Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
It’s Squarespace direct-listing day, and the SMB web hosting and design shop’s reference price has been set at $50 per share.
According to quick math from the IPO-watching group Renaissance Capital, Squarespace is worth $7.4 billion at that price, calculated using a fully diluted share count. The company’s new valuation is sharply under where Squarespace raised capital in March, when it added $300 million to its accounts at a $10 billion post-money valuation, according to Crunchbase data.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on Extra Crunch or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
The company’s reference price, however, is just that: a reference. It doesn’t mean that much. As we’ve seen from other notable direct listings, a company’s opening price does not necessarily align with its formal reference price. Until Squarespace opens, whether it will be valued at a discount to its final private price is unclear.
 While the benefits of a direct listing are understood, the post-listing performance for well-known direct listings is less obvious. Indeed, Coinbase is currently under its reference price after starting its life as a public company at a far-richer figure, and Spotify’s share price is middling at best compared to its 2018-era direct-listing reference price.
While the benefits of a direct listing are understood, the post-listing performance for well-known direct listings is less obvious. Indeed, Coinbase is currently under its reference price after starting its life as a public company at a far-richer figure, and Spotify’s share price is middling at best compared to its 2018-era direct-listing reference price.
This morning, we’re going over Squarespace’s recently disclosed Q2 and full-2021 guidance. Then we’ll ask how its expectations compare to its reference price-defined pre-trading valuation. Finally, we’ll set some stakes in the ground regarding historical direct-listing results and what we might expect from the company as it adds a third set of data to our quiver.
This will be lots of fun, so let’s get into the numbers!
Per Squarespace’s own reporting, it expects revenues between $186 million and $189 million in Q2 2021, which it calculates as a growth rate of between 24% and 26%. That pace of growth at its scale is perfectly acceptable for a company going public.
For all of 2021, Squarespace expects revenues of $764 million to $776 million, which works out to a very similar 23% to 25% growth rate.
In profit terms, Squarespace only shared its “non-GAAP unlevered free cash flow,” which is a technical thing I have no time to explain. But what matters is that the company expects some non-GAAP unlevered free cash flow in Q2 2021 ($10 million to $13 million), and lots more in all of 2021 ($100 million to $115 million).
Powered by WPeMatico
The podcasting world remains one of the most vibrant formats in media (and I am not just saying that since the Equity crew won a Webby yesterday for our not-that-humble podcast). Its openness, diversity, freedom and ease-of-authoring has broadened the medium to all sorts of hosts on every subject imaginable.
We experience that dynamism and verve in our own audio listening, but then we start to tune into our company’s internal communications, and, well, you certainly don’t need sleeping pills to zone out. Top-down, formal, banal — corporate comms remains mired in a 1950s way of speaking that is completely out-of-sync with the millennials and Gen Z majority of workers who expect something actually worth watching and listening to.
Spokn wants to make company-wide podcasting a must-listen event, not just for leaders to talk to their employees, but for every worker to have a voice and share their expertise and stories across their workplaces. Through its app, companies can deliver personalized podcast feeds on everything from a daily standup or weekly AMA to training and development content, all of which is secure and kept for internal use.
It’s an idea that has quickly attracted investor attention. The startup, which was part of Y Combinator’s most recent Winter 2021 batch, closed on a $4 million seed round two weeks before Demo Day led by Ann Bordetsky, a partner at NEA who joined earlier this year and previously served as COO of Rival. This is her first investment with the firm.
The company was founded by Fawzy Abu Seif, Mariel Davis and Mohammad Galal Eldeen. Abu Seif and Davis met each other in an Egyptian jazz club in November 2017, about a week after he had quit his job. They eventually came together not just as a couple — they got married in the fall of 2019 — but as business partners, linking up with Galal Eldeen and incorporating Spokn in April 2018.

Spokn’s Mohammad Galal Eldeen, Mariel Davis and Fawzy Abu Seif. Image Credits: Spokn
Spokn’s product evolved across three iterations. First, the team tried to create audio narrations of evergreen content at major publishers like The New York Times. The idea was to help publishers reuse their best content as a new revenue source while connecting more listeners into these brands. Getting publishers to commit was tough though. “The consumer app wasn’t doing that great, and we started hunting around the data to see if something was working,” Davis said.
What they found was that professional development podcasts were much more popular compared to other topics, and so they had an opportunity to re-jigger the product to focus on training and specifically target enterprises. The idea was “let’s empower companies with the same tools we had as a consumer company,” Abu Seif said.
Prior to Spokn, Davis had worked with an entrepreneur in the Middle East building out a social enterprise network focused on skills training, a role in which she handled internal communications. She saw just how little impact media like email made for employees, particularly in the distributed workforce she was attempting to engage. The new direction for Spokn was far more enticing.
The newly married couple moved to New York City from Egypt and signed an apartment lease in early March 2020 — just as the COVID-19 pandemic spread widely in the region. We “multiplied the living expenses by 8-10x while doing the same Zoom calls we could make from there,” Abu Seif joked.
Eventually, the company realized that it could do much more than just training, and expanded into broader internal comms. “Async audio is a lot more personal than email,” Abu Seif said. This latest product iteration launched in November 2020, and included push notifications, an app for streaming, personalization features and analytics to allow companies to track what was working and what was not for employees.
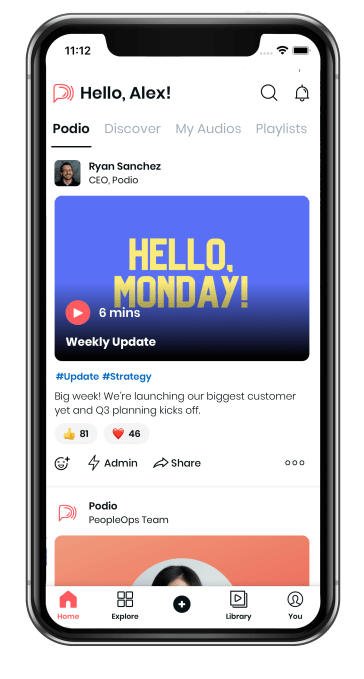
Spokn’s app offers a personalized feed of company podcasts. Image Credits: Spokn
Perhaps most importantly, companies can tailor the access lists for individual podcasts to particular groups of people, such as senior execs, people managers, sales employees or any other logical grouping. We “get a lot of inbound from companies that are trying to duct-tape solutions together,” Davis said. For Abu Seif, “all the tools that marketers have to engage consumers, we are empowering companies to engage with their employees.”
Despite the startup and product’s youth, it has attracted a quick following among companies, with customers including Podium, ShipBob, Cedar, Mixpanel, ServiceNow and Superhuman. Podium’s CEO, for example, records weekly podcasts that are shipping on Spokn, and apparently even installed a podcast studio near his office just to make it easier to produce his shows.
Podcasting inside companies fixes a lot of problems with traditional internal comms. First and foremost, it can create a deeper connection where email cannot. Audio can feel more personal than even video, and also can be played in the background. It’s also asynchronous, unlike live video, allowing employees in different time zones to connect with key stories at an appropriate time.
Plus, employees can avoid all the fatigue that comes from being onscreen. “No one wants Zoom zombies,” Bordetsky of NEA said. “We need intuitive and asynchronous communication tools like Spokn to build connection and community in the workplace.” Her thesis for the investment is that “flexible, distributed work is here to stay and employee communication is at the heart of building a modern, virtual-first employee experience.”
Buyers of Spokn range from heads of people to sales teams, and the company is also focused on recruiting and retention as well. “Companies are pretty freaked out about retaining their great talent,” Davis said. Some companies are now sharing “stories with prospects even before their first day at the company.”
While the product is mostly used by leaders today, Spokn wants to expand that remit to employees talking with their peer colleagues, helping to build community in hybrid offices where it is harder than ever to make a connection with others.
Of course, companies can screw up podcasting just as much as they have screwed up every other medium to communicate like humans, and Davis says it’s become her full-time job to help them think through storytelling and how to connect better with their own employees. We “work to find the right storytellers in the company,” she said.
Outside NEA, other investors in the seed round included Reach Capital, Funders Club, Liquid2, Share Capital, SOMA Capital, Scribble VC and Hack VC.
Powered by WPeMatico
Unbounce, a Vancouver startup best known for helping marketers create automated landing pages, added a new wrinkle this morning when it announced it has acquired Snazzy.ai, an early-stage automated copywriting startup. The two companies did not share the terms.
Unbounce Chief Strategy Officer Tamara Grominsky says that her company focuses on helping customers convert their customers into sales, and with Snazzy, it gets some pretty nifty technology based on GPT-3 artificial intelligence technology.
“We’re focused right now on building conversion intelligence software that will allow marketers to work with machines to really unlock their true conversion potential […] and we saw a huge opportunity with Snazzy to focus particularly on the content creation and copy creation space to help us accelerate that strategy,” Grominsky explained.
She points out that the product is really aimed at the marketing generalist charged with overseeing landing pages, and who is responsible for a range of tasks including writing copy. “The average Unbounce customer isn’t a specialized copywriter, so they don’t spend [their work] day writing copy. They’re what we would consider a marketing generalist or really someone who’s responsible for a wide range of marketing responsibilities,” she said.
Snazzy co-founder Chris Frantz says the tech is really about getting people started, and then they can tweak the results as needed. “The hardest part has always been to get that first line, that first page, the first couple of words in — and we eliminate that entirely. That might not always result in amazing copy, but on the plus side you can always click the button again and give it another try,” he said.
Frantz says that with so much competition in the space, he and his co-founder felt they could build a market much faster as part of a larger and broader marketing platform solution like Unbounce.
“I love Tamara’s vision for the future of Unbounce. I think she has a very ambitious vision. She sold me on that very early on in the process. At the same time, there was a lot of competition in the space, and to have a key differentiator with a company like Unbounce, which has a decade of marketing experience and a lot of trust within this community, I think it’s a very powerful wedge that we can use to further grow our audience,” Frantz said.
The tool lets you write a range of copy, from landing pages to Google ad copy. The company launched in alpha last October and already had 30,000 customers, which Grominsky says Unbounce hopes to convert into customers. The good news for those customers is that the company plans to leave Snazzy as a standalone product, while incorporating the tech into the platform in ways that make sense in the coming year.
Powered by WPeMatico
The University of Tokyo Edge Capital Partners (UTEC), a deep-tech investment firm, announced the first close of its fifth fund, which is expected to total 30 billion JPY (or about $275 million USD) by June 2021. UTEC currently has about $780 million in total assets under management, and says this makes it one of the largest venture capital funds focused on science and tech in Japan, and one of the largest deep-tech funds in Asia.
UTEC is an independent firm that works closely with universities. It is associated with The University of Tokyo (UTokyo), where it has a partnership with its Technology Licensing Office (TLO) to spin off and invest in companies that originated as research projects. It has also worked with researchers from Waseda University, Kyoto University, Stanford, UC Berkeley, Carnegie Mellon, Cambridge University, the National University of Singapore and the Indian Institute of Technology, among other institutions.
Broadly speaking, UTEC focuses on three areas: healthcare and life sciences, information technology and physical sciences and engineering. More specifically, it is looking for tech that addresses some of the most important issues in Japan, including an aging population, labor shortage and the digitization of legacy industries.
“UTEC 5 will allow us to provide more funds from seed/early to pre-IPO/M&A stages in Japan and worldwide, on a wider scale and in a more consistent manner,” said managing partner and president Tomotaka Goji in a statement. “I believe this will further help our startups expand to address the global issues of humankind.”
The firm also partners with other funds, including Arch Venture Partners and Blume Ventures, to find investment opportunities around the world.
UTEC’s portfolio already includes more than 80 Japanese startups and 30 startups from other places, including the United States, India, Southeast Asia and Europe. So far, 25 of its investments have exited. Thirteen went public and now have an aggregated market cap of about $15 billion, and 12 were through mergers and acquisitions.
Some of its exits include 908 Devices, a mass spectrometry company that went public on Nasdaq last year; Fyusion, a computer vision startup acquired by Cox Automotive; and Phyzios, which was acquired by Google in 2013.
About half of UTEC’s portfolio are university spin-offs. For companies that originated in academic research, UTEC supports their commercialization by helping hire crucial talent, including executive positions, business development and go-to-market strategies. The firm’s first check size is about $500,000 to $5 million, and it also usually provides follow-on capital.
“We typically double-down on our investment in subsequent funding rounds of the company and can invest up to about $23 million per company over its lifecycle,” UTEC principal Kiran Mysore, who leads their global AI investments, told TechCrunch.
UTEC’s other investments include personal mobility robotics company BionicM, which started at UTokyo and spatial intelligence solution developer Locix, spun-off from UC Berkeley. The firm also helps startups collaborate with academic institutions. For example, Indian biotech Bugworks collaborates with the Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japanese industrial robotics startup Mujin now works with Carnegie Mellon.
Powered by WPeMatico
Düsseldorf-based proptech startup Dabbel is using AI to drive energy efficiency savings in commercial buildings.
It’s developed cloud-based self-learning building management software that plugs into the existing building management systems (BMS) — taking over control of heating and cooling systems in a way that’s more dynamic than legacy systems based on fixed set-point resets.
Dabbel says its AI considers factors such as building orientation and thermal insulation, and reviews calibration decisions every five minutes — meaning it can respond dynamically to changes in outdoor and indoor conditions.
The 2018-founded startup claims this approach of layering AI-powered predictive modelling atop legacy BMS to power next-gen building automation is able to generate substantial energy savings — touting reductions in energy consumption of up to 40%.
“Every five minutes Dabbel reviews its decisions based on all available data,” explains CEO and co-founder, Abel Samaniego. “With each iteration, Dabbel improves or adapts and changes its decisions based on the current circumstances inside and outside the building. It does this by using cognitive artificial intelligence to drive a Model-Based Predictive Control (MPC) System… which can dynamically adjust all HVAC setpoints based on current/future conditions.”
In essence, the self-learning system predicts ahead of time the tweaks that are needed to adapt for future conditions — saving energy vs a pre-set BMS that would keep firing the boilers for longer.
The added carrot for commercial building owners (or tenants) is that Dabbel squeezes these energy savings without the need to rip and replace legacy systems — nor, indeed, to install lots of IoT devices or sensor hardware to create a ‘smart’ interior environment; the AI integrates with (and automatically calibrates) the existing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
All that’s needed is Dabbel’s SaaS — and less than a week for the system to be implemented (it also says installation can be done remotely).
“There are no limitations in terms of Heating and Cooling systems,” confirms Samaniego, who has a background in industrial engineering and several years’ experience automating high tech plants in Germany. “We need a building with a Building Management System in place and ideally a BACnet communication protocol.”
Average reductions achieved so far across the circa 250,000m² of space where its AI is in charge of building management systems are a little more modest but a still impressive 27%. (He says the maximum savings seen at some “peak times” is 42%.)
The touted savings aren’t limited to a single location or type of building/client, according to Dabbel, which says they’ve been “validated across different use cases and geographies spanning Europe, the U.S., China, and Australia”.
Early clients are facility managers of large commercial buildings — Commerzbank clearly sees potential, having incubated the startup via its early-stage investment arm — and several schools.
A further 1,000,000m² is in the contract or offer phase — slated to be installed “in the next six months”.
Dabbel envisages its tech being useful to other types of education institutions and even other use-cases. (It’s also toying with adding a predictive maintenance functionality to expand its software’s utility by offering the ability to alert building owners to potential malfunctions ahead of time.)
And as policymakers around the global turn their attention to how to achieve the very major reductions in carbon emissions that are needed to meet ambitious climate goals the energy efficiency of buildings certainly can’t be overlooked.
“The time for passive responses to addressing the critical issue of carbon emission reduction is over,” said Samaniego in a statement. “That is why we decided to take matters into our own hands and develop a solution that actively replaces a flawed human-based decision-making process with an autonomous one that acts with surgical precision and thanks to artificial intelligence, will only improve with each iteration.”
If the idea of hooking your building’s heating/cooling up to a cloud-based AI sounds a tad risky for Internet security reasons, Dabbel points out it’s connecting to the BMS network — not the (separate) IT network of the company/building.
It also notes that it uses one-way communication via a VPN tunnel — “creating an end-to-end encrypted connection under high market standards”, as Samaniego puts it.
The startup has just closed a €3.6 million (~$4.4M) pre-Series A funding round led by Target Global, alongside main incubator (Commerzbank’s early-stage investment arm), SeedX, plus some strategic angel investors.
Commenting in a statement, Dr. Ricardo Schaefer, partner at Target Global, added: “We are enthusiastic to work with the team at Dabbel as they offer their clients a tangible and frictionless way to significantly reduce their carbon footprint, helping to close the gap between passive measurement and active remediation.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Meet Finary, a new French startup that wants to change how you manage your savings, investments, mortgage, real estate assets and cryptocurrencies. The company lets you aggregate all your accounts across various banks and financial institutions so you can track your wealth comprehensively over time.
After attending Y Combinator, the startup has just closed a $2.7 million (€2.2 million) seed round led by Speedinvest, with Kima Ventures and angel investors such as Raphaël Vullierme also participating.
If you know people who have a ton of money, chances are they tend to be at least 40 or 50 years old — you don’t become rich overnight, after all. And they tend to manage their investment portfolio through a wealth management service with tailor-made services.
“There’s very little tech in wealth management. Advisors are also incentivized to sell you some financial products in particular,” co-founder and CEO Mounir Laggoune told me. In that situation, the company in charge of the financial product is generating revenue for the advisor — not the client.
At the same time, a new generation of investors is starting to accumulate a lot of wealth. And yet, they don’t have the right tools to allocate it properly. Younger people want to see information directly. They want a way to track information in real time, or near real time. And they want to be able to take some actions based on that data.
Finary wants to build that service based on those principles. It starts with an API-based aggregator. When you create a Finary account, you can connect it with all your other accounts — bank accounts, brokerage accounts, mortgage and real estate, gold, cryptocurrencies, etc.
The startup leverages various open banking APIs to be as exhaustive as possible. For instance, “you can connect a Robinhood account and a Crédit Mutuel de Bretagne account,” Laggoune said. Behind the scenes, Finary uses Plaid and Budget Insight, runs its own bitcoin and Ethereum nodes to track wallet addresses, and estimates the value of your home through public data and a proprietary algorithm.
After that, you can see how much money you have, how it is divided between your investment pools, the current value of your gold and cryptocurrency assets and more.
“Our long-term vision is that we want to build a virtual wealth manager for Europe,” Laggoune said.
That’s why Finary recently launched its premium subscription called Finary+. With a premium account, you can see how much you’re paying in fees and track your performance — more features will get added over time.
A few months after launching its platform, Finary already tracks €2 billion in assets across thousands of users. With today’s funding round, the startup will roll out its service to more countries and more financial institutions in France, Europe and the U.S. The company is also working on mobile apps.
This is an interesting take on wealth management, as Finary doesn’t try to reinvent the wheel. Legacy players want you to use a single bank for all your financial needs. But you end up paying a lot of fees and you have to use old and clunky interfaces.
Finary isn’t yet another wealth management service. It’s a holistic service that lets you use multiple banks and services while remaining on top of your assets.
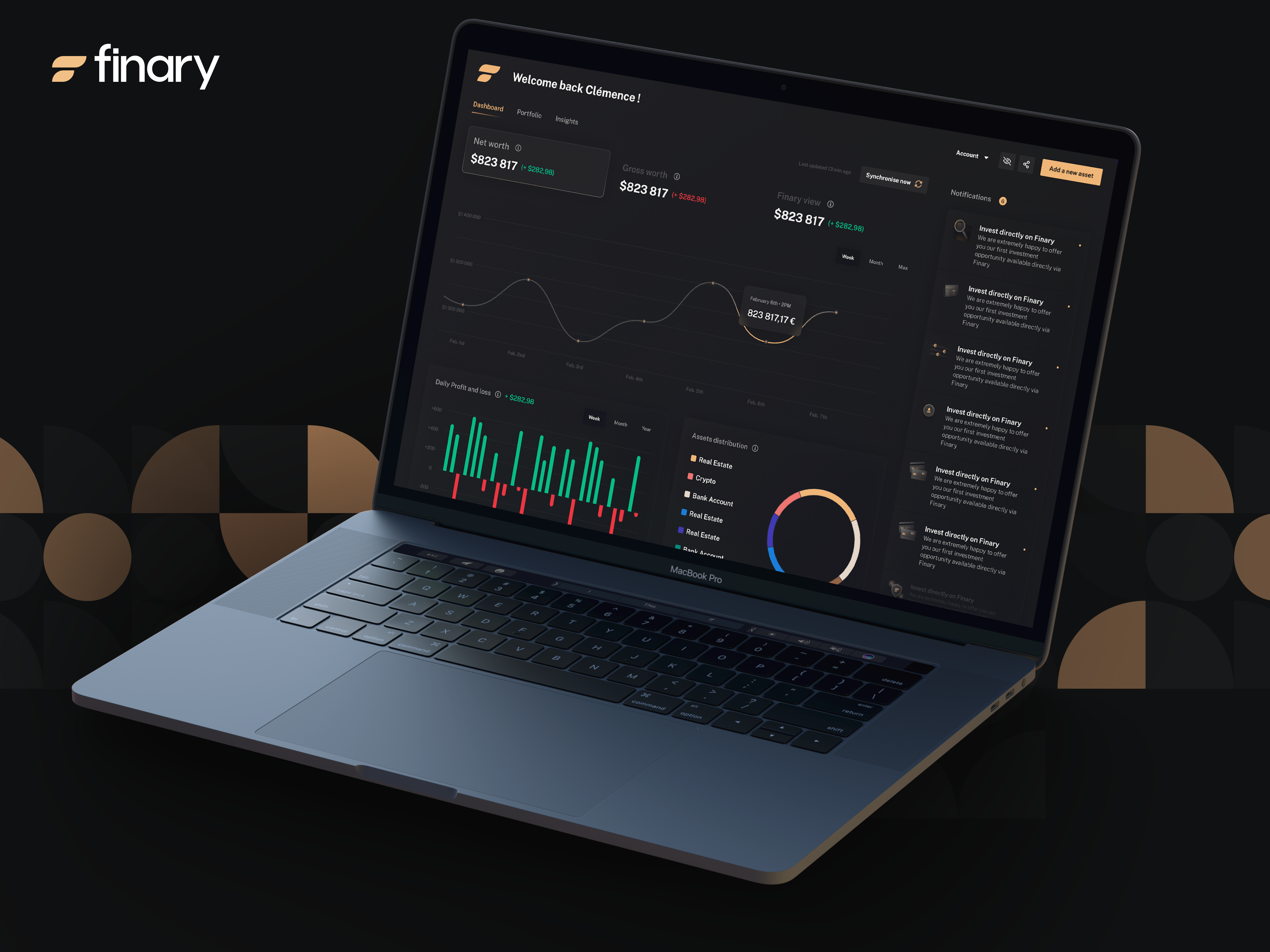
Image Credits: Finary
Powered by WPeMatico
Like “innovation,” machine learning and artificial intelligence are commonplace terms that provide very little context for what they actually signify. AI/ML spans dozens of different fields of research, covering all kinds of different problems and alternative and often incompatible ways to solve them.
One robust area of research here that has antecedents going back to the mid-20th century is what is known as stochastic optimization — decision-making under uncertainty where an entity wants to optimize for a particular objective. A classic problem is how to optimize an airline’s schedule to maximize profit. Airlines need to commit to schedules months in advance without knowing what the weather will be like or what the specific demand for a route will be (or, whether a pandemic will wipe out travel demand entirely). It’s a vibrant field, and these days, basically runs most of modern life.
Warren B. Powell has been exploring this problem for decades as a researcher at Princeton, where he has operated the Castle Lab. He has researched how to bring disparate areas of stochastic optimization together under one framework that he has dubbed “sequential decision analytics” to optimize problems where each decision in a series places constraints on future decisions. Such problems are common in areas like logistics, scheduling and other key areas of business.
The Castle Lab has long had industry partners, and it has raised tens of millions of dollars in grants from industry over its history. But after decades of research, Powell teamed up with his son, Daniel Powell, to spin out his collective body of research and productize it into a startup called Optimal Dynamics. Father Powell has now retired full-time from Princeton to become chief analytics officer, while son Powell became CEO.
The company raised $18.4 million in new funding last week from Bessemer led by Mike Droesch, who recently was promoted to partner earlier this year with the firm’s newest $3.3 billion fundraise. The company now has 25 employees and is centered in New York City.
So what does Optimal Dynamics actually do? CEO Powell said that it’s been a long road since the company’s founding in mid-2017 when it first raised a $450,000 pre-seed round. We were “drunkenly walking in finding product-market fit,” Powell said. This is “not an easy technology to get right.”
What the company ultimately zoomed in on was the trucking industry, which has precisely the kind of sequential decision-making that father Powell had been working on his entire career. “Within truckload, you have a whole series of uncertain variables,” CEO Powell described. “We are the first company that can learn and plan for an uncertain future.”
There’s been a lot of investment in logistics and trucking from VCs in recent years as more and more investors see the potential to completely disrupt the massive and fragmented market. Yet, rather than building a whole new trucking marketplace or approaching it as a vertically integrated solution, Optimal Dynamics decided to go with the much simpler enterprise SaaS route to offer better optimization to existing companies.
One early customer, which owned 120 power units, saved $4 million using the company’s software, according to Powell. That was a result of better utilization of equipment and more efficient operations. They “sold off about 20 vehicles that they didn’t need anymore due to the underlying efficiency,” he said. In addition, the company was able to reduce a team of 10 who used to manage trucking logistics down to one, and “they are just managing exceptions” to the normal course of business. As an example of an exception, Powell said that “a guy drove half way and then decided he wanted to quit,” leaving a load stranded. “Trying to train a computer on weird edge events [like that] is hard,” he said.
Better efficiency for equipment usage and then saving money on employee costs by automating their work are the two main ways Optimal Dynamics saves money for customers. Powell says most of the savings come in the former rather than the latter, since utilization is often where the most impact can be felt.
On the technical front, the key improvement the company has devised is how to rapidly solve the ultra-complex optimization problems that logistics companies face. The company does that through value function approximation, which is a field of study where instead of actually computing the full range of stochastic optimization solutions, the program approximates the outcomes of decisions to reduce compute time. We “take in this extraordinary amount of detail while handling it in a computationally efficient way,” Powell said. That’s where we have really “wedged ourselves as a company.”
Early signs of success with customers led to a $4 million seed round led by Homan Yuen of Fusion Fund, which invests in technically sophisticated startups (i.e. the kind of startups that take decades of optimization research at Princeton to get going). Powell said that raising the round was tough, transpiring during the first weeks of the pandemic last year. One corporate fund pulled out at the last minute, and it was “chaos ensuing with everyone,” he said. This Series A process meanwhile was the opposite. “This round was totally different — closed it in 17 days from round kickoff to closure,” he said.
With new capital in the bank, the company is looking to expand from 25 employees to 75 this year, who will be trickling back to the company’s office in the Flatiron neighborhood of Manhattan in the coming months. Optimal Dynamics targets customers with 75 trucks or more, either fleets for rent or private fleets owned by companies like Walmart who handle their own logistics.
Powered by WPeMatico
Email marketing is decades old, but it’s a category that has surprising life in it. Multiple generations of email marketing companies have come through and sustained success, from Constant Contact to Mailchimp. These brands often become household names — after all, you probably have hundreds of emails with their logos attached to the email footer.
Klaviyo is not as much of a household name right now, but it is absolutely on its way to the paramount of the next-generation of email marketing startups.
The company announced today that it has raised $320 million in new capital in a Series D round, led by Sands Capital, a private and public equity investor that has, among many areas of focus, a thesis in ecommerce. That brings the company’s total fundraising to $675 million, following a $200 million Series C round from just six months ago.
Klaviyo was the subject of one of our most recent EC-1 analyses, where we looked at the company’s history of growth, how it is rebuilding what’s been dubbed “owned marketing” (i.e. marketing channels that a business owns like email rather than channels owned by platforms like Facebook and Instagram), how marketers are using Klaviyo post-COVID, and some startup growth lessons from the business as well.
There is nearly 10,000 words of analysis packed into that whole story, so read that or save it for the weekend if you really want to get into the nitty-gritty of Klaviyo’s story and how it is fitting in to the wider email marketing space. But suffice it to say that the company’s secret sauce is perhaps obvious: it’s a marketing company that’s pretty damn good at marketing. That’s allowed it to pull in gargantuan numbers of new customers as many retailers and brick-and-mortar businesses fled online in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In its press statement, the company wrote that “Klaviyo’s customer base doubled over the past 12 months and the company now serves over 70,000 paying customers, a more than 110% increase from 2019 — ranging from small businesses to Fortune 500 companies, in more than 120 countries.” It also said that it plans to increase its head count from 800 to 1,300 people this year.
The company is headquartered in Boston, and Klaviyo’s all-but decacorn valuation is a major win for the Boston enterprise ecosystem, which continues to percolate on high.
In addition to Sands, Counterpoint Global, Whale Rock Capital Management, ClearBridge Investments, Lone Pine Capital, Owl Rock Capital, and Glynn Capital also joined the round as new investors. Previous investors Accel and Summit Partners also participated.
Powered by WPeMatico
In the absence of a real baseball league, it is perhaps not surprising that a simulated one should grow popular during the troubled year 2020. But even so, the absurdist horror and minimalist aesthetic of Blaseball seem an unlikely success. The text-based fantasy fantasy league has attracted hundreds of thousands of players and now $3 million in funding to build up the game and go mobile.
If you’re unfamiliar with Blaseball, feel free to go check it out now and sign up — it’s free. You’ll probably get a better idea of what the game is from 30 seconds of browsing than the next couple paragraphs.
For those of you who’d rather read, however, Blaseball is a web-based fictional baseball-esque league where players can bet in-game currency on the outcomes. But this is where things get weird. The teams aren’t the Mariners or the Mets but the Moist Talkers and the Worms; players have names like Chorby Soul and Peanutiel Duffy; their stats include things like allergies, pregame rituals and an inventory of RPG-like items.
Likewise, games — told through simple text summaries of the action like you might see in the corner of a sports site — involve hits, balls and stealing, but also incineration, shaming and secret bases. “Weather” might involve spontaneous blood transfusions between players, or birds that interfere with play.
In short, it’s totally ridiculous, utterly unpredictable and very funny. This totally unique concoction of fantasy leagues, baseball satire and cosmic horror has accrued a dedicated yet routinely puzzled fanbase over its 19-week-long seasons. And like so many hits, this one came as something of a shock to its creators.
“We’re as surprised as you are,” said Sam Rosenthal, founder and CEO of The Game Band, which developed (and is developing) the game. “Blaseball was an experimental side project for the studio — we were in the middle of a pandemic, publishers were in a spending freeze, it was a scary time. We wanted to make a game that brings people together in this really isolating time.”
The idea for it came from banter at a real baseball game, where Rosenthal and a friend speculated about a league where the rules were “different and more chaotic.” Of course the rules of real-life baseball are continually being revised, but so far there haven’t been any resurrections of players incinerated by rogue umpires, free runs for home teams or shrink rays.
While the resulting game-like product bears some resemblance to baseball, betting and fantasy leagues, it’s much too weird and random to really be considered the same thing. That’s led to some friction as players who expect a more traditional experience lose coins on a game decided by, say, a bird pecking their team’s star hitter inside an enormous peanut shell, or a guaranteed home run because the batter ate magma.
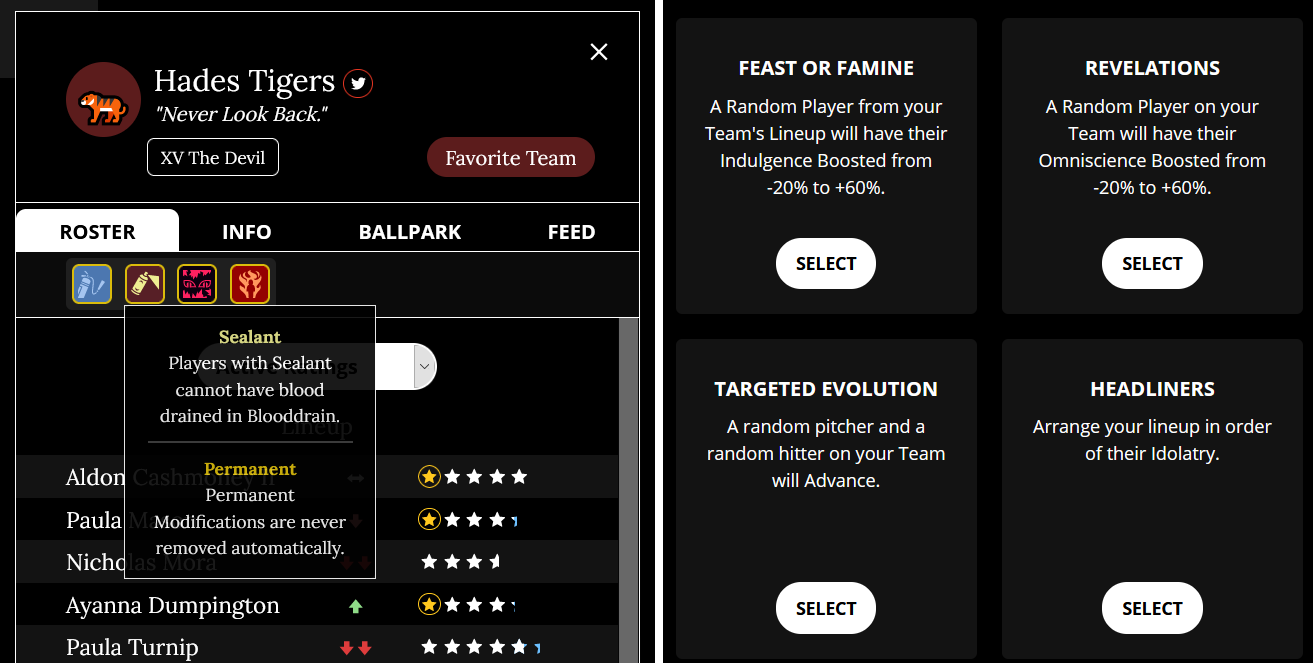
The Hades Tigers … so hot right now. The roster shows a team’s current and permanent attributes, while players can work together to create change by voting weekly. Image Credits: The Game Band
“Sometimes we have to remind the fans that this is a horror game,” Rosenthal admitted. The gameplay, as players discover in time, consists more in cooperation and guiding the league itself than in precision odds making. “This is not a game about individual success but collective success. The mechanics of the game reward organization, fans banding together with other fans of their team.”
Using those coins to buy votes to determine how the most idolized players are treated at the end of a season, for instance, could have huge repercussions on the next season. Ultimately the players are really participating in a sort of long-term alternative-reality game rather than a zany baseball sim, as the ominous announcements and events drive home now and again.
Next to the outcome of a match and the news that a player was walked to second base, you might learn that “Reality flickered in the Feedback” or see disembodied dialogue about the league or disordered cosmos.
It can be disconcerting and one may rightly wonder whether the creators have a narrative or goal in mind, or whether they’re just winging it and being weird for weirdness’s sake. I guessed the latter, but Rosenthal set me straight.
“It is going somewhere,” he assured me. “There are a lot of plans, we have a ton of lore written. We literally have a writers’ room every day, usually about 3-4 hours long. But we need to stay flexible because there’s two other creators: the simulation, since we don’t know what will happen in the games themselves, and the fans. There are things we don’t know they’ll latch onto, emergent narratives like the reincarnation of Jaylen Hotdogs. We’re always learning, and we give ourselves a lot of room to backtrack or change things quickly if needed.”
What was never clear even to the developers, however, was whether the game would live long enough to see those plans come to fruition. Blaseball, being a side project built during strange days, was never envisioned as a big money maker. For a small game developer to have a runaway success on their hands but little ability to monetize that success, the stresses of continuing development and support can overtake the benefits of popularity.
“Since we didn’t really set it up from the get-go to be profitable, we were just sort of slowly losing money,” said Rosenthal. “Fortunately our community has been really supportive through Patreon and sponsorships. But ultimately we wanted to make the game better and sustainable, and we wanted to pay our team what they deserve.”
The $3 million seed round keeps the lights on, to begin with, but also lets The Game Band staff up, so the writers don’t have to break up a meeting early because one of them is doubling as product support and the site is breaking. More importantly, however, the team plans to make a native mobile app. More than half of Blaseball‘s players (that is, the real ones, not Baby Triumphant and Wyatt Mason IV) are on mobile and Rosenthal admitted the mobile experience is “not great.”
The company comes from a mobile development background, he noted, so they know what they’re doing, but saw the web as the easiest platform to deploy on during the pandemic. Now they want to get mobile up and running, since the live, constantly shifting nature of the game fits well with the kind of updates sports and fantasy aficionados tend to sign up for. Who wouldn’t want to know right away that their favorite team has entered Party Time, or that their idolized player found a new piece of armor, or that a new non-physical law has been ratified?
Rosenthal said they resisted seeking funding to begin with due to a desire for independence, but was enthused about their choice of investor, Makers Fund, saying they actually understand Blaseball and have been partners rather than parents when it comes to moving the operation toward making money.
“They know we can’t just copy monetization from another game and put it in Blaseball, that would ruin the experience right away. They have an amazing network of people in the games industry, and at the end of the day they’re not prescriptive,” he said.
(They also gamely did not object to a line in the press release by the fictional Commissioner asserting that “Blaseball has acquired Makers Fund,” which says a lot.)
“We’re very cognizant that there are ways that free games can monetize that are detrimental to the community,” he continued. “So it will always be free to play and it will never be pay to win. Like, the Crabs are never going to run away with it because they’re the richest team. When we think about monetization we think about how it can benefit the community as a whole, not individuals.”
In the meantime the league slouches on, morphing from week to week in a live dialogue between players and developers. Don’t expect it go get any less weird, because the creators know that constant disorientation is part of the game’s charm.
Amazingly, Rosenthal even managed to suggest that Blaseball was, in the parlance of game design tropes, the Dark Souls of baseball simulators — “it [Dark Souls] gives you so little, it asks you to interpret and put a thesis together, to go linger on forums and talk with others about it. We wanted to create that kind of experience, and see how people would interpret this sort of weird, unknowable entity.”
They certainly got the weird and unknowable part right. You can try Blaseball out for yourself here.
(This story originally included the figure of $3.4 million for the round — this was an unforced error on my part and has been corrected to $3 million.)
Powered by WPeMatico
Amount, a company that provides technology to banks and financial institutions, has raised $99 million in a Series D funding round at a valuation of just over $1 billion.
WestCap, a growth equity firm founded by ex-Airbnb and Blackstone CFO Laurence Tosi, led the round. Hanaco Ventures, Goldman Sachs, Invus Opportunities and Barclays Principal Investments also participated.
Notably, the investment comes just over five months after Amount raised $86 million in a Series C round led by Goldman Sachs Growth at a valuation of $686 million. (The original raise was $81 million, but Barclays Principal Investments invested $5 million as part of a second close of the Series C round). And that round came just three months after the Chicago-based startup quietly raised $58 million in a Series B round in March. The latest funding brings Amount’s total capital raised to $243 million since it spun off from Avant — an online lender that has raised over $600 million in equity — in January of 2020.
So, what kind of technology does Amount provide?
In simple terms, Amount’s mission is to help financial institutions “go digital in months — not years” and thus, better compete with fintech rivals. The company formed just before the pandemic hit. But as we have all seen, demand for the type of technology Amount has developed has only increased exponentially this year and last.
CEO Adam Hughes says Amount was spun out of Avant to provide enterprise software built specifically for the banking industry. It partners with banks and financial institutions to “rapidly digitize their financial infrastructure and compete in the retail lending and buy now, pay later sectors,” Hughes told TechCrunch.
Specifically, the 400-person company has built what it describes as “battle-tested” retail banking and point-of-sale technology that it claims accelerates digital transformation for financial institutions. The goal is to give those institutions a way to offer “a secure and seamless digital customer and merchant experience” that leverages Amount’s verification and analytics capabilities.

Image Credits: Amount
HSBC, TD Bank, Regions, Banco Popular and Avant (of course) are among the 10 banks that use Amount’s technology in an effort to simplify their transition to digital financial services. Recently, Barclays US Consumer Bank became one of the first major banks to offer installment point-of-sale options, giving merchants the ability to “white label” POS payments under their own brand (using Amount’s technology).
“The pandemic dramatically accelerated banks’ interest in further digitizing the retail lending experience and offering additional buy now, pay later financing options with the rise of e-commerce,” Hughes, former president and COO at Avant, told TechCrunch. “Banks are facing significant disruption risk from fintech competitors, so an Amount partnership can deliver a world-class digital experience with significant go-to-market advantages.”
Also, he points out, consumers’ digital expectations have changed as a result of the forced digital adoption during the pandemic, with bank branches and stores closing and more banking done and more goods and services being purchased online.
Amount delivers retail banking experiences via a variety of channels and a point-of-sale financing product suite, as well as features such as fraud prevention, verification, decisioning engines and account management.
Overall, Amount clients include financial institutions collectively managing nearly $2 trillion in U.S. assets and servicing more than 50 million U.S. customers, according to the company.
Hughes declined to provide any details regarding the company’s financials, saying only that Amount “performed well” as a standalone company in 2020 and that the company is expecting “significant” year-over-year revenue growth in 2021.
Amount plans to use its new capital to further accelerate R&D by investing in its technology and products. It also will be eyeing some acquisitions.
“We see a lot of interesting technology we could layer onto our platform to unlock new asset classes, and acquisition opportunities that would allow us to bring additional features to our platform,” Hughes told TechCrunch.
Avant itself made its first acquisition earlier this year when it picked up Zero Financial, news that TechCrunch covered here.
Kevin Marcus, partner at WestCap, said his firm invested in Amount based on the belief that banks and other financial institutions have “a point-in-time opportunity to democratize access to traditional financial products by accelerating modernization efforts.”
“Amount is the market leader in powering that change,” he said. “Through its best-in-class products, Amount enables financial institutions to enhance and elevate the banking experience for their end customers and maintain a key competitive advantage in the marketplace.”
Powered by WPeMatico