computing
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Video game revenue in 2018 reached a new peak of $43.8 billion, up 18 percent from the previous years, surpassing the projected total global box office for the film industry, according to new data released by the Entertainment Software Association and The NPD Group.
Preliminary indicators for global box office revenues published at the end of last year indicated that revenue from ticket sales at box offices around the world would hit $41.7 billion, according to comScore data reported by Deadline Hollywood.
The $43.8 billion tally also surpasses numbers for streaming services, which are estimated to rake in somewhere around $28.8 billion for the year, according to a report in Multichannel News.
Video games and related content have become the new source of entertainment for a generation — and it’s something that has new media moguls like Netflix chief executive Reed Hastings concerned. In the company’s most recent shareholder letter, Netflix said that Fortnite was more of a threat to its business than TimeWarner’s HBO.
“We compete with (and lose to) Fortnite more than HBO,” the company’s shareholder letter stated. “When YouTube went down globally for a few minutes in October, our viewing and signups spiked for that time…There are thousands of competitors in this highly fragmented market vying to entertain consumers and low barriers to entry for those with great experiences.”
“The impressive economic growth of the industry announced today parallels the growth of the industry in mainstream American culture,” said acting ESA president and CEO Stanley Pierre-Louis, in a statement. “Across the nation, we count people of all backgrounds and stages of life among our most passionate video game players and fans. Interactive entertainment stands today as the most influential form of entertainment in America.”
Gains came from across the spectrum of the gaming industry. Console and personal computing, mobile gaming, all saw significant growth, according to Mat Piscatella, a video games industry analyst for The NPD Group.
According to the report, hardware and peripherals and software revenue increased from physical and digital sales, in-game purchases and subscriptions.
| U.S. Video Game Industry Revenue | 2018 | 2017 | Growth Percentage |
| Hardware, including peripherals | $7.5 billion | $6.5 billion | 15% |
| Software, including in-game purchases and subscriptions |
$35.8 billion |
$30.4 billion |
18% |
| Total: | $43.3 billion | $36.9 billion | 18% |
Source: The NPD Group, Sensor Tower
Powered by WPeMatico
Google is removing apps from Google Play that request permission to access call logs and SMS text message data but haven’t been manually vetted by Google staff.
The search and mobile giant said it is part of a move to cut down on apps that have access to sensitive calling and texting data.
Google said in October that Android apps will no longer be allowed to use the legacy permissions as part of a wider push for developers to use newer, more secure and privacy minded APIs. Many apps request access to call logs and texting data to verify two-factor authentication codes, for social sharing, or to replace the phone dialer. But Google acknowledged that this level of access can and has been abused by developers who misuse the permissions to gather sensitive data — or mishandle it altogether.
“Our new policy is designed to ensure that apps asking for these permissions need full and ongoing access to the sensitive data in order to accomplish the app’s primary use case, and that users will understand why this data would be required for the app to function,” wrote Paul Bankhead, Google’s director of product management for Google Play.
Any developer wanting to retain the ability to ask a user’s permission for calling and texting data has to fill out a permissions declaration.
Google will review the app and why it needs to retain access, and will weigh in several considerations, including why the developer is requesting access, the user benefit of the feature that’s requesting access and the risks associated with having access to call and texting data.
Bankhead conceded that under the new policy, some use cases will “no longer be allowed,” rendering some apps obsolete.
So far, tens of thousands of developers have already submitted new versions of their apps either removing the need to access call and texting permissions, Google said, or have submitted a permissions declaration.
Developers with a submitted declaration have until March 9 to receive approval or remove the permissions. In the meantime, Google has a full list of permitted use cases for the call log and text message permissions, as well as alternatives.
The last two years alone has seen several high-profile cases of Android apps or other services leaking or exposing call and text data. In late 2017, popular Android keyboard ai.type exposed a massive database of 31 million users, including 374 million phone numbers.
Powered by WPeMatico
A slew of banks are coming together to back a new roll-up strategy for the Los Angeles-based mobile gaming studio Jam City and giving the company $145 million in new funding to carry that out.
