real estate
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Managed by Q, the office management platform recently acquired by WeWork, has today announced the launch of Task Management.
The feature comes to Managed by Q by way of Hivy, a startup acquired by MBQ back in 2017, that focuses on connecting a company’s employees to the office manager that handles their requests.
Pre-Hivy, collecting requests and tracking projects across a large number of employees was a tedious, fragmented process. Hivy created a dashboard that organizes all those requests in a single place.
Since the acquisition, Managed by Q and Hivy have been working to integrate their respective platforms. Where Managed by Q connects office managers to the right vendor or MBQ operator to handle the job, the new Task Management system will connect office managers with the employees making the requests in the first place, essentially putting the entire pipeline in a single place.
Obviously, the path to full integration was a long one.
“What I think matters most,” said Hivy co-founder Pauline Tordeur, speaking about the process of intertwining two separate products, “is that we knew why we were doing this and what the future would look like when we integrate. Having this vision and outlook from the very beginning is important.”
The timing is interesting in that this is the first product announcement Managed by Q has made since it was acquired by WeWork.
“It’s hard to describe the feeling,” said Managed by Q co-founder and CEO Dan Teran of being acquired by The We Company. “There is a perception of WeWork from the outside, but since I’ve been spending a lot of time getting to learn the business firsthand, I think there is just so much potential.”
He noted that Managed by Q is indeed setting out to integrate with WeWork in a way that’s similar to the process Q just finished with Hivy.
“We set out to build the operating system for space, and one of the biggest things we missed is the space itself,” said Teran. “That’s actually the hardest part for most people. So now that becomes another ingredient we can deliver to our customers.”
Powered by WPeMatico
During my recent conversation with Peter Kraus, which was supposed to be focused on Aperture and its launch of the Aperture New World Opportunities Fund, I couldn’t help veering off into tangents about the market in general. Below is Kraus’ take on the availability of alpha generation, the Fed, inflation versus Amazon, housing, the cross-ownership of U.S. equities by a few huge funds and high-frequency trading.
Gregg Schoenberg: Will alpha be more available over the next five years than it has been over the last five?
To think that at some point equities won’t become more volatile and decline 20% to 30%… I think it’s crazy.
Peter Kraus: Do I think it’s more available in the next five years than it was in the last five years? No. Do I think people will pay more attention to it? Yes, because when markets are up to 30 percent, if you get another five, it doesn’t matter. When markets are down 30 percent and I save you five by being 25 percent down, you care.
GS: Is the Fed’s next move up or down?
PK: I think the Fed does zero, nothing. In terms of its next interest rate move, in my judgment, there’s a higher probability that it’s down versus up.
Powered by WPeMatico
Managed by Q, the office management platform based out of New York, has today been acquired by The We Company, formerly known as WeWork.
Financial terms were not disclosed. The WSJ reports that it was a cash and stock deal. Managed by Q, which has 500 employees, will remain as a wholly owned separate entity and CEO Dan Teran will remain following the acquisition to join WeWork leadership.
Upon its latest financing in January, Managed by Q was valued at $249 million, according to PitchBook.
Here’s what Teran had to say in a prepared statement:
We are excited for this incredible opportunity to deepen our commitment to realizing our ambitious vision of building an operating system for the built world. WeWork is uniquely positioned to invest in workplace technology and services, and I look forward to partnering with their team to build more robust products for our clients and create a global platform to help companies push the bounds on our collective potential.
Managed by Q was founded in 2014 with a plan to change the way that offices run. The platform allowed office managers and other decision-makers to handle supply stocking, cleaning, IT support and other non-work related tasks in the office by simply using the Managed by Q dashboard. Managed by Q serves the demand through a combination of in-house operators and third-party vendors and service providers.
Notably, Managed by Q took a different tack than most other logistics companies, employing their operators as W2 workers instead of 1099 contractors. Moreover, Managed by Q offered a stock option plan to operators that gives 5 percent of the company back to those employees.
The company has raised a total of $128.25 million since launch from investors such as GV, RRE and Kapor Capital. Managed by Q currently serves the markets of New York, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Chicago, Boston and Silicon Valley, with plans to aggressively expand following the acquisition, according to the WSJ.
Not only has Managed by Q swiftly matured into a big player in the NY tech scene and Future of Work space, but it has also fostered interesting competition and consolidation within the space. Managed by Q has itself made several acquisitions, including the purchase of NVS (an office space planning and project management service) and Hivy (an internal comms tool to let employees tell office managers what they need).
Powered by WPeMatico
Betaworks Studios, the brainchild of New York City seed-stage venture capital fund Betaworks, has amassed the support of WeWork, or The We Company, as they now call themselves.
