s explore the three key types of investors pouring money into and driving the growth of Southeast Asia’s tech ecosystem.
Over 229 family offices have been registered in Singapore since 2020, with total assets under management of an estimated $20 billion.
Southeast Asia has become an attractive market for U.S. and Chinese tech firms. Internet penetration here stands at 70%, higher than the global average, and digital adoption in the region remains nascent — it wasn’t until the pandemic that adoption of digital services such as e-wallets and online shopping took off.
China’s tech giants Tencent and Alibaba were among the first to support early e-commerce growth in Southeast Asia with investments in Sea Limited and Lazada, and have since expanded their footprint into other internet verticals. Alibaba has backed Akulaku, M-Pay (eMonkey), DANA, Wave Money and Mynt (GCash), while Tencent has invested in Voyager Innovations (PayMaya), SHAREit, iflix, Ookbee and Sanook.
U.S. tech firms have also recently entered the scene. In June 2020, Gojek closed a $3 billion Series F round from Google, Facebook, Tencent and Visa. Google, together with Singapore’s Temasek Holdings, invested some $350 million in Tokopedia in October. Meanwhile, Microsoft invested an undisclosed amount in Grab in 2018 and has invested $100 million in Indonesian e-commerce firm Bukalapak.
In Q1 2021, Southeast Asian startups raised $6 billion, according to DealStreetAsia, positioning 2021 as another record year for VC investment in the region.
The region is also rising in prominence as a destination for investment capital relative to the rest of Asia. Regional VC investment grew 5.2 times to $8.2 billion in 2020 from $1.6 billion in 2015, as we can see in the table below.
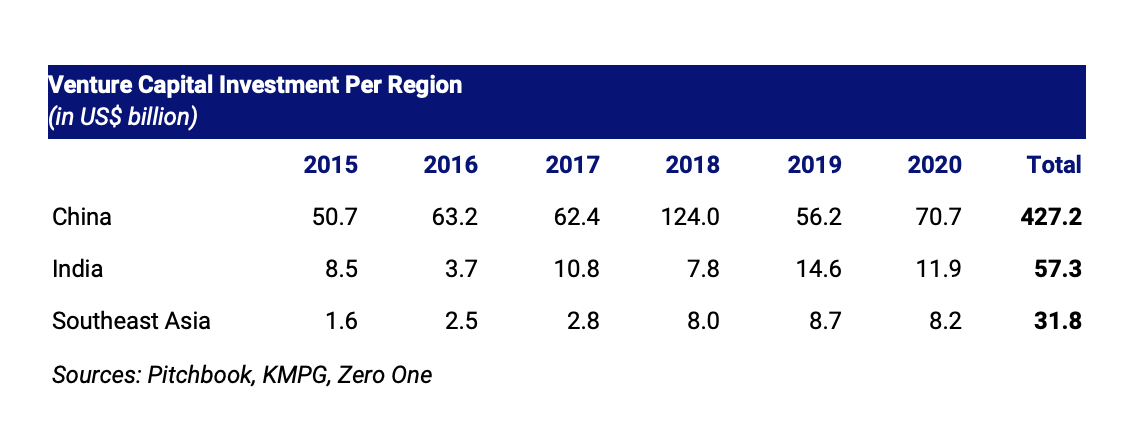
Image Credits: Jungle VC
Southeast Asia also has many opportunities for VC investment relative to its market size. From 2015 to 2020, China saw VC investment of nearly $300 per person; for Southeast Asia — despite a recent investment boom — this metric sits at just $47.50 per person, or just a sixth of that in China. This implies a substantial opportunity for investments to develop the region’s digital economy.
The region’s rising population and growth prospects are higher due to China’s population growth challenges, alongside the latter’s higher digital economy market saturation and maturity.
Powered by WPeMatico
Relationships ultimately close deals, but long-term relationships come with a lot of baggage, i.e. email interactions, documents and meetings.
Affinity wants to take what Ray Zhou, co-founder and CEO, refers to as “data exhaust,” all of those daily interactions and communications, and apply machine learning analysis and provide insights on who in the organization has the best chance of getting that initial meeting and closing the deal.
Today, the company announced $80 million in Series C funding, led by Menlo Ventures, which was joined by Advance Venture Partners, Sprints Capital, Pear Ventures, Sway Ventures, MassMutual Ventures, Teamworthy and ECT Capital Partners’ Brian N. Sheth. The new funding gives the company $120 million in total funding since it was founded in 2014.
