Asia
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Lalamove will extend its network to cover more small Chinese cities after raising $515 million in Series E funding, the on-demand logistics company announced on its site. The round was led by Sequoia Capital China, with participation from Hillhouse Capital and Shunwei Capital. All three are returning investors.
According to Crunchbase data, this brings Lalamove’s total raised so far to about $976.5 million. The company’s last funding announcement was in February 2019, when it hit unicorn status with a Series D of $300 million.
Bloomberg reported last week that Lalamove was seeking at least $500 million in new funding at $8 billion valuation, or four times what it raised last year.
Founded in 2013 for on-demand deliveries within the same city, Lalamove has since grown its business to include freight services, enterprise logistics, moving and vehicle rental. In addition to 352 cities in mainland China, Lalamove also operates in Hong Kong (where it launched), Taiwan, Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines and Thailand. The company entered the United States for the first time in October, and currently claims about 480,000 monthly active drivers and 7.2 million monthly active users.
Part of its Series D had been earmarked to expand into India, but Lalamove was among 43 apps that were banned by the government, citing cybersecurity concerns.
In its announcement, Lalamove CEO Shing Chow said its Series E will be used to enter more fourth and fifth-tier Chinese cities, adding “we believe the mobile internet’s transformation of China’s logistics industry is far from over.”
Other companies that have recently raised significant funding rounds for their logistics operations in China include Manbang and YTO.
Lalamove’s (known in Chinese as Huolala) Series E announcement said the company experienced a 93% drop in shipment volume at the beginning of the year, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but has experienced a strong rebound, with order volume up 82% year-over-year even before Double 11.
Powered by WPeMatico
WeRide, one of China’s most-funded startups developing autonomous driving capabilities, said on Wednesday that it has raised a $200 million strategic round from Chinese bus maker Yutong.
Mega investments aren’t uncommon at companies like WeRide developing the next-generation level 4 driving standard, which denotes that the car can handle the majority of driving situations independently without human intervention.
WeRide did not disclose its valuation for this round, which is the first tranche of its Series B round, a company spokesperson told TechCrunch.
The new funding will see WeRide joining hands with Yutong, a 57-year-old company, to make autonomous-driving minibuses and city buses as well as work together on R&D, vehicle platforms and mobility services. The partners have already jointly developed a front-loaded driverless minibus for mass-production. The model, which comes without a steering wheel, accelerator or brakes, is designed for operating in urban open roads, said WeRide.
Alliance Ventures, the strategic venture capital arm of Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi, became WeRide’s strategic investor in 2018 following the completion of the startup’s Series A round, which was partially funded by the Chinese facial recognition giant SenseTime.
Autonomous driving startups in China are racing to showcase their progress, in part to attract funding for their cash-bleeding businesses. Alibaba-backed AutoX, for instance, began deploying driverless cars on the roads in Shenzhen in a bold move. WeRide and its rivals are testing various levels of autonomous driving vehicles in both the United States and major Chinese cities where local policies are supporting the futurist transportation tech.
“Capital’s attitude is shifting and increasingly bullish about autonomous driving and its commercial future following the COVID-19 pandemic [in China]. Many investments are happening in this space because investors don’t want to miss out on any potential leaders in autonomous driving,” the WeRide spokesperson said. “Our Series B round has attracted a lot of interest.”
WeRide’s competitors include Pony.ai in its backyard Guangzhou, AutoX and Deeproute.ai in Shenzhen, Momenta in Suzhou and Baidu in Beijing, to name a few.
Powered by WPeMatico
Being “underbanked” doesn’t mean that someone lacks access to financial services. Instead, it often means they don’t have traditional bank accounts or credit cards. But in markets like Indonesia, many still use digital wallets or e-commerce platforms, creating alternative sources of user data that can help them secure working capital and other financial tools. Finantier, a Singapore-based open finance startup, wants to streamline that data with a single API that gives financial services access to user data, with their consent. It also includes machine-learning-based analytics to enable credit scoring and KYC verifications.
