Startups
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Startups are raising record sums around the world, thanks to several contributing factors. As The Exchange explored yesterday, historically low interest rates have helped venture capitalists raise more capital than ever, to pick an example.
Low rates have helped startups in another manner: As yields fell for certain assets, investors chased returns by betting on growth. And in recent years, the investing classes turned their attention to public software companies, bidding up the value of their revenue to record highs.
This raised the worth of startups in general terms, and private tech companies’ comps enjoyed a steady, upward climb in the value of their revenues. If the value of a dollar of SaaS revenue was worth $1 one year and $2 the next, the repricing was good for private companies even if we were tracking the metrics from the perspective of public companies.
The free ride could be ending.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on Extra Crunch or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
I’ve held back from covering the value of software (SaaS, largely) revenues for a few months after spending a bit too much time on it in preceding quarters — when VCs begin to point out that you could just swap out numbers quarter to quarter and write the same post, it’s time for a break. But the value of software revenues posted a simply incredible run, and I can’t say “no” to a chart.
 The pace at which software revenues were repriced upwards in the last few years is simply astounding. Per the Bessemer Cloud Index, back in 2016, the median revenue multiple for public SaaS companies was around 5x. When 2018 began, median SaaS multiples had expanded to around 7x.
The pace at which software revenues were repriced upwards in the last few years is simply astounding. Per the Bessemer Cloud Index, back in 2016, the median revenue multiple for public SaaS companies was around 5x. When 2018 began, median SaaS multiples had expanded to around 7x.
That’s a 40% climb in pricing, but it proved to be just a foretaste of the feast to come.
By the end of 2019, the median figure had appreciated to around the 9x mark. And today it has shot to just under 18x. That is why software companies have been able to raise so much money, earlier, and in larger chunks. Every dollar of recurring revenue they sold was worth $5 in market cap in mid-2016. At the end of 2019, that same dollar of revenue was worth $9. And today, for the median public software company, it’s valued at around $18.
There are nuances to the data, but we care less about exacting definitions than the directional change it describes: The median value of SaaS revenues more than tripled from 2016 to 2021. That’s an insane amount of growth.
Powered by WPeMatico
Aircover raised $3 million in seed funding to continue developing its real-time sales intelligence platform.
Defy Partners led the round with participation from Firebolt Ventures, Flex Capital, Ridge Ventures and a group of angel investors.
The company, headquartered in the Bay Area, aims to give sales teams insights relevant to closing the sale as they are meeting with customers. Aircover’s conversational AI software integrates with Zoom and automates parts of the sales process to lead to more effective conversations.
“One of the goals of launching the Zoom SDK was to provide developers with the tools they need to create valuable and engaging experiences for our mutual customers and integrations ecosystem,” said Zoom’s CTO Brendan Ittelson via email. “Aircover’s focus on building sales intelligence directly into the meeting, to guide customer-facing teams through the entire sales cycle, is the type of innovation we had envisioned when we set out to create a broader platform.”
Aircover’s founding team of Andrew Levy, Alex Young and Andrew’s brother David Levy worked together at Apteligent, a company co-founded and led by Andrew Levy, that was sold to VMware in 2017.
Chatting about pain points on the sales process over the years, Levy said it felt like the solution was always training the sales team more. However, by the time everyone was trained, that information would largely be out-of-date.
Instead, they created Aircover to be a software tool on top of video conferencing that performs real-time transcription of the conversation and then analysis to put the right content in front of the sales person at the right time based on customer issues and questions. This means that another sales expert doesn’t need to be pulled in or an additional call scheduled to provide answers to questions.
“We are anticipating that knowledge and parsing it out at key moments to provide more leverage to subject matter experts,” Andrew Levy told TechCrunch. “It’s like a sales assistant coming in to handle any issue.”
He considers Aircover in a similar realm with other sales team solutions, like Chorus.ai, which was recently scooped up by ZoomInfo, and Gong, but sees his company carving out space in real-time meeting experiences. Other tools also record the meetings, but to be reviewed after the call is completed.
“That can’t change the outcome of the sale, which is what we are trying to do,” Levy added.
The new funding will be used for product development. Levy intends to double his small engineering team by the end of the month.
He calls what Aircover is doing a “large interesting problem we are solving that requires some difficult technology because it is real time,” which is why the company was eager to partner with Bob Rosin, partner at Defy Partners, who joins Aircover’s board of directors as part of the investment.
Rosin joined Defy in 2020 after working on the leadership teams of Stripe, LinkedIn and Skype. He said sales and customer teams need tools in the moment, and while some are useful in retrospect, people want them to be live, in front of the customer.
“In the early days, tools helped before and after, but in the moment when they need the most help, we are not seeing many doing it,” Rosin added. “Aircover has come up with the complete solution.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Six months after securing a $23 million Series A round, Ketch, a startup providing online privacy regulation and data compliance, brought in an additional $20 million in A1 funding, this time led by Acrew Capital.
Returning with Acrew for the second round are CRV, super{set} (the startup studio founded by Ketch’s co-founders CEO Tom Chavez and CTO Vivek Vaidya), Ridge Ventures and Silicon Valley Bank. The new investment gives Ketch a total of $43 million raised since the company came out of stealth earlier this year.
In 2020, Ketch introduced its data control platform for programmatic privacy, governance and security. The platform automates data control and consent management so that consumers’ privacy preferences are honored and implemented.
Enterprises are looking for a way to meet consumer needs and accommodate their rights and consents. At the same time, companies want data to fuel their growth and gain the trust of consumers, Chavez told TechCrunch.
There is also a matter of security, with much effort going into ransomware and malware, but Chavez feels a big opportunity is to bring security to the data wherever it lies. Once the infrastructure is in place for data control it needs to be at the level of individual cells and rows, he said.
“If someone wants to be deleted, there is a challenge in finding your specific row of data,” he added. “That is an exercise in data control.”
Ketch’s customer base grew by more than 300% since its March Series A announcement, and the new funding will go toward expanding its sales and go-to-market teams, Chavez said.
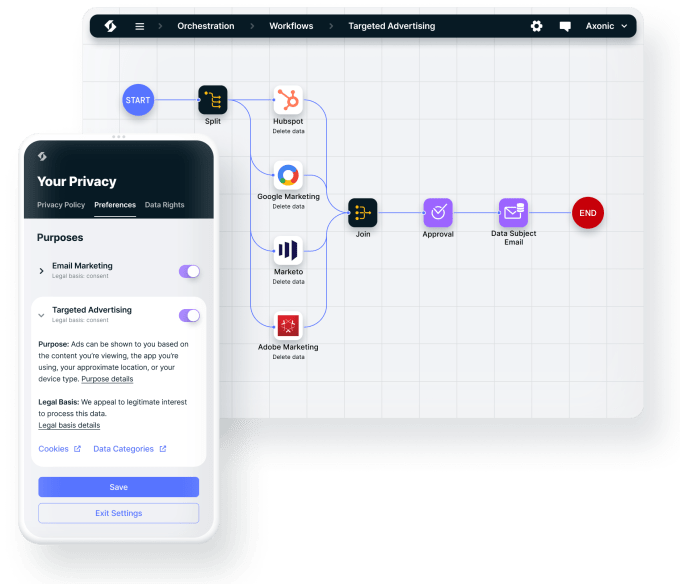
Ketch app. Image Credits: Ketch
This year, the company launched Ketch OTC, a free-to-use privacy tool that streamlines all aspects of privacy so that enterprise compliance programs build trust and reduce friction. Customer growth through OTC increased five times in six months. More recently, Qonsent, which developing a consent user experience, is using Ketch’s APIs and infrastructure, Chavez said.
When looking for strategic partners, Chavez and Vaidya wanted to have people around the table who have a deep context on what they were doing and could provide advice as they built out their products. They found that in Acrew founding partner Theresia Gouw, whom Chavez referred to as “the OG of privacy and security.”
Gouw has been investing in security and privacy for over 20 years and says Ketch is flipping the data privacy and security model on its head by putting it in the hands of developers. When she saw more people working from home and more data breaches, she saw an opportunity to increase and double down on Acrew’s initial investment.
She explained that Ketch is differentiating itself from competitors by taking data privacy and security and tying it to the data itself to empower software developers. With the OTC tool, similar to putting locks and cameras on a home, developers can download the API and attach rules to all of a user’s data.
“The magic of Ketch is that you can take the security and governance rules and embed them with the software and the piece of data,” Gouw added.
Powered by WPeMatico
You’ve probably learned from Reid Hoffman before, either through his inventions, investments or inspirational words. The entrepreneur is the co-founder of LinkedIn, a partner at Greylock and the author of a new book based off of his hit podcast, Masters of Scale.
His storied past makes him chock-full of interesting anecdotes and lessons, which is why we’re excited to have him back on the TechCrunch Disrupt stage happening next week from September 21-23. I’ll sit down with him to learn about his perspective on some of the biggest tensions that entrepreneurs face today. Hoffman’s advice is often fueled by his raw conversations with top tech CEOs and founders, so we’ll broaden access to his speed-dial list to understand how even his own perceptions on blitzscaling, growth and entrepreneurship are changing amid the pandemic. As I explained in my review of his new book, his words read like a well-networked mentor giving you a pep talk — so even if you’re not building a startup, there will be useful lessons to learn just by listening.
Here’s how it impacted my interview process, for example:
While press wasn’t a main character in the book, “Master of Scale” has already changed my perspective on how I interview founders. Lessons from Tristan Walker made me want to ask more questions about founders, and their most controversial beliefs, rather than how they plan to spend their new round of funding. A note from Andrés Ruzo made me realize that a startup that makes too much sense might be a comfortable read, but it might not be a moonshot that disrupts the world; in other words, pursue the startups that have too much seemingly foolish ambition — because they may be where the best strides, and stories, are made. Finally, it confirmed my belief that the best litmus test for a founder is if they are willing to talk about the hardships ahead of them in an honest, humble way.
OK, that’s all I’m hinting. Join me at Disrupt, where I’ll put Hoffman on the hot seat, balance out the cheerfulness with some cynical takes and push him to explain what his inevitable next book is about. Buy your tickets to TechCrunch Disrupt using this link, or use promo code “MASCARENHAS20” for a little discount from me.
Powered by WPeMatico
Businesses that don’t invest in their future may not have a future to look forward to.
Whether you’re investing in your human resources or in critical tech, some outlay in the short term is always needed for long-term success. That’s true when it comes to marketing as well — you can’t market your product or service without investing in advertising. But if that investment isn’t turning into leads and conversions, you’re in trouble.
A “good” ROAS score is different for each company and campaign. If your figure isn’t where you’d like it to be, you can leverage ROAS data to create targeted campaigns and personalized experiences.
It’s vital to identify and apply the most suitable metrics based on business goals, and there’s no one best practice or one-size-fits-all method.
However, smart use of the return on advertising spend (ROAS) data can triple lead generation, as I discovered when I joined Brightpearl to restructure the marketing campaigns. Let’s take a look at some of the ways Brightpearl used ROAS to improve campaigns and increase lead generation. The key is to work out what represents a healthy ROAS for your business so that you can optimize accordingly.
It is paramount to choose the right return metric to calculate your ROAS. This will depend partly on your sales cycle.
Brightpearl has a lengthy sales cycle. On average it’s two to three months, and sometimes up to six months, meaning we don’t have tons of data on a monthly basis if we want to use new customer’s revenue data as the return metric. A company with a shorter sales cycle could use revenue, but that doesn’t help us to optimize our campaigns.
We chose to use the sales accepted opportunity (SAO) value instead. It usually takes us about a month to measure, so we can get more ROAS data at the same time. It’s the last sales stage before a win, and it’s more in line with our company goal (to grow our recurring annual revenue), but takes less time to gather the data.
By the SAO stage, we know which leads are good quality — they have the budget, are a good fit, and our software can meet their requirements. We can use them to measure our campaign performance.
When you choose a return metric, you need to make sure it matches your company goal without taking ages to get the data. It also has to be measurable at the campaign level, because the aim of using ROAS or other metrics is to optimize your campaigns.
I’ve noticed that many companies harbor a fear of missing out on opportunities, which leads them to advertise on all available channels instead of concentrating resources on the most profitable areas.
Prospects usually do their research on multiple channels, so you might try to cover all the possible touch points. In theory, this could generate more leads, but only if you had an unlimited marketing budget and human resources.
Powered by WPeMatico
The speed at which gaming has proliferated is matched only by the pace of new buzzwords inundating the ecosystem. Marketers and decision-makers, already suffering from FOMO about opportunities within gaming, have latched onto buzzy trends like the applications of blockchain in gaming and the “metaverse” in an effort to get ahead of the trend rather than constantly play catch-up.
The allure is obvious, as the relationship between the blockchain, metaverse and gaming makes sense. Gaming has always been on the forefront of digital ownership (one can credit gaming platform Steam for normalizing the concept for games, and arguably other media such as movies), and most agreed upon visions of the metaverse rely upon virtual environments common in games with decentralized digital ownership.
Whatever your opinion of either, I believe they both have an interrelated future in gaming. However, the success or relevance of either of these buzzy topics is dependent upon a crucial step that is being skipped at this point.
Let’s start with the example of blockchain and, more specifically, NFTs. Collecting items of varying rarities and often random distribution form some of the core “loops” in many games (e.g., kill monster, get better weapon, kill tougher monster, get even better weapon, etc.), and collecting “skins” (i.e., different outfits/permutation of game character) is one of the most embraced paradigms of microtransactions in games.
The way NFTs are currently being discussed in relation to gaming are very much in danger of falling into this very trap: Killing the core gameplay loop via a financial fast track.
Now, NFTs are positioned to be a natural fit with various rare items having permanent, trackable and open value. Recent releases such as “Loot (for Adventurers)” have introduced a novel approach wherein the NFTs are simply descriptions of fantasy-inspired gear and offered in a way that other creators can use them as tools to build worlds around. It’s not hard to imagine a game built around NFT items, à la Loot.
But that’s been done before … kind of. Developers of games with a “loot loop” like the one described above have long had a problem with “farmers,” who acquire game currencies and items to sell to players for real money, against the terms of service of the game. The solution was to implement in-game “auction houses” where players could instead use real money to purchase items from one another.
Unfortunately, this had an unwanted side effect. As noted by renowned game psychologist Jamie Madigan, our brains are evolved to pay special attention to rewards that are both unexpected and beneficial. When much of the joy in some games comes from an unexpected or randomized reward, being able to easily acquire a known reward with real money robbed the game of what made it fun.
The way NFTs are currently being discussed in relation to gaming are very much in danger of falling into this very trap: Killing the core gameplay loop via a financial fast track. The most extreme examples of this phenomena commit the biggest cardinal sin in gaming — a game that is “pay to win,” where a player with a big bankroll can acquire a material advantage in a competitive game.
Blockchain games such as Axie Infinity have rapidly increased enthusiasm around the concept of “play to earn,” where players can potentially earn money by selling tokenized resources or characters earned within a blockchain game environment. If this sounds like a scenario that can come dangerously close to “pay to win,” that’s because it is.
What is less clear is whether it matters in this context. Does anyone care enough about the core game itself rather than the potential market value of NFTs or earning potential through playing? More fundamentally, if real-world earnings are the point, is it truly a game or just a gamified micro-economy, where “farming” as described above is not an illicit activity, but rather the core game mechanic?
The technology culture around blockchain has elevated solving for very hard problems that very few people care about. The solution (like many problems in tech) involves reevaluation from a more humanist approach. In the case of gaming, there are some fundamental gameplay and game psychology issues to be tackled before these technologies can gain mainstream traction.
We can turn to the metaverse for a related example. Even if you aren’t particularly interested in gaming, you’ve almost certainly heard of the concept after Mark Zuckerberg staked the future of Facebook upon it. For all the excitement, the fundamental issue is that it simply doesn’t exist, and the closest analogs are massive digital game spaces (such as Fortnite) or sandboxes (such as Roblox). Yet, many brands and marketers who haven’t really done the work to understand gaming are trying to fast-track to an opportunity that isn’t likely to materialize for a long time.
Gaming can be seen as the training wheels for the metaverse — the ways we communicate within, navigate and think about virtual spaces are all based upon mechanics and systems with foundations in gaming. I’d go so far as to predict the first adopters of any “metaverse” will indeed be gamers who have honed these skills and find themselves comfortable within virtual environments.
By now, you might be seeing a pattern: We’re far more interested in the “future” applications of gaming without having much of a perspective on the “now” of gaming. Game scholarship has proliferated since the early aughts due to a recognition of how games were influencing thought in fields ranging from sociology to medicine, and yet the business world hasn’t paid it much attention until recently.
The result is that marketers and decision-makers are doing what they do best (chasing the next big thing) without the usual history of why said thing should be big, or what to do with it when they get there. The growth of gaming has yielded an immense opportunity, but the sophistication of the conversations around these possibilities remains stunted, due in part to our misdirected attention.
There is no “pay to win” fast track out of this blind spot. We have to put in the work to win.
Powered by WPeMatico
Whatnot, a livestreaming shopping platform for collectors to buy and sell things like rare Pokémon cards and Funko Pops, has closed a $150 million Series C — its third round of fundraising in 2021 alone. This round pins Whatnot’s valuation at $1.5 billion, earning it a spot on the ever-growing list of unicorns.
So what’s a Whatnot? The app captures a trend that had been growing popular on platforms like Instagram in the U.S. (and was already hugely popular in China): live shopping. Verified sellers can go on the air at any time, hosting on-the-fly video auctions for their goods. Sometimes buyers know exactly what they’re getting. Other times it’s more of a mystery bag; with the popular “card break” concept, for example, users buy assigned portions of an unopened (and often itself rare) box of Pokémon or sports cards and watch its contents revealed live.
This round was funded by return investors a16z and Y Combinator’s Continuity Fund, along with one new firm joining them: CapitalG (which was known as Google Capital before the Google/Alphabet name change.) They’ve also added a few well-known names to their list of angel investors, including Andre Iguodala of the Golden State Warriors, Zion Williamson of the New Orleans Pelicans and Logan Paul of the YouTube. Initial word of this round broke last week, via The Information.
Whatnot originally started as a more standard (less live) resale platform, at first focused on authenticating just one kind of collectable: Funko Pops. As the pandemic took over and everyone was suddenly stuck at home, they leaned hard into live shopping — and grew rapidly as a result.
Meanwhile, the company has been quickly expanding its scope; it grew from just Funko Pops to all sorts of other collectables, including Pokémon cards, pins, vintage clothing, sneakers and more. Whatnot co-founder Grant Lafontaine tells me that its biggest driver is sports cards, followed by Pokémon and Funko Pops. With each category it dives into, Whatnot focuses on onboarding sellers that are already known and trusted in their respective community; each streamer on the platform is currently vetted by the company before they can go live, helping them keep fraud to a minimum. Doing anything sketchy just means getting booted off the platform and burning your own reputation in the process.
A few other key bits from my conversation with Lafontaine:
This round brings the company’s total funds raised to $225 million — pretty much all of that in the last year. Meanwhile, competition in the space is heating up; competitors like Popshop have been raising millions for their platforms, and Miami’s Loupe raised $12 million back in June (and is opening a physical retail space soon) with its focus laser-locked on sports cards live sales. Existing giants want in on it too: YouTube is playing with the live shopping concept, and Amazon has been bringing in influencers to host live sessions. In other words: watch this space. Maybe watch it via livestream.
Powered by WPeMatico
The art of pitching is perhaps the most important art that a founder learns on their journey to unicorn status and beyond. And like any art, it helps to get some critical feedback along the way from the judges on the other side of the table.
That’s why at every Disrupt, we host Pitch Deck Teardown, a panel of VCs who read and critique several pitch decks in a row to offer feedback on everything from the overarching narrative and story to the mundane details of format, typography and colors.
At TechCrunch Disrupt 2021 next week, I’m excited to be hosting Maren Bannon of January Ventures, Bling Capital’s Ben Ling and Vanessa Larco of NEA for our next iteration of this popular workshopping panel.
If you’re a founder and want to submit your deck for consideration, head on over to this trusty Google Form and upload a copy of your pitch deck in PDF format. Remember that this will be presented publicly, so make sure it’s appropriate for a live studio audience. We’ll be selecting roughly six of them for inclusion in the event, and we’ll notify by email the founders selected.
Come join us next week! And if you need tickets to Disrupt, we still have some available for all the virtual excitement across two stages and dozens of fireside chats and panels.
Powered by WPeMatico
Fiberplane, an Amsterdam-based early-stage startup that is building collaborative notebooks for SREs (site reliability engineers) to collaborate around an incident in a similar manner to group editing in a Google Doc, announced a €7.5 million (approximately $8.8 million USD) seed round today.
The round was co-led by Crane Venture Partners and Notion Capital, with participation from Northzone, System.One and Basecase Capital.
Micha Hernandez van Leuffen (known as Mies) is founder and CEO at Fiberplane. When his previous startup, Werker, was sold to Oracle in 2017, Hernandez van Leuffen became part of a much larger company where he saw people struggling to deal with outages (which happen at every company).
“We were always going back and forth between metrics, logs and traces, what I always call this sort of treasure hunt, and figuring out what was the underlying root cause of an outage or downtime,” Hernandez van Leuffen told me.
He said that this experience led to a couple of key insights about incident response: First, you needed a centralized place to pull all the incident data together, and secondly that as a distributed team managing a distributed system you needed to collaborate in real time, often across different time zones.
When he left Oracle in August 2020, he began thinking about the idea of giving DevOps teams and SREs the same kind of group editing capabilities that other teams inside an organization have with tools like Google Docs or Notion and an idea for his new company began to take shape.
What he created with Fiberplane is a collaborative notebook for SRE’s to pull in the various data types and begin to work together to resolve the incident, while having a natural audit trail of what happened and how they resolved the issue. Different people can participate in this notebook, just as multiple people can edit a Google Doc, fulfilling that original vision.
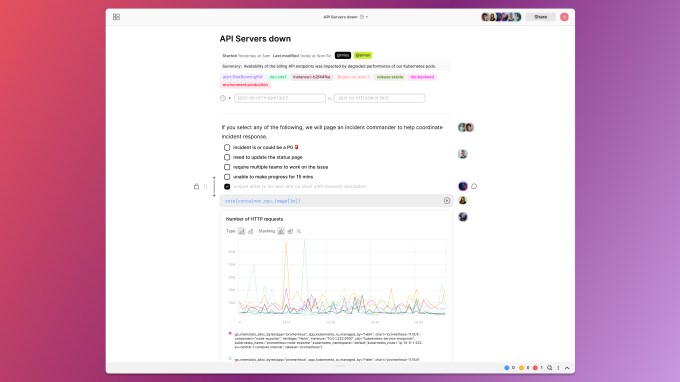
Fiberplane collaborative notebook example with multiple people involved. Image Credit: Fiberplane
He doesn’t plan to stop there though. The longer-term vision is an operational platform for SREs and DevOps teams to deal with every aspect of an outage. “This is our starting point, but we are planning to expand from there as more I would say an SRE workbench, where you’re also able to command and control your infrastructure,” he said.
Today the company has 13 employees and is growing, and as they do, they are exploring ways to make sure they are building a diverse company, looking at concrete strategies to find more diverse candidates.
“To hire diversely, we’re re-examining our top of the funnel processes. Our efforts include posting our jobs in communities of underrepresented people, running our job descriptions through a gender decoder and facilitating a larger time frame for jobs to remain open,” Elena Boroda, marketing manager at Fiberplane said.
While Hernandez van Leuffen is based in Amsterdam, the company has been hiring people in the U.K., Berlin, Copenhagen and the U.S., he said. The plan is to have Amsterdam as a central hub when offices reopen as the majority of employees are located there.
Powered by WPeMatico
APIs are the grease turning the gears and wheels for many organizations’ IT systems today, but as APIs grow in number and use, tracking how they work (or don’t work) together can become complex and potentially critical if something goes awry. Now, a startup that has built an innovative way to help with this is announcing some funding after getting traction with big enterprises adopting its approach.
Tyk, which has built a way for users to access and manage multiple internal enterprise APIs through a universal interface by way of GraphQL, has picked up $35 million, an investment that it will be using both for hiring and to continue enhancing and expanding the tools that it provides to users. Tyk has coined a term describing its approach to managing APIs and the data they produce — “universal data graph” — and today its tools are being used to manage APIs by some 10,000 businesses, including large enterprises like Starbucks, Societe Generale and Domino’s.
Scottish Equity Partners led the round, with participation also from MMC Ventures — its sole previous investor from a round in 2019 after boostrapping for its first five years. The startup is based out of London but works in a very distributed way — one of the co-founders is living in New Zealand currently — and it will be hiring and growing based on that principle, too. It has raised just over $40 million to date.
Tyk (pronounced like “tyke”, meaning small/lively child) got its start as an open source side project first for co-founder Martin Buhr, who is now the company’s CEO, while he was working elsewhere, as a “load testing thing,” in his words.
The shifts in IT toward service-oriented architectures, and building and using APIs to connect internal apps, led him to rethink the code and consider how it could be used to control APIs. Added to that was the fact that as far as Buhr could see, the API management platforms that were in the market at the time — some of the big names today include Kong, Apigee (now a part of Google), 3scale (now a part of RedHat and thus IBM), MuleSoft (now a part of Salesforce) — were not as flexible as his needs were. “So I built my own,” he said.
It was built as an open source tool, and some engineers at other companies started to use it. As it got more attention, some of the bigger companies interested in using it started to ask why he wasn’t charging for anything — a sure sign as any that there was probably a business to be built here, and more credibility to come if he charged for it.
“So we made the gateway open source, and the management part went into a licensing model,” he said. And Tyk was born as a startup co-founded with James Hirst, who is now the COO, who worked with Buhr at a digital agency some years before.
The key motivation behind building Tyk has stayed as its unique selling point for customers working in increasingly complex environments.
“What sparked interest in Tyk was that companies were unhappy with API management as it exists today,” Buhr noted, citing architectures using multiple clouds and multiple containers, creating more complexity that needed better management. “It was just the right time when containerization, Kubernetes and microservices were on the rise… The way we approach the multi-data and multi-vendor cloud model is super flexible and resilient to partitions, in a way that others have not been able to do.”
“You engage developers and deliver real value and it’s up to them to make the choice,” added Hirst. “We are responding to a clear shift in the market.”
One of the next frontiers that Tyk will tackle will be what happens within the management layer, specifically when there are potential conflicts with APIs.
“When a team using a microservice makes a breaking change, we want to bring that up and report that to the system,” Buhr said. “The plan is to flag the issue and test against it, and be able to say that a schema won’t work, and to identify why.”
Even before that is rolled out, though, Tyk’s customer list and its growth speak to a business on the cusp of a lot more.
“Martin and James have built a world-class team and the addition of this new capital will enable Tyk to accelerate the growth of its API management platform, particularly around the GraphQL focused Universal Data Graph product that launched earlier this year,” said Martin Brennan, a director at SEP, in a statement. “We are pleased to be supporting the team to achieve their global ambitions.”
Keith Davidson, a partner at SEP, is joining the Tyk board as a non-executive director with this round.
Powered by WPeMatico