JLL Spark Ventures and the co-working giant have led co-led a $4.4 million investment in the membership-based co-working club described as a supportive community for builders. Launched in 2018, Betaworks Studios offers entrepreneurs, artists, engineers and creatives a place to work on projects and accumulate a network, similar to a WeWork hub.
Betaworks Ventures, which filed today to raise a $75 million sophomore fund, and BBG Ventures have also participated in the funding for Betaworks Studio, which previously raised a pre-seed round led by BBG.
Founded in 2008 by John Borthwick, Betaworks operates an investment fund, an accelerator and builds companies internally with spinouts including Giphy, Digg and Bit.ly. The idea for Betaworks Studios was to expand its resources and network to the greater entrepreneurial community.
Borthwick brought on Daphne Kwon, the former chief financial officer of Goop, to run the studio arm, which charges $2400 per year or $225 per month.
Betaworks says its studio has hosted some 9,000 people for meetings and speaking events. It currently has only one club location in New York City’s Meatpacking District but plans to open additional studios with the fresh cash.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello Alfred — the startup that assigns in-home assistants to take care of your recurring chores and tasks — has announced the launch of a new service tier that will provide more properties and residents with access to the company’s underlying technology.
The company, which won the Startup Battlefield competition at our 2014 Disrupt event in San Francisco, looks to unlock valuable time for users by handling the long list of small routine items that add up over the course of a week and still require human oversight.
Hello Alfred partners with building owners to provide residents with dedicated home managers that assist with various errands and on-request services, such as apartment cleaning, grocery delivery, laundry services, prescription refills and more. Users have a direct line of communication with the company’s hospitality team through Hello Alfred’s mobile app, where they can manage tasks and set recurring appointments.
The new platform, “Powered by Alfred,” acts as a fairly similar but more accessible alternative to the company’s current offering. Residents in buildings equipped with “Powered by Alfred” are given access to all of the company’s solutions with the exception of the weekly visits from dedicated home managers currently included in the existing service. By excluding the dedicated in-home service, Hello Alfred is able to offer its new service tier at a lower price point and integrate with more buildings faster.
Property owners using “Powered by Alfred” can customize packages to include the services that best fit the needs of their residents and can upgrade or change service levels at any time. Both residents and building owners using the new platform are also given more control and direct access to Hello Alfred’s proprietary technology, allowing users to control functions that normally fall under the purview of the company’s dedicated home managers.
Additionally, with the launch of the new offering, Hello Alfred will be consolidating its various solutions under one central app, where residents and building managers can handle all inquiries, appointments and payments.
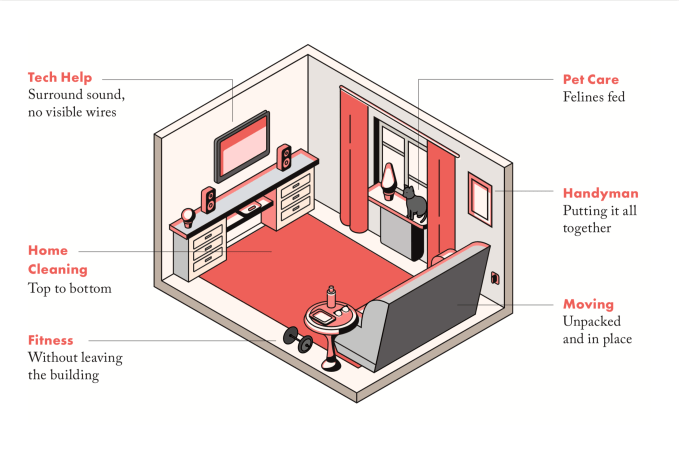
Hello Alfred’s new service tier, “Powered by Alfred,” provides a single, shared access point for resident and property owners to manage inquiries and drive property performance / Hello Alfred Press Kit
The launch of “Powered by Alfred” seems to be a natural evolution for the company, which seeks to make its offering more accessible to all residents of all backgrounds.
Hello Alfred previously employed a consumer-facing business model, in which customers would pay a monthly subscription fee for the array of in-home services and access to the company’s team of hospitality specialists, referred to as Alfreds.
However, around the time of the startup’s Series B round, Hello Alfred adopted the model of partnering directly with property owners to offer its services complimentary to residents. The partnership structure was not only a more conducive model for scaling but also enabled the company to offer the same services to any resident in an Alfred-equipped building, regardless of socioeconomic status.
Hello Alfred quickly built up a sizeable backlog of property owners hoping to integrate the platform into their units, according to the company. However, the task of maintaining dedicated staffing for every unit in every location made it difficult for the Alfred team to satisfy its swelling demand, having to instead focus resources primarily on luxury properties.
With “Powered by Alfred” removing in-home management services, the company has been able to improve accessibility and better satisfy the market’s appetite for its services, now rolling out the offering to non-luxury buildings and properties that previously sat in its pipeline.
Behind the launch of the new platform — which the company has piloted over the course of several months — Hello Alfred has increased its market share by more than 50 percent, with its services now available in more than 150,000 residential properties.
“We want Alfred to be a utility. We want to make “help” a universal utility and make it something anyone can access,” Hello Alfred CEO and co-founder Marcela Sapone told TechCrunch. “We wanted to find a way where we could accelerate growth and get human-focused help into urban buildings to help most urban environments.”
The launch represents the latest step in Hello Alfred’s broader expansion plans, which appear to have ramped up in recent months. Hello Alfred is now active in 16 cities — including Houston, where the company plans to launch next week — with its new offering available across all of its active markets. The startup already boasts an impressive partnership roster that includes more than 20 of the largest property owners in the U.S., and the Alfred team expects its new offering to open up further opportunities for partnerships across different property classes and different stages of a resident’s life cycle.
“As WeWork transformed commercial real estate, Hello Alfred is transforming residential real estate, and redefining what it means to live in a city today,” said Sapone. “This business expansion allows us to not only satisfy increasing demand for our service, but to connect every part of the resident experience — from the moment you sign your lease, until the moment you move to another Hello Alfred building.”
To date, the company has raised just over $63.5 million in venture capital, according to data from PitchBook, from prestigious investment brands that include New Enterprise Associates, Spark Capital, SV Angel, Moderne Ventures, Invesco and others.
Powered by WPeMatico
Cookie-cutter corporate housing turns people into worker drones. When an employee needs to move to a new city for a few months, they’re either stuck in bland, giant apartment complexes or Airbnbs meant for shorter stays. But Zeus lets any homeowner get paid to host white-collar transient labor. Through its managed ownership model, Zeus takes on all the furnishing, upkeep, and risk of filling the home while its landlords sit back earning cash.
Zeus has quietly risen to a $45 million revenue run rate from renting out 900 homes in 23 cities. That’s up 5X in a year thanks to Zeus’ 150 employees. With a 90 percent occupancy rate, it’s proven employers and their talent want more unique, trustworthy, well-equipped multi-month residences that actually make them feel at home.
Now while Airbnb is distracted with its upcoming IPO, Zeus has raised $24 million to steal the corporate housing market. That includes a previous $2.5 million seed round from Bowery, the new $11.5 million Series A led by Initialized Capital whose partner Garry Tan has joined Zeus’ board, and $10 million in debt to pay fixed costs like furniture. The plan is to roll up more homes, build better landlord portal software, and hammer out partnerships or in-house divisions for cleaning and furnishing.

“In the first decade out of school people used to have two jobs. Now it’s four jobs and it’s trending to five” says Zeus co-founder and CEO Kulveer Taggar. “We think in 10 years, these people won’t be buying furniture.” He imagines they’ll pay a premium for hand-holding in housing, which judging by the explosion in popularity of zero-friction on-demand services, seems like an accurate assessment of our lazy future. Meanwhile, Zeus aims to be “the quantum leap improvement in the experience of trying to rent out your home” where you just punch in your address plus some details and you’re cashing checks 10 days later.
“When I sold my first startup, I bought a home for my mom in Vancouver” Taggar recalls. It was payback for when she let him remortgage her old house while he was in college to buy a condo in Mumbai he’d rent out to earn money. “Despite not having much growing up, my mom was a travel agent and we got to travel a lot” which Taggar says inspired his goal to live nomadically in homes around the world. Zeus could let other live that dream.

Zeus co-founder and CEO Kulveer Taggar
After Oxford and working as an analyst at Deutsche Bank, Taggar built student marketplace Boso before moving to the United States. There, he co-founded auction tool Auctomatic with his cousin Harjeet Taggar and future Stripe co-founder Patrick Collison, went through Y Combinator, and sold it to Live Current Media for $5 million just 10 months later. That gave him the runway to gift a home to his mom and start tinkering on new ideas.
With Y Combinator’s backing again, Taggar started NFC-triggered task launcher Tagstand, which pivoted into app settings configurer Agent, which pivoted into automatic location sharing app Status. But when his co-founder Joe Wong had to move an hour south from San Francisco to Palo Alto, Taggar was dumbfounded by how distracting the process was. Listing and securing a new tenant was difficult, as was finding a medium-term rental without having to deal with exhorbitant prices or sketchy Cragislist. Having seen his former co-founder go on to great success with Stripe’s dead-simple payments integration, Taggar wanted to combine that vision with OpenDoor’s easy home sales to making renting or renting out a place instantaneous. That spawned Zeus.
To become a Zeus landlord, you just type in your address, how many bedrooms and bathrooms, and some aesthetic specs, and you get a monthly price quote for what you’ll be paid. Zeus comes in and does a 250-point quality assessment, collects floor plans, furnishes the property, and handles cleaning and maintenance. It works with partners like Helix mattresses, Parachute sheets, and Simple Human trash cans to get bulk rates. “We raised debt because we had these fixed investments into furniture. It’s not as dilutive as selling pure equity” Taggar explains.
