Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
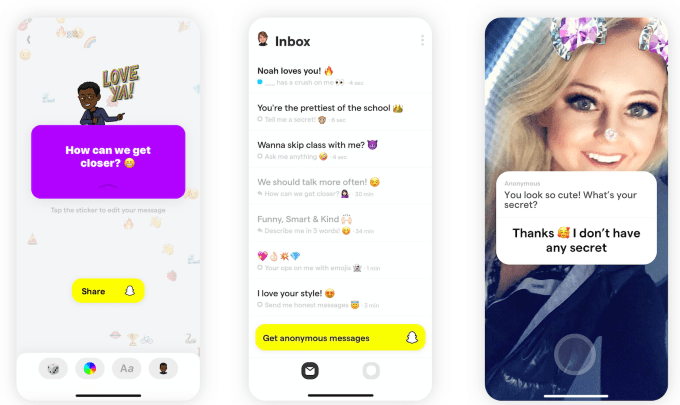
It wasn’t a fad. Yolo became the country’s No. 1 app just a week after launch by letting teens ask for anonymous replies to questions they posted on Snapchat. But nine months later, Yolo is still in the top 100 iOS apps and has 10 million active users. Now it’s safeguarding the app from predators while revealing a smart new feature for spinning up anonymous group chats, powered by $8 million in fresh funding.
“What we are trying to build is a new kind of network where there’s a fluidity to identity,” Yolo co-founder Greg Henrion tells me. “We weren’t sure if Yolo was here to stay, but we’re still ranking well and there seems to be a real opportunity in anonymity starting with Snapchat Q&A.”
Yolo is the first big win for Snapchat’s Snap Kit platform that lets developers piggyback on its login, Bitmoji avatars, stickers and Stories. This lets tiny development teams build apps that hundreds of millions of people, teens in particular, can instantly sign up for in just a few taps. Another Snap Kit app for meeting new people called Hoop recently spiked to No. 2 on the charts
We haven’t seen this kind of social platform success since Zynga’s empire rose atop Facebook. Spawning more blockbusters like Yolo could ensure that a Snapchat account is a must-have utility for the next generation.
“For two weeks we basically didn’t sleep,” Henrion recalls about the chaos he and co-founder Clément Raffenoux endured after Yolo shot to No. 1 last May. “You’re trying to stay afloat. It was very, very wild.”
The basic premise of Yolo is that you write a question like, “Who’s my celebrity look alike?”, “What do people really think of me?” or “How could I be nicer?” You’re then switched over to Snapchat, where you can post the question in your Story or messages with a link back to Yolo. There, people can anonymously leave a response; you can post that and your reply with another post on Snapchat.
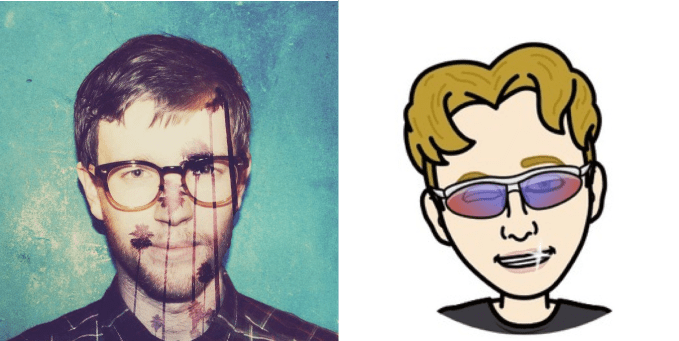
Yolo co-founder and CEO Greg Henrion, in real life and Bitmoji
The result is that friends and followers feel comfortable giving you real talk. They don’t have to sugarcoat their answers. And that makes people race to open Yolo each time they get a message. Yolo has seen 26 million downloads across iOS and Android globally, with nearly 70% in the U.S, according to Sensor Tower.
Other anonymous apps like tbh (acquired by Facebook) and Sarahah (kicked off the app stores) quickly faded, and others eventually imploded due to bullying, like Secret and YikYak. Although tbh hit No. 1 in September 2017, it was out of the top 500 by November. It seems a combination of inherent virality via Snapchat, easy user acquisition via Snap Kit and sharp product design has given Yolo some staying power. It still managed 2.2 million downloads last month versus a peak of 5.5 million in its first month back in May 2019.
 That June, Yolo quietly raised a $2 million seed round thanks to its sudden success. The team had been grinding since 2017 on a video reactions app called Popshow funded by a small pre-seed round from SV Angel, Shrug Capital and Product Hunt’s Ryan Hoover. They’d previously built music video-making app Mindie that eventually sold to influencer collective Shots Studios. Popshow never caught on, so the team began experimenting on Snap Kit, building a more official Q&A feature for Snapchat than predecessors like Sarahah and Polly. Then, boom. Days after launch, Yolo’s usage exploded.
That June, Yolo quietly raised a $2 million seed round thanks to its sudden success. The team had been grinding since 2017 on a video reactions app called Popshow funded by a small pre-seed round from SV Angel, Shrug Capital and Product Hunt’s Ryan Hoover. They’d previously built music video-making app Mindie that eventually sold to influencer collective Shots Studios. Popshow never caught on, so the team began experimenting on Snap Kit, building a more official Q&A feature for Snapchat than predecessors like Sarahah and Polly. Then, boom. Days after launch, Yolo’s usage exploded.
But to keep users interested, Yolo needed to evolve. That would require more funding for the eight-person team split between Snapchat’s home of Los Angeles and Henrion’s home of Paris.
The concept of a social app where users could shift between full anonymity and representation via avatar attracted its $8 million Series A to invest in product and engineering. The round was led by Thrive Capital, Ron Conway’s A.Capital, former TechCrunch editor Alexia Tsotsis’ Dream Machine (also in the seed round), Shrug, Day One, Goodwater, Knight VC, ex-Facebooker Bobby Goodlatte, Twitter co-founder Biz Stone and SV Angel’s Brian Pokorny.
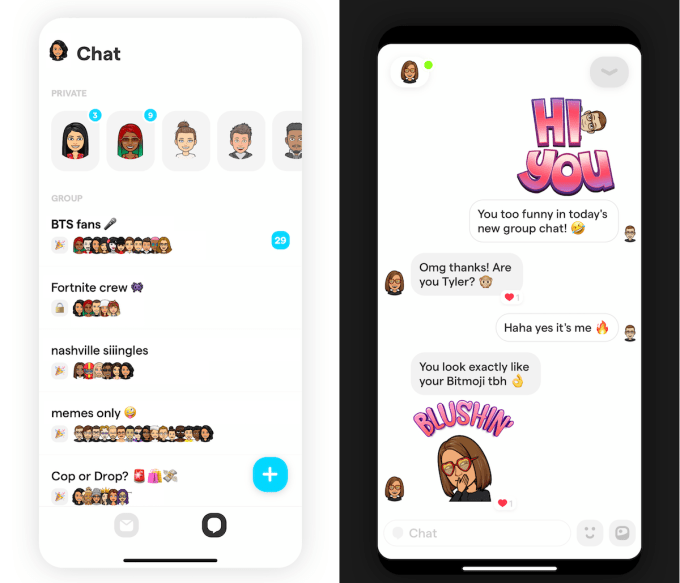
 That cash fueled the release of Yolo’s new group chat feature. You can set up a chat room, give it a name and generate an invite URL or sticker you can post on Snapchat, just like its previous question feature. Friends or friends of friends that are already in can join the group chat, represented by their Bitmoji instead of their name. Yolo suggests people join the more open “party mode” chats where their friends are active.
That cash fueled the release of Yolo’s new group chat feature. You can set up a chat room, give it a name and generate an invite URL or sticker you can post on Snapchat, just like its previous question feature. Friends or friends of friends that are already in can join the group chat, represented by their Bitmoji instead of their name. Yolo suggests people join the more open “party mode” chats where their friends are active.
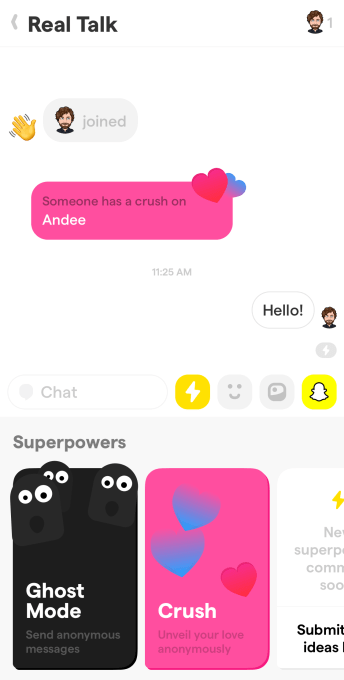
What makes this special is that once an hour, users can tap the Yolo Superpowers button to send a totally anonymous message to the group. More Superpowers are coming, but there’s also an anonymous “Someone has a crush on [name]” message so you can secretly profess your affection to anyone or someone else in the chat.