There’s no word on whether the new money is in equity or debt, but what is certain is that JPMorgan Chase Bank, Bank of America Merrill Lynch and syndicate partners, including Silicon Valley Bank, SunTrust Bank and CIT Bank, are all involved in the deal.
“In a global mobile games market that is consolidating, Jam City could not be more proud to be working with JPMorgan, Bank of America Merrill Lynch, Silicon Valley Bank, SunTrust Bank and CIT Group to strategically support the financing of our acquisition and growth plans,” said Chris DeWolfe, co-founder and CEO of Jam City. “This $145 million in new financing empowers Jam City to further our position as a global industry consolidator. As we grow our global business, we are honored to be working alongside such prestigious advisers who share Jam City’s mission of delivering joy to people everywhere through unique and deeply engaging mobile games.”
The new money comes after a few years of speculation on whether Jam City would be the next big Los Angeles-based startup company to file for an initial public offering. It also follows a new agreement with Disney to develop mobile games based on intellectual property coming from all corners of the mouse house — a sweet cache of intellectual property ranging from Pixar, to Marvel, to traditional Disney characters.
Jam City is coming off a strong year of company growth. The Harry Potter: Hogwarts Mystery game, which launched last year, became the company’s fastest title to hit $100 million in revenue.
Add that to the company’s expansion into new markets with strategic acquisitions to fuel development and growth in Toronto and Bogota and it’s clear that the company is looking to make more moves in 2019.
Jam City already holds intellectual property for a new game built on Disney’s “Frozen 2,” the company’s newly acquired Fox Studio assets like “Family Guy” and the Harry Potter property. Add that to its own Cookie Jam and Panda Pop properties and it seems like the company is ready to make moves.
Meanwhile, games are quickly becoming the go-to revenue driver for the entertainment industry. According to data collected by Newzoo, mobile games revenue reached a record $63.2 billion worldwide in 2018, representing roughly 47 percent of the total revenue for the gaming industry in the year. That number could reach $81.3 billion by 2020, the Newzoo data suggests.
Roughly half of the U.S. plays mobile games, and they’re spending significant dollars on those games in app stores. App Annie suggests that roughly 75 percent of the money spent in app stores over the past decade has been spent on mobile games. And consumers are expected to spend roughly $129 billion in app stores over the next year. The data and analytics firm suggests that mobile gaming will capture some 60 percent of the overall gaming market in 2019, as well.
All of that bodes well for the industry as a whole, and points to why Jam City is looking to consolidate. And the company isn’t the only mobile games studio making moves.
The publicly traded games studio Zynga, which rose to fame initially on the back of Facebook’s gaming platform, recently expanded its European footprint with the late-December acquisition of the Helsinki-based gaming studio Small Giant Games.
Powered by WPeMatico
The only kids’ programming language worth using, Scratch, just celebrated the launch of Scratch 3.0, an update that adds some interesting new functionality to the powerful open-source tool.
Scratch, for those without school-aged children, is a block-based programming language that lets you make little games and “cartoons” with sprites and animated figures. The system is surprisingly complex, and kids have created things like Minecraft platformers, fun arcade games and whatever this is.
The new version of scratch includes extensions that allow you to control hardware, as well as new control blocks.
Scratch 3.0 is the next generation of Scratch – designed to expand how, what, and where you can create with Scratch. It includes dozens of new sprites, a totally new sound editor, and many new programming blocks. And with Scratch 3.0, you are able to create and play projects on your tablet, in addition to your laptop or desk computer.
Scratch is quite literally the only programming “game” my kids will use again and again, and it’s an amazing introduction for kids as young as pre-school age. Check out the update and don’t forget to share your animations with the class!
Powered by WPeMatico
Epic Games had as good a year in 2018 as any company in tech. Fortnite became the world’s most popular game, growing the company’s valuation to $15 billion, but it has helped the company pile up cash, too. Epic grossed a $3 billion profit for this year fueled by the continued success of Fortnite, a source with knowledge of the business told TechCrunch.
Epic did not respond to a request for comment.