Zeus quickly finds a tenant thanks to listings in Airbnb and relationships with employers like Darktrace and ZS Associates with lots of employees moving around. After passing background checks, tenants get digital lock codes and access to 24/7 support in case something doesn’t look right. The goal is to get someone sleeping there in just 10 days. “Traditional corporate housing is $10,000 a month in SF in the summer or at extended stay hotels. Airbnb isn’t well suited [for multi-month stays]. ” Taggar claims. “We’re about half the price of traditional corporate housing for a better product and a better experience.”

Zeus signs minimum two-year leases with landlords and tries to extend them to five years when possible. It gets one free month of rent as is standard for property managers, but doesn’t charge an additional rate. For example, Zeus might lease your home for $4,000 per month but gets the first month free, and rent it out for $5,000 so it earns $60,000 but pays you $44,000. That’s a tidy margin if Zeus can get homes filled fast and hold down its upkeep costs.
“Zeus has been instrumental for my company to start the process of re-location to the Bay Area and to host our visiting employees from abroad now that we are settled” writes Zeus client Meitre’s Luis Caviglia. “I particularly like the ‘hard truths’ featured in every property, and the support we have received when issues arose during our stays.”
There’s no shortage of competitors chasing this $18 billion market in the US alone. There are the old-school corporations and chains like Oakwood and Barbary Coast that typically rent out apartments from vast, generic complexes at steep rates. Stays over 30 days made up 15 percent of Airbnb’s business last year, but the platform wasn’t designed for peace-of-mind around long-term stays. There are pure marketplaces like UrbanDoor that don’t always take care of everything for the landlord or provide consistent tenant experiences. And then there are direct competitors like $130 million-funded Sonder, $66 million-funded Domio, recently GV-backed 2nd Address, and European entants like MagicStay, AtHomeHotel, and Homelike.
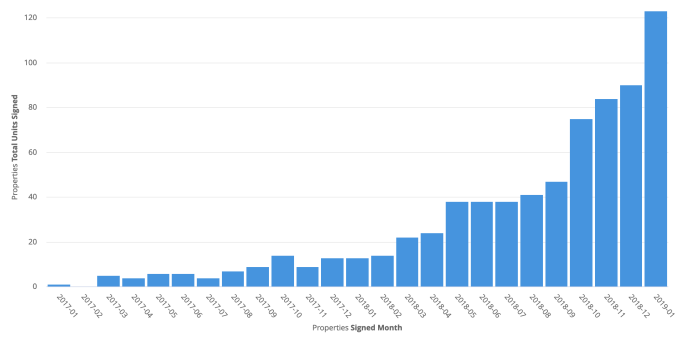
Zeus’ property unit growth
There’s plenty of pie, though. With 330,000 housing units in SF alone, Zeus has plenty of room to grow. The rise of remote work means companies whose employee typically didn’t relocate may now need to bring in distant workers for a multi-month sprint. A recession could make companies more expense-cautious, leading them to rethink putting up staffers in hotels for months on end. Regulatory red tape and taxes could scare landlords away from short-term rentals and towards coprorate housing. And the need to expand into new businesses could tempt the big vacation rental platforms like Airbnb to make acquisitions in the space — or try to crush Zeus.
Winners will be determined in part by who has the widest and cheapest selection of properties, but also by which makes people most comfortable in a new city. That’s why Taggar is taking a cue from WeWork by trying to arrange more community events for its tenants. Often in need of friends, Zeus could become a favorite by helping people feel part of a neighborhood rather than a faceless inmate in a massive apartment block or hotel. That gives Zeus network effect if it can develop density in top markets.

Taggar says the biggest challenge is that “I feels like I’m running five startups at once. Pricing, supply chain, customer service, B2B. We’ve decided to make everything custom — our own property manager software, our own internal CRM. We think these advantages compound, but I could be wrong and they could be wasted effort.”
The benefits of Zeus‘ success would go beyond the founder’s bank account. “I’ve had friends in New York get great opportuntiies in San Francisco but not take them because of the friction of moving” Taggar says. Routing talent where it belongs could get more things built. And easy housing might make people more apt to live abroad temporarily. Taggar concludes, “I think it’s a great way to build empathy.”
Powered by WPeMatico
AngelPad just wrapped the 12th run of its three months long New York City startup accelerator. For the second time, the program didn’t culminate in a demo day; rather, the 19 participating startups were given pre-arranged one-on-one meetings with venture capital investors late last week.
AngelPad co-founders Thomas Korte and Carine Magescas did away with the demo day tradition last year after nearly a decade operating AngelPad, which is responsible for mentoring startups including Postmates, Twitter-acquired Mopub, Pipedrive, Periscope Data, Zum and DroneDeploy.
“Demo days are great ways for accelerators to expose a large number of companies to a lot of investors, but we don’t think it is the most productive way,” Korte told TechCrunch last year. Competing accelerator Y Combinator has purportedly considered their eliminating demo day as well, though sources close to YC deny this. The firm cut its investor day, a similar opportunity for investors to schedule meetings with individual startups, “after analyzing its effectiveness” last year.
Feedback to AngelPad’s choice to forego demo day has been positive, Korte tells TechCrunch, with startup CEOs breathing a sigh of relief they aren’t forced to pitch to a large crowd with no promise of investment.
AngelPad invests $120,000 in each of its companies. Here’s a closer look at its latest batch:
LotSpot is a parking management tool for universities, parks and malls. The company installs cameras at the entrances and exits of customer parking lots and autonomously tracks lot occupancy as cars enter and exit. The LotSpot founders are Stanford University Innovation Fellows with backgrounds in engineering and sales.
Twic is a discretionary benefits management platform that helps businesses offer wellness benefits at a lower cost. The tool assists human resources professionals in selecting vendors, monitoring benefits usage and managing reimbursements with a digital wallet. Twic customers include Twitch and Oscar. The company’s current ARR is $265,000.
Zeal is an enterprise contract automation platform that helps sales teams manage custom routine agreements, like NDAs, independently and efficiently. The startup is currently working on test implementations with large companies. The founders are attorneys and management consultants who previously led sales and legal strategy at AXIOM.
ChargingLedger works with energy grid operators to optimize electric grid usage with smart charging technology for electric vehicles. The company’s paid pilot program is launching this month.
Piio, focused on SEO, helps companies boost their web presence with technology that optimizes website speed and performance based on user behavior, location, device, platform and connection speed. Currently, Piio is working with JomaShop and e-commerce retailers. Its ARR is $90,000.
Duality.ai is a QA platform for autonomous vehicles. It leverages human testers and simulation environments to accelerate time-to-market for AV sidewalk, cars and trucks. Its founders include engineers and designers from Caterpillar, Pixar and Apple. Its two first beta customers generated an ARR of $100,000.

COMUNITYmade partners with local manufacturers to sell their own brand of premium sneakers made in Los Angeles. The company has attracted brands, including Adidas, for collaborations. The founders are alums of Asics and Toms.
Spacey is a millennial-focused art-buying platform. The company sells limited-edition collections of fine-art prints at affordable prices and offers offline membership experiences, as well as a program for brand ambassadors with large social followings.
LegalPassage saves lawyers time with business process automation software for law firms. The company focuses on litigation, specifically class action and personal injury. The founder is a litigation attorney, former adjunct professor of law at UC Hastings and a past chair of the Family Law Section of the Bar Association of San Francisco.
Revetize helps local businesses boost revenue by managing reputation, encouraging referrals and increasing repeat business. The startup, headquartered in Utah, has an ARR of $220,000.
House of gigs helps people find short-term work near them, offering “employee-like” services and benefits to those freelancers and gig workers. The startup has 90,000 members. The San Francisco and Berlin-based founders previously worked together at a VC-backed HR startup.
MetaRouter provides fast, flexible and secure data routing. The cloud-based on-prem platform has reached an ARR of $250,000, with “two Fortune 500 retailers.”
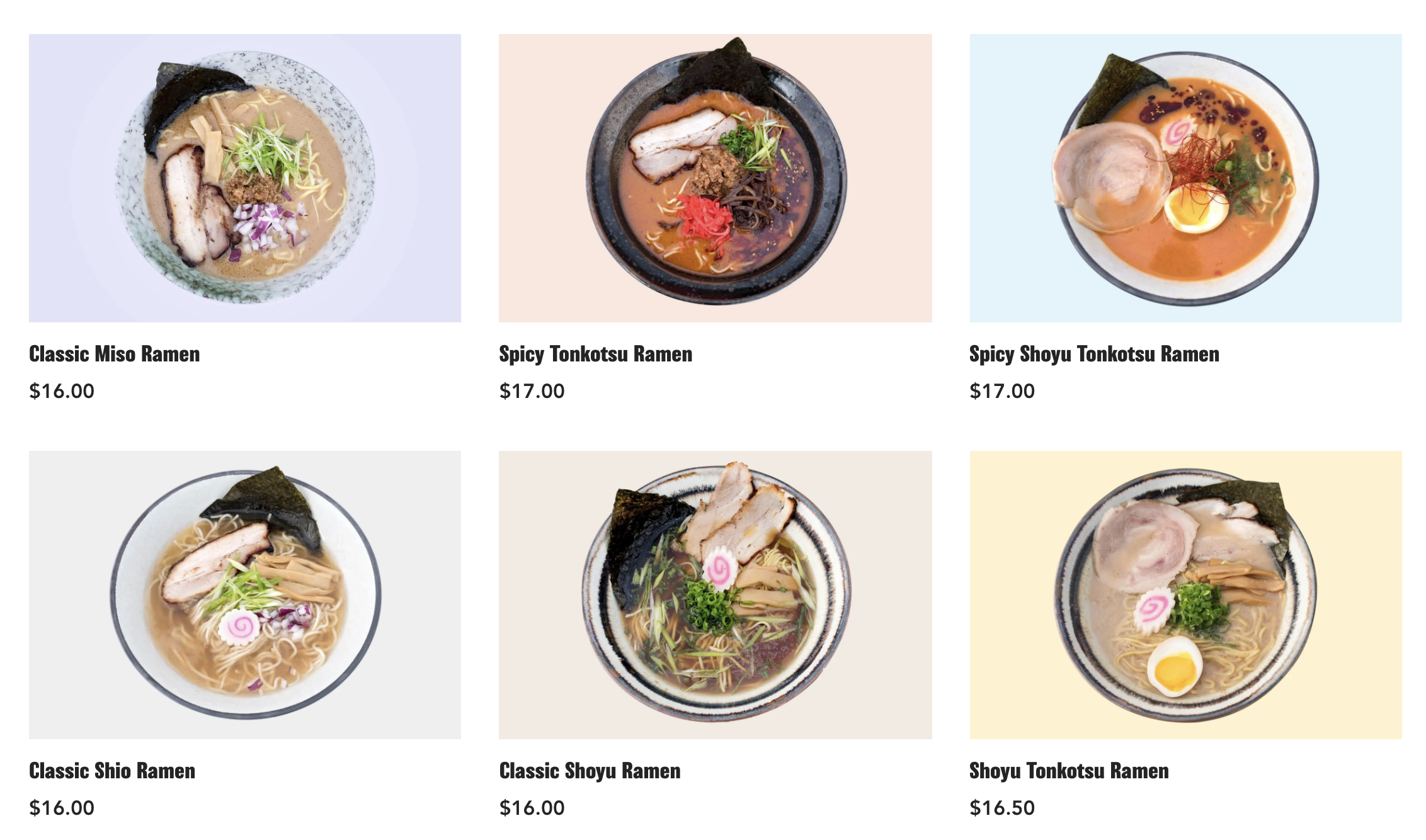
RamenHero offers a meal kit service for authentic gourmet ramen
RamenHero offers a meal kit for authentic gourmet ramen. The startup launched in 2018 and has roughly 1,700 customers and $125,000 in revenue. The startup’s founder, a serial entrepreneur, graduated from a culinary ramen school in Japan.
ByteRyde is insurance for autonomous vehicles, specifically Tesla Model 3s, taking into account the safety feature of self-driving cars.
Foresite.ai provides commercial real estate investors a real-time platform for data analysis and visualization of location-based trends.
PieSlice is a blockchain-based equity issuance and management platform that helps create fully compliant digital tokens that represent equity in a company. The founder is a former trader and stockbroker turned professional poker player.
Aitivity is a security hardware company that is developing a scalable blockchain algorithm for enterprises, specifically for IoT usage.
SmartAlto, a SaaS platform with $190,000 ARR, nurtures real estate leads. The company pairs agents with digital assistants to help the agents show more homes.
FunnelFox works with sales teams to help them spend less time on customer research, pipeline management and reporting. The AI-enabled platform has reached an ARR of $75,000 with customers including Botify and Paddle.
Powered by WPeMatico
Blueground, the startup providing turnkey flexible rental apartments, has raised $20 million in a round led by Athens-based VentureFriends, with participation from Endeavor Catalyst, Dubai’s Jabbar Internet Group and serial entrepreneur Kevin Ryan. Ryan — who helped found MongoDB, Gilt Groupe, Zola and others — will also join Blueground’s board of directors.
It’s no secret that remote work and frequent business travel are becoming more and more commonplace. As a result, a growing number of people are shying away from lengthy rental or lease commitments and are instead turning to companies like Blueground for more flexible short-term solutions.
Blueground is trying to be the go-to option for individuals moving or traveling to a city for as little as a month, or any duration longer. Similar to flexible office space providers, Blueground partners with major property owners to sign long-term leases for units it then furnishes and rents out with more flexible terms.
Users can rent listings for anywhere between one month to five years, and rates are set on a monthly basis, which can often lead to more favorable prices over medium-to-long-term stays relative to the short-term pricing structures commonly used by hospitality companies.
CEO Alex Chatzieleftheriou is intimately familiar with the value flexible leasing can unlock. Before founding Blueground, Chatzieleftheriou worked as a consultant for McKinsey, where he was frequently sent off to projects in far-off cities for months at a time — living in 15 cities over just seven years.
However, no matter how much time Alex logged in hotels, he constantly felt the frustration and mental strain of not having a stable personal living arrangement.
“I spent so much time in hotels but they never really resembled a home. They didn’t have enough space or enough privacy,” Chatzieleftheriou told TechCrunch. “But renting an apartment can be a huge pain in these cities. They can be hard to find, they usually have a minimum rental term of a year or more, and you usually have to deal with filling out paperwork and buying furniture.”
Knowing there were thousands of people at his company alone dealing with the same frustrations, Alex launched what would become Blueground, beginning with a handful of apartments in his home city of Athens, Greece.
Chatzieleftheriou and his team structured the platform to make the rental process as seamless as possible for the needs of flexible renters like himself. Through a quick plug-and-play checkout flow — more similar to the booking process for a hotel or Airbnb — renters can lock down an apartment without having to deal with the painful, costly and time-consuming traditional rental process. Tenants are also able to switch to any other Blueground listing during their rental period if their preferences change or if they want to explore different locations during their stay.
Every Blueground listing also comes completely furnished by the company’s design team, so renters don’t have to deal with buying, transporting — and eventually selling — furniture. And each apartment comes outfitted with digital and connected infrastructure so that tenants can monitor their apartment and arrange maintenance, housekeeping and other services directly through Blueground’s mobile app.
The value proposition is also fairly straightforward for the landlords Blueground partners with, as they avoid costs related to marketing and coordinating with fragmented brokers to fill open units, while also benefiting from steady rental payments, tenant vetting and free property management.
The offering certainly seems to be compelling for renters — while Chatzieleftheriou initially focused on serving business travelers and those moving for work, he quickly realized the market for flexible leasing was in fact much bigger. Blueground’s sales have tripled over the past three years and after its expansion in the U.S. last year, Blueground now hosts 1,700 listings in 10 cities across three continents.
“The trend of flexible and seamless real estate is bigger and is happening everywhere,” Chatzieleftheriou said. “A lot of people throughout the real estate sector really want this seamless, turnkey, furnished solution.”
To date, Blueground has raised a total of $28 million and plans to use funds from the latest round for additional hiring and to help the company reach its goal of growing its portfolio to 50,000 units over the next five years.
Powered by WPeMatico
A Chinese startup that’s taking a dorm-like approach to urban housing just raised $500 million as its valuation jumped over $2 billion. Danke Apartment, whose name means “eggshell” in Chinese, closed the Series C round led by returning investor Tiger Global Management and newcomer Ant Financial, Alibaba’s e-payment and financial affiliate controlled by Jack Ma.
Four years ago, Beijing-based Danke set out with a mission to provide more affordable housing for young Chinese working in large urban centers. It applies the co-working concept to housing by renting apartments that come renovated and fully furnished, a model not unlike that of WeWork’s WeLive. The idea is by slicing up a flat designed for a family of three to four — the more common type of urban housing in China — into smaller units, young professionals can afford to live in nicer neighborhoods as Danke takes care of hassles like housekeeping and maintenance. To date, the startup has set foot in 10 major Chinese cities.
With the new funds, Danke plans to upgrade its data processing system that deals with rental transactions. Housing prices are set by AI-driven algorithms that take into account market forces such as locations rather than rely on the hunches of a real estate agent. The more data it gleans, the smarter the system becomes. That layout is the engine of the startup, which believes an internet platform play is a win-win for both homeowners and tenants because it provides greater transparency and efficiency while allowing the company to scale faster.
“We are focused on business intelligence from day one,” Danke’s angel investor and chairman Derek Shen told TechCrunch in an interview. Shen was the former president of LinkedIn China and was instrumental in helping the professional networking site enter the country. “By doing so we are eliminating the need to set up offline retail outlets and are able to speed up the decision-making process. What landlords normally care is who will be the first to rent out their property. The model is also copyable because it requires less manpower.”
“We’ve proven that the rental housing business can be decentralized and done online,” added Shen.

Photo: Danke Apartment via Weibo
Danke doesn’t just want to digitize the market it’s after. Half of the company’s core members have hailed from Nuomi, the local services startup that Shen founded and was sold to Baidu for $3.2 billion back in 2015. Having worked for a business whose mission was to let users explore and hire offline services from their connected devices, these executives developed a propensity to digitize all business aspects, including Danke’s day-to-day operations, a scheme that will also take up some of the new funds. This will allow Danke to “boost operational efficiency and cut costs” as it “actively works with the government to stabilize rental prices in the housing market,” the company says.
The rest of the proceeds will go toward improving the quality of Danke’s apartment amenities and tenant experiences, a segment that Shen believes will see great revenue potential down the road, akin to how WeWork touts software services to enterprises. The money will also enable Danke, which currently zeroes in on office workers and recent college graduates, to explore the emerging housing market for blue-collar workers.
Other investors from the round include new backer Primavera Capital and existing investors CMC Capital, Gaorong Capital and Joy Capital.
China’s rental housing market has boomed in recent years as Beijing pledges to promote affordable apartments in a country where few have the money to buy property. As President Xi Jinping often stresses, “houses are for living in, not for speculation.” As such, investors and entrepreneurs have been piling into the rental flat market, but that fervor has also created unexpected risks.
One much-criticized byproduct is the development of so-called “rental loans.” It goes like this: Housing operators would obtain loans in tenants’ names from banks or other lending institutions allegedly by obscuring relevant details from contracts. So when a tenant signs an agreement that they think binds them to rents, they have in fact agreed to take on loans and their “rent” payments become monthly loan repayments.
Housing operators are keen to embrace such practices because the loans provide working capital for renovation and their pipeline of properties. On the other hand, the capital allows companies like Danke to lower deposits for cash-strapped young tenants. “There’s nothing wrong with the financial instrument itself,” suggested Shen. “The real issue is when the housing operator struggles to repay, so the key is to make sure the business is well-functioning.”
Danke, alongside competitors Ziroom and 5I5J, has drawn fire for not fully informing tenants when signing contracts. Shen said his company is actively working to increase transparency. “We will make it clear to customers that what they are signing are loans. As long as we give them enough notice, there should be little risk involved.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Compass, the real estate tech platform that is now worth $4.4 billion, has made an acquisition to give its agents a boost when it comes to looking for good leads on properties to sell. It is acquiring Contactually, an AI-based CRM platform designed specifically for the industry, which includes features like linking up a list of homes sold by a brokerage with records of sales in the area and other property indexes to determine which properties might be good targets to tap for future listings.
Contactually had already been powering Compass’s own CRM service that it launched last year, so there is already a degree of integration between the two.
Terms of the deal are not being disclosed. Crunchbase notes that Contactually had raised around $18 million from VCs that included Rally Ventures, Grotech and Point Nine Capital, and it was last valued at around $30 million in 2016, according to PitchBook. From what I understand, the startup had strong penetration in the market, so it’s likely that the price was a bit higher than this previous valuation.
The plan is to bring over all of Contactually’s team of 32 employees, led by Zvi Band, the co-founder and CEO, to integrate the company’s product into Compass’s platform completely. They will report to CTO Joseph Sirosh and head of product Eytan Seidman. It will also mean a bigger operation for Compass in Washington, DC, which is where Contactually had been based.
“The Contactually team has worked for the past 8 years to build a best-in-class CRM that aggregates relationships and automatically documents every touchpoint,” said Band in a statement “We are proud that our investment into machine learning has resulted in new features like Best Time to Email and other data-driven, follow-up recommendations which help agents be more effective in their day-to-day. After working extensively with the Compass team, it was apparent that joining forces would accelerate our missions of building the future of the industry.”
For the time being, customers who are already using the product — and a large number of real estate brokers and agents in the U.S. already were, at prices that ranged from $59/month to $399/month depending on the level of service — will continue their contracts as before.
I suspect that the longer-term plan, however, will be a little different: You have to wonder if agents who compete against Compass would be happy to use a service where their data is being processed by it, and for Compass itself. I would suspect that having this tech for itself would give it an edge over the others.
Compass, I understand from sources, is on track to make $2 billion in revenues in 2019 (its 2018 targets were $1 billion on $34 billion in property sales, and it had previously said it would be doubling that this year). Now in 100 cities, it’s come a long way from its founding in 2012 by Ori Allon and Robert Reffkin.
The bigger picture beyond real estate is that, as with many other analog industries, those who are tackling them with tech-first approaches are sweeping up not only existing business, but in many cases helping the whole market to expand. Contactually, as a tool that can help source potential properties for sale that owners hadn’t previously considered putting on the market, could end up serving that very end for Compass.
The focus on using tech to storm into a legacy industry is also coming at an interesting time. As we’ve pointed out before, the housing market is predicted to cool this year, and that will put the squeeze on agents who do not have strong networks of clients and the tools to maximise whatever opportunities there are out there to list and sell properties.
The likes of Opendoor — which appears to be raising money and inching closer to Compass in terms of valuation — is also trying out a different model, which essentially involves becoming a middle part in the chain, buying properties from sellers and selling them on to buyers, to speed up the process and cut out some of the expenses for the end users. That approach underscores the fact that, while the infusion of technology is an inevitable trend, there will be multiple ways of applying that.
This appears to be Compass’s first full acquisition of a tech startup, although it has made partial acqui-hires in the past.
Powered by WPeMatico