funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Aspire, a Singapore-based startup that helps SMEs secure working capital, has raised $32.5 million in a new financing round to expand its presence in several Southeast Asian markets.
The Series A round for the one-and-a-half-year-old startup was funded by MassMutual Ventures Southeast Asia. Arc Labs and existing investors Y Combinator — Aspire graduated from YC last year — Hummingbird and Picus Capital also participated in the round. Aspire has raised about $41.5 million to date.
Aspire operates a neo-banking-like platform to help small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) quickly and easily secure working capital of up to about $70,000. AspireAccount, the startup’s flagship product, provides merchants and startups with instant credit limit for daily business expenses, as well as a business-to-business acceptance and other tools to help them manage their cash flow.
Co-founder and CEO Andrea Baronchelli tells TechCrunch that about 1,000 business accounts are opened each month on Aspire and that the company plans to continue focusing on Southeast Asia, where he says there are about 78 million small businesses, leaving plenty of room to scale (applications can be made through Aspire’s mobile app and are reviewed using a proprietary risk assessment engine before getting final approval from a human). Aspire claims it has seen 30% month-over-month growth since it was founded in January 2018 and expects to open more than 100,000 business accounts by next year.
Baronchelli, who served as a CMO for Alibaba’s Lazada platform for four years, says Aspire launched to close the gap left by the traditional banking industry’s focus on consumer services or businesses that make more than $10 million in revenue a year. As a result, smaller businesses in Southeast Asia, including online vendors and startups, often lack access to credit lines, accounts and other financial services tailored to their needs.
Aspire currently operates in Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore and Vietnam. The startup said it will use the fresh capital to scale its footprints in those markets. Additionally, Aspire is building a scalable marketplace banking infrastructure that will use third-party financial service providers to “create a unique digital banking experience for its SME customers.”
Baronchelli adds that “the bank of the future will probably be a marketplace,” so Aspire’s goal is to provide a place where SMEs can not only open accounts and credit cards, but also pick from different services like point of sale systems. It is currently in talks with potential partners. The startup is also working on a business credit card that will be linked to each business account by as early as this year.
Southeast Asia’s digital economy is slated to grow more than six-fold to reach more than $200 billion per year, according to a report co-authored by Google. But for many emerging startups and businesses, getting financial services from a bank and securing working capital have become major pain points.
A growing number of startups are beginning to address these SMEs’ needs. In India, for instance, NiYo Bank and Open have amassed millions of businesses through their neo-banking platforms. Both of these startups have raised tens of millions of dollars in recent months. Drip Capital, which helps businesses in developing markets secure working capital, raised $25 million last week.
Powered by WPeMatico
Low-code programming is supposed to make things easier on companies, right? Low-code means you can count on trained administrators instead of more expensive software engineers to handle most tasks, but like any issue solved by technology, there are always unintended consequences. While running his former company, Steelbrick, which he sold to Salesforce in 2015 for $360 million, Max Rudman identified a persistent problem with low-code deployments. He decided to fix it with automation and testing, and the idea for his latest venture, Prodly, was born.
The company announced a $3.5 million seed round today, but more important than the money is the customer momentum. In spite of being a very early-stage startup, the company already has 100 customers using the product, a testament to the fact that other people were probably experiencing that same pain point Rudman was feeling, and there is a clear market for his idea.
As Rudman learned with his former company, going live with the data on a platform like Salesforce is just part of the journey. If you are updating configuration and pricing information on a regular basis, that means updating all the tables associated with that information. Sure, it’s been designed to be point and click, but if you have changes across 48 tables, it becomes a very tedious task, indeed.
The idea behind Prodly is to automate much of the configuration, provide a testing environment to be sure all the information is correct and, finally, automate deployment. For now, the company is just concentrating on configuration, but with the funding it plans to expand the product to solve the other problems, as well.
Rudman is careful to point out that his company’s solution is not built strictly for the Salesforce platform. The startup is taking aim at Salesforce admins for its first go-round, but he sees the same problem with other cloud services that make heavy use of trained administrators to make changes.
“The plan is to start with Salesforce, but this problem actually exists on most cloud platforms — ServiceNow, Workday — none of them have the tools we have focused on for admins, and making the admins more productive and building the tooling that they need to efficiently manage a complex application,” Rudman told TechCrunch.
Customers include Nutanix, Johnson & Johnson, Splunk, Tableau and Verizon (which owns this publication). The $3.5 million round was led by Shasta Ventures, with participation from Norwest Venture Partners.
Powered by WPeMatico
Just yesterday, we experienced yet another major breach when Capital One announced it had been hacked and years of credit card application information had been stolen. Another day, another hack, but the question is how can companies protect themselves in the face of an onslaught of attacks. Confluera, a Palo Alto startup, wants to help with a new tool that purports to stop these kinds of attacks in real time.
Today the company, which launched last year, announced a $9 million Series A investment led by Lightspeed Venture Partners . It also has the backing of several influential technology execs, including John W. Thompson, who is chairman of Microsoft and former CEO at Symantec; Frank Slootman, CEO at Snowflake and formerly CEO at ServiceNow; and Lane Bess, former CEO of Palo Alto Networks.
What has attracted this interest is the company’s approach to cybersecurity. “Confluera is a real-time cybersecurity company. We are delivering the industry’s first platform to deterministically stop cyberattacks in real time,” company co-founder and CEO Abhijit Ghosh told TechCrunch.
To do that, Ghosh says, his company’s solution watches across the customer’s infrastructure, finds issues and recommends ways to mitigate the attack. “We see the problem that there are too many solutions which have been used. What is required is a platform that has visibility across the infrastructure, and uses security information from multiple sources to make that determination of where the attacker currently is and how to mitigate that,” he explained.
Microsoft chairman John Thompson, who is also an investor, says this is more than just real-time detection or real-time remediation. “It’s not just the audit trail and telling them what to do. It’s more importantly blocking the attack in real time. And that’s the unique nature of this platform, that you’re able to use the insight that comes from the science of the data to really block the attacks in real time.”
It’s early days for Confluera, as it has 19 employees and three customers using the platform so far. For starters, it will be officially launching next week at Black Hat. After that, it has to continue building out the product and prove that it can work as described to stop the types of attacks we see on a regular basis.
Powered by WPeMatico
Before Tableau was the $15.7 billion key to Salesforce’s problems, it was a couple of founders arguing with a couple of venture capitalists over lunch about why its Series A valuation should be higher than $12 million pre-money.
Salesforce has generally been one to signify corporate strategy shifts through their acquisitions, so you can understand why the entire tech industry took notice when the cloud CRM giant announced its priciest acquisition ever last month.
The deal to acquire the Seattle-based data visualization powerhouse Tableau was substantial enough that Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff publicly announced it was turning Seattle into its second HQ. Tableau’s acquisition doesn’t just mean big things for Salesforce. With the deal taking place just days after Google announced it was paying $2.6 billion for Looker, the acquisition showcases just how intense the cloud wars are getting for the enterprise tech companies out to win it all.
The Exit is a new series at TechCrunch. It’s an exit interview of sorts with a VC who was in the right place at the right time but made the right call on an investment that paid off. [Have feedback? Shoot me an email at lucas@techcrunch.com]
Scott Sandell, a general partner at NEA (New Enterprise Associates) who has now been at the firm for 25 years, was one of those investors arguing with two of Tableau’s co-founders, Chris Stolte and Christian Chabot. Desperate to close the 2004 deal over their lunch meeting, he went on to agree to the Tableau founders’ demands of a higher $20 million valuation, though Sandell tells me it still feels like he got a pretty good deal.
NEA went on to invest further in subsequent rounds and went on to hold over 38% of the company at the time of its IPO in 2013 according to public financial docs.
I had a long chat with Sandell, who also invested in Salesforce, about the importance of the Tableau deal, his rise from associate to general partner at NEA, who he sees as the biggest challenger to Salesforce, and why he thinks scooter companies are “the worst business in the known universe.”
The interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Lucas Matney: You’ve been at this investing thing for quite a while, but taking a trip down memory lane, how did you get into VC in the first place?
Scott Sandell: The way I got into venture capital is a little bit of a circuitous route. I had an opportunity to get into venture capital coming out of Stanford Business School in 1992, but it wasn’t quite the right fit. And so I had an interest, but I didn’t have the right opportunity.
Powered by WPeMatico
Another day, another mega round for a fintech startup. And this one is mega-mega.
Brazil-based Nubank, which offers a suite of banking and financial services for Brazilian consumers, announced today that it has raised a $400 million Series F round of venture capital led by Woody Marshall of TCV. The growth-stage fund is best known for its investment in Netflix but has also made fintech a high priority, with over $1.5 billion in investments in the space. According to Nubank, the company has now raised $820 million across seven venture rounds.
Katie Roof and Peter Rudegeair of The Wall Street Journal reported this morning that the company secured a valuation above $10 billion, potentially making it one of a short list of startup decacorns. That’s up from the $4 billion valuation we wrote about back in October 2018.
Part of the reason for that big-ticket round is the company’s growth. Nubank said in a statement that it has now reached 12 million customers for its various products, making it the sixth-largest financial institution by customer count within its home market. Brazil has a population of roughly 210 million people — indicating that there is still a lot of local growth potential even before the company begins to consider its international expansion options. Nubank announced a few weeks ago that it will start to expand its offerings to Mexico and Argentina.
Over the past year, the company has expanded its product offerings to include personal loans and cash withdrawal options as part of its digital savings accounts.
As I wrote earlier this week, part of the reason for these fintech mega-rounds is that the cost of acquiring a financial customer is critical to the success of these startups. Once a startup has a customer for one financial product — say, a savings account — it can then upsell customers to other products at a very low marketing cost. That appears to be the strategy at Nubank as well, with its quickly expanding suite of products.
As my colleague Jon Shieber discussed last month, critical connections between Stanford, Silicon Valley and Latin America have forged a surge of investment from venture capitalists into the region, as the continent experiences the same digital transformation seen elsewhere throughout the world. As just one example from the healthcare space, Dr Consulta raised more than nine figures to address the serious healthcare needs of Brazilian consumers. Additionally, SoftBank’s Vision Fund, which was rumored to be investing in Nubank earlier this year, has vowed to put $5 billion to work in the region and recently invested $231 million in fintech startup Creditas.
In an email from TCV, Woody Marshall said that, “Leveraging unique technology, David Vélez and his team are continuously pushing the boundaries of delivering best in class financial services, grounded in a culture of tech and innovation. Nubank has all the core tenets of what TCV looks for in preeminent franchise investments.”
NuBank was founded in 2013 by co-founders Adam Edward Wible, Cristina Junqueira, and David Velez. In addition to TCV, existing backers Tencent, DST Global, Sequoia Capital, Dragoneer, Ribbit Capital and Thrive Capital also participated in the round.
Powered by WPeMatico
Elon Musk’s SpaceX managed to pull off something very few people thought it could — by disrupting one of the most fixed markets in the world with some of the most entrenched and protected players ever to benefit from government contract arrangements: rocket launches. The success of SpaceX, and promising progress from other new launch providers, including Blue Origin and Rocket Lab, have encouraged interest in space-based innovation among entrepreneurs and investors alike. But is this a true boom, or just a blip?
There’s an argument for both at once, with one type of space startup rapidly descending to Earth in terms of commercialization timelines and potential upside, and the other remaining a difficult bet to make unless you’re comfortable with long timelines before any liquidity event and a lot of upfront investment.
There’s no question that one broad category of technology at least is a lot more addressable by early-stage companies (and by extension, traditional VC investment). The word “satellite” once described almost exclusively gigantic, extremely expensive hunks of sophisticated hardware, wherein each component would eat up the monthly burn rate of your average early-stage consumer tech venture.
Powered by WPeMatico
Earlier this month, TechCrunch held its annual Mobility Sessions event, where leading mobility-focused auto companies, startups, executives and thought leaders joined us to discuss all things autonomous vehicle technology, micromobility and electric vehicles.
Extra Crunch is offering members access to full transcripts key panels and conversations from the event, including our panel on micromobility where TechCrunch VC reporter Kate Clark was joined by investors Sarah Smith of Bain Capital Ventures, Michael Granoff of Maniv Mobility, and Ted Serbinski of TechStars Detroit.
The panelists walk through their mobility investment theses and how they’ve changed over the last few years. The group also compares the business models of scooters, e-bikes, e-motorcycles, rideshare and more, while discussing Uber and Lyft’s role in tomorrow’s mobility ecosystem.
Sarah Smith: It was very clear last summer, that there was essentially a near-vertical demand curve developing with consumer adoption of scooters. E-bikes had been around, but scooters, for Lime just to give you perspective, had only hit the road in February. So by the time we were really looking at things, they only had really six months of data. But we could look at the traction and the adoption, and really just what this was doing for consumers.
At the time, consumers had learned through Uber and Lyft and others that you can just grab your cell phone and press a button, and that equates to transportation. And then we see through the sharing economy like Airbnb, people don’t necessarily expect to own every single asset that they use throughout the day. So there’s this confluence of a lot of different consumer trends that suggested that this wasn’t just a fad. This wasn’t something that was going to go away.
 For access to the full transcription below and for the opportunity to read through additional event transcripts and recaps, become a member of Extra Crunch. Learn more and try it for free.
For access to the full transcription below and for the opportunity to read through additional event transcripts and recaps, become a member of Extra Crunch. Learn more and try it for free.
Kate Clark: One of the first panels of the day, I think we should take a moment to define mobility. As VCs in this space, how do you define this always-evolving sector?
Michael Granoff: Well, the way I like to put it is that there have been four eras in mobility. The first was walking and we did that for thousands of years. Then we harnessed animal power for thousands of years.
And then there was a date — and I saw Ken Washington from Ford here — September 1st, 1908, which was when the Model T came out. And through the next 100 years, mobility is really defined as the personally owned and operated individual operated internal combustion engine car.
And what’s interesting is to go exactly 100 years later, September 2008, the financial crisis that affects the auto industry tremendously, but also a time where we had the first third-party apps, and you had Waze and you had Uber, and then you had Lime and Bird, and so forth. And really, I think what we’re in now is the age of digital mobility and I think that’s what defines what this day is about.
Ted Serbinski: Yeah, I think just to add to that, I think mobility is the movement of people and goods. But that last part of digital mobility, I really look at the intersection of the physical and digital worlds. And it’s really that intersection, which is enabling all these new ways to move around.
Clark: So Ted you run TechStars Detroit, but it was once known as TechStars Mobility. So why did you decide to drop the mobility?
Serbinski: So I’m at a mobility conference, and we no longer call ourselves mobility. So five years ago, when we launched the mobility program at TechStars, we were working very closely with Ford’s group and at the time, five years ago, 2014, where it started with the connected car, auto and [people saying] “you should use the word mobility.”
And I was like “What does that mean?” And so when we launched TechStars Mobility, we got all this stuff but we were like “this isn’t what we’re looking for. What does this word mean?” And then Cruise gets acquired for a billion dollars. And everyone’s like “Mobility! This is the next big gold rush! Mobility, mobility, mobility!”
And because I invest early-stage companies anywhere in the world, what started to happen last year is we’d be going after a company and they’d say, “well, we’re not interested in your program. We’re not mobility.” And I’d be scratching my head like, “No, you are mobility. This is where the future is going. You’re this digital way of moving around. And no, we’re artificial intelligence, we’re robotics.”
And as we started talking to more and more entrepreneurs, and hundreds of startups around the world, it became pretty clear that the word mobility is actually becoming too limiting, depending on your vantage where you are in the world.
And so this year, we actually dropped the word mobility and we just call it TechStars Detroit, and it’s really just intersection of those physical and digital worlds. And so now we don’t have a word, but I think we found more mobility companies by dropping the word mobility.
Powered by WPeMatico
GDPR, the European data privacy regulations, have been in effect for more than a year, but it’s still a challenge for companies to comply. Ethyca, a New York City startup, has created a solution from the ground up to help customers adhere to the regulations, and today it announced a $4.2 million investment led by IA Ventures and Founder Collective.
Table Management, Sinai Ventures, Cheddar founder Jon Steinberg and Moat co-founder Jonah Goodhart also participated.
At its heart, Ethyca is a data platform that helps companies discover sensitive data, then provides a mechanism for customers to see, edit or delete their data from the system. Finally, the solution enables companies to define who can see particular types of data across the organization to control access. All of these components are designed to help companies comply with GDPR regulations.
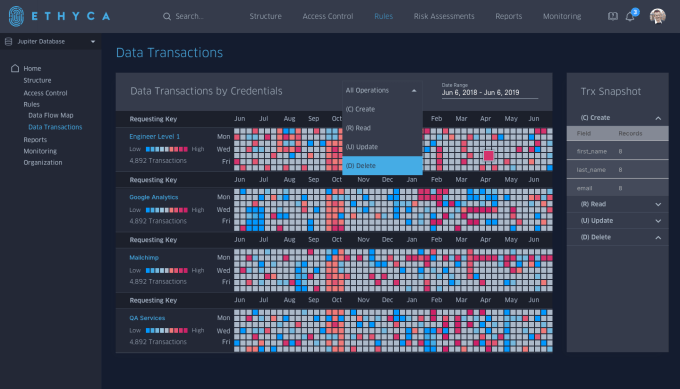
Ethyca enterprise transaction log (Screenshot: Ethyca)
Company co-founder Cillian Kieran says that the automation component is key and should greatly reduce the complexity and cost associated with complying with GDPR rules. From his perspective, current solutions that involve either expensive consultants or solutions that require some manual intervention don’t get companies all the way there.
“These solutions don’t actually solve the issue from an infrastructure point of view. I think that’s the distinction. You can go and use the consultants, or you can use a control panel that tells you what you need to do. But ultimately, at some point you’re either going to have to build or deploy code that fixes some issues, or indeed manually manage or remediate those [issues]. Ethyca is designed for that and takes away those risks because it is managing privacy by design at the infrastructure level,” Kieran explained.
If you’re worried about the privacy of providing information like this to a third-party vendor, Kieran says that his company never actually sees the raw data. “We are a suite of tools that sits between business processes. We don’t capture raw data, We don’t see personal information. We find information based on unique identifiers,” he said.
The company has been around for more than a year, but has been spending its first year developing the solution. He sees this investment as validation of the problem his startup is trying to solve. “I think the investment represents the growing awareness fundamentally from both with the investor community, and also in the tech world, that data privacy as a regulatory constraint is real and will compound itself,” he said.
He also points out that GDPR is really just the tip of the privacy regulation iceberg, with laws in Australia, Brazil and Japan, as well as California and other states in the U.S. due to come online next year. He says his solution has been designed to deal with a variety of privacy frameworks beyond GDPR. If that’s so, his company could be in a good position moving forward.
Powered by WPeMatico
At a conference in New Delhi early last year, Netflix CEO Reed Hastings was confronted with a question that his company has been asked many times over the years. Would he consider lowering the subscription cost in India?
It’s a tactic that most Silicon Valley companies have adapted to in the country over the years. Uber rides aren’t as costly in India as they are elsewhere. Spotify and Apple Music cost less than $2 per month to users in the country. YouTube Premium as well as subscriptions to U.S. news outlets such as WSJ and New York Times are also priced significantly lower compared to the prices they charge in their home turf.
Hastings had also come prepared: He acknowledged that the entertainment viewing industry in India is very different from other parts of the world. To be sure, much of the pay-TV in India is supported by ads and the access fee remains too low ($5). But that was not going to change how Netflix likes to roll, he said.
“We want to be sensitive to great stories and to fund those great stories by investing in local content,” he said. “So yes, our strategy is to build up the local content — and of course we have got the global content — and try to uplevel the industry,” he said, identifying movie-goers who spend about Rs 500 ($7.25) or more on tickets each month as Netflix’s potential customers.

Indian commuters walking below a poster of “Sacred Games”, an original show produced by Netflix (Image: INDRANIL MUKHERJEE/AFP/Getty Images)
Less than a year and a half later, Netflix has had a change of heart. The company today rolled out a lower-priced subscription plan in India, a first for the company. The monthly plan, which restricts usage of the service to mobile devices only, is priced at Rs 199 ($2.8) — a third of the least expensive plan in the U.S.
At a press conference in New Delhi today, Netflix executives said that the lower-priced subscription tier is aimed at expanding the reach of its service in the country. “We want to really broaden the audience for Netflix, want to make it more accessible, and we knew just how mobile-centric India has been,” said Ajay Arora, Director of Product Innovation at Netflix.
The move comes at a time when Netflix has raised its subscription prices in the U.S. by up to 18% and in the UK by up to 20%.
Netflix’s strategy shift in India illustrates a bigger challenge that Silicon Valley companies have been facing in the country for years. If you want to succeed in the country, either make most of your revenue from ads, or heavily subsidize your costs.
But whether finding users in India is a success is also debatable.
Powered by WPeMatico
CircleCI launched way back in 2011 when the notion of continuous delivery was just a twinkle in most developers’ eyes, but over the years with the rise of agile, containerization and DevOps, we’ve seen the idea of continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) really begin to mainstream with developers. Today, CircleCI was rewarded with a $56 million Series D investment.
The round was led by Owl Rock Capital Partners and Next Equity. Existing investors Scale Venture Partners, Top Tier Capital, Threshold Ventures (formerly DFJ), Baseline Ventures, Industry Ventures, Heavybit and Harrison Metal Capital also participated in the round. CircleCI’s most recent funding prior to this round was a $31 million Series C last January. Today’s investment brings the total raised to $115.5 million, according to the company.
CircleCI CEO Jim Rose sees a market that’s increasingly ready for the product his company is offering. “As we’re putting more money to work, there are just more folks that are now moving away from aspiring about doing continuous delivery and really leaning into the idea of, ‘We’re a software company, we need to know how to do this well, and we need to be able to automate all the steps between the time our developers are making changes to the code until that application gets in front of the customer,’ ” Rose told TechCrunch.
Rose sees a market that’s getting ready to explode and he wants to use the runway this money provides his company to take advantage of that growth. “Now, what we’re finding is that fintech companies, insurance companies, retailers — all of the more traditional brands — are now realizing they’re in a software business as well. And they’re really trying to build out the tool sets and the expertise to be effective at that. And so the real growth in our market is still right in front of us,” he said.
As CircleCI matures and the market follows suit, a natural question following a Series D investment is when the company might go public, but Rose was not ready to commit to anything yet. “We come at it from the perspective of keeping our heads down trying to build the best business and doing right by our customers. I’m sure at some point along the journey our investors will be itching for liquidity, but as it stands right now, everyone is really [focused]. I think what we have found is that the bulk of the market is just starting to arrive,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico