Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Global investors are running from Chinese tech stocks in the wake of the government’s crackdown on Ant Group and Alibaba, two high-flying businesses founded by Ma Yun (Jack Ma) that were once hailed as paragons of China’s new tech elite.
Shares of major technology companies in the country have fallen sharply in recent days, with Bloomberg calculating that Alibaba, Tencent, JD.com and Meituan have lost around $200 billion in value during a handful of trading sessions.
Already reeling from the last-minute halt of the public debut of Ant Group, a major Chinese fintech player with deep ties to Alibaba, the e-commerce giant came under new fire, as China’s markets watchdog opened a probe into its business practices concerning potentially anticompetitive behavior.
Ant Group was itself summoned by the government on December 26, leading to a plan that will force the company to “rectify” its business practices.
Shares of Alibaba are off around 30% from their recent record highs set in late October. Tech shares are also off in the country more broadly, with one Chinese-technology-focused ETC falling around 8% from recent highs, including a 1.5% drop today.
The American Depositary Receipts used by traders to invest in Alibaba fell from around $256 per share at the close of Wednesday trading on the New York Stock Exchange to around $222 last Thursday. The company is down another half point today. It was worth more than $319 per share earlier in the quarter.
It’s clear that the rising tensions between China’s tech giants and the country’s ruling Communist Party have investors spooked. But Jack Ma’s relationship with the Chinese government has always been a bit more fraught than that of his peers. Ma Huateng (Pony Ma), the founder of Tencent, and Xu Yong (Eric Yong) and Li Yanhong (Robin Li), the co-founders of Baidu, have kept lower profiles than the Alibaba founder.
Bloomberg has a good synopsis of the state of the market right now. The companies that are most directly in the crosshairs appear to be Ma Yun’s, but at different times, Tencent has been the focus of Chinese regulators bent on curbing the company’s influence through gaming.
Specifically for Alibaba things have gone from bad to worse, and a boosted share buyback program was not enough to halt the bleeding.
Whether this new round of regulations is a solitary blip on the radar or the signal of an increasing interest in Beijing tying tech companies closer to national interests remains to be seen. As the tit-for-tat tech conflict between the U.S. and China continues, many companies that had seen their growth as apolitical may become caught in the diplomatic crossfire.
Other tech companies are seeing their fortunes rise, boosted by newfound interest from the central government in Beijing.
This is already apparent in the chip industry, where China’s push for self-reliance has brought new riches and capital for new businesses. It’s true for Liu FengFeng, whose company, Tsinghon, was able to raise $5 million for its attempt at building a new semiconductor manufacturer in the country. Intellifusion, a manufacturer of chipsets focused on machine learning applications, was able to raise another $141 million back in April.
Private investors may be less enthused at the prospect of backing Chinese tech upstarts who could face government censure should the regulatory winds shift. Whether other startup markets in the region — India, Japan, among others — will benefit from the Chinese regulatory barrage will be interesting to track in 2021.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
This is Equity Monday, our weekly kickoff that tracks the latest private market news, talks about the coming week, digs into some recent funding rounds and mulls over a larger theme or narrative from the private markets. You can follow the show on Twitter here and myself here — and don’t forget to check out the first of our two holiday eps, the last one talking to VCs about what surprised them in 2020.
Anyhoo, from vacation, here’s what Chris and I got up to:
Tune in Thursday for one more fun episode, and then we’re back to regular programming the week after!
Equity drops every Monday at 7:00 a.m. PST and Thursday afternoon as fast as we can get it out, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast, Spotify and all the casts.
Powered by WPeMatico
The rivalry between China’s top online learning apps has become even more intense this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The latest company to score a significant funding round is Zuoyebang, which announced today (link in Chinese) that it has raised a $1.6 billion Series E+ from investors including Alibaba Group. Other participants included returning investors Tiger Global Management, SoftBank Vision Fund, Sequoia Capital China and FountainVest Partners.
Zuoyebang’s latest announcement comes just six months after it announced a $750 million Series E led by Tiger Global and FountainVest. The latest financing brings Zuoyebang’s total raised so far to $2.93 billion. The company did not disclose its latest worth, but Reuters reported in September that it was raising at a $10 billion valuation.
One of Zuoyebang’s main competitors is Yuanfudao, which announced in October that it had reached a $15.5 billion valuation after closing a $2.2 billion round led by Tencent. This pushed Yuanfudao ahead of Byju as the world’s most valuable edtech company. Another popular online learning app in China is Yiqizuoye, which is backed by Singapore’s Temasek.
Zuoyebang offers online courses, live lessons and homework help for kindergarten to 12th grade students, and claims about 170 million monthly active users, about 50 million of whom use the service each day. In comparison, there were about 200 million K-12 students in 2019 in China, according to the Ministry of Education (link in Chinese).
In fall 2020, the total number of students in Zuoyebang’s paid livestream classes reached more than 10 million, setting an industry record, the company claims. While a lot of the growth was driven by the pandemic, Zuoyebang founder Hou Jianbin said in the company’s funding announcement that it expects online education to continue growing in the longer term, and will invest in K-12 classes and expand its product categories.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast (now on Twitter!), where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
Today is our holiday look-back at the year, bringing not only our own Danny and Natasha and Chris and Alex into the mix, but also five venture capitalists who we got to leave us their notes as well. The goal for this episode was to reflect on a year that no one could have ever predicted, but with a specific angle, as always, on venture capital and startups.
We asked about the biggest surprise, non-portfolio companies to watch, and trends they got wrong and right. There was also banter on Zoom investing (Alex came up with Zesting, but we’re taking suggestions if anyone comes up with a better moniker) and startup pricing.
Here’s who we asked to call into our super Fancy Equity Hotline:
Thanks to them all for participating, and of course you, our dear Equity listeners, for a blockbuster year for the podcast.
Equity drops every Monday at 7:00 a.m. PST and Thursday afternoon as fast as we can get it out, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast, Spotify and all the casts.
Powered by WPeMatico
The last 12 months have provided us with shocking lows and surprising highs. In startup land, great expectations in January and February were followed by dashed hopes in March.
Those woes were followed by April despair, surprised optimism from May through June, and, finally, a straight shot all the way to the moon through December.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
It’s been a lot. But it’s all behind us. We don’t need to spend more time thinking about 2020 for now. We need to look ahead.
This morning, I’ve compiled notes on what’s coming. We have notes from GGV’s Hans Tung on the 2021 IPO market, Sapphires’s Beezer Clarkson on what fundraising will look like for VCs next year, and a prediction from the PitchBook analyst crew that caught my eye.
This is the last Exchange column for 2020. Thanks for reading so I could keep having fun every day at my job. Now, to work!
We’ll start with the 2021 IPO market, only because so many of you cared so very much about it this year.
Hans Tung, an investor at GGV and recent Extra Crunch Live guest, is an investor with an international perspective and a good read on global startup liquidity. So, when I got on the phone with him last week to catch up, I wanted to know his read on the 2021 IPO market.
Given that we’ve seen a number of blockbuster IPOs this year, I was expecting him to forecast an active start to the year. Correct.
But Tung added that while Q1 could be very busy, Q2 could present a lull. Why? Tung expects IPOs that failed to finish the job in Q4 2020 to slip into the first quarter of next year. That explains why the first quarter is busy. But why the slowdown in the following three months?
Powered by WPeMatico
Lalamove will extend its network to cover more small Chinese cities after raising $515 million in Series E funding, the on-demand logistics company announced on its site. The round was led by Sequoia Capital China, with participation from Hillhouse Capital and Shunwei Capital. All three are returning investors.
According to Crunchbase data, this brings Lalamove’s total raised so far to about $976.5 million. The company’s last funding announcement was in February 2019, when it hit unicorn status with a Series D of $300 million.
Bloomberg reported last week that Lalamove was seeking at least $500 million in new funding at $8 billion valuation, or four times what it raised last year.
Founded in 2013 for on-demand deliveries within the same city, Lalamove has since grown its business to include freight services, enterprise logistics, moving and vehicle rental. In addition to 352 cities in mainland China, Lalamove also operates in Hong Kong (where it launched), Taiwan, Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines and Thailand. The company entered the United States for the first time in October, and currently claims about 480,000 monthly active drivers and 7.2 million monthly active users.
Part of its Series D had been earmarked to expand into India, but Lalamove was among 43 apps that were banned by the government, citing cybersecurity concerns.
In its announcement, Lalamove CEO Shing Chow said its Series E will be used to enter more fourth and fifth-tier Chinese cities, adding “we believe the mobile internet’s transformation of China’s logistics industry is far from over.”
Other companies that have recently raised significant funding rounds for their logistics operations in China include Manbang and YTO.
Lalamove’s (known in Chinese as Huolala) Series E announcement said the company experienced a 93% drop in shipment volume at the beginning of the year, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but has experienced a strong rebound, with order volume up 82% year-over-year even before Double 11.
Powered by WPeMatico
When we examine any year in enterprise M&A, it’s tempting to highlight the biggest, gaudiest deals — and there were plenty of those in 2020. I’ve written about 34 acquisitions so far this year. Of those, 15 were worth $1 billion or more, 12 were small enough to not require that the companies disclose the price and the remainder fell somewhere in between.
Four deals involving chip companies coming together totaled over $100 billion on their own. While nobody does eye-popping M&A quite like the chip industry, other sectors also offered their own eyebrow-raising deals, led by Salesforce buying Slack earlier this month for $27.7 billion.
We are likely to see more industries consolidate the way chips did in 2020, albeit probably not quite as dramatically or expensively.
Yet in spite of the drama of these larger numbers, the most interesting targets to me were the pandemic-driven smaller deals that started popping up in May. Those small acquisitions are the ones that are so insignificant that the company doesn’t have to share the purchase price publicly. They usually involve early-stage companies being absorbed by cash-rich concerns looking for some combination of missing technology or engineering talent in a particular area like security or artificial intelligence.
It was certainly an active year in M&A, and we still might not have seen the last of it. Let’s have a look at why those minor deals were so interesting and how they compared with larger ones, while looking ahead to what 2021 M&A might look like.
It’s always hard to know exactly why an early-stage startup would give up its independence by selling to a larger entity, but we can certainly speculate on some of the reasons why this year’s rapid-fire dealing started in May. While we can never know for certain why these companies decided to exit via acquisition, we know that in April, the pandemic hit full force in the United States and the economy began to shut down.
Some startups were particularly vulnerable, especially companies low on cash in the April timeframe. Obviously companies fail when they run out of funding, and we started seeing early-stage startups being scooped up the following month.
We don’t know for sure of course if there is a direct correlation between April’s economic woes and the flurry of deals that started in May, but we can reasonably speculate that there was. For some percentage of them, I’m guessing it was a fire sale or at least a deal made under less than ideal terms. For others, maybe they simply didn’t have the wherewithal to keep going under such adverse economic conditions or the partnerships were just too good to pass up.
It’s worth noting that I didn’t cover any deals in April. But, beginning on May 7, Zoom bought Keybase for its encryption expertise; five days later Atlassian bought Halp for Slack integration; and the day after that VMware bought cloud native security startup Octarine — and we were off and running. Granted the big companies benefited from making these acquisitions, but the timing stood out.
Powered by WPeMatico
Bandit ML aims to optimize and automate the process of presenting the right offer to the right customer.
The startup was part of the summer 2020 class at accelerator Y Combinator . It also raised a $1.32 million seed round in September from YC, Haystack Fund, Webb Investment Network, Liquid 2 Ventures, Jigsaw Ventures, Basecamp Fund, Pathbreaker Ventures and various angels — including what CEO Edoardo Conti said are 10 current and former Uber employees.
Conti (who founded the company with Lionel Vital and Joseph Gilley) is a former Uber software engineer and researcher himself.
The idea, as he explained via email, is that one customer might be more excited about a $5 discount, while another might be more effectively enticed by free shipping, and a third might be completely uninterested because they just made a large purchase. Using a merchant’s order history and website activity data, Bandit ML is supposed to help them determine which offer will be most effective with which shopper.
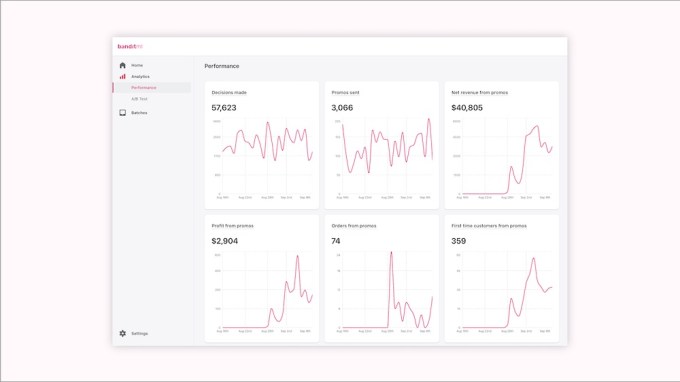
Image Credits: Bandit ML
Conti acknowledged that there’s other discount-optimizing software out there, but he suggested none of them offers what Bandit ML does: “off the shelf tools that use machine learning the way giants like Uber, Amazon and Walmart do.”
He added that Bandit ML’s technology is unique in its support for full automation (“some stores sent their first batch of offers within 10 minutes of signing up”) and its ability to optimize for longer-term metrics, like purchases over a 120-day period, rather than focusing on one-off redemptions. In fact, Conti said the technology the startup uses to make these decisions is similar to the ReAgent project that he worked on at Facebook.
Bandit ML is currently focused on merchants with Shopify stores, though it also supports other stores not on Shopify, like Calii. Conti said the platform has been used to send millions of dollars’ worth of promotions since July, with one clothing company seeing a 20% increase in net revenue.
“Starting with an always-on incentive engine for every online business, we aim to build functioning out-of-the-box machine learning tools that a small online business needs to compete with the Walmarts and Amazons of the world,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico
Being “underbanked” doesn’t mean that someone lacks access to financial services. Instead, it often means they don’t have traditional bank accounts or credit cards. But in markets like Indonesia, many still use digital wallets or e-commerce platforms, creating alternative sources of user data that can help them secure working capital and other financial tools. Finantier, a Singapore-based open finance startup, wants to streamline that data with a single API that gives financial services access to user data, with their consent. It also includes machine-learning-based analytics to enable credit scoring and KYC verifications.
Currently in beta mode with more than 20 clients, Finantier is busy getting ready to officially launch. It announced today that it has been accepted into Y Combinator’s Winter 2021 startup batch. The startup also recently raised an undisclosed amount of pre-seed funding led by East Ventures, with participation from AC Ventures, Genesia Ventures, Two Culture Capital and other investors.
Finantier was founded earlier this year by Diego Rojas, Keng Low and Edwin Kusuma, all of whom have experience building products for fintech companies, with the mission of enabling open finance in emerging markets.
Open finance grew out of open banking, the same framework that Plaid and Tink are built on. Meant to give people more control over their financial data instead of keeping it siloed within banks and other institutions, users can decide to grant apps or websites secure access to information from their online accounts, including bank accounts, credit cards and digital wallets. Open banking refers mainly to payment accounts, while open finance, Finantier’s specialty, covers a larger gamut of services, including business lending, mortgages and insurance underwriting.
While Finantier is focusing first on Singapore and Indonesia, it plans to expand into other countries and become a global fintech company like Plaid. It’s already eyeing Vietnam and the Philippines.
Before launching Finantier, Rojas worked on products for peer-to-peer lending platforms Lending Club and Dianrong, and served as chief technology officer for several fintech startups in Southeast Asia. He realized that many companies struggled to integrate with other platforms and fetch data from banks, or purchase data from different providers.
“People are discussing open banking, embedded finance and so on,” Rojas, Finantier’s chief executive officer, told TechCrunch. “But those are the building blocks of something bigger, which is open finance. Particularly in a region like Southeast Asia, where about 60% to 70% of adults are unbanked or underbanked, we believe in helping consumers and businesses leverage the data that they have in multiple platforms. It definitely doesn’t need to be a bank account, it could be in a digital wallet, e-commerce platform or other service providers.”
What this means for consumers is that even if someone doesn’t have a credit card, they can still establish creditworthiness: For example, by sharing data from completed transactions on e-commerce platforms. Gig economy workers can access more financial services and deals by giving data about their daily rides or other types of work they do through different apps.
Other open-banking startups focused on Southeast Asia include Brankas and Brick. Rojas said Finantier differentiates by specializing on open finance and creating infrastructure for financial institutions to build more services for end users.
The benefit of open finance for financial institutions is that they can create products for more consumers and find more opportunities for revenue sharing models. In Southeast Asia, this also means reaching more people who are underbanked or otherwise lack access to financial services.
While taking part in Y Combinator’s accelerator program, Finantier will also be participating in the Indonesia Financial Service Authority’s regulatory sandbox. Once it completes the program, it will be able to partner with more fintech companies in Indonesia, including bigger institutions.
There are 139 million adults in Indonesia who are underbanked or unbanked, said East Ventures co-founder and managing partner Willson Cuaca.
The investment firm, which focuses on Indonesia, conducts an annual survey called the East Ventures Digital Competitiveness Index and found that financial exclusion was where one of the largest divides existed. There are significant gaps in between the number of financial services available in heavily populated islands like Java, where Jakarta is located, and other islands in the archipelago.
To promote financial inclusion and alleviate the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has set a goal for 10 million micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) to go digital by the end of the year. There are currently about eight million Indonesian MSMEs that sell online, representing just 13% of MSMEs in the country.
“Providing equal access to financial services will create multiplier effects to the Indonesian economy,” Cuaca told TechCrunch about East Ventures’ decision to back Finantier. “Currently, hundreds of companies work with their own unique solutions to bring financial services to more people. We believe Finantier will help them offer more products and services to this underserved section of the population.”
Powered by WPeMatico
As we head toward the exits of 2020, we have one more name to add to our roll call of private companies that have reached the $100 million annual recurring revenue (ARR) milestone. Well, one and a half.
But before we get into Nexthink and give Coalition a honorable mention, let’s talk about the startups we’re looking for in 2021.
 The $100 million ARR list came together by accident, a quirk of a news cycle that happened to have a few companies reach the threshold when I was in transition back to working at TechCrunch. So, when I got back into our WordPress install, the group of companies that had each recently reached nine-figure revenues was top of mind.
The $100 million ARR list came together by accident, a quirk of a news cycle that happened to have a few companies reach the threshold when I was in transition back to working at TechCrunch. So, when I got back into our WordPress install, the group of companies that had each recently reached nine-figure revenues was top of mind.
But looking at $100 million ARR companies proved less useful than we might have hoped. Mostly what we managed was to collect a bucket of companies that were about to go public.
That was always a risk. As we wrote at the time:
Perhaps the startup market would do well to celebrate the $50 million ARR mark even more loudly. At $50 million ARR, a startup is scaling to IPO size. That’s the goal, after all.
This is our aim for 2021.
If your startup is approaching the $50 million ARR mark, or the $50 million annual run rate threshold, I want to hear from you. Drop a line if your startup has an annualized run rate between $35 million and $60 million, is privately held, and you are willing to chat about how quickly it is growing. (The Exchange first raised this idea in November.)
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
But that’s next year. Today, let’s chat about Nexthink, what the hell “digital employee experience” is and what’s good with cyber insurance and why it’s helping Coalition grow rapidly.
Nexthink is a venture-backed software company with headquarters in Lausanne, Switzerland and Boston. According to PitchBook, Nexthink raised external capital in modest amounts from 2006 until 2014, when the startup picked up a $14.5 million Series D. That round was its first worth more than $10 million.
From there, Nexthink was a venture capital success story, presumably scaling quickly as it raised two larger rounds in 2016 and 2018 worth an estimated $40 million and $85 million, respectively. Nexthink was valued at a little over $558 million (post-money) following its 2018 round.
How did it attract so much external funding? By building digital experience monitoring software. Which, after doing a bit of research this morning, appears to be software aimed at tracking what corporate end users are doing with devices and how well software running on those devices perform.
Powered by WPeMatico