Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
This is Equity Monday, our weekly kickoff that tracks the latest private market news, talks about the coming week, digs into some recent funding rounds and mulls over a larger theme or narrative from the private markets. You can follow the show on Twitter here and myself here — and make sure to check out our Friday show that featured the Square-Tidal deal, some recent IPOs and some super-neat rounds.
Much like today’s show, if I am being honest. Here’s the rundown:
A packed kickoff to what promises to be a packed week!
Equity drops every Monday at 7:00 a.m. PST, Wednesday, and Friday at 6:00 AM PST, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast, Spotify and all the casts!
Powered by WPeMatico
PayPal has announced that it plans to acquire Curv, a cryptocurrency startup based in Tel Aviv, Israel. Israeli newspaper Calcalist originally reported the move. And PayPal has now made an official announcement.
Curv is a cryptocurrency security company that helps you store your crypto assets securely. The company operates a cloud-based service that lets you access your crypto wallets without any hardware device.
Curv also lets you set up sophisticated policies so that the new intern cannot withdraw crypto assets without some sort of approval chain. Similarly, you can create allow lists so that regular transactions can go through more easily.
Behind the scenes, Curv uses multi-party computation to handle private keys. When you create a wallet, cryptographic secrets are generated on your device and on Curv’s servers. Whenever you’re trying to initiate a transaction, multiple secrets are used to generate a full public and private key.
Secrets are rotated regularly and you can’t do anything with just one secret. If somebody steals an unsecured laptop, a hacker cannot access crypto funds with the information stored on this device alone.
As you can see, Curv isn’t a cryptocurrency wallet for end users. The company offers its services to exchanges, brokers and over-the-counter desks. If you’re running a fund and you plan on buying a large amount of cryptocurrencies, you could also consider using Curv.
Finally, financial institutions that are looking for a solution to store digital assets and diversify their balance sheet could also work with Curv.
PayPal says that the Curv team will join the cryptocurrency group within PayPal. The payment giant has been gradually rolling out cryptocurrency products. It has partnered with Paxos so that users in the U.S. can buy, hold and sell cryptocurrencies from their PayPal account.
In the near future, PayPal also plans to let you buy and sell items using cryptocurrencies. During its most recent earnings release, the company also said that it plans to launch cryptocurrency products in other countries and in Venmo, the consumer fintech super app owned by PayPal.
Terms of the deal are undisclosed and the transaction should close at some point during the first half of 2021. Calcalist reported that PayPal was paying between $200 million and $300 million for the acquisition. A person close to the company says that the transaction was under $200 million. I guess we’ll find out what happened exactly in the next earnings release.
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Planted, a startup pursuing a unique method of creating a vegetarian chicken alternative, has raised an $18 million (CHF 17 million) Series A to expand its product offerings and international footprint. With new kebabs and pulled-style faux meats available and steak-like cuts in the (literal) pipeline, Planted has begun to set its sights outside central Europe.
The company was a spinout from ETH Zurich and made its debut in 2019, but has not rested on the success of its plain chicken recipe. Its approach, which relied on using pea protein and pea fiber extruded to recreate the fibrous structure of chicken for nearly 1:1 replacement in recipes, has proven to be adaptable for different styles and ingredients as well.
“We aim to use different proteins, so that there is diversity, both in terms of agriculture and dietary aspects,” said co-founder Christoph Jenny.
“For example our newly launched planted.pulled consists of sunflower, oat and yellow pea proteins, changing both structure and taste to resemble pulled pork rather than chicken. The great thing about the sunflower proteins, they are upcycled from sunflower oil production. Hence, we are establishing a circular economy approach.”
When I first wrote about Planted, its products were only being distributed through a handful of restaurants and grocery stores. Now the company has a presence in more than 3,000 retail locations across Switzerland, Germany and Austria, and works with restaurant and food service partners as well. No doubt this strong organic (so to speak) growth, and the growth of the meat alternative market in general, made raising money less of a chore.
The cash will be directed, as you might expect for a company at this stage, towards R&D and further expansion.
“The funding will be used to expand our tech stack, to commercialize our prime cuts that are currently produced at lab scale,” said Jenny. “On the manufacturing side we look to significantly increase our current capacity of half a ton per hour to serve the increasing demand coming from international markets, first in neighboring countries and then further into Europe and overseas.”
“We will further invest in our structuring and fermentation platforms. Combining structuring technologies with the biochemical toolboxes of natural microorganisms will allow us to create ultimately new products with transformative character – all clean, natural, healthy and tasty,” said co-founder Lukas Böni in a press release.
No doubt this all will also help lower the price, a goal from the beginning but only possible by scaling up.
As other companies in this space also raise money (incidentally, rather large amounts of it) and expand to other markets, competition will be fierce — but Planted seems to be specializing in a few food types that aren’t as commonly found, at least in the U.S., where sausages, ground “beef” and “chicken” nuggets have been the leading forms of meat alternatives.
No word on when Planted products will make it to American tables, but Jenny’s “overseas” suggests it is at least a possibility fairly soon.
The funding round was co-led by Vorwerk Ventures and Blue Horizon Ventures, with participation from Swiss football (soccer) player Yann Sommer and several previous investors.
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Welcome back to The TechCrunch Exchange, a weekly startups-and-markets newsletter. It’s broadly based on the daily column that appears on Extra Crunch, but free, and made for your weekend reading. Want it in your inbox every Saturday morning? Sign up here.
Ready? Let’s talk money, startups and spicy IPO rumors.
Despite some recent market volatility, the valuations that software companies have generally been able to command in recent quarters have been impressive. On Friday, we took a look into why that was the case, and where the valuations could be a bit more bubbly than others. Per a report written by few Battery Ventures investors, it stands to reason that the middle of the SaaS market could be where valuation inflation is at its peak.
Something to keep in mind if your startup’s growth rate is ticking lower. But today, instead of being an enormous bummer and making you worry, I have come with some historically notable data to show you how good modern software startups and their larger brethren have it today.
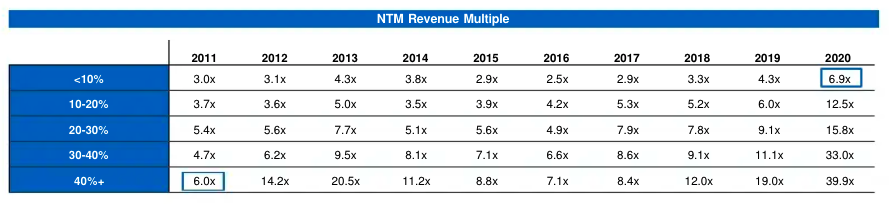
In case you are not 100% infatuated with tables, let me save you some time. In the upper right we can see that SaaS companies today that are growing at less than 10% yearly are trading for an average of 6.9x their next 12 months’ revenue.
Back in 2011, SaaS companies that were growing at 40% or more were trading at 6.0x their next 12 month’s revenue. Climate change, but for software valuations.
One more note from my chat with Battery. Its investor Brandon Gleklen riffed with The Exchange on the definition of ARR and its nuances in the modern market. As more SaaS companies swap traditional software-as-a-service pricing for its consumption-based equivalent, he declined to quibble on definitions of ARR, instead arguing that all that matters in software revenues is whether they are being retained and growing over the long term. This brings us to our next topic.
I’ve taken a number of earnings calls in the last few weeks with public software companies. One theme that’s come up time and again has been consumption pricing versus more traditional SaaS pricing. There is some data showing that consumption-priced software companies are trading at higher multiples than traditionally priced software companies, thanks to better-than-average retention numbers.
But there is more to the story than just that. Chatting with Fastly CEO Joshua Bixby after his company’s earnings report, we picked up an interesting and important market distinction between where consumption may be more attractive and where it may not be. Per Bixby, Fastly is seeing larger customers prefer consumption-based pricing because they can afford variability and prefer to have their bills tied more closely to revenue. Smaller customers, however, Bixby said, prefer SaaS billing because it has rock-solid predictability.
I brought the argument to Open View Partners Kyle Poyar, a venture denizen who has been writing on this topic for TechCrunch in recent weeks. He noted that in some cases the opposite can be true, that variably priced offerings can appeal to smaller companies because their developers can often test the product without making a large commitment.
So, perhaps we’re seeing the software market favoring SaaS pricing among smaller customers when they are certain of their need, and choosing consumption pricing when they want to experiment first. And larger companies, when their spend is tied to equivalent revenue changes, bias toward consumption pricing as well.
