Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Coronavirus cases in the United States are reaching new peaks. E-commerce is continuing to boom. And b8ta, a San Francisco startup that is betting on the future of physical retailers, is doubling down on its in-person footprint.
B8ta offers shelf space to unique digital products, such as electric skateboards or a coffee alarm clock, on behalf of brands that want a physical presence. Today, the company acquired a 1-year-old company doing the same for direct to consumer businesses, Re:store.
Backed by Sequoia and SPC, Re:store has a three-story physical location in Maiden Lane in San Francisco, and hosts products ranging from beauty to consumer electronics to lifestyle products. It also has a community co-working space.

The Re:store community hub.
“The pandemic has emphasized the need for brands to be flexible with their product mix and distribution,” says Selene Cruz, CEO of Re:store. “Some products do well in these times, and brands in a retail-as-a-service model can adapt their offering a lot faster than those in a traditional wholesale model that relies on buying cycles.”
It’s the high-touch startups that are expected to struggle during this time, as rising virus rates threaten the global economy. But, as today’s deal shows, both b8ta and Re:store are bullish on in-person shopping long term.
In fact, in March, b8ta CEO and co-founder Vibhu Norby penned an extensive Twitter thread in favor of keeping his startups’ stores open, noting that closures would require the company to lose millions and send tens of thousands of employees home. B8ta’s entire value proposition is based on high-touch interactions, and a world in which consumers want to try and experience their products before they buy them.
At b8ta, we are in the business of physical retail stores. While we sell products online, our stores are the reason for our existence. We encourage our shoppers to touch and try all of the products at b8ta. We are truly in the business of touch and human-to-human relationships.
— Vibhu Norby (@vibhu) March 13, 2020
“I feel like we’ve lived through three lifetimes since I wrote that thread back in March,” Norby said, noting that it’s been an “extremely difficult year” for the company. However, the Re:store acquisition comes off of new momentum he’s seen since b8ta was able to safely reopen its stores in May.
“We launched more brands last quarter than any other in our history,” Norby said. “The traditional retail model and traditional real estate model has completely collapsed and brands are looking for something better.” To note, Macy’s, which has backed b8ta, narrowly dodged bankruptcy by securing a $4.5 billion lifeline in financing to temper down sales.

Image Credits: b8ta
B8ta’s Re:store acquisition is a response to a rebound among physical retailers, one that favors an experience instead of a catalog of aisles. A focus on creative in-person experiences versus department stores is an acceleration of a pre-pandemic trend. As direct-to-consumer investors told us in late March, companies can’t depend on a few channels for customer acquisition. As the field gets crowded, brands are looking to stand out, and stores like b8ta and Re:store could help them do that.
To balance out some of b8ta’s bullishness, Norby did note that “on the shopping side, visitation is way down but sales have almost come back to where they were pre-pandemic.” In other words, people are buying b8ta products online without the physical presence, which means that online platforms are still a preference for consumers.
Powered by WPeMatico
Yesterday’s earnings deluge made plain that tech shares are not rocketing higher as 2020 comes to a close. Indeed, in pre-market trading this morning, Microsoft, Apple, Facebook and Amazon are all down.
Alphabet is the only member of the Big Five that is worth more today than yesterday. Strong advertising and cloud results helped the search giant post a return-to-form quarter. But in most other reports there were signs of weakness or underperformance compared to expectations that could undermine the relentlessly bullish attitude tech shares have enjoyed for several months.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
The tailwinds that lifted much of tech this year remain. Every CEO I speak to still thinks that the COVID-19 bump to digital services demand has room to run, and that the digital transformation’s acceleration that has been a regular point of optimism for VCs, founders and public company leaders, will continue.
 But that doesn’t mean all tech companies will benefit or post outsize results. Those facts don’t imply that pandemic-induced friction won’t add up.
But that doesn’t mean all tech companies will benefit or post outsize results. Those facts don’t imply that pandemic-induced friction won’t add up.
It’s not only the biggest companies that are treading water. We’re seeing valuations pause in tech’s hottest category — SaaS and cloud — despite continued growth in its constituent companies. The combined sentiment-and-share change could dampen enthusiasm for startup shares, perhaps undercutting some of the hype and FOMO that we keep hearing is driving private valuations higher.
Are we seeing a change in tech’s temperature while the weather changes? Let’s take a look.
