Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
There are now about 50 million people with dementia globally, a number the World Health Organization expects to triple by 2050. Alzheimer’s is the leading cause of dementia and caregivers are often overwhelmed, without enough support.
Neuroglee, a Singapore-based health tech startup, wants to help with a digital therapeutic platform created to treat patients in the early stages of the disease. Founded this year to focus on neurodegenerative diseases, Neuroglee announced today it has raised $2.3 million in pre-seed funding.
The round was led by Eisai Co., one of Japan’s largest pharmaceutical companies, and Kuldeep Singh Rajput, the founder and chief executive officer of predictive healthcare startup Biofourmis.
Neuroglee’s prescription digital therapy software for Alzheimer’s, called NG-001, is its main product. The company plans to start clinical trials next year. NG-001 is meant to complement medication and other treatments, and once it is prescribed by a clinician, patients can access its cognitive exercises and tasks through a tablet.
The software tracks patients’ progress, such as the speed of their fingers and the time it takes to complete an exercise, and delivers personalized treatment programs. It also has features to address the mental health of patients, including one that shows images that can bring up positive memories, which in turn can help alleviate depression and anxiety when used in tandem with other cognitive behavioral therapy techniques.
For caregivers and clinicians, NG-001 helps them track patient progress and their compliance with other treatments, like medications. This means that healthcare providers can work closely with patients even remotely, which is especially important during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Neuroglee founder and CEO Aniket Singh Rajput told TechCrunch that its first target markets for NG-001 are the United States and Singapore, followed by Japan. NG-001 needs to gain regulatory approval in each country, and it will start by seeking U.S. Food and Drug Administration clearance.
Once it launches, clinicians will have two ways to prescribe NG-001, through their healthcare provider platform or an electronic prescription tool. A platform called Neuroglee Connect will give clinicians, caregivers and patients access to support and features for reimbursement and coverage.
Powered by WPeMatico
Wellory, a startup that bills itself as taking an “anti-diet approach” to nutrition and wellness, is announcing that it has raised $4.2 million in funding.
The round was led by Story Ventures, with participation from Harlem Capital, Tinder co-founders Sean Rad and Justin Mateen, Ground Up Ventures, NBA player Wayne Ellington, Hannah Bronfman and others.
Wellory founder and CEO Emily Hochman (who was previously the head of customer success at WayUp) told me that she struggled with dieting in college, to the point where she was risking chronic illness and infertility. As a result, she became determined to gain a better understanding of nutrition and her own health, eventually studying and becoming a certified health coach at the Institute for Integrative Nutrition.
Hochman said that through Wellory, she wants to offer that same understanding to others, which she said has created a “managed marketplace” matching users with a licensed nutritionist, registered dietitian or certified health coach. Those coaches create a personalized plan for losing weight or achieving other health goals, then continue to provide feedback as users share photos of each meal and additional health data.
For example, she said that a customer who had just given birth and was interested in postpartum weight loss would get matched with a coach who specializes in that area.
“The thing that is so important is that we build personalized plans,” she added. “We don’t have anything that says, ‘At Wellory, we do these 10 things and that’s a standard diet.’ We’re actually going to help you learn how to make smart and healthy decisions.”

Wellory CEO Emily Hochman (Image Credit: Wellory)
Wellory officially launched in September, but Hochman said some beta testers have been using the service for nine, 10 or 11 months. She said early customers include people who are interested in weight loss, those who need nutrition advice due to chronic illness and “optimizers” who simply want to make sure they’re eating as healthily as possible.
She also noted that although customers usually sign up with a specific goal in mind, “once they hit their goal, because of the power of a strong relationship, they say, ‘I don’t want to go back to where I was, let’s keep building, let’s make sure I can sustain this.’ ”
The app is available on iOS and Android and currently costs $59.99 per month. Hochman plans to introduce additional pricing tiers. and she said the funding will allow Wellory to expand the technology and marketing teams, and to explore new partnerships.
“As a data technology investor, we get approached by different types of wearable or diagnostic companies nearly every week,” said Jake Yormak of Story Ventures in a statement. “We love the category but what we saw in Wellory was a way to put a human coach at the center of understanding this health data. With nutrition as the wedge, Wellory has built a trusted relationship with people who affirmatively want to better understand and improve their wellbeing.”
Powered by WPeMatico
BuildBuddy, whose software helps developers compile and test code quickly using a blend of open-source technology and proprietary tools, announced a funding round today worth $3.15 million.
The company was part of the Winter 2020 Y Combinator batch, which saw its traditional demo day in March turned into an all-virtual affair. The startups from the cohort then had to raise capital as the public markets crashed around them and fear overtook the startup investing world.
BuildBuddy’s funding round makes it clear that choppy market conditions and a move away from in-person demos did not fully dampen investor interest in YC’s March batch of startups, though it’s far too soon to tell if the group will perform as well as others, given how long it takes for startup winners to mature into exits.
BuildBuddy has foundations in how Google builds software. To get under the skin of what it does, I got ahold of co-founder Siggi Simonarson, who worked at the Mountain View-based search giant for a little over a half decade.
During that time he became accustomed to building software in the Google style, namely using its internal tool called Blaze to compile his code. It’s core to how developers at Google work, Simonarson told TechCrunch. “You write some code,” he added, “you run Blaze build; you write some code, you run Blaze test.”
What sets Blaze apart from other developer tools is that “opposed to your traditional language-specific build tools,” Simonarson said, it’s code agnostic, so you can use it to “build across [any] programming language.”
Google open-sourced the core of Blaze, which was named Bazel, an anagram of the original name.
So what does BuildBuddy do? In product terms, it’s building the pieces of Blaze that Google engineers have access to inside the company, for other developers using Bazel in their own work. In business terms, BuildBuddy wants to offer its service to individual developers for free, and charge companies that use its product.
Simonarson and his co-founder Tyler Williams started small, building a “results UI” tool that they shared with a Bazel user group. The members of that group picked up the tool, rapidly bringing it inside a number of sizable companies.
This origin story underlines something that BuildBuddy has that early-stage startups often lack, namely demonstrable enterprise market appetite. Lots of big companies use Bazel to help create software, and BuildBuddy found its way into a few of them early in its life.
Simply building a useful tool for a popular open-source project is no guarantee of success, however. Happily for BuildBuddy, early users helped it set direction for its product development, meaning that over the summer the startup added the features that its current users most wanted.
Simonarson explained that after BuildBuddy was initially used by external developers, they demanded additional tools, like authentication. In the words of the co-founder, the response from the startup was “great!” The same went for a request for dashboarding, and other features.
Even better for the YC graduate, some of the features requested were the sort that it intends to charge for. That brings us back to money and the round itself.
BuildBuddy closed its round in May. But like with most venture capital tales, it’s not a simple story.
According to Simonarson, his startup started raising the round during one of those awful early-COVID days when the stock market dropped by double-digit percentage points in a single trading session.
BuildBuddy’s goal was to raise $1.5 million. Simonarson was worried at the time, telling TechCrunch that it was his first time fundraising, and that he wasn’t sure if his startup was going to “raise anything at all” in that climate.
But the nascent company secured its first $100,000 check. And then a $300,000 check, over time managing to fill out its round.
So what happened that got the company from $1.5 million to just over $3 million? The investor that put in $300,000 wanted to put in another $2 million. The company talked them down to $1.5 million at a higher cap (BuildBuddy raised its round using a SAFE), and the deal was done at those terms.
The startup initially didn’t want to raise the extra cash, but Simonarson told TechCrunch that at the time it was not clear where the fundraising environment was heading; BuildBuddy raised back when startup layoffs were a leading story, and a return to high-cadence VC rounds was months away.
So BuildBuddy wound up securing $3.15 million to support a current headcount of four. It intends to hire, naturally, lower its comically long runway and keep building out its Bazel-focused service.
Picking a few names from the investor spreadsheet that BuildBuddy sent over — points for completeness to the startup — Y Combinator, Addition, Scribble and Village Global, among others put capital into the round.
Dev tools are hot at the moment. Given that, as soon as BuildBuddy’s ARR starts to get moving, I expect we’ll hear from them again.
Powered by WPeMatico
Voi, the Stockholm-headquartered micro mobility company known for its e-scooter rentals, has raised $160 million in new funding. The round, about two thirds equity and one third debt, is led by The Raine Group.