Affinity, based in San Francisco, is focused on industries like investment banking, private equity, venture capital, consulting and real estate, where Zhou told TechCrunch there aren’t customer relationship management systems or networking platforms that cater to the specific needs of the long-term relationship.
Stanford grads Zhou and co-founder Shubham Goel started the company after recognizing that while there was software for transactional relationships, there wasn’t a good option for the relationship journeys.
He cites data that show up to 90% of company profiles and contact information living in traditional CRM systems are incomplete or out of date. This comes as market researcher Gartner reported the global CRM software market grew 12.6% to $69 billion in 2020.
“It is almost bigger than sales,” Zhou said. “Our worldview is that relationships are the biggest industries in the world. Some would disagree, but relationships are an asset class, they are a currency that separates the winners from the losers.”
Instead, Affinity created “a new breed of CRM,” Zhou said, that automates the inputting of that data constantly and adds information, like revenue, staff size and funding from proprietary data sources, to assign a score to a potential opportunity and increase the chances of closing a deal.
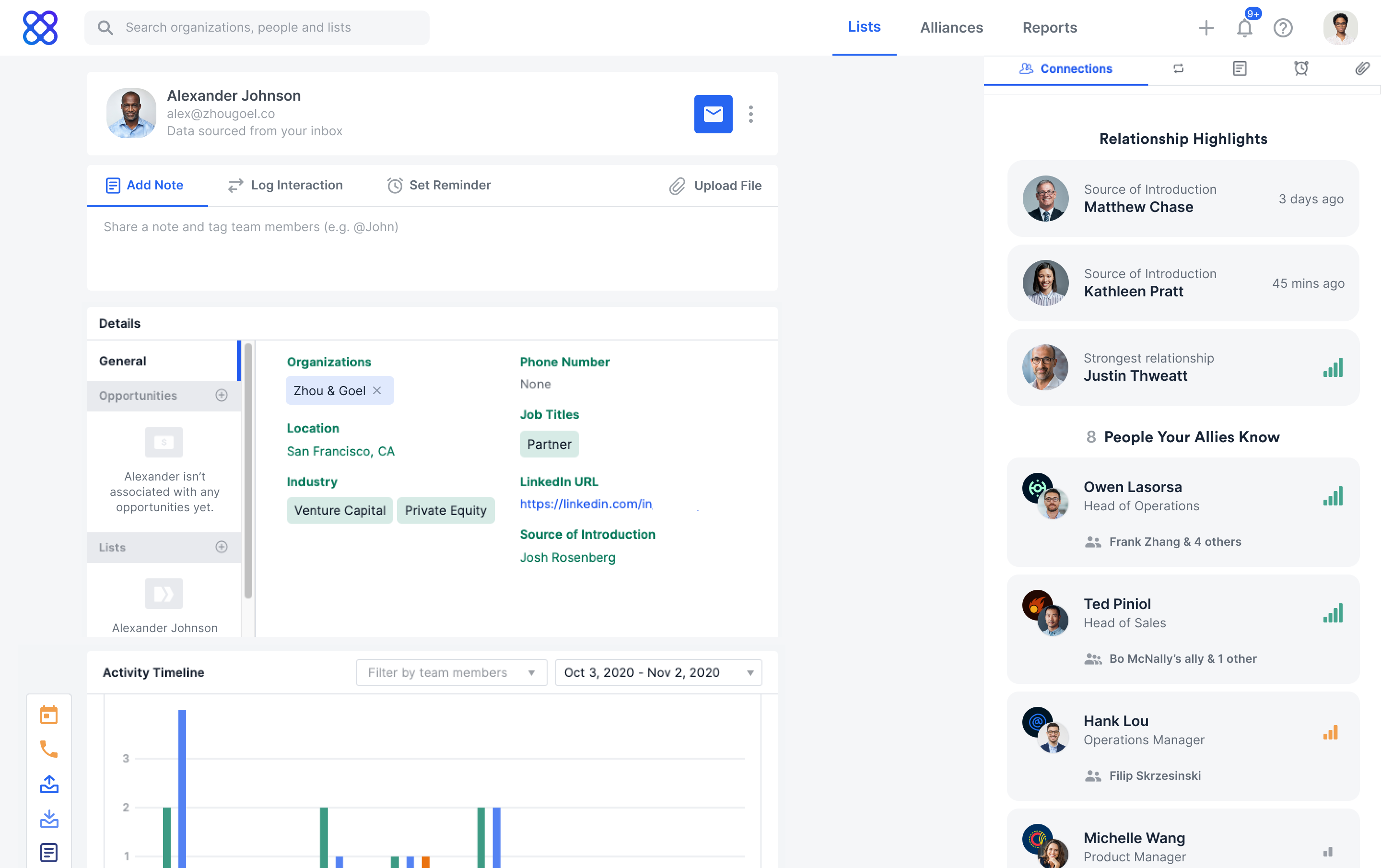
Affinity people profile. Image Credits: Affinity
He intends to use the new funding to expand sales, marketing and engineering to support new products and customers. The company has 125 employees currently; Zhou expects to be over 200 by next year.
