Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
The problem of how to find the potential treasure trove hidden in millions of pounds of trash is getting a high-tech answer as investors funnel $16 million into the recycling robots built by Denver-based AMP Robotics.
For recyclers, the commercialization of robots tackling industry problems couldn’t come at a better time. Their once-stable business has been turned on its head by trade wars and low unemployment.
Recycling businesses used to be able to rely on China to buy up any waste stream (no matter the quality of the material). However, about two years ago, China decided it would no longer serve as the world’s garbage dump and put strict standards in place for the kinds of raw materials it would be willing to receive from other countries. The result has been higher costs at recycling facilities, which actually are now required to sort their garbage more effectively.
At the same time, low unemployment rates are putting the squeeze on labor availability at facilities where humans are basically required to hand-sort garbage into recyclable materials and trash.
Given the economic reality, recyclers are turning to AMP’s technology — a combination of computer vision, machine learning and robotic automation to improve efficiencies at their facilities.

Photo courtesy of Flickr/Abulla Al Muhairi
That’s what attracted Sequoia Capital to lead the company’s latest investment round — a $16 million Series A investment the company will use to expand its manufacturing capacity and boost growth as it looks to expand into international markets.
“We are excited to partner with AMP because their technology is changing the economics of the recycling
industry,” said Shaun Maguire, partner at Sequoia, in a statement. “Over the last few years, the industry has had their margins squeezed by labor shortages and low commodity prices. The end result is an industry proactively searching for cost-saving alternatives and added opportunities to increase revenue by capturing more high-value recyclables, and AMP is emerging as the leading solution.”
The funding will be used to “broaden the scope of what we’re going after,” says chief executive Matanya Horowitz. Beyond reducing sorting costs and improving the quality of the materials that recycling facilities can ship to buyers, the company’s computer vision technologies can actually help identify branded packaging and be used by companies to improve their own product life cycle management.
“We can identify… whether it’s a Coke or Pepsi can or a Starbucks cup,” says Horowitz. “So that people can help design their product for circularity… we’re building out our reporting capabilities and that, to them, is something that is of high interest.”
That combination of robotics, computer vision and machine learning has potential applications beyond the recycling industry as well, according to Horowitz. Automotive scrap and construction waste are other areas where the company has seen interest for its combination of software and hardware.
Meanwhile, the core business of recycling is picking up. In October, the company completed the installation of 14 robots at Single Stream Recyclers in Florida. It’s the largest single deployment of robots in the recycling industry and the robots, which can sort and pick twice as fast as people with higher degrees of accuracy, are installed at sorting lines for plastics, cartons, fiber and metals, the company said.
AMP’s business has two separate revenue streams — a robotics as a service offering and a direct sales option — and the company has made other installations at sites in California, Colorado, Indiana, Minnesota, New York, Pennsylvania, Texas, Virginia and Wisconsin.
The traction the company is seeing in its core business was validating for early investors like BV, Closed Loop Partners, Congruent Ventures and Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners, the Alphabet subsidiary’s new spin-out that invests in technologies to support new infrastructure projects.
For Mike DeLucia, the Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners principal who led the company’s investment into AMP Robotics, the deal is indicative of where his firm will look to commit capital going forward.
“It’s a technology that enables physical assets to operate more efficiently,” he says. “Our goal is to find the technologies that enable really exciting infrastructure projects, back them and work with them to deliver projects in the physical world.”
Investors like DeLucia and Abe Yokell, from the investment firm Congruent Ventures, think that recycling is just the beginning. Applications abound for AMP Robotic’s machine learning and computer vision technologies in areas far beyond the recycling center.
“When you think about how technology is able to impact the built environment, one area is machine vision,” says Yokell. “[Machine learning] neural nets can apply to real-world environments, and that stuff has gotten cheaper and easier to deploy.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Moveworks, a startup using AI to help resolve help desk tickets in an automated fashion, announced a $75 million Series B investment today.
The round was led by Iconiq Capital, Kleiner Perkins and Sapphire Ventures. Existing investors Lightspeed Venture Partners, Bain Capital Ventures and Comerica Bank also participated. The round also included a personal investment from John W. Thompson, a partner at LightSpeed Venture Partners and chairman at Microsoft. Today’s investment brings the total raised to $105 million, according to the company.
That’s a lot of money for an early-stage company, but CEO and co-founder Bhavin Shah says his company is solving a common problem using AI. “Moveworks is a machine learning platform that uses natural language understanding to take tickets that are submitted by employees every day to their IT teams for stuff they need, and we understand [the content of the tickets], interpret them, and then we take the actions to resolve them [automatically],” Shah explained.
He said the company decided to focus on help desk tickets because they saw data when they were forming the company that suggested a common set of questions, and that would make it easier to interpret and resolve these issues. In fact, they are currently able to resolve 25-40% of all tickets autonomously.
He says this should lead to greater user satisfaction because some of their problems can be resolved immediately, even when IT personnel aren’t around to help. Instead of filing a ticket and waiting for an answer, Moveworks can provide the answer, at least part of the time, without human intervention.
Aditya Agrawal, a partner at Iconiq, says that the company really captured his attention. “Moveworks is not just transforming IT operations, they are building a more modern and enlightened way to work. They’ve built a platform that simplifies and streamlines every interaction between employees and IT, enabling both to focus on what matters,” he said in a statement.
The company was founded in 2016, and in the early days was only resolving 2% of the tickets autonomously, so it has seen major improvement. It already has 115 employees and dozens of customers (although Shah didn’t want to provide an exact number).
Powered by WPeMatico
One of the bigger trends in enterprise software has been the emergence of startups building tools to make the benefits of artificial intelligence technology more accessible to non-tech companies. Today, one that has built a platform to apply the power of machine learning and natural language processing to massive documents of unstructured data has closed a round of funding as it finds strong demand for its approach.
Eigen Technologies, a London-based startup whose machine learning engine helps banks and other businesses that need to extract information and insights from large and complex documents like contracts, is today announcing that it has raised $37 million in funding, a Series B that values the company at around $150 million – $180 million.
The round was led by Lakestar and Dawn Capital, with Temasek and Goldman Sachs Growth Equity (which co-led its Series A) also participating. Eigen has now raised $55 million in total.
Eigen today is working primarily in the financial sector — its offices are smack in the middle of The City, London’s financial center — but the plan is to use the funding to continue expanding the scope of the platform to cover other verticals such as insurance and healthcare, two other big areas that deal in large, wordy documentation that is often inconsistent in how its presented, full of essential fine print, and typically a strain on an organisation’s resources to be handled correctly — and is often a disaster if it is not.
The focus up to now on banks and other financial businesses has had a lot of traction. It says its customer base now includes 25% of the world’s G-SIB institutions (that is, the world’s biggest banks), along with others that work closely with them, like Allen & Overy and Deloitte. Since June 2018 (when it closed its Series A round), Eigen has seen recurring revenues grow sixfold with headcount — mostly data scientists and engineers — double. While Eigen doesn’t disclose specific financials, you can see the growth direction that contributed to the company’s valuation.
The basic idea behind Eigen is that it focuses what co-founder and CEO Lewis Liu describes as “small data.” The company has devised a way to “teach” an AI to read a specific kind of document — say, a loan contract — by looking at a couple of examples and training on these. The whole process is relatively easy to do for a non-technical person: you figure out what you want to look for and analyse, find the examples using basic search in two or three documents and create the template, which can then be used across hundreds or thousands of the same kind of documents (in this case, a loan contract).
Eigen’s work is notable for two reasons. First, typically machine learning and training and AI requires hundreds, thousands, tens of thousands of examples to “teach” a system before it can make decisions that you hope will mimic those of a human. Eigen requires a couple of examples (hence the “small data” approach).
Second, an industry like finance has many pieces of sensitive data (either because it’s personal data, or because it’s proprietary to a company and its business), and so there is an ongoing issue of working with AI companies that want to “anonymise” and ingest that data. Companies simply don’t want to do that. Eigen’s system essentially only works on what a company provides, and that stays with the company.
Eigen was founded in 2014 by Dr. Lewis Z. Liu (CEO) and Jonathan Feuer (a managing partner at CVC Capital Partners, who is the company’s chairman), but its earliest origins go back 15 years earlier, when Liu — a first-generation immigrant who grew up in the U.S. — was working as a “data-entry monkey” (his words) at a tire manufacturing plant in New Jersey, where he lived, ahead of starting university at Harvard.
A natural computing whiz who found himself building his own games when his parents refused to buy him a games console, he figured out that the many pages of printouts he was reading and re-entering into a different computing system could be sped up with a computer program linking up the two. “I put myself out of a job,” he joked.
His educational life epitomises the kind of lateral thinking that often produces the most interesting ideas. Liu went on to Harvard to study not computer science, but physics and art. Doing a double major required working on a thesis that merged the two disciplines together, and Liu built “electrodynamic equations that composed graphical structures on the fly” — basically generating art using algorithms — which he then turned into a “Turing test” to see if people could detect pixelated actual work with that of his program. Distill this, and Liu was still thinking about patterns in analog material that could be re-created using math.
Then came years at McKinsey in London (how he arrived on these shores) during the financial crisis where the results of people either intentionally or mistakenly overlooking crucial text-based data produced stark and catastrophic results. “I would say the problem that we eventually started to solve for at Eigen became tangible,” Liu said.
Then came a physics PhD at Oxford where Liu worked on X-ray lasers that could be used to decrease the complexity and cost of making microchips, cancer treatments and other applications.
While Eigen doesn’t actually use lasers, some of the mathematical equations that Liu came up with for these have also become a part of Eigen’s approach.
“The whole idea [for my PhD] was, ‘how do we make this cheaper and more scalable?,’ ” he said. “We built a new class of X-ray laser apparatus, and we realised the same equations could be used in pattern matching algorithms, specifically around sequential patterns. And out of that, and my existing corporate relationships, that’s how Eigen started.”
Five years on, Eigen has added a lot more into the platform beyond what came from Liu’s original ideas. There are more data scientists and engineers building the engine around the basic idea, and customising it to work with more sectors beyond finance.
There are a number of AI companies building tools for non-technical business end-users, and one of the areas that comes close to what Eigen is doing is robotic process automation, or RPA. Liu notes that while this is an important area, it’s more about reading forms more readily and providing insights to those. The focus of Eigen is more on unstructured data, and the ability to parse it quickly and securely using just a few samples.
Liu points to companies like IBM (with Watson) as general competitors, while startups like Luminance is another taking a similar approach to Eigen by addressing the issue of parsing unstructured data in a specific sector (in its case, currently, the legal profession).
Stephen Nundy, a partner and the CTO of Lakestar, said that he first came into contact with Eigen when he was at Goldman Sachs, where he was a managing director overseeing technology, and the bank engaged it for work.
“To see what these guys can deliver, it’s to be applauded,” he said. “They’re not just picking out names and addresses. We’re talking deep, semantic understanding. Other vendors are trying to be everything to everybody, but Eigen has found market fit in financial services use cases, and it stands up against the competition. You can see when a winner is breaking away from the pack and it’s a great signal for the future.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Freshworks, a company that makes a variety of business software tools, from CRM to help-desk software, announced a $150 million Series H investment today from Sequoia Capital, CapitalG (formerly Google Capital) and Accel on a hefty $3.5 billion valuation. The late-stage startup has raised almost $400 million, according to Crunchbase data.
The company has been building an enterprise SaaS platform to give customers a set of integrated business tools, but CEO and co-founder Girish Mathrubootham says they will be investing part of this money in R&D to keep building out the platform.
To that end, the company also announced today a new unified data platform called the “Customer-for-Life Cloud” that runs across all of its tools. “We are actually investing in really bringing all of this together to create the “Customer-for-Life Cloud,” which is how you take marketing, sales, support and customer success — all of the aspects of a customer across the entire life cycle journey and bring them to a common data model where a business that is using Freshworks can see the entire life cycle of the customer,” Mathrubootham explained.
While Mathrubootham was not ready to commit to an IPO, he said they are in the process of hiring a CFO and are looking ahead to one day becoming a public company. “We don’t have a definite timeline. We want to go public at the right time. We are making sure that as a company that we are ready with the right processes and teams and predictability in the business,” he said.
In addition, he says he will continue to look for good acquisition targets, and having this money in the bank will help the company fill in gaps in the product set should the right opportunity arise. “We don’t generally acquire revenue, but we are looking for good technology teams both in terms of talent, as well as technology that would help give us a jumpstart in terms of go-to-market.” It hasn’t been afraid to target small companies in the past, having acquired 12 already.
Freshworks, which launched in 2010, has almost 2,500 employees, a number that’s sure to go up with this new investment. It has 250,00 customers worldwide, including almost 40,000 paying customers. These including Bridgestone Tires, Honda, Hugo Boss, Toshiba and Cisco.
Powered by WPeMatico
On the heels of Google buying Fitbit for $2.1 billion, another player in wearables and health technology has picked up a big round of growth funding to continue expanding its business. Whoop, which makes a sensor-equipped (and screen-free) strap that continuously tracks your activities 24/7 and then provides a multitude of performance metrics and other data based on that activity, has closed a round of $55 million, a Series D that it will use to continue expanding its business into a wider range of wearables and analytics that can be gathered around them.
Today the devices measure things like how much strain a workout is causing you, how you are recovering afterwards, your sleep, whether training is having the desired effect, whether you are working at a level that will be less likely to cause injury and how you are likely to perform. Looking ahead, the plan is to bring the sensors into more places than just the strap it currently makes. “You’ll see Whoop over time worn throughout your body,” CEO Will Ahmed said. “The tech can live in other areas of the body, people will not even know you are wearing a sensor. We like the idea of tech being invisible while still being there.”
The funding brings the total to more than $100 million for the Boston-based company, and while Ahmed, who originally incubated the startup at Harvard with co-founders John Capodilupo and Aurelian Nicolae, said the valuation was not being disclosed, he did describe it as “healthy” — which I guess is appropriate for a health-tech company.
For some context, PitchBook notes that its last round of $25 million, in 2018, was at $125 million, post-money. That would mean a minimum of $180 million here, although the “healthy” implies it is actually higher. (We’ll continue to dig around and will update the number if we learn more.)
Whoop doesn’t disclose how many users it has currently, or anything about its financials, but its investor list is a good measure of the traction that Whoop has had to date, as a company pitching its product not just to the mass market, but to an elite group of sports people — who in turn are not just major athletes, but, in this day and age, major influencers when it comes to purchasing power.
This latest round was led by Foundry Group — coincidentally also an investor in Fitbit — with participation from Two Sigma Ventures, Accomplice, Thursday Ventures, Promus Ventures and Silicon Valley Bank. Individual investors included David Stern, the former NBA Commissioner; Ed Baker, former VP of product and growth at Uber, and former head of International Growth at Facebook; Marc Randolph, co-founder and first CEO of Netflix; and Nicholas Negroponte, MIT Media Lab.
Previous backers of the company include the Durant Company, the National Football League Players Association, Twitter chief executive Jack Dorsey, Los Angeles Chargers offensive tackle Russell Okung and Mike Novogratz, the chief executive of Galaxy Digital.
One notable shift Whoop has seen in the last year is that it has dropped the price of its wearable from an eye-watering $500 down to free. Instead, it bundles the strap into a wider membership program that you do pay for, starting at $30/month and decreasing, depending on what you would like to measure and use the data for (specifically, pricing is six months of data for $30/month; 12 months for $24/month; or 18 months for $18/month).
Offering its devices for free is just one of the ways that Whoop diverges from the usual wearables story.
At a time when wearables have become part of the gadget pantheon, equipped with screens and acting as little computers in their own right, Whoop has taken a very different turn, opting to build a device that looks nothing like a piece of electronics, even if behind the scenes it’s using just as much AI and other powerful technology to crunch the data that its five sensors are continuously collecting.
“The dirty secret with wearables is that the more features you try to pack in to them, the less effective they are,” Ahmed said. “We have been deliberate about what we want our tech to do. We think about the context of what will make the experience better, and if it doesn’t we’re not doing it.”
He gave me a flat “no comment” on the subject of whether Whoop had ever been approached for acquisition, but it’s notable to watch what has been happening around big tech. Apple has been seeing sales growth of its Watch outpace its other iconic products. Amazon is building a massive health services business that will likely also have a hardware component. And Google’s acquisition of Fitbit (if it clears all regulatory and other hurdles) is a big sign of how the company also sees this area as one where it will want to have a seat at the table.
“Google buying Fitbit is a sign that health data will be a big piece of the future for tech companies,” Ahmed said, pointing out that the company’s lack of growth in device sales is a strong sign that Google bought it largely for its data capabilities. “It puts a big value on data and what it’s done there and suggests Google will use the data to create health products.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Uploadcare, a startup that aims to make using CDN platforms cheaper and easier for businesses, today announced that it has raised a $1.7 million seed round led by Runa Capital and Vendep Capital, with existing investors Vaizra Capital and LVL1 Group participating, as well. Uploadcare promises to offer an end-to-end solution for businesses that automatically optimizes the files, images and videos of its clients and then delivers it over its CDN network or that of its partners.
Uploadcare founder and CEO Igor Debatur told me the idea for the service started quite a few years ago, while he was running a web development agency. Gathering files in different formats and sizes and then making those available in a way that was secure and easily scalable often turned out to be a challenge — and one that others in the industry faced as well. In the early days, Uploadcare was basically a file uploader for developers. Over time, Uploadcare added back-end features, including the smart CDN that can modify content on the fly based on the client where it’s displayed.
For a while, the team developed Uploadcare as a side project, but by 2016, the project started getting traction and they decided to shut down the development agency and focus solely on building out a proper product. “We started to build out a team and right now, we have more than 1,000 paying customers from very different sizes, starting from SMB to large enterprises using the product,” said Debatur.
Having worked for clients, the team obviously knew how to build products, but it had to figure out sales and marketing on the fly. Unsurprisingly, a lot of today’s new funding will go to exactly that: building out a sales and marketing team. Debatur also argues that unlike some of its competitors, Uploadcare invests a lot in its own technology, though the company does partner with other CDN vendors as well, based on its users’ needs.
“The amount of data that’s created per day is rising at a breakneck rate,” said Dmitry Chikhachev, general partner at Runa Capital . “With its robust infrastructure of delivery networks that span the globe, Uploadcare has quietly become a go-to solution for developers and engineers at some of the world’s largest companies. With differentiated technology and a strong leadership team, we believe that Uploadcare is well positioned to accelerate its growth and further solidify its leadership in the content delivery market.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Loop Returns, the startup that helps brands handle returns from online purchases, has today announced the close of a $10 million Series A funding round led by FirstMark Capital. Lerer Hippeau and Ridge Ventures also participated in the round.
Loop started when Jonathan Poma, a co-founder and COO and president, was working at an agency and consulting with a big Shopify brand on how to improve their system for returns and exchanges. After partnering with longtime friend Corbett Morgan, Loop Returns was born.
Loop sits on top of Shopify to handle all of a brand’s returns. It first asks the customer if they’d like a different size in the item they bought, quickly managing an exchange. It then asks if the customer would prefer to exchange for a new item altogether, depositing the credit in that person’s account in real time so they can shop for something new immediately.
If an exchange isn’t in the cards, Loop will ask the customer if they’d prefer credit with this brand over a straight-up refund.
The goal, according to Poma and Morgan, is to turn the point of return into a moment where brands can create a life-loyal customer when handled quickly and properly.
The more we shop online, the more brands extend themselves financially, and returns are a big part of that. Returns account for 20 to 30% of e-commerce sales, which can become a terrible financial burden on a growing direct-to-consumer brand. And what’s more, the cost of acquiring those users in the first place also goes down the drain.
Loop Returns hopes to keep that customer in the fold by giving them post-purchase options that are more sticky and more lucrative for the brand than a refund.
The company thinks of it as Connection Infrastructure. Most brands already have a customer acquisition architecture, and Shopify and Amazon are ahead when it comes to the infrastructure around customer convenience. But the ties that bind customers to brands haven’t been optimized for the many D2C brands out there looking to make an impact.
“The big problem we’re trying to solve long term is connection infrastructure,” said Morgan. “Why does this brand matter? Why does it mean something to me? Why does the product matter? We want to enforce more mindfulness and meaning into buying.”
Of course, a more mindful shopper doesn’t yield as many returns. Poma and Morgan admit that the goal of their software is to minimize returns, the very reason for the software’s existence. After all, return volume is one of a handful of variables that help Loop Returns determine what it will charge its brand clients.

But the team is thinking about other layers of the connection infrastructure, with plans to launch a product in 2020 that also focuses on the connection point after purchase. Poma and Morgan believe, with an almost religious reverence, that the brands themselves will help lead shoppers and infrastructure providers to a better, more connected shopping experience.
“Brands are the torch bearers,” said Poma. “They will lead us to a more enlightened era of how we think about buying. Empowerment of the brand will lead us to a better consumerism.”
The co-founders stayed mum on any specific plans for the 2020 product, but did say they will use the funding to expand operations and further build out its current and future products.
Of course, Loop is playing in a crowded space. Not only are there other players thinking about post-purchase connection, but Shopify has itself built out tools to help with exchanges and returns, and even acquired Return Magic, a similar service, in the summer of 2018.
That said, Loop Returns believes there is a long way to go as it builds the “connection infrastructure,” and that one clear path forward is actual personalization. With data from returns and exchanges, Loop Returns is relatively well-positioned to take on personalization in a meaningful way.
For now, Loop Returns has more than 200 customers and has handled more than 2 million returns, working with brands like Brooklinen, Allbirds, PuraVida and more.
Powered by WPeMatico
Counting billable time in six-minute increments is the most annoying part of being a lawyer. It’s a distracting waste. It leads law firms to conservatively under-bill. And it leaves lawyers stuck manually filling out timesheets after a long day when they want to go home to their families.
Life is already short, as Ping CEO and co-founder Ryan Alshak knows too well. The former lawyer spent years caring for his mother as she battled a brain tumor before her passing. “One minute laughing with her was worth a million doing anything else,” he tells me. “I became obsessed with the idea that we spend too much of our lives on things we have no need to do — especially at work.”
That’s motivated him as he’s built his startup Ping, which uses artificial intelligence to automatically track lawyers’ work and fill out timesheets for them. There’s a massive opportunity to eliminate a core cause of burnout, lift law firm revenue by around 10% and give them fresh insights into labor allocation.

Ping co-founder and CEO Ryan Alshak (Image Credit: Margot Duane)
That’s why today Ping is announcing a $13.2 million Series A led by Upfront Ventures, along with BoxGroup, First Round, Initialized and Ulu Ventures. Adding to Ping’s quiet $3.7 million seed led by First Round last year, the startup will spend the cash to scale up enterprise distribution and become the new timekeeping standard.
“I was a corporate litigator at Manatt Phelps down in LA and joke that I was voted the world’s worst timekeeper,” Alshak tells me. “I could either get better at doing something I dreaded or I could try and build technology that did it for me.”
The promise of eliminating the hassle could make any lawyer who hears about Ping an advocate for the firm buying the startup’s software, like how Dropbox grew as workers demanded easier file sharing. “I’ve experienced first-hand the grind of filling out timesheets,” writes Initialized partner and former attorney Alda Leu Dennis. “Ping takes away the drudgery of manual timekeeping and gives lawyers back all those precious hours.”
