Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
While it would be nice to write about something other than yet another tech company looking to list via a SPAC, the deals keep dropping, so our more traditional fare of covering startup trends will remain on hold for at least one day more.
This morning, we’re looking at the Jam City deal to merge with DPCM Capital. Jam City is a bit like Zynga, but unless you are a mobile-gaming aficionado, you might not have heard of it.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on Extra Crunch or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
You likely have not heard of DPCM Capital, either, but you know more about it than you’d think.
As Jam City notes in a release, the SPAC is “led by Emil Michael.” Michael is most famous for his time at Uber, where he served as chief business officer. He left the firm, as The New York Times wrote in 2014, after a board-called “investigation into [the company’s] culture and business practices” led to a “recommendation for Mr. Michael to exit Uber.”
He’s the gentleman who floated the idea of funding a team to “dig up dirt” on Uber’s “critics in the media,” as BuzzFeed News reported in late 2014.
 Regardless, we’re not here to go back through Uber and its various cultural messes. We’re here to dig into the Jam City SPAC deck to see if the company is similar to Zynga. Why do we want to know that? Because Zynga has done great in recent quarters, including posting record revenue and bookings in the first three months of 2021.
Regardless, we’re not here to go back through Uber and its various cultural messes. We’re here to dig into the Jam City SPAC deck to see if the company is similar to Zynga. Why do we want to know that? Because Zynga has done great in recent quarters, including posting record revenue and bookings in the first three months of 2021.
With lots of folks stuck at home in the last year, gaming has done well in aggregate. And mobile gaming is a huge chunk of the larger gaming world.
More broadly, why do we care about Jam City’s SPAC transaction? Because the mobile gaming concern has raised more than $300 million, including a $145 million round in 2019 that TechCrunch covered here.
The company attracted capital from Austin Ventures, Netmarble, Bank of America Merrill Lynch and JP Morgan Chase while private, per Crunchbase, so we’re very curious if Jam City has enjoyed a Zynga-like last few years and how it’s being valued as part of the SPAC deal. Let’s find out.
When Jam City raised that huge 2019 round, co-founder and CEO Chris DeWolfe said that the “global mobile games market [is] consolidating.” At the time, the company intended to use some of its new funding to acquire other mobile gaming companies.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast, where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
This week was good fun not only because we had the whole team together to record, but also because we are still basking in the endless glory of our winning a Webby earlier this week. Frankly we are still shocked. But happy-shocked, like when you get a new toy and it is covered in static electricity.
Anyhoo, we had a packed show with much, much left on the floor as we tried to shoehorn the week into our time slot. Here’s what we got into:
The show flew by, much like our days recently, simply because it was so fun and jam-packed with news. And we got to make jokes about our listeners and Monday.com PR timing, so what else could we ask for? Talk soon!
Equity drops every Monday at 7:00 a.m. PST, Wednesday, and Friday morning at 7:00 a.m. PST, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast, Spotify and all the casts.
Powered by WPeMatico
TaniHub Group, an Indonesian startup that helps farmers get better prices and more customers for their crops, has raised a $65.5 million Series B. The funding was led by MDI Ventures, the investment arm of Telkom Group, one of Indonesia’s largest telecoms, with participation from Add Ventures, BRI Ventures, Flourish Ventures, Intudo Ventures, Openspace Ventures, Tenaya Capital, UOB Venture Management and Vertex Ventures.
Openspace and Intudo are returning investors from TaniHub’s $10 million Series A, announced in May 2019. The new funding brings its total raised to about $94 million.
Founded in 2016, TaniHub now has more than 45,000 farmers and 350,000 buyers (including businesses and consumers) in its network. The company helps farmers earn more for their crops by streamlining distribution channels so there are fewer middlemen between farms and the restaurants, grocery stores, vendors and other businesses that buy their products. It does this through three units: TaniHub, TaniSupply and TaniFund.
TaniHub is its B2B e-commerce platform, which connects farmers directly to customers. Then orders are fulfilled through TaniSupply, the company’s logistics platform, which currently operates six warehousing and processing facilities where harvests can be washed, sorted and packed within an hour, before being delivered to buyers by TaniHub’s own couriers or third-party logistics providers.
Finally, TaniFund is a fintech platform that provides loans to farmers they can use while growing crops and pay off by selling through TaniHub. Co-founder and chief executive officer Eka Pamitra told TechCrunch its credit scoring system is based on three years of performance, the company’s agriculture value chain expertise and partnerships with financial institutions.
