computing
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
In a bid to cut down on the spread of false information and spam, WhatsApp recently added labels that indicate when a message has been forwarded. Now the company is sharpening that strategy by imposing limits on how many groups a message can be sent on to.
Originally, users could forward messages on to multiple groups, but a new trial will see that forwarding limited to 20 groups worldwide. In India, however, which is WhatsApp’s largest market with 200 million users, the limit will be just five. In addition, a ‘quick forward’ option that allowed users to pass on images and videos to others rapidly is being removed from India.
“We believe that these changes — which we’ll continue to evaluate — will help keep WhatsApp the way it was designed to be: a private messaging app,” the company said in a blog post.
The changes are designed to help reduce the amount of information that goes viral on the service, although clearly this isn’t a move that will end the problem altogether.
The change is in direct response to a series of incidents in India. The BBC recently wrote about an incident which saw one man dead and two others severely beaten after rumors of their efforts to abduct children from a village spread on WhatsApp. Reportedly 17 other people have been killed in the past year under similar circumstances, with police saying false rumors had spread via WhatsApp.
In response, WhatsApp — which is of course owned by Facebook — has bought full-page newspaper ads to warn about false information on its service.
Beyond concern about firing up vigilantes, the saga may also spill into India’s upcoming national general election next year. Times Internet today reports that Facebook and WhatsApp plan to introduce a fake news verification system that it used recently in Mexico to help combat spam messages and the spreading of incorrect news and information. The paper said that the companies have already held talks with India’s Election Commission.
Powered by WPeMatico
Another day, another blockchain project. This time sources are reporting that Knotel – an office space rental service in Manhattan – has acquired 42Floors, a commercial real estate search engine in order to, according to founder Amol Sarva, get “access to data and technology on over 10 billion square feet of office space, driving further liquidity to Knotel’s marketplace while also accelerating its plans for a blockchain platform.”
The deal is not yet complete.
Knotel is building the Agile HQ platform, a way to rent office space for a few hours or a few months without getting stuck in a lease. The company has 1 million square feet of space in New York, San Francisco, London, and Berlin and it raised $100 million in funding. The company claims it has more has more buildings in New York than WeWork.
“42Floors built a powerful tool to organize a dark market that hasn’t changed in a hundred years,” said Amol Sarva, CEO of Knotel. “It’s still backroom and bilateral while the rest of the world is becoming digital and standardized. This is what leads to transactions that take months to close with a dozen middlemen – no reliable information. You can buy a house faster than you can rent a floor. Partnering together will help give owners and customers what they both want: truth.”
The reported 42Floors acquisition enables the company to bring new properties onto its platform and could let non-blockchain-based contracts move to the blockchain.
UPDATE – Text changed to reflect the type of business and ICO plans.
Powered by WPeMatico
Once upon a time, it looked like cloud-based serviced would become the central hub for analyzing all IoT data. But it didn’t quite turn out that way because most IoT solutions simply generate too much data to do this effectively and the round-trip to the data center doesn’t work for applications that have to react in real time. Hence the advent of edge computing, which is spawning its own ecosystem of startups.
Among those is Swim.ai, which today announced that it has raised a $10 million Series B funding round led by Cambridge Innovation Capital, with participation from Silver Creek Ventures and Harris Barton Asset Management. The round also included a strategic investment from Arm, the chip design firm you may still remember as ARM (but don’t write it like that or their PR department will promptly email you). This brings the company’s total funding to about $18 million.
Swim.ai has an interesting take on edge computing. The company’s SWIM EDX product combines both local data processing and analytics with local machine learning. In a traditional approach, the edge devices collect the data, maybe perform some basic operations against the data to bring down the bandwidth cost and then ship it to the cloud where the hard work is done and where, if you are doing machine learning, the models are trained. Swim.ai argues that this doesn’t work for applications that need to respond in real time. Swim.ai, however, performs the model training on the edge device itself by pulling in data from all connected devices. It then builds a digital twin for each one of these devices and uses that to self-train its models based on this data.
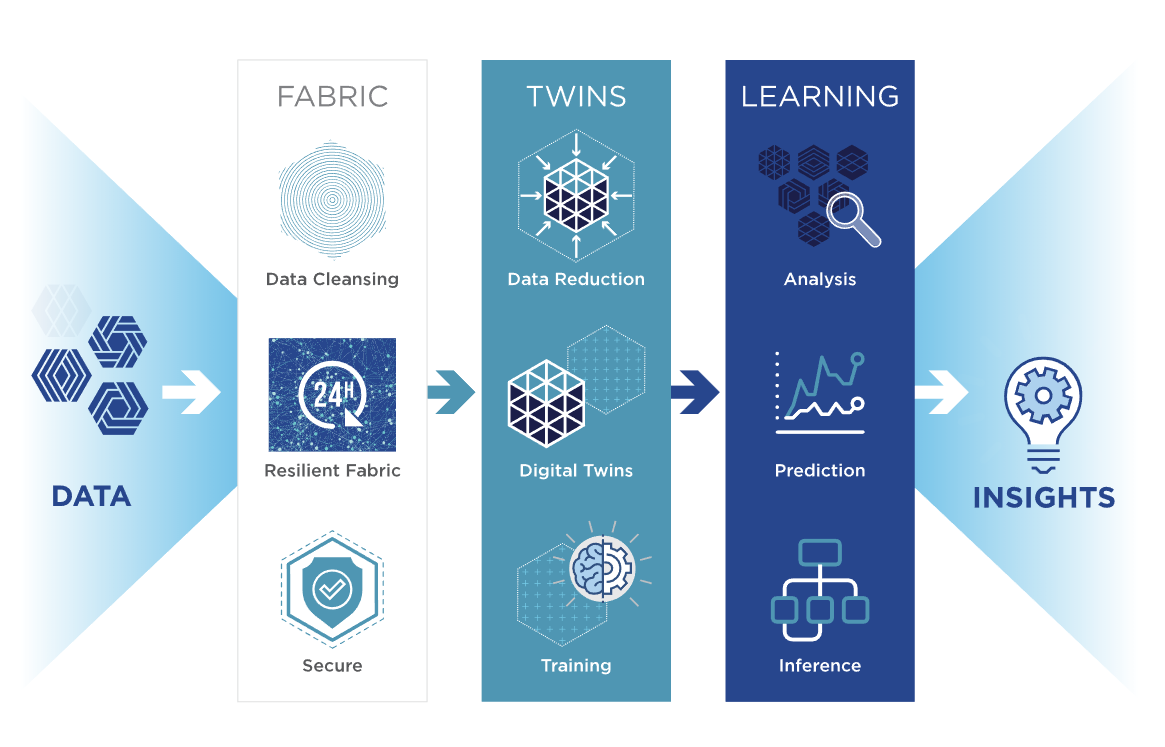
“Demand for the EDX software is rapidly increasing, driven by our software’s unique ability to analyze and reduce data, share new insights instantly peer-to-peer – locally at the ‘edge’ on existing equipment. Efficiently processing edge data and enabling insights to be easily created and delivered with the lowest latency are critical needs for any organization,” said Rusty Cumpston, co-founder and CEO of Swim.ai. “We are thrilled to partner with our new and existing investors who share our vision and look forward to shaping the future of real-time analytics at the edge.”
The company doesn’t disclose any current customers, but it is focusing its efforts on manufacturers, service providers and smart city solutions. Update: Swim.ai did tell us about two customers after we published this story: The City of Palo Alto and Itron.
Swim.ai plans to use its new funding to launch a new R&D center in Cambridge, UK, expand its product development team and tackle new verticals and geographies with an expanded sales and marketing team.
Powered by WPeMatico
At Google, the company offers a ‘Grab and Go’ program that allows employees to use self-service stations to quickly borrow and return Chromebooks without having to go through a lengthy IT approval process. Now, it’s bringing this same idea to other businesses.