Currently in beta mode with more than 20 clients, Finantier is busy getting ready to officially launch. It announced today that it has been accepted into Y Combinator’s Winter 2021 startup batch. The startup also recently raised an undisclosed amount of pre-seed funding led by East Ventures, with participation from AC Ventures, Genesia Ventures, Two Culture Capital and other investors.
Finantier was founded earlier this year by Diego Rojas, Keng Low and Edwin Kusuma, all of whom have experience building products for fintech companies, with the mission of enabling open finance in emerging markets.
Open finance grew out of open banking, the same framework that Plaid and Tink are built on. Meant to give people more control over their financial data instead of keeping it siloed within banks and other institutions, users can decide to grant apps or websites secure access to information from their online accounts, including bank accounts, credit cards and digital wallets. Open banking refers mainly to payment accounts, while open finance, Finantier’s specialty, covers a larger gamut of services, including business lending, mortgages and insurance underwriting.
While Finantier is focusing first on Singapore and Indonesia, it plans to expand into other countries and become a global fintech company like Plaid. It’s already eyeing Vietnam and the Philippines.
Before launching Finantier, Rojas worked on products for peer-to-peer lending platforms Lending Club and Dianrong, and served as chief technology officer for several fintech startups in Southeast Asia. He realized that many companies struggled to integrate with other platforms and fetch data from banks, or purchase data from different providers.
“People are discussing open banking, embedded finance and so on,” Rojas, Finantier’s chief executive officer, told TechCrunch. “But those are the building blocks of something bigger, which is open finance. Particularly in a region like Southeast Asia, where about 60% to 70% of adults are unbanked or underbanked, we believe in helping consumers and businesses leverage the data that they have in multiple platforms. It definitely doesn’t need to be a bank account, it could be in a digital wallet, e-commerce platform or other service providers.”
What this means for consumers is that even if someone doesn’t have a credit card, they can still establish creditworthiness: For example, by sharing data from completed transactions on e-commerce platforms. Gig economy workers can access more financial services and deals by giving data about their daily rides or other types of work they do through different apps.
Other open-banking startups focused on Southeast Asia include Brankas and Brick. Rojas said Finantier differentiates by specializing on open finance and creating infrastructure for financial institutions to build more services for end users.
The benefit of open finance for financial institutions is that they can create products for more consumers and find more opportunities for revenue sharing models. In Southeast Asia, this also means reaching more people who are underbanked or otherwise lack access to financial services.
While taking part in Y Combinator’s accelerator program, Finantier will also be participating in the Indonesia Financial Service Authority’s regulatory sandbox. Once it completes the program, it will be able to partner with more fintech companies in Indonesia, including bigger institutions.
There are 139 million adults in Indonesia who are underbanked or unbanked, said East Ventures co-founder and managing partner Willson Cuaca.
The investment firm, which focuses on Indonesia, conducts an annual survey called the East Ventures Digital Competitiveness Index and found that financial exclusion was where one of the largest divides existed. There are significant gaps in between the number of financial services available in heavily populated islands like Java, where Jakarta is located, and other islands in the archipelago.
To promote financial inclusion and alleviate the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has set a goal for 10 million micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) to go digital by the end of the year. There are currently about eight million Indonesian MSMEs that sell online, representing just 13% of MSMEs in the country.
“Providing equal access to financial services will create multiplier effects to the Indonesian economy,” Cuaca told TechCrunch about East Ventures’ decision to back Finantier. “Currently, hundreds of companies work with their own unique solutions to bring financial services to more people. We believe Finantier will help them offer more products and services to this underserved section of the population.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Google said on Tuesday it is investing in two Indian startups, Glance and DailyHunt, as the Android-maker makes a further push into the world’s second-largest internet market.
Two-year-old Indian startup Glance, which serves news, media content and games on the lock screen of more than 100 million smartphones, has raised $145 million in a new financing round from Google and existing investor Mithril Partners.
Glance, which is part of advertising giant InMobi Group, uses AI to offer personalized experience to its users. The service replaces the otherwise empty lock screen with locally relevant news, stories and casual games. Late last year, InMobi acquired Roposo, a Gurgaon-headquartered startup, that has enabled it to introduce short-form videos on the platform. Google is also investing in Roposo.
Roposo is a short-video platform with more than 33 million monthly active users. These users spend about 20 minutes consuming content across multiple genres in more than 10 languages on the app everyday.
Glance ships pre-installed on several smartphone models. The subsidiary maintains tie-ups with nearly every top Android smartphone vendor, including Xiaomi and Samsung, the two largest smartphone vendors in India. The service has amassed over 115 million daily active users.
“Glance is a great example of innovation solving for mobile-first and mobile-only consumption, serving content across many of India’s local languages,” said Caesar Sengupta, VP, Google, in a statement. “Still too many Indians have trouble finding content to read or services they can use confidently, in their own language. And this significantly limits the value of the internet for them, particularly at a time like this when the internet is the lifeline of so many people. This investment underlines our strong belief in working with India’s innovative startups and work towards the shared goal of building a truly inclusive digital economy that will benefit everyone.”
Naveen Tewari, founder and chief executive of Glance and InMobi Group, said the investment will pave the way for “deeper partnership between Google and Glance across product development, infrastructure, and global market expansion.” The startup plans to deploy the fresh capital to expand in the U.S.
Google said on Tuesday that it is also investing in VerSe Innovation, the parent firm of Indian startup DailyHunt. Across its apps including eponymous service and short-video platform Josh, DailyHunt claims to serve over 300 million users news and entertainment content in 14 Indian languages. The startup said it has completed a round of over $100 million from Google, Microsoft and AlphaWave among other investors, and this new round values it at over $1 billion, making it a unicorn.
DailyHunt — which is co-run by Umang Bedi, former Facebook India head — plans to deploy the fresh capital to scale the Josh app, the augmentation of local language content offerings, the development of content creator ecosystem, innovation in AI and ML and the growth of its truly “made-in-Bharat-for-Bharat short-video platform,” it said.
Josh and Roposo are among over a dozen apps in India that are attempting to fill the void New Delhi created after banning TikTok in late June in the country. TikTok identified India as its biggest overseas market prior to the ban.
Google is writing both these checks from India Digitization Fund that it unveiled this year. Google has committed to invest $10 billion in India over the course of the next few years. Prior to today, the company invested $4.5 billion from this fund in Indian telecom giant Jio Platforms.
Powered by WPeMatico
The rest of the world may be slowing down as we prepare for Christmas and the new year, but we are not taking our foot off the gas.
Alex Wilhelm keeps a close watch on the public markets in his column The Exchange, but this week, he branched out to look at some of the metrics underpinning soaring cryptocurrency prices and turned his gaze on StockX, the consumer reseller marketplace that just raised $275 million in a Series E that values the company at approximately $2.8 billion.
“Selling a tenth of your company for north of a quarter-billion may be somewhat common among late-stage software startups with tremendous growth,” he says, but “don’t laugh — the round actually makes pretty OK sense.”
Our staff continues to file their end-of-year stories: We ran a post this morning by Manish Singh that studies India’s massive total addressable market for retail. The nation has more than 60 million mom-and-pop neighborhood stores, and companies like Walmart and Amazon are eager to offer help with payments, logistics and inventory management — as are hundreds of native and foreign startups.
In an interview with author and MIT professor Sinan Aral, Managing Editor Danny Crichton discussed some of the debates currently swirling around the desire in some quarters to regulate social media platforms. In “The Hype Machine,” Aral explores topics like neuroscience, economics and misinformation before offering potential solutions for resolving what he calls “a full-blown social media crisis.”
The stories that follow are an overview of Extra Crunch from the last five days. Complete articles are only available to members, but you can use discount code ECFriday to save 20% off a one or two-year subscription. Details here.
Thank you very much for reading Extra Crunch this week; I hope you have a safe, relaxing weekend!
Walter Thompson
Senior Editor, TechCrunch
@yourprotagonist

Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
How did fashion marketplace Poshmark go from posting regular losses in 2019 to generating net income in 2020?
After the company filed a public S-1 last night, Alex Wilhelm pondered the question this morning in The Exchange.
Like many e-commerce platforms, Poshmark saw a surge in activity during the COVID-19 pandemic, but it also slashed its marketing spend, which helped boost profits. As the cash-rich company prepares its road show, “Poshmark is valuable,” Alex concluded.
“How valuable the market will decide. But who will it enrich with its final pricing decision?”

WASHINGTON, D.C. – APRIL 22, 2018: A statue of Albert Gallatin, a former U.S. Secretary of the Treasury, stands in front of The Treasury Building in Washington, D.C. The National Historic Landmark building is the headquarters of the United States Department of the Treasury. (Photo by Robert Alexander/Getty Images)
The breach of FireEye and SolarWinds by hackers working on behalf of Russian intelligence is “the nightmare scenario that has worried cybersecurity experts for years,” reports Zack Whittaker.
The intrusion began several months ago, but news of the breach wasn’t made public until this week.
“Given that potential victims include defense contractors, telecoms, banks, and tech companies, the implications for critical infrastructure and national security, although untold at this point, could be significant,” said Erin Kenneally, director of cyber risk analytics at Guidewire, an industry platform for insurance carriers.
In his analysis for Extra Crunch, Zack breaks down the rippling effects of supply-chain attacks that can compromise platforms like SolarWinds, which is used by more than 420 of the Fortune 500.

Image Credits: dowell (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Embedded finance connects services like payment processing with everyday activities like grabbing a coffee before unlocking an e-scooter.
“The ability to be at the right place at the right time, supporting consumers and merchants alike, where they want it, how they want it and when they want it — cannot be understated,” says Simon Wu, an investment director with Cathay Innovation.
In a post that identifies embedded finance’s top providers and enablers, he offers advice for startups and established brands that are hoping to “earn and build customer loyalty while generating new revenue streams.”

Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
Bitcoin is at an all-time high.
CoinMarketCap reports that crypto market values have reached almost $659 billion; that figure was just $140 billion in March 2020.
“These gains have created a huge amount of wealth for crypto holders,” Alex Wilhelm wrote yesterday.
To get a better handle on why crypto values are sky-bound, he parsed some basic industry metrics, including the number of unique bitcoin addresses, fees paid and transactions per day.
“Do the price gains make sense in the short term? Who knows,” he wrote, “but they are not based on nothing.”

Stage Light on Black. Image Credits: Fotograzia / Getty Images
For his year-end Extra Crunch story, security reporter Zack Whittaker looked back at the myriad security challenges and vulnerabilities COVID-19 brought to the fore.
The hacks of Fire Eyes and SolarWinds were just one link in the chain: How well is your company prepared to deal with file-encrypting malware, hackers backed by nation-states or employees accessing secure systems from home?
“With 2020 wrapping up, much of the security headaches exposed by the pandemic will linger into the new year,” says Zack.
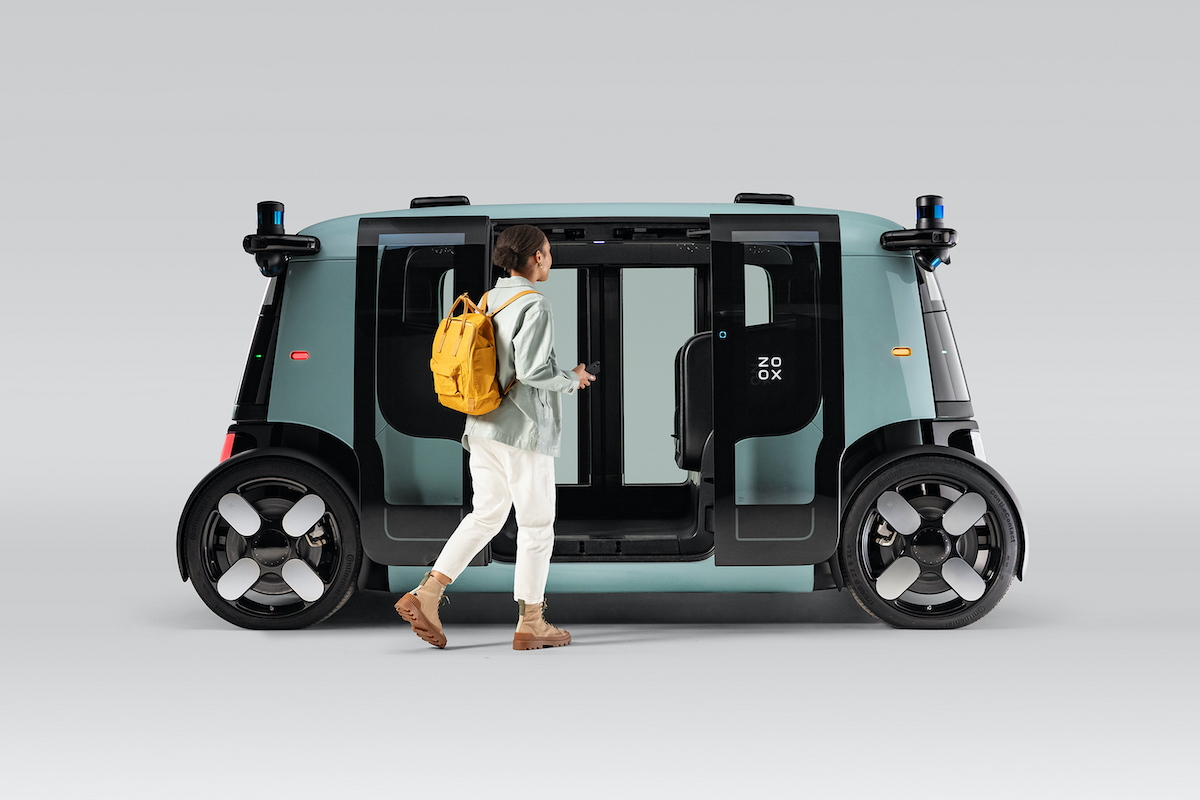

Zoox Fully Autonomous, All-electric Robotaxi. Image Credits: Zoox
After six years of research and development, autonomous vehicle company Zoox this week unveiled an electric robotaxi that can carry four people at a maximum speed of 75 miles per hour.
Automotive writer Kirsten Korosec interviewed Zoox co-founder and CTO Jesse Levinson to learn more about the vehicle’s development and how the company overcame a series of technical and legal challenges.
“I would say that if you have a big idea and you’re confident that it makes sense, you should at least explore the idea, rather than giving up because the current regulations aren’t designed for it,” said Levinson.
Kirsten only had 15 minutes to interview Levinson, but this comprehensive interview covers topics like regulatory compliance, Zoox’s relationship with parent company Amazon and the highest (and lowest) moments he experienced along the way.

Fairy dust flying in gold light rays. Computer-generated abstract raster illustration. Image Credits: gonin / Wikimedia Commons
In one of the largest enterprise acquisitions of 2020, Visa Equity Partners this week purchased Utah-based edtech startup Pluralsight for $3.5 billion.
According to the entrepreneurs and investors reporter Natasha Mascarenhas spoke to, this deal “shows the strength of edtech’s capital options as the pandemic continues.”
“What’s happening in edtech is that capital markets are liquidating,” a major change from “the old days where the options to exit were very narrow,” says Deborah Quazzo, a managing partner at GSV Advisors and seed investor in Pluralsight.

Image Credits: Sophie Alcorn
Dear Sophie:
I’m on an F1 OPT and am about to incorporate a startup with my two American co-founders.
What were the biggest immigration changes in 2020 affecting us?
—Ambitious in Albany
High angle view of young man walking towards white doorways on blue background Image Credits: Klaus Vedfelt / Getty Images
Founders and the VCs who back them may not be friends, but they’re usually friendly.
Investors are on a first-name basis with entrepreneurs from their portfolio companies and frequently have candid conversations with them about life, work and the world in general. In the before times, they might even have shared a meal or attended a baseball game together.
But make no mistake, it is a top-down relationship — the investor will always have the upper hand. When an entrepreneur accepts a check, they are hiring their next boss.
In an Extra Crunch guest post, Quiq CEO and founder Mike Myer poses two questions for founders who are considering a new relationship with a VC:

NEW DELHI, INDIA – 2011/12/18: Rice is sold at a night market in Paharganj, the urban suburb opposite New Delhi Railway Station. (Photo by Frank Bienewald/LightRocket via Getty Images)
In India, about 90% of consumers buy their everyday goods from neighborhood-based kirana stores instead of supermarkets.
As a result, U.S. retail giants like Walmart and Amazon have adopted an “if you can’t beat them, join them” approach, offering the nation’s 60 million mom-and-pop shops software for inventory control, payments and e-commerce.
India’s retail market will be worth an estimated $1.3 trillion by 2025, but e-commerce represents just 3% of that activity today, reports Manish Singh.
For his final Extra Crunch story of 2020, he looked at the startups and major players who are hoping to carve out their niche in one of the world’s largest retail ecosystems.

Image Credits: PM Images / Getty Images
Earlier this year, business productivity software startup ClickUp raised a $35 million Series A.
Now, just six months later, the company has closed a second round of $100 million that values the San Diego-based startup at $1 billion.
Lucas Matney interviewed CEO Zeb Evans this week to learn more about how the company was buoyed by pandemic-based behavior shifts that doubled its customer base and multiplied revenue by a factor of nine.
“I think that the biggest thing that we’ve always focused on is shipping a new version of ClickUp every week. That is our differentiation,” he said. “We’ve kind of created these iterative cycles called natural product-market fit and it’s been hard to keep up with that.”

Multi Colored Bling Bling Dollar Sign Shape Bokeh Backdrop on Dark Background, Finance Concept. Image Credits: MirageC / Getty Images.
In 2018, the total value of the year’s 10 top enterprise mergers and acquisitions reached $87 billion; last year, that figure fell to just $40 billion.
But in 2020, 10 M&A deals accounted for $165.2 billion.
“Last year’s biggest deal — Salesforce buying Tableau for $15.7 billion — would have only been good for fifth place on this year’s list,” notes enterprise reporter Ron Miller. “And last year’s fourth largest deal, where VMware bought Pivotal for $2.7 billion, wouldn’t have even made this year’s list at all.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Zomato has raised $660 million in a financing round that it kicked off last year as the Indian food delivery startup prepares to go public next year.
The Indian startup said Tiger Global, Kora, Luxor, Fidelity (FMR), D1 Capital, Baillie Gifford, Mirae and Steadview participated in the round — a Series J — which gives Zomato a post-money valuation of $3.9 billion. Zomato had previously disclosed a fundraise of about $212 million as part of a Series J round from Ant Financial, Tiger Global, Baillie Gifford and Temasek.
Deepinder Goyal, the co-founder and chief executive of Zomato, said the 12-year-old startup is also in the process of closing a $140 million secondary transaction. “As part of this transaction, we have already provided liquidity worth $30m to our ex-employees,” he tweeted.
The startup originally anticipated to close a round of about $600 million by January this year, but several obstacles, including the current pandemic, delayed the fundraise effort. Additionally, Ant Financial, which had originally committed to invest $150 million in this round, only delivered a third of it, Zomato’s investor Info Edge disclosed earlier this year.
The Gurgaon-headquartered startup, which acquired the Indian food delivery business of Uber early this year, competes with Prosus Ventures-backed Swiggy in India. A third player, Amazon, has also emerged in the market, though it currently offers its food delivery service in only parts of Bangalore.
At stake is India’s food delivery market, which analysts at Bernstein expect to balloon to be worth $12 billion by 2022, they wrote in a report to clients — accessed by TechCrunch. With about 50% of the market share, Zomato is the current leader among the three, Bernstein analysts wrote.
Zomato eliminated hundreds of jobs this year to improve its finances and navigate the coronavirus pandemic, which significantly hurt the food delivery business in India in the early months. Goyal said the food delivery market is “rapidly coming out of COVID-19 shadows. December 2020 is expected to be the highest ever GMV month in our history. We are now clocking ~25% higher GMV than our previous peaks in February 2020.” He added, “I am supremely excited about what lies ahead and the impact that we will create for our customers, delivery partners, and restaurant partners.”
In September, Goyal told employees that Zomato was working for its IPO for “sometime in the first half of next year” and was raising money to build a war-chest for “future M&A, and fighting off any mischief or price wars from our competition in various areas of our business.”
Making money with food delivery has been especially challenging in India. Unlike Western markets such as the U.S., where the value of each delivery item is about $33, in India, a similar item carries the price tag of $4, according to estimates by Bangalore-based research firm RedSeer.
“The problem is that there are very few people in India who can afford to place an order from a food delivery firm each day,” said Anand Lunia, a venture capitalist at India Quotient, in an interview with TechCrunch earlier this year.
Powered by WPeMatico
After spending more than a decade disrupting the neighborhood stores in the U.S. and several other markets, Amazon and Walmart are employing an unusual strategy in India to face off this competitor: Friending them.
Walmart and Amazon, both of which face restrictions from New Delhi on what all they could do in India, have partnered with tens of thousands of neighborhood stores in the world’s second-largest internet market this year to leverage the vast presence of these mom and pop stores.
In June this year, at the height of the pandemic, Amazon announced “Smart Stores.” Through this India-specific program, for instance, Amazon is providing physical stores with software to maintain a digital log of the inventory they have in the shop and supplying them with a QR code.
When consumers walk to the store and scan this QR code with the Amazon app, they see everything the shop has to offer, in addition to any discounts and past reviews from customers. They can select the items and pay for it using Amazon Pay. Amazon Pay in India supports a range of payments services, including the popular UPI, and debit and credit cards.
The world’s largest e-commerce giant also maintains partnerships that allow it to turn tens of thousands of neighborhood stores as its delivery point for customers — and sometimes even rely on them for inventory.
India has over 60 million small businesses that dot the thousands of cities, towns and villages across the country. These mom and pop stores offer all kinds of items, are family run, and pay low wages and little to no rent.
This has enabled them to operate at an economics that is better than most — if not all — of their digital counterparts, and their scale allows them to offer unmatched fast delivery.
Krishna Shah, a New Delhi-based doctor, on paper is one of the perfect customers of e-commerce services. She lives in an urban city, uses digital payments apps and her earnings put her in the top 5% income level in the country. Yet, when she needed to buy food for her cats and needed it as soon as possible, she realized the major giants would take hours, if not longer. She ended up placing a call to a neighborhood store, which delivered the item within 10 minutes.
That neighborhood store, which employs fewer than half a dozen people, was competing with over a dozen giants and heavily funded startups including Grofers and BigBasket — and it won.