“More than 100 data points are considered when doing the credit risk assessment. For example, for cultivation financing products, TaniFund tailors each credit scoring based on agriculture risks and market risk of each commodity, on top of the typical borrower E-KYC scoring and process,” he explained. “Beyond credit scoring, having TaniSupply and TaniHub as a standby buyer within the ecosystem also helps to mitigate risk of each loan. TaniFund aims to further boost its credit scoring system with smarter data processing and better machine learning models.”
Pamitra said TaniHub will use its new funding to build the upstream and midstream parts of its supply chain — in other words, new cultivation areas, processing, packing centers and warehouses. The company will also expand its coverage beyond Java and Bali to source and sell locally, and continue improving its supply-demand forecast model to help farmers plan crop cultivation and timing, with the goal of reducing price fluctuations and maintaining a consistent supply. Pamitra added that TaniHub will also explore precision farming technology.
Over the last couple of years, TaniHub has started exporting several types of fruits and spices to the United Arab Emirates, Singapore and South Korea. This year, it plans to focus on expanding within Indonesia because the F&B (food and beverage) market there is worth $137 billion and the Indonesian agriculture sector is still highly fragmented, Pamitra said.
Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, TaniHub says it was able to grow its revenue 600% year-on-year in 2020 as demand for online groceries increased.
“We postponed our branch expansion plan and focused on increasing the seven existing warehouses’ since there was a surge of demand on the B2C segment and the process of onboarding farmers. This benefited us since the adoption of purchasing fresh groceries online increased significantly, and the willingness of farmers to work with us became remarkably high because the local traditional markets were closed due to lockdowns,” Pamitra said. “Since COVID-19, the eagerness of provincial governments to open communications for TaniHub to work with local farmers and SMEs in their region has been quite impactful.”
TaniHub is now working with several Indonesian government agencies, including the Ministry of Trade, Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Cooperatives and SMEs, to onboard more farmers, F&B businesses and increase exports.
In a press statement, MDI Ventures director of portfolio management Sandhy Widyasthana said, “TaniHub Group has an important role in transforming the agriculture sector and has proven that its presence can deliver positive impact on the quality of life of farmers. We hope our investment can help them continue their work and expand their coverage to more and more farming communities in Indonesia.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Farmers and food businesses, like restaurants, deal with the same issue: a fragmented supply chain. Secai Marche wants to streamline agricultural logistics, making fulfillment more cost-efficient and enabling food businesses to bundle products from different farmers into the same order. The company is headquartered in Japan, with operations in Malaysia, and plans to expand into Singapore, Thailand and Indonesia. This week, it announced 150 million JPY (about $1.4 million USD) in pre-Series A funding from Rakuten Ventures and Beyond Next Ventures to build a B2B logistics platform for farmers that sell to restaurants, hotels and other F&B (food and beverage) businesses.
This round brings Secai Marche’s total raised to about $3 million. The capital will be used to expand its fulfillment infrastructure, including a network of warehouses and cold chain logistics, hire more people for its engineering team and sales and marketing.
Secai Marche was founded in 2018 by Ami Sugiyama and Shusaku Hayakawa, and currently serves 130 farmers and more than 300 F&B businesses. Before launching the startup, Sugiyama spent four years working in Southeast Asia, including managing restaurants and cafes in Malaysia. During that time, she started to import green tea from Japan, intending to sell it directly to customers in Malaysia. But she realized supply chain inefficiencies not only made it hard to meet demand, but also ensure quality for all kinds of ingredients.
Meanwhile, Hayakawa was operating a farm in Japan and working on agriculture control systems that predicted weather and crop growth to help farmers maintain consistent quality.
Both Sugiyama and Hayakawa ended up at consulting firm Deloitte, researching how to create a more efficient supply chain for Japanese agricultural exports to Singaporean F&B businesses. Policies implemented by Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga’s administration aim to increase Japanese agricultural exports from 922.3 billion JPY (about $8.5 billion) in 2020 to 2 trillion JPY (about $18.5 billion) by 2025, and 5 trillion JPY (about $46.1 billion) in 2030.
Seche Marche’s goal is to make it easier for farmers to sell their crops to F&B businesses domestically or overseas.
“We found that not only farmers in Japan, but also all farmers in Southeast Asia have the same problem in terms of the current supply chain,” Sugiyama told TechCrunch. “So we left Deloitte and started our own business to connect not only farmers in Japan, but farmers in all Asian countries.”
Secai Marche’s logistics management tech is what differentiates it from other wholesaler platforms. It uses an AI-based algorithm to predict demand based on consumption trends, seasonal products and farmer recommendations, said Hayakawa. Secai Marche runs its own warehouse network, but mostly relies on third-party logistics providers for fulfillment, and its platform assigns orders to the most efficient transportation method.
This allows F&B businesses to consolidate orders from farmers, so they can order smaller batches from different places without spending more money. About 30% of Secai Marche’s products are shipped to other countries, while the rest are sold domestically.
Secai Marche is reaching out to farmers who want to increase their customer base. About 30% of its products currently come from Japanese farms, 50% from Malaysia and the rest from other ASEAN countries. Sugiyama and Hayakawa said the COVID-19 pandemic affected Secai Marche’s expansion plans because it originally planned to enter Singapore this year, but had to slow down since they were unable to travel and meet with farmers.
On the other hand, many farmers have started selling directly to consumers through social media like Instagram or Facebook, and have approached Secai Marche for help with fulfillment, logistics, repacking and quality control.
Correction: Funding amount corrected to say $1.4 million instead of $1 million.
Powered by WPeMatico
Vietnam has one of the fastest-growing e-commerce markets in Southeast Asia, but many major platforms still focus on large cities. This means people in smaller cities or rural areas need to deal with longer wait times for deliveries. Social commerce company Mio is taking advantage of that gap by building a reseller network and logistics infrastructure that can offer next-day delivery to tier 2 and 3 cities.
The startup, which currently focuses on fresh groceries and plans to expand into more categories, announced today it has raised $1 million in seed funding. The round was co-led by Venturra Discovery and Golden Gate Ventures. Other participants included iSeed SEA, DoorDash executive Gokul Rajaram and Vidit Aatrey and Sanjeev Barnwal, co-founders of Indian social commerce unicorn Meesho.
Rajaram, Aatrey and Barnwal will become advisors to Mio co-founder and chief executive officer Trung Huynh, former investment associate at IDG Ventures Vietnam. Other founders include An Pham (who also co-founded Temasek-backed logistics startup SCommerce), Tu Le and Long Pham.
Founded in June 2020, Mio now claims hundreds of agents, or resellers. They are primarily women aged 25 to 35 years old who live in smaller cities or rural areas. Most join Mio because they want to supplement their household income, which is usually below $350, Huynh and Venturra investment associate Valerie Vu told TechCrunch in an email.
The social commerce model works for them because they are part of tight-knit communities that are already used to making group orders together. On average, Mio claims that its resellers make about $200 to $300, earning a 10% commission on each order, and additional commissions based on the monthly performance of resellers they referred to the platform.
Mio is among a crop of social commerce startups across Asia that leverage the buying power of areas where major e-commerce players haven’t reached dominance yet. For example, lower-tier cities fueled Pinduoduo’s meteoric rise in China, while Meesho has built a distribution network in 5,000 Indian cities. Other examples of social commerce areas focused on smaller cities and rural areas include “hyperlocal” startup Super and KitaBeli, both in Indonesia, and Resellee in the Philippines.
Social commerce companies typically don’t require resellers to carry inventory. Instead, resellers pick which items they want to market to their buyers. In Mio’s case, most of their resellers’ customers are friends, family members and neighbors, and they promote group orders through social media platforms like Facebook, TikTok, Instagram or Zalo, Vietnam’s most popular messaging app. Then they place and manage orders through Mio’s reseller app.
To address delivery challenges, Mio is building an in-house logistics and fulfillment system, including a new distribution center in Thu Duc that can distribute goods to all of Ho Chi Minh and the surrounding five cities in Binh Dong and Dong Nai provinces. Vu and Huynh said Mio can process up to tens of thousands of daily order units at the center. Mio is also able to perform next-day deliveries for orders that are made prior to 8 p.m.
To lower logistics costs and ensure quick delivery times, Mio limits the number of products in its inventory. The company currently focuses on grocery staples, including fresh produce and poultry, and plans to add FMCG (fast-moving consumer goods) and household appliances, too, especially white-label goods that have a higher profit margin.
Mio’s new funding will be used on its distribution center, and hiring for its tech and product teams. The startup plans to add more personalization options for product categories and resellers, so they can build their own brand identities.
Powered by WPeMatico
Trees, those deciduous entities you can occasionally see outdoors when not locked down or strapped down at a desktop ruminating on a video call, have long been the inspiration for fresh new ideas. Stories abound of how founders built companies while walking the foothills in Silicon Valley or around parks in San Francisco, and yet, we’ve managed over the past year to take movement mostly out of our remote work lives.
Chicago-based Spot Meetings wants to reinvigorate our meetings — and displace Zoom as the default meeting medium at the same time.
The product and company are just a few months old and remain in closed beta (albeit opening up a bit shortly here), and today the company is announcing $5 million in seed funding led by Ilya Fushman at Kleiner Perkins. That follows a $1.9 million pre-seed round led by Chapter One earlier this year.
CEO and co-founder Greg Caplan said that the team is looking to rebuild the meeting from the ground up for an audio-only environment. “On mobile, it needs to be abundantly simple to be very functional and understood for users so that they can actually use it on the go,” he described. In practice, that requires product development across a wide range of layers.
The product’s most notable feature today is that it has an assistant, aptly named Spot, which listens in on the call and which participants can direct commands to while speaking. For instance, saying “Spot Fetch” will pull the last 40 seconds of conversation, transcribe it, create a note in the meeting and save it for follow-up. That prevents the multi-hand tapping required to save a note or to-do list for follow-up with our current meeting products. You “don’t even need to take your phone out,” Caplan points out.
What gets more interesting is the collaboration layer the company has built into the product. Every audio meeting has a text-based scratch pad shared with all participants, allowing users to copy and paste snippets into the meeting as needed. Those notes and any information that Spot pulls in are saved into workspaces that can be referenced later. Spot also sends out emails to participants with follow-ups from these notes. If the same participants join another audio meeting later, Spot will pull in the notes from their last meeting so there is a running timeline of what’s been happening.
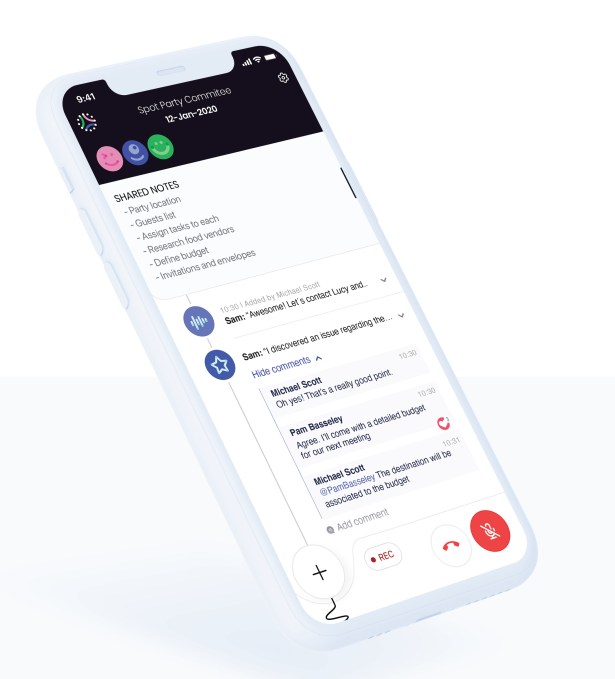
Spot’s product design emphasizes collaboration within an audio-focused experience. Image Credits: Spot Meetings
Obviously, transcription features are built-in, but Spot sees opportunities in offering edited transcripts of long calls where only a few minutes of snippets might be worth specifically following up on. So the product is a bit more deliberate in encouraging users to select the parts of a conversation that are relevant for their needs, rather than delivering a whole bolus of text that no one is ever actually going to read.
“Collaboration from now and the future is going to be primarily digital … in-person is forever going to be the exception and not the rule,” Caplan explained. Longer term, the company wants to add additional voice commands to the product and continue building an audio-first (and really, an audio-only) environment. Audio “very uniquely helps people focus on the conversation at hand,” he said, noting that video fatigue is a very real phenomenon today for workers. To that end, more audio features like smarter muting are coming. When a participant isn’t talking, their background noise will automatically melt away.
Before Spot Meetings, Caplan was the CEO and co-founder of Remote Year, a startup that was designing a service for company employees to take working trips overseas. I first covered it back in 2015, and it went on to raise some serious venture dollars before the pandemic hit last year and the company laid off 50% of its workforce. Caplan left as CEO in April last year, and the company was ultimately sold to Selina, which offers co-working spaces to travelers, in October.
Caplan’s co-founder who leads product and engineering at Spot Meetings is Hans Petter “HP” Eikemo. The duo met during the very first Remote Year cohort. “He has been a software engineer for two decades [and was] literally the first person I called,” Caplan said. The team will grow further with the new funding, and the company hopes to start opening its beta to its 6,000 waitlist users over the next 3-4 weeks.
Powered by WPeMatico
GPS is one of those science fiction technologies whose use is effortless for the end user and endlessly challenging for the engineers who design it. It’s now at the heart of modern life: everything from Amazon package deliveries to our cars and trucks to our walks through national parks are centered around a pin on a map that monitors us down to a few meters.
Yet, GPS technology is decades old, and it’s going through a much-needed modernization. The U.S., Europe, China, Japan and others have been installing a new generation of GNSS satellites (GNSS is the generic name for GPS, which is the specific name for the U.S. system) that will offer stronger signals in what is known as the L5 band (1176 MHz). That means more accurate map pinpoints compared to the original generation L1 band satellites, particularly in areas where line-of-sight can be obscured, like urban areas. L5 was “designed to meet demanding requirements for safety-of-life transportation and other high-performance applications,” as the U.S. government describes it.
It’s one thing to put satellites into orbit (that’s the easy part!), and another to build power-efficient chips that can scan for these signals and triangulate a coordinate (that’s the hard part!). So far, chipmakers have focused on creating hybrid chips that pull from the L1 and L5 bands simultaneously. For example, Broadcom recently announced the second-generation of its hybrid chip.
OneNav has a totally different opinion on product design, and it placed it right in its name. Eschewing the hybrid chip model of mixing old signals with new, it wants one chip monitoring the singular band of L5 signals to drive cost and power savings for devices. One nav to rule them all, as it were.
The company announced today that it has closed a $21 million Series B round led by Karim Faris at GV, which is solely funded by Alphabet. Other investors included Matthew Howard at Norwest and GSR Ventures, which invested in earlier rounds of the company. All together, OneNav has raised $33 million in capital and was founded about two years ago.
CEO and co-founder Steve Poizner has been in the location business a long time. His previous company, SnapTrack, built out a GPS positioning technology for mobile devices that sold to Qualcomm for $1 billion in stock in March 2000, at the height of the dot-com bubble. His co-founder and CTO at OneNav, Paul McBurney, has similarly spent decades in the GNSS space, most recently at Apple, according to his LinkedIn profile.

OneNav CEO and co-founder Steve Poizner, seen here in 2009. Image Credits: David McNew via Getty Images
They saw an opportunity to build a new navigation company as L5 band satellites have switched on in recent years. As they looked at the market and the L5 tech, they decided they wanted to go further than other companies by eliminating the legacy tech of older GPS technology and moving entirely into the future. By doing that, its design is “half the size of the old system, but much higher reliability and performance,” Poizner said. “We are aiming to get location technology into a much broader number of products.”
He differentiated between upgrading GPS from upgrading wireless signals. “With these L5 satellites, we don’t need the L1 satellites anymore [but] with 5G, you still need 4G,” he said. L5 band GPS does everything that earlier renditions did, but better, whereas with wireless technologies, they often need to complement each other to offer peak performance.
There’s one caveat here: The L5 signal is still considered “pre-operational” by the U.S. government, since the U.S. GPS system only has 16 satellites broadcasting the signal today, and is targeting 24 satellites for full deployment by later in this decade. However, other countries have also deployed L5 GNSS satellites, which means that while it may not be fully operational from the U.S. government’s perspective, it may well be good enough for consumers.
OneNav’s goal according to Poizner is to be “the Arm of the GNSS space.” What he means is that like Arm, which produces the chip designs for nearly all mobile phones globally, OneNav creates comprehensive designs for L5 band GPS chips that can be integrated as a system-on-chip into the products of other manufacturers so that they can “embed a high-performance location engine based on their silicon.”
The company today also announced that its first design customer will be In-Q-Tel, the U.S. intelligence community’s venture capital and business development organization. Poizner said that through In-Q-Tel, “we now have a development contract with a U.S. government agency.” The company is expecting that its customer evaluation units will be completed by the end of this year with the objective of potentially having OneNav’s technology in end-user devices by late 2022.
Location tracking has become a major area of investment for venture capitalists, with companies working on a variety of technologies outside of GPS to offer additional detail and functionality where GPS falls short. Poizner sees these technologies as ultimately complementary to what he and his team are building at OneNav. “The better the GPS, the less pressure on these augmentation systems,” he said, while acknowledging that, “it is the case though that in certain environments [like downtown Manhattan or underground in a subway], you will never get the GPS to work.”
For Poizner, it’s a bit of a return to entrepreneurship. Prior to starting OneNav, he had been heavily involved in California state politics. Several years after the sale of SnapTrack to Qualcomm, he unsuccessfully ran for a seat in the California State Assembly. He later was elected California’s insurance commissioner in 2007 under former Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger. He ran for governor in 2010, losing in the Republican primary against Meg Whitman, who made her name as the longtime head of eBay. He ran for his former seat of California insurance commissioner in 2018, this time as a political independent, but lost.
OneNav is based in Palo Alto and currently has more than 30 employees.
Powered by WPeMatico

Steve Sy, CEO of Great Deals, and William Chiongbian II, CEO of Fast Group, sign the contract for the companies’ strategic partnership. Image Credits: Great Deals
Founded in 2014, Great Deals is an e-commerce enabler that helps brands like Abbot, L’Oréal and Unilever build their online retail operations in the Philippines. The startup announced today that it has raised $30 million in Series B funding led by Fast Group, one of the Philippines’ biggest logistics firms, with support from CVC Capital Partners. Navegar, which led Great Deals’ Series A, also returned for this round.
The transaction was advised by Rocket Equities. The investment by Fast Group, which has a fleet of more than 2,500 vehicles and 90,000 stores in its distribution network, marks the beginning of a strategic partnership. Great Deals will use part of the new capital to build an automated fulfillment center, and the deal will help it increase its penetration outside the Greater Manila Area and offer more Instant Commerce, or deliveries under one hour.
Great Deals currently operates only in the Philippines, but plans to expand regionally next year, founder and chief executive officer Steve Sy told TechCrunch.
In a statement, Fast Group president and chief executive officer William Chiongbian II said, “The Fast Group sees a lot of synergies with Great Deals in building capacity. We are privileged to contribute to the growth of Philippine e-commerce, as it relies heavily on a strong supply chain backbone.”
Some of Great Deals’ other clients include Nestlé, Samsonite, GSK, Bayer and Fila. In addition to serving as an e-commerce distributor, it offers an end-to-end services for brands, including digital content production, marketing campaign coordination and management of marketplace listings (Great Deals’ partners include Lazada, Shopee, Zalora, Zilingo, Shopify and Magento).
Powered by WPeMatico
Part of learning to be an engineer is understanding the tools you’ll have to work with — voltmeters, spectrum analyzers, things like that. But why use two, or eight for that matter, where one will do? The Moku:Go combines several commonly used tools into one compact package, saving room on your workbench or classroom while also providing a modern, software-configurable interface. Creator Liquid Instruments has just raised $13.7 million to bring this gadget to students and engineers everywhere.
The idea behind Moku:Go is largely the same as the company’s previous product, the Moku:Lab. Using a standard input port, a set of FPGA-based tools perform the same kind of breakdowns and analyses of electrical signals as you would get in a larger or analog device. But being digital saves a lot of space that would normally go toward bulky analog components.
The Go takes this miniaturization further than the Lab, doing many of the same tasks at half the weight and with a few useful extra features. It’s intended for use in education or smaller engineering shops where space is at a premium. Combining eight tools into one is a major coup when your bench is also your desk and your file cabinet.
Those eight tools, by the way, are: waveform generator, arbitrary waveform generator, frequency response analyzer, logic analyzer/pattern generator, oscilloscope/voltmeter, PID controller, spectrum analyzer and data logger. It’s hard to say whether that really adds up to more or less than eight, but it’s definitely a lot to have in a package the size of a hardback book.
You access and configure them using a software interface rather than a bunch of knobs and dials — though let’s be clear, there are good arguments for both. When you’re teaching a bunch of young digital natives, however, a clean point-and-click interface is probably a plus. The UI is actually very attractive; you can see several examples by clicking the instruments on this page, but here’s an example of the waveform generator:
Love those pastels.
The Moku:Go currently works with Macs and Windows but doesn’t have a mobile app yet. It integrates with Python, MATLAB and LabVIEW. Data goes over Wi-Fi.
Compared with the Moku:Lab, it has a few perks. A USB-C port instead of a mini, a magnetic power port, a 16-channel digital I/O, optional power supply of up to four channels and of course it’s half the size and weight. It compromises on a few things — no SD card slot and less bandwidth for its outputs, but if you need the range and precision of the more expensive tool, you probably need a lot of other stuff too.
Since the smaller option also costs $500 to start (“a price comparable to a textbook”… yikes) compared with the big one’s $3,500, there’s major savings involved. And it’s definitely cheaper than buying all those instruments individually.
The Moku:Go is “targeted squarely at university education,” said Liquid Instruments VP of marketing Doug Phillips. “Professors are able to employ the device in the classroom and individuals, such as students and electronic engineering hobbyists, can experiment with it on their own time. Since its launch in March, the most common customer profile has been students purchasing the device at the direction of their university.”
About a hundred professors have signed on to use the device as part of their fall classes, and the company is working with other partners in universities around the world. “There is a real demand for portable, flexible systems that can handle the breadth of four years of curriculum,” Phillips said.
Production starts in June (samples are out to testers), the rigors and costs of which likely prompted the recent round of funding. The $13.7 million comes from existing investors Anzu Partners and ANU Connect Ventures, and new investors F1 Solutions and Moelis Australia’s Growth Capital Fund. It’s a convertible note “in advance of an anticipated Series B round in 2022,” Phillips said. It’s a larger amount than they intended to raise at first, and the note nature of the round is also not standard, but given the difficulties faced by hardware companies over the last year, some irregularities are probably to be expected.
No doubt the expected B round will depend considerably on the success of the Moku:Go’s launch and adoption. But this promising product looks as if it might be a commonplace item in thousands of classrooms a couple years from now.
Powered by WPeMatico
Netlify, the startup that’s bringing a micro services approach to building websites, announced today that it has acquired YC alum FeaturePeek. The two companies did not share the purchase price.
With FeaturePeek, the company gets a major upgrade in its design review capability. While Netlify has had a previewing capability called Deploy Previews in the platform since 2016, it lacked a good way for reviewers to discuss and comment on the design. The preview alone was useful as far as it goes, but having the ability to collaborate on the design remained a missing piece until today.
With FeaturePeek, the company can expand on Deploy Previews to not only preview the design, but also enable all the stakeholders in the design process to add their opinions, edits and changes as the design moves through the creation process instead of having to wait until the end or gather the comments in a separate document or communications channel.
As FeaturePeek co-founder Eric Silverman told me at the time of their seed funding last year, his product removed a lot of frustration when the web coders would get all their review comments at the last minute:
“Right now, there’s no dedicated place to give feedback on that new work until it hits their staging environment, and so we’ll spin up ad hoc deployment previews, either on commit or on pull requests and those fully running environments can be shared with the team. On top of that, we have our overlay where you can file bugs, you can annotate screenshots, record video or leave comments.”
Matt Biilmann, CEO and co-founder, Netlify says that when his company created Deploy Previews, it was in reaction to customers who were kloodging together their own solutions to the issue. They learned that even with their own preview feature, customers craved a communications capability.
In the classic build versus buy debate, the company began building its own, then it met the FeaturePeek team and decided to switch course. “We had a team working on a prototype when the founders of FeaturePeek, Eric and Jason, gave us a demo of their product. As the demo progressed, our jaws got increasingly closer to hitting the floor and we knew straight away that what we had just seen was miles away from both our internal prototypes and any of the other tools we had seen in the space,” Billmann told TechCrunch.
He added, “It also quickly became apparent that fully building towards this vision as two different companies, without a deep end-to-end experience from initial Pull Request to a new feature release, would never really allow us to build what we were dreaming of, so we decided to join forces.”
The companies’ combined effort actually comes together today in a new release of Deploy Previews that includes the new FeaturePeek collaboration/commenting capabilities.
FeaturePeek was founded in 2019, went through Y Combinator Summer 2019 batch, and raised around $2 million. Netlify was founded in 2014 and has raised over $97 million, according to Crunchbase. Its last raise was a $53 million Series C in March 2020.
Powered by WPeMatico