Singapore
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Carro, one of the largest automotive marketplaces in Southeast Asia, announced it has hit unicorn valuation after raising a $360 million Series C led by SoftBank Vision Fund 2. Other participants include insurance giant MSIG and Indonesian-based funds like EV Growth, Provident Growth and Indies Capital. About 90% of vehicles sold through Carro are secondhand, and it offers services that cover the entire lifecycle of a car, from maintenance to when it is broken down and recycled for parts.
Founded in 2015, Carro started as an online marketplace for cars, before expanding into more verticals. Co-founder and chief executive officer Aaron Tan told TechCrunch that, roughly speaking, the company’s operations are divided into three sections: wholesale, retail and fintech. Its wholesale business works with car dealers who want to purchase inventory, while its retail side sells to consumers. Its fintech operation offers products for both, including B2C car loans, auto insurance and B2B working capital loans.
Carro’s last funding announcement was in August 2019, when it said it had extended its Series B to $90 million. The company’s latest funding will be used to fund acquisitions, expand its financial services portfolio and develop its AI capabilities, which Carro uses to showcase cars online, develop pricing models and determine how much to charge insurance policyholders.
It also plans to expand retail services in its main markets: Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore. Carro currently employs about 1,000 people across the four countries and claims its revenue grew more than 2.5x during the financial year ending March 2021.
The COVID-19 pandemic helped Carro’s business because people wanted their own vehicles to avoid public transportation and became more receptive to shopping for cars online. Those factors also helped competitors like OLX Autos and Carsome fare well during the pandemic.
The adoption of electric vehicles across Southeast Asia has resulted in a new tailwind for Carro, because people who buy an EV usually want to sell off their combustion engine vehicles. Carro is currently talking to some of the largest electric vehicle countries in the world that want to launch in Southeast Asia.
“For every car someone typically buys in Southeast Asia, there’s always a trade-in. Where do cars go, right? We are a marketplace, but on a very high level, what we’re doing is reusing and recycling. That’s a big part in the environmental sustainability of the business, and something that sets us apart of other players in the region,” Tan said.
Cars typically stay in Carro’s inventory for less than 60 days. Its platform uses computer vision and sound technology to replicate the experience of inspecting a vehicle in-person. When someone clicks on a Carro listing, an AI bot automatically engages with them, providing more details about the cost of the car and answering questions. They also see a 360-degree view of the vehicle, its interior and can virtually start the engine to see how it sounds. Listings also provide information about defects and inspection reports.
Since many customers still want to get an in-person look before finalizing a purchase, Carro recently launched a beta product called Showroom Anywhere. Currently available in Singapore, it allows people to unlock Carro cars parked throughout the city, using QR codes, so they can inspect it at any time of the day, without a salesperson around. The company plans to add test driving to Showroom Anywhere.
“As a tech company, our job is to make sure we automate everything we can,” said Tan. “That’s the goal of the company and you can only assume that our cost structure and our revenue structure will get better along the years. We expect greater margin improvement and a lot more in cost reduction.”
Pricing is fixed, so shoppers don’t have to engage in haggling. Carro determines prices by using machine-learning models that look at details about a vehicle, including its make, model and mileage, and data from Carro’s transactions as well as market information (for example, how much of a particular vehicle is currently available for sale). Carro’s prices are typically in the middle of the market’s range.
Cars come with a three or seven-day moneyback guarantee and 30-day warranty. Once a customer decides to buy a car, they can opt to apply for loans and insurance through Carro’s fintech platform. Tan said Carro’s loan book is about five years old, almost as old as the startup itself, and is currently about $200 million.
Carro’s insurance is priced based on the policyholders driving behavior as tracked by sensors placed in their cars. This allows Carro to build a profile of how someone drives and the likelihood that they have an accident or other incident. For example, someone will get better pricing if they typically stick to speed limits.
“It sounds a bit futuristic,” said Tan. “But it’s something that’s been done in the United States for many years, like GEICO and a whole bunch of other insurers,” including Root Insurance, which recently went public.
Tan said MSIG’s investment in Carro is a “statement that we are really trying to triple down in insurance, because an insurer has so much linkage with what we do. The reason that MSIG is a good partner is that, like ourselves, they believe a lot in data and the difference in what we call ‘new age’ insurance, or data-driven insurance.”
Carro is also expanding its after-sale services, including Carro Care, in all four of its markets. Its after-sale services reach to the very end of a vehicle’s lifecycle and its customers include workshops around the world. For example, if a Toyota Corolla breaks down in Singapore, but its engine is still usable, it might be extracted and shipped to a repair shop in Nairobi, and the rest of its parts recycled.
“One thing I always ask in management meetings, is tell me where do cars go to die in Indonesia? Where do cars go to die in Thailand? There has to be a way, so if there is no way, we’re going to find a way,” said Tan.
In a statement, SoftBank Investment Advisers managing partner Greg Moon said, “Powered by AI, Carro’s technology platform provides consumers with full-stack services and transparency throughout the car ownership process. We are delighted to partner with Aaron and the Carro team to support their ambition to expand into new markets and use AI-powered technology to make the car buying process smarter, simpler and safer.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Zenyum, a startup that wants to make cosmetic dentistry more affordable, announced today it has raised a $40 million Series B. This includes $25 million from L Catterton, a private equity firm focused on consumer brands. The round’s other participants were Sequoia Capital India (Zenyum is an alum of its Surge accelerator program), RTP Global, Partech, TNB Aura, Seeds Capital and FEBE Ventures. L Catteron Asia’s head of growth investments, Anjana Sasidharan, will join Zenyum’s board.
This brings Zenyum’s total raised so far to $56 million, including a $13.6 million Series A announced in November 2019. In a press statement, Sasidharan said, “Zenyum’s differentiated business model gives it a strong competitive advantage, and we are excited to partner with the founder management team to help them realize their growth ambitions.” Other dental-related investments in L Catteron’s portfolio include Ideal Image, ClearChoice, dentalcorp, OdontoCompany, Espaçolaser and 98point6.
Founded in 2018, the company’s products now include ZenyumSonic electric toothbrushes; Zenyum Clear, or transparent 3D-printed aligners; and ZenyumClear Plus for more complex teeth realignment cases.
Founder and chief executive officer Julian Artopé told TechCrunch that ZenyumClear aligners can be up to 70% cheaper than other braces, including traditional metal braces, lingual braces and other clear aligners like Invisalign, depending on the condition of a patients’ teeth and what they want to achieve. Zenyum Clear costs $2,400 SGD (about $1,816 USD), while ZenyumClear Plus ranges from $3,300 to $3,900 SGD (about $2,497 to $2,951 USD).
The company is able to reduce the cost of its invisible braces by combining a network of dental partners with a technology stack that allows providers to monitor patients’ progress while reducing the number of clinic visits they need to make.
First, potential customers send a photo of their teeth to Zenyum to determine if ZenyumClear or ZenyumClear Plus will work for them. If so, they have an in-person consultation with a dentists, including an X-ray and 3D scan. This costs between $120 to $170 SGD, which is paid to the clinic. After their invisible braces are ready, the patient returns to the dentist for a fitting. Then dentists can monitor the progress of their patient’s teeth through Zenyum’s app, only asking them to make another in-person visit if necessary.
ZenyumClear is currently available in Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Hong Kong, Macau, Vietnam, Thailand and Taiwan, with more markets planned.
Sequoia India principal Pieter Kemps told TechCrunch, “There are 300M customers in Zenyum’s core markets—Southeast Asia, Hong Kong, Taiwan—who have increased disposable income for beauty. We believe spend on invisible braces will grow significantly from the current penetration, but what it requires is strong execution on a complex product to become the preferred choice for consumers. That is where Zenyum shines: excellent execution, leading to new products, best-in-class NPS, fast growth, and strong economics. This Series B is a testament to that, and of the belief in the large opportunity down the road.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Singapore-based Aspire, which wants to become the financial services “one-stop shop” for SMEs, announced that its business accounts have reached $1 billion in annualized transaction volume one year after launching. The company also unveiled Bill Pay, its latest feature that lets businesses manage and pay invoices by emailing them to Aspire’s AI-based digital assistant.
Launched in May 2020, Aspire’s online business accounts are targeted to startups and small- to medium-sized enterprises, and do not require minimum deposits or monthly fees. Co-founder and chief executive officer Andrea Baronchelli told TechCrunch more than 10,000 companies now use Aspire’s business accounts and that adoption was driven by two main reasons. The first was Aspire’s transition to a multi-product strategy early last year, after focusing on corporate cards and working capital loans. The second reason is the COVID-19 pandemic, which made it harder for companies to open accounts at traditional banks.
“We can go in and say we offer all-in-one financial tools for growing businesses,” he said. “People come in and use one thing first, and then we offer them other things later on, so that’s been a huge success for us.”
Founded in 2018, Aspire has raised about $41.5 million in funding so far, including a Series A announced in July 2019. Its investors include MassMutual Ventures Southeast Asia, Arc Labs and Y Combinator.
Baronchelli said Aspire’s business account users consist of two main segments. The first are “launchers,” or people who are starting their first businesses and need to set up a way to send and receive money. Launchers typically make less than $400,000 a year in revenue and their Aspire account serves as their primary business account. The second segment are companies that make about $500,000 to $2 million a year and already had another bank account, but started using Aspire for its credit line, expense management or foreign exchange tools, and decided to open an account on the platform as well.
The company has customers from across Southeast Asia, and is particularly focused on Singapore, Indonesia and Vietnam. For example, it launched Aspire Kickstart, with incorporation services for Singaporean companies, at the start of this year.
Bill Pay, its newest feature, lets business owners forward invoices by email to Aspire’s AI-based digital assistant, which uses optical character recognition and deep learning to pull out payment details, including terms and due dates. Then users get a notification to do a final check before approving and scheduling payments. The feature syncs with accounting systems integrated into Aspire, including Xero and QuickBooks. Baronchelli said Aspire decided to launch Bill Pay after interviewing businesses and finding that many still relied on Excel spreadsheets.
Aspire’s offerings overlap with several other fintech companies in Southeast Asia. For example, Volopay, Wise and Revolut offer business accounts, too, and Spenmo offers business cards. Aspire plans to differentiate by expanding its stack of multiple products. For example, it is developing tools for accounts receivable, such as invoice automation, and accounts payable, like a dedicated product for payroll management. Baronchelli said Aspire is currently interviewing users to finalize the set of features it will offer.
“I don’t want to close the door that others might come toward a multiple product approach, but if you ask me what our position is now, we are basically the only one that offers an all-in-one product stack,” he added. “So we are a couple years ahead of the competition and have a first-mover advantage.”
Powered by WPeMatico

Una Brands’ co-founders (from left to right): Tobias Heusch, Kiren Tanna and Kushal Patel. Image Credits: Una Brands
One of the biggest funding trends of the past year is companies that consolidate small e-commerce brands. Many of the most notable startups in the space, like Thrasio, Berlin Brands Group and Branded Group, focus on consolidating Amazon Marketplace sellers. But the e-commerce landscape is more fragmented in the Asia-Pacific region, where sellers use platforms like Tokopedia, Lazada, Shopee, Rakuten or eBay, depending on where they are. That is where Una Brands comes in. Co-founder Kiren Tanna, former chief executive officer of Rocket Internet Asia, said the startup is “platform agnostic,” searching across marketplaces (and platforms like Shopify, Magento or WooCommerce) for potential acquisitions.
Una announced today that it has raised a $40 million equity and debt round. Investors include 500 Startups, Kingsway Capital, 468 Capital, Presight Capital, Global Founders Capital and Maximilian Bitner, the former CEO of Lazada who currently holds the same role at secondhand fashion platform Vestiaire Collective.
Una did not disclose the ratio of equity and debt in the round. Like many other e-commerce aggregators, including Thrasio, Una raised debt financing to buy brands because it is non-dilutive. The round will also be used to hire aggressively in order to evaluate brands in its pipeline. Una currently has teams in Singapore, Malaysia and Australia and plans to expand in Southeast Asia before entering Taiwan, Japan and South Korea.
Tanna, who also founded Foodpanda and ZEN Rooms, launched Una along with Adrian Johnston, Kushal Patel, Tobias Heusch and Srinivasan Shridharan. He estimates that there are more than 10 million third-party sellers spread across different platforms in the Asia-Pacific.
“Every single seller in Asia is looking at multiple platforms and not just Amazon,” Tanna told TechCrunch. “We saw a big gap in the market where e-commerce is growing very quickly, but players in the West are not able to look at every platform, so that is why we decided to focus on APAC, launch the business there and acquire sellers who are selling on multiple platforms.”
Una looks for brands with annual revenue between $300,000 to $20 million and is open to many categories, as long as they have strong SKUs and low seasonality (for example, it avoids fast fashion). Its offering prices range from about $600,000 to $3 million.
Tanna said Una will maintain acquisitions as individual brands “because what’s working, we don’t change it.” How it adds value is by doing things that are difficult for small brands to execute, especially those run by just one or two people, like expanding into more distribution channels and countries.
“For example, in Indonesia there are at least five or six important platforms that you should be on, and many times the sellers aren’t doing that, so that’s something we do,” Tanna explained. “The second is cross-border in Southeast Asia, which sellers often can’t do themselves because of regulations around customs, import restrictions and duties. That’s something our team has experience in and want to bring to all brands.”
Amazon FBA roll-up players have the advantage of Amazon Marketplace analytics that allow them to quickly measure the performance of brands in their pipeline of potential acquisitions. Since it deals with different marketplaces and platforms, Una works with much more fragmented sources of data for revenue, costs, rankings and customer reviews. To scale up, the company is currently building technology to automate its valuation process and will also have local teams in each of its markets. Despite working with multiple e-commerce platforms, Tanna said Una is able to complete a deal within five weeks, with an offer usually happening within two or three days.
In countries where Amazon is the dominant e-commerce player, like the United States, many entrepreneurs launch FBA brands with the goal of flipping them for a profit within a few years, a trend that Thrasio and other Amazon roll-up startups are tapping into. But that concept is less common in Una’s markets, so it offers different team deals to appeal to potential sellers. Though Una acquires 100% of brands, it also does profit-sharing models with sellers, so they get a lump sum payment for the majority of their business first, then collect more money as Una scales up the brand. Tanna said Una usually continues working with sellers on a consulting basis for about three to six months after a sale.
“Something that Amazon players know very well is that they can find a product, sell it for four to five years, and then ideally make a multi-million deal exit and build another product or go on holiday,” said Tanna. “That’s something Asian sellers are not as familiar with, so we see this as an education phase to explain how the process works, and why it makes sense to sell to us.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Singapore is quickly turning into a hub for food-tech startups, partly because of government initiatives supporting the development of meat alternatives. One of the newest entrants is Next Gen, which will launch its plant-based “chicken” brand, called TiNDLE, in Singaporean restaurants next month. The company announced today that it has raised $10 million in seed funding from investors including Temasek, K3 Ventures, EDB New Ventures (an investment arm of the Singapore Economic Development Board), NX-Food, FEBE Ventures and Blue Horizon.
Next Gen claims this is the largest seed round ever raised by a plant-based food tech company, based on data from PitchBook. This is the first time the startup has taken external investment, and the funding exceeded its original target of $7 million. Next Gen was launched last October by Timo Recker and Andre Menezes, with $2.2 million of founder capital.
Next Gen’s first product is called TiNDLE Thy, an alternative to chicken thighs. Its ingredients include water, soy, wheat, oat fiber, coconut oil and methylcellulose, a culinary binder, but the key to its chicken-like flavor is a proprietary blend of plant-based fats, like sunflower oil, and natural flavors that allows it to cook like chicken meat.
Menezes, Next Gen’s chief operating officer, told TechCrunch that the company’s goal is to be the global leader in plant-based chicken, the way Impossible and Beyond are known for their burgers.
“Consumers and chefs want texture in chicken, the taste and aroma, and that is largely related to chicken fat, which is why we started with thighs instead of breasts,” said Menezes. “We created a chicken fat made from a blend, called Lipi, to emulate the smell, aroma and browning when you cook.”
Both Recker and Menezes have years of experience in the food industry. Recker founded German-based LikeMeat, a plant-based meat producer acquired by the LIVEKINDLY Collective last year. Menezes’ food career started in Brazil at one of the world’s largest poultry exporters. He began working with plant-based meat after serving as general manager of Country Foods, a Singaporean importer and distributor that focuses on innovative, sustainable products.
“It was clear to me after I was inside the meat industry for so long that it was not going to be a sustainable business in the long run,” Menezes said.
Over the past few years, more consumers have started to feel the same way, and began looking for alternatives to animal products. UBS expects the global plant-based protein market to increase at a compounded annual growth rate of more than 30%, reaching about $50 billion by 2025, as more people, even those who aren’t vegans or vegetarians, seek healthier, humane sources of protein.
Millennial and Gen Z consumers, in particular, are willing to reduce their consumption of meat, eggs and dairy products as they become more aware of the environmental impact of industrial livestock production, said Menezes. “They understand the sustainability angle of it, and the health aspect, like the cholesterol or nutritional values, depending on what product you are talking about.”
Low in sodium and saturated fat, TiNDLE Thy has received the Healthier Choice Symbol, which is administered by Singapore’s Health Promotion Board. Next Gen’s new funding will be used to launch TiNDLE Thy, starting in popular Singaporean restaurants like Three Buns Quayside, the Prive Group, 28 HongKong Street, Bayswater Kitchen and The Goodburger.
Over the next year or two, Next Gen plans to raise its Series A round, launch more brands and products, and expand in its target markets: the United States (where it is currently recruiting a growth director to build a distribution network), China, Brazil and Europe. After working with restaurant partners, Next Gen also plans to make its products available to home cooks.
“The reason we started with chefs is because they are very hard to crack, and if chefs are happy with the product, then we’re very sure customers will be, too,” said Menezes.
Powered by WPeMatico
Time is critical for healthcare providers, especially in the middle of the pandemic. Singapore-based Bot MD helps save time with an AI-based chatbot that lets doctors look up important information from their smartphones, instead of needing to call a hospital operator or access its intranet. The startup announced today it has raised a $5 million Series A led by Monk’s Hill Venture.
Other backers include SeaX, XA Network and SG Innovate, and angel investors Yoh-Chie Lu, Jean-Luc Butel and Steve Blank. Bot MD was also part of Y Combinator’s summer 2018 batch.
The funding will be used to expand in the Asia-Pacific region, including Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia, and to add new features in response to demand from hospitals and healthcare organizations during COVID-19. Bot MD’s AI assistant currently supports English, with plans to release Bahasa Indonesian and Spanish later this year. It is currently used by about 13,000 doctors at organizations including Changi General Hospital, National University Health System, National University Cancer Institute of Singapore, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore General Hospital, Parkway Radiology and the National Kidney Transplant Institute.
Co-founder and chief executive officer Dorothea Koh told TechCrunch that Bot MD integrates hospital information usually stored in multiple systems and makes it easier to access.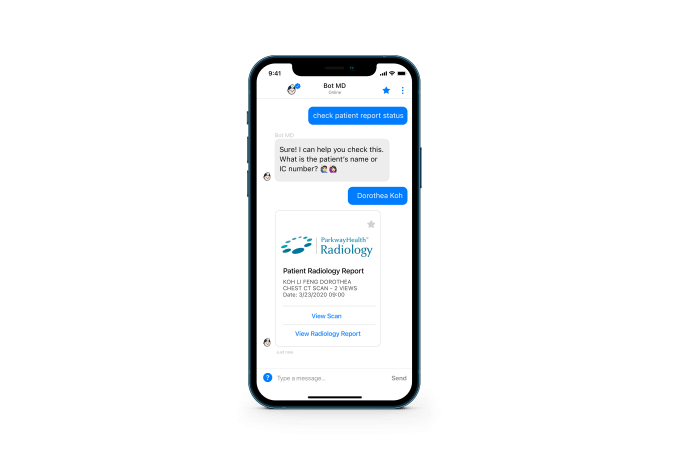
Image Credits: Bot MDWithout Bot MD, doctors may need to dial a hospital operator to find which staffers are on call and get their contact information. If they want drug information, that means another call to the pharmacy. If they need to see updated guidelines and clinical protocols, that often entails finding a computer that is connected to the hospital’s intranet.
“A lot of what Bot MD does is to integrate the content that they need into a single interface that is searchable 24/7,” said Koh.
For example, during COVID-19, Bot MD introduced a new feature that takes healthcare providers to a form pre-filled with their information when they type “record temperature” into the chatbot. Many were accessing their organization’s intranet twice a day to log their temperature and Koh said being able to use the form through Bot MD has significantly improved compliance.
The time it takes to onboard Bot MD varies depending on the information systems and amount of content it needs to integrate, but Koh said its proprietary natural language processing chat engine makes training its AI relatively quick. For example, Changi General Hospital, a recent client, was onboarded in less than 10 days.
Bot MD plans to add new clinical apps to its platform, including ones for electronic medical records (EMR), billing and scheduling integrations, clinical alerts and chronic disease monitoring.
Powered by WPeMatico
Volopay, a Singapore-based startup building a “financial control center” for businesses, announced today it has raised $2.1 million in seed funding. The round was led by Tinder co-founder Justin Mateen, and included participation from Soma Capital, CP Ventures, Y Combinator, VentureSouq, the founders of Razorpay and other angel investors.
The funding will be used on hiring, product development, strategic partnerships and Volopay’s international expansion. It plans to launch operations in Australia later this month. The company currently has about 100 clients, including Smart Karma, Dathena, Medline, Sensorflow and Beam.
Launched in 2019 by Rajith Shaiji and Rajesh Raikwar, Volopay took part in Y Combinator’s accelerator program last year. It was created after chief executive officer Shaji, who worked for several fintech companies before launching Volopay, became frustrated by the process of reconciling business expenses, especially with accounting departments located in different countries. Shaiji and Raikwar also saw that many companies, especially startups and SMEs, struggled to track different kinds of spending, including subscriptions and vendor payments.
Most of Volopay’s clients are in the tech sector and have about 15 to 150 employees. Volopay’s platform integrates multicurrency corporate cards (issued by Visa Corporate), domestic and international bank transfers, automated payments and expense and accounting software, allowing companies to save money on foreign exchange fees and reconcile expenses more quickly.
In order to speed up its development, Volopay integrated Airwallex’s APIs. Its corporate cards offer up to 2% cash back on software subscriptions, hosting and international travel, which Volopay says are the three top expense categories for tech companies, and it in November 2020, it launched a credit facility for corporate cards to help give SMEs more liquidity during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Compared to traditional credit products, like credit cards and working capital loans, Shaji said Volopay’s credit facility, which is also issued by Visa Corporate, has a more competitive fixed-free pricing structure that depends on the level of credit used. This means companies know how much they owe in advance, which in turn helps them manage their cashflows more easily. The average credit line provided by Volopay is about $30,000.
Since TechCrunch last covered Volopay in July 2020, it has grown 70% month on month in terms of total funds flowing through its platform, Shaji said. It also launched two new features: A bill pay feature that allows clients to transfer money domestically and internationally with low foreign exchange rates and transaction fees, and the credit facility. The bill pay feature now contributes about 40% to Volopay’s total payment volume, while the credit product makes up 30% of its card spending.
Shaji told TechCrunch that Volopay decided to expand into Australia because because not only is it a much larger market than Singapore, but “SMEs in Australia are very comfortable using paid digital software to streamline internal operations and scale their businesses.” He added that there is currently no other provider in Australia that offers both expense management and credit to SMEs like Volopay.
Powered by WPeMatico
Being “underbanked” doesn’t mean that someone lacks access to financial services. Instead, it often means they don’t have traditional bank accounts or credit cards. But in markets like Indonesia, many still use digital wallets or e-commerce platforms, creating alternative sources of user data that can help them secure working capital and other financial tools. Finantier, a Singapore-based open finance startup, wants to streamline that data with a single API that gives financial services access to user data, with their consent. It also includes machine-learning-based analytics to enable credit scoring and KYC verifications.
Currently in beta mode with more than 20 clients, Finantier is busy getting ready to officially launch. It announced today that it has been accepted into Y Combinator’s Winter 2021 startup batch. The startup also recently raised an undisclosed amount of pre-seed funding led by East Ventures, with participation from AC Ventures, Genesia Ventures, Two Culture Capital and other investors.
Finantier was founded earlier this year by Diego Rojas, Keng Low and Edwin Kusuma, all of whom have experience building products for fintech companies, with the mission of enabling open finance in emerging markets.
Open finance grew out of open banking, the same framework that Plaid and Tink are built on. Meant to give people more control over their financial data instead of keeping it siloed within banks and other institutions, users can decide to grant apps or websites secure access to information from their online accounts, including bank accounts, credit cards and digital wallets. Open banking refers mainly to payment accounts, while open finance, Finantier’s specialty, covers a larger gamut of services, including business lending, mortgages and insurance underwriting.
While Finantier is focusing first on Singapore and Indonesia, it plans to expand into other countries and become a global fintech company like Plaid. It’s already eyeing Vietnam and the Philippines.
Before launching Finantier, Rojas worked on products for peer-to-peer lending platforms Lending Club and Dianrong, and served as chief technology officer for several fintech startups in Southeast Asia. He realized that many companies struggled to integrate with other platforms and fetch data from banks, or purchase data from different providers.
“People are discussing open banking, embedded finance and so on,” Rojas, Finantier’s chief executive officer, told TechCrunch. “But those are the building blocks of something bigger, which is open finance. Particularly in a region like Southeast Asia, where about 60% to 70% of adults are unbanked or underbanked, we believe in helping consumers and businesses leverage the data that they have in multiple platforms. It definitely doesn’t need to be a bank account, it could be in a digital wallet, e-commerce platform or other service providers.”
What this means for consumers is that even if someone doesn’t have a credit card, they can still establish creditworthiness: For example, by sharing data from completed transactions on e-commerce platforms. Gig economy workers can access more financial services and deals by giving data about their daily rides or other types of work they do through different apps.
Other open-banking startups focused on Southeast Asia include Brankas and Brick. Rojas said Finantier differentiates by specializing on open finance and creating infrastructure for financial institutions to build more services for end users.
The benefit of open finance for financial institutions is that they can create products for more consumers and find more opportunities for revenue sharing models. In Southeast Asia, this also means reaching more people who are underbanked or otherwise lack access to financial services.
While taking part in Y Combinator’s accelerator program, Finantier will also be participating in the Indonesia Financial Service Authority’s regulatory sandbox. Once it completes the program, it will be able to partner with more fintech companies in Indonesia, including bigger institutions.
There are 139 million adults in Indonesia who are underbanked or unbanked, said East Ventures co-founder and managing partner Willson Cuaca.
The investment firm, which focuses on Indonesia, conducts an annual survey called the East Ventures Digital Competitiveness Index and found that financial exclusion was where one of the largest divides existed. There are significant gaps in between the number of financial services available in heavily populated islands like Java, where Jakarta is located, and other islands in the archipelago.
To promote financial inclusion and alleviate the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has set a goal for 10 million micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) to go digital by the end of the year. There are currently about eight million Indonesian MSMEs that sell online, representing just 13% of MSMEs in the country.
“Providing equal access to financial services will create multiplier effects to the Indonesian economy,” Cuaca told TechCrunch about East Ventures’ decision to back Finantier. “Currently, hundreds of companies work with their own unique solutions to bring financial services to more people. We believe Finantier will help them offer more products and services to this underserved section of the population.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Carsome, which bills itself as Southeast Asia’s largest e-commerce platform for used cars, announced it has closed a $30 million Series D. The funding was led by Asia Partners, with participation from returning investors Burda Principal Investments and Ondine Capital.
The startup described this as one of the largest “all-equity financings to date in Southeast Asia’s online automotive industry.” Part of the Series D may be used for mergers and acquisitions to consolidate the company’s supply chain.
Founded five years ago in Malaysia, Carsome’s platform serves both C2C and B2C segments, and ensures quality by conducting inspections before vehicles are listed on its platform. It now has 1,000 employees and claims to transact 70,000 cars on an annualized basis, totaling $600 million.
In a press statement, co-founder and group chief executive officer Eric Cheng said that the company, which now also operates in Indonesia, Thailand and Singapore, doubled its monthly revenue over the past six months, compared to pre-pandemic levels. The company says that this is partly because more people and businesses are buying their own cars for safety reasons.
While sales of new vehicles have plummeted around the world, used car sales, especially through e-commerce platforms, are recovering more quickly, according to Counterpoint Research. This largely because people want to avoid public transportation and ride-hailing, but also want cheaper options.
Other used car platforms in Southeast Asia include Carro, OLX Autos (formerly called BeliMobilGue) and Carmudi.
Powered by WPeMatico
There are now about 50 million people with dementia globally, a number the World Health Organization expects to triple by 2050. Alzheimer’s is the leading cause of dementia and caregivers are often overwhelmed, without enough support.
Neuroglee, a Singapore-based health tech startup, wants to help with a digital therapeutic platform created to treat patients in the early stages of the disease. Founded this year to focus on neurodegenerative diseases, Neuroglee announced today it has raised $2.3 million in pre-seed funding.
The round was led by Eisai Co., one of Japan’s largest pharmaceutical companies, and Kuldeep Singh Rajput, the founder and chief executive officer of predictive healthcare startup Biofourmis.
Neuroglee’s prescription digital therapy software for Alzheimer’s, called NG-001, is its main product. The company plans to start clinical trials next year. NG-001 is meant to complement medication and other treatments, and once it is prescribed by a clinician, patients can access its cognitive exercises and tasks through a tablet.
The software tracks patients’ progress, such as the speed of their fingers and the time it takes to complete an exercise, and delivers personalized treatment programs. It also has features to address the mental health of patients, including one that shows images that can bring up positive memories, which in turn can help alleviate depression and anxiety when used in tandem with other cognitive behavioral therapy techniques.
For caregivers and clinicians, NG-001 helps them track patient progress and their compliance with other treatments, like medications. This means that healthcare providers can work closely with patients even remotely, which is especially important during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Neuroglee founder and CEO Aniket Singh Rajput told TechCrunch that its first target markets for NG-001 are the United States and Singapore, followed by Japan. NG-001 needs to gain regulatory approval in each country, and it will start by seeking U.S. Food and Drug Administration clearance.
Once it launches, clinicians will have two ways to prescribe NG-001, through their healthcare provider platform or an electronic prescription tool. A platform called Neuroglee Connect will give clinicians, caregivers and patients access to support and features for reimbursement and coverage.
Powered by WPeMatico