funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
As a result of the pandemic, accelerators have moved operations fully remote to abide by social distancing. The shift has forced well-known programs like 500 Startups, Y Combinator and Techstars to go fully online, while encouraging existing venture capital firms to launch new digital-only fellowships like Cleo Capital and NextView Ventures.
Before the pandemic, accelerators could advertise their value by lending desk space once used by Airbnb, Twilio and Brex’s co-founders, plus a glitzy demo day. Now, stripped of their in-person element, the actual value of an accelerator program — and the network they provide — is being tested in new ways.
So a question remains for participating founders: Are they getting the benefits of what they thought they signed up for?
The last thing Michael Vega-Sanz wanted to do was was join another Zoom get-together for entrepreneurs. But the car-sharing company he co-founded with twin brother Matthew was in the middle of a pivot, so they joined NextView Ventures’ inaugural remote accelerator program.
“I envisioned an accelerator with awkward happy hours, mass Zoom calls,” Vega-Sanz said. Fast-forward one month into the program, he says it “has been quite the opposite.”
Before joining NextView’s accelerator, Vega-Sanz did an in-person incubator at Babson College in Boston, but there’s “a lot less fluff” in being virtual, he told TechCrunch.
“[With in-person] the reality was you’d go to lunch, and by the time you drove over there and had all your side talk, small talk, chit-chat and actually got into the nitty-gritty of the event, there was a lot of time loss,” he said. “You could have been working for your company during that time.”
If possible, Vega-Sanz still recommends that first-time founders attend a physical accelerator instead of a virtual one for the energy it brings, even with the downside of useless events.
Powered by WPeMatico
As we move deeper into the pandemic, companies are looking for ways to digitize processes that previously required in-person meetings with manual approaches. Investors appear to be rewarding companies that can achieve this. IObeya, a French company that helps digitize management planning processes like lean and agile, announced a $17 million Series A today.
Red River West led the round with help from Atlantic Bridge Capital and Fortino Capital Partners. It has now raised a total of $20 million, according to the company.
Tim McCracken, who heads up the company’s U.S. operations, says the name comes from the Japanese word for the large room where companies did all their planning. Many companies gather a group of people in a conference room and line the walls with sticky notes and white boards with their plans for the coming weeks and months.
Even before the pandemic struck, it wasn’t the most effective way to record this valuable business content, and iObeya has developed a service to put it in the digital realm. “And so one of the things that they did with those obeya rooms was they had lots of different visual management boards with Post-it notes and with different types of indicators that they would use to manage their business. And so what iObeya does is digitize that type of visual management, so that you can access it from multiple locations and share it amongst teams and basically eliminate the need for doing it on paper and on walls,” McCracken explained.
This involves digitizing four main areas that include lean management, factory floor management, agile programming and, finally, what they call the digital workplace, which includes design thinking, virtual whiteboarding and brainstorming. All of these approaches have lots of planning associated with them and could benefit from being moved online.
Image Credits: iObeya
They are approaching 100 employees, with the majority in France right now, with a small office in the U.S. (in Seattle), but they will be using this money to expand with plans to add 50 more people. He says the company has always looked at diversity when it comes to its hiring practices.
“We want to try to attract, not only experienced salespeople, as well as the support organization around them, but also really do as much outreach in the local community to see how we can ensure that our workforce reflects the community,” he said.
As the company had to shut down offices due to COVID-19, McCracken says their own software helped them make that transition more smoothly. “We actually use our own software to manage business so we had very little disruption to our actual work. At the same time, the volume of work increased probably four to five fold, simply because of increased demand for the software. So we had to manage not only moving from working in an office to work at home, but also the increased workload,” he said.
The company was founded near Paris in 2011. They plan to use the money to expand operations in the U.S. and build awareness of the company through greater sales and marketing spend.
Powered by WPeMatico
The wider field of cybersecurity — not just defending networks, but identifying fraudulent activity — has seen a big boost in activity in the last few months, and that’s no surprise. The global health pandemic has led to more interactions and transactions moving online, and the contractions we’re feeling across the economy and society have led some to take more desperate and illegal actions, using digital challenges to do it.
Today, a U.K. company called Quantexa — which has built a machine learning platform branded “Contextual Decision Intelligence” (CDI) that analyses disparate data points to get better insight into nefarious activity, as well as to (more productively) build better profiles of a company’s entire customer base — is raising a growth round of funding to address that opportunity.
The London-based startup has picked up $64.7 million, a Series C it will be using to continue building out both its tools and the use cases for applying them, as well as expanding geographically, specifically in North America, Asia-Pacific and more European territories.
The mission, said Vishal Marria, Quantexa’s founder and CEO, is to “connect the dots to make better business decisions.”
The startup built its business on the back of doing work for major banks and others in the financial services sector, and Marria added that the plan will be to continue enhancing tools for that vertical while also expanding into two growing opportunities: working with insurance and government/public sector organizations.
The backers in this round speak to how Quantexa positions itself in the market, and the traction it’s seen to date for its business. It’s being led by Evolution Equity Partners — a VC that specialises in innovative cybersecurity startups — with participation also from previous backers Dawn Capital, AlbionVC, HSBC and Accenture, as well as new backers ABN AMRO Ventures. HSBC, Accenture and ABN AMRO are all strategic investors working directly with the startup in their businesses.
Altogether, Quantexa has “thousands of users” across 70+ countries, it said, with additional large enterprises, including Standard Chartered, OFX and Dunn & Bradstreet.
The company has now raised some $90 million to date, and reliable sources close to the company tell us that the valuation is “well north” of $250 million — which to me sounds like it’s between $250 million and $300 million.
Marria said in an interview that he initially got the idea for Quantexa — which I believe may be a creative portmanteau of “quantum” and “context” — when he was working as an executive director at Ernst & Young and saw “many challenges with investigations” in the financial services industry.
“Is this a money launderer?” is the basic question that investigators aim to answer, but they were going about it, “using just a sliver of information,” he said. “I thought to myself, this is bonkers. There must be a better way.”
That better way, as built by Quantexa, is to solve it in the classic approach of tapping big data and building AI algorithms that help, in Marria’s words, connect the dots.
As an example, typically, an investigation needs to do significantly more than just track the activity of one individual or one shell company, and you need to seek out the most unlikely connections between a number of actions in order to build up an accurate picture. When you think about it, trying to identify, track, shut down and catch a large money launderer (a typical use case for Quantexa’s software) is a classic big data problem.
While there is a lot of attention these days on data protection and security breaches that leak sensitive customer information, Quantexa’s approach, Marria said, is to sell software, not ingest proprietary data into its engine to provide insights. He said that these days deployments typically either are done on premises or within private clouds, rather than using public cloud infrastructure, and that when Quantexa provides data to complement its customers’ data, it comes from publicly available sources (for example, Companies House filings in the U.K.).
There are a number of companies offering services in the same general area as Quantexa. They include those that present themselves more as business intelligence platforms that help detect fraud (such as Looker) through to those that are secretive and present themselves as AI businesses working behind the scenes for enterprises and governments to solve tough challenges, such as Palantir, through to others focusing specifically on some of the use cases for the technology, such as ComplyAdvantage and its focus on financial fraud detection.
Marria says that it has a few key differentiators from these. First is how its software works at scale: “It comes back to entity resolution that [calculations] can be done in real time and at batch,” he said. “And this is a platform, software that is easily deployed and configured at a much lower total cost of ownership. It is tech and that’s quite important in the current climate.”
And that is what has resonated with investors.
“Quantexa’s proprietary platform heralds a new generation of decision intelligence technology that uses a single contextual view of customers to profoundly improve operational decision making and overcome big data challenges,” said Richard Seewald, founding and managing partner of Evolution, in a statement. “Its impressive rapid growth, renowned client base and potential to build further value across so many sectors make Quantexa a fantastic partner whose team I look forward to working with.” Seewald is joining the board with this round.
Powered by WPeMatico
Back in 2016, Mobalytics wowed the judges at Disrupt SF with its data-based coach for the exploding competitive gaming world, winning the Startup Battlefield. The company is building on the success of the past few years with a new funding round and a compelling new collaboration with Tobii that uses eye-tracking to provide powerful insights into gamers’ skills.
Mobalytics began with the idea that, by leveraging the in-game data of a competitive esport like League of Legends (LoL), they could provide objective feedback to players along the lines of how fast or effective they are in different situations. Quantifying things like survivability or teamplay provides an analogue to similar measures in physical sports.
“On an athlete you have all these measurements, like pulse oximeters, ECGs, the 40-yard dash,” said Amine Issa, co-founder and “Warchief of Science.” Not so much with PC games. Their challenge at that time was to take the LoL API provided by Riot and transform it into actionable feedback, which the company’s success in the years since suggests they managed to do.
But Issa had always wanted to use another, more direct and objective measurement of a gamer’s mental processes: eye tracking. And last year they began an internal project to evaluate doing just that, in partnership with eye-tracking hardware maker Tobii.
“If you know where someone is looking, it’s the closest thing to knowing what they’re thinking,” Issa said. “When you combine that with the larger picture you can put together something to help them along. So we spent six months conducting research, taking players of different levels and roles and studying their eye tracking data to find some metrics we could organize the platform around.”
Not surprisingly, there are characteristics of the highly skilled (and practiced) that set them apart, and the team was able to collect them into a set of characteristics that any player can relate to.

Well, the gif compression isn’t so hot, but you get the idea — the purple square indicates attention. Image Credits: Mobalytics
“We had to think about how to build a product that people want to use. One thing we learned after TechCrunch is that even a simple score from 0-100 doesn’t work for everyone. You need to provide the context for that. So with something like eye tracking, you’re getting 30 data points per second — how do you break that down in a way that players understand it?”
Talking to professional gamers and coaches during the study helped them form the main categories that Mobalytics now tracks with the aid of a Tobii device, like information processing, map awareness and tunnel vision.
“It’s important to be able to tell a narrative to people. Say you get ganked a lot,” said Issa, referring to the unfortunate occurrence of being picked off by enemy players while alone. “Why are you getting ganked? If your vision score is high but map awareness is low, that’s one thing. Did you know all the information and go in arrogantly, or were you not aware? League is a very complicated game, so players want to know, in this specific fight, what did I do wrong, and what should I have done instead?”
That second question is a tougher one (though perhaps AI MOBA players may have something to say about it), but the metrics are powerful in and of themselves. “Pros are fascinated by this technology,” Issa said. “There’s a lot of ‘I had no idea’ moments. Coaches have said, these are my fastest players but it’s cool to see that as a quantifiable variable.”
Tobii’s head of gaming, Martin Lindgren, echoed this feeling: “Pro teams aren’t interested in being told what to do. They want the data so they can draw their own conclusions.”
Tobii now has a gaming-focused eye-tracker and integrates with a number of AAA games, like Rise of the Tomb Raider, where it can be used in place of fiddly aiming using the analog sticks. As someone who’s bad at specifically that part of games, this is attractive to me, and Lindgren said opportunities like that are only increasing as gaming companies embrace both accessibility and try to stand out in a crowded market.
The companies have worked together to improve the eye-tracking coaching, for instance lowering the number of games a user must play before the system can accurately track their in-game actions; Lindgren said the collaboration with Mobalytics is ongoing — “definitely a long-term partnership” — in fact Tobii’s relationship with the founders predates their startup.
The ultimate goal of Mobalytics is to have a gaming assistant that adapts itself to your playing and preferences, making intelligent suggestions to improve your skills. That’s a ways off, but the company is getting the hang of it. Its first product, the LoL assistant, took a year to build, Issa said. A more recent one, for Legends of Runeterra, took three months. Teamfight Tactics took three weeks.
Admittedly it was more difficult to design one for Valorant, which, being a first-person shooter, is wildly different from the other games — but now that it’s done, a lot of that work could be applied to an assistant for Counter-Strike or Overwatch.
Expansion to other games and genres is the reason for raising an $11 million Series A, led by Almaz Capital and Cabra VC, with HP Tech Ventures, General Catalyst, GGV Capital, RRE Ventures, Axiomatic and T1 Esports participating.
“It was a very different experience from the post-TechCrunch one, where you’re in the spotlight and everyone’s throwing money your way,” said Issa. “But we’ve built a successful product on LoL, expanded to four games, today we have more than seven million monthly active users… Our plan is to double down on what’s worked for us and create the ultimate gaming companion.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Now that I’ve offered an overview to help you think through where concentrated stock sits in your overall plan, let’s take a closer look at why selling can be challenging for some.
In the following section, I reveal the facts of the concentrated stock “get rich” myths that reside in the minds of many first-time concentrated stock owners, and I show why it is prudent to consider greater diversification.
Keep reading to learn more about the benefits of diversification, discover how much company stock is likely too much to hold, and the options you have when it comes to diversifying strategically.
There are several hard facts to keep in mind in contemplating maintaining a concentrated position:
The odds of any new IPO being among the top 4% is just slightly better than hitting your lucky number on the roulette wheel. But is your investment portfolio success and the odds of achieving your long-term financial goals something you want to spin the wheel on?
Excess volatility can harm returns. Note the example below that shows the comparison between a low-volatility diversified portfolio versus a high-volatility concentrated portfolio. Despite the same simple average return, the low-volatility portfolio below materially outperforms the high-volatility portfolio.
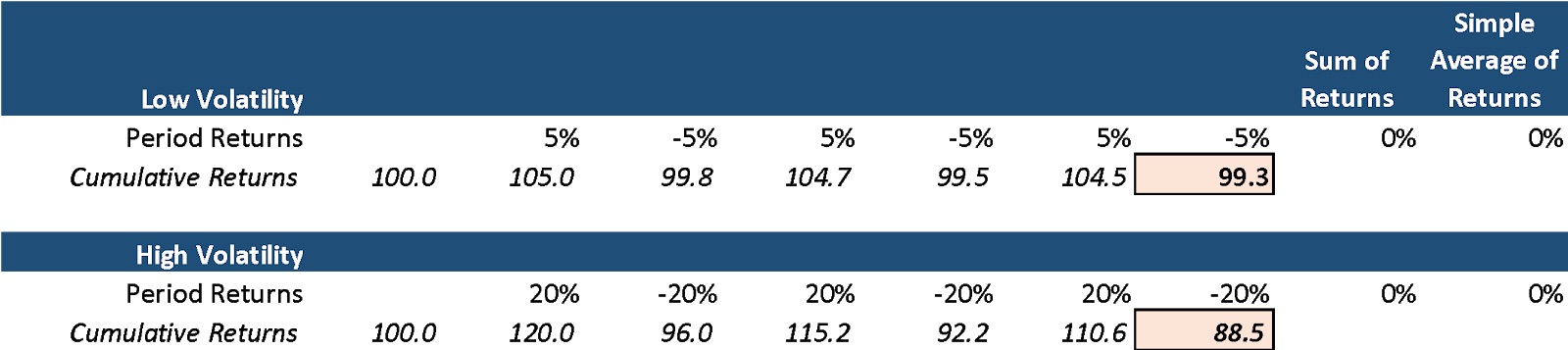
Image Credits: Peyton Carr
Beyond the math, unexpected spikes in volatility can cause significant price declines. Volatility increases the chances that an investor reacts emotionally and makes a poor investment decision. I’ll cover the behavioral finance aspect of this later. Lowering your portfolio volatility can be as simple as increasing your portfolio diversification.
The Russell 3000, an index representing the 3,000 largest U.S.-based publicly traded companies, has lower volatility when compared against 95%+ of all single stocks. So, how much return do you give up for having lower volatility?
According to Northern Trust Research, the 5.96% annualized average return of the Russell 3000 is 0.73% more than the 5.23% return of the median stock. Additionally, owning the Russell 3000, rather than a single stock, eliminates the likelihood of catastrophic loss scenarios — more than 20% of shares averaged a loss of more than 10% per year over a 20-year time frame.
If this establishes that the avoidance of overly concentrated portfolios is important, how much stock is too much? And at what price should you sell?
We consider any stock position or exposure greater than 10% of a portfolio to be a concentrated position. There is no hard number, but the appropriate level of concentration is dependent on several factors, such as your liquidity needs, overall portfolio value, the appetite for risk and the longer-term financial plan. However, above 10% and the returns and volatility of that single position can begin to dominate the portfolio, exposing you to high degrees of portfolio volatility.
The company “stock” in your portfolio often is only a fraction of your overall financial exposure to your company. Think about your other sources of possible exposure such as restricted stock, RSUs, options, employee stock purchase programs, 401k, other equity compensation plans, as well as your current and future salary stream tied to the company’s success. In most cases, the prudent path to achieving your financial goals involves a well-diversified portfolio.
Facts aside, maintaining a concentrated position in your company stock is far more tempting than taking a more measured approach. Token examples like Zuckerberg and Bezos tend to outshine the dull rationale of reality, and it’s hard to argue against the possibility of becoming fabulously wealthy by betting on yourself. In other words, your emotions can get the best of you.
But your goals — not your emotions — should be driving your investment strategy and decisions regarding your stock. Your investment portfolio and the company stock(s) within it should be used as tools to achieve those goals.
So first, we’ll take a deep dive into the behavioral psychology that influences our decision-making.
Despite all the evidence, sometimes that little voice remains.
“I want to hold the stock.”
Why is it so hard to shake? This is a natural human tendency. I get it. We have a strong impetus to rationalize our biases and not believe we are vulnerable to being influenced by them.
Becoming attached to your company is common, since after all, that stock has made you, or has the potential of making you wealthy. More often than not, selling and diversifying is the tough, but more rational decision.
Numerous studies have furnished insights into the correlation between investing and psychology. Many unrecognized psychological barriers and behavioral biases can influence you to hold concentrated stock even when the data shows that you should not.
Understanding these biases can be helpful when deciding what to do with your stock. These behavioral biases are hard to spot and even harder to overcome. However, awareness is the first step. Here are a few more common behavioral biases, see if any apply to you:
Familiarity bias: Familiarity is likely why so many founders are willing to hold concentrated positions in their own company’s stock. It is easy to confuse the familiarity with your own company with the safety in the stock. In the stock market, familiarity and safety are not always related. A great (safe) company sometimes can have a dangerously overvalued stock price, and terrible companies sometimes have terrifically undervalued stock prices. It’s not just about the quality of the company but the relationship between the quality of a company and its stock price that dictates whether a stock is likely to perform well in the future.
Another way this manifests is when a founder has less experience with stock market investing and has only owned their company stock. They may think the market has more risk than their company when in actuality, it is usually safer than holding just their individual position.
Overconfidence: Every investor is exhibiting overconfidence when they hold an overly concentrated position in an individual stock. Founders are likely to believe in their company; after all, it already achieved enough success to IPO. This confidence can be misplaced in the stock. Founders often are reluctant to sell their stock if it has been going up since they believe it will continue to go up. If the stock has sold off, the opposite is true, and they are convinced it will recover. Often, it is challenging for founders to be objective when they are so close to the company. They commonly believe that they have unique information and know the “true” value of the stock.
Anchoring: Some investors will anchor their beliefs to something they experienced in the past. If the price of the concentrated stock is down, investors may anchor their belief that the stock is worth its recent previous higher value and be unwilling to sell. This previous value of the stock is not an indicator of its real value. The real value is the current price where buyers and sellers exchange the stock while incorporating all presently available information.
Endowment effect: Many investors tend to place a higher value on an asset they currently own than if they did not own it at all. It makes it harder to sell. An excellent way to check for the endowment effect is to ask yourself: “If I did not own these shares, would I purchase them today at this price?” If you are not willing to purchase the shares at this price today, it likely means you are only holding onto the shares because of the endowment effect.
A fun spin on this is to look into the IKEA effect study, which demonstrates that people assign more value to something that they made than it is potentially worth.
When framed this way, investors can make more intentional decisions on whether to continue holding concentrated stock or selling. At times, these biases are hard to spot, which is why having a second person, a co-pilot, or an advisor, is helpful.
Congratulations to those of you with a concentrated stock position in your company; it is hard-earned and likely represents a material wealth. Understand, there is no “right” answer when it comes to managing concentrated stock. Each situation is unique, so it is essential to speak with a professional about options specific to your situation.
It starts with having a financial plan, complete with specific investment goals that you want to achieve. Once you have a clear picture of what you want to accomplish, you can look at the facts in a new light and gain a deeper appreciation for the dangers of holding a concentrated position in company stock versus the benefits of diversification, considering all of the implications and opportunities involved in rational decision-making and investment behavior.
Most individuals understand they can simply and directly sell their equity, but there are a variety of other strategies. Some of these opportunities may be far better at minimizing taxes or better at achieving the desired risk or return profile. Some might wonder what the best timing is to sell. I will cover these topics in the final article of the series.
Powered by WPeMatico
The venture capital world is constantly changing, and its evolution can sometimes flip pieces of conventional wisdom on their heads. For example, a recent flurry of extension rounds from Silicon Valley’s hottest startups like Stripe and Robinhood seem to signal that the investment type has suddenly become cool.
Extensions evolving from unloved to hot is not the first time that a type of VC deal has gained, or lost luster. In past times, for example, raising consecutive rounds from the same lead investor was often perceived as a negative signal; why couldn’t the startup find a new, different lead investor? Today, in contrast, venture capitalists are using inside rounds to double-down on winning startups, a way of helping ensure returns for their own backers.
The recent phenomenon of extensions becoming vogue is a tale of the times, in which the best startups get to play offense, and startups that can’t show accelerating growth are left behind. Let’s explore what has changed.
TechCrunch first wrote about the new extension-round trend after seeing what felt like a wave of the deals crop up. Some were large, like MariaDB’s huge $25 million add-on to its Series C, or Robinhood’s biblical $320 million addition to its Series F.
But most were smaller events like Sayari adding $2.5 million to its Series B, or CALA adding $3 million to its seed round. Even more recently, Eterneva raised another $3 million on top of its seed round, and also out this week was a million pounds more for Edinburgh-based Machine Labs’ seed round.
One reason for the growth of extension rounds in 2020 has been runway — making sure that a startup has enough. Upstarts often raise on an 18-month cadence. But because of COVID-19 and its constituent economic disruptions, many have reduced costs in a bid to bolster how long they have until their cash stores reach zero.
Powered by WPeMatico
Puppet, the Portland, Oregon-based infrastructure automation company, announced a $40 million debt round today from BlackRock Investments.
CEO Yvonne Wassenaar says the company sees this debt round as part of a longer-term relationship with BlackRock . “What’s interesting, and I think part of the reason why we decided to go with BlackRock, is that typically when you look at how they invest this is the first step of a much longer-term relationship that we will have with them over time that has different elements that we can tap into as the company scales,” Wassenaar told TechCrunch.
In terms of the arrangement, rather than BlackRock taking a stake in the company, Puppet will pay back the money. “We’ve borrowed a sum of money that we will pay back over time. BlackRock does have a board observer seat, and that’s really because they’re very interested in working with us on how we grow and accelerate the business,” Wassenaar said.
Puppet has been in the process of rebuilding its executive team, with Wassenaar coming on board about 18 months ago. Last year she brought in industry veterans Erik Frieberg and Paul Heywood as CMO and CRO, respectively. This year she brought in former Cloud Foundry Foundation director Abby Kearns to be CTO.
All of these moves are with an eye to a future IPO, says Wassenaar. “We’re looking at how do we progress ultimately, ideally on a path to an IPO, and what is it going to take for Puppet to go through that journey,” she said.
She points out that in some ways, the pandemic has forced companies to look more closely at automation solutions like the ones that Puppet provides. “What’s really interesting is […] that the pandemic in many ways has put wind in our sails in terms of the need for corporations to automate and think about how they leverage and extend from a technology perspective going forward,” she said.
As Puppet continues to grow, she says that diversity is a core organizational value, and that while the company has made progress from a gender perspective (as illustrated by the presence of her and Kearns in the C Suite), they still are working at being more racially diverse.
“Where I believe we have a lot more work and there’s a lot more focus right now is further complementing that [gender diversity] from a racial perspective. And it’s an area that I have personally taken on, and I’m committed to making changes in the company as we go forward to support more racial diversity as well,” she said.
Previously the company had raised almost $150 million, with the most recent round being a $42 million Series F in 2018, according to Crunchbase data. The company previously took $22 million in debt financing in 2016, prior to Wassenaar coming on board.
Powered by WPeMatico
Lex, a new social app for women, trans, genderqueer and non-binary people offering the ability to post personal ads, has today announced the close of a $1.5 million seed funding round.
Investors in the round include Corigin Ventures, X-Factor Ventures and Tusk Ventures, as well as angels Michelle Kennedy (Peanut), Andy Dunn (Bonobos) Amanda Bradford (The League), Rei Wang (The Grand), Bumble Fund, Elisabeth Hartley, Tavi Gevinson, Nisha Dua, A.G. Breitenstein, Albert Lee, Alice Cheng, Justin Stefano, Piera Gelardi, Philippe von Borries, Debbie Millman and Roxane Gay. Female Founders Fund led the round.
Short for Lexicon, Lex was founded by Kell Rakowski, who originally rose to some prominence after starting an Instagram account called Herstory that curated cool lesbian content from the 1800s to the 90s, including the Personals Ads found in the backs of lesbian erotica magazines from the 80s.
“[The personal ads] were just so hot, and so cool,” said Rakowski. “They were really witty and the women were super direct, and were able to express themselves in a really clear and inspiring way.”
Rakowski had an idea: What if the queer personal ad came back? She asked her Herstory followers if they’d want to post their own personals and the premise quickly took off, with hundreds of personal ads flooding in over the two-day period each month when submissions were open.
The popularity of the format led to yet another idea. Rakowski decided to set up a dating/social app that was focused on these text-based personal ads for women, trans, genderqueer and non-binary people.
Lex, which launched on the App Store in November 2019, is an MVP that does just that.
Users can set up their own profile and post personals, as well as browse the feed of other personals and like the ones that pique their interest. While the personals themselves can be rather graphic, the app is not. There are currently no pictures on Lex, with the caveat that users can link out to their Instagram account if they so choose.
Rather, users can browse through the text-based personals and like them, or message the author of the personal to start up a conversation.
Moreover, unlike traditional dating apps, there is no mutuality required to start a private conversation. In other words, people don’t have to be “matched” to chat. Just like the personal ads of yesteryear, the author sends out a call for responses and the responses flow in.
It’s still early days for the app, but Rakowski has plans to set up the ability to post pictures to profiles (which would not be included in the feed, but would be clickable should the text intrigue you), as well as adding group chat to the app for folks looking to build community.
Lex also has plans to eventually introduce a freemium subscription model to the app, giving users extended functionality for a monthly price. For now, however, the focus is on growth and building out the app.
With the new funding, Lex is looking to hire underrepresented talent in tech for product and engineering positions. The team, comprised of five people, is currently 80% cis women and 20% cis men, with 80% identifying as LGBTQ. Three of the five team members are people of color.
Lex is being aggressive about this hiring sprint, posting its open positions on the app and on Instagram.
“I’ve gotten so many incredible queer tech talent applying for positions at Lex,” said Rakowski. “It’s so inspiring and also emotional. People are writing the most beautiful emails about how much they like Lex. Hiring is 100% our main focus.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Qumulo, a Seattle storage startup helping companies store vast amounts of data, announced a $125 million Series E investment today on a $1.2 billion valuation.
BlackRock led the round with help from Highland Capital Partners, Madrona Venture Group, Kleiner Perkins and new investor Amity Ventures. The company reports it has now raised $351 million.
CEO Bill Richter says the valuation is more than 2x its most recent round, a $93 million Series D in 2018. While the valuation puts his company in the unicorn club, he says that it’s more important than simple bragging rights. “It puts us in the category of raising at a billion-plus dollar level during a very complicated environment in the world. Actually, that’s probably the more meaningful news,” he told TechCrunch.
It typically hasn’t been easy raising money during the pandemic, but Richter reports the company started getting inbound interest in March just before things started shutting down nationally. What’s more, as the company’s quarter closed at the end of April, they had grown almost 100% year over year, and beaten their pre-COVID revenue estimate. He says they saw that as a signal to take additional investment.
“When you’re putting up nearly 100% year over year growth in an environment like this, I think it really draws a lot of attention in a positive way,” he said. And that attention came in the form of a huge round that closed this week.
What’s driving that growth is that the amount of unstructured data, which plays to the company’s storage strength, is accelerating during the pandemic as companies move more of their activities online. He says that when you combine that with a shift to the public cloud, he believes that Qumulo is well positioned.
Today the company has 400 customers and more than 300 employees, with plans to add another 100 before year’s end. As he adds those employees, he says that part of the company’s core principles includes building a diverse workforce. “We took the time as an organization to write out a detailed set of hiring practices that are designed to root out bias in the process,” he said.
One of the keys to that is looking at a broad set of candidates, not just the ones you’ve known from previous jobs. “The reason for that is that when you force people to go through hiring practices, you open up the position to a broader, more diverse set of candidates and you stop the cycle of continuously creating what I call ‘club memberships’, where if you were a member of the club before you’re a member in the future,” he says.
The company has been around since 2012 and spent the first couple of years conducting market research before building its first product. In 2014 it released a storage appliance, but over time it has shifted more toward hybrid solutions.
Powered by WPeMatico
SocialChorus, a startup that helps distribute communications internally in a similar way marketers reach customers externally, announced a $100 million investment today led by Sumeru Equity Partners. With this investment, the firm has bought a majority stake in the company. As part of today’s deal, Sumeru will be adding three members to the SocialChorus board.
“Sumeru Equity Partners is making a majority investment in the company but also well capitalizing the business for future growth,” Mark Haller, principal at Sumeru told TechCrunch.
The company previously raised $47 million, according to Crunchbase data. Haller says this is not a buyout, so much as a partnership with those previous investors. “We’re seeing continued partnership with existing investors and we’re coming in and making that majority investment, and we’ll also be making another investment in the balance sheet,” he said.
What Sumeru is getting is a company that helps with internal communications using marketing techniques, says company CEO Gary Nakamura. “You can run campaigns with targeting segmentation and all the telemetry back that you need as a leader, as a manager, as an organization to understand how your communications are landing with your workforce,” Nakamura told TechCrunch.
The target is large companies and customers, including big names like Ford, Archer Daniels Midland and Boeing. The company reports it has 120 large customers around the world, and the business has been growing at 50% year over year.
While the company is getting this infusion of cash from Sumeru, Nakamura says he will continue to try to manage the company in a thoughtful way, and that means being careful about how they hire beyond the 120 employees the company already has.
“What we have built is a business that doesn’t require a lot of heads to run it. We can maintain a 50% growth rate with financial discipline that we’ve implemented. Historically that is what we’ve been able to do,” he said.
Sumeru Equity Partners is a private equity firm based in San Francisco. It targets mid-market companies, according to the company website, and then tries to apply operational efficiency by working with them on areas like product strategy, go-to-market acceleration and organizational development, with the goal of building up the company and taking it to exit.
Powered by WPeMatico