To date, the company’s platform has analyzed over 18 trillion emails and 213 million calendar events and currently drives over 500,000 new introductions and tracks 450,000 deals per month. It also has more than 1,700 customers in 70 countries, boasting a list that includes Bain Capital Ventures, Kleiner Perkins, SoftBank Group, Nike, Qualcomm and Twilio.
Tyler Sosin, partner at Menlo Ventures, said he met Zhou and Goel at a time when the firm was looking into CRM companies, but it wasn’t until years later that Affinity came up again when Menlo itself wanted to work with a more modern platform.
As a user of Affinity himself, Sosin said the platform gives him the data he cares about and “removes the manual drudgery of entry and friction in the process.” Affinity also built a product that was intuitive to navigate.
“We have always had an interest in getting CRMs to the next generation, and Affinity is defining itself in a new category of relationship intelligence and just crushing it in the private capital markets,” he said. “They are scaling at an impressive growth rate and solving a hard problem that we don’t see many other companies in the space doing.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Work insights platform Fin raised $20 million in Series A funding and brought in Evan Cummack, a former Twilio executive, as its new chief executive officer.
The San Francisco-based company captures employee workflow data from across applications and turns it into productivity insights to improve the way enterprise teams work and remain engaged.
Fin was founded in 2015 by Andrew Kortina, co-founder of Venmo, and Facebook’s former VP of product and Slow Ventures partner Sam Lessin. Initially, the company was doing voice assistant technology — think Alexa but powered by humans and machine learning — and then workplace analytics software in 2020. You can read more about Fin’s origins at the link below.
The new round was led by Coatue, with participation from First Round Capital, Accel and Kleiner Perkins. The original team was talented, but small, so the new funding will build out sales, marketing and engineering teams, Cummack said.
“At that point, the right thing was to raise money, so at the end of last year, the company raised a $20 million Series A, and it was also decided to find a leadership team that knows how to build an enterprise,” Cummack told TechCrunch. “The company had completely pivoted and removed ‘Analytics’ from our name because it was not encompassing what we do.”
Fin’s software measures productivity and provides insights on ways managers can optimize processes, coach their employees and see how teams are actually using technology to get their work done. At the same time, employees are able to manage their workflow and highlight areas where there may be bottlenecks. All combined, it leads to better operations and customer experiences, Cummack said.
Graphic showing how work is really done. Image Credits: Fin
Fin’s view is that as more automation occurs, the company is looking at a “renaissance of human work.” There will be more jobs and more types of jobs, but people will be able to do them more effectively and the work will be more fulfilling, he added.
Particularly with the use of technology, he notes that in the era before cloud computing, there was a small number of software vendors. Now with the average tech company using over 130 SaaS apps, it allows for a lot of entrepreneurs and adoption of best-in-breed apps so that a viable company can start with a handful of people and leverage those apps to gain big customers.
“It’s different for enterprise customers, though, to understand that investment and what they are spending their money on as they use tools to get their jobs done,” Cummack added. “There is massive pressure to improve the customer experience and move quickly. Now with many people working from home, Fin enables you to look at all 130 apps as if they are one and how they are being used.”
As a result, Fin’s customers are seeing metrics like 16% increase in team utilization and engagement, a 25% decrease in support ticket handle time and a 71% increase in policy compliance. Meanwhile, the company itself is doubling and tripling its customers and revenue each year.
Now with leadership and people in place, Cummack said the company is positioned to scale, though it already had a huge head start in terms of a meaningful business.
