Startups
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Startups Weekly, a weekend newsletter that dives into the week’s noteworthy startups and venture capital news. Before I jump into today’s topic, let’s catch up a bit. Last week, I noted some challenges plaguing mental health tech startups. Before that, I wrote about Zoom and Superhuman’s PR disasters.
Remember, you can send me tips, suggestions and feedback to kate.clark@techcrunch.com or on Twitter @KateClarkTweets. If you don’t subscribe to Startups Weekly yet, you can do that here.
Anyway, onto the subject on everyone’s mind this week: SoftBank’s second Vision Fund.
Well into the evening on Thursday, SoftBank announced a target of $108 billion for the Vision Fund 2. Yes, you read that correctly, $108 billion. SoftBank indeed plans to raise even more capital for its sophomore vehicle than it did for the record-breaking debut vision fund of $98 billion, which was majority-backed by the government funds of Saudi Arabia and Abu Dhabi, as well as Apple, Foxconn and several other limited partners.
Its upcoming fund, to which SoftBank itself has committed $38 billion, has attracted investment from the National Investment Corporation of National Bank of Kazakhstan, Apple, Foxconn, Goldman Sachs, Microsoft and more. Microsoft, a new LP for SoftBank, reportedly hopped on board with the Japanese telecom giant as part of a grand scheme to convince the massive fund’s portfolio companies to transition to Microsoft Azure, the company’s cloud platform that competes with Amazon Web Services . Here’s more on that and some analysis from TechCrunch editor Jonathan Shieber.
News of the second Vision Fund comes as somewhat of a surprise. We’d heard SoftBank was having some trouble landing commitments for the effort. Why? Well, because SoftBank’s investments have included a wide-range of upstarts, including some uncertain bets. Brandless, a company into which SoftBank injected a lot of money, has struggled in recent months, for example. Wag is said to be going downhill fast. And WeWork, backed with billions from SoftBank, still has a lot to prove.
Here’s everything else we know about The Vision Fund 2:
On to other news…

WeWork is planning a September listing
The company made headlines again this week after word slipped it was accelerating its IPO plans and targeting a September listing. We don’t know much about its IPO plans yet as we are still waiting on the co-working business to unveil its S-1 filing. Whether WeWork can match or exceed its current private market valuation of $47 billion is unlikely. I expect it will pull an Uber and struggle, for quite some time, to earn a market cap larger than what VCs imagined it was worth months earlier.
The consumer financial app made headlines twice this week. The first time because it raised a whopping $323 million at a $7.6 billion valuation. That is a whole lot of money for a business that just raised a similarly sized monster round one year ago. In fact, it left us wondering, why the hell is Robinhood worth $7.6 billion? Then, in a major security faux pas, the company revealed it has been storing user passwords in plaintext. So, go change your Robinhood password and don’t trust any business to value your security. Sigh.
Another day, another huge fintech round
While we’re on the subject on fintech, TechCrunch editor Danny Crichton noted this week the rise of mega-rounds in the fintech space. This week, it was personalized banking app MoneyLion, which raised $100 million at a near unicorn valuation. Last week, it was N26, which raised another $170 million on top of its $300 million round earlier this year. Brex raised another $100 million last month on top of its $125 million Series C from late last year. Meanwhile, companies like payments platform Stripe, savings and investment platform Raisin, traveler lender Uplift, mortgage backers Blend and Better and savings depositor Acorns have also raised massive new rounds this year. Naturally, VC investment in fintech is poised to reach record levels this year, according to PitchBook.
Arianna Huffington, the CEO of Thrive Global, stepped down from Uber’s board of directors this week, a team she had been apart of since 2016. She addressed the news in a tweet, explaining that there were no disagreements between her and the company, rather, she was busy and had other things to focus on. Fair. Benchmark’s Matt Cohler also stepped down from the board this week, which leads us to believe the ride-hailing giant’s advisors are in a period of transition. If you remember, Uber’s first employee and longtime board member Ryan Graves stepped down from the board in May, just after the company’s IPO.
Today I told my fellow @Uber board members that given @Thrive‘s growth, I will no longer be able to give my board duties the attention they deserve, so I will be stepping down. I look forward to watching Uber go from strength to strength! Here is the email I sent to the board: pic.twitter.com/sck0CPLwAV
— Arianna Huffington (@ariannahuff) July 24, 2019
Unity, now valued at $6B, raising up to $525M
Bird is raising a Sequoia-led Series D at $2.5B valuation
SMB payroll startup Gusto raises $200M Series D
Elon Musk’s Boring Company snags $120M
a16z values camping business HipCamp at $127M
An inside look at the startup behind Ashton Kutcher’s weird tweets
Dataplor raises $2M to digitize small businesses in Latin America
While we’re on the subject of amazing TechCrunch #content, it’s probably time for a reminder for all of you to sign up for Extra Crunch. For a low price, you can learn more about the startups and venture capital ecosystem through exclusive deep dives, Q&As, newsletters, resources and recommendations and fundamental startup how-to guides. Here are some of my current favorite EC posts:
If you enjoy this newsletter, be sure to check out TechCrunch’s venture-focused podcast, Equity. In this week’s episode, available here, Equity co-host Alex Wilhelm, TechCrunch editor Danny Crichton and I unpack Robinhood’s valuation and argue about scooter startups. Equity drops every Friday at 6:00 am PT, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast and Spotify.
That’s all, folks.
Powered by WPeMatico
Earlier this month, TechCrunch held its inaugural Mobility Sessions event, where leading mobility-focused auto companies, startups, executives and thought leaders joined us to discuss all things autonomous vehicle technology, micromobility and electric vehicles.
Extra Crunch is offering members access to full transcripts of key panels and conversations from the event, such as Megan Rose Dickey‘s chat with Voyage CEO and co-founder Oliver Cameron and Uber’s prediction team lead Clark Haynes on the ethical considerations for autonomous vehicles.
Megan, Oliver and Clark talk through how companies should be thinking about ethics when building out the self-driving ecosystem, while also diving into the technical aspects of actually building an ethical transportation product. The panelists also discuss how their respective organizations handle ethics, representation and access internally, and how their approaches have benefited their offerings.
Clark Haynes: So we as human drivers, we’re naturally what’s called foveate. Our eyes go forward and we have some mirrors that help us get some situational awareness. Self-driving cars don’t have that problem. Self-driving cars are designed with 360-degree sensors. They can see everything around them.
But the interesting problem is not everything around you is important. And so you need to be thinking through what are the things, the people, the actors in the world that you might be interacting with, and then really, really think through possible outcomes there.
I work on the prediction problem of what’s everyone doing? Certainly, you need to know that someone behind you is moving in a certain way in a certain direction. But maybe that thing that you’re not really certain what it is that’s up in front of you, that’s the thing where you need to be rolling out 10, 20 different scenarios of what might happen and make certain that you can kind of hedge your bets against all of those.
For access to the full transcription below and for the opportunity to read through additional event transcripts and recaps, become a member of Extra Crunch. Learn more and try it for free.
Megan Rose Dickey: Ready to talk some ethics?
Oliver Cameron: Born ready.
Clark Haynes: Absolutely.
Rose Dickey: I’m here with Oliver Cameron of Voyage, a self-driving car company that operates in communities, like retirement communities, for example. And with Clark Haynes of Uber, he’s on the prediction team for autonomous vehicles.
So some of you in the audience may remember, it was last October, MIT came out with something called the moral machine. And it essentially laid out 13 different scenarios involving self-driving cars where essentially someone had to die. It was either the old person or the young person, the black person, or the white person, three people versus one person. I’m sure you guys saw that, too.
So why is that not exactly the right way to be thinking about self-driving cars and ethics?
Haynes: This is the often-overused trolley problem of, “You can only do A or B choose one.” The big thing there is that if you’re actually faced with that as the hardest problem that you’re doing right now, you’ve already failed.
You should have been working harder to make certain you never ended up in a situation where you’re just choosing A or B. You should actually have been, a long time ago, looking at A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and like thinking through all possible outcomes as far as what your self-driving car could do, in low probability outcomes that might be happening.
Rose Dickey: Oliver, I remember actually, it was maybe a few months ago, you tweeted something about the trolley problem and how much you hate it.
Cameron: I think it’s one of those questions that doesn’t have an ideal answer today, because no one’s got self-driving cars deployed to tens of thousands of people experiencing these sorts of issues on the road. If we did an experiment, how many people here have ever faced that conundrum? Where they have to choose between a mother pushing a stroller with a child and a regular, normal person that’s just crossing the road?
Rose Dickey: We could have a quick show of hands. Has anyone been in that situation?
Powered by WPeMatico
A week is obviously not enough time to truly understand a market as massive and fascinating as China. Hell, it’s not really even enough time to adjust to the 12-hour time difference from New York. That said, each of the three visits I’ve taken to the country in the past two years has yielded some useful insights into my role as hardware editor here at TechCrunch.
Late last week, I got back from an eight-day trip to Shenzhen in the Guangdong Province of South China and nearby Hong Kong. In some respects, the cities are worlds apart, though a newly opened high-speed rail system has reduced the trip to 30 minutes. Customs issues aside, it’s the height of convenience. Though for political and cultural reasons I’ll not get into here, some have bemoaned the access it’s provided.
This particular visit was sort of a scouting trip. In November, TechCrunch will be hosting its first Hardware Battlefield event in a couple of years. Previous events had been held at CES for reasons of easy access to young startups. This time out, however, we’ve opted to go straight to the source.
Powered by WPeMatico
Another day, another mega round for a fintech startup. And this one is mega-mega.
Brazil-based Nubank, which offers a suite of banking and financial services for Brazilian consumers, announced today that it has raised a $400 million Series F round of venture capital led by Woody Marshall of TCV. The growth-stage fund is best known for its investment in Netflix but has also made fintech a high priority, with over $1.5 billion in investments in the space. According to Nubank, the company has now raised $820 million across seven venture rounds.
Katie Roof and Peter Rudegeair of The Wall Street Journal reported this morning that the company secured a valuation above $10 billion, potentially making it one of a short list of startup decacorns. That’s up from the $4 billion valuation we wrote about back in October 2018.
Part of the reason for that big-ticket round is the company’s growth. Nubank said in a statement that it has now reached 12 million customers for its various products, making it the sixth-largest financial institution by customer count within its home market. Brazil has a population of roughly 210 million people — indicating that there is still a lot of local growth potential even before the company begins to consider its international expansion options. Nubank announced a few weeks ago that it will start to expand its offerings to Mexico and Argentina.
Over the past year, the company has expanded its product offerings to include personal loans and cash withdrawal options as part of its digital savings accounts.
As I wrote earlier this week, part of the reason for these fintech mega-rounds is that the cost of acquiring a financial customer is critical to the success of these startups. Once a startup has a customer for one financial product — say, a savings account — it can then upsell customers to other products at a very low marketing cost. That appears to be the strategy at Nubank as well, with its quickly expanding suite of products.
As my colleague Jon Shieber discussed last month, critical connections between Stanford, Silicon Valley and Latin America have forged a surge of investment from venture capitalists into the region, as the continent experiences the same digital transformation seen elsewhere throughout the world. As just one example from the healthcare space, Dr Consulta raised more than nine figures to address the serious healthcare needs of Brazilian consumers. Additionally, SoftBank’s Vision Fund, which was rumored to be investing in Nubank earlier this year, has vowed to put $5 billion to work in the region and recently invested $231 million in fintech startup Creditas.
