Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Knife Capital, a South African venture capital firm, is raising a $50 million fund for startups looking to raise Series B financing. With Knife Fund III called the African Series B Expansion Fund, the firm seeks to directly invest in the aggressive expansion of South African breakout companies. It also plans to co-invest in companies across the rest of Africa.
The first fund, known as Knife Capital Fund I or HBD Venture Capital, was a closed private equity fund managed by Eben van Heerden and Keet van Zyl. The firm offered seed capital to startups. It also generated significant exits from its portfolio — Visa acquisition of fintech startup Fundamo, and orderTalk’s acquisition by UberEats come to mind.
In 2016, the VC firm launched its current 12J offering with Knife Capital Fund II. The fund (KNF Ventures), which invests primarily in Series A stage, has eight startups in its portfolio. Last year the firm told TechCrunch of its intention to extend the Fund II and open to new investors. The plan was to give startups access to networks, money and expansion opportunities.
“We want to help South African and African companies internationalize,” said co-managing partner Andrea Bohmert at the time. A testament to its cause, one of its portfolio companies, DataProphet, raised $6 million Series A to expand into the U.S. and Europe.
Bohmert tells TechCrunch that the third fund aims to address the critical Series B funding gap that has characterised the venture capital asset class in South Africa, resulting in businesses not reaching full potential or exiting too early.
“Lately, we see an increase in companies able to raise $2 million to $5 million funding rounds. And while the companies are operating within their home country, in our case South Africa, such amounts take you far due to the local cost structure,” Bohmert says. “However, once these companies start gaining international traction and need to build an infrastructure outside of their home country, they need to raise significant amounts to afford so. There are currently hardly any South African VC funds, perhaps other than Naspers Foundry, that can write checks of $5 million or more and are willing to deploy them to finance the externalization of South African companies into larger markets.”
As a result, Bohmert argues that Africa has become an incubator for international VCs who can write these checks but cannot provide the local support most of these companies still need. Likewise, there are instances where international investors actively search for local co-investors in South Africa to invest in a round, and not finding one might blow the chances of them going further with the investment. This is the gap Knife Capital intends to fill by launching this fund, Bohmert says.
“We want to be the local lead investor of choice for South African technology companies looking to internationalise, co-investing with international investors who can lead the Series B discussion and further.”
This week, Knife Capital secured $10 million from Mineworkers Investment Company (MIC), a South Africa-based investment firm. The commitment positions MIC as an anchor investor to the fund alongside other local and international investors.
Nchaupe Khaole, the CIO at MIC, explained that the move to change the way local institutional investors approach venture capital investment has been in MIC’s pipeline for a while. And by partnering with Knife Capital, this idea can begin to materialize.
“Our commitment brings to the table the investment, along with many of our strengths as an experienced player. One of which is our ability to influence the companies within our portfolio to partner with us and effect real, tangible change to the South African economy. We are delighted to be a key catalyst in the success of this funding round,” he said.
As per other details, Knife Capital aims for a first close by May and a final close by the end of the year. Most of its participation will be co-investing, and the idea is to do that in 10 to 12 companies.
Powered by WPeMatico
Public.com, a social-focused free stock trading service, is nearing the close of a Series D just two months after raising a $65 million Series C, sources familiar with the matter told TechCrunch.
The San Francisco-based fintech aims to give people the ability to invest in companies using any amount of money, with a focus on community activity over active trading. It competes with Robinhood, M1 Finance and other American fintech companies that offer consumers a way to invest in equities with low or zero fees.
Public.com apparently got a flurry of investor interest over the past couple of weeks after Robinhood found itself in hot water and essentially raised $3.4 billion in a matter of days to help get itself out of a mess.
That new capital came at a challenging time for the unicorn, which could pursue an IPO this year. And some investors reportedly want a piece of rival Public.com’s pie.
One source told TechCrunch that many of those offering term sheets believe there could be “a mass exodus from Robinhood” and want a way to capture that value.
Public recently shook up its business model, moving from generating revenue from order flow payments, a key way that Robinhood monetizes, to collecting tips from users in exchange for executing their orders. Payment for order flow, or PFOF, has become a touchstone in the debate surrounding low-cost trading platforms, and how users may pay for their transactions if not in direct fees.
Investors betting on Public, then, would be placing a wager on not merely future user growth, but the startup’s ability to monetize effectively in the future.
The sources for this story were granted anonymity due to the sensitivity of the discussions.
Public grew quickly in 2020, expanding its user base by a multiple of 10 since the start of the year.
Co-founder Leif Abraham told TC’s Alex Wilhelm in December that the company’s growth has been consistent instead of lumpy, expanding at around 30% each month. The co-founder also stressed that most of Public’s users find its service organically, implying that the startup’s marketing costs have not been extreme, nor its growth artificially boosted.
We don’t know yet how much Public is raising in its Series D, or who all is investing. Public has not responded to multiple requests for comment. VC firm Accel — which led its Series A, B and C rounds — also declined to comment. But we’ll definitely report details as we get them.
Powered by WPeMatico
Metromile began trading as a public company yesterday. Its exit from the private market was accelerated by its decision to combine with a special purpose acquisition company, or SPAC.
Such transactions have exploded in popularity in recent years, bridging the gap between a host of richly valued private companies and endless bored capital. SPACs raise cash, go public and then merge with a private entity. The SPAC then dissolves itself into the combined entity, a process that often includes an additional slug of money (PIPE) for good measure.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
SPAC-led debuts can move faster than a traditional IPO, making them attractive to companies in a hurry. And with more visibility into how much capital might be raised than during a traditional public-offering pricing run, they can smooth worries amongst target-companies regarding how much cash they can attract by leaving the private-market fold.
 Metromile is hardly the final company we expect to debut this year via a SPAC. The list is long and may include fellow neoinsurance company Hippo. (Hippo declined to comment on the matter.)
Metromile is hardly the final company we expect to debut this year via a SPAC. The list is long and may include fellow neoinsurance company Hippo. (Hippo declined to comment on the matter.)
But with many more SPACs coming our way, we took Metromile’s debut as a learning moment. To that end, we got on the horn with CEO Dan Preston to chat about what the day meant for his company, and to elicit a note or two on the SPAC process for our own enjoyment.
TechCrunch asked Preston about the SPAC world and how his combination came about. He said his firm started by dipping its toe into the blank-check waters, kicking off with a small set of conversations, chats that quickly gathered traction.
But don’t take that to mean that any company will elicit a similar market response. Preston said SPACs are designed for a specific class of company; namely those that want or need to share a bit more story when they go public. Younger companies, in other words, for whom a traditional S-1 filing might not be provide a sufficient summation of its potential.
Powered by WPeMatico
The team at Reduct.Video is hoping to dramatically increase the amount of videos created by businesses.
The startup’s technology is already used by customers including Intuit, Autodesk, Facebook, Dell, Spotify, Indeed, Superhuman and IDEO. And today, Reduct is announcing that it has raised a $4 million round led by Greylock and South Park Commons, with participation from Figma CEO Dylan Field, Hopin Chief Business Officer Armando Mann and former Twitter exec Elad Gil.
Reduct was founded by CEO Prabhas Pokharel and CTO Robert Ochshorn (both pictured above). Pokharel argued that despite the proliferation of streaming video platforms and social media apps on the consumer side, video remains “underutilized” in a business context, because it simply takes so much time to sort through video footage, much less edit it down into something watchable.
As Pokharel demonstrated for me, Reduct uses artificial intelligence, natural language processing and other technologies to simplify the process by automatically transcribing video footage (users can also pay for professional transcription), then tying that transcript to the video.
“The magic starts there: Once the transcription has been made, every single word is connected to the [corresponding] moment in the video,” he said.
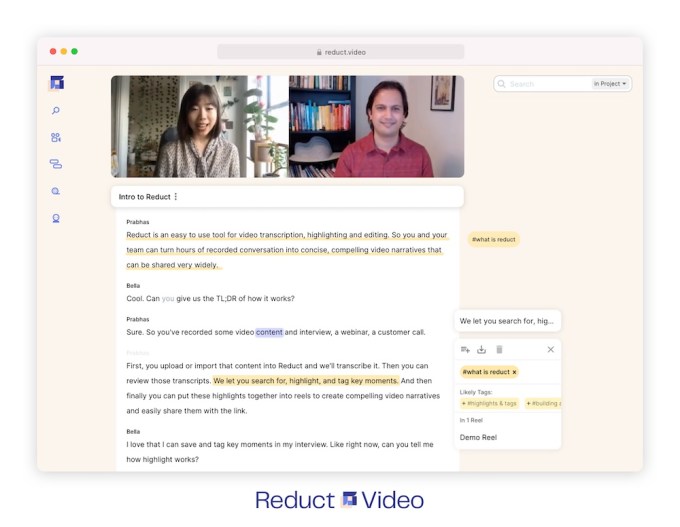
Image Credits: Reduct.Video
That means editing a video is as simple as editing text. (I’ve taken advantage of a similar linkage between text and media in Otter, but Otter is focused on audio and I’ve treated it more as a transcription tool.) It also means you can search through hours of footage for every time a topic is mentioned, then organize, tag and share it.
Pokharel said that AI allows Reduct to simplify parts of the sorting and editing process, like understanding how different search terms might be related. But he doesn’t think the process will ever become fully automated — instead, he compared the product to an “Iron Man suit,” which makes a human editor more powerful.
He also suggested that this approach changes businesses’ perspective on video, and not just by making editing faster and easier.
“Users on Reduct emphasize authenticity over polish, where it’s much more the content of the video that matters,” Pokharel said. He added that Reduct has been “learning from our customers” about what they can do with the product — user research teams can now easily organize and share hundreds of hours of user footage, while marketers can turn customer testimonials and webinars into short, shareable videos.
“Video has been so supply constrained, it’s crazy,” he continued. “There are all these use cases for asynchronous video that [companies] haven’t even bothered with.”
For example, he recalled one customer who said that she used to insist that team members attend a meeting even if there was only two minutes of it that they needed to hear. With Reduct, she can “give them that time back” and just share the parts they need.
Powered by WPeMatico
This afternoon Bumble priced its IPO at $43 per share, ahead of its raised IPO range of $37 to $39 per share.
Bumble filed to go public in mid-January, and offered up its first price range on February 2. That range, $28 to $30 per share, wound up coming up short. Bumble raised its price range to $37 to $39 per share earlier this week.
Before counting a possible underwriters’ option, Bumble raised $2.15 billion by selling 50,000,000 million shares in its public offering. The company will begin to trade tomorrow morning.
Bumble’s debut comes amidst a number of other 2021 offerings, including MetroMile’s SPAC-led public combination earlier this week. Other well-known companies are anticipated to list this year, including Coinbase and, perhaps, Robinhood.
The public offering of Bumble shares comes after a sustained period when one company, Match, was presumed to be the only possible public dating company. However, the smaller Bumble has proven that there is room for at least one more.
TechCrunch explored Bumble’s financial results here, if you’d like more.
Powered by WPeMatico
Scalarr, a startup that says it uses machine learning to combat ad fraud, is announcing that it has raised $7.5 million in Series A funding.
The company was founded by CEO Inna Ushakova and CPO Yuriy Yashunin, who previously led the mobile marketing agency Zenna. Ushakova told me that while at Zenna, they realized that ad fraud had grown to the point that it posed a real threat to their business.
At the same time, the team wasn’t impressed by any of the existing anti-fraud solutions, so it built its own technology. Eventually, they shut down Zenna completely and moved the entire team over to Scalarr.
The startup’s products include AutoBlock, which is supposed to detect fraud before the advertiser bids on an ad, and DeepView, which is used by adtech platforms (including ad exchanges, demand-side platforms and supply-side platforms).
Scalarr says it can detect 60% more fraud than existing products on the market and that it saved its clients $22 million in ad fraud refunds in 2020. Ushakova attributed this in large part to the startup’s extensive use of machine learning technology.
She added that while large ad attribution companies are adding anti-fraud products, they aren’t the focus. And historically, companies have tried to detect fraud through a “rules-based approach,” where there’s a list of behaviors that suggest fraudulent activity — but no matter how quickly they create those rules, it’s hard to keep up with the fraudsters.
“Fraud is ever evolving,” Ushakova said. “It’s like a Tom and Jerry game, so they are ahead of you and we are trying to catch them.”
As for why machine learning works so much more effectively, she said, “Only ML could help you predict the next step, and with ML, you should be able to detect abnormalities that are not classified. Right after that, our analytics should be able to take a look at those abnormalities and decide whether something is statistically important.”
Scalarr’s Series A was led by the European Bank of Reconstruction and Development, with participation from TMT Investments, OTB Ventures and Speedinvest. Among other things, the company will use the money to expand its presence in Asia and continue developing the product.
Powered by WPeMatico
Since the start of the year, I’ve covered nine M&A deals already, the largest being Citrix buying Wrike for $2.25 billion. But not every deal involves a huge price tag. Today we are going to look at three smaller deals that show there is plenty of activity at the lower-end of the acquisition spectrum.
As companies look for ways to enhance their offerings, and bring in some talent at the same time, smaller acquisitions can provide a way to fill in the product road map without having to build everything in-house.
This gives acquiring companies additional functionality for a modest amount of cash. In smaller deals, we often don’t even get the dollar amount, although in one case today we did. If the deal isn’t large enough to have a material financial impact on a publicly traded company, they don’t have to share the price.
Let’s have a look at three such deals that came through in recent days.
For starters, Tenable, a network security company that went public in 2018, bought French Active Directory security startup Alsid for $98 million. Active Directory, Microsoft’s popular user management tool, is also a target of hackers. If they can get a user’s credentials, it’s an easy way to get on the network and Alsid is designed to prevent that.
Security companies tend to enhance the breadth of their offerings over time and Alsid gives Tenable another tool and broader coverage across their security platform. “We view the acquisition of Alsid as a natural extension into user access and permissioning. Once completed, this acquisition will be a strategic complement to our Cyber Exposure vision to help organizations understand and reduce cyber risk across the entire attack surface,” according to the investor FAQ on this acquisition.
Emmanuel Gras, CEO and co-founder, Alsid says he started the company to prevent this kind of attack. “We started Alsid to help organizations solve one of the biggest security challenges, an unprotected Active Directory, which is one of the most common ways for threat actors to move laterally across enterprise systems,” Gras said in a statement.
Alsid is based in Paris and was founded in 2014. It raised a modest amount, approximately $15,000, according to Crunchbase data.
Copper, a CRM tool built on top of the Google Workspace, announced it has purchased Sherlock, a customer experience platform. They did not share the purchase price.
The pandemic pushed many shoppers online and providing a more customized experience by understanding more about your customer can contribute to and drive more engagement and sales. With Sherlock, the company is getting a tool that can help Copper users understand their customers better.
“Sherlock is an innovative engagement analytics and scoring platform, and surfaces your prospects’ and customers’ intentions in a way that drives action for sales, account management and customer success professionals,” Copper CEO Dennis Fois wrote in a blog post announcing the deal.
He added, “Relationships are based on engagement, and with Sherlock we are going to create CRM that is focused on action and momentum.”
It’s clear that APIs have changed the way we think about software development, but they have also created a management problem of their own as they proliferate across large organizations. RapidAPI, an API management platform, announced today that it has acquired Paw.
With Paw, RapidAPI adds the ability to design your own APIs, essentially giving customers a one-stop shop for everything related to creating and managing the API environment inside a company. “The acquisition enables RapidAPI to extend its open API platform across the entire API development lifecycle, creating a connected experience for developers from API development to consumption, across multiple clouds and gateways,” the company explained in a statement.
RapidAPI was founded in 2015 and has raised over $67 million, according to Crunchbase data. Its most recent funding came last May, a $25 million round from Andreessen Horowitz, DNS Capital, Green Bay Ventures, M12 (Microsoft’s Venture Fund) and Grove.
Each of these purchases fills an important need for the acquiring company and expands the abilities of the existing platform to offer more functionality to customers without putting out a ton of cash to do it.
Powered by WPeMatico
SLAs, SLOs, SLIs. If there’s one thing everybody in the business of managing software development loves, it’s acronyms. And while everyone probably knows what a Service Level Agreement (SLA) is, Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service Level Indicators (SLIs) may not be quite as well known. The idea, though, is straightforward, with SLOs being the overall goals a team must hit to meet the promises of its SLA agreements, and SLIs being the actual measurements that back up those other two numbers. With the advent of DevOps, these ideas, which are typically part of a company’s overall Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) efforts, are becoming more mainstream, but putting them into practice isn’t always straightforward.
Nobl9 aims to provide enterprises with the tools they need to build SLO-centric operations and the right feedback loops inside an organization to help it hit its SLOs without making too many trade-offs between the cost of engineering, feature development and reliability.
The company today announced that it has raised a $21 million Series B round led by its Series A investors Battery Ventures and CRV. In addition, Series A investors Bonfire Ventures and Resolute Ventures also participated, together with new investors Harmony Partners and Sorenson Ventures.
Before starting Nobl9, co-founders Marcin Kurc (CEO) and Brian Singer (CPO) spent time together at Orbitera, where Singer was the co-founder and COO and Kurc the CEO, and then at Google Cloud, after it acquired Orbitera in 2016. In the process, the team got to work with and appreciate Google’s site reliability engineering frameworks.
As they started looking into what to do next, that experience led them to look into productizing these ideas. “We came to this conclusion that if you’re going into Kubernetes, into service-based applications and modern architectures, there’s really no better way to run that than SRE,” Kurc told me. “And when we started looking at this, naturally SRE is a complete framework, there are processes. We started looking at elements of SRE and we agreed that SLO — service level objectives — is really the foundational part. You can’t do SRE without SLOs.”
As Singer noted, in order to adopt SLOs, businesses have to know how to turn the data they have about the reliability of their services, which could be measured in uptime or latency, for example, into the right objectives. That’s complicated by the fact that this data could live in a variety of databases and logs, but the real question is how to define the right SLOs for any given organization based on this data.
“When you go into the conversation with an organization about what their goals are with respect to reliability and how they start to think about understanding if there’s risks to that, they very quickly get bogged down in how are we going to get this data or that data and instrument this or instrument that,” Singer said. “What we’ve done is we’ve built a platform that essentially takes that as the problem that we’re solving. So no matter where the data lives and in what format it lives, we want to be able to reduce it to very simply an error budget and an objective that can be tracked and measured and reported on.”
The company’s platform launched into general availability last week, after a beta that started last year. Early customers include Brex and Adobe.
As Kurc told me, the team actually thinks of this new funding round as a Series A round, but because its $7.5 million Series A was pretty sizable, they decided to call it a Series A instead of a seed round. “It’s hard to define it. If you define it based on a revenue milestone, we’re pre-revenue, we just launched the GA product,” Singer told me. “But I think just in terms of the maturity of the product and the company, I would put us at the [Series] B.”
The team told me that it closed the round at the end of last November, and while it considered pitching new VCs, its existing investors were already interested in putting more money into the company and since its previous round had been oversubscribed, they decided to add to this new round some of the investors that didn’t make the cut for the Series A.
The company plans to use the new funding to advance its roadmap and expand its team, especially across sales, marketing and customer success.
Powered by WPeMatico
Meet Powder, a French startup that helps you share video clips of your favorite games, follow people with the same interests and interact with them. The company has raised a $14 million Series A round led by Serena.
Powder wants to build the video infrastructure for social gaming. While many communities of gamers already share content on Twitch, Discord and Reddit, there isn’t a dominant mobile app focused on gaming.
You could call it an Instagram or Snapchat for gamers, but the startup has built specific tools that make it similar and yet different from those mainstream social platforms.
Powder can capture video content from any platform. You can record with your console and access your footage by connecting your account with Powder. You can capture videos on your PC using the company’s desktop app. You can also capture videos of mobile games.
The company tries to identify the most relevant events in your favorite game — it can be when you score a goal on Rocket League, when you are the last person standing in Fortnite, etc.
You can then trim your video, add filters, music and stickers and share a video with your followers. Other users can share reactions, add comments and send messages.
Image Credits: Powder
Overall, the company has raised $18 million and is pretty transparent about its funding story. In August 2018, the company raised a $400,000 pre-seed round with Kima Ventures and the co-founders of Zenly, Antoine Martin and Alexis Bonillo. In March 2019, General Catalyst, Slow Ventures, Dream Machine, SV Angel, Brian Pokorny, Florian Kahn and Guillaume Luccisano invested $1.5 million.
Around May 2020, the company had to raise a $1.3 million seed extension with Alven Capital, Seraam Invest, Farmers, Maxime Demeure, Jean-Nicolas Vernin and some existing investors. Bpifrance and CNC also put some money in the company. And now, Serena is leading the $14 million Series A round with General Catalyst, Slow Ventures, Alven Capital, Bpifrance’s Digital Venture fund, Secocha Ventures, Turner Novak and Kevin Hartz also participating in today’s round.
As you can see, it’s been a long and winding road. That’s because Powder didn’t come up with its social app for gamers overnight. The company tried many different consumer apps. It would iterate on an idea for a few weeks and then kill the concept if it didn’t pan out. With Powder, the company seems to have found a great distribution mechanism to attract more downloads, leading to more users.
“The idea behind Powder started in December 2019. We had already worked on several projects and none of them really took off. We thought we would create a community first and then a product,” co-founder and CEO Stanislas Coppin told me. He previously co-founded Mindie, a music video app.
Powder started as a Discord server with tens of thousands of members. The team then developed an app that would appeal to that community, the “metaverse camera” as Coppin says. Overall, 1.5 million people have downloaded the iOS app since its launch.
There are three other co-founders: Barthélémy Kiss, Yannis Mangematin and Christian Navelot. There are 18 employees and the company just launched on Android.
Image Credits: Powder
Powered by WPeMatico
Podz is the latest startup trying to solve the problem of podcast discovery, with backing from investors like M13, Katie Couric and Paris Hilton.
“Even though podcasts have gained a lot of momentum — there are 100 million folks in the U.S. who listen to podcasts — we still haven’t seen that crossover behavior, where audio becomes a part of everyday lives,” CEO Doug Imbruce argued. “We think that’s because the experience of discovering and consuming podcasts is ancient. It literally feels like browsing the web in 1997.”
Imbruce’s name may be familiar to longtime TechCrunch readers, as he was previously the chief executive at Qwiki, which won the Startup Battlefield at TechCrunch Disrupt in 2010 (Cloudflare was one of the runners up), then acquired by Yahoo a few years later.
By Imbruce’s own admission, Qwiki never quite lived up to his hopes for remaking online media consumption, but he said that its vision of “machine-created media” offered “a taste of the future” — a future that he’s hoping to help usher in with Podz.
The problem the startup aims to solve is pretty straightforward. Because podcasts often consist of 30 or 60 minutes or more of spoken-word audio, they’re difficult to browse, and when you discover new ones, it’s usually through word-of-mouth recommendations or clunky search tools.
While tools like Headliner make it easier for podcasters to promote their content with short clips on social media, Podz automates that creation process and makes those clips the centerpiece of the listening experience.
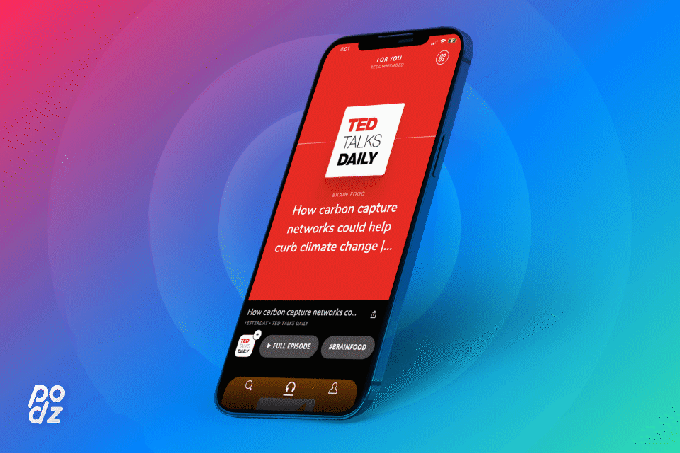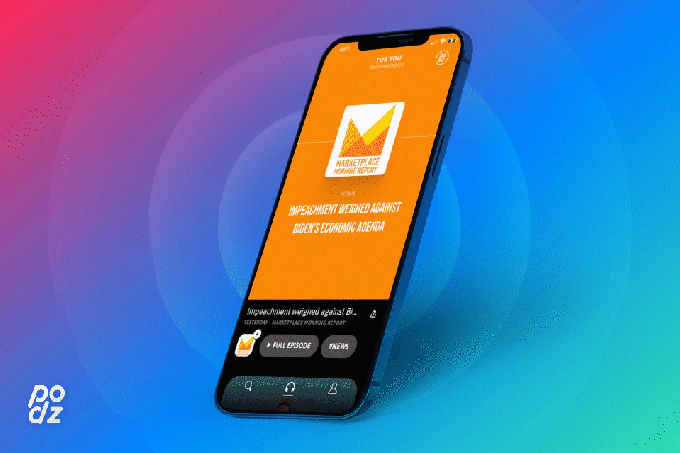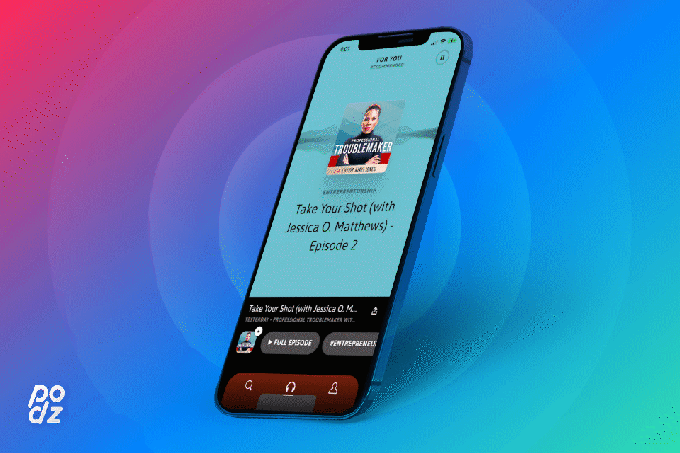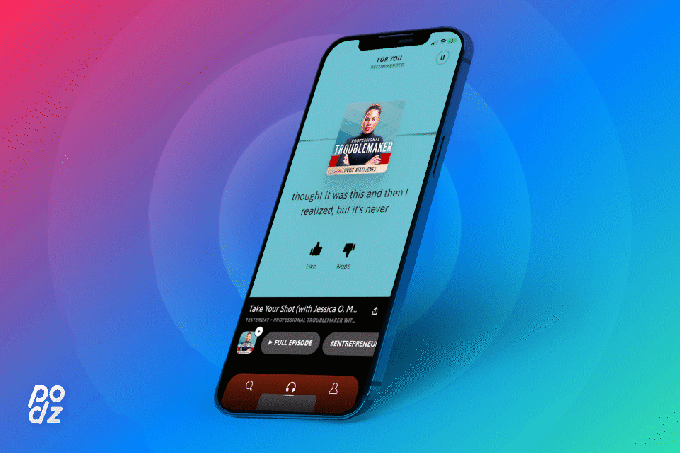
Image Credits: Podz
In the Podz mobile app, users browse what the startup calls “the first audio newsfeed,” consisting of 60-second podcast clips. These clips are designed to highlight the best moment from each podcast, making it easier to sample a much wider array of titles than the ones to which you currently subscribe. Each clip should stand on its own, but if you want to dive deeper, you can save the full episode for listening later.
These clips are created automatically, and Imbruce said “the beating heart of the Podz platform” is a machine learning model that “identifies the most engaging parts of podcasts.” The model was trained on more than 100,000 hours of audio, in consultation with journalists and audio editors.
For example, here are the clips chosen from the three most recent episodes of the Original Content podcast — our reviews of “Soul,” “The White Tiger” and “Bridgerton.” Each clip seems reasonably self-contained, and although I was a little dismayed to discover that they all focused on me (rather than my more eloquent co-hosts), a Podz spokesperson explained that’s because the app focuses on “the highest density speakers.”
The Podz newsfeed is personalized to your interests (and, if you choose, it also can draw on the podcasts you follow in Apple Podcasts and the accounts you follow on Twitter). Imbruce said it should become smarter over time as it observes listener behavior.
He added that the team is hoping to introduce more creative and monetization tools for podcasters over time: “We are really hopeful that we can both increase amount of audio being created by 10x and increase the monetization of audio by 100x.”
In addition to Imbruce, the Podz founding team includes CTO Seye Ojumu, Head of Design Rasmus Zwickson and iOS lead Greg Page. The startup has raised $2.5 million in pre-seed funding from M13, Canaan Partners, Charge Ventures and Humbition, as well as notable angel investors like Couric, Hilton (who’s launching her own podcast) and Mara Schiavocampo (The Trend Reporter).
“We are living in a golden age of audio, but only 1% of podcasts reach an audience of 5,000+,” M13 General Partner Latif Peracha told me via email. “Podz plans to grow the audience for existing audio but the real focus will be on growing new audio by leveraging their creator tools. Already, the average podcast listener subscribes to seven podcasts but follows almost 30 on Podz. Early signals make us optimistic the team can build a transformative product in the category.”
Powered by WPeMatico