“The limits of Q&A is that it doesn’t generate real conversation. It’s an ice breaker, but we also want conversations to happen,” Henrion stresses. “‘What do you think about this dress?’ The group chat is more about ‘let’s talk about the dress.’” The chats could be focused on people you actually know offline, or those you share interests with. The option to restrict group chats to either just your contacts or friends of friends “limits the amount of meeting strangers,” Henrion explains. “This is very different from the public communities like Reddit or the dating apps.”
Still, anonymous apps have consistently proven to be havens for cyberbullying and unsafe behavior. Without the accountability of having your name attached, people are free to say awful things. That can be even worse amongst teenagers who might get in trouble for being mean at school but not on an app.
Yolo first focused on messages blocking 10% of overall messages that contained offensive content. That meant blatant hate speech and trolling couldn’t spread through the app. “We’re strict on moderation. When looking at the reviews about bullying, it’s like nothing compared to any other anonymous app. I think we solved 90% of the problem.”

Now it’s working with Snapchat to safeguard the group chats feature. The goal is to ensure Yolo doesn’t actively recommend chat amongst adults to minors and vice-versa. Henrion says this update should roll out soon.
“It’s 2020 and we need to be very responsible” Henrion tells me. “Moderation and growth are the most difficult things to balance. It’s moderation first for sure. We don’t care about growth if it’s not healthy or sustainable.” The new funding also gives Yolo the luxury of pushing back monetization while it focuses on safely adding more users.

By making anonymity more private, Yolo has a chance to sidestep some of the worst elements of human behavior. Making fun of someone has less appeal if there’s no wider audience like trolls exploited in the feeds and comment reels of Secret and YikYak.
That could let the brighter side of anonymity shine through: vulnerability, honesty and deep connections that are enhanced by the absence of embarrassment. With all the change, uncertainty and anxiety that’s part of growing up, teens deserve a place where they can be open with each other and speak their minds. After all, you only live once.
Powered by WPeMatico
A quick hit as we have a podcast to record, but a few public companies in the broader SaaS market reported earnings in the past week. Their results are worth unpacking as they paint a good picture of what the markets are hunting for in modern software companies.
Of course, we’re covering the firms’ share-price movements in the context of an epic selloff stemming from global conditions that are already impacting earnings.
But, hey, not all the news out there is bad. In fact, for our three companies, public investors are waving green flags. So let’s take a peek regarding why Dropbox, Box and Sprout Social — one recent IPO and two slightly-out-of-favor SaaS shops — each shot higher after reporting their Q4-era results.
Let’s proceed in alphabetical order, putting Box at the top of our list. We’ll then work through Dropbox and Sprout Social.
Box’s calendar Q4-era earnings report (the company’s Fiscal 2020 Q4) beat investor expectations three times. It reported more revenue than anticipated, $183.6 million over expectations of $181.6 million; a slimmer loss than predicted, $0.07 per-share in adjusted profit against a projected $0.04; and the storage-grounded, corporate productivity company’s quarterly forecast of $183.0 million to $184.0 million was a few million ahead of expectations ($181.8 million, per Yahoo Finance).
Powered by WPeMatico
Earlier today, during an eye-popping market selloff, DoorDash announced that it has privately filed to go public. The decision to file privately will allow the high-valued startup to get its S-1 documents in good order with the SEC before showing the rest of us what it has up its sleeve.
The move to announce its private filing is more interesting and could be related to prepping demand for its shares, providing some PR-cover for backer SoftBank, which could use the assist, or, perhaps, to dampen investor excitement for rival companies, in the face of DoorDash’s implied success and maturity.
Whatever the reasons behind the timing — some of which must deal with the capital requirements of long-running cash burn — the filing is a new milestone for the on-demand and gig economies. And how well DoorDash’s filing is received, predicated in no small part on its recent financial performance, will help set sentiment for a number of other, richly backed startups.
So let’s remind ourselves of what we know about DoorDash’s financial history. This will give us a workable foundation heading into its eventual S-1, and, we presume, old-fashioned IPO. (It’s hard to imagine the cash-fired engine that is DoorDash looking toward a direct listing.) We’ll dig through its fundraising, unearth what we know about its revenue over time and turn over some data concerning its hiring efforts in recent months to better understand its IPO prep.
DoorDash’s fundraising history is well-known but worth recalling sequentially.
Powered by WPeMatico
Coding and other computer science expertise remain some of the more important skills that a person can have in the working world today, but in the last few years, we have also seen a big rise in a new generation of tools providing an alternative way of reaping the fruits of technology: “no-code” software, which lets anyone — technical or non-technical — build apps, games, AI-based chatbots, and other products that used to be the exclusive terrain of engineers and computer scientists.
Today, one of the newer startups in the category — London-based Gyana, which lets non-technical people run data science analytics on any structured dataset — is announcing a round of £3 million to fuel its next stage of growth.
Led by U.K. firm Fuel Ventures, other investors in this round include Biz Stone of Twitter, Green Shores Capital and U+I , and it brings the total raised by the startup to $6.8 million since being founded in 2015.
Gyana (Sanskrit for “knowledge”) was co-founded by Joyeeta Das and David Kell, who were both pursuing post-graduate degrees at Oxford: Das, a former engineer, was getting an MBA, and Kell was doing a Ph. D. in physics.

Das said the idea of building this tool came out of the fact that the pair could see a big disconnect emerging not just in their studies, but also in the world at large — not so much a digital divide, as a digital light year in terms of the distance between the groups of who and who doesn’t know how to work in the realm of data science.
“Everyone talks about using data to inform decision making, and the world becoming data-driven, but actually that proposition is available to less than one percent of the world,” she said.
Out of that, the pair decided to work on building a platform that Das describes as a way to empower “citizen data scientists,” by letting users upload any structured data set (for example, a .CSV file) and running a series of queries on it to be able to visualise trends and other insights more easily.
While the longer term goal may be for any person to be able to produce an analytical insight out of a long list of numbers, the more practical and immediate application has been in enterprise services and building tools for non-technical knowledge workers to make better, data-driven decisions.
To prove out its software, the startup first built an app based on the platform that it calls Neera (Sanskrit for “water”), which specifically parses footfall and other “human movement” metrics, useful for applications in retail, real estate and civic planning — for example to determine well certain retail locations are performing, footfall in popular locations, decisions on where to place or remove stores, or how to price a piece of property.
Starting out with the aim of mid-market and smaller companies — those most likely not to have in-house data scientists to meet their business needs — startup has already picked up a series of customers that are actually quite a lot bigger than that. They include Vodafone, Barclays, EY, Pret a Manger, Knight Frank and the UK Ministry of Defense. It says it has some £1 million in contracts with these firms currently.
That, in turn, has served as the trigger to raise this latest round of funding and to launch Vayu (Sanskrit for “air”) — a more general purpose app that covers a wider set of parameters that can be applied to a dataset. So far, it has been adopted by academic researchers, financial services employees, and others that use analysis in their work, Das said.

With both Vayu and Neera, the aim — refreshingly — is to make the whole experience as privacy-friendly as possible, Das noted. Currently, you download an app if you want to use Gyana, and you keep your data local as you work on it. Gyana has no “anonymization” and no retention of data in its processes, except things like analytics around where your cursor hovers, so that Gyana knows how it can improve its product.
“There are always ways to reverse engineer these things,” Das said of anonymization. “We just wanted to make sure that we are not accidentally creating a situation where, despite learning from anaonyised materials, you can’t reverse engineer what people are analysing. We are just not convinced.”
While there is something commendable about building and shipping a tool with a lot of potential to it, Gyana runs the risk of facing what I think of as the “water, water everywhere” problem. Sometimes if a person really has no experience or specific aim, it can be hard to think of how to get started when you can do anything. Das said they have also identified this, and so while currently Gyana already offers some tutorials and helper tools within the app to nudge the user along, the plan is to eventually bring in a large variety of datasets for people to get started with, and also to develop a more intuitive way to “read” the basics of the files in order to figure out what kinds of data inquiries a person is most likely to want to make.
