funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Airtable, the no-code relational database that has amassed a customer base that spans 250,000 different organizations, has today announced the close of $270 million in Series E funding. The valuation comes out to $5.77 billion post-money, more than doubling its valuation from September, when it raised $185 million in Series D funding.
This latest round was led by Greenoaks Capital, with participation from WndrCo, as well as existing investors Caffeinated Capital, CRV and Thrive.
The company says it plans to use the funding to accelerate the development of its enterprise product and growing the team. Also of note: Founder and CEO Howie Liu told Forbes that he was approached by Greenoaks, rather than actively seeking funding.
Airtable is a relational database that many describe as a souped-up version of Excel or Google Sheets. Being such, and having the infrastructure to support an app ecosystem on top of that, means that this no-code tool can actually be used to write software. In other words, the use cases are nearly infinite, and so is the potential customer base.
Greenoaks Capital partner Neil Mehta basically said as much in the press release:
We believe Airtable is chasing a massive opportunity to become the ‘residual’ software platform for every bespoke and custom use case that is either performed manually today or structurally underserved by rigid third-party software. By equipping business users with fundamental software primitives that can be assembled together into powerful business applications, Airtable has become central to its users’ everyday workflows but at the same time is scalable and extensible enough to support incredibly complex enterprise use cases like ticketing, content management, and CRM.
Airtable has raised a total of $617 million since inception, according to Crunchbase.
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion. Use code “TCARTICLE” at checkout to get 20% off tickets right here.
Powered by WPeMatico
Low-code and no-code tools have been a huge hit with enterprises keen to give their operations more of a tech boost, but often lack the resources to handle more complex integrations. Today, one of the startups that has been building low-code finance tools is announcing funding to tap into that trend and expand its business.
Genesis — which has to date primarily worked with financial services companies, giving non-technical employees the tools to create ways to monitor and manage real-time risk, high-frequency trades and other activities — has picked up $45 million. It plans to use the funding to bring the tools it has already built to a wider set of verticals that have some of the same needs to manage risk, compliance and other factors as finance — healthcare and manufacturing are two examples — as well as to continue building more into the stack.
This Series B includes a mix of financial investors along with strategic backers that speak to who already integrates with Genesis’ tools on their own platforms.
Led by Accel, it also includes participation from new backers GV (formerly Google Ventures) and Salesforce Ventures, in addition to existing investors Citi, Illuminate Financial and Tribeca Venture Partners, who also invested in this round. To give you an idea of who it works with, Citi, ING, London Clearing House and XP Investments are some of Genesis’ customers.
Originally conceived in 2012 in Brazil by a pair of British co-founders — Stephen Murphy (CEO) and James Harrison (CTO), who cut their teeth in the world of investment banking — Genesis had raised less than $5 million before this round, mostly bootstrapping its business and leaning on Murphy and Harrison’s existing relationships in the world of finance to grow its customer base.
Today, Murphy lives in and leads the business from Miami — where he moved from New York just as the COVID-19 pandemic was starting to gain steam last year — while James Harrison (CTO) leads part of the team based out of the U.K.
As you might imagine with so little funding before now for a company going on nine years old, Genesis was doing fine financially before this Series B, so the plan is to use the funding specifically to grow faster than it could have on its own steam. The startup is not disclosing its valuation with this round.
“We were not really fixated on valuation,” said Murphy in an interview, who said the funding came about after a number of VCs had approached the startup. “The most important thing is the future opportunity and where we could take the company with additional funding… this will help us hyper scale up.” He did note that the term sheets contained “some amazing numbers and multiples,” given the current interest in no-code and low-code technology.
Indeed, the vogue for no-code and low-code tech — other well-funded names in the crowded space include startups like Zapier, Airtable, Rows, Gyana, Bryter, Ushur, Creatio and EasySend, as well as significant launches from Google and Microsoft and other bigger players — is coming out of two trends colliding.
On one side, we’ve well and truly entered an era in enterprise technology — with the same trend playing out in consumer tech, too — where smart developers are taking sophisticated and complex services and putting “wrappers” around them by way of APIs and simpler (low- or no-code) interfaces, so that those sophisticated tools can in turn be integrated and implemented in more places. This saves needing to build or integrate that complexity from scratch and expands access to the processes within those wrappers.
On the other side, the thirst for tech knowledge has become well and truly mainstream and as a result is getting far more democratized. Working in a variety of applications, using different digital tools and devices and seeing the fruits of tech pay off are all second nature to today’s working world — whether or not you are a technologist. So it’s no surprise to see more proactive, non-technical people looking for more ways to get their hands on these tools themselves.
“You now have a whole citizen developer world, for example business analysts who understand the solution you want but might not know how to get there,” Murphy said. “We play to seasoned developers first but the investment will help us put more low-code and no-code tools into place to widen the tools out to them.”
Starting out in finance made sense not just because that was where the two founders had previously worked, but also because of the history of how different software tools were already being used. Specifically, he noted that the ubiquity of microservices — which themselves are collections of services as apps — laid the groundwork for more low-code. “We saw that if we could build a low-code entry point to microservices, that would be powerful.”
On top of that, investment banks, he said, have a history of wanting to build things themselves to tailor to their specific needs. “Buying off the shelf means you are at the mercy of the vendor,” he said. These factors made financial services companies very receptive to what Genesis was offering.
While a lot of the no/low-code players are coming at the concept with specific verticals in mind — no surprise, since different verticals have very specific use cases and needs — what’s interesting with Genesis is how the company is leveraging what it already knows about finance, and then looking at other industries that have similar demands, structures and rules.
Murphy said that Genesis will stay “very focused on financial markets for 2021” but that it’s identified a number of other verticals similar to it, and is actually already seeing some inbound interest from them.
“A number of people have already approached us from the world of healthcare,” he said, pointing out that these organizations, like financial services, face challenges around how to audit data and regulations around performing transactions. Manufacturing, meanwhile, has some parallels around the area of complex event processing similar to equity algorithmic trading, he said. (In short, this relates to how external events might trigger more transactions, not unlike how external factors affect manufacturing operations.)
The trend is one that analysts forecast will only grow in the coming years: Gartner, for example, says that by 2024, low-code platforms will account for no less than 65% of all app development activity.
“Low-code promises business users the autonomy to make their own technology usage and purchase decisions while enabling them to actually build their own applications without having to rely on IT,” said Andrei Brasoveanu, a partner at Accel, said in a statement. “By bringing one of the most transformative innovations in software development to financial services, Steve and the Genesis team are taking on a huge market of legacy vendors — and winning too — while delivering on the promise of low-code. The confidence they’ve gained from serving such large institutions is proof that there’s a real and urgent need for a purpose-built low-code solution for financial markets. We’re excited to partner with Genesis and support them in delivering this across the world.” Brasoveanu is joining the startup’s board with this round.
Powered by WPeMatico
St. Louis-based voice assistant startup Disruptel is announcing that it has raised $1.1 million in seed funding.
The money comes from an impressive group of investors who seem well-aligned with what the startup is aiming to do — namely, build a voice assistant that can provide detailed information about what’s happening on your TV screen. Those investors include PJC and Progress Ventures (which led the round), along with DataXu co-founder and former CEO Mike Baker, Siri co-founder Adam Cheyer, Sky executive Andrew Olson and DataXu co-founder Bill Simmons.
Disruptel CEO Alex Quinn told me that he began to pursue the idea in high school — the initial idea was more focused on TV gesture controls, but he decided that there was a bigger opportunity in the fact that “smart TVs don’t know what’s going on on their own screen.”
So he said Disruptel has built technology that has “a contextual understanding of everything that’s happening on the screen — every product, all of that data.” So for example, you could use the technology to ask your TV, “Who is the person in the brown shirt?”
Quinn’s description reminded me of Amazon’s X-Ray technology, which can tell you about the actors on-screen, as well as additional trivia about whatever movie or TV you’re watching on Amazon Prime. But he said that Amazon’s solution (as well as a similar one from Google) involves “static data — the videos have all been pre-processed.” With Disruptel, on the other hand, “everything is happening in real time,” which means it could theoretically work with any piece of content.
Disruptel’s flagship product Context is a voice assistant designed to work with smart TVs and their remotes. Quinn said he’s hoping to partner with smart TV manufacturers and streaming services and get this into the hands of viewers in the second half of this year.
In the meantime, the company has already created a Smart Screen extension for Google Chrome that you can try right now (using the extension, I successfully identified the actors on-screen during multiple scenes of an episode of “The Flash”). Quinn said the company is using the extension as way to test the product and gather engagement data.
Baker (who sold his adtech company dataxu to Roku in 2019) said that he was convinced to back the company after seeing a demo of the product: “It was interesting to see the power, the fluidity of the experience.”
He also suggested that Disruptel’s tech creates new opportunities to improve on the smart TV advertising experience, which he described as largely consisting of “crap” — though he also pointed to Hulu as an example of a service that can be successful with “non-intrusive advertising and interstitial ads.”
Asked how a high school student could create this kind of technology, Quinn (who is now 21) said, “We had to learn. Our team is very focused on machine learning, and our machine learning engineers were reading research paper after research paper. We think that we have found the best research solutions.”
He added that if Disruptel had followed the leads of the big players and focused on pre-processing content, “We would never even have begun that journey.”
Powered by WPeMatico
From the point of view of a consumer, customer service sometimes feels like a monolith, but behind the scenes it can be a very fragmented business, with dozens of companies providing various different tools to help agents do their jobs.
Today, a startup founded by three Stripe alums that has set out to build a platform that helps organizations manage that spaghetti of customer service IT, and use it more efficiently, is announcing a round of funding to continue growing its business.
Assembled, which has built a platform that it describes as the “operating system” for support teams, has raised $16.6 million, a Series A that it plans to use to continue expanding its team and platform, and to bring on more customers.
The round is being led by Emergence Capital, the VC that specializes in enterprise startups, backing other communications-centric companies in its time like Salesforce, Zoom, Yammer, ServiceMax, SalesLoft and Lithium. Stripe, Basis Set Ventures and Felicis Ventures also participated. Stripe has a strong connection to Assembled. It is a customer. It led Assembled’s $3.1 million seed round a year ago.
And, it was the company where the three co-founders met and built the earliest version of the product it offers today. CEO Brian Sze was one of the first employees, overseeing business operations, where he built the customer support platform that inspired him to eventually leave to found Assembled. His two co-founders, brothers Ryan and John Wang, were engineers at the payments and financial services behemoth.
Assembled’s current platform is priced in tiers starting at $15 per agent per month. Integrating with Salesforce, Zendesk, Intercom, Kustomer, Gladly and other services by way of API integrations, it provides not just a way to manage and view customer support data from different sources in one place, but alongside that it provides tools focused on the support teams themselves. This includes tools to manage and roster teams, analyze team performance, and forecast demand depending on different factors in order to be better prepared.
As with all other aspects of how organizations work, customer service and people management are being digitally transformed. Typically, Sze said that many companies still use spreadsheets to manage and plan customer support rosters. That is now gradually shifting into what he describes as “support ops” where a strategic person is tasked not just with handling what is happening with incoming customer support right now, but also needs to figure out what will happen in the next year, and the tools that might help cope with that. “That is our emergent buyer,” Sze said.
“The sheer number of channels being supported is much bigger, when you consider email, messaging, phone lines, social media and more,” said Sze, adding that the pandemic had a particularly strong effect on Assembled’s business. It saw a big bump in especially in Q3 of last year, when its customer base doubled. “I think it came down to support being one of the most critical teams at the organization.”
Assembled today has a number of tech companies, and tech-first consumer companies as customers, including Stripe, GoFundMe, challenger bank Monzo, Google-owned Looker, D2C clothing brand Everlane and Harrys. It has grown customers five-fold in the last year, said Sze, while revenues have grown 300% (absolute numbers for both were not disclosed).
The concept of an “operating system” for customer support makes a lot of sense when you think about how the role has evolved over the years.
In the decades before the internet and digital interactions became the norm, support either focused on in-person visits, or phone-based interactions where you might find yourself calling toll-free numbers, sitting on hold for a long time, maybe being shuffled from one person to another depending on the nature of your issue.
Over time, those systems picked up some automated responses and companies started getting better systems in place to triage those calls. Then, as marketing became “marketing tech” and sales took on a software life of its own, those customer support people started to pick up more responsibilities, not just listening to customers but turning around and offering to sell them things, too, or take stock of customer satisfaction and overall sentiment. Then more channels for connecting came with the internet. Then came more efficient tools, cloud-based services, mobile services, and more to handle all of the above, and so on.
All of these iterations often came with different pieces of software, and while some companies have set out to build one-stop shops to take everything on, Assembled takes a Slack-like approach, making it easy to bring in data and manage different tools from one place, providing a place to bring them all together to help them work more harmoniously. At the same time, it provides a way to manage the teams of people who are there to work with those pieces of software. This is because, when it comes to customer support, it’s always as much about the teams running it as it is the software they are using (hence: “assmebled”).
The company’s approach has been especially relevant in the last year. Not only have teams — including customer service teams — been forced to work remotely, but they have generally seen a surge of traffic from customers who are going online for all of their services, and using digital tools when they need to get in touch with organizations. Still, the opportunity for Assembled is that by and large, there are still a large proportion of businesses that are still playing catch up here.
“Today’s customer support teams operate in a dynamic, increasingly remote environment vastly different from that of a decade ago,” said Jake Saper, Emergence General Partner, in a statement. “But it’s shocking to learn how many support teams are still operating out of spreadsheets. At Emergence, we believe that Support Ops will become a critical complement to support teams, much like DevOps has become for developers. Having initially built their product to manage Stripe’s support function, we believe the Assembled team is the world’s best to build the core operating platform for Support Ops.”
Valuation is not being disclosed.
Early Stage is the premier ‘how-to’ event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear first-hand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company-building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in – there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion. Use code “TCARTICLE at checkout to get 20 percent off tickets right here.
Powered by WPeMatico
We know that a lot of elements go into the formation of a startup ecosystem. When your city is outside of the major coastal tech centers, it takes a deliberate effort to get such a system off the ground. For Indianapolis, Indiana, it started with the creation of ExactTarget in 2000. When that company was sold to Salesforce for $2.5 billion in 2013, it helped bring a bushel of cash into the startup system.
Today, the venture capital firm that connects back to that ExactTarget acquisition, High Alpha Capital, announced a new $110 million fund. The company concentrates on B2B SaaS startups. Kristian Andersen, partner and co-founder at High Alpha sees the fund in the context of the pandemic and the changes it has brought to how businesses are run.
“We are living in a [time] of almost unrivaled disruption, which has created a host of challenges for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. In spite (or possibly because) of those challenges, we’re more confident and motivated than ever to help support the next generation of founders as they seek to transform the world through the marriage of entrepreneurship and technology,” Andersen said.
Of course, cash is a key ingredient in any startup system recipe. ExactTarget’s founders were flush with it after the acquisition and Scott Dorsey, one of the firm’s founders says they wanted to build a system from the ground up that included education, a system to encourage entrepreneurship, math skills, a pool of engineering talent and of course, a venture capital firm to drive investment.
“I think of the recipe as talent, capital, support and mentorship. So talent has to be a sharp focus, which is certainly is for us at High Alpha and across the Indianapolis market. The second piece is capital, and markets like Indy often don’t have access to capital and that’s been important that we’re raising our own funds,” he said.
He added, “Thirdly, I think it’s just support and mentorship and that’s really what High Alpha is built to do. We have 40 of us on the team with SaaS experts across design, marketing, product engineering, finance and HR — all Centers of Excellence you need to start and scale a SaaS company,” he said.
The firm is divided into two parts. The first is High Alpha Studio, which is a kind of incubator for really early stage founders and the second is High Alpha Capital, which is the focus of today’s announcement.
This is third fund for the company. The first was High Alpha One worth $21 million. The second one, High Alpha Two was worth $85 million. Combined with today’s announcement, the total raised across the three funds is $216 million. While the first two funds’ investments were mostly in the Indy area, the plan with the newest one is to expand beyond the region with at least some of the investments.
The firm concentrates on enterprise B2B SaaS companies from pre-seed through Series A investments, so concentrating on early stage companies that it can help nurture and learn from their experiences building ExactTarget into a successful company.
Among the companies they invested in include Attentive, SalesLoft, Zylo, Terminus, The Mom Project, Lessonly, LogicGate, MetaCX and Socio.
Powered by WPeMatico
Montreal-based Heyday announced today that it has raised $6.5 million Canadian ($5.1 million in US dollars) in additional seed funding.
Co-founder and CEO Steve Desjarlais told me that the startup’s goal is to allow retailers to support more automation and more personalization in their online customer interactions, while co-founder and CMO Etienne Merineau described it as an “all-in-one unified customer messaging platform.”
So whether a customer is sending a message from Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp and Google’s Business Messages or just via email, Heyday brings all that communication together in one dashboard. It then uses artificial intelligence to determine whether it’s a customer service or sales-related interaction, and it automates basic responses when possible.
Heyday chatbots can provide order updates or even recommend products (it integrates with Salesforce, Shopify, Magento, Lightspeed and PrestaShop), then route the conversation to a human team member when necessary.
There are other platforms that combine customer service and sales, but at the same time, Merineau said it’s important to treat the two categories as distinct and trust that a good service experience will lead to sales in the feature.
Image Credits: Heyday
“We believe that helping is the new selling,” he said.
Desjarlais added, “We’re really against the ticket ID system. A customer is not a ticket …
I truly believe that every single customer is a relationship with a brand that needs to be nurtured over time and that will give more value to the brand over time.”
Heyday was founded in 2017 and says that over the past two quarters, it has doubled recurring revenue. Customers include French sporting good company Decathlon, Danish fashion house Bestseller to food and consumer product brand Dannon — Merineau noted that the platform was “bilingual out of the box” and has seen strong international growth.
“Retailers who believe that [the changes brought about by] COVID-19 are temporary are in the wrong mindset,” he said. “The new mantra of future-forward brands is ‘adapt or die.’ … Brands obviously want to delvier great service, but they care about the bottom line. We help them kill two birds with one stone.”
The startup had previously raised $2 million Canadian, according to Crunchbase. This new round comes from existing investors Innovobot and Desjardins Capital. Merineau said the money will help Heyday “double down on the U.S. and scale.”
Powered by WPeMatico
DataGrail, a startup that helps customers understand where their data lives in order to help comply with a growing body of privacy regulations, announced a $30 million Series B today.
Felicis Ventures led the round with help from Basis Set Ventures, Operator Collective and previous investors. One of the interesting aspects of this round was the participation from several strategic investors including HubSpot, Okta and Next47, the venture firm backed by Siemens. The company has now raised over $39 million, according to Crunchbase data.
That investor interest could stem from the fact that DataGrail helps organizations find data by building connectors to popular applications and then helps ensure that they are in compliance with customer privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA and similar laws.
“DataGrail [is really] the first integrated solution with over 900 integrations (up from 180 in 2019) to different apps and infrastructure platforms that allow the product to detect when new apps or new infrastructure platforms are added, and then also perform automated data discovery across those applications,” company CEO and co-founder Daniel Barber explained to me. This helps users find customer data wherever it lives and enables them to comply with legal requirements to manage and protect that data.
Victoria Treyger, general partner at lead investors Felicis Ventures says that one of the things that attracted her to DataGrail was that she had to help implement GDPR regulations at a previous venture and felt the pain first hand. She said that her firm tends to look for startups in large markets where the product or service being offered is a critical need, rather an option, and she believes that DataGrail is an example of that.
“I really liked the fact that privacy management is such a hard problem, and it is not optional. As a business, you have to manage privacy requests, which you may do manually or you may do it with a solution like DataGrail,” Treyger told me.
HubSpot’s Andrew Lindsay, who is SVP of corporate and business development, says his company is both a customer and an investor because DataGrail is helping HubSpot customers navigate the complexity of privacy regulation. “DataGrail’s unique ecosystem approach, where they are integrating with key Saas and business applications is an easy way for many of our joint customers to protect their customers’ privacy,” Lindsay said.
The company has 40 employees today with plans to grow to 90 or 100 by the end of this year. It’s worth noting that Treyger is joining the Board, which already has 3 other women. That shows shows a commitment to gender diversity at the board level that is not typical for startups.
Powered by WPeMatico
The team behind Songclip thinks that social media could use more music.
Yes, music is a big part of the experience on a handful of apps like TikTok and Triller, but Songclip co-founder and COO John vanSuchtelen told me, “That is not the end of how music is going to be a feature, that is a beginning.”
He added, “In the next nine to 12 months … just like you never have a phone without a camera, you’re not going to have an app without music clips as a feature when you make videos.”
That’s what vanSuchtelen and his co-founder and CEO Andy Blacker are hoping to enable with Songclip, which announced today that it has raised $11 million in new funding.
The startup has created an API that, when integrated with other apps (current integrations include photo- and video-editing app PicsArt), allows users to search for and share music. VanSuchtelen said that like Giphy, Songclip plans to popularize a new media format — the short audio clip — and make it accessible across a wide range of services.
“If I were to say, I’m going to send you a four-minute song,’ it’s just not going to work that way, that’s not how we communicate anymore,” vanSuchtelen said. “How do you take the music and turn it into the bite that you want to use in a social context?”
To do this, Blacker said Songclip doesn’t just license music, it also does its own tagging and clipping, while offering tools for music labels to protect their intellectual property and providing data on how people are interacting with the music. And unlike Giphy, Songclip isn’t looking to build a consumer brand.
All of this involves a combination of human editors and technology. Blacker said the human element is key to understand the nuances of songs and their association, like the fact that Simon & Garfunkel’s “Bridge Over Troubled Water” isn’t really about bridges or water, or that Katrina and the Waves’ “Walking on Sunshine” is a happy song even though it doesn’t have the word “happy” in it.
Songclip has now raised a total of $23 million. The new round was led by Gregg Smith of Evolution VC Partners. The Kraft Group, Michael Rubin, Raised in Space, Gaingels and Forefront Venture Partners also participated, as did industry executives Jason Flom and Steve Greenberg and the band AJR.
Powered by WPeMatico
Wrapbook, a startup that simplifies the payroll process for TV, film and commercial productions, has raised $27 million in Series A funding from noteworthy names in both the tech and entertainment worlds.
The round was led by Andreessen Horowitz, with participation from Equal Ventures and Uncork Capital, as well as from WndrCo (the investment and holding company led by DreamWorks and Quibi founder/co-founder Jeffrey Katzenberg) and from CAA co-founder Michael Ovitz.
“It’s time we bring production financial services into the 21st century,” Katzenberg said in a statement. “We need a technology solution that will address the increasing complexities of production onboarding, pay and insuring cast and crew, only exacerbated by COVID-19, and I believe that Wrapbook delivers.”
Wrapbook co-founder and CEO Ali Javid explained that entertainment payroll has remained a largely old-fashioned, paper-based process, which can be particularly difficult to track as cast and crew move from project to project, up to 30 times in single year. Wrapbook digitizes and simplifies the process — electronically collecting all the forms and signatures needed at the beginning of production, handling payroll itself, creating a dashboard to track payments and also making it easy to obtain the necessary insurance.

Wrapbook founders Cameron Woodward, Ali Javid, Hesham El-Nahhas and Naysawn Naji
Although the startup was founded in 2018, Javid told me that demand has increased dramatically as production resumed during the pandemic, with COVID-19 “totally” changing the industry’s culture and prompting production companies to say, “Hey, if there’s an easier, faster way to do this from my house, then yeah let’s look at it.”
Javid also described the Wrapbook platform as a “a vertical fintech solution that’s growing really fast in an industry that we understand really well and not many others have thought about.” In fact, he said the company’s revenue grew 7x in 2020.
And while Wrapbook’s direct customers are the production companies, co-founder and CMO Cameron Woodward (who previously worked in filmmaking insurance and commercial production) said that the team has also focused on creating a good experience for the cast and crew who get paid through the platform — a growing number of them (12% thus far) have used their Wrapbook profiles to get paid on multiple productions.
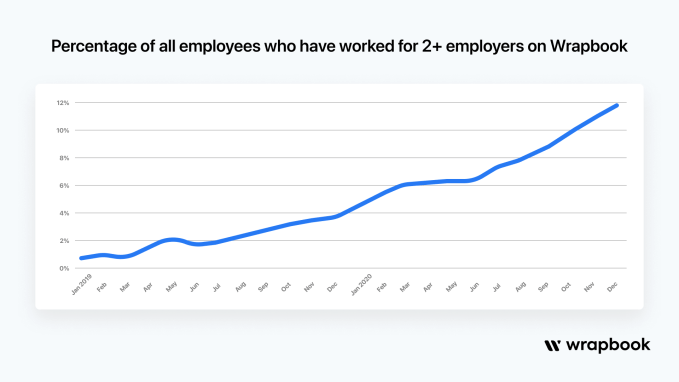
Image Credits: Wrapbook
The startup previously raised $3.6 million in seed funding. Looking ahead, Javid and Woodward said that Wrapbook’s solution could eventually be adopted in other project-based industries. But for now, they see plenty of opportunity to continue growing within entertainment alone — they estimated that the industry currently sees $200 billion in annual payments.
“We’re going to double down on what’s working and build things out based on what customers have asked for within entertainment,” Javid said. “To that end, we’re working towards hiring 100 people in the next 12 months.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Each of the big three cloud vendors — Amazon, Microsoft and Google — has a marketplace where software vendors can sell their wares. It seems like an easy enough proposition to throw your software up there and be done with it, but it turns out that it’s not quite that simple, requiring a complex set of business and technical tasks.
Tackle, a startup that wants to help ease the process of getting a product onto one of these marketplaces, announced a $35 million Series B today. Andreessen Horowitz led the investment with help from existing investor Bessemer Venture Partners. The company reports it has now raised $48.5 million.
Company founder Dillon Woods says that at previous jobs, he found that it took several months with a couple of engineers dedicated to the task to get a product onto the AWS marketplace, and he noticed that it was a similar set of tasks each time.
“What I saw [in my previous jobs] was that we were kind of redoing the same work. And I thought everybody out there was probably reinventing the same wheel. And so when I started Tackle, my goal was to create a software platform that would take that time down to one or two days. So it’s really a no-code solution, and it makes it much more of a business decision, rather than this big technical integration project,” Woods told me.
While you may think it’s a pretty simple task to put an app on one of these marketplaces, Woods points out that the AWS user guide explaining the ins and outs is a 700-page pdf. He says that it’s not just the technical complexity of setting up the various API calls to get it connected, there is also the business side of selling in the marketplace, and that requires additional APIs.
“There’s not just the initial sale. There could be things later like upgrades, refunds, cancellations — maybe you need to do overage charges against that same contract. And so there are all of these downstream things that happen that all require API integration, and Tackle takes care of all of that for you,” Woods explained.
CEO John Jahnke says that the company usually starts with one product in one marketplace, which acts as a kind of proof of concept for the customer, then builds up from there. Once customers see what Tackle can do, they can expand usage.
It seems to be working, with the startup reporting that it tripled annual recurring revenue (ARR), although it didn’t want to share a specific number. It also doubled headcount and the number of customers and was responsible for over $200 million in transactions across the three cloud marketplaces.
Jahnke didn’t share the exact number of customers, but he said there were currently hundreds on the platform, including companies like Snowflake, GitHub, New Relic and PagerDuty.
The company currently has 67 employees spread across 25 states, with plans to almost double that by the end of 2021. He says that it’s essential to put systems in place to build a diverse company now.
“How we scale through this next 100% increase in headcount is going to define the mix of the company into the future. If we can get this right right now and continue to extend on the foundation for diversity and inclusion that we started and make it a real part of our conversation at some scale, we think we’ll be set up as we go from 100 employees to 1,000 employees over the long period of time to continue to grow and create opportunities for people wherever they are,” Jahnke said.
Martin Casado, general partner at lead investor a16z, says this type of selling has become essential for businesses and that’s why he wanted to invest in the company. “Cloud marketplaces have become a primary channel for selling software quickly and conveniently. Tackle is the leading player for enabling companies to sell software through the cloud,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico