computing
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Netflix today announced it will begin testing mobile games inside its Android app for its members in Poland. At launch, paying subscribers will be able to try out two games, “Stranger Things: 1984” and “Stranger Things 3” — titles that have been previously available on the Apple App Store, Google Play and, in the case of the newer release, on other platforms, including desktop and consoles. While the games are offered to subscribers from within the Netflix mobile app’s center tab, users will still be directed to the Google Play Store to install the game on their devices.
To then play, members will need to confirm their Netflix credentials.
Members can later return to the game at any time by clicking “Play” on the game’s page from inside the Netflix app or by launching it directly from their mobile device.
“It’s still very, very early days and we will be working hard to deliver the best possible experience in the months ahead with our no ads, no in-app purchases approach to gaming,” a Netflix spokesperson said about the launch.
The company has been expanding its investment in gaming for years, seeing the potential for a broader entertainment universe that ties in to its most popular shows. At the E3 gaming conference back in 2019, Netflix detailed a series of gaming integrations across popular platforms like Roblox and Fortnite and its plans to bring new “Stranger Things” games to the market.
On mobile, Netflix has been working with the Allen, Texas-based game studio BonusXP, whose first game for Netflix, “Stranger Things: The Game,” has now been renamed “Stranger Things: 1984” to better differentiate it from others. While that game takes place after season 1 and before season 2, in the “Stranger Things” timeline, the follow-up title, “Stranger Things 3,” is a playable version of the third season of the Netflix series. (So watch out for spoilers!)
Netflix declined to share how popular the games had been in terms of users or installs, while they were publicly available on the app stores.
With the launch of the test in Poland, Netflix says users will need to have a membership to download the titles as they’re now exclusively available to subscribers. However, existing users who already downloaded the game from Google Play in the past will not be impacted. They will be able to play the game as usual or even re-download it from their account library if they used to have it installed. But new players will only be able to get the game from the Netflix app.
The test aims to better understand how mobile gaming will resonate with Netflix members and determine what other improvements Netflix may need to make to the overall functionality, the company said. It chose Poland as the initial test market because it has an active mobile gaming audience, which made it seem like a good fit for this early feedback.
Netflix couldn’t say when it would broaden this test to other countries, beyond “the coming months.”
The streamer recently announced during its second-quarter earnings that it would add mobile games to its offerings, noting that it views gaming as “another new content category” for its business, similar to its “expansion into original films, animation and unscripted TV.”
The news followed what had been a sharp slowdown in new customers after the pandemic-fueled boost to streaming. In North America, Netflix in Q2 lost a sizable 430,000 subscribers — its third-ever quarterly decline in a decade. It also issued weaker guidance for the upcoming quarter, forecasting the addition of 3.5 million subscribers when analysts had been looking for 5.9 million. But Netflix downplayed the threat of competition on its slowing growth, instead blaming a lighter content slate, in part due to COVID-related production delays.
Powered by WPeMatico
A London-headquartered startup called LOVE, valued at $17 million following its pre-seed funding, aims to redefine how people stay in touch with close family and friends. The company is launching a messaging app that offers a combination of video calling as well as asynchronous video and audio messaging, in an ad-free, privacy-focused experience with a number of bells and whistles, including artistic filters and real-time transcription and translation features.
But LOVE’s bigger differentiator may not be its product alone, but rather the company’s mission.
LOVE aims for its product direction to be guided by its user base in a democratic fashion as opposed to having the decisions made about its future determined by an elite few at the top of some corporate hierarchy. In addition, the company’s longer-term goal is ultimately to hand over ownership of the app and its governance to its users, the company says.
These concepts have emerged as part of bigger trends towards a sort of “Web 3.0,” or next phase of internet development, where services are decentralized, user privacy is elevated, data is protected and transactions take place on digital ledgers, like a blockchain, in a more distributed fashion.
LOVE’s founders are proponents of this new model, including serial entrepreneur Samantha Radocchia, who previously founded three companies and was an early advocate for the blockchain as the co-founder of Chronicled, an enterprise blockchain company focused on the pharmaceutical supply chain.
As someone who’s been interested in emerging technology since her days of writing her anthropology thesis on currency exchanges in “Second Life’s” virtual world, she’s now faculty at Singularity University, where she’s given talks about blockchain, AI, Internet of Things, Future of Work, and other topics. She’s also authored an introductory guide to the blockchain with her book “Bitcoin Pizza.”
Co-founder Christopher Schlaeffer, meanwhile, held a number of roles at Deutsche Telekom, including chief product & innovation officer, corporate development officer and chief strategy officer, where he along with Google execs introduced the first mobile phone to run Android. He was also chief digital officer at the telecommunication services company VEON.
The two crossed paths after Schlaeffer had already begun the work of organizing a team to bring LOVE to the public, which includes co-founders Chief Technologist Jim Reeves, also previously of VEON, and Chief Designer Timm Kekeritz, previously an interaction designer at international design firm IDEO in San Francisco, design director at IXDS and founder of design consultancy Raureif in Berlin, among other roles.
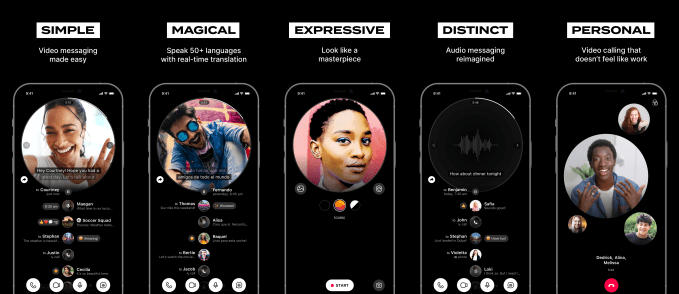
Image Credits: LOVE
Explained Radocchia, what attracted her to join as CEO was the potential to create a new company that upholds more positive values than what’s often seen today — in fact, the brand name “LOVE” is a reference to this aim. She was also interested in the potential to think through what she describes as “new business models that are not reliant on advertising or harvesting the data of our users,” she says.
To that end, LOVE plans to monetize without any advertising. While the company isn’t ready to explain its business model in full, it would involve users opting in to services through granular permissions and membership, we’re told.
“We believe our users will much rather be willing to pay for services they consciously use and grant permissions to in a given context than have their data used for an advertising model which is simply not transparent,” says Radocchia.
LOVE expects to share more about the model next year.
As for the LOVE app itself, it’s a fairly polished mobile messenger offering an interesting combination of features. Like any other video chat app, you can video call with friends and family, either in one-on-one calls or in groups. Currently, LOVE supports up to five call participants, but expects to expand that as it scales. The app also supports video and audio messaging for asynchronous conversations. There are already tools that offer this sort of functionality on the market, of course — like WhatsApp, with its support for audio messages, or video messenger Marco Polo. But they don’t offer quite the same expanded feature set.

Image Credits: LOVE
For starters, LOVE limits its video messages to 60 seconds, for brevity’s sake. (As anyone who’s used Marco Polo knows, videos can become a bit rambling, which makes it harder to catch up when you’re behind on group chats.) In addition, LOVE allows you to both watch the video content as well as read the real-time transcription of what’s being said — the latter which comes in handy not only for accessibility’s sake, but also for those times you want to hear someone’s messages but aren’t in a private place to listen or don’t have headphones. Conversations can also be translated into 50 languages.
“A lot of the traditional communication or messenger products are coming from a paradigm that has always been text-based,” explains Radocchia. “We’re approaching it completely differently. So while other platforms have a lot of the features that we do, I think that…the perspective that we’ve approached it has completely flipped it on its head,” she continues. “As opposed to bolting video messages on to a primarily text-based interface, [LOVE is] actually doing it in the opposite way and adding text as a sort of a magically transcribed add-on — and something that you never, hopefully, need to be typing out on your keyboard again,” she adds.
The app’s user interface, meanwhile, has been designed to encourage eye-to-eye contact with the speaker to make conversations feel more natural. It does this by way of design elements where bubbles float around as you’re speaking and the bubble with the current speaker grows to pull your focus away from looking at yourself. The company is also working with the curator of Serpentine Gallery in London, Hans Ulrich-Obrist, to create new filters that aren’t about beautification or gimmicks, but are instead focused on introducing a new form of visual expression that makes people feel more comfortable on camera.
For the time being, this has resulted in a filter that slightly abstracts your appearance, almost in the style of animation or some other form of visual arts.
The app claims to use end-to-end encryption and the automatic deletion of its content after seven days — except for messages you yourself recorded, if you’ve chosen to save them as “memorable moments.”
“One of our commitments is to privacy and the right-to-forget,” says Radocchia. “We don’t want to be or need to be storing any of this information.”
LOVE has been soft-launched on the App Store, where it’s been used with a number of testers and is working to organically grow its user base through an onboarding invite mechanism that asks users to invite at least three people to join. This same onboarding process also carefully explains why LOVE asks for permissions — like using speech recognition to create subtitles.
LOVE says its valuation is around $17 million USD following pre-seed investments from a combination of traditional startup investors and strategic angel investors across a variety of industries, including tech, film, media, TV and financial services. The company will raise a seed round this fall.
The app is currently available on iOS, but an Android version will arrive later in the year. (Note that LOVE does not currently support the iOS 15 beta software, where it has issues with speech transcription and in other areas. That should be resolved next week, following an app update now in the works.)
Powered by WPeMatico
At a time when remote work, cybersecurity attacks and increased privacy and compliance requirements threaten a company’s data, more companies are collecting and storing their observability data, but are being locked in with vendors or have difficulty accessing the data.
Enter Cribl. The San Francisco-based company is developing an “open ecosystem of data” for enterprises that utilizes unified data pipelines, called “observability pipelines,” to parse and route any type of data that flows through a corporate IT system. Users can then choose their own analytics tools and storage destinations like Splunk, Datadog and Exabeam, but without becoming dependent on a vendor.
The company announced Wednesday a $200 million round of Series C funding to value Cribl at $1.5 billion, according to a source close to the company. Greylock and Redpoint Ventures co-led the round and were joined by new investor IVP, existing investors Sequoia and CRV and strategic investment from Citi Ventures and CrowdStrike. The new capital infusion gives Cribl a total of $254 million in funding since the company was started in 2017, Cribl co-founder and CEO Clint Sharp told TechCrunch.
Sharp did not discuss the valuation; however, he believes that the round is “validation that the observability pipeline category is legit.” Data is growing at a compound annual growth rate of 25%, and organizations are collecting five times more data today than they did 10 years ago, he explained.
“Ultimately, they want to ask and answer questions, especially for IT and security people,” Sharp added. “When Zoom sends data on who started a phone call, that might be data I need to know so I know who is on the call from a security perspective and who they are communicating with. Also, who is sending files to whom and what machines are communicating together in case there is a malicious actor. We can also find out who is having a bad experience with the system and what resources they can access to try and troubleshoot the problem.”
Cribl also enables users to choose how they want to store their data, which is different from competitors that often lock companies into using only their products. Instead, customers can buy the best products from different categories and they will all talk to each other through Cribl, Sharp said.
Though Cribl is developing a pipeline for data, Sharp sees it more as an “observability lake,” as more companies have differing data storage needs. He explains that the lake is where all of the data will go that doesn’t need to go into an existing storage solution. The pipelines will send the data to specific tools and then collect the data, and what doesn’t fit will go back into the lake so companies have it to go back to later. Companies can keep the data for longer and more cost effectively.
Cribl said it is seven times more efficient at processing event data and boasts a customer list that includes Whole Foods, Vodafone, FINRA, Fannie Mae and Cox Automotive.
Sharp went after additional funding after seeing huge traction in its existing customer base, saying that “when you see that kind of traction, you want to keep doubling down.” His aim is to have a presence in every North American city and in Europe, to continue launching new products and growing the engineering team.
Up next, the company is focusing on go-to-market and engineering growth. Its headcount is 150 currently, and Sharp expects to grow that to 250 by the end of the year.
Over the last fiscal year, Cribl grew its revenue 293%, and Sharp expects that same trajectory for this year. The company is now at a growth stage, and with the new investment, he believes Cribl is the “future leader in observability.”
“This is a great investment for us, and every dollar, we believe, is going to create an outsized return as we are the only commercial company in this space,” he added.
Scott Raney, managing director at Redpoint Ventures, said his firm is a big enterprise investor in software, particularly in companies that help organizations leverage data to protect themselves, a sweet spot that Cribl falls into.
He feels Sharp is leading a team, having come from Splunk, that has accomplished a lot, has a vision and a handle on the business and knows the market well. Where Splunk is capturing the machine data and using its systems to extract the data, Cribl is doing something similar in directing the data where it needs to go, while also enabling companies to utilize multiple vendors and build apps to sit on top of its infrastructure.
“Cribl is adding opportunity by enriching the data flowing through, and the benefits are going to be meaningful in cost reduction,” Raney said. “The attitude out there is to put data in cheaper places, and afford more flexibility to extract data. Step one is to make that transition, and step two is how to drive the data sitting there. Cribl is doing something that will go from being a big business to a legacy company 30 years from now.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Bodo.ai, a parallel compute platform for data workloads, is developing a compiler to make Python portable and efficient across multiple hardware platforms. It announced Wednesday a $14 million Series A funding round led by Dell Technologies Capital.
Python is one of the top programming languages used among artificial intelligence and machine learning developers and data scientists, but as Behzad Nasre, co-founder and CEO of Bodo.ai, points out, it is challenging to use when handling large-scale data.
Bodo.ai, headquartered in San Francisco, was founded in 2019 by Nasre and Ehsan Totoni, CTO, to make Python higher performing and production ready. Nasre, who had a long career at Intel before starting Bodo, met Totoni and learned about the project that he was working on to democratize machine learning and enable parallel learning for everyone. Parallelization is the only way to extend Moore’s Law, Nasre told TechCrunch.
Bodo does this via a compiler technology that automates the parallelization so that data and ML developers don’t have to use new libraries, APIs or rewrite Python into other programming languages or graphics processing unit code to achieve scalability. Its technology is being used to make data analytics tools in real time and is being used across industries like financial, telecommunications, retail and manufacturing.
“For the AI revolution to happen, developers have to be able to write code in simple Python, and that high-performance capability will open new doors,” Totoni said. “Right now, they rely on specialists to rewrite them, and that is not efficient.”
Joining Dell in the round were Uncorrelated Ventures, Fusion Fund and Candou Ventures. Including the new funding, Bodo has raised $14 million in total. The company went after Series A dollars after its product had matured and there was good traction with customers, prompting Bodo to want to scale quicker, Nasre said.
Nasre feels Dell Technologies Capital was “uniquely positioned to help us in terms of reserves and the role they play in the enterprise at large, which is to have the most effective salesforce in enterprise.”
Though he was already familiar with Nasre, Daniel Docter, managing director at Dell Technologies, heard about Bodo from a data scientist friend who told Docter that Bodo’s preliminary results “were amazing.”
Much of Dell’s investments are in the early-stage and in deep tech founders that understand the problem. Docter puts Totoni and Nasre in that category.
“Ehsan fits this perfectly, he has super deep technology knowledge and went out specifically to solve the problem,” he added. “Behzad, being from Intel, saw and lived with the problem, especially seeing Hadoop fail and Spark take its place.”
Meanwhile, with the new funding, Nasre intends to triple the size of the team and invest in R&D to build and scale the company. It will also be developing a marketing and sales team.
The company is now shifting from financing to customer- and revenue-focused as it aims to drive up adoption by the Python community.
“Our technology can translate simple code into the fast code that the experts will try,” Totoni said. “I joined Intel Labs to work on the problem, and we think we have the first solution that will democratize machine learning for developers and data scientists. Now, they have to hand over Python code to specialists who rewrite it for tools. Bodo is a new type of compiler technology that democratizes AI.”
Powered by WPeMatico
On October 27, we’re taking on the ferociously competitive field of software as a service (SaaS), and we’re thrilled to announce our packed agenda, overflowing with some of the biggest names and most exciting startups in the industry. And you’re in luck, because $75 early-bird tickets are still on sale — make sure you book yours so you can enjoy all the agenda has to offer and save $100 bucks before prices go up!
Throughout the day, you can expect to hear from industry experts, and take part in discussions about the potential of new advances in data, open source, how to deal with the onslaught of security threats, investing in early-stage startups and plenty more.
We’ll be joined by some of the biggest names and the smartest and most prescient people in the industry, including Javier Soltero at Google, Kathy Baxter at Salesforce, Jared Spataro at Microsoft, Jay Kreps at Confluent, Sarah Guo at Greylock and Daniel Dines at UiPath.
You’ll be able to find and engage with people from all around the world through world-class networking on our virtual platform — all for $75 and under for a limited time, with even deeper discounts for nonprofits and government agencies, students and up-and-coming founders!
Our agenda showcases some of the powerhouses in the space, but also plenty of smaller teams that are building and debunking fundamental technologies in the industry. We still have a few tricks up our sleeves and will be adding some new names to the agenda over the next month, so keep your eyes open.
In the meantime, check out these agenda highlights:
We’ll have more sessions and names shortly, so stay tuned. But get excited in the meantime, we certainly are.
Pro tip: Keep your finger on the pulse of TC Sessions: SaaS. Get updates when we announce new speakers, add events and offer ticket discounts.
Why should you carve a day out of your hectic schedule to attend TC Sessions: SaaS? This may be the first year we’ve focused on SaaS, but this ain’t our first rodeo. Here’s what other attendees have to say about their TC Sessions experience.
“TC Sessions: Mobility offers several big benefits. First, networking opportunities that result in concrete partnerships. Second, the chance to learn the latest trends and how mobility will evolve. Third, the opportunity for unknown startups to connect with other mobility companies and build brand awareness.” — Karin Maake, senior director of communications at FlashParking.
“People want to be around what’s interesting and learn what trends and issues they need to pay attention to. Even large companies like GM and Ford were there, because they’re starting to see the trend move toward mobility. They want to learn from the experts, and TC Sessions: Mobility has all the experts.” — Melika Jahangiri, vice president at Wunder Mobility.
TC Sessions: SaaS 2021 takes place on October 27. Grab your team, join your community and create opportunity. Don’t wait — jump on the early bird ticket sale right now.
Powered by WPeMatico
The Pareto principle, also known as the 80-20 rule, asserts that 80% of consequences come from 20% of causes, rendering the remainder way less impactful.
Those working with data may have heard a different rendition of the 80-20 rule: A data scientist spends 80% of their time at work cleaning up messy data as opposed to doing actual analysis or generating insights. Imagine a 30-minute drive expanded to two-and-a-half hours by traffic jams, and you’ll get the picture.
As tempting as it may be to think of a future where there is a machine learning model for every business process, we do not need to tread that far right now.
While most data scientists spend more than 20% of their time at work on actual analysis, they still have to waste countless hours turning a trove of messy data into a tidy dataset ready for analysis. This process can include removing duplicate data, making sure all entries are formatted correctly and doing other preparatory work.
On average, this workflow stage takes up about 45% of the total time, a recent Anaconda survey found. An earlier poll by CrowdFlower put the estimate at 60%, and many other surveys cite figures in this range.
None of this is to say data preparation is not important. “Garbage in, garbage out” is a well-known rule in computer science circles, and it applies to data science, too. In the best-case scenario, the script will just return an error, warning that it cannot calculate the average spending per client, because the entry for customer #1527 is formatted as text, not as a numeral. In the worst case, the company will act on insights that have little to do with reality.
The real question to ask here is whether re-formatting the data for customer #1527 is really the best way to use the time of a well-paid expert. The average data scientist is paid between $95,000 and $120,000 per year, according to various estimates. Having the employee on such pay focus on mind-numbing, non-expert tasks is a waste both of their time and the company’s money. Besides, real-world data has a lifespan, and if a dataset for a time-sensitive project takes too long to collect and process, it can be outdated before any analysis is done.
What’s more, companies’ quests for data often include wasting the time of non-data-focused personnel, with employees asked to help fetch or produce data instead of working on their regular responsibilities. More than half of the data being collected by companies is often not used at all, suggesting that the time of everyone involved in the collection has been wasted to produce nothing but operational delay and the associated losses.
The data that has been collected, on the other hand, is often only used by a designated data science team that is too overworked to go through everything that is available.
The issues outlined here all play into the fact that save for the data pioneers like Google and Facebook, companies are still wrapping their heads around how to re-imagine themselves for the data-driven era. Data is pulled into huge databases and data scientists are left with a lot of cleaning to do, while others, whose time was wasted on helping fetch the data, do not benefit from it too often.
The truth is, we are still early when it comes to data transformation. The success of tech giants that put data at the core of their business models set off a spark that is only starting to take off. And even though the results are mixed for now, this is a sign that companies have yet to master thinking with data.
Data holds much value, and businesses are very much aware of it, as showcased by the appetite for AI experts in non-tech companies. Companies just have to do it right, and one of the key tasks in this respect is to start focusing on people as much as we do on AIs.
Data can enhance the operations of virtually any component within the organizational structure of any business. As tempting as it may be to think of a future where there is a machine learning model for every business process, we do not need to tread that far right now. The goal for any company looking to tap data today comes down to getting it from point A to point B. Point A is the part in the workflow where data is being collected, and point B is the person who needs this data for decision-making.
Importantly, point B does not have to be a data scientist. It could be a manager trying to figure out the optimal workflow design, an engineer looking for flaws in a manufacturing process or a UI designer doing A/B testing on a specific feature. All of these people must have the data they need at hand all the time, ready to be processed for insights.
People can thrive with data just as well as models, especially if the company invests in them and makes sure to equip them with basic analysis skills. In this approach, accessibility must be the name of the game.
Skeptics may claim that big data is nothing but an overused corporate buzzword, but advanced analytics capacities can enhance the bottom line for any company as long as it comes with a clear plan and appropriate expectations. The first step is to focus on making data accessible and easy to use and not on hauling in as much data as possible.
In other words, an all-around data culture is just as important for an enterprise as the data infrastructure.
Powered by WPeMatico
Automation will displace 85 million jobs while simultaneously creating 97 million new jobs by 2025, according to the World Economic Forum. Although that sounds like good news, the hard reality is that millions of people will have to retrain in the jobs of the future.
A number of startups are addressing these problems of employee skills, and are looking at talent development, neuroscience-based assessments and prediction technologies for staffing. These include Pymetrics (raised $56.6 million), Eightfold (raised $396.8 million) and EmPath (raised $1 million). But this sector is by no means done yet.
Retrain.ai bills itself as a “Talent Intelligence Platform”, and it’s now closed an additional $7 million from its current investors Square Peg, Hetz Ventures, TechAviv, .406 Ventures and Schusterman Family Investments. It’s also now added Splunk Ventures as a strategic investor. The new round of funding takes its total raised to $20 million.
Retrain.ai says it uses AI and machine learning to help governments and organizations retrain and upskill talent for jobs of the future, enable diversity initiatives, and help employees and jobseekers manage their careers.
Dr. Shay David, co-founder and CEO of retrain.ai said: “We are thrilled to have Splunk Ventures join us on this exciting journey as we use the power of data to solve the widening skills gap in the global labor markets.”
The company says it helps companies tackle future workforce strategies by “analyzing millions of data sources to understand the demand and supply of skill sets.”
The new funding will be used for U.S. expansion, hiring talent and product development.
Powered by WPeMatico
Houston-based ThirdAI, a company building tools to speed up deep learning technology without the need for specialized hardware like graphics processing units, brought in $6 million in seed funding.
Neotribe Ventures, Cervin Ventures and Firebolt Ventures co-led the investment, which will be used to hire additional employees and invest in computing resources, Anshumali Shrivastava, Third AI co-founder and CEO, told TechCrunch.
Shrivastava, who has a mathematics background, was always interested in artificial intelligence and machine learning, especially rethinking how AI could be developed in a more efficient manner. It was when he was at Rice University that he looked into how to make that work for deep learning. He started ThirdAI in April with some Rice graduate students.
ThirdAI’s technology is designed to be “a smarter approach to deep learning,” using its algorithm and software innovations to make general-purpose central processing units (CPU) faster than graphics processing units for training large neural networks, Shrivastava said. Companies abandoned CPUs years ago in favor of graphics processing units that could more quickly render high-resolution images and video concurrently. The downside is that there is not much memory in graphics processing units, and users often hit a bottleneck while trying to develop AI, he added.
“When we looked at the landscape of deep learning, we saw that much of the technology was from the 1980s, and a majority of the market, some 80%, were using graphics processing units, but were investing in expensive hardware and expensive engineers and then waiting for the magic of AI to happen,” he said.
He and his team looked at how AI was likely to be developed in the future and wanted to create a cost-saving alternative to graphics processing units. Their algorithm, “sub-linear deep learning engine,” instead uses CPUs that don’t require specialized acceleration hardware.
Swaroop “Kittu” Kolluri, founder and managing partner at Neotribe, said this type of technology is still early. Current methods are laborious, expensive and slow, and for example, if a company is running language models that require more memory, it will run into problems, he added.
“That’s where ThirdAI comes in, where you can have your cake and eat it, too,” Kolluri said. “It is also why we wanted to invest. It is not just the computing, but the memory, and ThirdAI will enable anyone to do it, which is going to be a game changer. As technology around deep learning starts to get more sophisticated, there is no limit to what is possible.”
AI is already at a stage where it has the capability to solve some of the hardest problems, like those in healthcare and seismic processing, but he notes there is also a question about climate implications of running AI models.
“Training deep learning models can be more expensive than having five cars in a lifetime,” Shrivastava said. “As we move on to scale AI, we need to think about those.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Operating in the cloud is soon going to be a reality for many businesses whether they like it or not. Points of contention with this shift often arise from unfamiliarity and discomfort with cloud operations. However, cloud migrations don’t have to be a full lift and shift.
Instead, leaders unfamiliar with the cloud should start by moving over their disaster recovery program to the cloud, which helps to gain familiarity and understanding before a full migration of production workloads.
Disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) is cloud-based disaster recovery delivered as a service to organizations in a self-service, partially managed or fully managed service model. The agility of DR in the cloud affords businesses a geographically diverse location to failover operations and run as close to normal as possible following a disruptive event. DRaaS emphasizes speed of recovery so that this failover is as seamless as possible. Plus, technology teams can offload some of the more burdensome aspects of maintaining and testing their disaster recovery.
When it comes to disaster recovery testing, allow for extra time to let your IT staff learn the ins and outs of the cloud environment.
DRaaS is a perfect candidate for a first step into the cloud for five main reasons:
Do your research to determine if DRaaS is right for you given your long-term organizational goals. You don’t want to start down a path to one cloud environment if that cloud isn’t aligned with your company’s objectives, both for the short and long term. Having cross-functional conversations among business units and with company executives will assist in defining and iterating your strategy.
Powered by WPeMatico
With two giants calling the shots and collecting whatever tolls they see fit, mobile software makers have long complained that app stores take an unfair cut of the cash that should be flowing directly to developers. Hearing those concerns, a group of senators introduced a new bill this week that, if passed, would greatly diminish Apple and Google’s ability to control app purchases in their operating systems and completely shake up the way that mobile software gets distributed.