The rise of “no-code” software has been a swift one in the world of tech spanning the proliferation of startups, big acquisitions, and large funding rounds. Companies like Airtable and DashDash are aimed at building analytics leaning on interfaces that follow the basic design of a spreadsheet; AppSheet, which is a no-code mobile app building platform, was recently acquired by Google; and Roblox (for building games without needing to code) and Uncorq (for app development) have both raised significant funding just this week. In the area of no-code data analytics and visualisation, there are biggies like Tableau, as well as Trifacta, RapidMiner and more.
Gartner predicts that by 2024, some 65% of all app development will be made on low- or no-code platforms, and Forrester estimates that the no- and low-code market will be worth some $10 billion this year, rising to $21.2 billion by 2024.
That represents a big business opportunity for the likes of Gyana, which has been unique in using the no-code approach specifically to tackle the area of data science.
However, in the spirit of citizen data scientists, the intention is to keep a consumer version of the apps free to use as it works on signing up enterprise users with more enhanced paid products, which will be priced on an annual license basis (currently clients are paying between $6,000 and $12,000 depending on usage, she said).
“We want to do free for as long as we can,” Das said, both in relation to the data tools and the datasets that it will offer to users. “The biggest value add is not about accessing premium data that is hard to get. We are not a data marketplace but we want to provide data that makes sense to access,” adding that even with business users, “we’d like you to do 90% of what you want to do without paying for anything.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Twilio is best known for its communications API, which allows developers to add messaging, voice or video to their apps with just a small slice of code. The company’s tools are used by customers like Lyft, Airbnb, Salesforce, Box and Duke University.
The former startup went public in 2016 at $15 a share. Yesterday Twilio’s stock closed at $113.90, giving the company a market cap of about $15.6 billion (after a horrendous week on Wall Street). It’s easy to look at its value (among other measures) and declare Twilio a successful public company. But just like every former startup out there, its ascent wasn’t always so certain.
Founded in 2008, Twilio was once a tentative early-stage company feeling its way forward in the market with an unproven product and more future potential than actual results. Recently, the company’s CEO Jeff Lawson shared a Twilio board deck from March 2010.
Naturally, we read through it — how could we not? — but we also decided to analyze it for you, pulling out what we learned and using the snapshot of Twilio’s history to illustrate how far the company has come in the last decade.
The presentation’s original time stamp lands after Twilio’s Series A and just before its Series B, allowing us to see a company molting from a hatchling to something more sturdy that could stand on its own two feet. The company raised $12 million six months after the deck was presented.
To get everyone on the same page, we’ll start with a little history, and then get into the deck itself. Let’s go!
Powered by WPeMatico
Stonly is building a service for customer support teams so that they can share step-by-step guides to solve the most common issues users have. The startup just raised a $3.5 million funding round led by Accel with business angels also participating, such as Eventbrite CTO Renaud Visage and PeopleDoc founders Jonathan Benhamou and Clément Buyse.
The startup isn’t building a chatbot for customer support — chatbots usually don’t understand what you mean and you end up contacting customer support anyway. Stonly believes that scripted guides with multiple questions work much better than both chatbots and intimidating knowledge bases.
But the company is well aware that it isn’t going to replace Zendesk or Intercom overnight. That’s why a Stonly guide is a module that you can embed in your existing tools. The startup currently supports Intercom, Zendesk, Freshdesk and Front.
This way, if somebody contacts you on Front or Intercom, you can reply with a Stonly guide to help your users solve their own issues (at least if it’s a common issue). Stonly is also launching its own more traditional knowledge base powered by Stonly guides so that your client can access common questions through a chat widget.
Putting together a Stonly guide doesn’t require any technical skills. After defining the steps, you can write text, add images, videos and buttons in a web interface. Stonly also supports translations.
And it’s been working well for the startup’s first clients. For instance, Dashlane noticed a 25% decrease in opened tickets for their most frequent issues after using Stonly. Other clients include Devialet, Happn and Calendly.
With today’s funding round, the startup is expanding to the U.S. with a new office in New York and David Rostan, VP of Sales and Marketing at Calendly, is joining as head of revenue.
Powered by WPeMatico
It’s been a big news day for Salesforce . It announced that co-CEO Keith Block would be stepping down, and that it had acquired Vlocity for $1.33 billion in an all-cash deal.
It’s no coincidence that Salesforce targeted this startup. It’s a firm that builds six industry-specific CRMs on top of Salesforce — communications, media and entertainment, insurance and financial services, health, energy and utilities and government and nonprofits — and Salesforce Ventures was also an investor. This would appear to have been a deal waiting to happen.
Brent Leary, founder and principal analyst at CRM Essentials, says Salesforce saw this as an important target to keep building the business. “Salesforce has been beefing up their abilities to provide industry-specific solutions by cultivating strategic ISV partnerships with companies like Vlocity and Veeva (which is focused on life sciences). But this move signals the importance of making these industry capabilities even more a part of the platform offerings,” Leary told TechCrunch.
Ray Wang, founder and principal analyst at Constellation Research, also liked the deal for Salesforce. “It’s a great deal. Vlocity gives them the industries platform they need. More importantly, it keeps Google from buying them and [could generate] $10 billion in additional industries revenue growth over next four years,” he said.
Vlocity had raised about $163 million on a valuation of around $1 billion as of its most recent round, a $60 million Series C last March. If $1.33 billion seems a little light, given what Vlocity is providing the company, Wang says it’s because Vlocity needed Salesforce more than the other way around.
“Vlocity on its own doesn’t have as big a future without Salesforce. They have to be together. So Salesforce doesn’t need to buy them. They could keep building out, but it’s better for them to buy them now,” Wang said.
Still, the company was valued at $1 billion just under a year ago, and sold for $1.33 billion after raising $163 million. That means it received 8.2x total invested capital ($1.33 billion/ $163 million invested capital), which isn’t a bad return.
In a blog post on the Vlocity website, founder and CEO David Schmaier put a positive spin on the deal. “Upon the close of the transaction, Vlocity — this wonderful company that we, as a team, have created, built, and grown into a transformational solution for six of the most important industries in the enterprise — will become part of Salesforce,” he wrote.
Per usual, the deal will be predicated on regulatory approval and close some time during Salesforce’s second quarter in fiscal 2021.
Powered by WPeMatico
Fintech startup Revolut is raising a large Series D round of funding. TCV is leading the $500 million round, valuing the company at $5.5 billion. Over the past few years, Revolut has raised $836 million in total.
Some existing investors are also participating in today’s funding round, but Revolut isn’t sharing names. Previous investors include DST Global, Index Ventures, Balderton Capital and many others.
If you’re not familiar with Revolut, the company is building a financial service to replace traditional bank accounts. You can open an account from an app in just a few minutes. You can then receive, send and spend money from the app or using a debit card.
On top of that, Revolut has added a ton of features that it has built in-house or through partnerships. You can insure your phone, get a travel medical insurance package, buy cryptocurrencies, buy shares, donate to charities, save money and more.
Revolut currently has more than 10 million customers, mostly in Europe and the U.K. The company doesn’t share specific numbers when it comes to transaction volume and monthly active customers, but here are some percentage-based metrics:
With the new influx of cash, the company says that it’ll focus on improving its product for existing users as well as revenue. It’s all about making Revolut more useful and stickier going forward.
In particular, you can expect new lending services for both retail customers as well as companies using Revolut for Business. While Revolut provides a ton of services in the U.K., customers in other markets don’t have the same feature set. For instance, Revolut recently launched savings vaults in the U.K. — customers in other markets will be able to open savings sub-accounts in the future, as well.
Other than that, Revolut wants to double down on the core features. The company will improve its two subscription tiers (Premium and Metal) and improve banking operations across Europe — you can expect full bank accounts in Europe in the future.
There are currently 2,000 people working for Revolut. “We’re on a mission to build a global financial platform — a single app where our customers can manage all of their daily finances, and this investment demonstrates investor confidence in our business model. Going forward, our focus is on rolling-out banking operations in Europe, increasing the number of people who use Revolut as their daily account, and striving towards profitability,” Revolut co-founder and CEO Nik Storonsky said in the release.
Revolut is currently live in the U.K., Europe, Singapore and Australia (in beta). While the company has announced plans to expand to a handful of countries, the main focus is on launching in the U.S. and Japan in the coming months.
Powered by WPeMatico
DSP Concepts — a startup whose Audio Weaver software is used by companies as varied as Tesla, Porsche, GoPro and Braun Audio — is announcing that it has raised $14.5 million in Series B funding.
The startup goal, as explained to me by CEO Chin Beckmann and CTO Paul Beckmann (yep, they’re a husband-and-wife founding team), is to create the standard framework that companies use to develop their audio processing software.
To that end, Chin told me they were “picky about who we wanted on the B round, we wanted it to represent the support and endorsement of the industry.”
So the round was led by Taiwania Capital, but it also includes investments from the strategic arms of DSP Concepts’ industry partners — BMW i Ventures (which led the Series A), the Sony Innovation Growth Fund by Innovation Growth Ventures, MediaTek Ventures, Porsche Ventures and the ARM IoT Fund.
Paul said Audio Weaver started out as the “secret weapon” of the Beckmanns’ consulting business, which he could use to “whip out” the results of an audio engineering project. At a certain point, consulting customers started asking him, “Hey, how about you teach me how to use that?,” so they decided to launch a startup focused on the Audio Weaver platform.
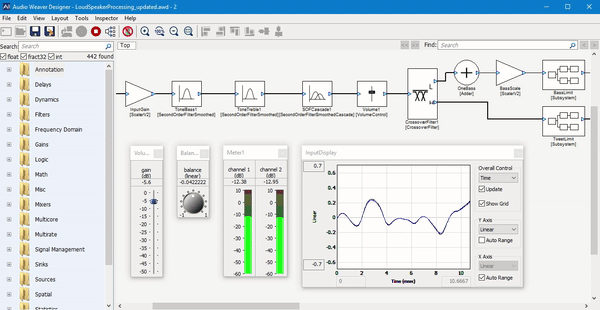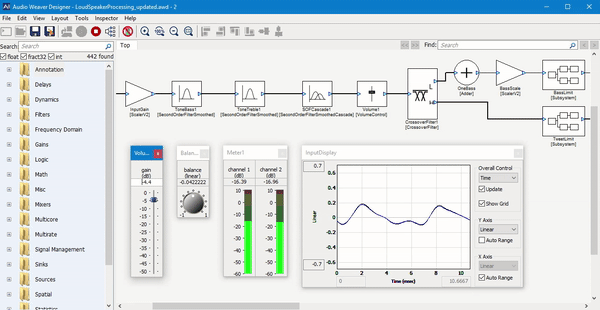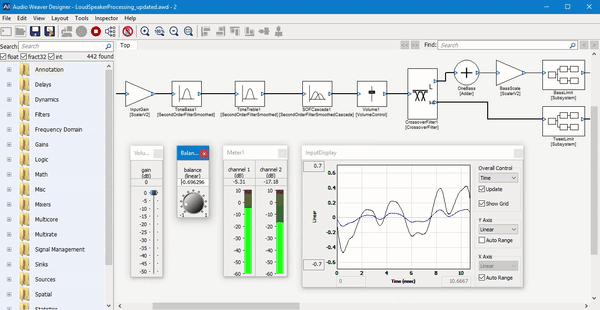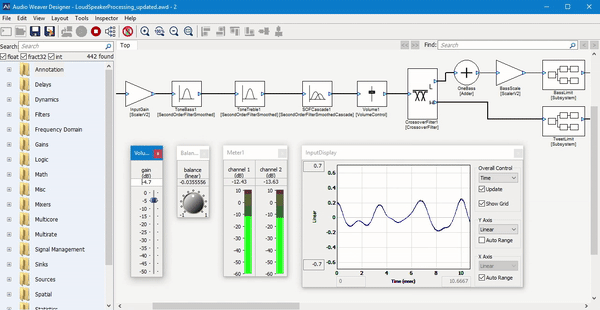
Paul described the software as a “graphical block diagram editor.” Basically, it provides a way for audio engineers to combine and customize different software modules for audio processing.
“Audio is still in the Stone Ages compared to other industries,” he said. “Suppose you’re building a product with a touchscreen — are you going write the graphics from scratch or use a framework like Qt?”
Similarly, he suggested that while many audio engineers are still “down in the weeds writing code,” they can take advantage of Audio Weaver’s graphical interface to piece everything together, as well as the company’s “hundreds of different modules — pre-written, pre-tested, pre-optimized functions to build up your system.”
For example, Paul said that by using the Audio Weaver platform, DSP Concepts engineers could test out “hundreds of ideas” for algorithms for reducing wind noise in the footage captured by GoPro cameras, then ultimately “hand the algorithms over to GoPro,” whose team could them plug the algorithms into their software and modify it themselves.
The Beckmanns said the company also works closely with chip manufacturers to ensure that audio software will work properly on any device powered by a given chipset.
Other modules include TalkTo, which is designed to give voice assistants like Alexa “super-hearing,” so that they can still isolate voice commands and cancel out all the other noise in loud environments, even rock concerts. (You can watch a TalkTo demo in the video below.)
DSP Concepts has now raised more than $25 million in total funding.
Powered by WPeMatico
Amazon may have a market cap of more than $1 trillion, but Finbarr Taylor, CEO of Y Combinator-backed startup Shogun, said the e-commerce giant is “kind of dropping the ball.”
Specifically, he argued that the experience of shopping on Amazon — not what happens after you buy something, but browsing the website itself — is pretty bad, full of sponsored results and fake products.
“What we’re seeing happen is that all this vast wave of direct-to-consumer brands is nibbling around edges of Amazon and beating them on buying experience,” Taylor said.
Shogun was designed to support those brands. Taylor and his co-founder Nick Raushenbush created the first product in 2015, and they treated it as a side project at first. But Taylor said that by May 2017, “It ate up all of our free time and it was obviously much bigger than we expected,” so they quit their jobs (Taylor was working as a software engineer at Y Combinator) and devoted themselves to it full-time.
The company now has 11,000 customers, including MVMT, K-Swiss and Leesa. And today, Shogun is announcing that it has raised a $10 million Series A, led by Initialized Capital, with participation from VMG Partners and YC. (The startup has now raised a total of $12 million.)
The company’s first product, Page Builder, offers a drag-and-drop interface to make it easier for e-commerce brands to build their storefronts on Shopify, BigCommerce, Salesforce and Magento.
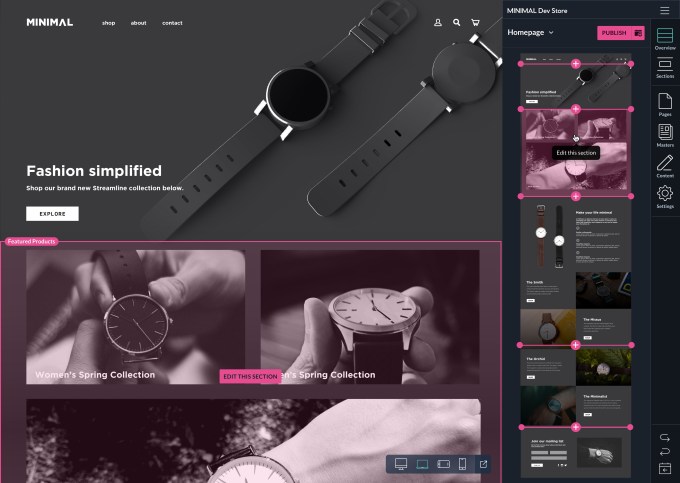
And there’s a new product, Shogun Frontend, which allows brands to create a web storefront that’s entirely customized while still using one of the big commerce platforms as their back end.
Taylor pitched this as part of a broader trend toward “headless commerce,” where the e-commerce front end and back end are handled separately. He suggested that this is a “mutually beneficial” split, as Shopify and its competitors are going “super deep” on building the infrastructure needed to operate a store online, while Shogun focuses on the actual experience of the customer visiting that store.
Meanwhile, website builders like Squarespace and Weebly (owned by Square) have introduced e-commerce features, but Taylor suggested that they’re still “not really a professional choice” for most e-commerce businesses.
As one of the key features of Shogun Frontend, Taylor pointed to the fact that it creates progressive web apps that should be as fast and smooth as a native app.
Brett Gibson, general partner at Initialized Capital and a Shogun board member, made a similar point in a statement:
For DTC brands competing against goliaths like Amazon, Shogun Frontend now gives them features and capabilities once only reserved for enterprise companies. And when it comes to speed, Shogun Frontend’s sub-second load time is the critical difference between retaining or losing a customer.
Taylor added that the company will be “continuing to invest in Page Builder too,” but he suggested that Frontend is “more of an enterprise offering” that can help Shogun’s biggest customers “future proof themselves.”
Powered by WPeMatico