Startups
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Around 15% of website traffic comes through paid search ads. But to turn passive searchers into active shoppers, your ads should answer their question and entice them to click.
We’ve tested thousands of paid search ads at Demand Curve and through our agency Bell Curve. This post breaks down 14 questions your paid search ads should answer to ensure you’re only paying for the highest-intent shoppers.
An important distinction between paid search and organic search is that paid ads are an interruption. Users of search engines are simply looking for an answer to their question. The people who see your ads don’t owe you anything. Just because you’re paying to have your ad show up first doesn’t mean they’re going to pay attention to it.
To generate genuine interest in your paid ads, reframe your offer as a favor.
You can do this in two ways:
For example, reframing free delivery as an extra convenience makes the offer that much more attractive.
Use ad extensions by listing additional benefits in the description of the page. For example, including “customized plans” in the pricing extension page signals to your customer that they’ll have control over the cost. This will help to attract the curiosity of even the most cost-conscious buyers.
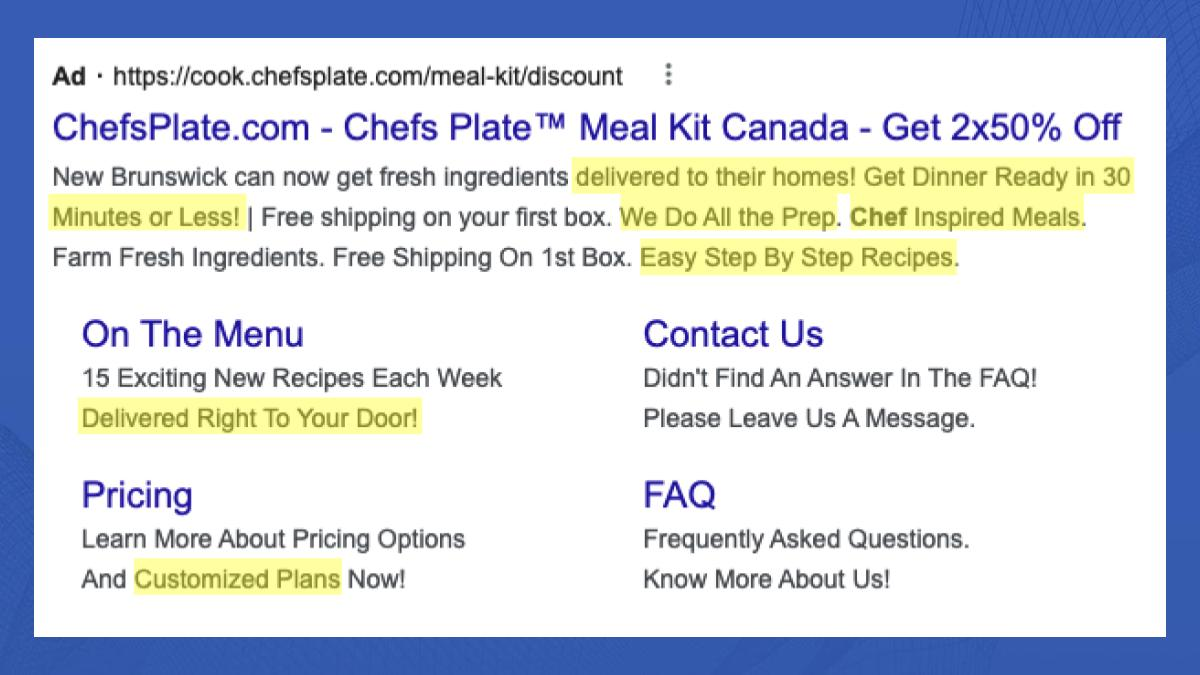
Image Credits: Demand Curve
Approximately 80% of e-commerce shopping carts are abandoned, mostly because shoppers don’t feel any urgency to complete the transaction. Online shoppers aren’t in any rush, as the internet is open 24/7 and inventory feels unlimited.
Use ad copy that bridges the gap between their problem and your solution. The easiest way to create that curiosity bridge is by asking a question.
To answer the question, “Why should I buy now?”, you’re going to have to create an incentive to get them to take action now.
Powered by WPeMatico
Swiss alternative protein company Planted has raised its second round of the year, a CHF 19 million (about $21 million at present) “pre-B” fundraise that will help it continue its growth and debut new products. A U.S. launch is in the cards eventually, but for now Planted’s exclusively European customers will be able to give its new veggie schnitzel a shot.
Planted appeared in 2019 as a spinoff from Swiss research university ETH Zurich, where the founders developed the original technique of extruding plant proteins and water into fibrous structures similar to real meat’s. Since then the company has diversified its protein sources, adding oat and sunflower to the mix, and developed pulled pork and kebab alternative products as well.
Over time the process has improved as well. “We added fermentation/biotech technologies to enhance taste and texture,” wrote CEO and co-founder Christoph Jenny in an email to TechCrunch. “Meaning 1) we can create structures without form limitation and 2) can add a broader taste profile.”
The latest advance is schnitzel, which is of course a breaded and fried piece of pounded-thin meat style popular around the world, but especially in the company’s core markets of Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Jenny noted that Planted’s schnitzel is produced as one piece, not pressed together from smaller bits. “The taste and texture benefit from fermentation approach, that makes the flavor profile mouth watering and the texture super juicy,” he said, though of course we will have to test it to be sure. Expect schnitzel to debut in Q3.
It’s the first of several planned “whole” or “prime” cuts, larger pieces that can be prepared like any other piece of meat — the team says their products require no special preparation or additives and can be dropped in as 1:1 replacements in most recipes. Right now the big cuts are leaving the lab and entering consumer testing for taste tuning and eventually scaling.
The funding round came from “Vorwerk Ventures, Gullspång Re:food, Movendo Capital, Good Seed Ventures, Joyance, ACE & Company (SFG strategy) and Be8 Ventures,” and was described as a follow-on to March’s CHF 17M series A. No doubt the exploding demand for alternative proteins and growing competition in the space has spurred Planted’s investors to opt for more aggressive growth and development strategies.
The company plans to enter several new markets over Q3 and Q4, but the U.S. is still a question mark due to COVID-19 restrictions on travel. Jenny said they are preparing so that they can make that move whenever it becomes possible, but for now Planted is focused on the European market.
(Update: This article originally misstated the new round as also being CHF 17M — entirely my mistake. This has been corrected.)
Powered by WPeMatico
MGA Thermal wants to help utility companies transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources with shoebox-sized thermal energy storage blocks. The company says a stack of 1,000 blocks is about the size of a small car and can store enough energy to power 27 homes for 24 hours. This gives utility providers the ability to store large amounts of energy and have it ready to dispatch even when weather conditions aren’t ideal for generating solar or wind power. The modular blocks also make it easier to convert infrastructure, like coal-fired power plants, into grid-scale energy storage.
MGA Thermal announced today it has raised $8 million AUD (about $5.9 million USD), bring its total funding so far to $9 million AUD. The round was led by Main Sequence, a venture firm founded by Australia’s national science agency that recently launched a new $250 million AUD fund. Alberts Impact Capital, New Zealand’s Climate Venture Capital Fund, The Melt and returning investor CP Ventures participated, along with angel investors like Chris Sang, Emlyn Scott and Glenn Butcher.
Based in Newcastle, Australia, MGA Thermal was founded in April 2019 by Erich Kisi and Alexander Post after nearly a decade spent researching and developing miscibility gap alloys technology at the University of Newcastle. When asked to explain MGA tech in layperson’s terms, Kisi used a delicious analogy.
MGA Thermal’s blocks “essentially comprise metal particles that melt when heated embedded in an inert matrix material. Think of a block as being like a choc-chip muffin heated in a microwave. The muffin consists of a cake component, which holds everything in shape when heated, and the choc chips, which melt,” he told TechCrunch.
“The energy that goes into melting the choc chips is stored and can burn your mouth when you bite into the muffin,” he added. “Melting energy is more intense than merely heating something up and that melting energy is concentrated near the melting temperature so energy can be released in a consistent way.”
Energy stored in MGA Thermal’s blocks can be used to heat water to power steam turbines and generators. In this scenario, blocks are designed with internal tubing for pumping and boiling water, or interact with a heat exchanger. Kisi said MGA Thermal’s blocks enable aging thermal power plans to continue running on renewable energy that would usually be switched off in situations like overheating caused by too much sun or high winds.
Other thermal energy solutions include heating low-cost solid materials in blocks or granules to high temperatures in an insulated container. But many of these materials aren’t good at moving thermal energy around and have temperature limitations, Kisi said. This means thermal energy decreases in temperature as it is discharged, making it less effective.
Another method for storing thermal energy involves molten salts that are heated by a renewable energy source and stored in a hot tank. The hot salt is then pumped through a heat exchanger to make steam, while colder (but still molten) salt is returned to a “cold” tank.
“These systems are widely used in concentrating solar thermal energy but have found little use elsewhere,” Kisi said. “That’s mostly because there is a large infrastructure cost for piping pumps and heaters, and a large amount of power is wasted keeping the salt from freezing.”
MGA Thermal is establishing a manufacturing plant in New South Wales to scale to commercial levels production of its blocks, and plans to double its team over the next 12 months so it can make hundreds of thousands of blocks each month. It is also currently working with partners like Swiss company E2S Power ASG and U.S.-based Peregrine Turbine Technologies to deploy its tech in Australia, Europe and North America. For example, E2S Power AG will use MGA Thermal’s tech to repurpose retired and active coal-fired thermal plants in Europe.
While MGA Thermal’s tech has many industrial use cases, like converting power stations, building off-grid storage and supplying power to remote communities and commercial spaces, it can also help consumers consume less fossil fuel. For example, MGA blocks can be used by households to store excess energy generated from rooftop solar panels or small wind turbines. Then that energy can be used to heat homes.
“Around the world an estimated three billion people heat their homes by burning fuel,” said Kisi. “That’s a lot of CO2, especially in very cold climates.”
In a statement, Main Sequence partner Martin Duursma said, “A core focus of our new fund is uncovering the scientific discoveries, and helping to turn them into real, tangible technologies so we can reverse our climate impact. Erich Kisi and Alexander Post’s impressive deep research backgrounds, their expert team and innovative technology are paving the way for grid-scale energy storage and boosting the capability of a renewable energy future globally.”
Powered by WPeMatico
The President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology predicts that U.S. companies will spend upward of $100 billion on AI R&D per year by 2025. Much of this spending today is done by six tech companies — Microsoft, Google, Amazon, IBM, Facebook and Apple, according to a recent study from CSET at Georgetown University. But what if you’re a startup whose product relies on AI at its core?
Can early-stage companies support a research-based workflow? At a startup or scaleup, the focus is often more on concrete product development than research. For obvious reasons, companies want to make things that matter to their customers, investors and stakeholders. Ideally, there’s a way to do both.
Before investing in staffing an AI research lab, consider this advice to determine whether you’re ready to get started.
Assuming it’s your organization’s priority to do innovative AI research, the first step is to hire one or two researchers. At Unbabel, we did this early by hiring Ph.D.s and getting started quickly with research for a product that hadn’t been developed yet. Some researchers will build from scratch and others will take your data and try to find a pre-existing model that fits your needs.
While Google’s X division may have the capital to focus on moonshots, most startups can only invest in innovation that provides them a competitive advantage or improves their product.
From there, you’ll need to hire research engineers or machine learning operations professionals. Research is only a small part of using AI in production. Research engineers will then release your research into production, monitor your model’s results and refine the model if it stops predicting well (or otherwise is not operating as planned). Often they’ll use automation to simplify monitoring and deployment procedures as opposed to doing everything manually.
None of this falls within the scope of a research scientist — they’re most used to working with the data sets and models in training. That said, researchers and engineers will need to work together in a continuous feedback loop to refine and retrain models based on actual performance in inference.
The CSET research cited above shows that 85% of AI labs in North America and Europe do some form of basic AI research, and less than 15% focus on development. The rest of the world is different: A majority of labs in other countries, such as India and Israel, focus on development.
Powered by WPeMatico
Sunday was a big day in fintech: Afterpay has agreed to merge with Square. This agreement sets two of the most admired financial technology companies in recent history on a path to becoming one.
Afterpay and Square have the potential to build one of the world’s most important payments networks. Square has built a very significant merchant payment network, and, via Cash App, a thriving high-growth consumer payment service. However, these two lines of business have historically not been integrated. Together, Square and Afterpay will be able to weave all of these services together into a single integrated experience.
Afterpay and Cash App each have double-digit millions of consumers, and Square’s seller ecosystem and Afterpay’s merchant network both record double-digit billions of payment volume per year. From the offline register and the online checkout flow to sending money in just a few taps, Square and Afterpay will tell a complete story of next-generation economic empowerment.
As Afterpay’s only institutional venture investor, I wanted to share some perspective on how we got here and what this merger means for the future of consumer finance and the payments industry.
Afterpay and Square have the potential to build one of the world’s most important payments networks.
Every five to 10 years, the global payments industry undergoes a critical innovation cycle that determines the winners and losers for the next several decades. The last major transition was the shift to NFC-based mobile payments, which I wrote about in 2015. The major mobile OS vendors (Apple and Google) cemented their position in the global payments stack by deftly bridging the needs of the networks (Visa, Mastercard, etc.) and consumers by way of the mobile devices in their pockets.
Afterpay sparked the latest critical innovation cycle. Conceived in a living room in Sydney by a millennial, Nick Molnar, for millennials, Afterpay had a key insight: Millennials don’t like credit.
Millennials came of age during the global mortgage crisis of 2008. As young adults, they watched their friends and family lose their homes by overextending on mortgage debt, bolstering their already lower trust for banks. They also have record levels of student debt. Therefore, it’s no surprise that millennials (and Gen Z right behind them) strongly prefer debit cards over credit cards.
But it’s one thing to recognize the paradigm shift and quite another to do something about it. Nick Molnar and Anthony Eisen did something, ultimately building one of the fastest-growing payments startups in history on their core product: Buy now, pay later … and never any interest.
Afterpay’s product is simple. If you have $100 in your cart and choose to pay with Afterpay, it will charge your bank card (typically a debit card) $25 every two weeks in four installments. No interest, no revolving debt and no fees with on-time payments. For the millennial consumer, this meant they could get the primary benefit of a credit card (the ability to pay later) with their debit card, without the need to worry about all the bad things that come with credit cards — high interest rates and revolving debt.
All upside, no downside. Who could resist? For the early merchants, virtually all of whom relied on millennials as their key growth segment, they got a fair trade: Pay a small fee above payment processing to Afterpay, get significantly higher average order values and conversions to purchase. It was a win-win proposition and, with lots of execution, a new payment network was born.
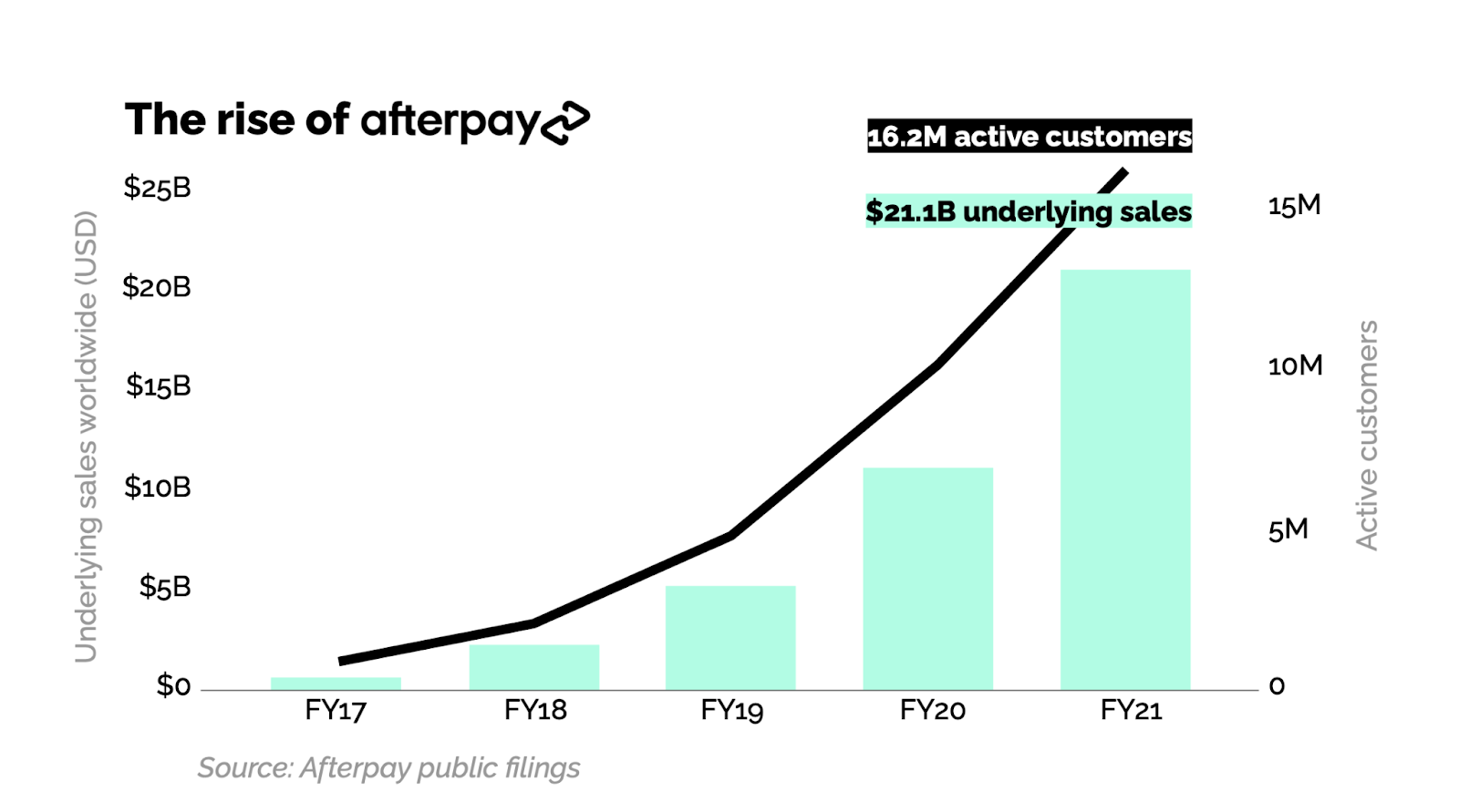
Image Credits: Matrix Partners
Afterpay went somewhat unnoticed outside Australia in 2016 and 2017, but once it came to the U.S. in 2018 and built a business there that broke $100 million net revenues in only its second year, it got attention.
Klarna, which had struggled with product-market fit in the U.S., pivoted their business to emulate Afterpay. And Affirm, which had always been about traditional credit — generating a significant portion of their revenue from consumer interest — also noticed and introduced their own BNPL offering. Then came PayPal with “Pay in 4,” and just a few weeks ago, there has been news that Apple is expected to enter the space.
Afterpay created a global phenomenon that has now become a category embraced by mainstream players across the industry — a category that is on track to take a meaningful share of global retail payments over the next 10 years.
Afterpay stands apart. It has always been the BNPL leader by virtually every measure, and it has done it by staying true to their customers’ needs. The company is great at understanding the millennial and Gen Z consumer. It’s evident in the voice, tone and lifestyle brand you experience as an Afterpay user, and in the merchant network it continues to build strategically. It’s also evident in the simple fact that it doesn’t try to cross-sell users revolving debt products.
Most importantly, it’s evident in the usage metrics relative to competition. This is a product that people love, use and have come to rely on, all with better, fairer terms than were ever available to them than with traditional consumer credit.
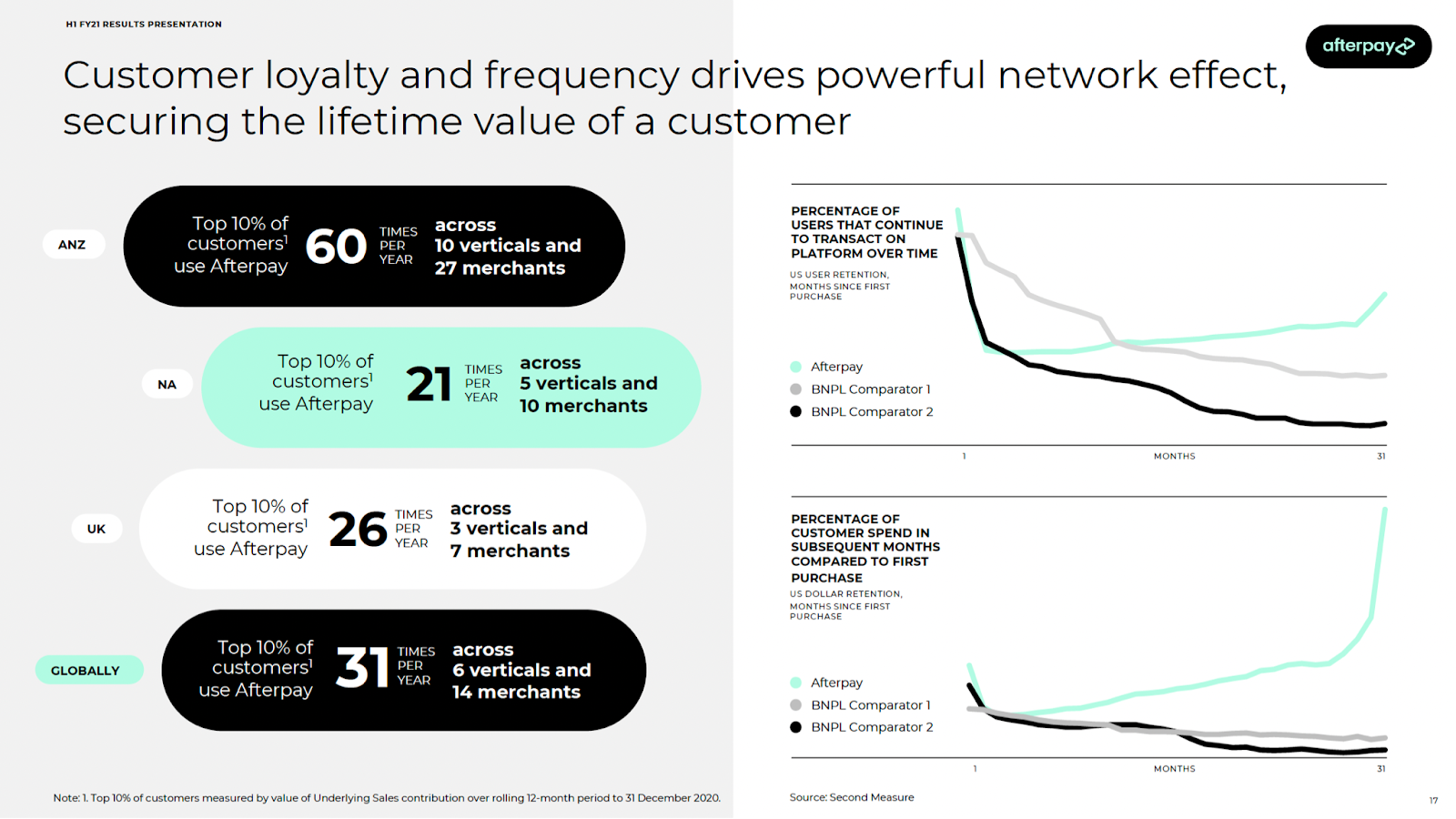
Image Credits: Afterpay H1 FY21 results presentation
I’ve been building payment companies for over 15 years now, initially in the early days of PayPal and more recently as a venture investor at Matrix Partners. I’ve never seen a combination that has such potential to deliver extraordinary value to consumers and merchants. Even more so than eBay + PayPal.
Beyond the clear product and network complementarity, what’s most exciting to me and my partners is the alignment of values and culture. Square and Afterpay share a vision of a future with more opportunity and fewer economic hurdles for all. As they build toward that future together, I’m confident that this combination is a winner. Square and Afterpay together will become the world’s next generation payment provider.
Powered by WPeMatico
German electric aircraft startup Lilium is negotiating the terms for a 220-aircraft, $1 billion order with one of Brazil’s largest domestic airlines, the companies said Monday. Should the deal with Azul move forward, it would mark the largest order in Lilium’s history and its first foray into South American markets.
“A term sheet has been signed and we will move toward a final agreement in the coming months,” a Lilium spokesperson told TechCrunch.
The 220 aircraft would fly as part of a new, co-branded airline network that would operate in Brazil. Should the two companies come to an agreement, Azul would operate and maintain the fleet of the flagship seven-seater aircraft, and Lilium would provide custom spare parts, including replacement batteries, and an aircraft health monitoring platform.
Deliveries would commence in 2025, a year after Lilium has said it plans to begin commercial operations in Europe and the United States. These timelines are dependent upon Lilium receiving key certification approvals from each country’s requisite aerospace regulator. Azul said in a statement it would “support Lilium with the necessary regulatory approval processes in Brazil” as part of the agreement.
Even if a deal is reached, it would likely be subject to Lilium hitting certain performance standards and benchmarks, similar to the conditions of Archer Aviation’s $1 billion order with United Airlines. Still, orders of this value are seen as a positive signal to markets and investors that an electric vertical take-off and landing aircraft is more than smoke and mirrors.
Also like Archer, Lilium is planning on taking the SPAC route to going public. The company in March announced its intention to merge with Qell Acquisition Corp. and list on Nasdaq under ticker symbol “LILM.” SPACs have become a popular vehicle for public listing across the transportation sector, but they’ve become especially popular with capital-intensive eVTOL startups.
The merger may be necessary for the company’s continued operations. According to the German news website Welt, Lilium added a risk warning to its 2019 balance sheet noting that it will run out of money in December 2022 should the SPAC merger not be completed.
Powered by WPeMatico
Shares of Square are up this morning after the company announced its second-quarter earnings and that it will buy Afterpay, an Australian buy now, pay later (BNPL) player in a $29 billion deal. As TechCrunch reported this morning, Afterpay shareholders will receive 0.375 shares of Square in exchange for their existing equity.
Shares of Afterpay are sharply higher after the deal was announced thanks to its implied premium, while shares of Square are up 7% in early-morning trading.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on Extra Crunch or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
Over the past year, we’ve written extensively about the BNPL market, usually from the perspective of earnings from companies in the space. Afterpay has been a key data source, along with the yet-private Klarna and U.S. public BNPL outfit Affirm. Recall that each company has posted strong growth in recent periods, with the United States arising as a prime competitive market.
 Most recently, consumer hardware and services giant Apple is reportedly preparing a move into the BNPL space. Our read at the time was that any such movement by Cupertino would impact mass-market BNPL players more than niche-focused companies. Apple has a fintech base and broad IRL payment acceptance, making it a potentially strong competitor for BNPL services aimed at consumers; BNPL services targeted at particular industries or niches would likely see less competition from Apple.
Most recently, consumer hardware and services giant Apple is reportedly preparing a move into the BNPL space. Our read at the time was that any such movement by Cupertino would impact mass-market BNPL players more than niche-focused companies. Apple has a fintech base and broad IRL payment acceptance, making it a potentially strong competitor for BNPL services aimed at consumers; BNPL services targeted at particular industries or niches would likely see less competition from Apple.
From that landscape, let’s explore the Square-Afterpay deal. We want to know what Afterpay brings to Square in terms of revenue, growth and reach. We also want to do some math on the price Square is willing to pay for the company — and what that might tell us about the value of BNPL and fintech revenues more broadly. Then we’ll eyeball the numbers and try to decide if Square is overpaying for Afterpay.
As with most major deals these days, Square and Afterpay released an investor presentation detailing their argument in favor of their combination. Let’s dig through it.
Square is a two-part company. It has a large consumer business via Cash App, and it has a large business division that offers payments tech and other fintech services to corporate customers. Recall that Square is also building out banking services for its business customers and that Cash App also serves some banking and investing functionality for consumers.
Powered by WPeMatico
It’s no secret that the technology for easy business-to-business payments has not yet caught up to its peer-to-peer counterparts, but Yaydoo thinks it has the answer.
The Mexico City-based B2B software and payments company provides three products, VendorPlace, P-Card and PorCobrar, for managing cash flow, optimizing access to smart liquidity, and connecting small, midsize and large businesses to an ecosystem of digital tools.
Sergio Almaguer, Guillermo Treviño and Roberto Flores founded Yaydoo — the name combines “yay” and “do” to show the happiness of doing something — in 2017. Today, the company announced the close of a $20.4 million Series A round co-led by Base10 Partners and monashees.
Joining them in the round were SoftBank’s Latin America Fund and Leap Global Partners. In total, Yaydoo has raised $21.5 million, Almaguer told TechCrunch.
Prior to starting the company, Almaguer was working at another company in Mexico doing point-of-sale. His large enterprise customers wanted automation for their payments, but he noticed that the same tools were too expensive for small businesses.
The co-founders started Yaydoo to provide procurement, accounts payable and accounts receivables, but in a simpler format so that the collection and payment of B2B transactions was affordable for small businesses.
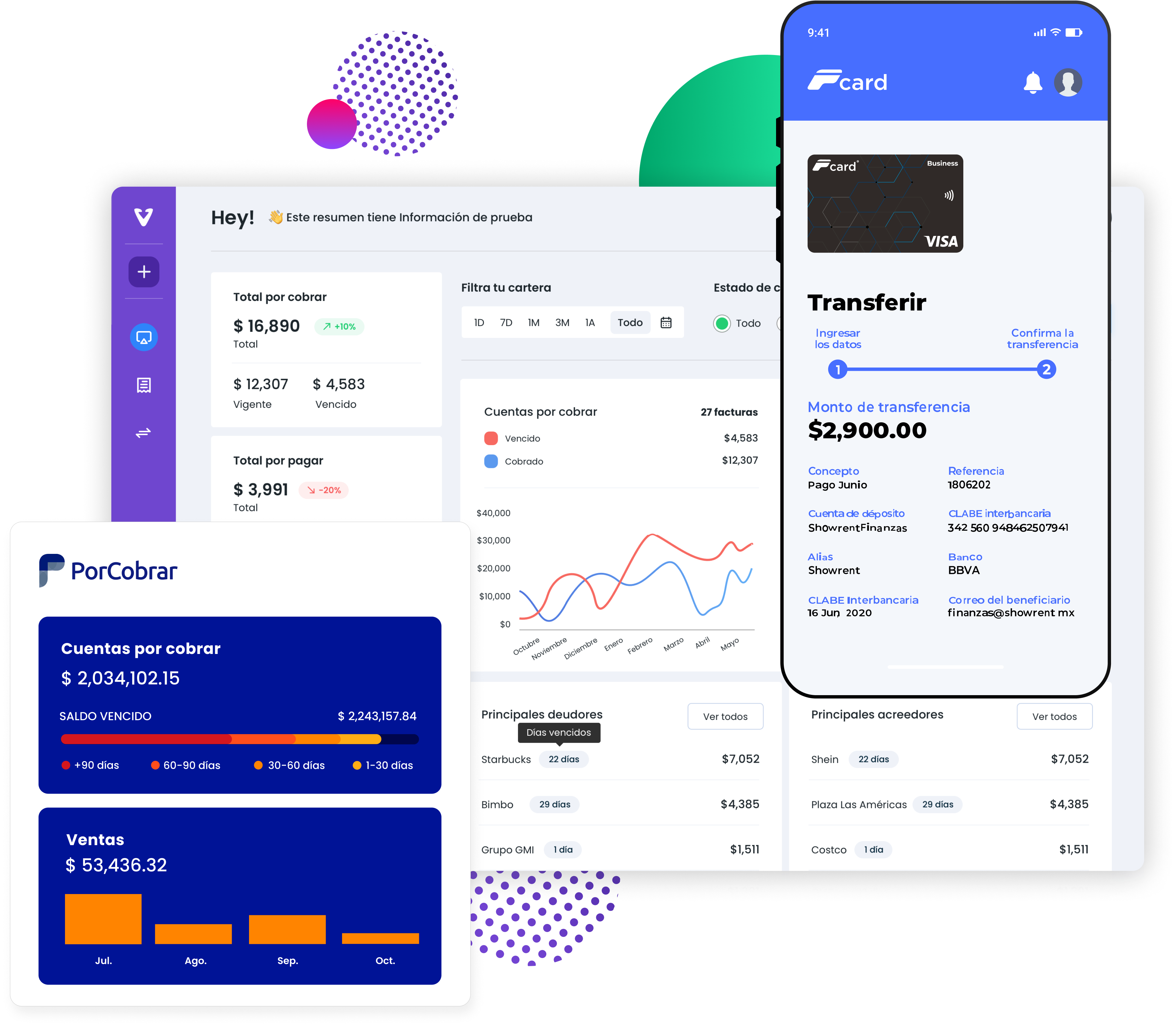
Image Credits: Yaydoo
The idea is taking off, and vendors are adding their own customers so that they are all part of the network to better link invoices to purchase orders and then connect to accounts payable, Almaguer said. Yaydoo estimates that the automation workflows reduced 80% of time wasted paying vendors, on average.
Yaydoo is joining a sector of fintech that is heating up — the global B2B payments market is valued at $120 trillion annually. Last week, B2B payments platform Nium announced a $200 million in Series D funding on a $1 billion valuation. Others attracting funding recently include Paystand, which raised $50 million in Series C funding to make B2B payments cashless, while Dwolla raised $21 million for its API that allows companies to build and facilitate fast payments.
The new funding will enable the company to attract new hires in Mexico and when the company expands into other Latin American countries. Yaydoo is also looking at future opportunities for its working capital business, like understanding how many invoices customers are setting, the access to actual payments, and how money flows out and in so that it can provide insights on working capital funding gaps. The company will also invest in product development.
The company has grown to over 800 customers, up from 200 in the first quarter of 2020. Its headcount also grew to 100 from 30 during the same time. In the last 12 months, over 70,000 companies have transacted on the Yaydoo network, and total payment volume grew to hundreds of millions of dollars.
Yaydoo is a SaaS subscription model, but the new funding will also enable the company to create a pool of potential customers with a “freemium” offering with the goal of converting those customers into the subscription model as they grow, Almaguer said.
Rexhi Dollaku, partner at Base10 Partners, said the firm saw the way B2B payments were becoming modernized and “was impressed” by the Yaydoo team and how it built a complicated infrastructure, but made it easy to use.
He believes Latin America is 10 years behind in terms of B2B payments but will catch up sooner than later because of the digital transformation going on in the region.
“We are starting to see early signs of the network being built out of the payments product, and that is a good indication,” Dollaku said. “With the funding, Yaydoo will be also able to provide more financial services options for businesses to address a working fund gap.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Pet pharmacy Mixlab has developed a digital platform enabling veterinarians to prescribe medications and have them delivered — sometimes on the same day — to pet parents.
The New York-based company raised a $20 million Series A in a round of funding led by Sonoma Brands and including Global Founders Capital, Monogram Capital, Lakehouse Ventures and Brand Foundry. The new investment gives Mixlab total funding of $30 million, said Fred Dijols, co-founder and CEO of Mixlab.
Dijols and Stella Kim, chief experience officer, co-founded Mixlab in 2017 to provide a better pharmacy experience, with the veterinarian at the center.
Dijols’ background is in medical devices as well as healthcare investment banking, where he became interested in the pharmacy industry, following TruePill and PillPack, which he told TechCrunch were “creating a modern pharmacy model.”
As more pharmacy experiences revolved around at-home delivery, he found the veterinary side of pharmacy was not keeping up. He met Kim, a user experience expert, whose family owns a pharmacy, and wanted to bring technology into the industry.
“The pharmacy industry is changing a lot, and technology allows us to personalize the care and experience for the veterinarian, pet parent and the pet,” Kim said. “Customer service is important in healthcare as is dignity and empathy. We kept that in mind when starting Mixlab. Many companies use technology to remove the human element, but we use it to elevate it.”
Mixlab’s technology includes a digital service for veterinarians to streamline their daily medication workflow and gives them back time to spend with patient care. The platform manages the home delivery of medications across branded, generic and over-the-counter medications, as well as reduces a clinic’s on-site pharmacy inventories. Veterinarians can write prescriptions in seconds and track medication progress and therapy compliance.
The company also operates its own compound pharmacy where it specializes in making medications on-demand that are flavored and dosed.
On the pet parent side, they no longer have to wait up to a week for medications nor have to drive over to the clinic to pick them up. Medications come in a personalized care package that includes a note from the pharmacist, clear and easy-to-read instructions and a new toy.
Over the past year, adoptions of pets spiked as more people were at home, also leading to an increase in vet visits. This also caused the global pet care industry to boom, and it is now projected to reach $343 billion by 2030, when it had been valued at $208 billion in 2020.
Pet parents are also spending more on their pets, and a Morgan Stanley report showed that they see pets as part of their family, and as a result, 37% of people said they would take on debt to pay for a pet’s medical expenses, while 29% would put a pet’s needs before their own.
To meet the increased demand in veterinary care, the company will use the new funding to improve its technology and expand into more locations where it can provide same-day delivery. Currently it is shipping to 47 states and Dijols expects to be completely national by the end of the year. He also expects to hire more people on both the sales team and in executive leadership positions.
The company is already operating in New York and Los Angeles and growing 3x year over year, though Dijols admits operating during the pandemic was a bit challenging due to “a massive surge of orders” that came in as veterinarians had to shut down their offices.
As part of the investment, Keith Levy, operating partner at Sonoma Brands and former president of pet food manufacturer Royal Canin USA, will join Mixlab’s board of directors. Sonoma Brands is focused on growth sectors of the consumer economy, and pets was one of the areas that investors were interested in.
Over time, Sonoma found that within the veterinary community, there was space for a lot of players. However, veterinarians want to home in on one company they trust, and Mixlab fit that description for many because they were getting medication out faster, Levy said.
“What Mixlab is doing isn’t completely unique, but they are doing it better,” he added. “When we looked at their customer service metrics, we saw they had a good reputation and were relentlessly focused on providing a better experience.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Duolingo landed onto the public markets this week, rallying excitement and attention for the edtech sector and its founder cohort. The language learning business’ stock price soared when it began to trade, even after the unicorn raised its IPO price range, and priced above the raised interval.
Duolingo’s IPO proves that public market investors can see the long-term value in a mission-driven, technology-powered education concern; the company’s IPO carries extra weight considering the historically few edtech companies that have listed.
Duolingo’s IPO proves that public market investors can see the long-term value in a mission-driven, technology-powered education concern; the company’s IPO carries extra weight considering the historically few edtech companies that have listed.
For those that want the entire story of Duolingo, from origin to messy monetization to historical IPO, check out our EC-1. It has dozens of interviews from executives, investors, linguists and competitors.
For today, though, we have fresh additions. We sat down with Duolingo CEO Luis von Ahn earlier in the week to discuss not only his company’s IPO, but also what impact the listing may have on startups. Duolingo’s IPO can be looked at as a case study into consumer startups, mission-driven companies that monetize a small base of users, or education companies that recently hit scale. Paraphrasing from von Ahn, Duolingo doesn’t see itself as just an edtech company with fresh branding. Instead, it believes its growth comes from being an engineering-first startup.
Selling motivation, it seems, versus selling the fluency in a language is a proposition that international consumers are willing to pay for, and an idea that investors think can continue to scale to software-like margins.
Duolingo has gone through three distinct phases: Growth, in which it prioritized getting as many users as it could to its app; monetization, in which it introduced a subscription tier for survival; and now, education, in which it is focusing on tacking on more sophisticated, smarter technology to its service.
Powered by WPeMatico