Chromebooks have found their place in education and a number of larger enterprise companies are also getting on board with the idea of a centrally managed device that mostly focuses on the browser. That’s maybe no surprise, given that both schools and enterprises are pretty much looking for the same thing from these devices.
 At Google, the system has seen more than 30,000 users that have completed more than 100,000 loans so far.
At Google, the system has seen more than 30,000 users that have completed more than 100,000 loans so far.
While Google wants others to run similar programs (and use more Chromebooks in the process) it’s worth noting that this is a limited preview program and that Google isn’t building and selling racks or other infrastructure for this. As a Google spokesperson told us, Google will give companies that want to try this the open source code to build this system and advise them through the setup and deployment. It will also engage with partners to help them build the hardware or set up a ‘Grab and Go’ as a service system.
Employees who want to use one of these ‘Grab and Go’ stations simply pick up a laptop, sign in and move on with their day. When they are done, they simply return the laptop. That’s it. Easy.
That’s not quite as exciting as Google building and selling racks of Chromebooks, but this project is clearly another move to bring Chromebooks to the enterprise. Specifically, Google says that this program is meant for frontline workers who only need devices for a short period of time, as well as shift workers and remote workers.

Powered by WPeMatico
The Opera Android browser will soon be able to hold your cryptocurrencies. The system, now in beta, lets you store crypto and ERC20 tokens in your browser, send and receive crypto on the fly, and secures your wallet with your phone’s biometric security or passcode.
You can sign up to try the beta here.
The feature, called Crypto Wallet, “makes Opera the first major browser to introduce a built-in crypto wallet” according to the company. The feature could allow for micropayments in the browser and paves the way for similar features in other browsers.
From the release:
We believe the web of today will be the interface to the decentralized web of tomorrow. This is why we have chosen to use our browser to bridge the gap. We think that with a built-in crypto wallet, the browser has the potential to renew and extend its important role as a tool to access information, make transactions online and manage users’ online identity in a way that gives them more control.
In addition to being able to send money from wallet to wallet and interact with Dapps, Opera now supports online payments with cryptocurrency where merchants support exists. Users that choose to pay for their order using cryptocurrency on Coinbase Commerce-enabled merchants will be presented with a payment request dialog, asking them for their signature. The payment will then be signed and transmitted directly from the browser.
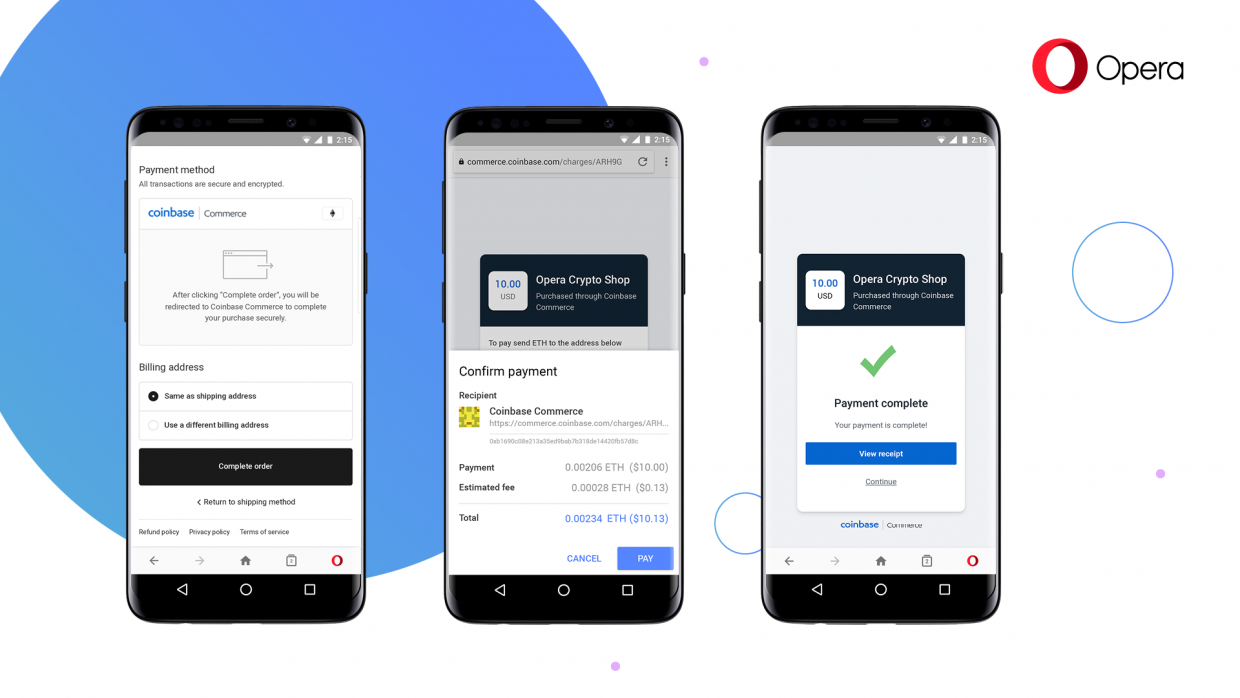
While it’s still early days for this sort of technology it’s interesting to see a mainstream browser entering the space. Don’t hold your breath on seeing crypto in Safari or Edge but Chrome and other “open source” browsers could easily add these features given enough demand.
Powered by WPeMatico
In what amounted to one of the most far-reaching and interesting conversations at TC Sessions in Zug, Ethereum masterminds Vitalik Buterin, Justin Drake, and Karl Floersch spoke openly – and often candidly – about a bright future for Ethereum scaling and, more interestingly, their way to build teams that work.
“There’s definitely changes that we could have made into the protocol,” said Buterin when asked whether or not he would have changed anything if he could start Ethereum again. But, he said, “there are ways in which that the problem is fundamentally hard.” In other words, growth was the only option.
“The demand for using public blockchains is high and we need to up the stability in order the meet that demand,” he said.
Floersch discussed the problems associated with Ethereum in the context of “adversarial networks.”
The network, he said, should “penalize people who don’t provide guarantees” and he felt that the tools available to simulate economic actors – including bad actors – are still weak.
“We come up with ideas, try to formalize them, and implement them,” he said. But, he said, the simulations still aren’t available.
The team expects aspects of Ethereum 2.0 – namely the Casper upgrade and the addition of sharding – to begin rolling out in 2019. After that, said Floersch, Ethereum 3.0 would enable quantum secure systems i.e. systems that can withstand the power of quantum computers.
“We’ll push quantum secure updates before there are commercial quantum computers,” he said.
Ultimately, said Buterin, Ethereum runs because the team is so tightly knit thanks to a clear roadmap. He said Bitcoin has many heads and the gridlock created was dangerous.
“Can they agree? No. You have gridlock,” he said.
“Part of the reason is that the Ethereum community early on [continued] to promote the idea of the Ethereum roadmap,” he said. “I feel that the roadmap is part of the social contract.”
“People who buy into ethereum buy in knowing that these are the things that people are going to want to push it forward. There may be deadlock on what specific path the community should take,” he said. But, he noted the roadmap keeps everyone on the same path. Given the expansive popularity and reach of the technology, it’s a fascinating bit of team-building that should inform other open source and blockchain projects over time.
You can watch the entire panel below:
Powered by WPeMatico
Right now, the cable that comes with a new iPhone does not plug into a new MacBook Pro without a dongle. #donglelife is for real. If this leak is correct, though, that wrong might soon be righted.
Photos have surfaced showing what is an engineering prototype of an Apple 18 W USB-C charger, which is supposedly to be bundled with the next iPhone. If correct, this will let owners take advantage of the iPhone’s fast charging capabilities without purchasing anything else. Plus, it will let users connect the iPhone to a MacBook Pro out of the box.
This rumor surfaced last year, too, though no photos ever surfaced to back up the claim.
If true, this adapter will mark the first major change in the iPhone’s wall charger. Apple has long bundled a 5W charger with the iPhone. It works fine, but does not supply the phone with the necessary power to charge at its fastest possible speed. Even if the photos here show something other than an official Apple product, chances are Apple is readying something similar. Previous leaks show something similar.