Arielle Zuckerberg, partner at Coatue, said via email that she was part of a previous firm that invested in Fin’s seed round to build a virtual assistant. She was also a customer of Fin Assistant until it was discontinued.
When she heard the company was pivoting to enterprise, she “was excited because I thought it was a natural outgrowth of the previous business, had a lot of potential and I was already familiar with management and thought highly of them.”
She believed the “brains” of the company always revolved around understanding and measuring what assistants were doing to complete a task as a way to create opportunities for improvement or automation. The pivot to agent-facing tools made sense to Zuckerberg, but it wasn’t until the global pandemic that it clicked.
“Service teams were forced to go remote overnight, and companies had little to no visibility into what people were doing working from home,” she added. “In this remote environment, we thought that Fin’s product was incredibly well-suited to address the challenges of managing a growing remote support team, and that over time, their unique data set of how people use various apps and tools to complete tasks can help business leaders improve the future of work for their team members. We believe that contact center agents going remote was inevitable even before COVID, but COVID was a huge accelerant and created a compelling ‘why now’ moment for Fin’s solution.”
Going forward, Coatue sees Fin as “a process mining company that is focused on service teams.” By initially focusing on customer support and contact center use case — a business large enough to support a scaled, standalone business — rather than joining competitors in going after Fortune 500 companies where implementation cycles are long and there is slow time-to-value, Zuckerberg said Fin is better able to “address the unique challenges of managing a growing remote support team with a near-immediate time-to-value.”
Powered by WPeMatico
A Canadian startup called Nuula that is aiming to build a super app to provide a range of financial services to small and medium businesses has closed $120 million of funding, money that it will use to fuel the launch of its app and first product, a line of credit for its users.
The money is coming in the form of $20 million in equity from Edison Partners, and a $100 million credit facility from funds managed by the Credit Group of Ares Management Corporation.
The Nuula app has been in a limited beta since June of this year. The plan is to open it up to general availability soon, while also gradually bringing in more services, some built directly by Nuula itself but many others following an embedded finance strategy: business banking, for example, will be a service provided by a third party and integrated closely into the Nuula app to be launched early in 2022. Alongside that, the startup will also be making liberal use of APIs to bring in other white-label services, such as B2B and customer-focused payment services, starting first in the U.S. and then expanding to Canada and the U.K. before expanding further into countries across Europe.
Current products include cash flow forecasting, personal and business credit score monitoring, and customer sentiment tracking; and monitoring of other critical metrics including financial, payments and e-commerce data are all on the roadmap.
“We’re building tools to work in a complementary fashion in the app,” CEO Mark Ruddock said in an interview. “Today, businesses can project if they are likely to run out of money, and monitor their credit scores. We keep an eye on customers and what they are saying in real time. We think it’s necessary to surface for SMBs the metrics that they might have needed to get from multiple apps, all in one place.”
Nuula was originally a side-project at BFS, a company that focused on small business lending, where the company started to look at the idea of how to better leverage data to build out a wider set of services addressing the same segment of the market. BFS grew to be a substantial business in its own right (and it had raised its own money to that end, to the tune of $184 million from Edison and Honeywell). Over time, it became apparent to management that the data aspect, and this concept of a super app, would be key to how to grow the business, and so it pivoted and rebranded earlier this year, launching the beta of the app after that.
Nuula’s ambitions fall within a bigger trend in the market. Small and medium enterprises have shaped up to be a huge business opportunity in the world of fintech in the last several years. Long ignored in favor of building solutions either for the giant consumer market, or the lucrative large enterprise sector, SMBs have proven that they want and are willing to invest in better and newer technology to run their businesses, and that’s leading to a rush of startups and bigger tech companies bringing services to the market to cater to that.
Super apps are also a big area of interest in the world of fintech, although up to now a lot of what we’ve heard about in that area has been aimed at consumers — just the kind of innovation rut that Nuula is trying to get moving.
“Despite the growth in services addressing the SMB sector, overall it still lacks innovation compared to consumer or enterprise services,” Ruddock said. “We thought there was some opportunity to bring new thinking to the space. We see this as the app that SMBs will want to use everyday, because we’ll provide useful tools, insights and capital to power their businesses.”
Nuula’s priority to build the data services that connect all of this together is very much in keeping with how a lot of neobanks are also developing services and investing in what they see as their unique selling point. The theory goes like this: banking services are, at the end of the day, the same everywhere you go, and therefore commoditized, and so the more unique value-added for companies will come from innovating with more interesting algorithms and other data-based insights and analytics to give more power to their users to make the best use of what they have at their disposal.
It will not be alone in addressing that market. Others building fintech for SMBs include Selina, ANNA, Amex’s Kabbage (an early mover in using big data to help loan money to SMBs and build other financial services for them), Novo, Atom Bank, Xepelin and Liberis, biggies like Stripe, Square and PayPal, and many others.
The credit product that Nuula has built so far is a taster of how it hopes to be a useful tool for SMBs, not just another place to get money or manage it. It’s not a direct loaning service, but rather something that is closely linked to monitoring a customers’ incomings and outgoings and only prompts a credit line (which directly links into the users’ account, wherever it is) when it appears that it might be needed.
“Innovations in financial technology have largely democratized who can become the next big player in small business finance,” added Gary Golding, General Partner, Edison Partners. “By combining critical financial performance tools and insights into a single interface, Nuula represents a new class of financial services technology for small business, and we are excited by the potential of the firm.”
“We are excited to be working with Nuula as they build a unique financial services resource for small businesses and entrepreneurs,” said Jeffrey Kramer, Partner and Head of ABS in the Alternative Credit strategy of the Ares Credit Group, in a statement. “The evolution of financial technology continues to open opportunities for innovation and the emergence of new industry participants. We look forward to seeing Nuula’s experienced team of technologists, data scientists and financial service veterans bring a new generation of small business financial services solutions to market.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Earlier this year, Apple officially discontinued Music Memos, an iPhone app that allowed musicians to quickly record audio and develop new song ideas. Now, a new startup called Tape It is stepping in to fill the void with an app that improves audio recordings by offering a variety of features, including higher-quality sound, automatic instrument detection, support for markers, notes and images, and more.
The idea for Tape It comes from two friends and musicians, Thomas Walther and Jan Nash.
Walther had previously spent three and a half years at Spotify, following its 2017 acquisition of the audio detection startup Sonalytic, which he had co-founded. Nash, meanwhile, is a classically trained opera singer, who also plays bass and is an engineer.
They’re joined by designer and musician Christian Crusius, previously of the design consultancy Fjord, which was acquired by Accenture.
The founders, who had played in a band together for many years, were inspired to build Tape It because it was something they wanted for themselves, Walther says. After ending his stint at Spotify working in their new Soundtrap division (an online music startup Spotify also bought in 2017), he knew he wanted to work on a project that was more focused on the music-making side of things. But while Soundtrap worked for some, it wasn’t what either Walther or his friends had needed. Instead, they wanted a simple tool that would allow them to record their music with their phone — something that musicians often do today using Apple’s Voice Memos app and, briefly, Music Memos — until its demise.

Image Credits: Tape It
“Regardless of whether you’re an amateur or even like a touring professional…you will record your ideas with your phone, just because that’s what you have with you,” Walther explains. “It’s the exact same thing with cameras — the best camera is the one you have with you. And the best audio recording tool is the one you have with you.”
That is, when you want to record, the easiest thing to do is not to get out your laptop and connect a bunch of cables to it, then load up your studio software — it’s to hit the record button on your iPhone.
The Tape It app allows you to do just that, but adds other features that make it more competitive with its built-in competition, Voice Memos.
When you record using Tape It, the app leverages AI to automatically detect the instrument, then annotate the recording with a visual indication to make those recordings easier to find by looking for the colorful icon. Musicians can also add their own markers to the files right when they record them, then add notes and photos to remind themselves of other details. This can be useful when reviewing the recordings later on, Walther says.

Image Credits: Tape It
“If I have a nice guitar sound, I can just take a picture of the settings on my amplifier, and I have them. This is something musicians do all the time,” he notes. “It’s the easiest way to re-create that sound.”
Another novel, but simple, change in Tape It is it that breaks longer recordings into multiple lines, similar to a paragraph of text. The team calls this the “Time Paragraph,” and believes it will make listening to longer sessions easier than the default — which is typically a single, horizontally scrollable recording.
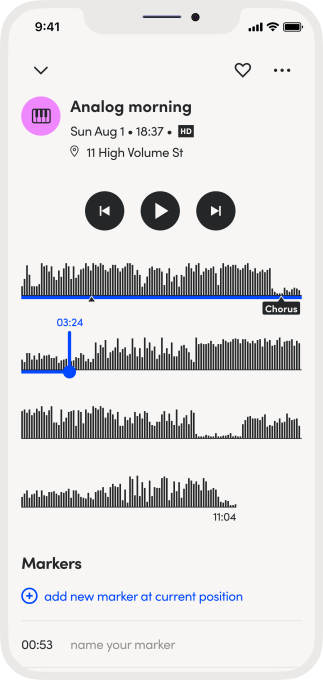
Image Credits: Tape It
The app has also been designed so it’s easier to go back to the right part of recordings, thanks to its smart waveforms, in addition to the optional markers and photos. And you can mark recordings as favorites so you can quickly pull up a list of your best ideas and sounds. The app offers full media center integration as well, so you can play back your music whenever you have time.
However, the standout feature is Tape It’s support for “Stereo HD” quality. Here, the app takes advantage of the two microphones on devices like the iPhone XS, XR, and other newer models, then improves the sound using AI technology and other noise reduction techniques, which it’s developed in-house. This feature is part of its $20 per year premium subscription.
Over time, Tape It intends to broaden its use of AI and other IP to improve the sound quality further. It also plans to introduce collaborative features and support for importing and exporting recordings into professional studio software. This could eventually place Tape It into the same market that SoundCloud had initially chased before it shifted its focus to becoming more of a consumer-facing service.
But first, Tape It wants to nail the single-user workflow before adding on more sharing features.
“We decided that it’s so important to make sure it’s useful, even just for you. The stuff that you can collaborate on — if you don’t like using it yourself, you’re not going to use it,” Walther says.
Tape It’s team of three is based in Stockholm and Berlin and is currently bootstrapping.
The app itself is a free download on iOS and will later support desktop users on Mac and Windows. An Android version is not planned.
Powered by WPeMatico
As companies try to navigate an ever-changing security landscape, it can be challenging to protect everything. Security startup TrueFort has built a zero trust solution focusing on protecting enterprise applications. Today, the company announced a $30 million Series B.
Shasta Ventures led today’s round with participation from new firms Canaan and Ericsson Ventures along with existing investors Evolution Equity Partners, Lytical Ventures and Emerald Development Managers. Under the terms of the agreement Nitin Chopra, managing director at Shasta Ventures, will be joining the company board. Today’s investment brings the total raised to almost $48 million.
CEO and co-founder Sameer Malhotra says that TrueFort protects customers by analyzing at each application and figuring out what normal behavior looks like. Once it understands that, it will flag anything that falls outside of the norm. The company achieves this by gathering data from partners like CrowdStrike and from multiple points within the application and infrastructure.
“Once we get this telemetry, whether it’s networks, endpoints, servers or third-party partners, we then help the customer build a picture of what those applications are doing and what’s normal behavior. We then help them baseline that, and monitor that in real time with response and real-time controls to continue those applications through their normal life cycle,” he said.
Zero trust is a concept where as a matter of policy you assume that you cannot trust any individual or device until the entity proves it belongs on your systems. Malhotra says that customers are becoming more comfortable with the concept and in 2020 the company saw massive 650% YoY revenue growth, with it up 120% YoY this year so far.
“We are seeing the demand, especially as zero trust is becoming a more familiar vernacular amongst the security community […]. Again, it’s having the visibility and understanding, and then being able to then reduce it to the limited number of acceptable relationships or executions,” he said. And he believes that it all comes down to understanding your applications and how they operate.

TrueFort co-founders Nazario Parsacala and Sameer Malhotra. Image Credits: TrueFort
The company currently has 60 employees, with hopes of reaching 85 or 90 by the end of the year. Malhotra says that as they build the employee base, they are driving to make it diverse at every level.
“We look at diversity across our whole management team, all the way from the board down to our different levels. We are quite aggressive in hiring diverse candidates, whether they’re women or LGBTQ or people of color. And we have focused programs where we work with different universities […] to bring on new employees from a diverse talent pool. We also work with different recruiters from that perspective, and our focus is always to look at a different palette and to make sure that we’re as diverse an organization as we can,” he said.
The company was founded in 2015 by Malhotra and his partner Nazario Parsacala, both of whom spent more than 20 years working at big financial services companies — Goldman Sachs and JP Morgan. They worked for a couple of years building the program, launching the first beta in 2017 before bringing the first generally available product to market the following year.
Currently customers can install the solution on prem or in the cloud of their choice, but the company has a SaaS solution in the works as well, that will be ready in the next couple of months.
Powered by WPeMatico
Mayors have the toughest job in the world, and leading a city is only getting harder. Even as populations swell in urban cores across the world, climate change is constraining the geographies where that growth can happen. Coastal communities that are popular with residents are also taking a gamble when it comes to rising sea levels. How do you trade off a need for growth with the requirement for protecting residents from disaster?
In most cases, the pendulum is fully tilted toward growth. Coastal towns continue to allow widespread sprawl and development, chasing ever more property taxes and residents even as sea levels get ever more uncomfortably high. It’s a recipe for disaster — and one that many cities have chosen to bake anyway.
Forerunner wants that pendulum to swing the other way. Its platform allows city planners and building managers to survey, investigate and enforce stricter building codes and land use standards with a focus on mitigating future flood damage. It’s particularly focused on American cities with heavy usage of the federal flood insurance program, and Forerunner helps cities maximize their adherence to that program’s byzantine rules.

Image Credits: Forerunner
The company pulls in data from FEMA and other sources to determine a property’s mandatory lowest floor height requirement, and whether the property conforms to that rule. It also tracks flood zone boundaries and helps with the administrative overhead of processing federal flood insurance documentation, such as creating and managing elevation certificates.
Co-founders JT White and Susanna Pho have been friends for years and worked at the MIT Media Lab before eventually coming together in early 2019 to build out this floodplain management product. “It cannot be underscored enough that a lot of communities just don’t follow [federal flood] regulations,” Pho said. “They will revert their ordinances from something more strict … since they can’t do a lot of day-to-day compliance.”
Coastal cities devastated by floods are protected by federal flood insurance, but that often creates a moral hazard: since damage is paid for, there isn’t much incentive to avoid it in the first place. The federal government is attempting to tighten those standards, and there is also a sense among a new generation of city planners and municipal leaders that the build-devastation-rebuild model of many cities needs to stop, given climate change. After flooding, “we want to see communities rebuild to higher standards,” White said. “The sort of cycle of rebuilding and doing the same thing over and over again is infuriating to us.”
Transitioning to a new model isn’t easy of course. “There are a lot of hard decisions that these communities must make,” he said, but “our software makes it a bit easier to do these things.” So far, the company has gotten early traction, with 33 communities currently using Forerunner, according to the founders.
Although it has customer clusters in Louisiana and northern New Jersey, the company’s largest customer is Harris County, which includes much of the Houston, Texas metro area. The county could potentially save $5 million on their flood insurance premiums with better adherence to federal standards, according to White. “One of the benefits of our product is that we can help you protect and increase this immediate discount to every flood insurance policyholder in your community starting next year,” he said. Ultimately though, FEMA focuses on disincentives rather than incentives. “The biggest stick that FEMA has is that it can suspend communities from the flood insurance program,” he noted.
The company raised an early seed round in 2019, and has been focused on building up the platform’s capabilities and getting the sales flywheel spinning — which can be a tough order in the govtech space.
Even as demand intensifies for more housing and growth, climate change is simultaneously placing its own demands on cities. Mayors and city leaders are increasingly going to have to transition from the growth models of the past to the resilient models of the future.
Powered by WPeMatico
Organizations are swimming in data these days, and so solutions to help manage and use that data in more efficient ways will continue to see a lot of attention and business. In the latest development, SingleStore — which provides a platform to enterprises to help them integrate, monitor and query their data as a single entity, regardless of whether that data is stored in multiple repositories — is announcing another $80 million in funding, money that it will be using to continue investing in its platform, hiring more talent and overall business expansion. Sources close to the company tell us that the company’s valuation has grown to $940 million.
The round, a Series F, is being led by Insight Partners, with new investor Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and previous backers Khosla Ventures, Dell Technologies Capital, Rev IV, Glynn Capital and GV (formerly Google Ventures) also participating. The startup has to date raised $264 million, including most recently an $80 million Series E last December, just on the heels of rebranding from MemSQL.
The fact that there are three major strategic investors in this Series F — HPE, Dell and Google — may say something about the traction that SingleStore is seeing, but so too do its numbers: 300%+ increase in new customer acquisition for its cloud service and 150%+ year-over-year growth in cloud.
Raj Verma, SingleStore’s CEO, said in an interview that its cloud revenues have grown by 150% year over year and now account for some 40% of all revenues (up from 10% a year ago). New customer numbers, meanwhile, have grown by over 300%.
“The flywheel is now turning around,” Verma said. “We didn’t need this money. We’ve barely touched our Series E. But I think there has been a general sentiment among our board and management that we are now ready for the prime time. We think SingleStore is one of the best-kept secrets in the database market. Now we want to aggressively be an option for people looking for a platform for intensive data applications or if they want to consolidate databases to one from three, five or seven repositories. We are where the world is going: real-time insights.”
With database management and the need for more efficient and cost-effective tools to manage that becoming an ever-growing priority — one that definitely got a fillip in the last 18 months with COVID-19 pushing people into more remote working environments. That means SingleStore is not without competitors, with others in the same space, including Amazon, Microsoft, Snowflake, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Redis and more. Others like Firebolt are tackling the challenges of handing large, disparate data repositories from another angle. (Some of these, I should point out, are also partners: SingleStore works with data stored on AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform and Red Hat, and Verma describes those who do compute work as “not database companies; they are using their database capabilities for consumption for cloud compute.”)
But the company has carved a place for itself with enterprises and has thousands now on its books, including GE, IEX Cloud, Go Guardian, Palo Alto Networks, EOG Resources and SiriusXM + Pandora.
“SingleStore’s first-of-a-kind cloud database is unmatched in speed, scale, and simplicity by anything in the market,” said Lonne Jaffe, managing director at Insight Partners, in a statement. “SingleStore’s differentiated technology allows customers to unify real-time transactions and analytics in a single database.” Vinod Khosla from Khosla Ventures added that “SingleStore is able to reduce data sprawl, run anywhere, and run faster with a single database, replacing legacy databases with the modern cloud.”
Powered by WPeMatico
PayPal Holdings, the U.S. fintech company, announced an acquisition of Paidy, a Japanese buy now, pay later (BNPL) service platform, for approximately $2.7 billion (300 billion yen), mostly in cash, to enhance its business in Japan.
The transaction completion, including the regulatory approval, is expected in the fourth quarter of 2021.
After the acquisition, the Japan-based company will continue to operate its existing business and maintain the brand while the leaders, Paidy’s president and CEO Riku Sugie and founder and executive chairman Russell Cummer, keep their positions.
Japan is the third largest e-commerce market in the world, and so this is a significant move by PayPal to gain more market share both in the country and the region, specifically in the area of providing deferred payment services as an alternative to credit cards.
PayPal has long played nice with payment cards — users can upload details of their cards to PayPal and use it as a kind of digital wallet to manage how they pay for things online through it — but it got its start actually as a payment platform in itself, where people could pay into and out of PayPal accounts. Paidy is, in that sense, a strengthening of PayPal’s first-party rails, providing a way to “own” that flow of money on its own infrastructure, not involving the card networks.
Paidy is basically a two-sided payments service, acting as a middleman between consumers and merchants in Japan. Using machine learning it determines the creditworthiness of a consumer related to a particular purchase, and then it underwrites those transactions in seconds, guaranteeing payments to merchants. Consumers then make deferred payment to Paidy for those goods.
Paidy’s platform, which offers a monthly payment installment service branded “3-Pay”, enables shoppers to make purchases online and then pay for them each month in a consolidated bill at a convenience store or via bank transfer.
“Paidy pioneered buy now, pay later solutions tailored to the Japanese market and quickly grew to become the leading service, developing a sizable two-sided platform of consumers and merchants,” said Peter Kenevan, vice president, head of Japan at PayPal.
Paidy has more than 6 million registered users, and the plan is to integrate PayPal and other digital and QR wallets with Paidy Link to connect further online and offline merchants.
In April 2021, the Japan-based company launched Paidy Link, allowing users to link digital wallets with their Paidy account. PayPal was the first digital wallet partner to integrate with Paidy Link.
“PayPal was a founding partner for Paidy Link and we look forward to looking together to create even more value,” Sugie said in a statement.
“Japan has been a vibrant environment for our growth to date and we’re honored to have our team’s hard work and potential recognized by a global leader. Together with PayPal, we will be able to further achieve our mission of taking the hassle out of shopping,” Cummer said.
Powered by WPeMatico