computing
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Google today announced that it is providing the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) with $9 million in Google Cloud credits to help further its work on the Kubernetes container orchestrator and that it is handing over operational control of the project to the community. These credits will be split over three years and are meant to cover the infrastructure costs of building, testing and distributing the Kubernetes software.
Why does this matter? Until now, Google hosted virtually all the cloud resources that supported the project, like its CI/CD testing infrastructure, container downloads and DNS services on its cloud. But Google is now taking a step back. With the Kubernetes community reaching a state of maturity, Google is transferring all of this to the community.
Between the testing infrastructure and hosting container downloads, the Kubernetes project regularly runs more than 150,000 containers on 5,000 virtual machines, so the cost of running these systems quickly adds up. The Kubernetes container registry has served almost 130 million downloads since the launch of the project.
 It’s also worth noting that the CNCF now includes a wide range of members that typically compete with each other. We’re talking Alibaba Cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, Oracle, SAP and VMware, for example. All of these profit from the work of the CNCF and the Kubernetes community. Google doesn’t say so outright, but it’s fair to assume that it wanted others to shoulder some of the burdens of running the Kubernetes infrastructure, too. Similarly, some of the members of the community surely didn’t want to be so closely tied to Google’s infrastructure, either.
It’s also worth noting that the CNCF now includes a wide range of members that typically compete with each other. We’re talking Alibaba Cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, Oracle, SAP and VMware, for example. All of these profit from the work of the CNCF and the Kubernetes community. Google doesn’t say so outright, but it’s fair to assume that it wanted others to shoulder some of the burdens of running the Kubernetes infrastructure, too. Similarly, some of the members of the community surely didn’t want to be so closely tied to Google’s infrastructure, either.
“By sharing the operational responsibilities for Kubernetes with contributors to the project, we look forward to seeing the new ideas and efficiencies that all Kubernetes contributors bring to the project operations,” Google Kubernetes Engine product manager William Deniss writes in today’s announcement. He also notes that a number of Google’s will still be involved in running the Kubernetes infrastructure.
“Google’s significant financial donation to the Kubernetes community will help ensure that the project’s constant pace of innovation and broad adoption continue unabated,” said Dan Kohn, the executive director of the CNCF. “We’re thrilled to see Google Cloud transfer management of the Kubernetes testing and infrastructure projects into contributors’ hands — making the project not just open source, but openly managed, by an open community.”
It’s unclear whether the project plans to take some of the Google-hosted infrastructure and move it to another cloud, but it could definitely do so — and other cloud providers could step up and offer similar credits, too.
Powered by WPeMatico
Cloudian, a company that specializes in helping businesses store petabytes of data, today announced that it has raised a $94 million Series E funding round. Investors in this round, which is one of the largest we have seen for a storage vendor, include Digital Alpha, Fidelity Eight Roads, Goldman Sachs, INCJ, JPIC (Japan Post Investment Corporation), NTT DOCOMO Ventures and WS Investments. This round includes a $25 million investment from Digital Alpha, which was first announced earlier this year.
With this, the seven-year-old company has now raised a total of $174 million.
As the company told me, it now has about 160 employees and 240 enterprise customers. Cloudian has found its sweet spot in managing the large video archives of entertainment companies, but its customers also include healthcare companies, automobile manufacturers and Formula One teams.

What’s important to stress here is that Cloudian’s focus is on on-premise storage, not cloud storage, though it does offer support for multi-cloud data management, as well. “Data tends to be most effectively used close to where it is created and close to where it’s being used,” Cloudian VP of worldwide sales Jon Ash told me. “That’s because of latency, because of network traffic. You can almost always get better performance, better control over your data if it is being stored close to where it’s being used.” He also noted that it’s often costly and complex to move that data elsewhere, especially when you’re talking about the large amounts of information that Cloudian’s customers need to manage.
Unsurprisingly, companies that have this much data now want to use it for machine learning, too, so Cloudian is starting to get into this space, as well. As Cloudian CEO and co-founder Michael Tso also told me, companies are now aware that the data they pull in, whether from IoT sensors, cameras or medical imaging devices, will only become more valuable over time as they try to train their models. If they decide to throw the data away, they run the risk of having nothing with which to train their models.
Cloudian plans to use the new funding to expand its global sales and marketing efforts and increase its engineering team. “We have to invest in engineering and our core technology, as well,” Tso noted. “We have to innovate in new areas like AI.”
As Ash also stressed, Cloudian’s business is really data management — not just storage. “Data is coming from everywhere and it’s going everywhere,” he said. “The old-school storage platforms that were siloed just don’t work anywhere.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Mixmax, a service that aims to make email and other outbound communications more usable and effective, today announced the official launch of its new IFTTT-like rules for automating many of the most repetitive aspects of your daily email workflow.
On the one hand, this new feature is a bit like your standard email filter on steroids (and with connections to third-party tools like Slack, Salesforce, DocuSign, Greenhouse and Pipedrive). Thanks to this, you can now receive an SMS when a customer who spends more than $5,000 a month emails you, for example.
But rules also can be triggered by any of the third-party services the company currently supports. Maybe you want to send out a meeting reminder based on your calendar entries, for example. You can then set up a rule that always emails a reminder a day before the meeting, together with all the standard info you’d want to send in that email.
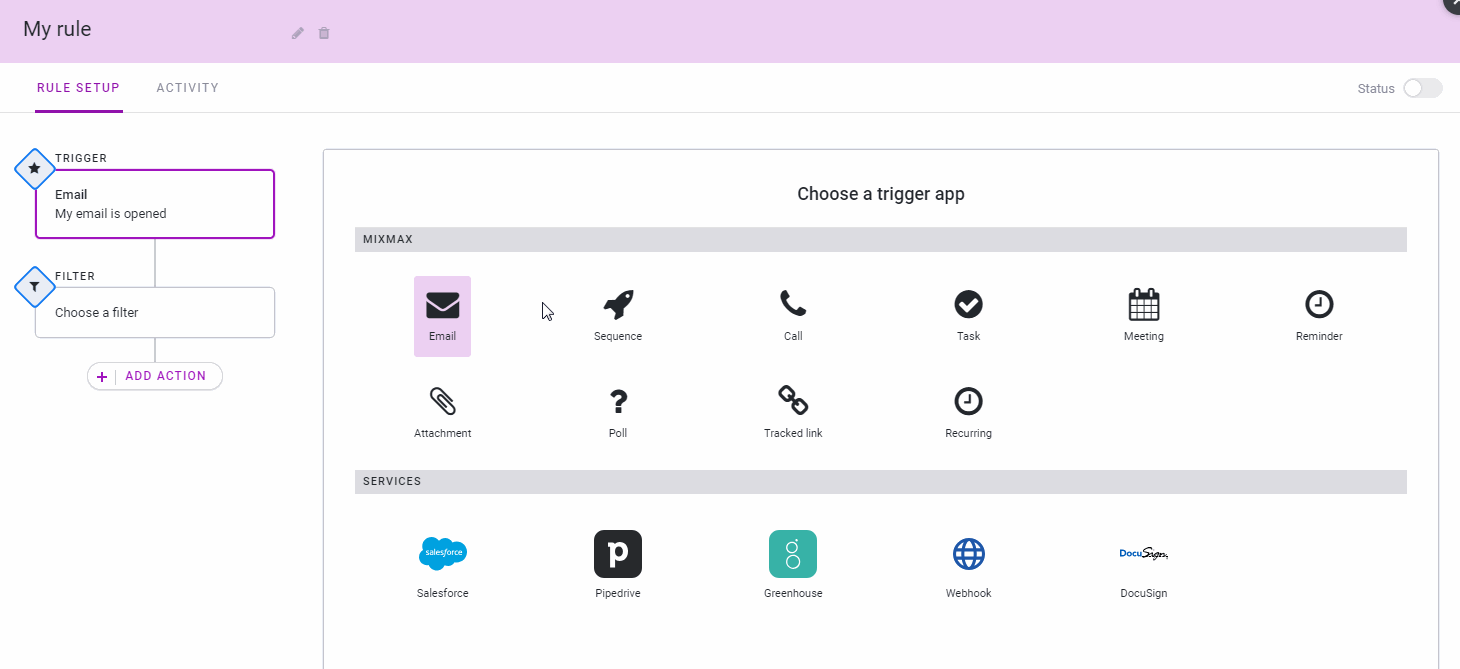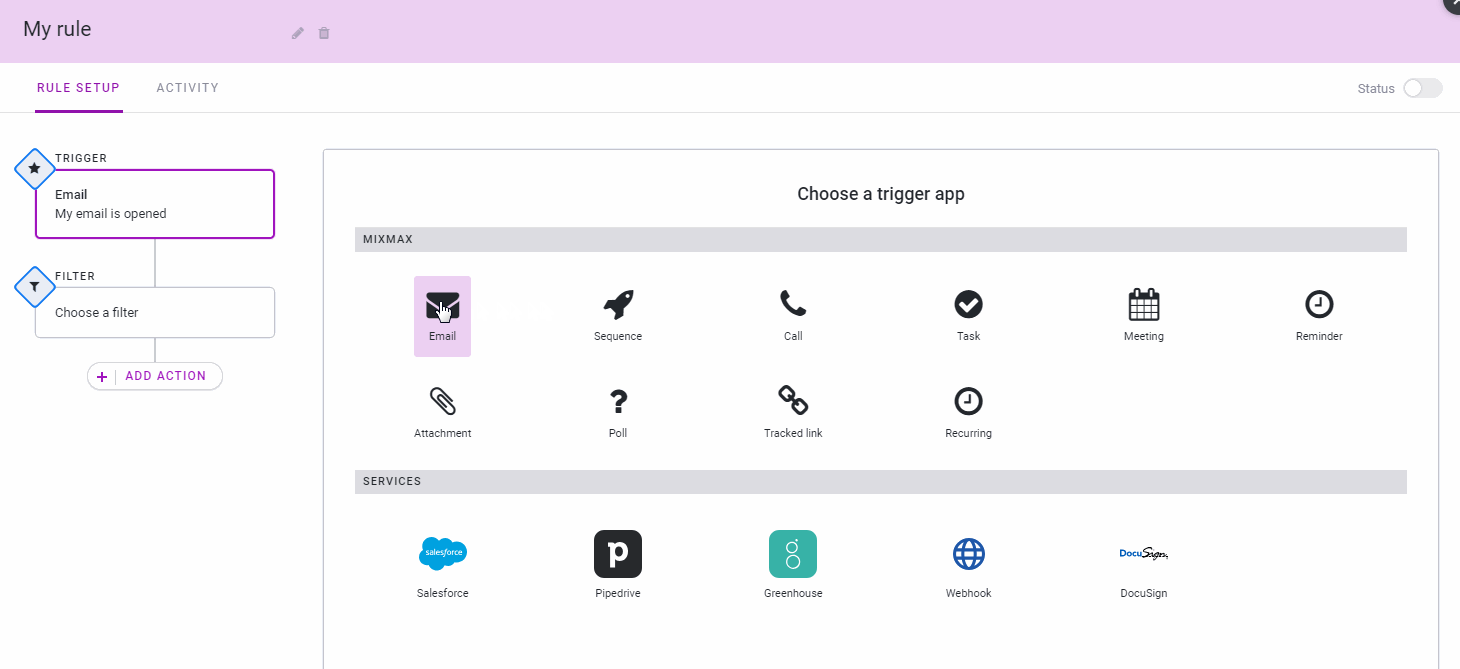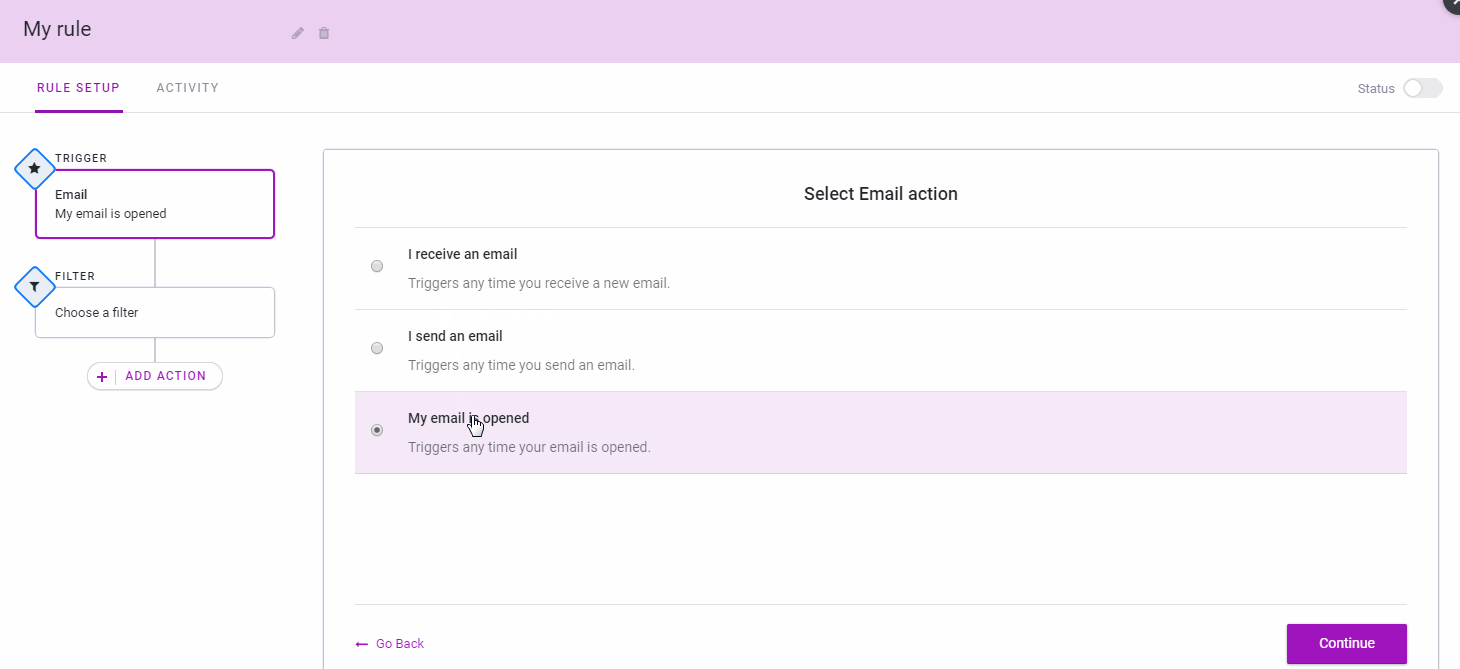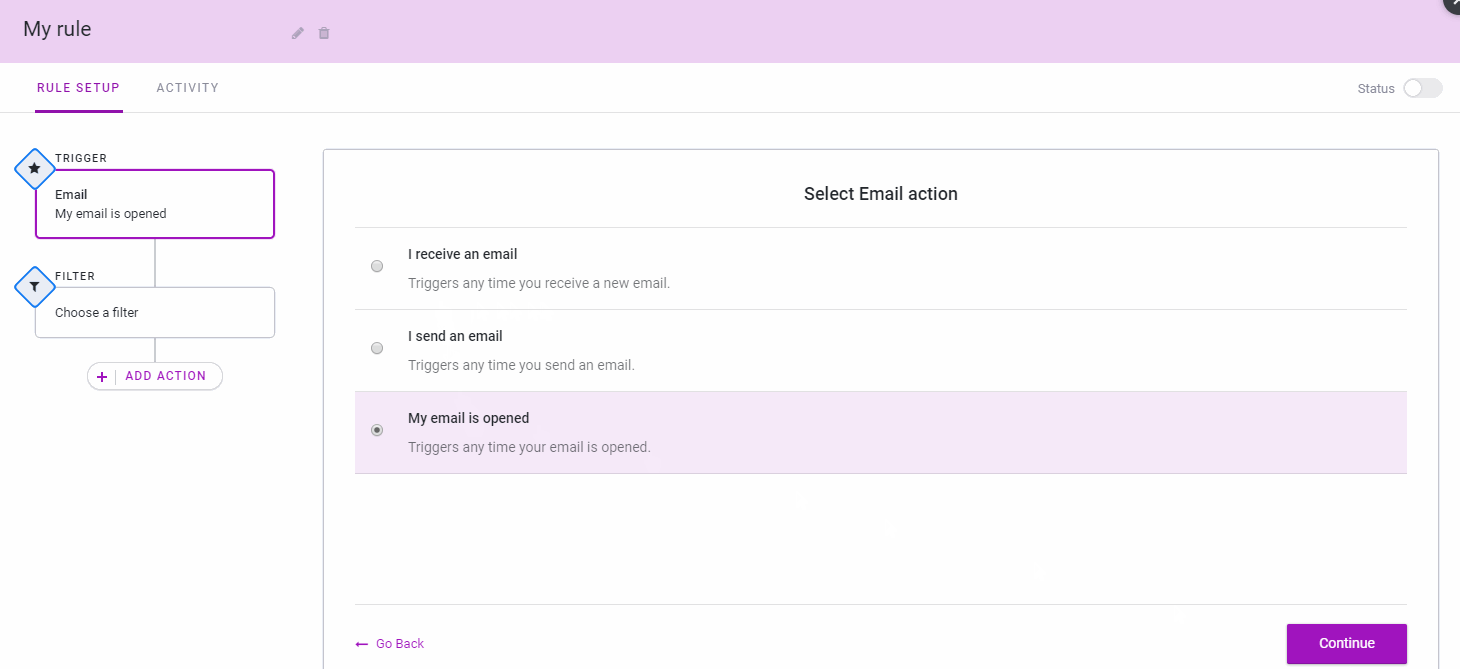
“One way we think about Mixmax is that we want to do for externally facing teams and people who talk a lot of customers what GitHub did for engineering and what Slack did for internal team communication,” Mixmax co-founder and CEO Olof Mathé told me. “That’s what we do for external communication.”
While the service started out as a basic Chrome extension for Gmail, it’s now a full-blown email automation system that offers everything from easy calendar sharing to tracking when recipients open an email and, now, building rules around that. Mathé likened it to an executive assistant, but he stressed that he doesn’t think Mixmax is taking anybody’s jobs away. “We’re not here to replace other people,” he said. “We amplify what you are able to do as an individual and give you superpowers so you can become your own personal chief of staff so you get more time.”
The new rules feature takes this to the next level and Mathé and his team plan to build this out more over time. He teased a new feature called “beast mode” that’s coming in the near future and that will see Mixmax propose actions you can take across different applications, for example.
Many of the new rules and connectors will be available to all paying users, though some features, like access to your Salesforce account, will only be available to those on higher-tier plans.
Powered by WPeMatico
The BitFi crypto wallet was supposed to be unhackable and none other than famous weirdo John McAfee claimed that the device – essentially an Android-based mini tablet – would withstand any attack. Spoiler alert: it couldn’t.
First, a bit of background. The $120 device launched at the beginning of this month to much fanfare. It consisted of a device that McAfee claimed contained no software or storage and was instead a standalone wallet similar to the Trezor. The website featured a bold claim by McAfee himself, one that would give a normal security researcher pause:

Further, the company offered a bug bounty that seems to be slowly being eroded by outside forces. They asked hackers to pull coins off of a specially prepared $10 wallet, a move that is uncommon in the world of bug bounties. They wrote:
We deposit coins into a Bitfi wallet
If you wish to participate in the bounty program, you will purchase a Bitfi wallet that is preloaded with coins for just an additional $10 (the reason for the charge is because we need to ensure serious inquiries only)
If you successfully extract the coins and empty the wallet, this would be considered a successful hack
You can then keep the coins and Bitfi will make a payment to you of $250,000
Please note that we grant anyone who participates in this bounty permission to use all possible attack vectors, including our servers, nodes, and our infrastructure
Hackers began attacking the device immediately, eventually hacking it to find the passphrase used to move crypto in and out of the the wallet. In a detailed set of tweets, security researchers Andrew Tierney and Alan Woodward began finding holes by attacking the operating system itself. However, this did not match the bounty to the letter, claimed BitFi, even though they did not actually ship any bounty-ready devices.
Something that I feel should be getting more attention is the fact that there is zero evidence that a #bitfi bounty device was ever shipped to a researcher. They literally created an impossible task by refusing to send the device required to satisfy the terms of the engagement.
— Gallagher (@DanielGallagher) August 8, 2018
Then, to add insult to injury, the company earned a Pwnies award at security conference Defcon. The award was given for worst vendor response. As hackers began dismantling the device, BitFi went on the defensive, consistently claiming that their device was secure. And the hackers had a field day. One hacker, 15-year-old Saleem Rashid, was able to play Doom on the device.
Well, that’s a transaction made with a MitMed Bitfi, with the phrase and seed being sent to a remote machine.
That sounds a lot like Bounty 2 to me. pic.twitter.com/qBOVQ1z6P2
— Ask Cybergibbons! (@cybergibbons) August 13, 2018
The hacks kept coming. McAfee, for his part, kept refusing to accept the hacks as genuine.
The press claiming the BitFi wallet has been hacked. Utter nonsense. The wallet is hacked when someone gets the coins. No-one got any coins. Gaining root access in an attempt to get the coins is not a hack. It’s a failed attempt. All these alleged “hacks” did not get the coins.
— John McAfee (@officialmcafee) August 3, 2018
Unfortunately, the latest hack may have just fulfilled all of BitFi’s requirements. Rashid and Tierney have been able to pull cash out of the wallet by hacking the passphrase, a primary requirement for the bounty. “We have sent the seed and phrase from the device to another server, it just gets sent using netcat, nothing fancy.” Tierney said. “We believe all conditions have been met.”
The end state of this crypto mess? BitFi did what most hacked crypto companies do: double down on the threats. In a recently deleted Tweet they made it clear that they were not to be messed with:
I haven’t really been following this Bitfi nonsense, but I do so love when companies threaten security researchers. pic.twitter.com/McyBGqM3bt
— Matthew Green (@matthew_d_green) August 6, 2018
The researchers, however, may still have the last laugh.
Claiming your front door has an unpickable lock does not make your house secure. No more does offering a reward only for defeating that front door lock, and repeatedly saying no one has claimed the reward, prove your house is secure, especially when you’ve left the windows open.
— Alan Woodward (@ProfWoodward) August 14, 2018
Powered by WPeMatico
Sometimes smart contracts can be pretty dumb.
All of the benefits of a cryptographically secured, publicly verified, anonymized transaction system can be erased by errant code, malicious actors or poorly defined parameters of an executable agreement.
Hoping to beat back the tide of bad contracts, bad code and bad actors, Sagewise, a new Los Angeles-based startup, has raised $1.25 million to bring to market a service that basically hits pause on the execution of a contract so it can be arbitrated in the event that something goes wrong.
Co-founded by a longtime lawyer, Amy Wan, whose experience runs the gamut from the U.S. Department of Commerce to serving as counsel for a peer-to-peer real estate investment platform in Los Angeles, and Dan Rice, a longtime entrepreneur working with blockchain, Sagewise works with both Ethereum and the Hedera Hashgraph (a newer distributed ledger technology, which purports to solve some of the issues around transaction processing speed and security which have bedeviled platforms like Ethereum and Bitcoin).
The company’s technology works as a middleware, including an SDK and a contract notification and monitoring service. “The SDK is analogous to an arbitration clause in code form — when the smart contract executes a function, that execution is delayed for a pre-set amount of time (i.e. 24 hours) and users receive a text/email notification regarding the execution,” Wan wrote to me in an email. “If the execution is not the intent of the parties, they can freeze execution of the smart contract, giving them the luxury of time to fix whatever is wrong.”
Sagewise approaches the contract resolution process as a marketplace where priority is given to larger deals. “Once frozen, parties can fix coding bugs, patch up security vulnerabilities, or amend/terminate the smart contract, or self-resolve a dispute. If a dispute cannot be self-resolved, parties then graduate to a dispute resolution marketplace of third party vendors,” Wan writes. “After all, a $5 bar bet would be resolved differently from a $5M enterprise dispute. Thus, we are dispute process agnostic.”
Wavemaker Genesis led the round, which also included strategic investments from affiliates of Ari Paul (Blocktower Capital), Miko Matsumura (Gumi Cryptos), Youbi Capital, Maja Vujinovic (Cipher Principles), Jordan Clifford (Scalar Capital), Terrence Yang (Yang Ventures) and James Sowers.
“Smart contracts are coded by developers and audited by security auditing firms, but the quality of smart contract coding and auditing varies drastically among service providers,” said Wan, the chief executive of Sagewise, in a statement. “Inevitably, this discrepancy becomes the basis for smart contract disputes, which is where Sagewise steps in to provide the infrastructure that allows the blockchain and smart contract industry to achieve transactional confidence.”
In an email, Wan elaborated on the thesis to me, writing that, “smart contracts may have coding errors, security vulnerabilities, or parties may need to amend or terminate their smart contracts due to changing situations.”
Contracts could also be disputed if their execution was triggered accidentally or due to the actions of attackers trying to hack a platform.
“Sagewise seeks to bring transactional confidence into the blockchain industry by building a smart contract safety net where smart contracts do not fulfill the original transactional intent,” Wan wrote.
Powered by WPeMatico
Arm, the semiconductor firm you probably still remember as ARM, today announced that it has acquired Treasure Data, a data management platform for large enterprise customers. The companies didn’t announce the financial details of the transaction, but earlier reporting by Bloomberg pegged the price at $600 million.
This move strengthens Arm’s IoT nascent play, given that Treasure Data’s specialty is dealing with the large streams of data that these systems produce (as well as data from CRM, e-commerce systems and other third-party services).
This move follows Arm’s recent acquisition of Stream and indeed, the company calls the acquisition of Treasure Data “the final piece” of its “IoT enablement puzzle.” The result of this completed puzzle is the Arm Pelion IoT Platform, which combines Stream, Treasure Data and the existing Arm Mbed Cloud into a single solution for connecting and managing IoT devices and the data they produce.
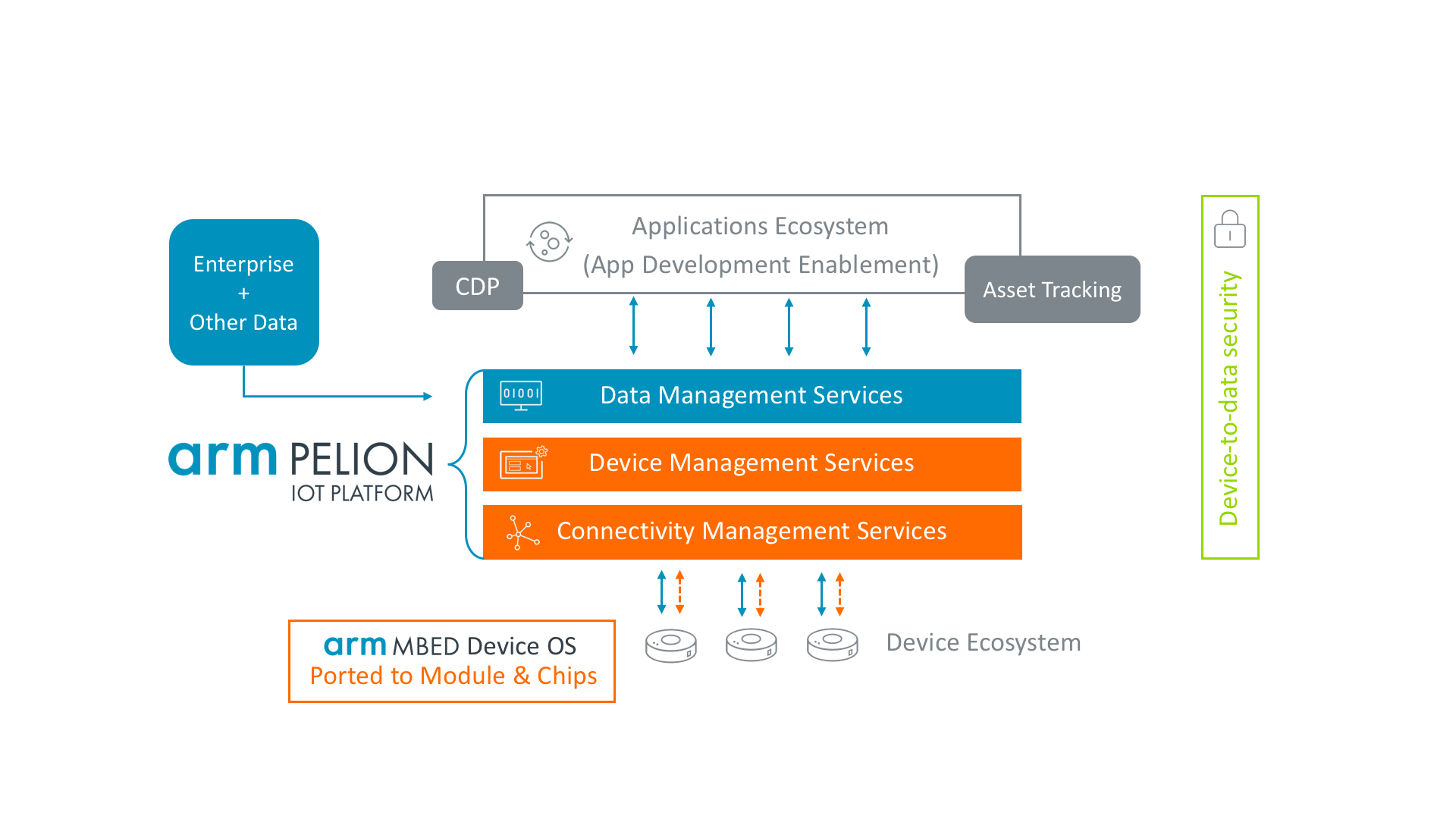
Arm says Treasure Data will continue to operate as before and continue to serve new clients as well as its existing users. “It will remain an important part of industry IoT enablement, providing the ability to harness new, complex edge and device data within a comprehensive customer profile to personalize their products and improve their experiences,” the company says.
Powered by WPeMatico
A look back at the past decade of consumer technology use in the UK has shone a light on changing gadget habits, underlining how Brits have gone from being smartphone dabblers back in 2008 when a top-of-the-range smartphone cost ~£500 to true addicts in today’s £1k+ premium smartphone era.
The report also highlights what seems to be, at times, a conflicted relationship between Brits and the Internet.
While nine in ten people in the UK have home access to the Internet, here in 2018, some web users report feeling being online is a time-sink or a constraint on their freedom.
But even more said they feel lost or bored without it.
Over the past decade the Internet looks to have consolidated its grip on the spacetime that boredom occupied for the less connected generations that came before.
The overview comes via regulator Ofcom’s 2018 Communications Market report. The full report commenting on key market developments in the country’s communications sector is a meaty, stat and chart-filled read.
The regulator has also produced a 30-slide interactive version this year.
Commenting on the report findings in a statement, Ian Macrae, Ofcom’s director of market intelligence, said: “Over the last decade, people’s lives have been transformed by the rise of the smartphone, together with better access to the Internet and new services. Whether it’s working flexibly, keeping up with current affairs or shopping online, we can do more on the move than ever before.
“But while people appreciate their smartphone as their constant companion, some are finding themselves feeling overloaded when online, or frustrated when they’re not.”
We’ve pulled out some highlights from the report below…
Smartphone screen addicts, much?
Social and emotional friction, plus the generation gap…
The impact of (multifaceted and increasingly powerful and capable) smartphones can also be seen on some other types of gadgets. Though TV screens continue to compel Brits (possibly because they feel it’s okay to keep using their smartphones while sitting in front of a bigger screen… )
BBC mightier than Amazon …
What else are UK citizens getting up to online? More of a spread of stuff than ever, it would appear…
One more thing: Women in the UK are bigger Internet fans than men.
Perhaps contrary to some people’s expectations, women in the UK spend more time online on average than men across almost all age groups, with the sole exception being the over 55s (where the time difference is pretty marginal)…
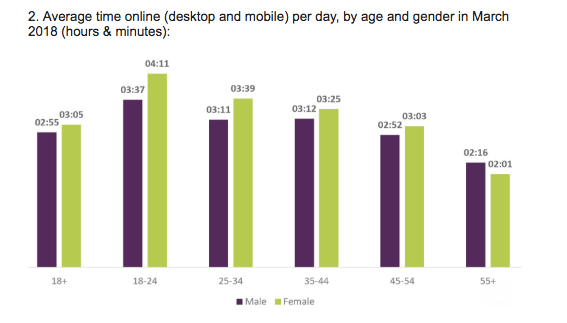
Powered by WPeMatico
Istio, the service mesh for microservices from Google, IBM, Lyft, Red Hat and many other players in the open-source community, launched version 1.0 of its tools today.
If you’re not into service meshes, that’s understandable. Few people are. But Istio is probably one of the most important new open-source projects out there right now. It sits at the intersection of a number of industry trends, like containers, microservices and serverless computing, and makes it easier for enterprises to embrace them. Istio now has more than 200 contributors and the code has seen more than 4,000 check-ins since the launch of version 0.1.
Istio, at its core, handles the routing, load balancing, flow control and security needs of microservices. It sits on top of existing distributed applications and basically helps them talk to each other securely, while also providing logging, telemetry and the necessary policies that keep things under control (and secure). It also features support for canary releases, which allow developers to test updates with a few users before launching them to a wider audience, something that Google and other webscale companies have long done internally.
 “In the area of microservices, things are moving so quickly,” Google product manager Jennifer Lin told me. “And with the success of Kubernetes and the abstraction around container orchestration, Istio was formed as an open-source project to really take the next step in terms of a substrate for microservice development as well as a path for VM-based workloads to move into more of a service management layer. So it’s really focused around the right level of abstractions for services and creating a consistent environment for managing that.”
“In the area of microservices, things are moving so quickly,” Google product manager Jennifer Lin told me. “And with the success of Kubernetes and the abstraction around container orchestration, Istio was formed as an open-source project to really take the next step in terms of a substrate for microservice development as well as a path for VM-based workloads to move into more of a service management layer. So it’s really focused around the right level of abstractions for services and creating a consistent environment for managing that.”
Even before the 1.0 release, a number of companies already adopted Istio in production, including the likes of eBay and Auto Trader UK. Lin argues that this is a sign that Istio solves a problem that a lot of businesses are facing today as they adopt microservices. “A number of more sophisticated customers tried to build their own service management layer and while we hadn’t yet declared 1.0, we hard a number of customers — including a surprising number of large enterprise customer — say, ‘you know, even though you’re not 1.0, I’m very comfortable putting this in production because what I’m comparing it to is much more raw.’”
IBM Fellow and VP of Cloud Jason McGee agrees with this and notes that “our mission since Istio’s launch has been to enable everyone to succeed with microservices, especially in the enterprise. This is why we’ve focused the community around improving security and scale, and heavily leaned our contributions on what we’ve learned from building agile cloud architectures for companies of all sizes.”
A lot of the large cloud players now support Istio directly, too. IBM supports it on top of its Kubernetes Service, for example, and Google even announced a managed Istio service for its Google Cloud users, as well as some additional open-source tooling for serverless applications built on top of Kubernetes and Istio.
Two names missing from today’s party are Microsoft and Amazon. I think that’ll change over time, though, assuming the project keeps its momentum.
Istio also isn’t part of any major open-source foundation yet. The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), the home of Kubernetes, is backing linkerd, a project that isn’t all that dissimilar from Istio. Once a 1.0 release of these kinds of projects rolls around, the maintainers often start looking for a foundation that can shepherd the development of the project over time. I’m guessing it’s only a matter of time before we hear more about where Istio will land.
Powered by WPeMatico
Line, the company best-known for its popular Asian messaging app, is doubling down on games after it acquired a controlling stake in Korean studio NextFloor for an undisclosed amount.
NextFloor, which has produced titles like Dragon Flight and Destiny Child, will be merged with Line’s games division to form the Line Games subsidiary. Dragon Flight has racked up 14 million users since its 2012 launch — it clocked $1 million in daily revenue at peak. Destiny Child, a newer release in 2016, topped the charts in Korea and has been popular in Japan, North America and beyond.
Line’s own games are focused on its messaging app, which gives them access to social features such as friend graphs, and they have helped the company become a revenue generation machine. Alongside income from its booming sticker business, in-app purchases within games made Line Japan’s highest-earning non-game app publisher last year, according to App Annie, and the fourth highest worldwide. For some insight into how prolific it has been over the years, Line is ranked as the sixth highest earning iPhone app of all time.
But, despite revenue success, Line has struggled to become a global messaging giant. The big guns WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger have in excess of one billion monthly users each, while Line has been stuck around the 200 million mark for some time. Most of its numbers are from just four countries: Japan, Taiwan, Thailand and Indonesia. While it has been able to tap those markets with additional services like ride-hailing and payments, it is certainly under pressure from those more internationally successful competitors.
With that in mind, doubling down on games makes sense and Line said it plans to focus on non-mobile platforms, which will include the Nintendo Switch among others consoles, from the second half of this year.
Line went public in 2016 via a dual U.S.-Japan IPO that raised over $1 billion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Xiaomi gave Google’s well-intentioned but somewhat-stalled Android One project a major boost last year when it unveiled its first device under the program, Mi A1. That’s now joined by not one but two sequel devices, after the Chinese phone maker unveiled the Mi A2 and Mi A2 Lite at an event in Spain today.
Xiaomi in Spain? Yes, that’s right. International growth is a major part of the Xiaomi story now that it is a listed business, and Spain is one of a handful of countries in Europe where Xiaomi is aiming to make its mark. These two new A2 handsets are an early push and they’ll be available in over 40 countries, including Spain, France, Italy and 11 other European markets.
Both phones run on Android One — so none of Xiaomi’s iOS-inspired MIUI Android fork — and charge via type-C USB. The 5.99-inch A2 is the more premium option, sporting a Snapdragon 660 processor and 4GB or 6GB RAM with 32GB, 64GB or 128GB in storage. There’s a 20-megapixel front camera and dual 20-megapixel and 16-megapixel cameras on the rear. On-device storage ranges between 32GB, 64GB and 128GB.
The Mi A2 Lite is the more budget option that’s powered by a lesser Snapdragon 625 processor with 3GB or 4GB RAM, and 32GB or 64GB storage options. It comes with a smaller 5.84-inch display, there’s a 12- and 5-megapixel camera array on the reverse and a front-facing five-megapixel camera.

The A2 is priced from €249 to €279 ($291-$327) based on specs. The A2 Lite will sell for €179 or €229 ($210 or $268), against based on RAM and storage selection.
The 40 market availability mirrors the A1 launch last year, but on this occasion, Xiaomi has been busy preparing the ground in a number of countries, particularly in Europe. It has been in Spain for the past year, but it also launched local operations in France and Italy in May and tied up with CK Hutchison to sell phones in other parts of the continent via its 3 telecom business. While it isn’t operational in the U.S., Xiaomi has expanded into Mexico and it has set up partnerships with local retailers in dozens of other countries.
Xiaomi has been successful with its move into India, where it one of the top smartphone sellers, but it has not yet replicated that elsewhere outside of China so far.
China is, as you’d expect, the primary revenue market but Xiaomi is increasingly less dependent on its homeland. For 2017 sales, China represented 72 percent, but it had been 94 percent and 87 percent, respectively, in 2015 and 2016.
Powered by WPeMatico