Apple included fast charging in the iPhone 8, iPhone 8 Plus and iPhone X but didn’t include the necessary charger to take advantage of the technology. Owners have to buy a third-party charger of the $50 30W charger from Apple.
Powered by WPeMatico
I’m not sure if you’re aware, but the launch of Apple Maps went poorly. After a rough first impression, an apology from the CEO, several years of patching holes with data partnerships and some glimmers of light with long-awaited transit directions and improvements in business, parking and place data, Apple Maps is still not where it needs to be to be considered a world-class service.
Maps needs fixing.
Apple, it turns out, is aware of this, so it’s re-building the maps part of Maps.
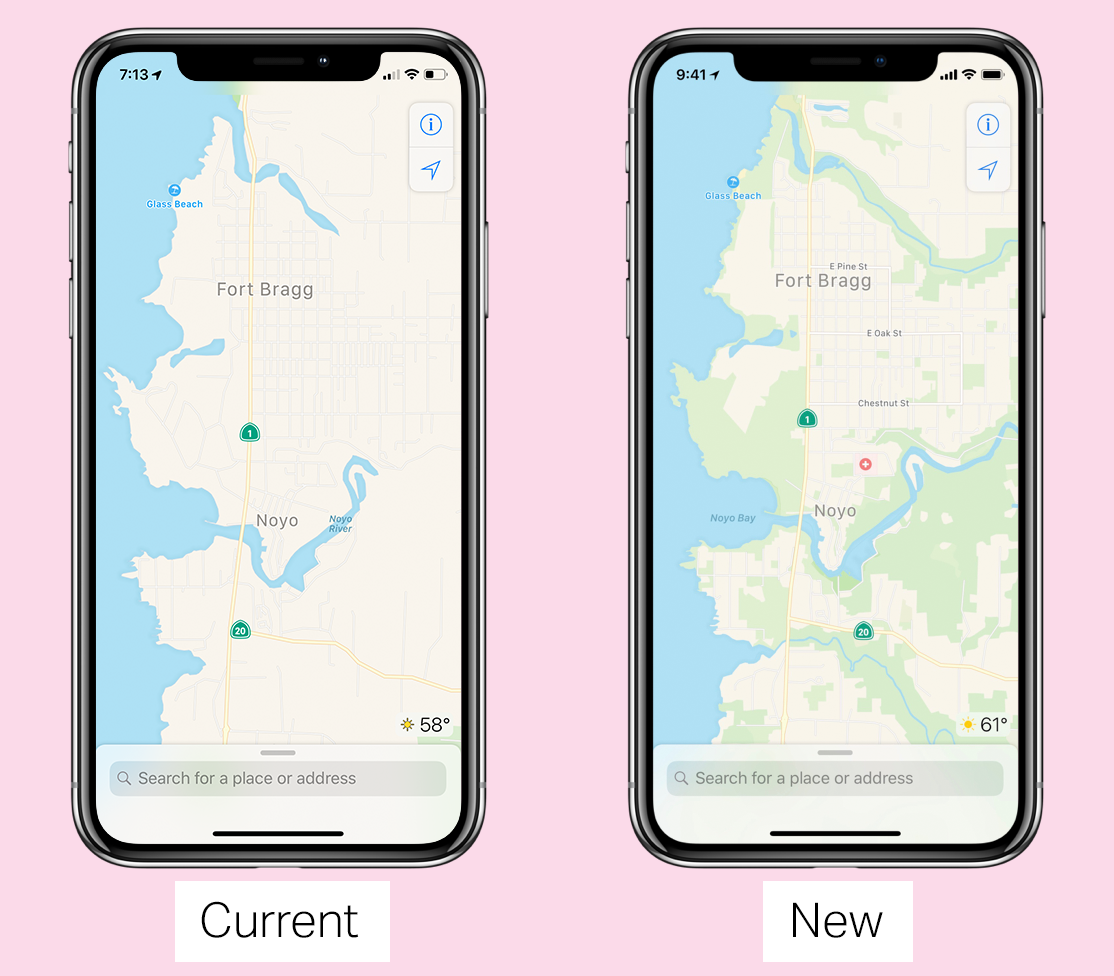
It’s doing this by using first-party data gathered by iPhones with a privacy-first methodology and its own fleet of cars packed with sensors and cameras. The new product will launch in San Francisco and the Bay Area with the next iOS 12 beta and will cover Northern California by fall.
Every version of iOS will get the updated maps eventually, and they will be more responsive to changes in roadways and construction, more visually rich depending on the specific context they’re viewed in and feature more detailed ground cover, foliage, pools, pedestrian pathways and more.
This is nothing less than a full re-set of Maps and it’s been four years in the making, which is when Apple began to develop its new data-gathering systems. Eventually, Apple will no longer rely on third-party data to provide the basis for its maps, which has been one of its major pitfalls from the beginning.
“Since we introduced this six years ago — we won’t rehash all the issues we’ve had when we introduced it — we’ve done a huge investment in getting the map up to par,” says Apple SVP Eddy Cue, who now owns Maps, in an interview last week. “When we launched, a lot of it was all about directions and getting to a certain place. Finding the place and getting directions to that place. We’ve done a huge investment of making millions of changes, adding millions of locations, updating the map and changing the map more frequently. All of those things over the past six years.”
But, Cue says, Apple has room to improve on the quality of Maps, something that most users would agree on, even with recent advancements.
“We wanted to take this to the next level,” says Cue. “We have been working on trying to create what we hope is going to be the best map app in the world, taking it to the next step. That is building all of our own map data from the ground up.”
In addition to Cue, I spoke to Apple VP Patrice Gautier and more than a dozen Apple Maps team members at its mapping headquarters in California this week about its efforts to re-build Maps, and to do it in a way that aligned with Apple’s very public stance on user privacy.
If, like me, you’re wondering whether Apple thought of building its own maps from scratch before it launched Maps, the answer is yes. At the time, there was a choice to be made about whether or not it wanted to be in the business of maps at all. Given that the future of mobile devices was becoming very clear, it knew that mapping would be at the core of nearly every aspect of its devices, from photos to directions to location services provided to apps. Decision made, Apple plowed ahead, building a product that relied on a patchwork of data from partners like TomTom, OpenStreetMap and other geo data brokers. The result was underwhelming.
Almost immediately after Apple launched Maps, it realized that it was going to need help and it signed on a bunch of additional data providers to fill the gaps in location, base map, point-of-interest and business data.
It wasn’t enough.
“We decided to do this just over four years ago. We said, ‘Where do we want to take Maps? What are the things that we want to do in Maps?’ We realized that, given what we wanted to do and where we wanted to take it, we needed to do this ourselves,” says Cue.
Because Maps are so core to so many functions, success wasn’t tied to just one function. Maps needed to be great at transit, driving and walking — but also as a utility used by apps for location services and other functions.
Cue says that Apple needed to own all of the data that goes into making a map, and to control it from a quality as well as a privacy perspective.

There’s also the matter of corrections, updates and changes entering a long loop of submission to validation to update when you’re dealing with external partners. The Maps team would have to be able to correct roads, pathways and other updating features in days or less, not months. Not to mention the potential competitive advantages it could gain from building and updating traffic data from hundreds of millions of iPhones, rather than relying on partner data.
Cue points to the proliferation of devices running iOS, now over a billion, as a deciding factor to shift its process.
“We felt like because the shift to devices had happened — building a map today in the way that we were traditionally doing it, the way that it was being done — we could improve things significantly, and improve them in different ways,” he says. “One is more accuracy. Two is being able to update the map faster based on the data and the things that we’re seeing, as opposed to driving again or getting the information where the customer’s proactively telling us. What if we could actually see it before all of those things?”
I query him on the rapidity of Maps updates, and whether this new map philosophy means faster changes for users.