Others participating include VNV Global, Balderton, Creandum, Project A, Inbox, and “sustainability-focused investor” Stena Sessan, along with individual backers with links to tech companies such as Delivery Hero, Klarna, iZettle, Zillow, Kry/Livi and Amazon.
Voi co-founder and CEO Fredrik Hjelm says the company — which competes with the likes of Bird, Tier, Bolt and Lime — has secured an “asset-backed” debt facility tied to the scooters and e-bikes it will have on its books in 2021.
The idea is that, having proven its model can be sustained, capital funnelled into the expense of purchasing the vehicles needed to expand the service, can be secured against those assets, even if they will depreciate relatively quickly over time.
“I think, going forward, we will increase the debt ratio to equity,” he tells me. “What you wanna avoid, of course, as a startup, is dilution. We want as much debt as possible because we want cash to grow because we think we can have good ROI in capital. But the debt market is usually closed for startups, until they get to a very proven business model”.
Hjelm says, as the unit economics improved, which Voi has shown by becoming operationally profitable for a few months this year on a group level, it puts the company in a position where, coupled with enough historical data, it can understand “the payback” time on vehicles. This means a financing model similar to rental car companies, or other companies with assets that have a proven value, becomes more of a possibility.
Once it’s proven to work, he says in 6-9 months from now Voi hopes to be able to increase the debt facility. “Probably you will never write about Voi raising equity again,” Hjelm teases, likely in reference to my scooping one of the company’s earlier funding rounds.
By thinking about and funding the vehicles and the operations as two separate parts of the business, it also points to where the Voi founder believes the industry and his company in particular, is heading. “I think the direction we’re going is, we’re becoming more and more of a tech enabled infrastructure company,” he says, comparing it to a telco or other infrastructure plays.
This makes more sense when you consider that many cities around the world are holding tendering processes and only licensing two or three and sometimes only a single provider. And it’s here where Voi has also made good transaction over the last year — sped by the Coronavirus pandemic which has forced cities to open up micro mobility services faster in order to offer an alternative to packed trains and busses.
“With major new markets, including the U.K. opening up to e-scooter mobility solutions, Voi has become Europe’s preferred operator, winning over 2/3 of city license tenders across Europe, including recent wins in Birmingham, Liverpool, Bern and Cambridge,” says Voi.
A decision on which operators are awarded London’s tender is expected on December 14th. Up to three operators will be selected to operate trials, which are due to start in Spring 2021.
Voi says the new funding will be used to invest in technology platform development, fuel growth in current Voi markets and bring Voi’s latest e-scooter model — Voiager 4 — to more cities. In addition, Voi will use funds to further enhance the safety infrastructure of its platform, “the company’s number one priority,” says the company.
Powered by WPeMatico
Video has worked the same way for a long, long time. And because of its unique qualities, video has been largely immune to the machine learning explosion upending industry after industry. WaveOne hopes to change that by taking the decades-old paradigm of video codecs and making them AI-powered — while somehow avoiding the pitfalls that would-be codec revolutionizers and “AI-powered” startups often fall into.
The startup has until recently limited itself to showing its results in papers and presentations, but with a recently raised $6.5M seed round, they are ready to move towards testing and deploying their actual product. It’s no niche: video compression may seem a bit in the weeds to some, but there’s no doubt it’s become one of the most important processes of the modern internet.
Here’s how it’s worked pretty much since the old days when digital video first became possible. Developers create a standard algorithm for compressing and decompressing video, a codec, which can easily be distributed and run on common computing platforms. This is stuff like MPEG-2, H.264, and that sort of thing. The hard work of compressing a video can be done by content providers and servers, while the comparatively lighter work of decompressing is done on the end user’s machines.
This approach is quite effective, and improvements to codecs (which allow more efficient compression) have led to the possibility of sites like YouTube. If videos were 10 times bigger, YouTube would never have been able to launch when it did. The other major change was beginning to rely on hardware acceleration of said codecs — your computer or GPU might have an actual chip in it with the codec baked in, ready to perform decompression tasks with far greater speed than an ordinary general-purpose CPU in a phone. Just one problem: when you get a new codec, you need new hardware.
But consider this: many new phones ship with a chip designed for running machine learning models, which like codecs can be accelerated, but unlike them the hardware is not bespoke for the model. So why aren’t we using this ML-optimized chip for video? Well, that’s exactly what WaveOne intends to do.
I should say that I initially spoke with WaveOne’s cofounders, CEO Lubomir Bourdev and CTO Oren Rippel, from a position of significant skepticism despite their impressive backgrounds. We’ve seen codec companies come and go, but the tech industry has coalesced around a handful of formats and standards that are revised in a painfully slow fashion. H.265, for instance, was introduced in 2013, but years afterwards its predecessor, H.264, was only beginning to achieve ubiquity. It’s more like the 3G, 4G, 5G system than version 7, version 7.1, etc. So smaller options, even superior ones that are free and open source, tend to get ground beneath the wheels of the industry-spanning standards.
This track record for codecs, plus the fact that startups like to describe practically everything is “AI-powered,” had me expecting something at best misguided, at worst scammy. But I was more than pleasantly surprised: In fact WaveOne is the kind of thing that seems obvious in retrospect and appears to have a first-mover advantage.
The first thing Rippel and Bourdev made clear was that AI actually has a role to play here. While codecs like H.265 aren’t dumb — they’re very advanced in many ways — they aren’t exactly smart, either. They can tell where to put more bits into encoding color or detail in a general sense, but they can’t, for instance, tell where there’s a face in the shot that should be getting extra love, or a sign or trees that can be done in a special way to save time.
But face and scene detection are practically solved problems in computer vision. Why shouldn’t a video codec understand that there is a face, then dedicate a proportionate amount of resources to it? It’s a perfectly good question. The answer is that the codecs aren’t flexible enough. They don’t take that kind of input. Maybe they will in H.266, whenever that comes out, and a couple years later it’ll be supported on high-end devices.
So how would you do it now? Well, by writing a video compression and decompression algorithm that runs on AI accelerators many phones and computers have or will have very soon, and integrating scene and object detection in it from the get-go. Like Krisp.ai understanding what a voice is and isolating it without hyper-complex spectrum analysis, AI can make determinations like that with visual data incredibly fast and pass that on to the actual video compression part.
Variable and intelligent allocation of data means the compression process can be very efficient without sacrificing image quality. WaveOne claims to reduce the size of files by as much as half, with better gains in more complex scenes. When you’re serving videos hundreds of millions of times (or to a million people at once), even fractions of a percent add up, let alone gains of this size. Bandwidth doesn’t cost as much as it used to, but it still isn’t free.
Understanding the image (or being told) also lets the codec see what kind of content it is; a video call should prioritize faces if possible, of course, but a game streamer may want to prioritize small details, while animation requires yet another approach to minimize artifacts in its large single-color regions. This can all be done on the fly with an AI-powered compression scheme.
There are implications beyond consumer tech as well: A self-driving car, sending video between components or to a central server, could save time and improve video quality by focusing on what the autonomous system designates important — vehicles, pedestrians, animals — and not wasting time and bits on a featureless sky, trees in the distance, and so on.
Content-aware encoding and decoding is probably the most versatile and easy to grasp advantage WaveOne claims to offer, but Bourdev also noted that the method is much more resistant to disruption from bandwidth issues. It’s one of the other failings of traditional video codecs that missing a few bits can throw off the whole operation — that’s why you get frozen frames and glitches. But ML-based decoding can easily make a “best guess” based on whatever bits it has, so when your bandwidth is suddenly restricted you don’t freeze, just get a bit less detailed for the duration.
These benefits sound great, but as before the question is not “can we improve on the status quo?” (obviously we can) but “can we scale those improvements?”
“The road is littered with failed attempts to create cool new codecs,” admitted Bourdev. “Part of the reason for that is hardware acceleration; even if you came up with the best codec in the world, good luck if you don’t have a hardware accelerator that runs it. You don’t just need better algorithms, you need to be able to run them in a scalable way across a large variety of devices, on the edge and in the cloud.”
That’s why the special AI cores on the latest generation of devices is so important. This is hardware acceleration that can be adapted in milliseconds to a new purpose. And WaveOne happens to have been working for years on video-focused machine learning that will run on those cores, doing the work that H.26X accelerators have been doing for years, but faster and with far more flexibility.
Of course, there’s still the question of “standards.” Is it very likely that anyone is going to sign on to a single company’s proprietary video compression methods? Well, someone’s got to do it! After all, standards don’t come etched on stone tablets. And as Bourdev and Rippel explained, they actually are using standards — just not the way we’ve come to think of them.
Before, a “standard” in video meant adhering to a rigidly defined software method so that your app or device could work with standards-compatible video efficiently and correctly. But that’s not the only kind of standard. Instead of being a soup-to-nuts method, WaveOne is an implementation that adheres to standards on the ML and deployment side.
They’re building the platform to be compatible with all the major ML distribution and development publishers like TensorFlow, ONNX, Apple’s CoreML, and others. Meanwhile the models actually developed for encoding and decoding video will run just like any other accelerated software on edge or cloud devices: deploy it on AWS or Azure, run it locally with ARM or Intel compute modules, and so on.
It feels like WaveOne may be onto something that ticks all the boxes of a major b2b event: it invisibly improves things for customers, runs on existing or upcoming hardware without modification, saves costs immediately (potentially, anyhow) but can be invested in to add value.
Perhaps that’s why they managed to attract such a large seed round: $6.5 million, led by Khosla Ventures, with $1M each from Vela Partners and Incubate Fund, plus $650K from Omega Venture Partners and $350K from Blue Ivy.
Right now WaveOne is sort of in a pre-alpha stage, having demonstrated the technology satisfactorily but not built a full-scale product. The seed round, Rippel said, was to de-risk the technology, and while there’s still lots of R&D yet to be done, they’ve proven that the core offering works — building the infrastructure and API layers comes next and amounts to a totally different phase for the company. Even so, he said, they hope to get testing done and line up a few customers before they raise more money.
The future of the video industry may not look a lot like the last couple decades, and that could be a very good thing. No doubt we’ll be hearing more from WaveOne as it migrates from lab to product.
Powered by WPeMatico
We’re live! Check the links below!
Today’s the day! In just a few hours I am chatting with with Jai Das, a managing director at Sapphire Ventures.
The conversation is part of the second season of our Extra Crunch Live series that has seen all sorts of investors and founders join TechCrunch for a dig into their work.
Das’ participation comes at the perfect moment: He invested early in MuleSoft, which sold to Salesforce for $6.5 billion back in 2018. Salesforce is expected to announce its purchase of Slack later today, perhaps before our chat. Either way, we’ll ask Das about selling companies, selling them to Salesforce in particular and what we should take away concerning the enterprise software M&A market from the deal.
Here are notes from the last episode of Extra Crunch Live with Bessemer’s Byron Deeter.
And as we noted last week, we will also dig into the role of corporate venture capital in 2020 and beyond, the state of early-to-growth stage investing as Sapphire leads rounds from Series A to Series C, API-led startups, along with the importance of geographic location in the pandemic for founding teams and more.
It’s going to be fun! And it’s in just a few hours. So make sure that your Extra Crunch login works, hit the jump, save the time to your calendar and submit a question ahead of time if you want me to see your notes before we start. In the meantime, I’m going to find my most Zoom-friendly shirt and run through my intro a few times.
We’re live in mere hours! See you soon.
Below are links to add the event to your calendar and to save the Zoom link. We’ll share the YouTube link shortly before the discussion:
Powered by WPeMatico
This morning Airbnb released an S-1/A filing that details its initial IPO price range. The home-sharing unicorn intends to price its shares between $44 and $50 in its debut.
Per the company’s own accounting, it will have 596,399,007 or 601,399,007 shares outstanding, depending on whether its underwriters exercise their option. That gives the company a valuation range of $26.2 billion to $30.1 billion at the extremes.
The company’s simple share count does not include a host of other shares that have vested but not yet been exercised. Including those shares, the company’s fully diluted valuation stretches to $35 billion, by CNBC’s arithmetic.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
The top end of Airbnb’s simple valuation places it near its Series F valuation set in 2017. Its fully diluted valuation exceeds that $30.5 billion valuation and is far superior to the $18 billion, post-money valuation that it raised at during its troubled period early in the COVID-19 pandemic.
 For those investors, Silver Lake and Sixth Street, the company’s initial IPO price range is a win. For the company’s preceding investors, to see the company appear ready to at least match its preceding private valuation is a win as well, given how much damage Airbnb’s business sustained early in the pandemic.
For those investors, Silver Lake and Sixth Street, the company’s initial IPO price range is a win. For the company’s preceding investors, to see the company appear ready to at least match its preceding private valuation is a win as well, given how much damage Airbnb’s business sustained early in the pandemic.
But how do those Airbnb valuation numbers match up against its revenues, and will public market investors value the company based on its current results, or expectations for a return-to-form once a vaccine comes to market? And if so, is Airbnb expensive or not?
Shares of Booking Holdings, which owns travel services like Kayak, Priceline, OpenTable and others, have almost doubled in value since its pandemic lows and is within spitting distance of its all-time highs. This despite its revenues falling 48% in its most recent quarter. There’s optimism in the market that travel companies are on the cusp of a return to form, buoyed — we presume — by good news regarding effective coronavirus vaccines.
My expectation is that Airbnb is enjoying a similar bump, as investors intend to buy its shares not to bask in awe of its Q4 2020 results, but instead to enjoy what happens in the back half of 2021 as vaccines roll out and the travel industry recovers.
But what happens if we stack Airbnb’s revenues against its valuation today?
Powered by WPeMatico
French startup Ankorstore has raised a $29.9 million Series A round (€25 million) with Index Ventures leading the round. Existing investors GFC, Alven and Aglaé are also participating.
Ankorstore is building a wholesale marketplace that connects independent shop owners with brands selling household supplies, maple syrup, headbands, bath salts, stationery items and a lot more. That list alone should remind you of neighborhood stores that sell a ton of cutesy stuff that you don’t necessarily need but that tend to be popular.
The company works with 2,000 brands and 15,000 shops. And the startup isn’t just connecting buyers and sellers, as it has a clear set of rules. For instance, the minimum first order is €100, which means that you can try out new products without ordering hundreds of items at once.
By default, Ankorstore withdraws the money 60 days after placing an order. Brands get paid upon delivery. And of course, buying from several brands through Ankorstore should simplify your admin tasks.
Ankorstore is currently live in eight countries — France, Spain, Austria, Germany, Belgium, Holland, Switzerland and Luxembourg. France is the biggest market followed by Germany. Up next, the startup plans to launch in the U.K. in 2021.
In many ways, Ankorstore reminds me of Faire, the wholesale marketplace that has raised hundreds of millions of dollars in the U.S.
“There are a number of different retail marketplaces connecting retailers with makers and brands. Where we believe we differ is in our clear focus on the independent shop owner, offering the tools and the terms that make it really easy and cost-effective to discover and access some of the most desirable up-and-coming brands,” Ankorstore co-founder Pierre-Louis Lacoste said.
Given that the startup is working with small suppliers, chances are they’re only selling their products in Europe. So there should be enough room for a European leader in that space that I would describe as wholesale Etsy-style marketplaces with a strong focus on curation.
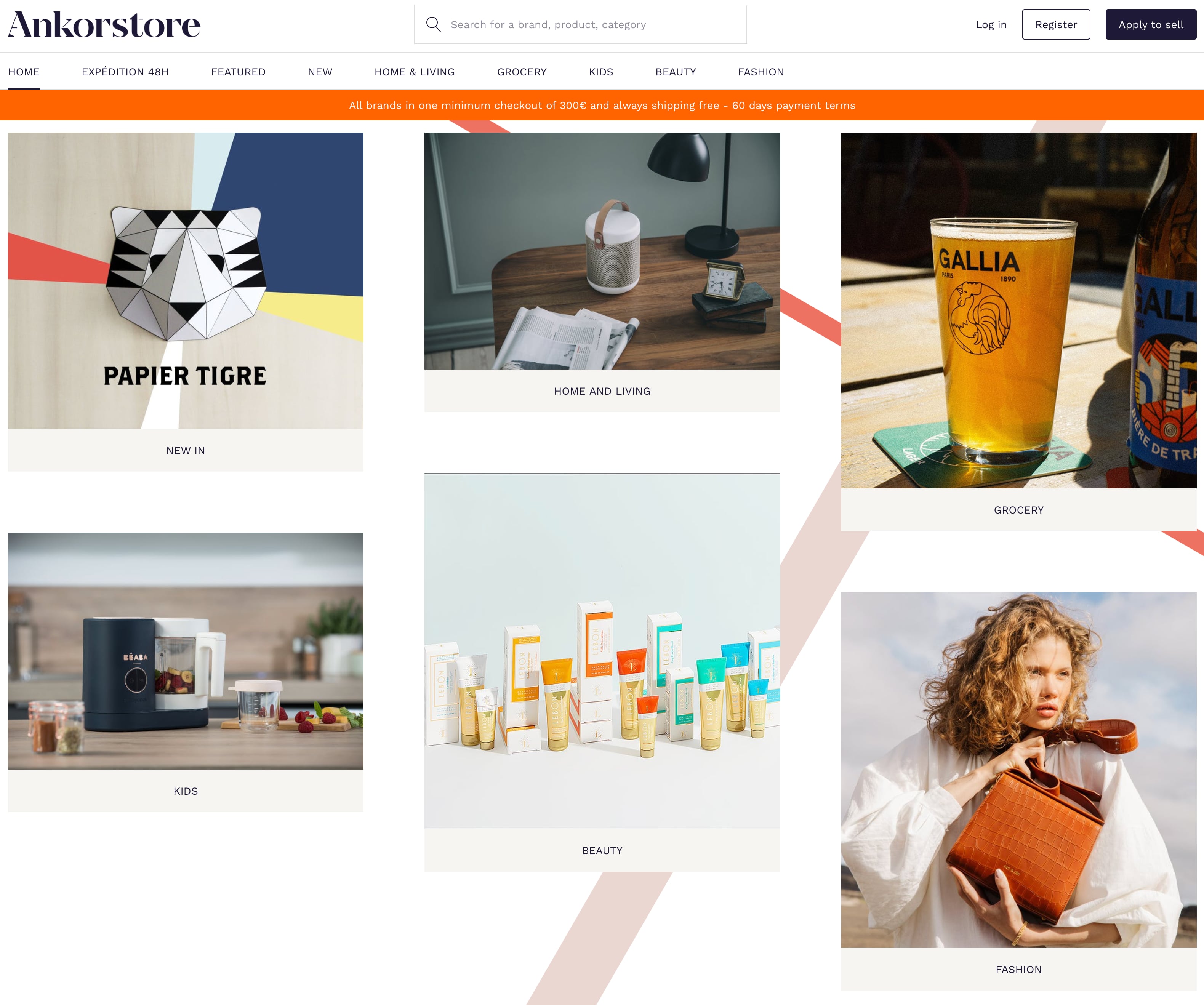
Image Credits: Ankorstore
Powered by WPeMatico

Theodoric Chew, co-founder and chief executive officer of mental health app Intellect
Intellect, a Singapore-based startup that wants to lower barriers to mental health care in Asia, says it has reached more than one million users just six months after launching. Google also announced today that the startup’s consumer app, also called Intellect, is one of its picks for best personal growth apps of 2020.
The company recently closed an undisclosed seed round led by Insignia Ventures Partners . Angel investors including e-commerce platform Carousell co-founder and chief executive officer Quek Siu Rui; former Sequoia partner Tim Lee; and startup consultancy xto10x’s Southeast Asia CEO J.J. Chai also participated.
In a statement, Insignia Ventures Partners principal Samir Chaibi said, “In Intellect, we see a fast-scaling platform addressing a pain that has become very obvious amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. We believe that pairing clinically-backed protocols with an efficient mobile-first delivery is the key to break down the barriers to access for millions of patients globally.”
Co-founder and chief executive officer Theodoric Chew launched Intellect earlier this year because while there is a growing pool of mental wellness apps in the United States and Europe that have attracted more funding during the COVID-19 pandemic, the space is still very young in Asia. Intellect’s goal is to encourage more people to incorporate mental health care into their daily routines by lowering barriers like high costs and social stigma.
Intellect offers two products. One is a consumer app with self-guided programs based on cognitive behavioral therapy techniques that center on issues like anxiety, self-esteem or relationship issues.
The other is a mental health platform for employers to offer as a benefit and includes a recently launched telehealth service called Behavioural Health Coaching that connects users with mental health professionals. The service, which includes one-on-one video sessions and unlimited text messaging, is now a core part of Intellect’s services, Chew told TechCrunch.
Intellect’s enterprise product now reaches 10,000 employees, and its clients include tech companies, regional operations for multinational corporations and hospitals. Most are located in Singapore, Hong Kong, Indonesia and India, and range in size from 100 to more than 3,000 employees.
For many small to mid-sized employers, Intellect is often the first mental health benefit they have offered. Larger clients may already have EAP (employee assistance programs), but Chew said those are often underutilized, with an average adoption rate of 1% to 2%. On the other hand, he said Intellect’s employee benefit program sees an average adoption rate of 30% in the first month after it is rolled out at a company.
Chew added that the COVID-19 pandemic has prompted more companies to address burnout and other mental health issues.
“In terms of larger trends, we’ve seen a huge spike in companies across the region having mental health and wellbeing of their employees being prioritized on their agenda,” said Chew. “In terms of user trends, we see a significantly higher utilization in work stress and burnout, anxiety and relationship-related programs.”
Intellect’s seed round will be used to expand in Asian markets and to help fund clinical research studies it is currently conducting with universities and organizations in Singapore, Australia and the United Kingdom.
Powered by WPeMatico
Vista Equity Partners hasn’t been shy about scooping up enterprise companies over the years, and today it added to a growing portfolio with its purchase of Gainsight. The company’s software helps clients with customer success, meaning it helps create a positive customer experience when they interact with your brand, making them more likely to come back and recommend you to others. Sources pegged the price tag at $1.1 billion.
As you might expect, both parties are putting a happy face on the deal, talking about how they can work together to grow Gainsight further. Certainly, other companies like Ping Identity seem to have benefited from joining forces with Vista. Being part of a well-capitalized firm allowed them to make some strategic investments along the way to eventually going public last year.
Gainsight and Vista are certainly hoping for a similar outcome in this case. Monti Saroya, co-head of the Vista Flagship Fund and senior managing director at the firm, sees a company with a lot of potential that could expand and grow with help from Vista’s consulting arm, which helps portfolio companies with different aspects of their business like sales, marketing and operations.
“We are excited to partner with the Gainsight team in its next phase of growth, helping the company to expand the category it has created and deliver even more solutions that drive retention and growth to businesses across the globe,” Saroya said in a statement.
Gainsight CEO Nick Mehta likes the idea of being part of Vista’s portfolio of enterprise companies, many of whom are using his company’s products.
“We’ve known Vista for years, since 24 of their portfolio companies use Gainsight. We’ve seen Gainsight clients like JAMF and Ping Identity partner with Vista and then go public. We believe we are just getting started with customer success, so we wanted the right partner for the long term and we’re excited to work with Vista on the next phase of our journey,” Mehta told TechCrunch.
Brent Leary, principle analyst at CRM Essentials, who covers the sales and marketing space, says that it appears that Vista is piecing together a sales and marketing platform that it could flip or go public in a few years.
“It’s not only the power that’s in the platform, it’s also the money. And Vista seems to be piecing together an engagement platform based on the acquisitions of Gainsight, Pipedrive and even last year’s Acquia purchase. Vista isn’t afraid to spend big money, if they can make even bigger money in a couple years if they can make these pieces fit together,” Leary told TechCrunch.
While Gainsight exits as a unicorn, the deal might not have been the outcome it was looking for. The company raised more than $187 million, according to PitchBook data, though its fundraising had slowed in recent years. Gainsight raised $50 million in April of 2017 at a post-money valuation of $515 million, again per PitchBook. In July of 2018 it added $25 million to its coffers, and the final entry was a small debt investment raised in 2019.
It could be that the startup saw its growth slow down, leaving it somewhere between ready for new venture investment and profitability. That’s a gap that PE shops like Vista look for, write a check, shake up a company and hopefully exit at an elevated price.
Gainsight hired a new chief revenue officer last month, notably. Per Forbes, the company was on track to reach “about” $100 million ARR by the end of 2020, giving it a revenue multiple of around 11x in the deal. That’s under current market norms, which could imply that Gainsight had either lower gross margins than comparable companies, or as previously noted, that its growth had slowed.
A $1.1 billion exit is never something to bemoan — and every startup wants to become a unicorn — but Gainsight and Mehta are well known, and we were hoping for the details only an S-1 could deliver. Perhaps one day with Vista’s help that could happen.
Powered by WPeMatico