Starting with the biggest tech companies, Alphabet’s results were pretty good. The company’s YouTube and cloud segments outperformed expectations, helping the company best expectations.
From there, things get choppier. Apple beat expectations, but its shares fell after investors were less than impressed with its aggregate results. Microsoft posted good calendar Q3 earnings, including strong Azure performance, but its guidance left investors underwhelmed and its shares also fell. Facebook beat expectations in the quarter, but rising costs seemed to dampen investor sentiment. It lost a little ground after earnings. Amazon’s Q3 was hot, but its Q4 should reduce operating income due to COVID-19 costs. It also lost ground after reporting.
From that malaise we turn to the SaaS and cloud world. Redpoint’s Jamin Ball is doing his usual roundups, one of which we’re borrowing this morning. Here’s his digest of SaaS and cloud earnings thus far:
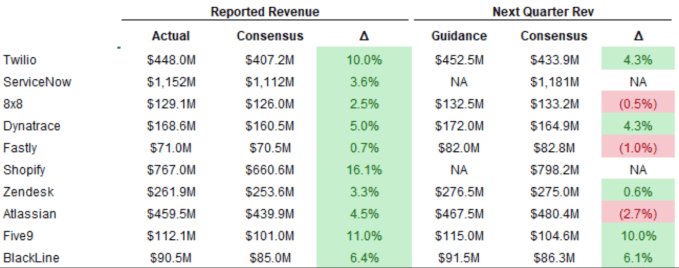
Takeaways? Every SaaS and cloud company crushed Q3, but Q4 is looking a bit more dicey. Beats look slim, some companies are declining to project and aside from an outlier or two, the numbers look slimmer overall.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast (now on Twitter!), where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
A few notes before we get into this. One, we have a bonus episode coming this Saturday focused on this week’s earnings reports. And, second, we did not record video this week. So, if you like watching the show on YouTube, this is not the week for that!
Right, here’s what Natasha, Danny and your humble servant got into this week:
We capped off with the latest from r2c, and then got the hell off the mics. Catch you all Saturday, and then back to regular programming on Monday morning.
Equity drops every Monday at 7:00 a.m. PDT and Thursday afternoon as fast as we can get it out, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast, Spotify and all the casts.
Powered by WPeMatico
If you miss hanging out with your co-workers but don’t want to spend a single second more on Zoom, the latest product from Donut might be the answer.
The startup is launching its new Watercooler product today while also announcing that it has raised $12 million in total funding, led by Accel and with participation from Bloomberg Beta, FirstMark, Slack Fund and various angel investors.
Co-founder and CEO Dan Manian told me that this is actually money that the startup raised before the pandemic, across multiple rounds. It just didn’t announce the fundraising until now.
The startup’s vision, Manian said, is “to create human connection between people at work.” Its first product, Intros, connects via Slack teammates who didn’t already know each other, often with the goal of setting up quick coffee meetings (originally in-person and now virtual).
Donut says it has facilitated 4 million connections across 12,000 companies (including The New York Times, Toyota and InVision), with 1 million of those connections made since the beginning of the pandemic.
However, Manian said customers have been asking Donut to facilitate more frequent interactions, especially since most people aren’t going to have these coffee meetings every day. At the same time, people face the dueling issues of isolation and Zoom fatigue, where “the antidote to one thing makes the other pain worse.” And he suggested that one of the hardest things to recreate while so many of us are working remotely are “all the little microinteractions that you have while you’re working.”
That’s where Watercooler comes in — as the name suggests, it’s designed to replicate the feeling of hanging out at the office watercooler, having brief, low-key conversations. Like Intros, it integrates with Slack, creating a new channel where Watercooler will post fun, conversation-starting questions like “‘What’s your favorite form of potato?” or “What’s one thing you’ve learned in your career that you wish you knew sooner?”
Talking about these topics shouldn’t take much time, but Manian argued that brief conversations are important: “Those things add up to friendship over time, they’re what actually transform you from co-worker to friend.” And those friendships are important for employers too, because they help with team cohesion and retention.
I fully endorse the idea of a Slack watercooler — in fact, the TechCrunch editorial team has a very active “watercooler” channel and I’m always happy to waste time there. My big question was: Why do companies need to purchase a product for this?
Donut Watercooler. Image Credits: Donut
Manian said that there were “a bunch of our early adopters” who had tried doing this manually, but it was always in the “past tense”: “It got too hard to come up with the questions, or it took real work coming up with them, whoever was doing it already had a it full time job.”
With Watercooler, on the other hand, the company can choose from pre-selected topics and questions, set the frequency with which those questions are posted and then everything happens automatically.
Manian also noted that different organizations will focus on different types of questions. There are no divisive political questions included, but while some teams will stick to easy questions about things like potatoes and breakfast foods, others will get into more substantive topics like the ways that people prefer to receive feedback.
And yes, Manian thinks companies will still need these tools after the pandemic is over.
“Work has fundamentally changed,” he said. “I don’t think we’ll put remote work back in the bottle. I think it’s here to stay.”
At the same time, he described the past few months as “training wheels” for a hybrid model, where some team members go back to the office while others continue working remotely. In his view, teams will face an even bigger challenge then: To keep their remote members feeling like they’re connected and in-the-loop.
Powered by WPeMatico
It’s been quite a time for chip industry consolidation, and today Marvell joined the acquisition parade when it announced it is acquiring Inphi in a combination of stock and cash valued at approximately $10 billion, according to the company.
Marvell CEO Matt Murphy believes that by adding Inphi, a chip maker that helps connect internal servers in cloud data centers, and then between data centers, using fiber cabling, it will complement Marvell’s copper-based chip portfolio and give it an edge in developing more future-looking use cases where Inphi shines.
“Our acquisition of Inphi will fuel Marvell’s leadership in the cloud and extend our 5G position over the next decade,” Murphy said in a statement.
In the classic buy versus build calculus, this acquisition uses the company’s cash to push it in new directions without having to build all this new technology. “This highly complementary transaction expands Marvell’s addressable market, strengthens customer base and accelerates Marvell’s leadership in hyperscale cloud data centers and 5G wireless infrastructure,” the company said in a statement.
It’s been a busy time for the chip industry as multiple players are combining, hoping for a similar kind of lift that Marvell sees with this deal. In fact, today’s announcement comes in the same week AMD announced it was acquiring Xilinx for $35 billion and follows Nvidia acquiring ARM for $40 billion last month. The three deals combined come to a whopping $85 billion.
There appears to be prevailing wisdom in the industry that by combining forces and using the power of the checkbook, these companies can do more together than they can by themselves.
Certainly Marvell and Inphi are suggesting that. As they highlighted, their combined enterprise value will be more than $40 billion, with hundreds of millions of dollars in market potential. All of this of course depends on how well these combined entities work together, and we won’t know that for some time.
For what it’s worth, the stock market appears unimpressed with the deal, with Marvell’s stock down more than 7% in early trading — but Inphi stock is being bolstered in a big way by the announcement, up almost 23% this morning so far.
The deal, which has been approved by both companies’ boards, is expected to close by the second half of 2021, subject to shareholder and regulatory approval.
Powered by WPeMatico
Code is the lifeblood of the modern world, yet the tooling for some programming environments can be remarkably spartan. While developers have long had access to graphical programming environments (IDEs) and performance profilers and debuggers, advanced products to analyze and improve lines of code have been harder to find.
These days, the most typical tool in the kit is a linter, which scans through code pointing out flaws that might cause issues. For instance, there might be too many spaces on a line, or a particular line might have a well-known ambiguity that could cause bugs that are hard to diagnose and would best be avoided.
What if we could expand the power of linters to do a lot more though? What if programmers had an assistant that could analyze their code and actively point out new security issues, erroneous code, style problems and bad logic?
Static code analysis is a whole interesting branch of computer science, and some of those ideas have trickled into the real-world with tools like semgrep, which was developed at Facebook to add more robust code-checking tools to its developer workflow. Semgrep is an open-source project, and it’s being commercialized through r2c, a startup that wants to bring the power of this tool to the developer masses.
The whole project has found enough traction among developers that Satish Dharmaraj at Redpoint and Jim Goetz at Sequoia teamed up to pour $13 million into the company for its Series A round, and also backed the company in an earlier, unannounced seed round.
The company was founded by three MIT grads — CEO Isaac Evans and Drew Dennison were roommates in college, and they joined up with head of product Luke O’Malley. Across their various experiences, they have worked at Palantir, the intelligence community, and Fortune 500 companies, and when Evans and Dennison were EIRs at Redpoint, they explored ideas based on what they had seen in their wide-ranging coding experiences.

The r2c team, which I assume only writes bug-free code. Image by r2c.
“Facebook, Apple, and Amazon are so far ahead when it comes to what they do at the code level to bake security [into their products compared to] other companies, it’s really not even funny,” Evans explained. The big tech companies have massively scaled their coding infrastructure to ensure uniform coding standards, but few others have access to the talent or technology to be on an equal playing field. Through r2c and semgrep, the founders want to close the gap.
With r2c’s technology, developers can scan their codebases on-demand or enforce a regular code check through their continuous integration platform. The company provides its own template rulesets (“rule packs”) to check for issues like security holes, complicated errors and other potential bugs, and developers and companies can add their own custom rulesets to enforce their own standards. Currently, r2c supports eight programming languages, including JavaScript and Python, and a variety of frameworks, and it is actively working on more compatibility.
One unique focus for r2c has been getting developers onboard with the model. The core technology remains open-sourced. Evans said that “if you actually want something that’s going to get broad developer adoption, it has to be predominantly open source so that developers can actually mess with it and hack on it and see whether or not it’s valuable without having to worry about some kind of super restrictive license.”
Beyond its model, the key has been getting developers to actually use the tool. No one likes bugs, and no developer wants to find more bugs that they have to fix. With semgrep and r2c though, developers can get much more immediate and comprehensive feedback — helping them fix tricky errors before they move on and forget the context of what they were engineering.
“I think one of the coolest things for us is that none of the existing tools in the space have ever been adopted by developers, but for us, it’s about 50/50 developer teams who are getting excited about it versus security teams getting excited about it,” Evans said. Developers hate finding more bugs, but they also hate writing them in the first place. Evans notes that the company’s key metric is the number of bugs found that are actually fixed by developers, indicating that they are offering “good, actionable results” through the product. One area that r2c has explored is actively patching obvious bugs, saving developers time.
Breaches, errors and downtime are a bedrock of software, but it doesn’t have to be that way. With more than a dozen employees and a hefty pool of capital, r2c hopes to improve the reliability of all the experiences we enjoy — and save developers time in the process.
Powered by WPeMatico
Deep learning has made tremendous strides in recent years, with new systems and models like GPT-3 offering higher-quality interpretations of human language, empowering developers to use these concepts in more diverse applications. We can see these developments in our text-to-speech voice recorders and dual language translation apps, which have gotten shockingly good these days.
But what is the next wave of functionality that this AI infrastructure can empower? Hebbia wants to find out.
Hebbia today is a startup but really a product studio, a sort of sketchpad for AI ideas founded by George Sivulka (a PhD student from Stanford currently on leave) and a mélange of three other Stanford AI researchers and engineers. The group, using the new deep learning techniques and models available today, is trying to push the boundaries of what knowledge graphs, semantic analysis and AI can ultimately do for human productivity.
Sivulka was inspired to focus on this domain from witnessing his friends’ experiences working in the knowledge economy. “A lot of my peers … everyone goes into these white-collar jobs where they’re sitting down and just reading immense quantities of information all day,” Sivulka said. “People become banking analysts and dig through SEC forms for one or two lines of information, or go to law school or become legal analysts and do the same thing… [They’re] just bogged down by these walls of text, by this like avalanche of information that is impossible to make sense of.”
(Tell me about it).
What he and his team want to do is supercharge human productivity by building search, analysis and summarization tools that can help you make sense of your own, personal universe of knowledge. “The idea is that Hebbia is building these productivity tools for thought that augment the way you do work. They’re things that actually control the information input and outputs that you have to deal with every day,” Sivulka said.
It’s an ambitious vision, so they had to start somewhere. Their first product, which is what got me excited about the vision, is a Chrome plugin that’s been in private beta and is being released to the world more broadly today (note: it’s still unlisted in the Chrome Store for now). The plugin upgrades the search functionality in Chrome to go beyond mere text pattern matching to begin to comprehend what your query actually is and how it might be answered given the text on a page. Here’s a demo of the plugin on TechCrunch:
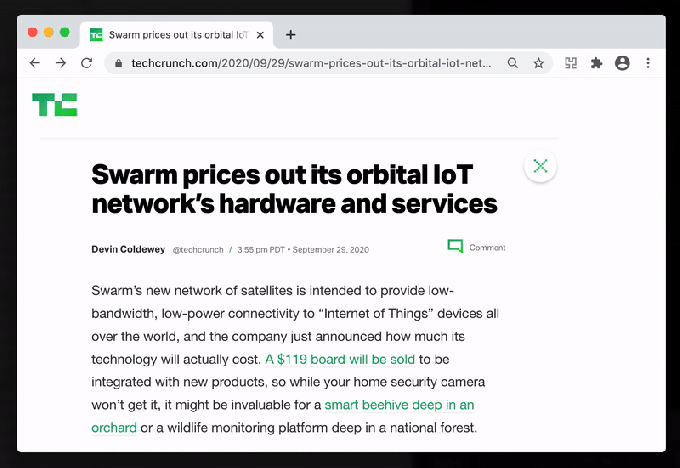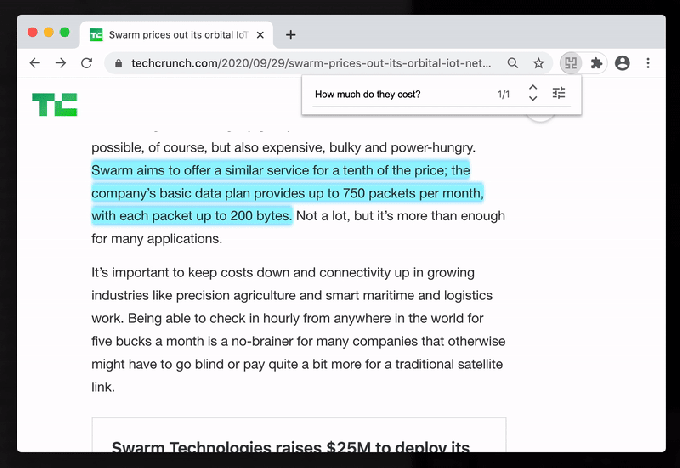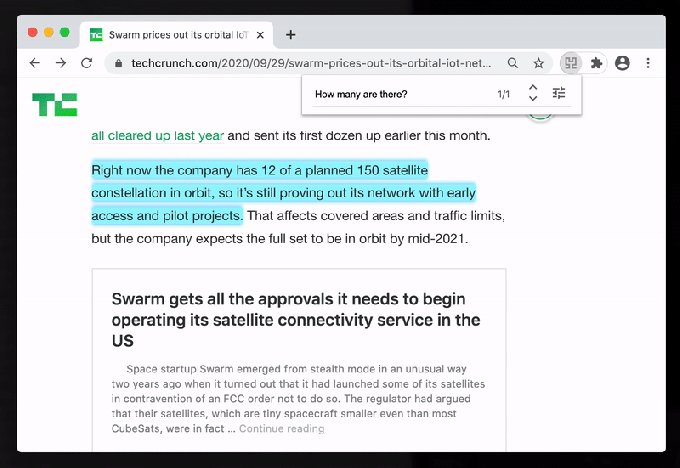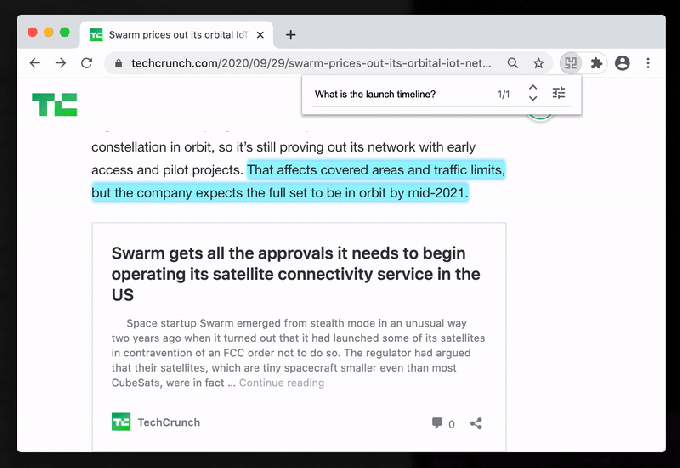
Hebbia’s Ctrl-F product on TechCrunch. Image via Hebbia.
So, for instance, you could Ctrl-F on a Wikipedia page and ask “Where did this person live?” and the plugin can determine that you are asking for locations and begin to highlight text on that page with relevant information. It’s AI, and pretty beta AI at that, so of course, your experience can and will be inconsistent right now. But as Hebbia tunes its models and improves its understanding of text, the hope is that browser search can be completely transformed and become a massive productivity boost.
Sivulka is something of an early wunderkind. He worked at NASA as a teenager, and graduated from his bachelor’s at Stanford in 2.5 years, finishing his master’s a bit more than a year later, and started a PhD before getting waylaid by Hebbia.
Hebbia’s vision has already attracted the notice of VCs in just its early months. Ann Miura-Ko at Floodgate led a $1.1 million pre-seed round that was joined by Naval Ravikant, Peter Thiel, Kevin Hartz, Michael Fertik and Cory Levy.
Sivulka notes that their Ctrl-F product is the main focus for the company right now, and acts as a sort of gateway into the larger potential that knowledge graphs and personal productivity offer. “This is one of the final frontiers of what computers can do,” Sivulka said, noting that computation has already revolutionized many fields by digitizing data and making it easier to process. With Ctrl-F, “this is a baseline technology, [we’re] just scratching the surface of what we can do with this.”
Powered by WPeMatico
The American venture capital world has staged an impressive comeback from the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic. For a moment, there was worry that startups would struggle to raise for quarters, leading to layoffs, slowed hiring and budget cuts.
But as the pandemic accelerated plans to shift operations online, many startups wound up more popular than expected. Those tailwinds helped the venture capital world get back into its own game in a big way, leading to Q3 being an outsized quarter for domestic venture capital activity.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
Today, in a first, we have two editions of The Exchange for you. Get hype.
As The Exchange reported last week, “How much money was raised by U.S.-based startups in Q3 2020? $36.5 billion, according to CBInsights, $37.8 billion according to PitchBook. [The former data provider] calls the number a seven-quarter high, up 22% from the Q3 2019 number and 30% from the Q2 2020 result.”
 This lends itself to a question: What’s up with venture debt during all of this?
This lends itself to a question: What’s up with venture debt during all of this?
Venture debt, in various forms, is a type of capital provided to startups that may or may not have raised equity-based funds, like venture capital. One variety comes from institutions like Silicon Valley Bank, which might provide a growing startup with well-known backers an additional fraction of its last raise in debt, allowing the young company to take on more total capital than it otherwise might without greater dilution.
Other forms of venture debt, like revenue-based financing, share startup income streams to repay borrowings. And there are other, more exotic forms of the capital source.
I’ve been curious about the space for a few quarters now. So, when some survey data on the venture debt market from Runway Growth Capital came in, I started collecting my notes into a single entry.
Venture debt has a place in today’s market, but while venture capital is back to setting records, it appears that its less-known sibling won’t manage to match its last few years’ worth of results, according to new PitchBook data. Let’s talk about it.
Runway Growth is a venture debt player that did $41.5 million in “funded loans” in Q3 2020, it told TechCrunch. That’s for your own reference. Its new survey of 493 entrepreneurs who had raised venture capital and 50 providers of startup capital from the VC and lending worlds noted that 60% of founders felt that “venture debt has become more founder-friendly,” which you might think would imply that more venture debt was being used, overall.
That was my read, at least.
From the same survey, two related data points explain why venture debt has a place in the market: 86% of providers felt that “venture debt was key to extend the company’s runway to reach an important milestone,” while just over a quarter of founders agreed. Regardless of who is right on that point, venture debt has seen impressive growth in recent years.
Via PitchBook, here are updated venture debt metrics for the United States through 2019:
Powered by WPeMatico
Last night neo-insurance provider and former startup Root priced its IPO at $27 per share, $2 per share ahead of its $22 to $25 target price range.
According to Root, it sold 26,830,845 shares in its IPO, including 24,249,330 from the company itself. Its underwriting banks have the option to buy another 4,024,626 at the IPO price, less “underwriting discounts and commissions.” The remaining shares are being sold by existing shareholders.
At $27 per share, Root raised $654,731,910, but that figure will rise to $763,396,812 if its underwriters exercise their option in full, using the full $27 price for our calculation. Per its S-1 filings, both Dragoneer and Silver Lake will purchase $250 million of Root stock at the IPO price once the IPO has closed.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
Today, in a first, we have two editions of The Exchange for you. Get hype.
Root will therefore raise north of $1 billion in its IPO, once all shares sold are counted. Doing some loose math, Root is worth around $6.8 billion at its IPO price, though Renaissance Capital, an IPO specialist, puts the figure at $7.1 billion on a fully diluted basis.
 For the Midwest, Ohio-based Root’s IPO is a win. The company shows that it is possible to build high-growth technology companies worth billions of dollars far from coastal hubs. For the broader insurtech space, Root’s IPO is a win. The company follows Lemonade to the public markets, setting a strong valuation mark again for the neo-insurance startup market.
For the Midwest, Ohio-based Root’s IPO is a win. The company shows that it is possible to build high-growth technology companies worth billions of dollars far from coastal hubs. For the broader insurtech space, Root’s IPO is a win. The company follows Lemonade to the public markets, setting a strong valuation mark again for the neo-insurance startup market.
For similar companies like Clearcover, MetroMile and all startups that related to Root and Lemonade, it’s a good day. Let’s get into what we can learn from Root’s pricing.
Insurance multiples are hot. Key from Root’s IPO is the fact that we can now see insurance revenue being treated similarly to software revenue. How so? In multiples terms. Let me explain.
Root generated $245.4 million in revenue during the first and second quarters of 2020. That’s a run rate of around $491 million. At $7 billion, that’s a 14x revenue multiple. For an insurance provider with scant gross margins! Wild. Given Root’s weak-looking Q3 2020 revenues, that number isn’t going to fall anytime soon.
For companies that are not pure-play software outfits and want to go public, Root’s strong, above-range pricing makes it plain that there is investor demand for more than one type of revenue growth.
Investors are betting that Root’s history of growth will continue. In the first half of 2019, the company’s revenues were a mere 42% of what it pulled off during the same period in 2020. If the company can more than double again next year, then, hey, maybe all the numbers work. But to see public shareholders take such a growth-and-valuation flyer on an insurtech player is notable.
Kyle Nakatsuji, co-founder and CEO of Clearcover, another neo-insurance provider, explained to TechCrunch via email what he thinks is going on: “It’s clear that the market is aware of the massive opportunity for technology-enabled disruption in the category and it is rewarding those companies that focus on customer-oriented, digital innovation. The rapid growth of key players in the space is now proving this will play out and the winners will be consumers seeing lower prices and investors seeing better returns. ”
Powered by WPeMatico
Priori Legal, a startup rethinking the way that large corporations hire outside counsel, has raised $6.3 million in Series A funding.
Founded by CEO Basha Rubin and CPO Mirra Levitt (who met while classmates at Yale Law School), Priori launched as a legal marketplace for small and medium businesses before finding its current model in 2016.
Rubin explained that although Fortune 500 companies have their own in-house legal teams, they still spend an average of $150 million a year on outside legal counsel. And finding that counsel can be an arduous process — a consumer goods company, for example, might need to hire lawyers in all 50 states.
So by creating a marketplace of vetted lawyers (it says it only accepts 10% of applicants), by running a bidding process for the work and by streamlining the billing and on-boarding process, the startup can save companies an average of 60% of the money they spend on outside counsel and reduce the search time by 80%.
“We don’t get involved in the substance of the lawyer-client relationship,” Levitt added. “We are not a law firm, we don’t do any of the legal work. Our innovation is focused entirely on the process of rapidly identifying the right talent and, once the matter is up and running, making billing seamless.”
There are currently more than 1,500 lawyers in the marketplace, representing all 50 states in the U.S., as well as 47 countries and 700 practice proficiencies. Levitt said that while the first lawyers to join the platform were usually independent or worked at small firms that might not previously had access to these kinds of clients, there are now larger firms signing up as well.

Priori founders Mirra Levitt and Basha Rubin
And Rubin said interest in Priori has only grown during the pandemic and the resulting economic downturn. Companies are trying to do “more with less,” and “part of our value proposition is fundamentally cost savings.” For example, she noted that client spending on the platform has increased 200% in the last year.
“We began to see so much inbound demand that we would log onto Slack at 11pm and the entire team would be working,” she said. “We have a truly extraordinary team, but a) that’s not sustainable from a human perspective, and b) we saw an opportunity to really grow dramatically if we could throw resources at it.”
The Series A comes from Hearst Corporation (also a Priori customer), Great Oaks Venture Capital, Jambhala, Tim Steinert (former general counsel of Alibaba Group), Mindset Ventures, Bridge Venture Fund and Orrick’s Legal Technology Fund.
In addition to growing the team, Rubin said that the new funding will allow Priori to expand its network of lawyers, especially internationally.
“From a product perspective, we’re really building out our use of data throughout the platform,” Levitt said, adding that the company plans to use machine learning to improve attorney vetting, matchmaking, bidding, project scoping and more.
Powered by WPeMatico