In an email from TCV, Woody Marshall said that, “Leveraging unique technology, David Vélez and his team are continuously pushing the boundaries of delivering best in class financial services, grounded in a culture of tech and innovation. Nubank has all the core tenets of what TCV looks for in preeminent franchise investments.”
NuBank was founded in 2013 by co-founders Adam Edward Wible, Cristina Junqueira, and David Velez. In addition to TCV, existing backers Tencent, DST Global, Sequoia Capital, Dragoneer, Ribbit Capital and Thrive Capital also participated in the round.
Powered by WPeMatico
It is a simple question with a complex answer. How does a startup get from zero to execution when negotiating contracts with potential customers that are large enterprises? The 800-pound gorillas. Situations in which your negotiating leverage is limited (often severely so).
As a commercial contracts attorney, clients often ask me about the one right way to approach deals. Many are looking for a cheat sheet of universal terms they should push for in contracts. But there is no one answer.
Deals are not cookie-cutter, and neither are the contracts on which they are built. That said, a basic framework can help provide startups with some grounding to better think about negotiations with large enterprises. The idea is to avoid over-lawyering, and instead approach the discussion with a legally prudent yet deal-centric mindset.
There are generally six overarching considerations as you head into negotiations with large, enterprise organizations.
Powered by WPeMatico
Unity’s private valuation is climbing but it’s growing unclear whether the company’s leadership is planning to take the 15-year-old gaming powerhouse public anytime soon.
The company announced today that is has received signed agreements from D1 Capital Partners, Canada Pension Plan Investment Board, Light Street Capital, Sequoia Capital, and Silver Lake Partners to fund a $525 million tender offer that will allow Unity’s common shareholders — the majority of which are early or current employees — to sell their shares in the company.
The tender offer gives employees “the opportunity for some liquidity,” Unity CFO Kim Jabal says. The total amount raised will depend on the enthusiasm of common shareholders to sell their stakes in Unity.
This event could potentially signify that the company is pushing back its timeline for an IPO, keeping employees that have been sitting on equity for several years happy as Unity labors on in private markets. It’s worth noting that the company has raised hundreds of million previously with the same intent of buying back employee shares.
It was reported earlier this year that Unity was targeting an IPO in the first half of 2020.
The company also confirmed that it wrapped up a $150M Series E funding round in May that doubled the company’s valuation to $6 billion. The announcement confirms the valuation we reported on in May though at a higher amount of capital raised.
SF-based Unity has more than 2,000 employees. The company builds developer tools which are used game studios to create video games across a number of platforms. The company claims that half of all games are created using the company’s game engine.
Powered by WPeMatico
Elon Musk’s SpaceX managed to pull off something very few people thought it could — by disrupting one of the most fixed markets in the world with some of the most entrenched and protected players ever to benefit from government contract arrangements: rocket launches. The success of SpaceX, and promising progress from other new launch providers, including Blue Origin and Rocket Lab, have encouraged interest in space-based innovation among entrepreneurs and investors alike. But is this a true boom, or just a blip?
There’s an argument for both at once, with one type of space startup rapidly descending to Earth in terms of commercialization timelines and potential upside, and the other remaining a difficult bet to make unless you’re comfortable with long timelines before any liquidity event and a lot of upfront investment.
There’s no question that one broad category of technology at least is a lot more addressable by early-stage companies (and by extension, traditional VC investment). The word “satellite” once described almost exclusively gigantic, extremely expensive hunks of sophisticated hardware, wherein each component would eat up the monthly burn rate of your average early-stage consumer tech venture.
Powered by WPeMatico
When it comes to VC, vehicles, and startups, Africa’s ride-hail markets are becoming a multi-wheeled and global affair.
The big players such as Uber and Bolt are competing in Kampala and Nairobi—where in addition to car-service—they offer rickshaw taxis. On-demand motorcycle startups are multiplying and piloting EVs with funds from international partners. And many ride-hail companies in Africa are adapting unique product solutions to local transit needs.
In this analysis, I take a look at the leading startups in the mobility space and how the future of transportation on the continent will increasingly come from new entrants.
Africa’s in the midst of digital innovation boom, the components of which are intersecting rapidly across its 54 countries and 1.2 billion people.
Smartphone penetration is improving and in 2017, the continent saw the largest global increase in internet users—20 percent.
By Partech data, the continent surpassed the $1 billion VC mark in 2018. And greater connectivity and venture funding are fueling thousands of startups in every imaginable sector, including digital-transit.
While reliable markets stats for the size and potential of Africa’s ride-hail markets are sparse, there are some indicators of the sector’s potential.
Car ownership and cars per capita in Africa is among the lowest in the world. Parallel to that, any eyes and ears survey of the continent’s big cities reveals that shared transport by buses, cars, or motorcycles is big business that’s already ingrained in consumer culture. Millions of people daily pay fares to pack onto East and West Africa’s Mutatu and Danfo minibuses and Okada and Boda Boda motorbike taxis.
As Africa continues to urbanize, converts to smartphones, and discretionary consumer spending continues to rise—it all adds up to suggest strong potential for conversion to on-demand mobility services.
Unsurprisingly, the most active markets for ride-hail startups and investment in Africa align with the continent’s top spots for VC and tech activity: primarily Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa.
Powered by WPeMatico
In 2017, Matthew Peltier walked barefoot into a pitch meeting with venture capitalists. Young, male, man bun intact, he certainly resembled the stereotypical successful entrepreneur, but it was his startup, an app designed to bring social media stars and their fans into conversation, that drew skepticism.
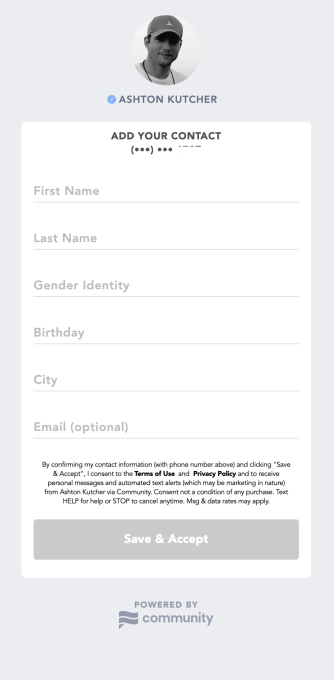
Shimmur, as it was called, ultimately succeeded in raising about $7 million from Greycroft, Arena Ventures, Luma Launch, Right Side Capital Management and Techstars, according to PitchBook, but the business never took off. That is until a pivot to direct messaging in 2018 attracted the support of Hollywood talent manager Guy Oseary and his Sound Ventures investment partner Ashton Kutcher, who jumped on board to relaunch Shimmur, now known as Community.
The Santa Monica-based company has raised nearly $35 million in the form of two convertible notes following a recapitalization that occurred alongside its rebranding earlier this year, TechCrunch has learned. Investors, including the Sony Innovation Fund, have valued the text marketing platform at upwards of $200 million, sources tell TechCrunch. A spokesperson for Community, however, said there is currently “no valuation attached to the company” because of the nature of the recap and convertible notes, and declined to comment further on fundraising activity.
Community has yet to complete a public launch and is in the process of onboarding both companies and celebrities. We’re told efforts to generate attention for the business will increase in the next couple of weeks.
Shimmur was initially conceived of in 2014 as a Reddit-style mobile application that encouraged users to join “Tribes,” or groups, where they could create and upload content about their favorite YouTube or Instagram stars. Social media accounts affiliated with Shimmur went dark in 2017, and in early 2018 the site began redirecting to Digits.Chat, a service currently in private beta assumedly linked to Community. Now in their second act, Peltier and Community co-founder Josh Rosenheck are committed to building a platform for influencers and fans to interact at scale.
Questions of Community’s business began to surface in January 2019, when Ashton Kutcher took to Twitter to subtly promote the service with a phone number and a simple request to text him. Naturally, many assumed the tweet included the actor and investor’s personal cell number. In reality, he’d been working with Community to develop a better method of communication with his followers. This week, the actor resurfaced on Twitter to promote the service again. This time stating that the phone number included in the tweet would be “the only place [he] responds to public queries” because the “open web has just become too toxic.”
Just text me it’s easier. +1 (319) 519-0576
— ashton kutcher (@aplusk) July 23, 2019
This reporter, of course, followed up Kutcher on his offer and sent a text to his now preferred contact. Instantaneously, I received this reply: “Ashton here. This is an auto-text to let you know I got your message, the rest will be from me. Click the link so I can respond to you. I likely can’t respond to everything but I’ll try to be in touch. Dream bigger.” The message was accompanied by a link to a Community sign-up page for Kutcher-specific updates. The fine print read that the personal messages and automated text alerts from Kutcher “may be marketing in nature,” but little other information was provided.
While Kutcher has used his large Twitter following to spread awareness for Community, Guy Oseary has remained mum. Sources tell TechCrunch, however, that Oseary is a “co-founder” of Community, further evidence he’s put money in the business and perhaps adopted a co-founder title because of the nature of his investment. Oseary is not only a co-founder of Sound Ventures alongside Kutcher, but he’s also a longtime executive at Maverick, an entertainment and music management business behind the likes of Madonna and U2. His network would be much more valuable to Community than VC dollars.
Sound Ventures, Kutcher and Oseary’s venture capital fund, did not respond to a request for comment. Community declined to name its investors, but did say Oseary is “not a co-founder,” declining to provide additional details on his affiliation with the business.
On its website, Community describes itself as a tool that enables its clients, e.g. influencers, musicians, athletes, brands, actors, their agents and others, to have direct and meaningful communication with their “community members” using a 10-digit phone number provided by Community: “Imagine getting to know and interact with your audience as individuals—with names and faces, interests and opinions, hometowns and pronouns. Imagine reaching every single one of them,” the company writes.
Peltier, in the company’s first blog post published in June, emphasized the power of text messaging, citing an Adobe statistic that 90% of text messages are read within three seconds. Peltier also described Community’s business model, noting that they are not an ads business, rather, clients pay Community monthly or annual service fees “for 100% audience reach and limitless segmentation, in a climate free from bullying and toxicity.” Community’s terms of service agreement additionally states that once a subscription is initiated, clients can create and send text marketing campaigns to promote themselves or products with members of their community.
If Community sounds familiar — it should. Its efforts to leverage SMS to facilitate celebrity-fan relationships is akin to SuperPhone. Founded by musician Ryan Leslie in 2015, SuperPhone is a mobile messaging platform designed to meet the needs of entrepreneurs, entertainers and anyone else that juggles clients or sales contacts.
“SuperPhone is the first foray into personal relationship management,” Leslie told TechCrunch last year. The startup has raised a total of roughly $5 million at a $10 million valuation, according to PitchBook. In a blog post addressing Kutcher’s January tweet, Leslie welcomed the competition to the text marketing space.
“The game is changing, messaging is here to stay, and platforms are stepping up to help you leverage the power of this currently undervalued direct communication channel,” Leslie wrote. “This is my game. SuperPhone was conceived, developed, deployed, and battle-tested years before this week’s A-list endorsement of text over social.”
We reached out to SuperPhone for comment and in a very on-brand reply, a spokesperson for the business told me to submit my phone number to Leslie here and “unlike Ashton, Ry will text you right back once you introduce yourself.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Earlier this month, TechCrunch held its annual Mobility Sessions event, where leading mobility-focused auto companies, startups, executives and thought leaders joined us to discuss all things autonomous vehicle technology, micromobility and electric vehicles.
Extra Crunch is offering members access to full transcripts key panels and conversations from the event, including our panel on micromobility where TechCrunch VC reporter Kate Clark was joined by investors Sarah Smith of Bain Capital Ventures, Michael Granoff of Maniv Mobility, and Ted Serbinski of TechStars Detroit.
The panelists walk through their mobility investment theses and how they’ve changed over the last few years. The group also compares the business models of scooters, e-bikes, e-motorcycles, rideshare and more, while discussing Uber and Lyft’s role in tomorrow’s mobility ecosystem.
Sarah Smith: It was very clear last summer, that there was essentially a near-vertical demand curve developing with consumer adoption of scooters. E-bikes had been around, but scooters, for Lime just to give you perspective, had only hit the road in February. So by the time we were really looking at things, they only had really six months of data. But we could look at the traction and the adoption, and really just what this was doing for consumers.
At the time, consumers had learned through Uber and Lyft and others that you can just grab your cell phone and press a button, and that equates to transportation. And then we see through the sharing economy like Airbnb, people don’t necessarily expect to own every single asset that they use throughout the day. So there’s this confluence of a lot of different consumer trends that suggested that this wasn’t just a fad. This wasn’t something that was going to go away.
 For access to the full transcription below and for the opportunity to read through additional event transcripts and recaps, become a member of Extra Crunch. Learn more and try it for free.
For access to the full transcription below and for the opportunity to read through additional event transcripts and recaps, become a member of Extra Crunch. Learn more and try it for free.
Kate Clark: One of the first panels of the day, I think we should take a moment to define mobility. As VCs in this space, how do you define this always-evolving sector?
Michael Granoff: Well, the way I like to put it is that there have been four eras in mobility. The first was walking and we did that for thousands of years. Then we harnessed animal power for thousands of years.
And then there was a date — and I saw Ken Washington from Ford here — September 1st, 1908, which was when the Model T came out. And through the next 100 years, mobility is really defined as the personally owned and operated individual operated internal combustion engine car.
And what’s interesting is to go exactly 100 years later, September 2008, the financial crisis that affects the auto industry tremendously, but also a time where we had the first third-party apps, and you had Waze and you had Uber, and then you had Lime and Bird, and so forth. And really, I think what we’re in now is the age of digital mobility and I think that’s what defines what this day is about.
Ted Serbinski: Yeah, I think just to add to that, I think mobility is the movement of people and goods. But that last part of digital mobility, I really look at the intersection of the physical and digital worlds. And it’s really that intersection, which is enabling all these new ways to move around.
Clark: So Ted you run TechStars Detroit, but it was once known as TechStars Mobility. So why did you decide to drop the mobility?
Serbinski: So I’m at a mobility conference, and we no longer call ourselves mobility. So five years ago, when we launched the mobility program at TechStars, we were working very closely with Ford’s group and at the time, five years ago, 2014, where it started with the connected car, auto and [people saying] “you should use the word mobility.”
And I was like “What does that mean?” And so when we launched TechStars Mobility, we got all this stuff but we were like “this isn’t what we’re looking for. What does this word mean?” And then Cruise gets acquired for a billion dollars. And everyone’s like “Mobility! This is the next big gold rush! Mobility, mobility, mobility!”
And because I invest early-stage companies anywhere in the world, what started to happen last year is we’d be going after a company and they’d say, “well, we’re not interested in your program. We’re not mobility.” And I’d be scratching my head like, “No, you are mobility. This is where the future is going. You’re this digital way of moving around. And no, we’re artificial intelligence, we’re robotics.”
And as we started talking to more and more entrepreneurs, and hundreds of startups around the world, it became pretty clear that the word mobility is actually becoming too limiting, depending on your vantage where you are in the world.
And so this year, we actually dropped the word mobility and we just call it TechStars Detroit, and it’s really just intersection of those physical and digital worlds. And so now we don’t have a word, but I think we found more mobility companies by dropping the word mobility.
Powered by WPeMatico