The new bill, called the Open App Markets Act, would enshrine quite a few rights that could benefit app developers tired of handing 30% of their earnings to Apple and Google. The bill, embedded in full below, would require companies that control operating systems to allow third-party apps and app stores.
It would also prevent those companies from blocking developers from telling users about lower prices for their software that they might find outside of official app stores. Apple and Google would also be barred from leveraging “non-public” information collecting through their platforms to create competing apps.
“This legislation will tear down coercive anticompetitive walls in the app economy, giving consumers more choices and smaller startup tech companies a fighting chance,” said Senator Richard Blumenthal (D-CT), who introduced the bipartisan bill with Sen. Marsha Blackburn (R-TN), and Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-MN). Klobuchar chairs the Senate’s antitrust subcommittee and Blackburn and Blumenthal are both subcommittee members.
Senator Blackburn called Apple and Google’s app store practices a “direct affront to a free and fair marketplace” and Sen. Klobuchar noted that their behavior raises “serious competition concerns.”
The bill draws on information collected earlier this year from that subcommittee’s hearing on app stores and competition. In the hearing, lawmakers heard from Apple and Google as well as Spotify, Tile and Match Group, three companies that argued their businesses have been negatively impacted by anti-competitive app store policies.
“… We urge Congress to swiftly pass the Open App Markets Act,” Spotify Chief Legal Officer Horacio Gutierrez said of the new bill. “Absent action, we can expect Apple and others to continue changing the rules in favor of their own services, and causing further harm to consumers, developers and the digital economy.”
The Coalition for App Fairness, a developer advocacy group, praised the bill for its potential to spur innovation in digital markets. “The bipartisan Open App Markets Act is a step towards holding big tech companies accountable for practices that stifle competition for developers in the U.S. and around the world,” CAF executive director Meghan DiMuzio said.
Hoping to head off future regulatory headaches, Apple dropped its own fees for companies that generate less than $1 million in App Store revenue from 30% to 15% last year. Google followed suit with its own gesture, dropping fees to 15% for the first $1 million in revenue a developer earns through the Play Store in a year. Some developers critical of the companies’ practices saw those changes as little more than a publicity stunt.
Developers have long complained about the high tolls they pay to distribute their software through the world’s two major mobile operating systems. That fight escalated over the last year when Epic Games circumvented Apple’s payments rules by allowing Fortnite players to pay Epic directly, setting off a legal fight that has huge implications for the mobile software world. Following a May trial, the verdict is expected later this year.
“This will make it easier for developers of all sizes to challenge these harmful practices and seek relief from retaliation, be it during litigation or simply because they dared speak up,” Epic Games VP of Public Policy Corie Wright said of the new bill.
Unlike Apple, Google does allow apps to be “sideloaded,” installed onto devices outside of the Google Play Store. But documents unsealed in Epic’s parallel case against Google revealed that the Play Store’s creator knows the sideloading process is a terrible experience for users — something the company brings up when pressuring developers to stick with its official app marketplace.
The counterargument here is that official app stores make apps safer and smoother for consumers. While Apple and Google extract heavy fees for selling mobile software through the App Store and the Google Play Store, the companies both argue that streamlining apps through those official channels protects people from malware and allows for prompt software updates to patch security concerns that could jeopardize user privacy.
“At Apple, our focus is on maintaining an App Store where people can have confidence that every app must meet our rigorous guidelines and their privacy and security is protected,” an Apple spokesperson told TechCrunch.
Adam Kovacevich, a former Google policy executive who leads the new tech-backed industry group Chamber of Progress, called the new bill “a finger in the eye” for Android and iPhone owners.
“I don’t see any consumers marching in Washington demanding that Congress make their smartphones dumber,” Kovacevich said. “And Congress has better things to do than intervene in a multi-million-dollar dispute between businesses.”
At least in Google’s case, the counterargument has its own counterargument. Android has long been notorious for malware, but apparently most of that malicious software isn’t making its way onto devices through sideloading — it’s walking through the Google Play Store’s front door.
Powered by WPeMatico