“The truth is that Maps needs to be [updated more], and even are today,” says Cue. “We’ll be doing this even more with our new maps, [with] the ability to change the map in real time and often. We do that every day today. This is expanding us to allow us to do it across everything in the map. Today, there’s certain things that take longer to change.
“For example, a road network is something that takes a much longer time to change currently. In the new map infrastructure, we can change that relatively quickly. If a new road opens up, immediately we can see that and make that change very, very quickly around it. It’s much, much more rapid to do changes in the new map environment.”
So a new effort was created to begin generating its own base maps, the very lowest building block of any really good mapping system. After that, Apple would begin layering on living location data, high-resolution satellite imagery and brand new intensely high-resolution image data gathered from its ground cars until it had what it felt was a “best in class” mapping product.
There is only really one big company on earth that owns an entire map stack from the ground up: Google .
Apple knew it needed to be the other one. Enter the vans.
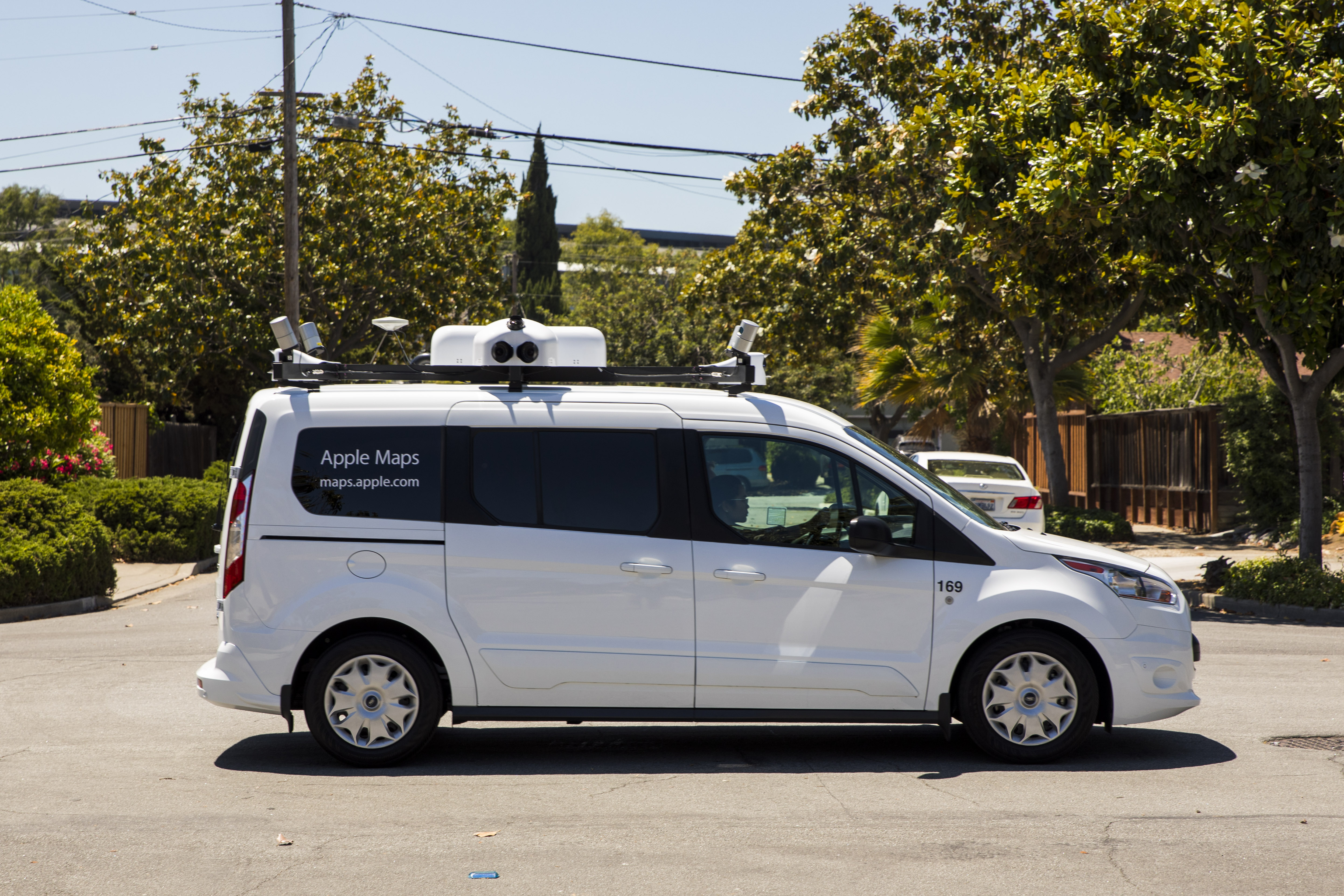

Though the overall project started earlier, the first glimpse most folks had of Apple’s renewed efforts to build the best Maps product was the vans that started appearing on the roads in 2015 with “Apple Maps” signs on the side. Capped with sensors and cameras, these vans popped up in various cities and sparked rampant discussion and speculation.
The new Apple Maps will be the first time the data collected by these vans is actually used to construct and inform its maps. This is their coming out party.
Some people have commented that Apple’s rigs look more robust than the simple GPS + Camera arrangements on other mapping vehicles — going so far as to say they look more along the lines of something that could be used in autonomous vehicle training.
Apple isn’t commenting on autonomous vehicles, but there’s a reason the arrays look more advanced: they are.
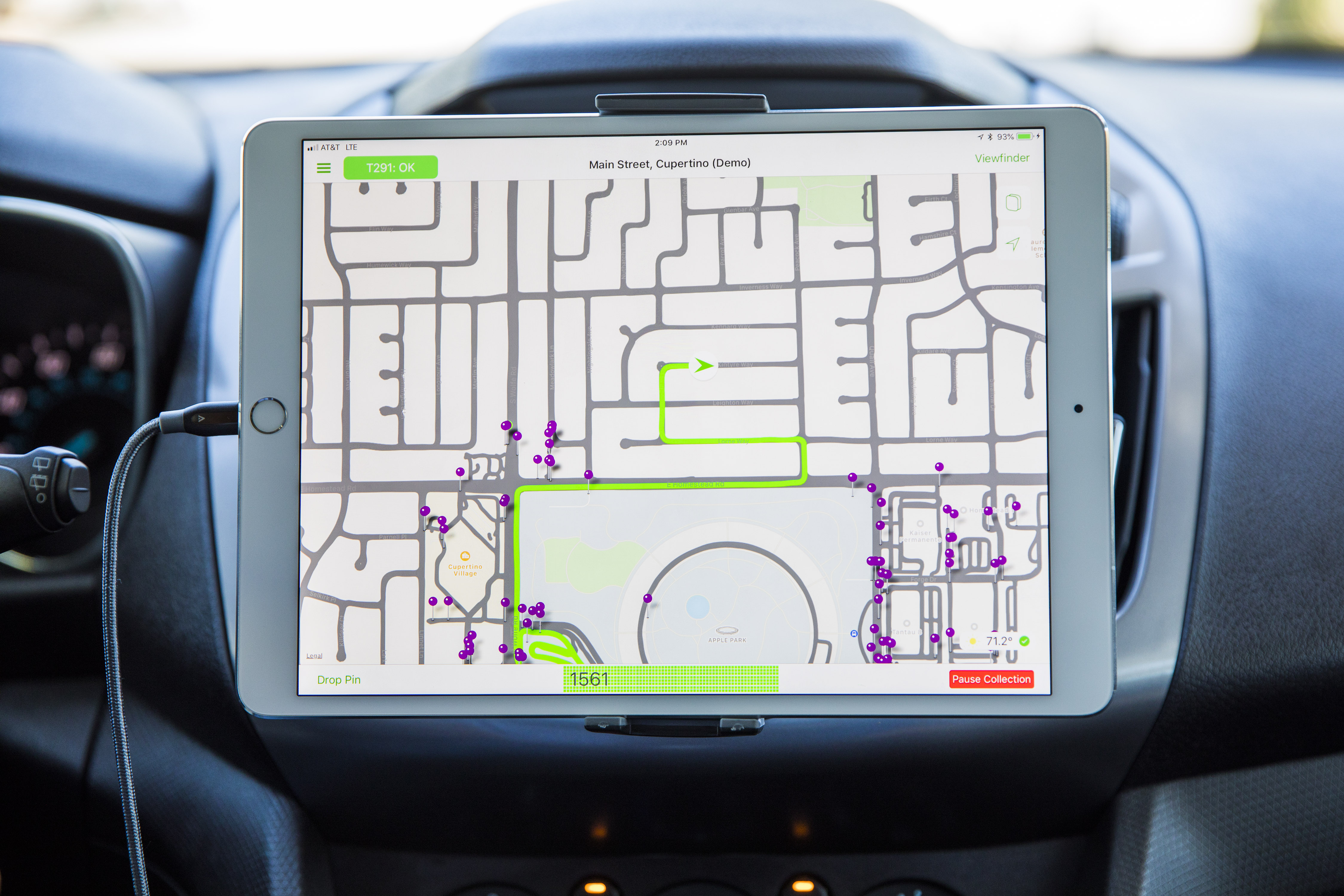
Earlier this week I took a ride in one of the vans as it ran a sample route to gather the kind of data that would go into building the new maps. Here’s what’s inside.

In addition to a beefed-up GPS rig on the roof, four LiDAR arrays mounted at the corners and eight cameras shooting overlapping high-resolution images, there’s also the standard physical measuring tool attached to a rear wheel that allows for precise tracking of distance and image capture. In the rear there is a surprising lack of bulky equipment. Instead, it’s a straightforward Mac Pro bolted to the floor, attached to an array of solid state drives for storage. A single USB cable routes up to the dashboard where the actual mapping-capture software runs on an iPad.
While mapping, a driver…drives, while an operator takes care of the route, ensuring that a coverage area that has been assigned is fully driven, as well as monitoring image capture. Each drive captures thousands of images as well as a full point cloud (a 3D map of space defined by dots that represent surfaces) and GPS data. I later got to view the raw data presented in 3D and it absolutely looks like the quality of data you would need to begin training autonomous vehicles.
More on why Apple needs this level of data detail later.
When the images and data are captured, they are then encrypted on the fly and recorded on to the SSDs. Once full, the SSDs are pulled out, replaced and packed into a case, which is delivered to Apple’s data center, where a suite of software eliminates from the images private information like faces, license plates and other info. From the moment of capture to the moment they’re sanitized, they are encrypted with one key in the van and the other key in the data center. Technicians and software that are part of its mapping efforts down the pipeline from there never see unsanitized data.
This is just one element of Apple’s focus on the privacy of the data it is utilizing in New Maps.
Throughout every conversation I have with any member of the team throughout the day, privacy is brought up, emphasized. This is obviously by design, as Apple wants to impress upon me as a journalist that it’s taking this very seriously indeed, but it doesn’t change the fact that it’s evidently built in from the ground up and I could not find a false note in any of the technical claims or the conversations I had.
Indeed, from the data security folks to the people whose job it is to actually make the maps work well, the constant refrain is that Apple does not feel that it is being held back in any way by not hoovering every piece of customer-rich data it can, storing and parsing it.
The consistent message is that the team feels it can deliver a high-quality navigation, location and mapping product without the directly personal data used by other platforms.
“We specifically don’t collect data, even from point A to point B,” notes Cue. “We collect data — when we do it — in an anonymous fashion, in subsections of the whole, so we couldn’t even say that there is a person that went from point A to point B. We’re collecting the segments of it. As you can imagine, that’s always been a key part of doing this. Honestly, we don’t think it buys us anything [to collect more]. We’re not losing any features or capabilities by doing this.”
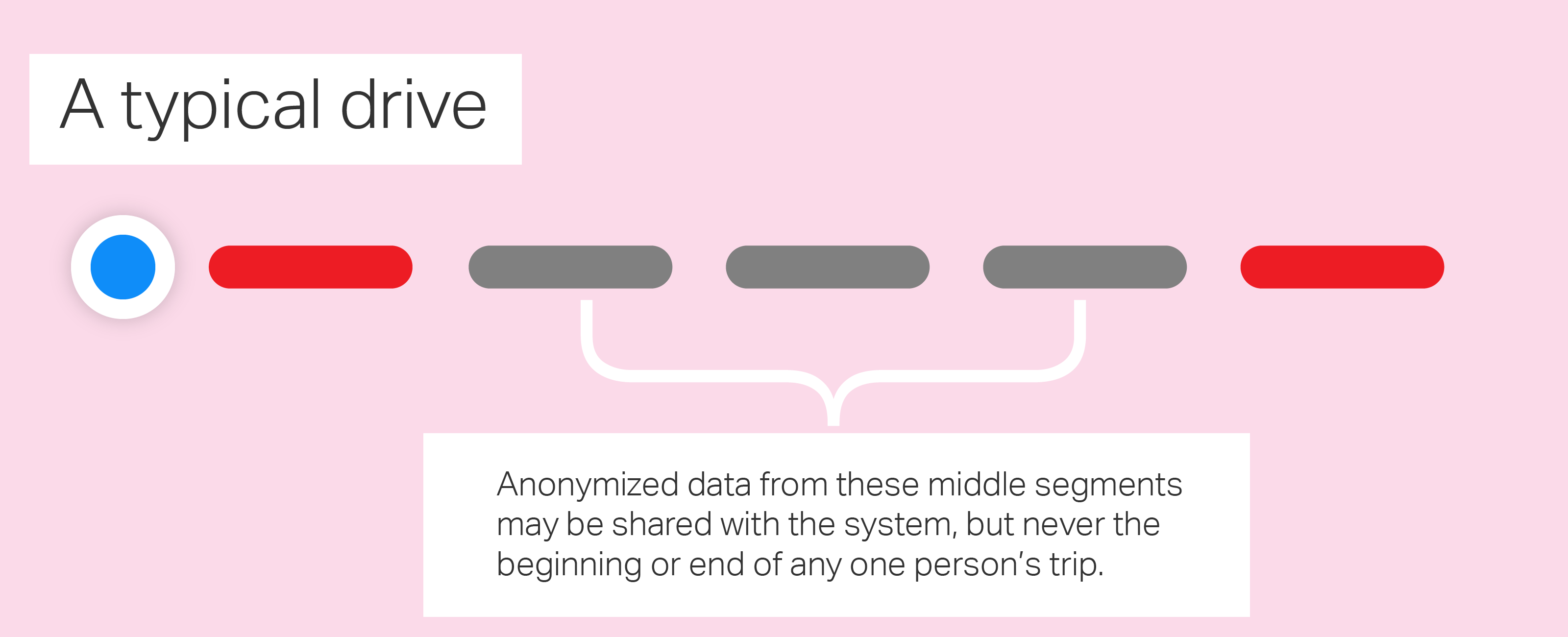
The segments that he is referring to are sliced out of any given person’s navigation session. Neither the beginning or the end of any trip is ever transmitted to Apple. Rotating identifiers, not personal information, are assigned to any data or requests sent to Apple and it augments the “ground truth” data provided by its own mapping vehicles with this “probe data” sent back from iPhones.
Because only random segments of any person’s drive is ever sent and that data is completely anonymized, there is never a way to tell if any trip was ever a single individual. The local system signs the IDs and only it knows to whom that ID refers. Apple is working very hard here to not know anything about its users. This kind of privacy can’t be added on at the end, it has to be woven in at the ground level.
Because Apple’s business model does not rely on it serving to you, say, an ad for a Chevron on your route, it doesn’t need to even tie advertising identifiers to users.
Any personalization or Siri requests are all handled on-board by the iOS device’s processor. So if you get a drive notification that tells you it’s time to leave for your commute, that’s learned, remembered and delivered locally, not from Apple’s servers.
That’s not new, but it’s important to note given the new thing to take away here: Apple is flipping on the power of having millions of iPhones passively and actively improving their mapping data in real time.
In short: Traffic, real-time road conditions, road systems, new construction and changes in pedestrian walkways are about to get a lot better in Apple Maps.
The secret sauce here is what Apple calls probe data. Essentially little slices of vector data that represent direction and speed transmitted back to Apple completely anonymized with no way to tie it to a specific user or even any given trip. It’s reaching in and sipping a tiny amount of data from millions of users instead, giving it a holistic, real-time picture without compromising user privacy.
If you’re driving, walking or cycling, your iPhone can already tell this. Now if it knows you’re driving, it also can send relevant traffic and routing data in these anonymous slivers to improve the entire service. This only happens if your Maps app has been active, say you check the map, look for directions, etc. If you’re actively using your GPS for walking or driving, then the updates are more precise and can help with walking improvements like charting new pedestrian paths through parks — building out the map’s overall quality.
All of this, of course, is governed by whether you opted into location services, and can be toggled off using the maps location toggle in the Privacy section of settings.
Apple says that this will have a near zero effect on battery life or data usage, because you’re already using the ‘maps’ features when any probe data is shared and it’s a fraction of what power is being drawn by those activities.
But maps cannot live on ground truth and mobile data alone. Apple is also gathering new high-resolution satellite data to combine with its ground truth data for a solid base map. It’s then layering satellite imagery on top of that to better determine foliage, pathways, sports facilities, building shapes and pathways.
After the downstream data has been cleaned up of license plates and faces, it gets run through a bunch of computer vision programming to pull out addresses, street signs and other points of interest. These are cross referenced to publicly available data like addresses held by the city and new construction of neighborhoods or roadways that comes from city planning departments.
But one of the special sauce bits that Apple is adding to the mix of mapping tools is a full-on point cloud that maps in 3D the world around the mapping van. This allows them all kinds of opportunities to better understand what items are street signs (retro-reflective rectangular object about 15 feet off the ground? Probably a street sign) or stop signs or speed limit signs.
It seems like it also could enable positioning of navigation arrows in 3D space for AR navigation, but Apple declined to comment on “any future plans” for such things.
Apple also uses semantic segmentation and Deep Lambertian Networks to analyze the point cloud coupled with the image data captured by the car and from high-resolution satellites in sync. This allows 3D identification of objects, signs, lanes of traffic and buildings and separation into categories that can be highlighted for easy discovery.
The coupling of high-resolution image data from car and satellite, plus a 3D point cloud, results in Apple now being able to produce full orthogonal reconstructions of city streets with textures in place. This is massively higher-resolution and easier to see, visually. And it’s synchronized with the “panoramic” images from the car, the satellite view and the raw data. These techniques are used in self-driving applications because they provide a really holistic view of what’s going on around the car. But the ortho view can do even more for human viewers of the data by allowing them to “see” through brush or tree cover that would normally obscure roads, buildings and addresses.
This is hugely important when it comes to the next step in Apple’s battle for supremely accurate and useful Maps: human editors.
Apple has had a team of tool builders working specifically on a toolkit that can be used by human editors to vet and parse data, street by street. The editor’s suite includes tools that allow human editors to assign specific geometries to flyover buildings (think Salesforce tower’s unique ridged dome) that allow them to be instantly recognizable. It lets editors look at real images of street signs shot by the car right next to 3D reconstructions of the scene and computer vision detection of the same signs, instantly recognizing them as accurate or not.
Another tool corrects addresses, letting an editor quickly move an address to the center of a building, determine whether they’re misplaced and shift them around. It also allows for access points to be set, making Apple Maps smarter about the “last 50 feet” of your journey. You’ve made it to the building, but what street is the entrance actually on? And how do you get into the driveway? With a couple of clicks, an editor can make that permanently visible.
“When we take you to a business and that business exists, we think the precision of where we’re taking you to, from being in the right building,” says Cue. “When you look at places like San Francisco or big cities from that standpoint, you have addresses where the address name is a certain street, but really, the entrance in the building is on another street. They’ve done that because they want the better street name. Those are the kinds of things that our new Maps really is going to shine on. We’re going to make sure that we’re taking you to exactly the right place, not a place that might be really close by.”
Water, swimming pools (new to Maps entirely), sporting areas and vegetation are now more prominent and fleshed out thanks to new computer vision and satellite imagery applications. So Apple had to build editing tools for those, as well.
Many hundreds of editors will be using these tools, in addition to the thousands of employees Apple already has working on maps, but the tools had to be built first, now that Apple is no longer relying on third parties to vet and correct issues.
And the team also had to build computer vision and machine learning tools that allow it to determine whether there are issues to be found at all.
Anonymous probe data from iPhones, visualized, looks like thousands of dots, ebbing and flowing across a web of streets and walkways, like a luminescent web of color. At first, chaos. Then, patterns emerge. A street opens for business, and nearby vessels pump orange blood into the new artery. A flag is triggered and an editor looks to see if a new road needs a name assigned.
A new intersection is added to the web and an editor is flagged to make sure that the left turn lanes connect correctly across the overlapping layers of directional traffic. This has the added benefit of massively improved lane guidance in the new Apple Maps.
Apple is counting on this combination of human and AI flagging to allow editors to first craft base maps and then also maintain them as the ever-changing biomass wreaks havoc on roadways, addresses and the occasional park.
Apple’s new Maps, like many other digital maps, display vastly differently depending on scale. If you’re zoomed out, you get less detail. If you zoom in, you get more. But Apple has a team of cartographers on staff that work on more cultural, regional and artistic levels to ensure that its Maps are readable, recognizable and useful.
These teams have goals that are at once concrete and a bit out there — in the best traditions of Apple pursuits that intersect the technical with the artistic.
The maps need to be usable, but they also need to fulfill cognitive goals on cultural levels that go beyond what any given user might know they need. For instance, in the U.S., it is very common to have maps that have a relatively low level of detail even at a medium zoom. In Japan, however, the maps are absolutely packed with details at the same zoom, because that increased information density is what is expected by users.
This is the department of details. They’ve reconstructed replicas of hundreds of actual road signs to make sure that the shield on your navigation screen matches the one you’re seeing on the highway road sign. When it comes to public transport, Apple licensed all of the type faces that you see on your favorite subway systems, like Helvetica for NYC. And the line numbers are in the exact same order that you’re going to see them on the platform signs.
It’s all about reducing the cognitive load that it takes to translate the physical world you have to navigate into the digital world represented by Maps.
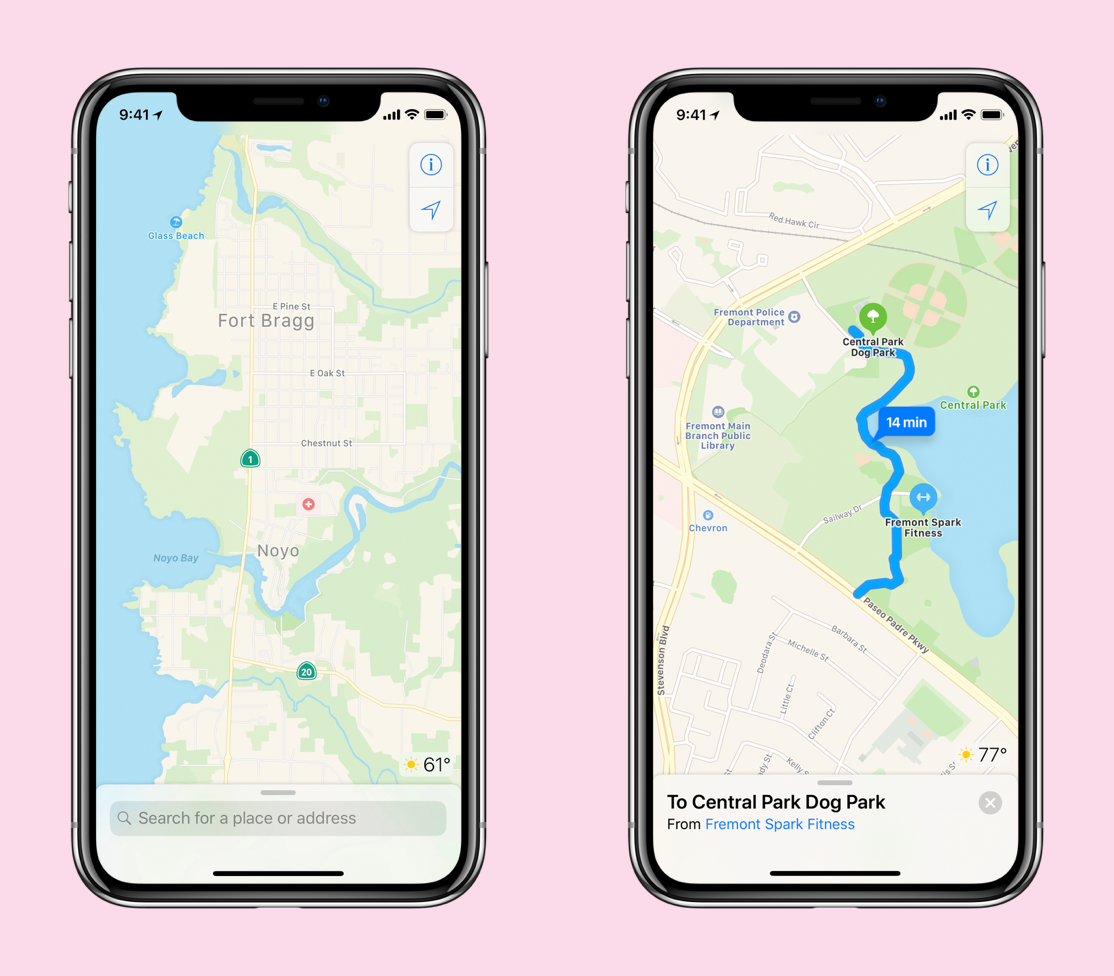
The new version of Apple Maps will be in preview next week with just the Bay Area of California going live. It will be stitched seamlessly into the “current” version of Maps, but the difference in quality level should be immediately visible based on what I’ve seen so far.
Better road networks, more pedestrian information, sports areas like baseball diamonds and basketball courts, more land cover, including grass and trees, represented on the map, as well as buildings, building shapes and sizes that are more accurate. A map that feels more like the real world you’re actually traveling through.
Search is also being revamped to make sure that you get more relevant results (on the correct continents) than ever before. Navigation, especially pedestrian guidance, also gets a big boost. Parking areas and building details to get you the last few feet to your destination are included, as well.
What you won’t see, for now, is a full visual redesign.
“You’re not going to see huge design changes on the maps,” says Cue. “We don’t want to combine those two things at the same time because it would cause a lot of confusion.”
Apple Maps is getting the long-awaited attention it really deserves. By taking ownership of the project fully, Apple is committing itself to actually creating the map that users expected of it from the beginning. It’s been a lingering shadow on iPhones, especially, where alternatives like Google Maps have offered more robust feature sets that are so easy to compare against the native app but impossible to access at the deep system level.
The argument has been made ad nauseam, but it’s worth saying again that if Apple thinks that mapping is important enough to own, it should own it. And that’s what it’s trying to do now.
“We don’t think there’s anybody doing this level of work that we’re doing,” adds Cue. “We haven’t announced this. We haven’t told anybody about this. It’s one of those things that we’ve been able to keep pretty much a secret. Nobody really knows about it. We’re excited to get it out there. Over the next year, we’ll be rolling it out, section by section in the U.S.”
Powered by WPeMatico
An app like Bannersnack is something you never think you need — until you do. Designed by a digital marketer from Romania, Gabriel Ciordas, the app was originally called FlashEff and was used to create Flash banners for online marketers. Over time, however, HTML5 and graphics overtook Flash and the company pivoted to offering easy-to-use design tools for marketers and business owners.
The service is free to try and costs $7 a month 30 static images; $18 a month gets you embedded banners with full analytics. The company is completely bootstrapped and has been working in the space since 2008.
“Bannersnack has always been self-funded. We built our resources step by step, as our business grew together with our efforts. We think it’s fair to say that we worked for every penny we’ve ever gotten and further invested it back into growing our business,” said Ciordas.
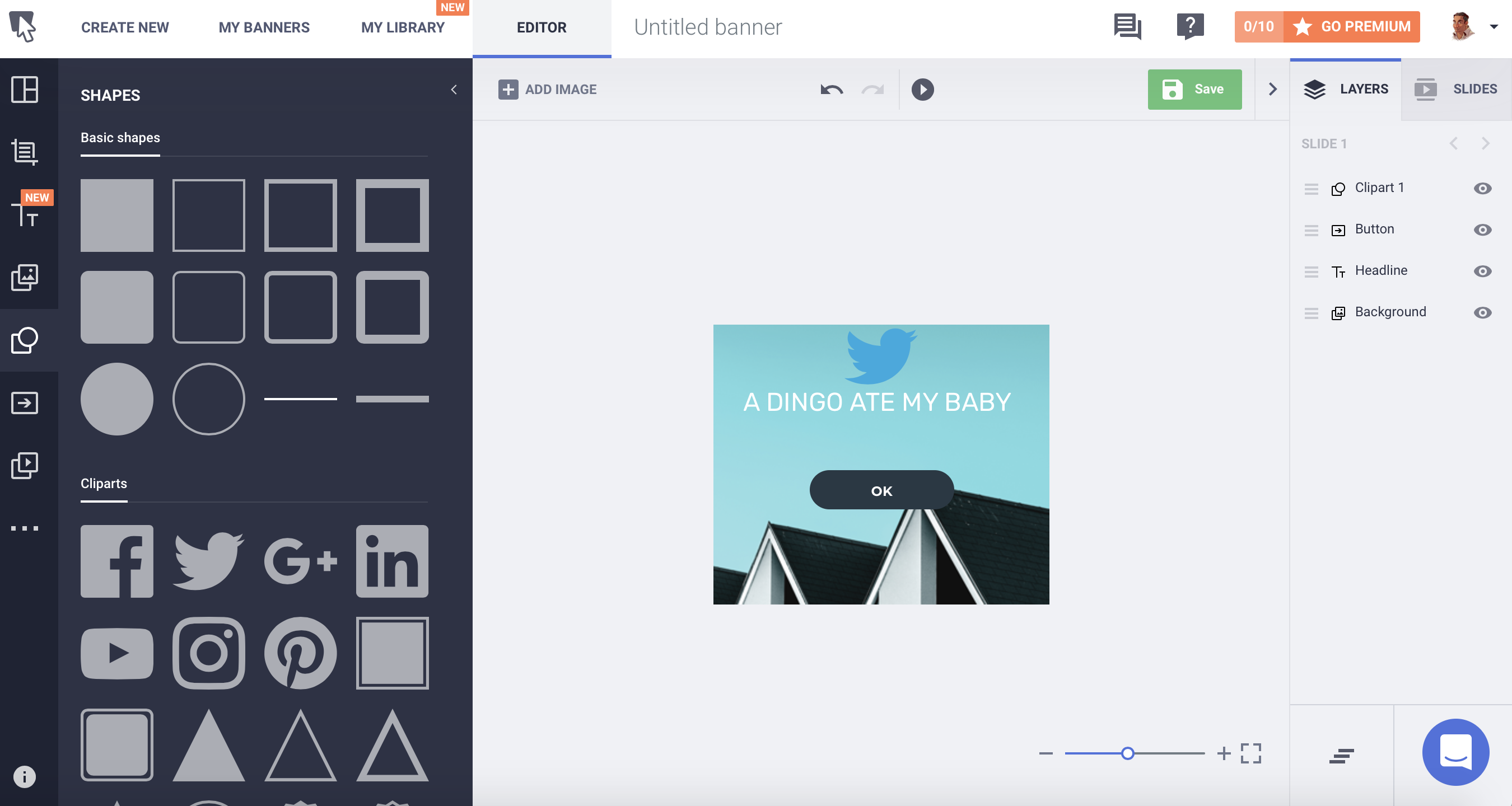
The service has 100,000 monthly users who create 180,000 visuals a month. They offer standalone graphics as well as responsive HTML5 images. The most interesting tool, the Banner Generator, creates banners in multiple sizes instantly, freeing business owners up to do what they do best: sell stuff.
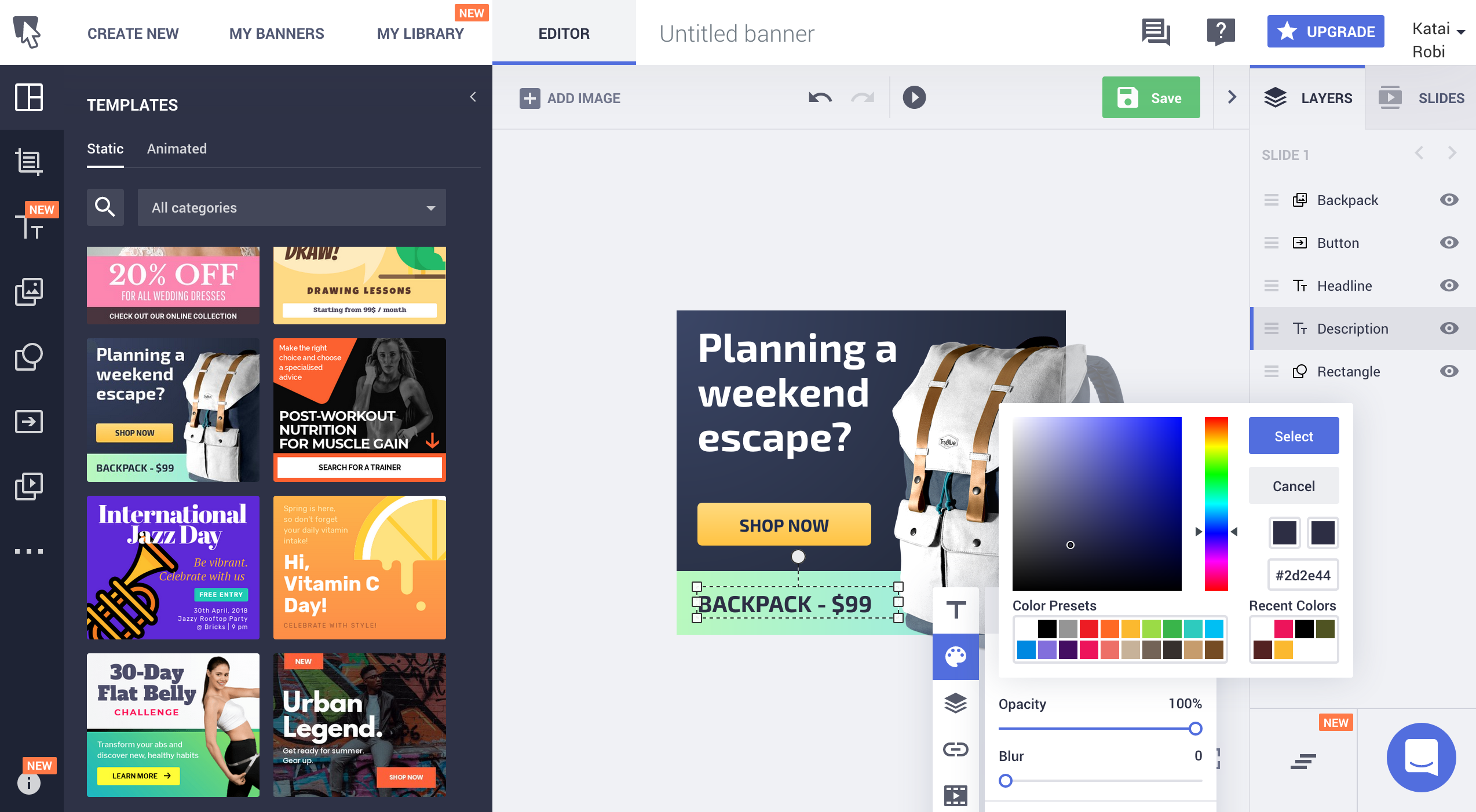
Again, it is rare to see a product so focused on a single, important niche, and Bannersnack fits the bill. While you could fire up Pixelmator and try to make your own banners, this tool is surprisingly pleasant to use and works quite well.
“Our main objective is to empower marketers, designers, and business owners, while reshaping the way agencies and businesses create visuals for their marketing purposes,” said Ciordas. After all, not everyone has the skills or talent to create flashing banners featuring exciting mortgage reduction opportunities and free iPad sweepstakes.
Powered by WPeMatico
In what appears to be the latest salvo in a new, wired form of protest, developer Sam Lavigne posted code that scrapes LinkedIn to find Immigration and Customs Enforcement employee accounts. His code, which basically a Python-based tool that scans LinkedIn for keywords, is gone from Github and Gitlab and Medium took down his original post. The CSV of the data is still available here and here and WikiLeaks has posted a mirror.
“I find it helpful to remember that as much as internet companies use data to spy on and exploit their users, we can at times reverse the story, and leverage those very same online platforms as a means to investigate or even undermine entrenched power structures. It’s a strange side effect of our reliance on private companies and semi-public platforms to mediate nearly all aspects of our lives. We don’t necessarily need to wait for the next Snowden-style revelation to scrutinize the powerful — so much is already hiding in plain sight,” said Lavigne.
Doxxing is the process of using publicly available information to target someone online for abuse. Because we can now find out anything on anyone for a few dollars – a search for “background check” brings up dozens of paid services that can get you names and addresses in a second – scraping public data on LinkedIn seems far easier and innocuous. That doesn’t make it legal.
“Recent efforts to outlaw doxxing at the national level (like the Online Safety Modernization Act of 2017) have stalled in committee, so it’s not strictly illegal,” said James Slaby, Security Expert at Acronis. “But LinkedIn and other social networks usually consider it a violation of their terms of service to scrape their data for personal use. The question of fairness is trickier: doxxing is often justified as a rare tool that the powerless can use against the powerful to call attention to perceived injustices.”
“The problem is that doxxing is a crude tool. The torrent of online ridicule, abuse and threats that can be heaped on doxxed targets by their political or ideological opponents can also rain down on unintended and undeserving targets: family members, friends, people with similar names or appearances,” he said.
The tool itself isn’t to blame. No one would fault a job seeker or salesperson who scraped LinkedIn for targeted employees of a specific company. That said, scraping and publicly shaming employees walks a thin line.
“In my opinion, the professor who developed this scraper tool isn’t breaking the law, as it’s perfectly legal to search the web for publicly available information,” said David Kennedy, CEO of TrustedSec. “This is known in the security space as ‘open source intelligence’ collection, and scrapers are just one way to do it. That said, it is concerning to see ICE agents doxxed in this way. I understand emotions are running high on both sides of this debate, but we don’t want to increase the physical security risks to our law enforcement officers.”
“The decision by Twitter, Github and Medium to block the dissemination of this information and tracking tool makes sense – in fact, law enforcement agents’ personal information is often protected. This isn’t going to go away anytime soon, it’s only going to become more aggressive, particularly as more people grow comfortable with using the darknet and the many available hacking tools for sale in these underground forums. Law enforcement agents need to take note of this, and be much more careful about what (and how often) they post online.”
Ultimately, doxxing is problematic. Because we place our information on public forums there should be nothing to stop anyone from finding and posting it. However, the expectation that people will use our information for good and not evil is swiftly eroding. Today, wrote one security researcher, David Kavanaugh, doxxing is becoming dangerous.
“Going after the people on the ground is like shooting the messenger. Decisions are made by leadership and those are the people we should be going after. Doxxing is akin to a personal attack. Change policy, don’t ruin more lives,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico