Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Kaleido, makers of a drag-and-drop background removal service for images and video, have been acquired by up-and-coming digital design platform Canva. While the price and terms are not disclosed, it is speculated that this young company may have fetched nearly nine figures.
It’s the right product at the right time, seemingly. In 2019, the Vienna-based Kaleido made remove.bg, a quick, simple, free and good-enough background removal tool for images. It became a hit among the many people who need to quickly do that kind of work but don’t want to fiddle around in Photoshop.
Then late last year they took the wraps off Unscreen, which did the same thing for video — a similar task conceptually, but far more demanding to actually engineer and deploy. The simplicity and effectiveness of the tool practically begged to be acquired and integrated into a larger framework by the likes of Adobe, but Canva seems to have beaten the others to the punch.
The acquisition was announced at the same time as another by Canva: product mockup generator Smartmockups, suggesting a major product expansion by the growing design company.
“We completely bootstrapped Kaleido with no investors involved from day one,” said co-founder and CEO of Kaleido, Benjamin Groessing, in a press release. “It has just been two founders and an incredible team. We’ve been profitable from the start — so this acquisition wasn’t essential for our existence. It just made sense on so many levels.”
The company declined to provide any further details on the acquisition beyond that the brand and name are expected to survive — at least Unscreen, which makes perfect sense as a product name even under another company.
German outlets Die Presse and Der Brutkasten cited sources putting the purchase “reiht sich dahinter ein” or in the same rank as the largest Austrian exits (the largest of which was Runtastic at €220 million), though still in the two-digit millions — which suggests a price approaching $100M.
Whatever the exact amount, it seems to have made the team very happy. And don’t worry — they put that image together using their own product for each person.
Powered by WPeMatico
This morning MealMe.ai, a food search engine, announced that it has closed a $900,000 pre-seed round. Palm Drive Capital led the round, with participation from Slow Ventures and CP Ventures.
TechCrunch first became familiar with MealMe when it presented as part of the Techstars Atlanta demo day last October, mentioning it in a roundup of favorite startups from a group of the accelerator’s startup cohorts.
The company’s product allows users to search for food, or a restaurant. It then displays price points from various food-delivery apps for what the user wants to eat and have delivered. And, notably, MealMe allows for in-app checkout, regardless of the selected provider.
The service could boost pricing and delivery-speed transparency amongst the different apps that help folks eat, like DoorDash and Uber Eats. But Mealme didn’t start out looking to build a search engine. Instead it took a few changes in direction to get there.
MealMe is an example of a startup whose first idea proved only directionally correct. The company began life as a food-focused social network, co-founder Matthew Bouchner told TechCrunch. That iteration of the service allowed users to view posted food pictures, and then find ordering options for what they saw.
While still operating as a social network, MealMe applied to both Y Combinator and Techstars, but wasn’t accepted at either.
The startup discovered that some of its users were posting food pics simply to get the service to tell them which delivery services would be able to bring them what they wanted. From that learning the company focused on building a food search engine, allowing users to search for restaurants, and then vet various delivery options and prices. That iteration of the product got the company into Techstars Atlanta, eventually leading to the demo day that TechCrunch reviewed.
During its time in Techstars, the company adjusted its model to not merely link to DoorDash and others, but to handle checkout inside of its own application. This captures more gross merchandize value (GMV) inside of MealMe, Bouchner explained in an interview. The capability was rolled out in September of 2020.
Since then the company has seen rapid growth, which it measures at around 20% week-on-week. During TechCrunch’s interview with MealMe, the company said that it had reached a GMV run rate of more than $500,000, and was scaling toward the $1 million mark. In the intervening weeks the company passed the $1 million GMV run-rate threshold.
MealMe was slightly coy on its business model, but it appears to make margin between what it charges users for orders and the total revenue it passes along to food delivery apps.
TechCrunch was curious about platform risk at MealMe; could the company get away with offering price comparison and ordering across multiple third-party delivery services without raising the ire of the companies behind those apps? At the time of our interview, Bouchner said that his company had not seen pushback from the services it sends users to. His company’s goal is to grow quickly, become a useful revenue source for the DoorDashes of the world, and then reach out for some of formal agreement, he explained.
“We continue to be a powerful revenue generator and drive thousands of orders to food delivery services per week,” the co-founder said in a written statement. Certainly MealMe found investors more excited by its growth than concerned about Uber Eats or other apps cutting the startup off from their service.
What first caught my eye about MealMe was the realization of how much I would have used it in my early 20s. Perhaps the company can find enough users like my younger self to help it scale to sufficient size that it can go to the major food ordering companies and demand a cut, not merely avoid being cut off.
Powered by WPeMatico
Back when I was a wee lad with a very security-compromised MySQL installation, I used to answer every web request with multiple “SELECT *” database requests — give me all the data and I’ll figure out what to do with it myself.
Today in a modern, data-intensive org, “SELECT *” will kill you. With petabytes of information, tens of thousands of tables (on the small side!), and millions and perhaps billions of calls flung at the database server, data science teams can no longer just ask for all the data and start working with it immediately.
Big data has led to the rise of data warehouses and data lakes (and apparently data lake houses), infrastructure to make accessing data more robust and easy. There is still a cataloguing and discovery problem though — just because you have all of your data in one place doesn’t mean a data scientist knows what the data represents, who owns it or what that data might affect in the myriad web and corporate reporting apps built on top of it.
That’s where Select Star comes in. The startup, which was founded about a year ago (in March 2020), is designed to automatically build out metadata within the context of a data warehouse. From there, it offers a full-text search that allows users to quickly find data as well as “heat map” signals in its search results, which can quickly pinpoint which columns of a data set are most used by applications within a company and have the most queries that reference them.
The product is SaaS, and it is designed to allow for quick onboarding by connecting to a customer’s data warehouse or business intelligence (BI) tool.
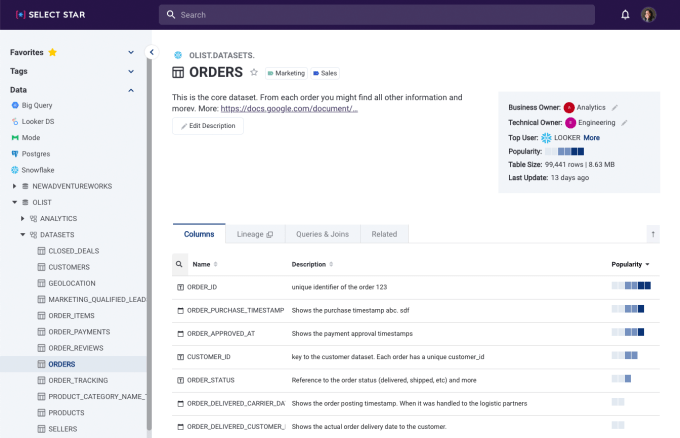
Select Star’s interface allows data scientists to understand what data they are looking at. Image via Select Star.
Shinji Kim, the sole founder and CEO, explained that the tool is a solution to a problem she has seen directly in corporate data science teams. She formerly founded Concord Systems, a real-time data processing startup that was acquired by Akamai in 2016. “The part that I noticed is that we now have all the data and we have the ability to compute, but now the next challenge is to know what the data is and how to use it,” she explained.
She said that “tribal knowledge is starting to become more wasteful [in] time and pain in growing companies,” and pointed out that large companies like Facebook, Airbnb, Uber, Lyft, Spotify and others have built out their own homebrewed data discovery tools. Her mission for Select Star is to allow any corporation to quickly tap into an easy-to-use platform to solve this problem.
The company raised a $2.5 million seed round led by Bowery Capital, with participation from Background Capital and a number of prominent angels including Spencer Kimball, Scott Belsky, Nick Caldwell, Michael Li, Ryan Denehy and TLC Collective.
Data discovery tools have been around in some form for years, with popular companies like Alation having raised tens of millions of VC dollars over the years. Kim sees an opportunity to compete by offering a better onboarding experience and also automating large parts of the workflow that remain manual for many alternative data discovery tools. With many of these tools, “they don’t do the work of connecting and building the relationship,” between data she said, adding that “documentation is still important, but being able to automatically generate [metadata] allows data teams to get value right away.”

Select Star’s team, with CEO and founder Shinji Kim in top row, middle. Image via Select Star.
In addition to just understanding data, Select Star can help data engineers begin to figure out how to change their databases without leading to cascading errors. The platform can identify how columns are used and how a change to one may affect other applications or even other data sets.
Select Star is coming out of private beta today. The company’s team currently has seven people, and Kim says they are focused on growing the team and making it even easier to onboard users by the end of the year.
Powered by WPeMatico
Virtual events platform Hopin is hopin’ for a mega valuation.
According to multiple sources who spoke with TechCrunch, the company, which was founded in mid-2019, is running around the fundraise circuit and perhaps nearing the end of a fundraise in which it is looking to raise roughly $400 million at a pre-money valuation of $5 billion for its Series C. The two names out in front, likely part of a joint ticket, are thought to be Andreessen Horowitz and General Catalyst.
Two sources implied that the valuation could have gone as high as $6 billion, but with greater dilution based on some offered terms the company has received. The deal is in flux, and both the round size and valuation are subject to change.
One source told TechCrunch that the company’s ARR has grown to $60 million, implying a valuation multiple of 80-100x if the valuation we’re hearing pans out. That sort of multiple wouldn’t be out of line with other major fundraises for star companies with SaaS-based business models.
Hopin has been on a fundraise tear in recent months. The company raised $125 million at a $2.125 billion valuation late last year for its Series B, which came just a few months after it raised a Series A of $40 million over the summer and a $6.5 million seed round last winter. All told, the roughly 20-month-old company has raised a known $171.4 million in VC according to Crunchbase.
When we last reported on the company, Hopin’s ARR had gone from $0 to $20 million, while its overall userbase had grown from essentially zero to 3.5 million users in November. The company reported then that it had 50,000 groups using its platform.
Hopin’s platform is designed to translate the in-person events experience into a virtual one, providing tools to recreate the experience of walking exhibition floors, networking one-on-one and spontaneously joining fireside chats and panels. It’s become a darling in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has seen most business and educational conferences canceled in the midst of mass restrictions on domestic and international travel worldwide.

It’s probably also useful to note that our business team uses Hopin to run all of TechCrunch’s editorial events, including Disrupt, Early Stage, Extra Crunch Live and next week’s TechCrunch Sessions: Justice 2021 event (these software selections and their costs are — thankfully — outside the purview of our editorial team).
Hopin may be the mega-leader of the virtual events space right now, but it isn’t the only startup trying to take on this suddenly vital industry. Run The World raised capital last year, Welcome wants to be the “Ritz-Carlton for event platforms,” Spotify is getting into the business, Clubhouse is arguably a contender here, InEvent raised a seed earlier this month and Hubilo is another entrant, which nabbed a check from Lightspeed a few months ago. Plus, quite literally dozens of other startups have either started in the space or are pivoting toward it.
We have reached out to Hopin for comment.
Post updated to report that Andreessen Horowitz and General Catalyst are in the lead.
Powered by WPeMatico
While more businesses are turning to text messages as a marketing channel, Emotive CEO Brian Zatulove argued that most of them are just treating it as another “newsletter blast.”
“The reason the channel performs so well is it’s not saturated,” Zatulove said. But that’s changing, and as it does, companies will have to do more to “cut through the noise.”
That’s what he said Emotive enables, with a platform focused on text marketing that feels like a real conversation with another human being, rather than just another email blast. He compared it to the sales associate who would greet you when you first walked into a department store, pre-COVID.
“The online sales associate really didn’t exist,” he said. “That’s what we’re trying to provide.”
Emotive saw 466% year-over-year revenue growth in 2020 and is announcing today that it has raised $50 million in a Series B funding round that values the company at $400 million. It was led by CRV, with participation from Mucker Capital, TenOneTen Ventures and Stripes.
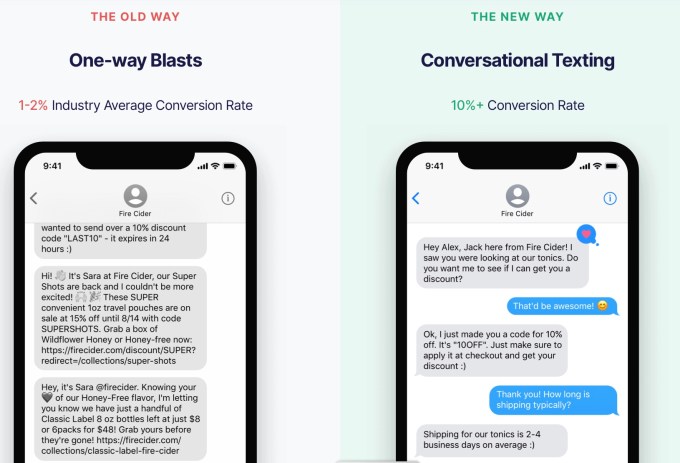
Image Credits: Emotive
“Never underestimate the importance of building a product that your customers, and your customers’ customers adore,” said CRV general partner Murat Bicer in a statement. “One of the things that struck us about Emotive is the sheer amount of customer love Brian and [co-founder Zachary Wise] get from meal delivery services, manufacturing companies and even toddler shoe brands. Small businesses find it easy to set up campaigns and their customers genuinely prefer communicating with someone over text rather than email.”
Zatulove said he founded the company with Wise after they’d worked together on cannabis loyalty startup Reefer, eventually deciding there was a bigger opportunity after their early successes with text marketing. He explained that while Emotive works with larger customers, its sweet spot is mid-sized e-commerce businesses on Shopify, Magento, BigCommerce and WooCommerce.
Because those businesses usually don’t have any salespeople of their own yet, Emotive serves that function. It can start conversations around shopping cart abandonment and promote sales and new products, resulting in what the company says are 8% to 10% conversion rates (compared to 1% or 2% for a standard text marketing campaign). Zatulove said the platform largely relied on human responders at first, and although it’s become increasingly automated, Emotive still has an internal team handling responses when necessary.
“We never plan on losing that human touch as part of the dialog,” he added. “We see ourselves as a human-to-human marketing platform. That’s our biggest differentiator.”
Emotive had previously raised $8.2 million in funding, according to Crunchbase. Zatulove said this new round will allow the company to continue developing the product, to grow its headcount to more than 200 people and to open offices in Atlanta and Boston. Eventually, it could also expand beyond texting.
“Longer term, we see ourselves more as a conversation platform, not just as a text message platform,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico
Amidst all the hype that Lemonade (IPO), Root (IPO), Metromile (SPAC-led debut) and other insurtech players have generated in the last year, it’s been easy to forget about Oscar Health. But now that the company founded in 2012 is approaching the public markets, one of the early tech-themed insurance companies is catching up on the attention front.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
So this morning we’re digging into Oscar Health’s first IPO pricing interval, hoping to understand how the market is valuing its unprofitable health-insurance enterprise.
 Recall that Oscar Health was valued at around $3.2 billion in March of 2018. That datapoint, via PitchBook, is dated. Oscar Health raised hundreds of millions since (per several venture-capital tracking databases, including Crunchbase) but we lack a final private valuation for the company.
Recall that Oscar Health was valued at around $3.2 billion in March of 2018. That datapoint, via PitchBook, is dated. Oscar Health raised hundreds of millions since (per several venture-capital tracking databases, including Crunchbase) but we lack a final private valuation for the company.
Regardless, with Oscar Health now targeting a $32 to $34 per-share IPO range, we can get our hands dirty.
Let’s get some valuation numbers and then decide if Oscar Health feels cheap or expensive at that price.
Oscar Health is looking to reap as much as $1.21 billion in its IPO, a huge sum. The company is selling 30,350,920 shares, with 4,650,000 additional shares reserved for its underwriters. Existing shareholders are selling another 649,080 shares.
This means that after the IPO, Oscar Health will have 197,037,445 Class A and B shares in circulation, or 201,687,445 after counting shares reserved for its underwriters.
Using the company’s $32 to $34 per-share range, we can calculate a valuation minimum of $6.31 billion for the company (lower share count, low-end of price range) and $6.86 billion (higher share count, high-end of price range). That’s the company’s simple IPO valuation.
Oscar Health may also sell up to $375 million of its shares at its IPO price to three different funds. The company advises that the “indication of interest is not a binding agreement or commitment to purchase,” so we can ignore it for now.
Powered by WPeMatico
This morning the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite index is off 2.34% after falling yesterday. Shares of Tesla are off more than 6% today, now mired in a bear-market correction after reaching new all-time highs earlier this year. Apple stock is worth $122.02 per share, down from its recent highs of more than $145.
After a long period of time when it felt like tech stocks only went up, the recent correction is starting to feel material.
There are other ways to measure the selloff. Bessemer’s cloud index is off 4.5% today, after falling over 5% yesterday. And the now-infamous $ARKK, or ARK Innovation ETF that many investors have used as a proxy for growthy tech stocks, is off 6.6% today after falling 5.9% yesterday.
Hell, even bitcoin has taken a pounding in the last few days, after its recent, relentless rise.
What’s driving the rapid turnaround in the value of tech companies, tech-focused indices and tech-adjacents, like cryptocurrencies? Not merely one thing, of course, in an environment as complex as the world’s capital markets. But there is a rising narrative that you should consider.
Namely that the money-is-cheap-and-bond-yield-is-garbage-so-everyone-is-putting-money-into-stocks trade is losing steam. As some yields rise, bonds are become more attractive bets. And as COVID-19 vaccines roll out, some investors are pushing their stock-market bets into categories other than tech.
The result is that the landscape of value is shifting; the winds that were at the back of every tech company are receding, at least for now. If the changed weather persists until the very investment climate that tech stocks exist in reaches a new equilibrium, we could see the appetite for tech IPOs lessen, late-stage private valuations for startup shares dip, and more.
Here’s CNBC from earlier today on what’s changing:
Stocks dropped again on Tuesday as tech shares continued to tumble in the face of higher interest rates and a rotation into stocks more linked to the economic comeback.
Here’s The Wall Street Journal on the same theme, from yesterday:
The lift in yields largely reflects investor expectations of a strong economic recovery. However, the collateral damage could include higher borrowing costs for businesses, more options for investors who had seen few alternatives to stocks and less favorable valuation models for some hot technology shares, investors and analysts said.
And here’s Barrons from this morning, noting that what we’re seeing at home is not merely a U.S. issue:
While members of the NYSE FANG+ index including Tesla, Facebook and Apple have dropped sharply as the yield on the 10-year Treasury has climbed, the sector also is on the retreat overseas.
Powered by WPeMatico
This morning Shippo, a software company that provides shipping-related services to e-commerce companies, announced a new $45 million investment. The new capital values the startup at $495 million. TechCrunch is calling the new funding a Series D as it is a priced round that followed its Series C; the company did not award the round a moniker.
Shippo’s 2020 Series C, a $30 million transaction that was announced last April, valued the company at around $220 million. D1 Capital led both Shippo’s Series C and D rounds, implying that it was content to pay around twice as much for the company’s equity in 2021 than it was in 2020. (Recall that investors doubling-down on previous bets as lead investor in successive rounds is no longer considered to be a negative signal concerning startup quality, but a positive indicator.)
Why raise more money so soon after its last round? According to Shippo CEO and founder Laura Behrens Wu, her company made material progress on customer acquisition and partnerships last year. That led to a decision around the time of Shippo’s Q4 board meeting with her investors that it was a good time to put more capital into the company.
In a sense the timing is reasonable. As Shippo scales its customer base, it can negotiate better shipping deals with various providers, which, in turn, help it continue to attract new customers. Behrens Wu noted in an interview with TechCrunch that when her company was helping its early customers ship just a few packages, shipping companies it supports on its platform didn’t want to meet with the startup. Now armed with more volume, Shippo can recycle customer demand into partner leverage, improving its total customer offering.
Behrens Wu said that Shippo had secured such a partnership with UPS before it raised its new round.
Turning to growth, Shippo doubled its platform spend, or “GPV” last year. GPV is the company’s acronym for gross postage volume. It roughly tracks with revenue, TechCrunch confirmed. So Shippo likely doubled its top-line last year. That’s good. Shippo wants to do that again this year, Behrens Wu told TechCrunch. The startup will also double its headcount this year, adding around 150 people.
Now flush with more capital, what’s next for Shippo? Per its CEO, the startup wants to invest more in platforms (where Shippo is baked into a marketplace, for example), international expansion (Shippo only does a “little bit” of international shipping, per Behrens Wu), and double-down on what it considers its core customer base.
TechCrunch was curious about how broad Shippo might take its product from its original home in shipping labels. The startup said that there’s lots of room in the journey of a package, from pre-purchase on, where her company might expand into. However, Behrens Wu cautioned that such a broadening of product work is not an immediate focus at her company.
Let’s see how long the current e-commerce boom lasts and how far this new capital can take Shippo. If it doubles in size again this year we’ll have to start its IPO countdown sometime in mid-2022.
Powered by WPeMatico
This morning Wisetack, a startup that provides buy-now-pay-later services to in-person business transactions, announced that is has closed a total of $19 million across two rounds, a seed investment and a Series A.
Greylock led both rounds, with the seed round clocking in at $4 million and the Series A at $15 million. Bain Capital Ventures also took part in the company’s fundraising.
Notably both rounds were closed in 2019, making these amongst the more aged rounds that we’ve heard of in recent quarters. However, as much venture reporting was delayed last year due to the pandemic and political unsettlement, I am still willing to cover the occasional antique deal.
Wisetack caught our eye not only due to its fundraising activity, but also thanks the buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) space becoming all the more interesting in the wake of Affirm’s direct listing. Affirm is perhaps the best-known service of its type, making its liquidity moment — and post-IPO performance — impactful for its broader business category.
But while Affirm wants to offer point-of-sale BNPL services to online merchants, Wisetack is taking a different approach. It focuses on the in-person business world, helping finance consumer transactions involving things like home improvement and car repair; the sort of big transactions that your average family might not have the cash to cover but also doesn’t want to put on a credit card.
Wisetack partners with vertical SaaS players in different areas. Say, plumbing. This allows users of those vertical SaaS applications — the plumbers, sticking to the same example — to offer Wisetack’s BNPL service to their customers.
It’s well known that vertical SaaS has wide application. A favorite recent example is SingleOps, which provides software for the so-called “green industry,” the world of lawns and landscaping. There’s SaaS for all sorts of IRL work, which could mean that Wisetack has a good number of software providers to sell into.
The model appears to be working, at least thus far. Wisetack shared with TechCrunch that its loan volume rose 20x between January of 2020 and January of 2021. As the company generates revenues from merchants (loan processing costs), and consumer interest, it’s likely that its revenue scales with loan volume. If the relationship is even closer to direct, Wisetack grew quite a lot last year.
The startup also said that the number of businesses using Wisetack grew 25-fold last year to a number in the “thousands.”
Wisetack fits neatly into a number of recent trends. The first is its work with vertical SaaS, a notable slice of the software market. The second is that Wisetack is another example of an API-led business, offering its service as a tech-powered add-on to other bits of code. And, third, that Wisetack had the same lead investor twice in sequential rounds. This sort of doubling-down from the venture community has become common in recent quarters as the signaling risk of having the lead twice in a row has been zeroed out by general investor enthusiasm for more equity in what appear to be winning startups.
Finally, the Wisetack round is interesting as it is nearly a sort of vertical BNPL, or at least a vertically focused BNPL. The company was reticent to share notes on how it comes to credit decisions, but we presume that all BNPL players that do focus on a particular niche or segment.
Powered by WPeMatico
Mobile advertising company ironSource is announcing its second acquisition of the year — Luna Labs, a startup that’s built a platform allowing app developers to create and manage video and playable ads.
When I first wrote about the startup in 2019, its main selling point was the ability to create those ads directly from the Unity game engine used by many developers. Since then, it has expanded its platform to support the creation of both playable and video ads (including unlimited variations of a gameplay video), manage their entire ad library, analyze their performance and even automatically optimize them based on install data. Its customers include Crazy Labs, Supersonic Studios, Lion Studios, Kwalee and Voodoo.
IronSource, meanwhile, has built a platform for mobile user growth and monetization. It was valued at more than $1 billion in its most recent funding round of more than $400 million, and in January it announced the acquisition of ad measurement company Soomla.
In a statement, ironSource’s co-founder and chief revenue officer Omer Kaplan said:
Our vision at ironSource is to build the most comprehensive growth platform for app developers, allowing them to focus on content creation and on building a great user experience, while we provide the infrastructure for their business expansion. Creatives are a key part of that and have only become more important as competition for user attention grows. But ad creative development and testing at scale is incredibly difficult and costly. Luna Labs solves that by bringing high quality end-to-end ad creation management to app developers, and we’re excited to be able to add that capability into the ironSource platform.
The financial terms of the acquisition were not disclosed. IronSource says that the Luna Labs team (currently based in the United Kingdom) will remain in its current offices, where it will continue developing its technology “under the ironSource umbrella.”
Powered by WPeMatico