Evolution in SaaS pricing will be slow, and never complete. But folks really are thinking about it. Appian CEO Matt Calkins has a general pricing thesis that price should “hover” under value delivered. Asked about the consumption-versus-SaaS topic, he was a bit coy, but did note that he was not “entirely happy” with how pricing is executed today. He wants pricing that is a “better proxy for customer value,” though he declined to share much more.
If you aren’t thinking about this conversation and you run a startup, what’s up with that? More to come on this topic, including notes from an interview with the CEO of BigCommerce, who is betting on SaaS over the more consumption-driven Shopify.
Next Insurance bought another company this week. This time it was AP Intego, which will bring integration into various payroll providers for the digital-first SMB insurance provider. Next Insurance should be familiar because TechCrunch has written about its growth a few times. The company doubled its premium run rate to $200 million in 2020, for example.
The AP Intego deal brings $185.1 million of active premium to Next Insurance, which means that the neo-insurance provider has grown sharply thus far in 2021, even without counting its organic expansion. But while the Next Insurance deal and the impending Hippo SPAC are neat notes from a hot private sector, insurtech has shed some of its public-market heat.
Stocks of public neo-insurance companies like Root, Lemonade and MetroMile have lost quite a lot of value in recent weeks. So, the exit landscape for companies like Next and Hippo — yet-private insurtech startups with lots of capital backing their rapid premium growth — is changing for the worse.
Hippo decided it will debut via a SPAC. But I doubt that Next Insurance will pursue a rapid ramp to the public markets until things smooth out. Not that it needs to go public quickly; it raised a quarter billion back in September of last year.
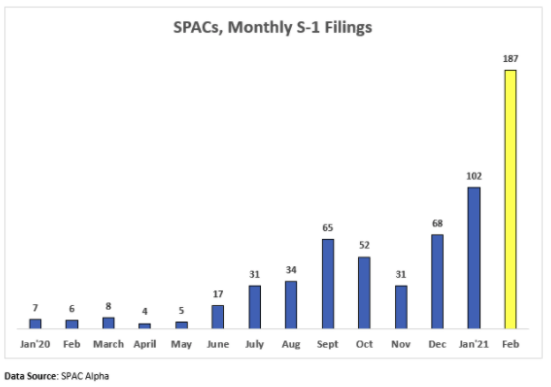
What else? Sisense, a $100 million ARR club member, hired a new CFO. So we expect them to go public inside the next four or five quarters.
And the following chart, which is via Deena Shakir of Lux Capital, via Nasdaq, via SPAC Alpha:
Powered by WPeMatico
After TechCrunch broke the news yesterday that Coursera was planning to file its S-1 today, the edtech company officially dropped the document Friday evening.
Coursera was last valued at $2.4 billion by the private markets, when it most recently raised a Series F round in October 2020 that was worth $130 million.
Coursera’s S-1 filing offers a glimpse into the finances of how an edtech company, accelerated by the pandemic, performed over the past year. It paints a picture of growth, albeit one that came at steep expense.
In 2020, Coursera saw $293.5 million in revenue. That’s a roughly 59% increase from the year prior when the company recorded $184.4 million in top line. During that same period, Coursera posted a net loss of nearly $67 million, up 46% from the previous year’s $46.7 million net deficit.
Notably the company had roughly the same noncash, share-based compensation expenses in both years. Even if we allow the company to judge its profitability on an adjusted EBITDA basis, Coursera’s losses still rose from 2019 to 2020, expanding from $26.9 million to $39.8 million.
To understand the difference between net losses and adjusted losses it’s worth unpacking the EBITDA acronym. Standing for “earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization,” EBITDA strips out some nonoperating costs to give investors a possible better picture of the continuing health of a business, without getting caught up in accounting nuance. Adjusted EBITDA takes the concept one step further, also removing the noncash cost of share-based compensation, and in an even more cheeky move, in this case also deducts “payroll tax expense related to stock-based activities” as well.
For our purposes, even when we grade Coursera’s profitability on a very polite curve it still winds up generating stiff losses. Indeed, the company’s adjusted EBITDA as a percentage of revenue — a way of determining profitability in contrast to revenue — barely improved from a 2019 result of -15% to -14% in 2020.
Powered by WPeMatico
Optimizely co-founder Dan Siroker said the idea for his new startup Scribe goes back to a couple of personal experiences — and although Scribe’s first product is focused on Zoom, those experiences weren’t Zoom-related at all.
Instead, Siroker recalled starting to go deaf and then having an “epiphany” the first time he put in a hearing aid, as he recovered a sense he thought he’d lost.
“That really was the spark that got me thinking about other opportunities to augment things your body naturally fails at,” he said.
Siroker added that memory was an obvious candidate, particularly since he also has aphantasia — the inability to visualize mental images, which made it “hard to remember certain things.”
It may jog your own memory if I note that Siroker founded Optimizely with Pete Koomen in 2010, then stepped down from the CEO role in 2017, with the testing and personalization startup acquired by Episerver last year. (And now Episerver itself is rebranding as Optimizely.)
Fast-forward to the present day and Siroker is now CEO at Scribe, which is taking signups for its first product. That product integrates into Zoom meetings and transforms them into searchable, shareable transcripts.
Siroker demonstrated it for me during our Zoom call. Scribe appears in the meeting as an additional participant, recording video and audio while creating a real-time transcript. During or after the meeting, users can edit the transcript, watch or listen to the associated moment in the recording and highlight important points.
From a technological perspective, none of this feels like a huge breakthrough, but I was impressed by the seamlessness of the experience — just by adding an additional participant, I had a full recording and searchable transcript of our conversation that I could consult later, including while I was writing this story.
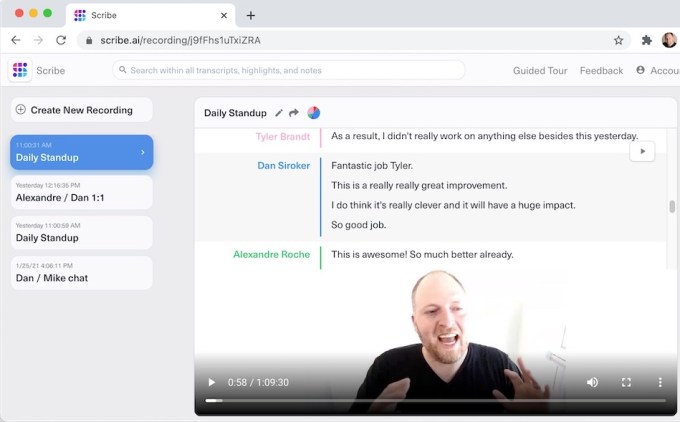
Image Credits: Scribe
Although Scribe is recording the meeting, Siroker said he wants this to be more like a note-taking replacement than a tape recorder.
“Let’s say you and I were meeting and I came to that meeting with a pen and paper and I’m writing down what you’re saying,” he said. “That’s totally socially acceptable — in some ways, it’s flattering … If instead, I brought a tape recorder and plopped in front of you and hit record — you might actually have this experience — with some folks, that feels very different.”
The key, he argued, is that Scribe recordings and transcripts can be edited, and you can also turn individual components on and off at any time.
“This is not a permanent record,” he said. “This is a shared artifact that we all create as we have a meeting that — just like a Google Doc — you can go back and make changes.”
That said, it’s still possible that Scribe could record some embarrassing comments, and the recordings could eventually get meeting participants in trouble. (After all, leaked company meeting recordings have already prompted a number of news stories.) Siroker said he hopes that’s “not common,” but he also argued that it could create an increased sense of transparency and accountability if it happens occasionally.
Scribe has raised around $5 million in funding, across a round led by OpenAI CEO Sam Altman and another led by First Round Capital.
Image Credits: Scribe
Siroker told me he sees Zoom as just the “beachhead” for Scribe’s ambitions. Next up, the company will be adding support for products like Google Meet and Microsoft Teams. Eventually, he hopes to build a new “hive mind” for organizations, where everyone is “smarter and better” because so many of their conversations and knowledge are now searchable.
“Where we go after that really depends on where we think we can have the biggest positive impact on people’s lives,” he said. “It’s harder to make a case for personal conversations you have with a spouse but … I think if you strike the right balance between value and privacy and control, you could really get people to adopt this in a way that actually is a win-win.”
And if Scribe actually achieves its mission of helping us to record and recall information in a wide variety of contexts, could that have an impact on our natural ability to remember things?
“Yes is the answer, and I think that’s okay,” he responded. “Your brain has limited energy … Remembering the things somebody said a few weeks ago is something a computer can do amazingly. Why waste your precious brain cycles doing that?”
Early Stage is the premier ‘how-to’ event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear first-hand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company-building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in – there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Eco, which has built out a digital global cryptocurrency platform, announced Friday that it has raised $26 million in a funding round led by a16z Crypto.
Founded in 2018, the SF-based startup’s platform is designed to be used as a payment tool around the world for daily-use transactions. The company emphasizes that it’s “not a bank, checking account, or credit card.”
“We’re building something better than all of those combined,” it said in a blog post. The company’s mission has also been described as an effort to use cryptocurrency as a way “to marry savings and spending,” according to this CoinList article.
Eco users can earn up to 5% annually on their deposits and get 5% cash back when transacting with merchants such as Amazon, Uber and others. Next up: The company says it will give its users the ability to pay bills, pay friends and more “all from the same, single wallet.” That same wallet, it says, rewards people every time they spend or save.
After a “successful” alpha test with millions of dollars deposited, the company’s Eco App is now available to the public.
A slew of other VC firms participated in Eco’s latest financing, including Founders Fund, Activant Capital, Slow Ventures, Coinbase Ventures, Tribe Capital, Valor Capital Group and more than one hundred other funds and angels. Expa and Pantera Capital co-led the company’s $8.5 million funding round.
CoinList co-founder Andy Bromberg stepped down from his role last fall to head up Eco. The startup was originally called Beam before rebranding to Eco “thanks to involvement by founding advisor, Garrett Camp, who held the Eco brand,” according to Coindesk. Camp is an Uber co-founder and Expa is his venture fund.
For a16z Crypto, leading the round is in line with its mission.
In a blog post co-written by Katie Haun and Arianna Simpson, the firm outlined why it’s pumped about Eco and its plans.
“One of the challenges in any new industry — crypto being no exception — is building things that are not just cool for the sake of cool, but that manage to reach and delight a broad set of users,” they wrote. “Technology is at its best when it’s improving the lives of people in tangible, concrete ways…At a16z Crypto, we are constantly on the lookout for paths to get cryptocurrency into the hands of the next billion people. How do we think that will happen? By helping them achieve what they already want to do: spend, save, and make money — and by focusing users on tangible benefits, not on the underlying technology.”
Eco is not the only crypto platform offering rewards to users. Lolli gives users free bitcoin or cash when they shop at over 1,000 top stores.
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Tech stocks are getting hammered today, with previously high-flying shares of software companies taking even more damage.
For a sector that has enjoyed a year in the sun, recent trading sessions have punctured a period of market adoration. It is too soon to say that the market is repricing tech stocks, but the selloff has reached the point of materiality and is therefore something we need to note.
As we write, the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite is off another 1.2% today after previous declines. The now-infamous ARK Innovation ETF is off 6.5% and the list of individual declines worth noting in the tech sector is very long indeed.
The change in sentiment is clear in recent results. Here’s the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite:
And the damage intensifies if we consider just SaaS and cloud stocks. Here’s the Bessemer cloud index:
In more prosaic terms, the Nasdaq is in a technical correction, while SaaS stocks have reached bear-market territory. That’s quite a turnabout from recent all-time highs for both.
Lost on the TechCrunch editing floor from late yesterday is a post we wrote noting the sharp declines in the value of insurtech stocks ahead of the impending public debut of Hippo, another neo-insurance company. The SPAC-led Hippo flotation will not touch down in a warm market. Instead, its contemporaries look like this today:
The damage is widespread. Hell, recent IPO success-story Snowflake announced yesterday that it grew from revenues of $88 million in its year-ago quarter to $190 million in its most recent. And its stock is off more than 7% today.
We’ll leave it to you whether the changing public valuations are just a blip or a more staid change in the winds. But it does feel different out there.
For startups, this is all somewhat poor news. Valuations for public comps were strong in 2020. To lose that halo in 2021 could crimp late-stage valuations, perhaps even reaching back to Series A and B rounds to limit some upside for growing upstarts. But such an impact will lag the public markets, so don’t expect things to change quite yet.