Fortnite, which is free to play but makes money selling digital items, has popularized the battle royale category — think Lord of the Flies meets Hunger Games — almost single-handedly, and it has been the standout title for the U.S.-based game publisher.
Founded way back in 1991, Epic hasn’t given revenue figures for its smash hit — which has 125 million players — but this new profit milestone, combined with other pieces of data, gives an idea of the success the company is seeing as a result of a prescient change in strategy made six years ago.
This past September, Epic commanded a valuation of nearly $15 billion, according to The Wall Street Journal, as marquee investors like KKR, Kleiner Perkins and Lightspeed piled on in a $1.25 billion round to grab a slice of the red-hot development firm. However, the investment cards haven’t always been stacked in Epic’s favor.
China’s Tencent, the maker of blockbuster chat app WeChat and a prolific games firm in its own right, became the first outside investor in Epic’s business back in 2012 when it injected $330 million in exchange for a 40 percent stake in the business.
Back then, Epic was best known for Unreal Engine, the third-party development platform that it still operates today, and top-selling titles like Gears of War.
Why would a proven company give up such a huge slice of its business? Executives believed that Epic, as it was, was living on borrowed time. They sensed a change in the way games were headed based on diminishing returns and growing budgets for console games, the increase of “live” games like League of Legends and the emerging role of smartphones.
Speaking to Polygon about the Tencent deal, Epic CEO Tim Sweeney explained that the investment money from Tencent allowed the company to go down the route of freemium games rather than big box titles. That’s a strategy Sweeney called “Epic 4.0.”
“We realized that the business really needed to change its approach quite significantly. We were seeing some of the best games in the industry being built and operated as live games over time rather than big retail releases. We recognized that the ideal role for Epic in the industry is to drive that, and so we began the transition of being a fairly narrow console developer focused on Xbox to being a multi-platform game developer and self publisher, and indie on a larger scale,” he explained.
Tencent, Sweeney added, has provided “an enormous amount of useful advice,” while the capital enabled Epic to “make this huge leap without the immediate fear of money.”
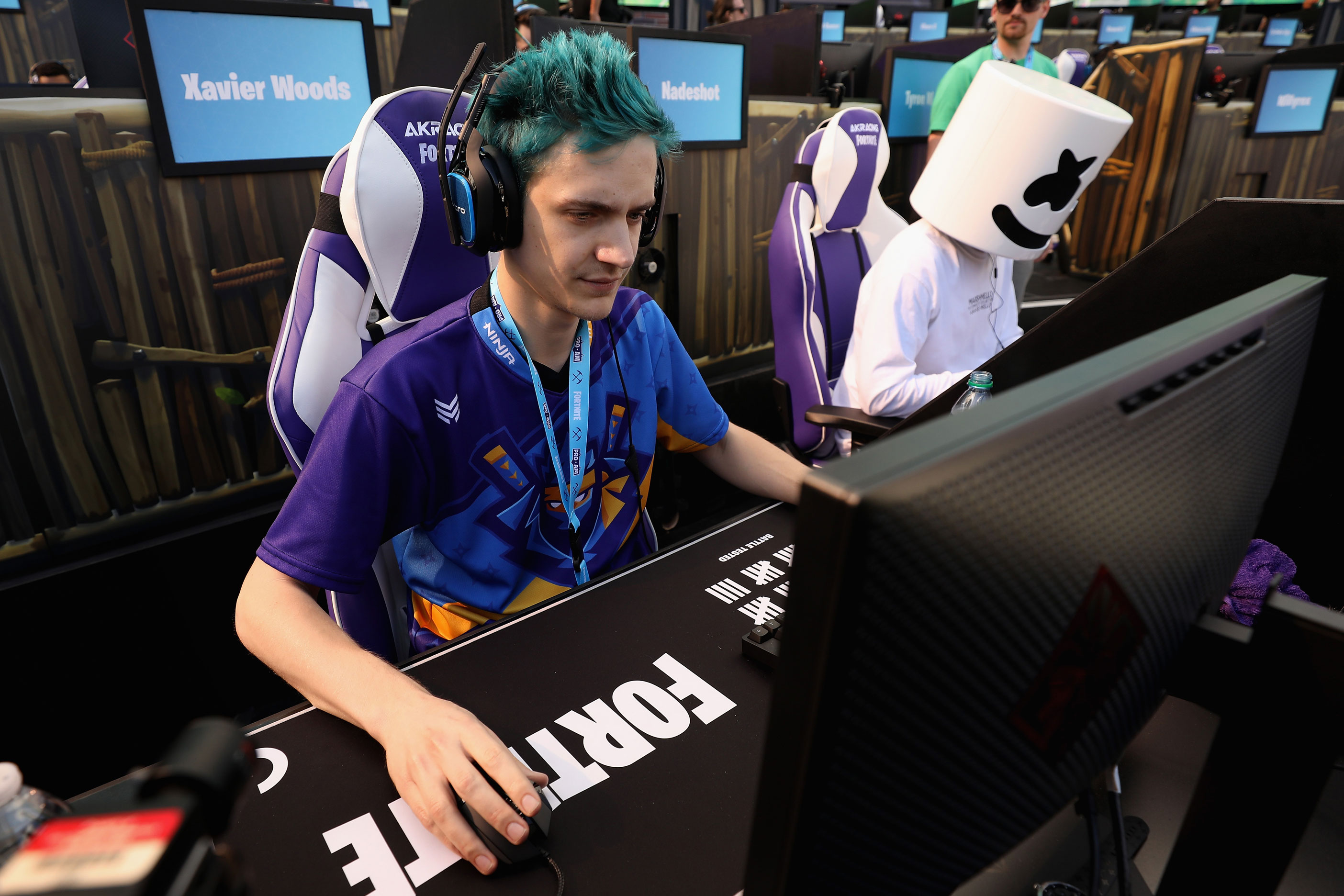

LOS ANGELES, CA – JUNE 12: Gamers ‘Ninja’ (L) and ‘Marshmello’ compete in the Epic Games Fortnite E3 Tournament at the Banc of California Stadium on June 12, 2018 in Los Angeles, California. (Photo by Christian Petersen/Getty Images)
Epic never had a problem making money — Sweeney told Polygon the first Gear of Wars release grossed $100 million on a $12 million development budget. But with Fortnite, the company has redefined modern gaming, both by making true cross-platform experiences possible and by pulling in vast amounts of money.
As a private company, Epic keeps its financials closely guarded. But digging beyond the $3 billion figure — which, to be clear, is annual profit not revenue — there are clues as to just how big a money-spinner Fortnite is. Certainly, there’s room to wonder whether analyst predictions this summer that Fortnite would gross $2 billion this year were too conservative.
The most recent data comes from November when Sensor Tower estimates that iOS users alone were spending $1.23 million per day. That helped the game bank $37 million in the month and take its total earnings within Apple’s iOS platform to more than $385 million.
But, as mentioned, Fortnite is a cross-platform title that supports PlayStation, Xbox, Switch, PC, Mac, Android and iOS. Aggregating revenue across those platforms isn’t easy, and the only real estimate comes from earlier this year when Super Data Research concluded that the game made $318 million in May across all platforms.
That is, of course, when Fortnite was fresh on iOS, non-existent on Android and with fewer overall players.
We can deduce from Sensor Tower’s November estimate that iOS pulled in $385 million over eight months — between April and November — which is around $48 million per month on average. Android is harder to calculate since Epic skipped Google’s Play Store by distributing its own launcher. While it quickly picked up 15 million Android users within the first month, tracking that spending off-platform is a huge challenge. Some estimates predicted that Google would miss out on around $50 million in lost earnings this year because in-app purchases on Android would not cross its services.
There are a few factors to add further uncertainty.
Fortnite spending tends to spike around the release of new seasons — updated versions of the game — since users are encouraged to buy specific packages at the start. The latest, Season 7, dropped early this month with a range of tweaks for the Christmas period. Given the increased velocity at which Fortnite is picking up players and the appeal of the festive period, this could have been its biggest revenue generator to date, but there’s not yet any indicator of how it performed.
More broadly, Fortnite has undoubtedly lost out on revenue in China, which froze new game licenses nine months ago, thereby preventing any publishers from monetizing new titles over that period.
Tencent, which publishes Fortnite in China, did release the game in the country but it hasn’t been able to draw revenue from it yet. The Chinese government announced last week that it is close to approving its first batch of new titles, but it isn’t clear which games are included and when the process will be done.
Already, the effects have been felt.
Games are forecast to generate nearly $40 billion in revenue in China this year, according to market researcher Newzoo. However, the industry saw its slowest growth over the last 10 years as it grew 5.4 percent year-over-year during the first half of 2018, according to a report by Beijing-based research firm GPC and China’s official gaming association CNG.
Fortnite and PUBG — another battle royale title backed by Tencent — have perhaps suffered the most since they are universally popular worldwide but unable to monetize in China. It seems almost certain that those two titles will receive a major marketing push if, as and when they receive the license and, if Epic can keep the game competitive as Sweeney believed it could back in 2012, then it could go on and make even more money in 2019.

Epic Games is taking on Steam with its own digital game store, which includes higher take-home revenue rates for developers.
But Epic isn’t relying solely on Fortnite.
A more low-key but significant launch this month was the opening of the Epic Games store, which is aimed squarely at Steam, the leader in digital game sales.
While Fortnite is its most prolific release, Epic also makes money from other games, Unreal Engine and a recently launched online game store that rivals Steam. Epic’s big differentiator for the store is that it gives developers 88 percent of their revenue, as opposed to Value — the firm behind Steam — which keeps 30 percent, although it has added varying rates for more successful titles. Customers are promised a free title every two weeks.
Either way, Epic is betting that it can do a lot more than Fortnite, which could mean that its profit margin will be even higher come this time next year.
Powered by WPeMatico
Social game developer Zynga has entered into an agreement to acquire Small Giant Games, the startup behind the popular mobile game Empires & Puzzles, in a deal expected to total $700 million.
Zynga, which has tumbled since its 2011 Nasdaq initial public offering, will initially acquire 80 percent of Small Giant Games for $560 million, composed of $330 million in cash and $230 million of unregistered Zynga common stock. Zynga will fund part of the transaction with a $200 million credit facility.
“We’ve been impressed by the quality and momentum of Empires & Puzzles as we add another Forever Franchise into Zynga’s portfolio,” Zynga chief executive officer Frank Gibeau said in a statement. “Small Giant has created an innovative game that delivers a unique player experience that engages over the long term.”
The deal is expected to close on January 1. Zynga will purchase the remaining 20 percent of Small Giant over the next three years “at valuations based on specified profitability goals.”
Helsinki-based Small Giant Games had raised $52 million in equity funding from EQT Ventures, Creandum, Spintop Ventures, Profounders and others since it was founded in 2013. The company reported $33 million of revenue for Empires & Puzzles, its most popular game, 10 months after its launch in 2017. Small Giant, which is also behind Alliance Wars and Season 2: Atlantis, says they exceeded 2017’s revenue just four months into 2018.
“Our studio was founded on the idea that small, skillful teams can accomplish giant things, and I am confident that partnering with Zynga is the right next step in our evolution,” Small Giant CEO Timo Soininen said in a statement. “We will now operate as a separate studio within Zynga, maintaining our identity, culture and creative independence. By leveraging the expertise and support from the wider Zynga team, we will amplify the reach of Empires & Puzzles and the new games in our development pipeline.”
Zynga, founded in 2007, is the developer of FarmVille, Zynga
Zynga expects to bring in $243 million in revenue in the fourth quarter of 2018.
Powered by WPeMatico
The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), the open-source home of projects like Kubernetes and Vitess, today announced that its technical committee has voted to bring a new project on board. That project is etcd, the distributed key-value store that was first developed by CoreOS (now owned by Red Hat, which in turn will soon be owned by IBM). Red Hat has now contributed this project to the CNCF.
Etcd, which is written in Go, is already a major component of many Kubernetes deployments, where it functions as a source of truth for coordinating clusters and managing the state of the system. Other open-source projects that use etcd include Cloud Foundry, and companies that use it in production include Alibaba, ING, Pinterest, Uber, The New York Times and Nordstrom.
“Kubernetes and many other projects like Cloud Foundry depend on etcd for reliable data storage. We’re excited to have etcd join CNCF as an incubation project and look forward to cultivating its community by improving its technical documentation, governance and more,” said Chris Aniszczyk, COO of CNCF, in today’s announcement. “Etcd is a fantastic addition to our community of projects.”
Today, etcd has well over 450 contributors and nine maintainers from eight different companies. The fact that it ended up at the CNCF is only logical, given that the foundation is also the host of Kubernetes. With this, the CNCF now plays host to 17 projects that fall under its “incubated technologies” umbrella. In addition to etcd, these include OpenTracing, Fluentd, Linkerd, gRPC, CoreDNS, containerd, rkt, CNI, Jaeger, Notary, TUF, Vitess, NATS Helm, Rook and Harbor. Kubernetes, Prometheus and Envoy have already graduated from this incubation stage.
That’s a lot of projects for one foundation to manage, but the CNCF community is also extraordinarily large. This week alone about 8,000 developers are converging on Seattle for KubeCon/CloudNativeCon, the organization’s biggest event yet, to talk all things containers. It surely helps that the CNCF has managed to bring competitors like AWS, Microsoft, Google, IBM and Oracle under a single roof to collaboratively work on building these new technologies. There is a risk of losing focus here, though, something that happened to the OpenStack project when it went through a similar growth and hype phase. It’ll be interesting to see how the CNCF will manage this as it brings on more projects (with Istio, the increasingly popular service mesh, being a likely candidate for coming over to the CNCF as well).
Powered by WPeMatico
Solo.io, a Cambridge, Mass-based startup that helps enterprises adopt cloud-native technologies, is coming out of stealth mode today and announcing both its Series A funding round and the launch of its Gloo Enterprise API gateway.
Redpoint Ventures led the $11 million Series A round, with participation from seed investor True Ventures . Like most companies at the Series A state, Solo.io plans to use the money to invest in the product development of its enterprise and open-source tools, as well as to grow its sales and marketing teams.
