Startups
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Back in early July, TechCrunch covered the Envision Accelerator. The program was put together by a group of students and recent graduates, often with some early venture capital experience, to help give some young startups a boost, and to shake up industry diversity metrics at the same time.
Now on the other side of their first batch’s official program and into its investor week, Envision shared a number of statistics regarding that first cohort, and talked about plans for its second.
What I appreciate about the Envision group is that by simply going out and making their own accelerator, they have shown that it is possible to attract a diverse group of startups to a program. How diverse? Let’s find out.
According to data provided to TechCrunch by Annabel Strauss and Eliana Berger from the Envision team (more on them here, if you’re curious), 17 companies made it into the first group. Of those 17 companies and their founding teams, around one-third of founders were black, around one in five were Latinx and more than 75% had a female founder.
Those are impressive metrics, frankly, especially when we consider what other groups have managed in recent sessions. Envision’s founders also skew young, not a surprise, given that the effort was effectively students making a program for their fellow students, with a three-to-one bias in favor of undergrads versus graduate students.
We’ll list the participating companies with links to their sites below, as per usual with this sort of accelerator roundup.
But, before we do, a few notes on how the first batch went down. When we last talked about Envision, they were still fundraising to pull together more capital to give to their selected companies. The idea was to provide $10,000 in equity-free capital, along with an eight-week program of lectures, networking and hands-on help from the Envision collective and a group of advisors.
According to Strauss and Berger, Envision was able to raise all the money that it needed to provide funding to its selected companies, though not every team picked up the full $10,000, with the duo noting that the amount varied based somewhat on need.
It will not be clear for a bit if the companies that went through Envision’s maiden class manage to raise more capital, scale, and become success. But for the Envision team itself, round one went well enough that a second effort is just around the corner.
And when it comes to that second push — or class, really — Envision remains in a hurry. After putting together its initial cohort while building its own organization on the fly, the group is going to kick off its second batch in October, giving it slim breathing room between cohorts.
There’s a reason for the haste, however. First, Envision wants to add two weeks to its programming, bringing the accelerator to a total of 10 weeks to include more training, and to fit that into the current semester, October was the kickoff month. Strauss and Berger noted that some students are taking leave during the first semester of this academic year.
More on Envision itself when we hear more on how the first batch did in attracting investor interest.
Here are the companies from batch one:
- Adora: Adora is a personalized, digital campus visit platform that makes compelling visits accessible to everyone.
- Devie: Devie is a parent coaching app that guides parents through challenges in a personal, accessible and actionable way.
- Forage: Forage is a mobile application that provides real-time pricing at grocery stores so families can save money.
- Holdette: At Holdette, we make professional work wear with real pockets for women entering the workforce for the first time.
- Justice Text: Justice Text makes video evidence management software to produce fair outcomes in the criminal justice system.
- Klara: Klara is a data science platform transforming the way consumers discover skincare and haircare products.
- Mindstand: Mindstand helps leaders identify implicit bias, employee engagement and culture fit within their internal communications.
- MODE: MODE helps people discover and purchase clothes through a personalized, social shopping experience.
- Mylabox: Mylabox is a cross-border e-commerce marketplace enabling SMBs in LatAm to access high-quality overseas products.
- Nibble: Nibble is a platform solving food waste by helping restaurants sell excess meals and ingredients at a discount.
- Pareto: Pareto is building a library of quick-to-launch workflows that startups can deploy for operations as they scale.
- Schefs: Schefs is a platform for college students to facilitate and participate in themed conversations over a virtual meal.
- UrConvey: UrConvey is a safe app that makes it easy to ride share with people you know by harnessing your network.
- Vngle: Vngle is a decentralized grassroots news network bringing “various angles” of local reality coverage to news deserts.
- Wellnest: Wellnest is a joyful journaling app that increases mindfulness by prioritizing user experience, voice and insights.
- Winkshare: Winkshare is a secure messaging app designed for the modern relationship. Your relationship, your business.
- Yup: Yup rewards valuable opinions across the web. Rate anything, earn rewards for accuracy, and gain status.
Powered by WPeMatico
We’re seeing a gradual expansion of national regulations that require data from SaaS applications to be stored locally in the country where it’s sourced and used. Today a startup that’s built a service around that need — specifically, data residency-as-a-service — is announcing some funding to continue building out its company amid strong demand.
InCountry, which provides a set of solutions — comprising software as well as some consultancy — that helps companies comply with local regulations when adopting SaaS products, has raised $18 million in funding.
This is technically an extension to its Series A, but in keeping with the growth of its business, it comes with a big bump to its valuation: the startup is now valued at “north” of $150 million. Founder and CEO Peter Yared said this is more than double the valuation of its previous round a little over a year ago.
The money is coming from a mix of strategic and financial investors. It’s being led by Caffeinated Capital and Abu Dhabi’s Mubadala, with participation from new investor Accenture Ventures and previous investors Arbor Ventures, Felicis, Ridge Ventures, Bloomberg Beta and Team Builder Ventures. Accenture is one of InCountry’s key channel partners, reselling the software as part of bigger data management and integration contracts, Yared tells me.
The company has seen a decent bump in its business in the last year, expanding to 90 countries from 65, where it provides guidance and services to store and use data in compliance with legal requirements. Alongside that it has an increasingly long list of software packages that it covers with its products. The list currently includes Salesforce, ServiceNow, Twilio, Mambu and Segment, with customers including a large list of enterprises including stock exchanges, banks and pharmaceutical companies.
“This company was based off a crazy thesis,” Yared said with an almost incredulous laugh (he has a very jocular way of talking, even when he’s being serious). “Now it’s 20 months old, and our customers are banks, pharma giants, stock exchanges. We are proud that large institutions can trust us.”
A big bump in its business in recent times has been in Asia Pacific and the Middle East, which are two main regions when it comes to data residency regulations and therefore ripe ground for winning new customers — one reason why Mubadala is part of this round, Yared said.
“At Mubadala we are committed to backing visionary founders whose innovations fuel economies,” said Ibrahim Ajami, head of Ventures at Mubadala Capital. “Since day one, InCountry’s cloud solution has addressed a massive challenge in this era of regulation by giving businesses the tools to grow internationally while remaining compliant with data residency regulations. We’re doubling down on our investment and are supporting InCountry’s expansion into the MENA region because we believe they are the best team to help drive global business forward.”
Partly due to the growing ubiquity, flexibility and relatively cheap cost of cloud computing, software as a service has been on a fast growth trajectory for years now. But even within that trend, it has had a huge boost in 2020 as a result of the global health pandemic.
COVID-19 has given the need for remote computing, and being able to access data wherever you happen to be — which in many cases today is no longer in your usual office space. On top of that, we have a lot more “wiggle room” in business, with organizations quickly scaling up and down with demand.
The knock-on effect has been a big boost for SaaS. But that growth has come with some caveats, and one of the biggest alongside security has been around data protection, and specifically national requirements in how data is stored and used. Arguably, SaaS companies have been more concerned with scaling their software and business funnels than they have been with how data is handled and how that has changed in keeping with local regulations, and that’s the opportunity that InCountry has stepped in to fill.
It provides not just a set of software to store and handle data in a secure way, but also an extensive list of legal advisors with expertise at the local level to help companies get their data policies in order. It’s an interesting model: While InCountry’s been an early mover in identifying this market opportunity and building technology to address it, it’s buffered its competitive position not with a sole focus on technology, but an extensive amount of human capital to get each implementation right.
That can prove to be a costly thing to get wrong. In the EU in July, the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) put down the EU-US Privacy Shield — a framework that let businesses transfer personal data between the European Union and the United States while ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. This has impacted some 5,000 companies, which now have to rethink how they handle their data. The fine for not complying with storing data locally means that they can be fined up to 4% of their revenues.
Yared tells me that for now, the main competitor to something like InCountry has been companies building their own policies in house. Some of those solutions would have been done completely in house and some in partnership with integrators, but all of them were hard to scale and were painful to maintain, one reason why companies and their business partners are turning to working with his startup.
“Accenture Ventures is pleased to support InCountry as it continues to expand globally,” said Tom Lounibos, managing director, Accenture Ventures, in a statement. “InCountry’s software solutions are helping companies address the critical issue of becoming and remaining compliant with a multitude of data residency laws. This expansion will help support enterprises as they unlock their business across borders.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Gong announced a $200 million Series D investment just last month, and loaded with fresh cash, the company wasted no time taking advantage. Today, it announced it was buying early-stage Isreali sales technology startup Vayo. The companies did not share terms of the deal, but Gong CEO Amit Bendov said the deal closed a couple of weeks ago.
The two companies match up quite well from a tech standpoint. While Gong searches unstructured data like emails and phone call transcripts and finds nuggets of data, Vayo looks at structured data, which is essentially the output of the Gong search process. What’s more, it handles large amounts of data at scale.
“Vayo helps find customer interactions at a large scale to identify trends like customers likely to churn or usage is going up, or your deals are starting to slow down — and they do this for structured data at scale,” Bendov told TechCrunch.
He said this ability to identify trends was really what attracted him to the company, even though it was still at an early stage of development. “It’s a perfect fit for Gong. We take unstructured data — emails, audio calls video calls — and extract insights. Customers, especially with a large organization, don’t want to see individual interactions but high order insights […] and they’ve developed [a solution] to identify trends on large data volumes for customer interactions,” he said.
Vayo was founded in 2018 and raised $1.7 million in seed capital, according to Crunchbase. Joining forces with Gong gives them an opportunity to develop the technology inside a company that’s growing quickly and is extremely well capitalized, having raised more than $300 million in the last 18 months.
Avshi Avital, CEO at Vayo, who has joined Gong with his four fellow employees, gave a familiar argument for selling the company. “With Gong we found the perfect partner to realize this mission faster and maximize the impact of the technology we built given the scale of their customer base and growth potential,” he said.
The plan is to fold the Vayo tech into the Gong platform, a process that will take three to six months, according to Bendov.
Powered by WPeMatico
Four years after the Great Recession, France’s newly elected socialist president François Hollande raised taxes and increased regulations on founder-led startups. The subsequent flight of entrepreneurs to places like London and Silicon Valley portrayed France as a tough place to launch a company. By 2016, France’s national statistics bureau estimated that about three million native-born citizens had moved abroad.
Those who remained fought back: The Family was an early accelerator that encouraged French entrepreneurs to adopt Silicon Valley’s startup methodology, and the 2012 creation of Bpifrance, a public investment bank, put money into the startup ecosystem system via investors. Organizers founded La French Tech to beat the drum about native startups.
When President Emmanuel Macron took office in May 2017, he scrapped the wealth tax on everything except property assets and introduced a flat 30% tax rate on capital gains. Station F, a giant startup campus funded by billionaire entrepreneur Xavier Niel on the site of a former railway station, began attracting international talent. Tony Fadell, one of the fathers of the iPod and founder of Nest Labs, moved to Paris to set up investment firm Future Shape; VivaTech was created with government backing to become one of Europe’s largest startup conference and expos.
Now, in the COVID-19 era, the government has made €4 billion available to entrepreneurs to keep the lights on. According to a recent report from VC firm Atomico, there are 11 unicorns in France, including BlaBlaCar, OVHcloud, Deezer and Veepee. More appear to be coming; last year Macron said he wanted to see “25 French unicorns by 2025.”
According to Station F, by the end of August, there had been 24 funding rounds led by international VCs and a few big transactions. Enterprise artificial intelligence and machine-learning platform Dataiku raised a $100 million Series D round, and Paris-based gaming startup Voodoo raised an undisclosed amount from Tencent Holdings.
We asked 12 Paris-based investors to comment on the state of play in their city:
What trends are you most excited about investing in, generally?
All the fintechs addressing SMBs to help them to focus more on their core business (including banks disintermediation by fintech, new infrastructures tech that are lowering the barrier to entry to nonfintech companies).
What’s your latest, most exciting investment?
77foods (plant-based bacon) — love that alternative proteins trend as well. Obviously, we need to transform our diet toward more sustainable food. It’s the next challenge for humanity.
What are you looking for in your next investment, in general?
Impact investment: Logistic companies tackling the life cycle of products to reduce their carbon footprint and green fintech that reinvent our spending and investment strategy around more sustainable products.
Which areas are either oversaturated or would be too hard to compete in at this point for a new startup? What other types of products/services are you wary or concerned about?
D2C products.
How much are you focused on investing in your local ecosystem versus other startup hubs (or everywhere) in general? More than 50%? Less?
100% investing in France as I’m managing Paris Saclay Seed Fund, a €53 million fund, investing in pre-seed and seed startups launched by graduates and researchers from the best engineering and business schools from this ecosystem.
Which industries in your city and region seem well-positioned to thrive, or not, long term? What are companies you are excited about (your portfolio or not), which founders?
Deep tech, biotech and medical devices. Paris, and France in general, has thousands of outstanding engineers that graduate each year. Researchers are more and more willing to found companies to have a true impact on our society. I do believe that the ecosystem is more and more structured to help them to build such companies.
How should investors in other cities think about the overall investment climate and opportunities in your city?
Paris is booming for sure. It’s still behind London and Berlin probably. But we are seeing more and more European VC offices opening in the city to get direct access to our ecosystem. Even in seed rounds, we start to have European VCs competing against us. It’s good — that means that our startups are moving to the next level.
Do you expect to see a surge in more founders coming from geographies outside major cities in the years to come, with startup hubs losing people due to the pandemic and lingering concerns, plus the attraction of remote work?
For sure startups will more and more push for remote organizations. It’s an amazing way to combine quality of life for employees and attracting talent. Yet I don’t think it will be the majority. Not all founders are willing/able to build a fully remote company. It’s an important cultural choice and it’s adapted to a certain type of business. I believe in more flexible organization (e.g., tech team working remotely or 1-2 days a week for any employee).
Which industry segments that you invest in look weaker or more exposed to potential shifts in consumer and business behavior because of COVID-19? What are the opportunities startups may be able to tap into during these unprecedented times?
Travel and hospitality sectors are of course hugely impacted. Yet there are opportunities for helping those incumbents to face current challenges (e.g., better customer care and services, stronger flexibility, cost reduction and process automation).
How has COVID-19 impacted your investment strategy? What are the biggest worries of the founders in your portfolio? What is your advice to startups in your portfolio right now?
Cash is king more than ever before. My only piece of advice will be to keep a good level of cash as we have a limited view on events coming ahead. It’s easy to say but much more difficult to put in practice (e.g., to what extend should I reduce my cash burn? Should I keep on investing in the product? What is the impact on the sales team?). Startups should focus only on what is mission-critical for their clients. Yet it doesn’t impact our seed investments as we invest pre-revenue and often pre-product.
What is a moment that has given you hope in the last month or so? This can be professional, personal or a mix of the two.
There is no reason to be hopeless. Crises have happened in the past. Humanity has faced other pandemics. Humans are resilient and resourceful enough to adapt to a new environment and new constraints.
Powered by WPeMatico
Data protection and data privacy have gone from niche concerns to mainstream issues in the last several years, thanks to new regulations and a cascade of costly breaches that have laid bare the problems that arise when information and data security are treated haphazardly.
Yet that swing has also thrown up a whole series of issues for organisations and business functions that depend on sharing and exchanging data in order to work. Today, a startup that has built a new way of exchanging data while still keeping privacy in mind — starting first by applying the concept to the “marketing industrial complex” — is announcing a round of funding as it continues to pick up momentum.
InfoSum, a London startup that has built a way for organizations to share their data with each other without passing it on to each other — by way of a federated, decentralized architecture that uses mathematical representations to organise, “read” and query the data — is today announcing that it has raised $15.1 million.
Data may be the new oil, but according to founder and CEO Nick Halstead, that just means “it’s sticky and gets all over the place.” That is to say, InfoSum is looking for a new way to use data that is less messy, and less prone to leakage, and ultimately devaluation.
The Series A is being co-led by Upfront Ventures and IA Ventures. A number of strategics using InfoSum — Ascential, Akamai, Experian, British broadcaster ITV and AT&T’s Xandr — are also participating in the round. The startup has raised $23 million to date.
Nicholas Halstead, the founder and CEO who previously had founded and led another big data company, DataSift (the startup that gained early fame as a middleman for Twitter’s firehose of data, until Twitter called time on that relationship to push its own business strategy), said in an interview that the plan is to use the funding to continue fueling its growth, with a specific focus on the U.S. market.
To that end, Brian Lesser — the founder and former CEO of Xandr (AT&T’s adtech business that is now a part of AT&T’s WarnerMedia), and previous to that the North American CEO of GroupM — is joining the company as executive chairman. Lesser had originally led Xandr’s investment into InfoSum and had previously been on the board of the startup.
InfoSum got its start several years ago as CognitiveLogic, founded at a time when Halstead was first starting to get his head around the problems that were becoming increasingly urgent in how data was being used by companies, and how newer information architecture models using data warehousing and cloud computing could help solve that.
“I saw the opportunity for data collaboration in a more private way, helping enable companies to work together when it came to customer data,” he said. This eventually led to the company releasing its first product two years ago.
In the interim, and since then, that trend, he noted, has only gained momentum, spurred by the rise of companies like Snowflake that have disrupted the world of data warehousing, cookies have started to increasingly go out of style (and some believe will disappear altogether over time) and the concept of federated architecture has become much more ubiquitous, applied to identity management and other areas.
All of this means that InfoSum’s solution today may be aimed at martech, but it is something that affects a number of industries. Indeed, the decision to focus on marketing technology, he said, was partly because that is the industry that Halstead worked most closely with at DataSift, although the plan is to expand to other verticals as well.
“We’ve done a lot of work to change the marketing industrial complex,” said Lesser, “but its bigger use cases are in areas like finance and healthcare.”
Powered by WPeMatico
TechCrunch is on the hunt to feature 10 early-stage mobility startups at our virtual TC Sessions: Mobility 2020 pitch night. The pitch-off event, originally set for May, will now be held October 5th — the evening before Mobility 2020.
The top five companies from pitch night will take the stage at the main event with industry heavy hitters like Boris Sofman of Waymo, Nancy Sun of Ike and Trucks VC’s Reilly Brennan. Now we are shining a light on game changing startups — hardware and software breaking the mobility mold. From battery advancements to mapping, fuel processing to micromobility, TechCrunch wants the next generation of mobility’s brightest on stage. The process is simple:
Apply. TechCrunch editorial will review every application and demo video submitted. Companies will be reviewed based on innovation, scope of impact, uniqueness of product idea and potential for exit — IPO or acquisition. Selected companies will get to pitch onstage, receive two complimentary event tickets, an hour training with the Startup Battlefield Editor and a spot in CrunchMatch (TC’s meeting matching program).
Pitch Part I. The top 10 startups from around the world will be selected to pitch live to the TC audience on the virtual stage. After a private pitch coaching session, founders will have one minute to pitch, followed by a Q&A with our expert panel of investor and industry expert judges.
Pitch Part II. The top five companies from pitch night will get a prime slot to pitch and demo their product on the main stage at Mobility 2020 in front of thousands of TC viewers — press, industry leaders and VCs.
The deadline to apply is September 15th. Selections will occur on a rolling basis so get your application in ASAP!
Powered by WPeMatico
Another busy week in cybersecurity.
In case you missed it: A widely used messaging app used by over a million protesters has several major security flaws; a little-known loophole has let the DMV sell driver’s licenses and Social Security records to private investigators; and the U.S. government is suing to reclaim over $2.5 million in cryptocurrency stolen by North Korean hackers from two major exchanges.
But this week we are focusing on how a Tesla employee foiled a ransomware attack, and, ahead of Palantir’s debut on the stock market, how much of a risk factor is the company’s public image?
$1 million. That’s how much a Tesla employee would have netted if they accepted a bribe from a Russian operative to install malware on Tesla’s Gigafactory network in Nevada. Instead, the employee told the FBI and the Russian was arrested.
The Justice Department charged the 27-year-old Russian, Egor Igorevich, weeks later as he tried to flee the United States. According to the indictment, his plan was to ask the employee to deliberately deploy ransomware on the Gigafactory’s network, grinding the network to a halt for a ransom of several million dollars. The would-be insider threat is likely the first of its kind, one ransomware expert told Wired, as financially driven hackers continue to up their game.
Tesla founder Elon Musk tweeted earlier this week confirming that Tesla was the target of the failed attack.
The attack, if carried out, could have been devastating. The indictment said that the malware was designed to extract data from the network before locking its files. This data-stealing ransomware is an increasing trend. These hacker groups not only encrypt a victim’s files but also exfiltrate the data to their servers. The hackers typically threaten to publish the victim’s files if the ransom isn’t paid.
Powered by WPeMatico
With Dorian, co-founder and CEO Julia Palatovska said she’s hoping to empower fiction writers and other storytellers to create their own games.
The startup is announcing that it has raised $3.25 million in seed funding led by March Capital Partners, with participation from VGames, Konvoy Ventures, London Venture Partners, Michael Chow (co-creator of the Twitch series “Artificial”), Andover Ventures and talent management company Night Media.
In addition, John Howell, the former vice president of partnerships at Twitch, has joined the board as an independent director.
Palatskova previously worked in gaming as the head of business development at G5 Entertainment, and she said she’d also become entranced by narrative games and interactive fiction. And while there are existing interactive fiction platforms, she saw “an opportunity that I felt was missing,” particularly in the fact that those platforms are “entirely single player, with no opportunity to play and collaborate with other people.”
So she gave me a quick tour of the Dorian platform, showing me how, without coding, a writer can essentially design characters and backgrounds by choosing from a variety of visual assets (and they’ll eventually be able to upload assets of their own), while using a flowchart-style interface to allow the writer to connect different scenes in the story and create player choices. And as Palatskova noted, you can also collaborate on a story in real-time with other writers.
“In terms of writer productivity, I would say there is almost no difference between creating interactive fiction on our engine and just writing fiction,” she said.
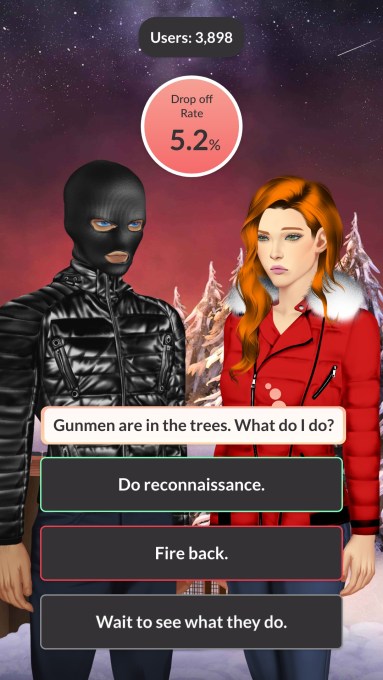
Image Credits: Dorian
From what I could see, the resulting games look similar to what you’d find on platforms like Pocket Gems’ Episode, where there aren’t a lot of technical bells and whistles, so the story, dialogue and character choices move to the forefront.
When I brought up the open-source game creation software Twine, Palatskova said Twine is “just a tool.”
“We want to be more like Roblox, both the tools and the distribution,” she said.
In other words, writers use Dorian to create interactive stories, but they also publish those stories using the Dorian app. (The writer still owns the resulting intellectual property.) Palatskova noted that Dorian also provides detailed analytics on how readers are responding, which is helpful not just for creating stories, but also for monetizing via premium story choices.
In fact, Dorian says that in early tests involving around 50,000 players, writers were able to improve monetization by 70% after only one or two iterations. And Palatskova noted that with Dorian’s games — unlike an interactive film such as “Black Mirror: Bandersnatch” —”It’s fast and easy to test multiple branches.”
Dorian is currently invite-only, but the plan is to launch more broadly later this year. Palatskova is recruiting writers with and without gaming experience, but she also expects plenty of successful contributions to come from complete novices. She wants Dorian to be “a completely open platform, like Roblox or Twitch for writers.”
“Dorian’s success in creating an interactive platform that values storytelling while prioritizing monetization for its writers is a game-changer,” said March Capital’s Gregory Milken in a statement. “Julia and her team are creating a community that is primed to capture the attention of today’s influential but underrepresented audiences of diverse content creators.”
Update: An earlier version of this post incorrectly stated that Dorian had raised $3.15 million.
Powered by WPeMatico
Welcome back to The TechCrunch Exchange, a weekly startups-and-markets newsletter. It’s broadly based on the daily column that appears on Extra Crunch, but free, and made for your weekend reading. (You can sign up for the newsletter here!)
Ready? Let’s talk money, startups and spicy IPO rumors.
During Monday’s IPO wave I was surprised to see Asana join the mix.
After news had broken in June that the company had raised hundreds of millions in convertible debt, I hadn’t guessed that the productivity unicorn wouldn’t give us an S-1 in the very next quarter. I was contentedly wrong. But the reason why Asana’s IPO is notable isn’t really much to do with the company itself, though do take the time to dig into its results and history.
What matters about Asana’s debut is that it appears set to test out a model that, until very recently, could have become the new, preferred way of going public amongst tech companies.
Here’s what I mean: Instead of filing to go public, and raising money in a traditional IPO, or simply listing directly, Asana executed two, large, convertible debt offerings pre-debut, thus allowing it to direct list with lots of cash without having raised endless equity capital while private.
The method looked like a super-cool way to get around the IPO pricing issue that we’ve seen, and also provide a ramp to direct listing for companies that didn’t get showered with billions while private. (That Asana co-founder Dustin Moskovitz’s trust led the debt deal is simply icing on this particular Pop-Tart).
This brief column was going to be all about how we may see unicorns follow the Asana route in time, provided that its debt-powered direct listing goes well. But then the NYSE got permission from the SEC to allow companies to raise capital when they direct-list.
In short, some companies that direct-list in the future will be able to sell a bloc of shares at a market-set value that would have previously set their “open” price. So instead of flogging the stock and setting a price and selling shares to rich folks and then finding out what public investors would really pay, all that IPO faff is gone and bold companies can simply offer shares at whatever price the market will bear.
All that is great and cool, but as companies will be able to direct-list and raise capital, the NYSE’s nice news means that Asana is blazing a neat trail, but perhaps not one that will be as popular as we had expected.
The NASDAQ is working to get in on the action. As Danny said yesterday on the show, this new NYSE method is going to crush traditional IPOs, provided that we’re understanding it during this, its nascent period.
Look, this week was bananas, and my brain is scrambled toast. You, like myself, are probably a bit confused about how it is only finally Saturday and not the middle of next week. But worry not, I have a quick roundup of the big stuff from our world. And, notes from calls with the COO of Okta and the CEO of Splunk, from after their respective earnings report:
Over to our chats, starting with Okta COO and co-founder Frederic Kerrest:
And then there was new McLaren F-1 sponsor Splunk, data folks who are in the midst of a transition to SaaS that is seeing the firm double-down on building ARR and letting go of legacy incomes:
And finally for Market Notes, my work BFF and IRL friend Ron Miller wrote about Box’s earnings this week, and how the changing world is bolstering the company. It’s worth a read. (Most public software companies are doing well, mind.)
We’re already over length, so I’ll have to keep our bits-and-bobs section brief. Thus, only the brightest of baubles for you, my friend:
And with that, we are out of room. Hugs, fist bumps and good vibes,
Powered by WPeMatico
A breeding ground for European entrepreneurs, Berlin has a knack for producing a lot of new startups: the city attracts top international, diverse talent, and it is packed with investors, events and accelerators. Also important: it’s a more affordable place to live and work when compared to many other cities in the region.
Berlin ranked 10th place in the 2019 Global Ecosystem Report, trailing behind only two other European cities: London and Paris. It’s home to unicorns such as N26, Zalando, HelloFresh and pioneers of the scene such as SoundCloud.
Top VCs include Earlybird, Point Nine, Project A, Rocket Internet, Holtzbrinck Ventures and accelerators such as Axel Springer Plug and Play Accelerator, hub:raum and The Family.
To get a sense of how the novel coronavirus has changed the landscape, we asked ten investors to give us an insight into their thinking during these pivotal times:
What trends are you most excited about investing in, generally?
Generally, we believe in a future in which we can leverage technology to free up humans from repetitive and tedious work and to empower them to shift their focus to what they consider more meaningful and impactful: that is creative and interpersonal activities. Thus, we are excited about founders working towards that future and finding answers across multiple industries, such as manufacturing or logistics, across all working-classes, and across different eras – before, during and after COVID.
What’s your latest, most exciting investment?
One of the recent additions of our new fund is Luminovo, a Munich-based company that develops a solution in the electronics industry to reduce the time and resources needed to go from an idea to a market-ready circuit board.
Are there startups that you wish you would see in the industry but don’t? What are some overlooked opportunities right now?
So far, we have only scratched the surface of the kind of efficiency gains that can potentially be achieved – particularly in industries that were considered to be boring and sluggish in the past, such as insurance or logistics. Even small improvements driven by technology can have a massive direct impact on P&L.
What are you looking for in your next investment, in general?
In general, we love to back visionary founders in the seed-stage that tap into giant industries with a high potential for digitization across Europe and the US.
Which areas are either oversaturated or would be too hard to compete in at this point for a new startup? What other types of products/services are you wary or concerned about?
COVID has sprung a myriad of companies in the communication and collaboration space into existence. While we believe in a future in which products and processes will be inherently remote-first, we will see a consolidation of that space that only allows for an oligopolistic market structure similar to how there is only one Zoom and Google Meet in the video communication space today.
How much are you focused on investing in your local ecosystem versus other startup hubs (or everywhere) in general? More than 50%? Less?
We have always considered ourselves as one of the few funds in Germany with a significant investment footprint both in Europe and the US. COVID has emphasized that we are able to invest entirely remotely and hence we will continue and even increase our activities across multiple hubs, such as Munich, Paris, or London.
Which industries in your city and region seem well-positioned to thrive, or not long-term? What are companies you are excited about (your portfolio or not), which founders?
Germany’s economy relies on wealthy traditional companies sitting on top of capital to be unlocked which new entrants can make use of. This has been true before 2020, and COVID will only demand more and accelerated innovation across these traditional industries ranging from automotive, manufacturing, to the chemical industry.
How should investors in other cities think about the overall investment climate and opportunities in your city?
Berlin and other German cities have consistently proven to develop and grow new leaders across multiple categories such as banking (N26), mobility (Flixbus and Lilium), or data analytics (Celonis). This is certainly driven by a mix of talents coming out of world-class educational institutions, the relative low cost of living in tech hubs, and large local incumbents with massive capital to invest and spend.
Do you expect to see a surge in more founders coming from geographies outside major cities in the years to come, with startup hubs losing people due to the pandemic and lingering concerns, plus the attraction of remote work?
While COVID has accelerated remote-first products and processes, we still believe that people will flock back to startup hubs such as Berlin or Munich, especially given the relatively low cost of living compared to other tech hubs like San Francisco. Nevertheless, we will continue to see an increasing number of companies scattered across multiple time zones building products that are inherently remote first, regardless where the general work environment will shift into.
Which industry segments that you invest in look weaker or more exposed to potential shifts in consumer and business behavior because of COVID-19? What are the opportunities startups may be able to tap into during these unprecedented times?
We are lucky in that our investment focus has been on sector verticals such as Logistics, Supply chain, manufacturing or the future of work, which have all captured significant tailwind from Covid.
How has COVID-19 impacted your investment strategy? What are the biggest worries of the founders in your portfolio? What is your advice to startups in your portfolio right now?
While our investment strategy on a high level will not change, we are putting longer sales cycles into consideration as potential customers of our portfolio companies now are focusing on capital efficiency which also holds true for our founders. Thus, we advise them to focus on extending the runway both by increasing capital efficiency as well as taking on additional funding.
Are you seeing “green shoots” regarding revenue growth, retention or other momentum in your portfolio as they adapt to the pandemic?
As our economy is still in the midst of dealing with the effects of COVID, it is too early to tell, but we definitely see positive indications driven by efforts of portfolio companies that could adapt quickly and shipped features catered to the current needs. One example is Personio, which extended their HR offerings with features that solve the need of customers who shifted to short-time work.
What is a moment that has given you hope in the last month or so? This can be professional, personal or a mix of the two.
What gave me hope was the cohesion of the German economy that fought together for solutions and support during these difficult times. One positive example was the German Startup Association that helped achieve additional governmental financial aid for German SMEs.
Any other thoughts you want to share with TechCrunch readers?
Similar to how the past financial crisis allowed companies such as Stripe or Shopify to become ubiquitous parts of our daily life, these unprecedented times now will also give birth to new forms and shapes in which new ideas will grow into large businesses and we are excited to partner up with founders willing to take a bet on that future.
Powered by WPeMatico