Still, every private investor has their eye on the exit when it comes to their deals. And if that exit is suddenly shrinking, so too might their interest in paying for quite so great a markup on their next deal.
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Pangea, a marketplace startup that wants to connect college freelancers and companies in need of digital help, is seeing its growth rate accelerate as it races toward the impending Y Combinator demo day.
It’s traditional around this time that startups in the accelerator reach out to say hello. Provided that they are willing to chat growth metrics, we’re willing to listen.
Pangea, based in Providence, Rhode Island, is one such company. TechCrunch previously covered the company when it announced a $400,000 pre-seed round last April. Now most of the way through the YC accelerator, the company dished regarding its recent growth and the fact that it added more capital to its accounts late last year.

The Pangea team, from their shared house/office. Via the company.
On the growth side of the coin, Pangea CEO Adam Alpert told TechCrunch the company has grown its gross merchandise volume (GMV) sequentially by 35% in each of the last two months. That’s a steep pace of GMV expansion. And the growth is adding up to real numbers, with Pangea facilitating $50,000 in transactions between college freelancers and businesses in the last four weeks.
Alpert said that its year-ago number was around $3,000 or $4,000.
And the company has managed to expand its market take rate to around 25%, tinkering with how it charges for its service. The result is a model that might resonate with anyone familiar with Fiverr, and may help the company more rapidly expand its net revenue.
The company’s recent growth comes after it secured another $350,000 in November 2020 at a higher cap to its previously known pre-seed round. And, of course, it raised $125,000 from Y Combinator, funds that landed in its accounts this January.
Pangea is now active in 600 campuses, Alpert said. And it has found where its service is most in-demand, namely among emerging brands and smaller tech startups. Those firms often need the types of services that college kids are good at — social media, design, etc. — making them a good fit.
The company was somewhat coy on upcoming product news but was clear that it’s looking for investing partners as it works toward Series A scale. Let’s see how Pangea does in a few weeks.
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
We’re not digging into another IPO filing today. You can read all about AppLovin’s filing here, or ThredUp’s document here.
This morning, instead, we’re talking about an old favorite: software valuations. The folks over at Battery Ventures have compiled a lengthy dive into the 2020 software market that’s worth our time — you can read along here; I’ll provide page numbers as we go — because it helps explain some software valuations.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
There’s little doubt that there is some froth in the software market, but it may not be where you think it is.
The Battery report has a lot of data points that we’ll also work through in this week’s newsletter, but this morning, let’s narrow ourselves to thinking about rising aggregate software multiples, the breakdown of multiples expansion through the lens of relative growth rates, and cap it off with a nibble on the importance, or lack thereof, of cash flow margins for the valuation of high-growth software companies.
 We’ll look at the changing public market perspective, and then ask ourselves if the aggregate image that appears is good or not good for software startups.
We’ll look at the changing public market perspective, and then ask ourselves if the aggregate image that appears is good or not good for software startups.
I chatted through pieces of the report with its authors, Battery’s Brandon Gleklen and Neeraj Agrawal. So, we’ll lean on their perspective a little as we go to help us move quickly. This is our Friday treat. Or at least mine. Let’s get into it.
Let’s start with an affirmation. Yes, software valuations have risen to record-high multiples in recent years. Here’s the Battery chart that makes the change clear:
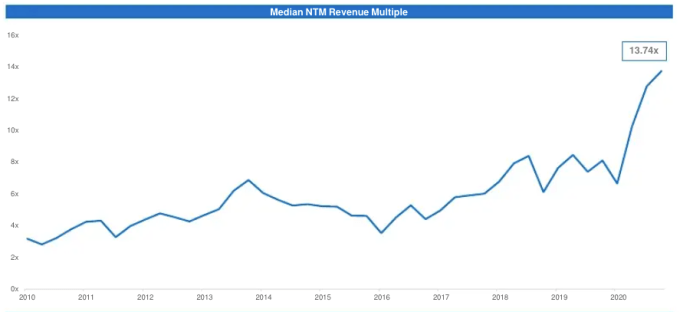
Page 31, Battery report. Image Credits: Battery Ventures
Powered by WPeMatico