Solo.io offers a number of open-source tools, like the Gloo function gateway, the Sqoop GraphQL server and the SuperGloo (see a theme here?) service mesh orchestration platform. In addition, the team has also, among others, open-sourced its Kubernetes debugger, a tool for building and running unikernels.
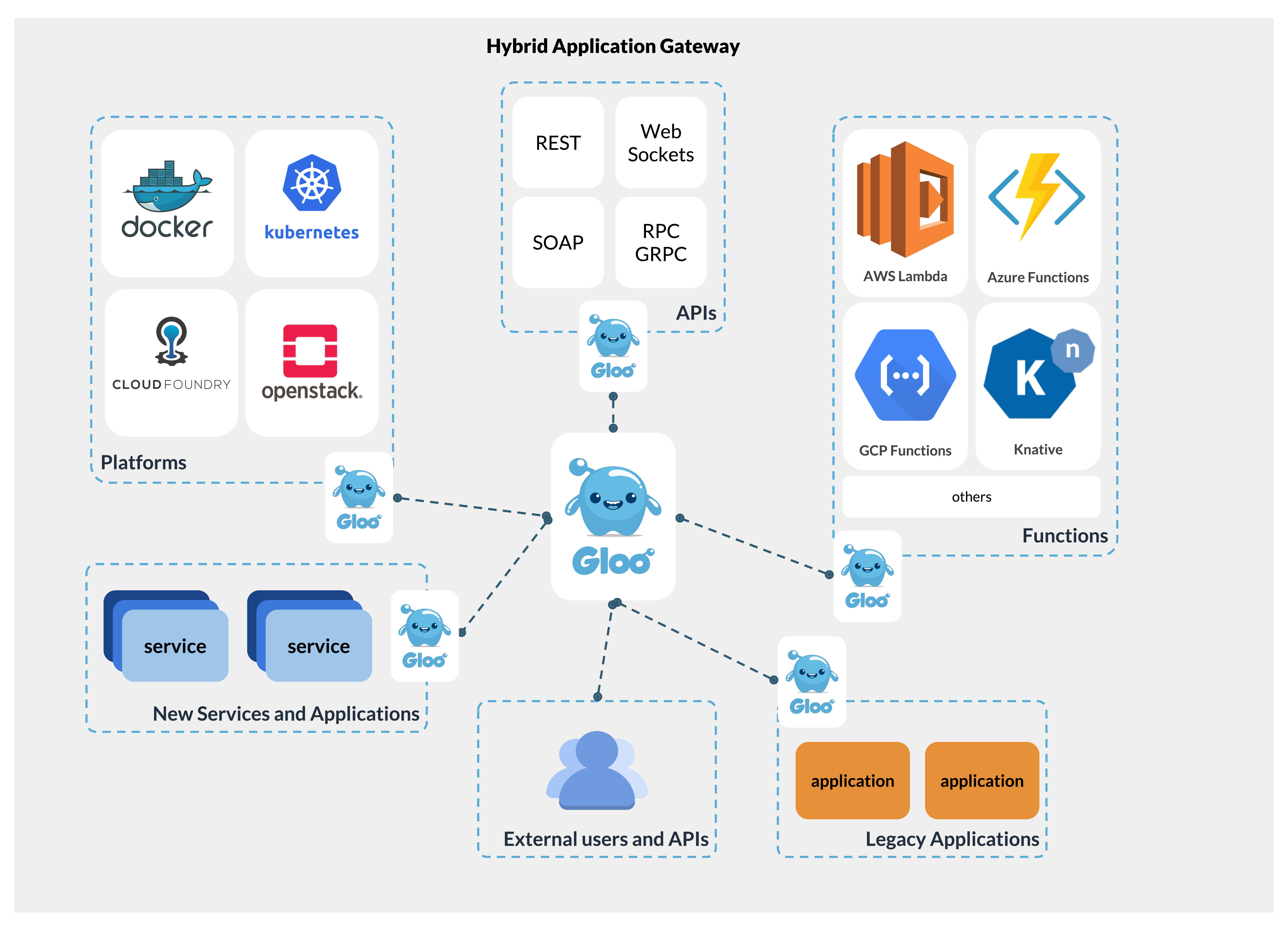
Its first commercial offering, though, is an enterprise version of the Gloo function gateway. Built on top of the Envoy proxy, Gloo can handle the routing necessary to connect incoming API requests to microservices, serverless applications (on the likes of AWS Lambda) and traditional monolithic applications behind the proxy. Gloo handles the load balancing and other functions necessary to aggregate the incoming API requests and route them to their destinations.
“Costumers who use Gloo to connect between microservices and serverless found that invocation of [AWS] Lambda is 350ms faster than the AWS API Gateway,” Idit Levine, the founder and CEO of Solo.io, told me. “Gloo also offers them direct money saving, since AWS bills per invocation. In general, Gloo offers money saving because it allows our clients to use the less expensive technologies — like their legacy apps, and sometimes containers — whenever they can, and limit the use of more expensive stuff to whenever it’s necessary.”
The enterprise version adds features like audit controls, single sign-on and more advanced security tools to the platform.
In addition to broadening its customer base, the company plans to invest heavily into its customer success and support teams, as well as its evangelism and education efforts, Levine tells me.
“Helping enterprises easily adopt innovative technologies like microservices, serverless and service mesh is our goal at Solo.io,” Levine in today’s announcement. “Melding different technologies into one coherent environment, by supplying a suite of tools to route, debug, manage, monitor and secure applications, lets organizations focus on their software without worrying about the complexity of the underlying environment.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Contentful, a Berlin- and San Francisco-based startup that provides content management infrastructure for companies like Spotify, Nike, Lyft and others, today announced that it has raised a $33.5 million Series D funding round led by Sapphire Ventures, with participation from OMERS Ventures and Salesforce Ventures, as well as existing investors General Catalyst, Benchmark, Balderton Capital and Hercules. In total, the company has now raised $78.3 million.
 It’s been less than a year since the company raised its Series C round and, as Contentful co-founder and CEO Sascha Konietzke told me, the company didn’t really need to raise right now. “We had just raised our last round about a year ago. We still had plenty of cash in our bank account and we didn’t need to raise as of now,” said Konietzke. “But we saw a lot of economic uncertainty, so we thought it might be a good moment in time to recharge. And at the same time, we already had some interesting conversations ongoing with Sapphire [formerly SAP Ventures] and Salesforce. So we saw the opportunity to add more funding and also start getting into a tight relationship with both of these players.”
It’s been less than a year since the company raised its Series C round and, as Contentful co-founder and CEO Sascha Konietzke told me, the company didn’t really need to raise right now. “We had just raised our last round about a year ago. We still had plenty of cash in our bank account and we didn’t need to raise as of now,” said Konietzke. “But we saw a lot of economic uncertainty, so we thought it might be a good moment in time to recharge. And at the same time, we already had some interesting conversations ongoing with Sapphire [formerly SAP Ventures] and Salesforce. So we saw the opportunity to add more funding and also start getting into a tight relationship with both of these players.”
The original plan for Contentful was to focus almost explicitly on mobile. As it turns out, though, the company’s customers also wanted to use the service to handle its web-based applications and these days, Contentful happily supports both. “What we’re seeing is that everything is becoming an application,” he told me. “We started with native mobile application, but even the websites nowadays are often an application.”
In its early days, Contentful focused only on developers. Now, however, that’s changing, and having these connections to large enterprise players like SAP and Salesforce surely isn’t going to hurt the company as it looks to bring on larger enterprise accounts.
Currently, the company’s focus is very much on Europe and North America, which account for about 80 percent of its customers. For now, Contentful plans to continue to focus on these regions, though it obviously supports customers anywhere in the world.
Contentful only exists as a hosted platform. As of now, the company doesn’t have any plans for offering a self-hosted version, though Konietzke noted that he does occasionally get requests for this.
What the company is planning to do in the near future, though, is to enable more integrations with existing enterprise tools. “Customers are asking for deeper integrations into their enterprise stack,” Konietzke said. “And that’s what we’re beginning to focus on and where we’re building a lot of capabilities around that.” In addition, support for GraphQL and an expanded rich text editing experience is coming up. The company also recently launched a new editing experience.
Powered by WPeMatico
Terms of the deal weren’t disclosed.
The deal is part of a broader effort to expand the Jam City portfolio of games and geographic footprint. In recent months the company has inked agreements with Disney — taking over development duties on some of the company’s games like Disney Emoji Blitz and signing on to develop new ones — and launching new games in conjunction with other famous franchises like Harry Potter.
The Bingo Pop acquisition will bring a gambling game into the casual game developer’s stable of titles that pulled in roughly $700,000 in revenue through October, according to data from SensorTower.
“We are so proud to be continuing Jam City’s rapid global expansion with the acquisition of one of the most popular bingo titles, and its highly talented team,” said Chris DeWolfe, co-founder and CEO of Jam City, in a statement. “This acquisition provides Jam City with access to leading creative talent in one of the fastest growing and most exciting tech markets in the world. We look forward to working with the talented Jam City team in Toronto as we supercharge the live operations of Bingo Pop and develop innovative new titles and mobile entertainment experiences.”
Founded in Los Angeles in 2009 by DeWolfe, who previously helped create and launch Myspace, and 20th Century Fox exec Josh Yguado, Jam City rose to prominence on the back of its Cookie Jam and Panda Pop games. Now, the company has expanded through licensing deals with Harry Potter, Family Guy, Marvel and now Disney. Jam City has offices in Los Angeles, San Francisco, San Diego, Bogota and Buenos Aires.
Powered by WPeMatico