Traditionally, lawyers have to keep track of their time by themselves down to the tenth of an hour — reviewing documents for the Johnson case, preparing a motion to dismiss for the Lee case, a client phone call for the Sriram case. There are timesheets built into legal software suites like MyCase, legal billing software like TimeSolv and one-off tools like Time Miner and iTimeKeep. They typically offer timers that lawyers can manually start and stop on different devices, with some providing tracking of scheduled appointments, call and text logging, and integration with billing systems.
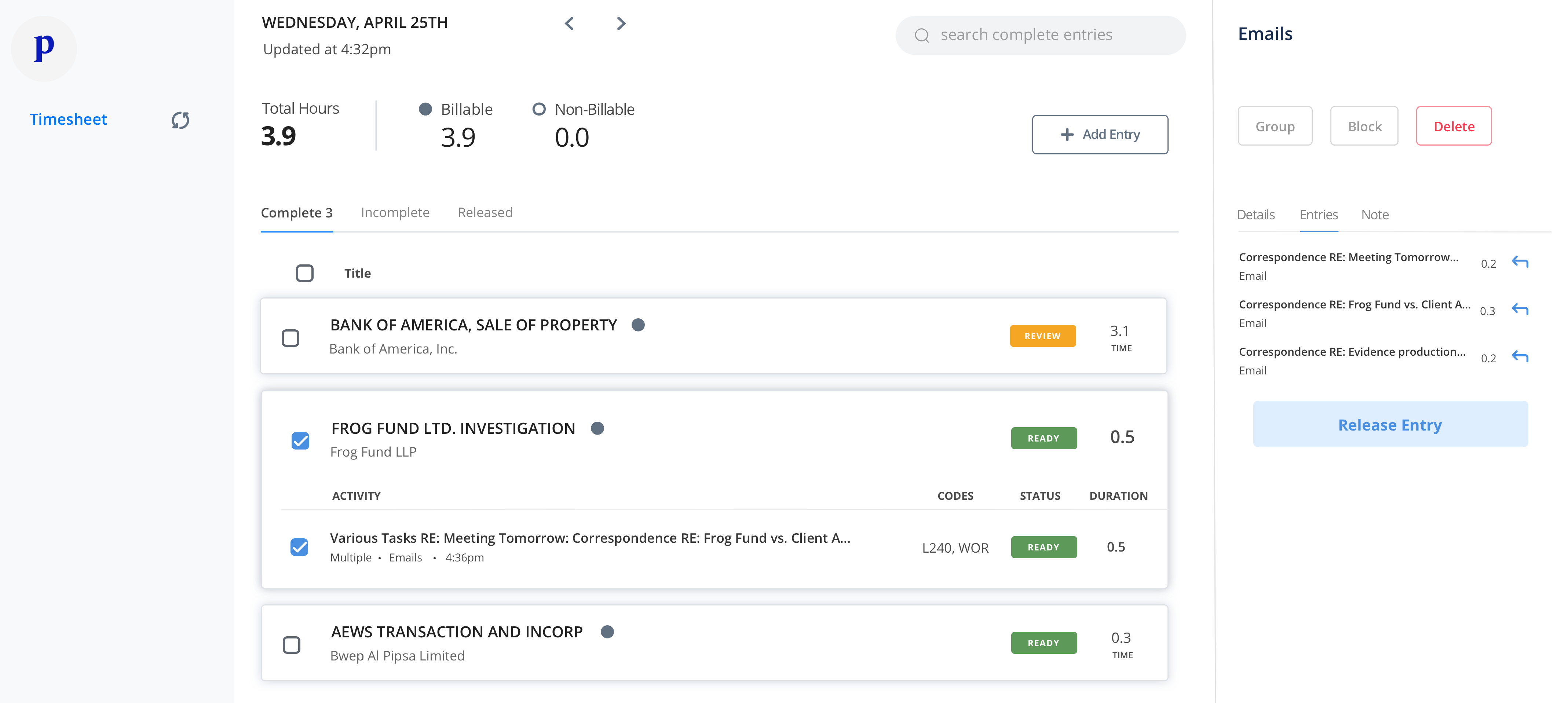
Ping goes a big step further. It uses AI and machine learning to figure out whether an activity is billable, for which client, a description of the activity and its codification beyond just how long it lasted. Instead of merely filling in the minutes, it completes all the logs automatically, with entries like “Writing up a deposition – Jenkins Case – 18 minutes.” Then it presents the timesheet to the user for review before they send it to billing.
The big challenge now for Alshak and the team he’s assembled is to grow up. They need to go from cat-in-sunglasses logo Ping to mature wordmark Ping. “We have to graduate from being a startup to being an enterprise software company,” the CEO tells me. That means learning to sell to C-suites and IT teams, rather than just build a solid product. In the relationship-driven world of law, that’s a very different skill set. Ping will have to convince clients it’s worth switching to not just for the time savings and revenue boost, but for deep data on how they could run a more efficient firm.

Along the way, Ping has to avoid any embarrassing data breaches or concerns about how its scanning technology could violate attorney-client privilege. If it can win this lucrative first business in legal, it could barge into the consulting and accounting verticals next to grow truly huge.
With eager customers, a massive market, a weak status quo and a driven founder, Ping just needs to avoid getting in over its heads with all its new cash. Spent well, the startup could leap ahead of the less tech-savvy competition.
Alshak seems determined to get it right. “We have an opportunity to build a company that gives people back their most valuable resource — time — to spend more time with their loved ones because they spent less time working,” he tells me. “My mom will live forever because she taught me the value of time. I am deeply motivated to build something that lasts . . . and do so in her name.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Frontier Car Group, the Berlin-based startup building used car marketplaces targeting high-growth, emerging markets, has picked up another significant round of funding from a strategic backer also focusing on the same geographical opportunity.
Today, OLX, the online classifieds division Prosus (the digital division of Naspers that listed earlier this year in Europe) announced that it would invest up to $400 million in Frontier, in a mix of equity, secondary share acquisitions and existing business shares. The deal will include a primary capital injection of an unspecified amount, which OLX has confirmed to me values Frontier Car Group at $700 million, post-money.
In terms of business shares: OLX also said that it will be contributing its shares in a JV it had in place with Frontier in India and Poland. Meanwhile, the secondary acquisitions — the shares are currently held by other investors, founders and management — are subject to a tender process. The markets that Frontier operates in now include Nigeria, Mexico, Chile, Pakistan, Indonesia and the USA (where it acquired WeBuyAnyCar last year), in addition to India and Poland.
Notably, even before the full $400 million amount is exercised (that is, after the tender process is completed), an OLX spokesperson confirmed that first capital injection will make it Frontier’s largest single shareholder (but not the majority shareholder), which essentially values the deal at less than $350 million (based on the $700 million valuation).
Today, Frontier Car Group offers buyers and sellers a range of services: in addition to basic inventory listings, there are inspection reports, financial, pricing guides, warranties and insurance. The plan will be to expand more services for one of the key players in the used-car space, dealers — via Frontier’s Dealer Management System — more resale services (via OLX) and more CarFax/Blue Book-style pricing guides and other products.
Frontier sold about $700 million worth of cars in the past year, triple its value of a year before.
As a point of reference, in May of last year, when the company raised $58 million, it had sold 50,000 cars to date and was on track for $200 million in annualised revenues. CEO and co-founder Sujay Tyle says the company has been on a growth tear.
“FCG has nearly tripled performance across every key metric since the first OLX Group investment less than 18 months ago and has expanded to four new countries in that time,” said Tyle in a statement. “This is a testament to FCG’s team, the ripe market opportunity, and the results of early integration with OLX in our key markets. Together with OLX and Prosus, we are aiming to revolutionize the used car market in several emerging and developed economies by adding trust, transparency and a comprehensive suite of services to all participants in the ecosystem.”
“Together with FCG, we are aiming to build the leading global used car marketplace, offering a premium and convenient service to millions of car buyers, sellers and dealers,” said Martin Scheepbouwer, CEO of OLX Group. “We’re in a unique position to accelerate the expansion of this platform worldwide. Our experience in India is a great proof of concept, where within the space of a year, our joint venture has already increased the number of stores threefold, with car purchase volumes continuing to grow by 10% month-on-month.”
This is the second time that OLX has invested in Frontier: In May 2018, Naspers invested $89 million in the business, an investment that came just weeks after Frontier had raised $58 million from Balderton, TPG and others.
The deal underscores the longtime trend of consolidation in e-commerce businesses — something Prosus is also seeing played out in a completely different arena, that of food delivery.
The basics of the economy-of-scale principle, as applied to used car sales, goes something like this: economies of scale makes a platform more useful (there will be more cars on it, and less on competitors’ sites); but it also potentially means that Frontier would be making more transactions, thereby more revenues overall; and building and running more sales on the same platform improves the margins on the investment that gets made in building and operating that platform.
Targeting P2P used car sales in emerging markets is a big potential business: In part because of the nature of those economies, car owners are more likely to sweat out assets rather than go for buying completely new vehicles. OLX notes that combining the operations in Frontier’s footprint with those of the JV businesses that it is now taking over, plus OLX’s own business in Latin America, Asia and Poland, results in a market where some 30 million used cars are sold annually, “more than double that of China.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Stock trading app Robinhood is valued at $7.6 billion, but it only operates in the U.S. Freshly funded fintech startup Alpaca does the dirty work so developers worldwide can launch their own competitors to that investing unicorn. Like the Stripe of stocks, Alpaca’s API handles the banking, security and regulatory complexity, allowing other startups to quickly build brokerage apps on top for free. It has already crossed $1 billion in transactions within a year of launch.
The potential to power the backend of a new generation of fintech apps has attracted a $6 million Series A round for Alpaca led by Spark Capital . Instead of charging developers, Alpaca earns its money through payment for order flow, interest on cash deposits and margin lending, much like Robinhood.
“I want to make sure that people even outside the U.S. have access” to a way of building wealth that’s historically only “available to rich people” Alpaca co-founder and CEO Yoshi Yokokawa tells me.

Alpaca co-founder and CEO Yoshi Yokokawa
Hailing from Japan, Yokokawa followed his friends into the investment banking industry, where he worked at Lehman Brothers until its collapse. After his grandmother got sick, he moved into day-trading for three years and realized “all the broker dealer business tools were pretty bad.” But when he heard of Robinhood in 2013 and saw it actually catering to users’ needs, he thought, “I need to be involved in this new transformation” of fintech.
Yokokawa ended up first building a business selling deep learning AI to banks and trading firms in the foreign exchange market. Watching clients struggle to quickly integrate new technology revealed the lack of available developer tools. By 2017, he was pivoting the business and applying for FINRA approval. Alpaca launched in late 2018, letting developers paste in code to let their users buy and sell securities.
Now international developers and small hedge funds are building atop the Alpaca API so they don’t have to reinvent the underlying infrastructure themselves right away. Alpaca works with clearing broker NTC, and then marks up margin trading while earning interest and payment for order flow. It also offers products like AlpacaForecast, with short-term predictions of stock prices, AlpacaRadar for detecting price swings and its MarketStore financial database server.
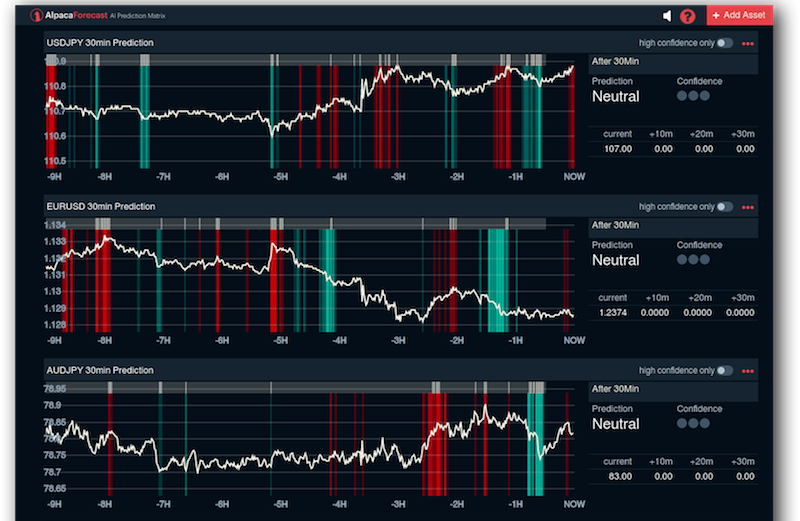
AlpacaForecast
The $6 million from Spark Capital, Social Leverage, Portag3, Fathom Capital and Zillionize adds to $5.8 million in previous funding from investors, including Y Combinator. The startup plans to spend the cash on hiring to handle partnerships with bigger businesses, supporting its developer community and ensuring compliance.
One major question is whether fintech businesses that start to grow atop Alpaca and drive its revenues will try to declare independence and later invest in their own technology stack. There’s the additional risk of a security breach that might scare away clients.
Alpaca’s top competitor, Interactive Brokers, offers trading APIs, but other services as well that distract it from fostering a robust developer community, Yokokawa tells me. Alpaca focuses on providing great documentation, open-source contribution and SDKs in different languages that make it more developer-friendly. It will also have to watch out for other fintech services startups like DriveWealth and well-funded Galileo.
There’s a big opportunity to capitalize on the race to integrate stock trading into other finance apps to drive stickiness because it’s a consistent, voluntary behavior rather than a chore or something only done a few times a year. Lender SoFi and point-of-sale system Square both recently became broker dealers as well, and Yokokawa predicts more and more apps will push into the space.
Why would we need so many stock trading apps? “Every single person is involved with money, so the market is huge. Instead of one-player takes all, there will be different players that can all do well,” Yokokawa tells me. “Like banks and investment banks co-exist, it will never be that Bank of America takes 80% of the pie. I think differentiation will be on customer acquisition, and operations management efficiency.”
The co-founder’s biggest concern is keeping up with all the new opportunities in financial services, from cash management and cryptocurrency that Robinhood already deals in, to security token offerings and fractional investing. Yokokawa says, “I need to make sure I’m on top of everything and that we’re executing with the right timing so we don’t lose.”
The CEO hopes that Alpaca will one day power broader access to the U.S. stock market back in Japan, noting that if a modern nation still lags behind in fintech, the rest of the world surely fares even worse. “I want to connect this asset class to as many people as possible on the earth.”
Powered by WPeMatico