At stake is India’s retail market, which is estimated to be worth $1.3 trillion by 2025, from about $700 billion last year, according to Boston Consulting Group and the Retailers’ Association India. E-commerce, by several estimates, accounts for just 3% of the retail market in the country.
If that figure wasn’t small enough already, consider this: Some of the biggest customers of Flipkart and Amazon are these small retail stores. An executive with direct knowledge of the matter told TechCrunch that during some sales, as high as 40% of all smartphone units are bought by physical stores. The idea is, the executive said, to buy the devices at a discounted price, sit on them for a few days and when Amazon and Flipkart are done with their sales, sell the same phones at their standard prices.
Sujeet Kumar, co-founder of Udaan, a Bangalore-based startup that works with merchants, said that even as smartphones and the internet have reached all corners of India, e-commerce hasn’t been able to disrupt the retail market.
“The problem is that it is very difficult for e-commerce companies to build a supply chain and distribution network that is more efficient than those established by neighborhood stores. These mom and pop stores operate on an insanely different kind of cost economics. E-commerce companies are not able to match it,” he said.
Powered by WPeMatico
Only about a third of the yields Indian farmers produce reaches the big markets. Those whose produce makes it there today are able to leverage post-harvest services. Everyone else is missing out.
A Noida-based startup is working with all the stakeholders — farmers, food processors, traders and financial institutions — to bridge this post-harvest services gap — and it just secured new funds to continue its journey.
Seven-year-old Arya said on Tuesday it has raised $21 million in its Series B financing round. The round was led by Quona Capital, a venture firm that focuses on fintech in emerging markets. Existing investors LGT Lightstone Aspada and Omnivore also participated in the round, while multiple unnamed lenders are providing additional debt financing to the startup, Arya said.
Nearly all post-harvest interventions that exist in India today are focused largely toward major agriculture centres such as Kota in the northern Indian state of Rajasthan and Azadpur Mandi in capital New Delhi, explained Prasanna Rao, co-founder and chief executive of Arya, in an interview with TechCrunch.
This uneven concentration has deprived millions of farmers in the country of reasonable options to efficiently store and sell their produce and of financing options to maintain their cash flow, he said.
“Our belief is that we should cater to the two-thirds of the market that are currently underserved. The Kota mandi (market), for instance, has 35 bank branches in a kilometre of radius. But if you travel 70 to 80 kilometres away from Kota, this really declines,” said Rao, who previously worked at a bank.
Arya is solving all the aforementioned challenges: It operates a network of more than 1,500 warehouses in 20 Indian states where it stores over $1 billion worth of commodities. This network allows farmers to store their produce at a centre that is much nearer to their farms, avoiding any spillage and exorbitant real estate costs of the big markets. On the credit side, Arya has disbursed over $36.5 million to farmers and its banking partners have disbursed more than $95 million.
“Arya is addressing a vastly underserved market of farmers in India, half of whom previously had little access to post-harvest finance,” said Ganesh Rengaswamy, co-founder and partner at Quona Capital, in a statement. “We believe Arya’s unique approach, providing a full-service digital platform with embedded finance and differentiated efficiencies for small farmholders, will drive the future of farming in India.”
The startup’s offerings have proven even more useful during the coronavirus pandemic, which saw New Delhi enforce one of the world’s strictest lockdowns earlier this year. The lockdown broke the supply chain network, and prices of agricultural commodities dropped by over 20%.
To navigate this, Arya connected farmer produce organizers, or FPOs, with buyers through its own digital marketplace a2zgodaam.com. “The need for immediate liquidity saw demand increase for credit against these warehouse receipts. Arya’s credit portfolio saw a 3x jump year-on-year,” wrote Prashanth Prakash, a founding partner at Accel in India, and Mark Kahn, managing partner at Omnivore in an industry report last week.
Rao said Arya will deploy the fresh capital to scale its fintech platform in a “big way” as the startup broadens its network of warehouses across the country. Additionally, the startup plans to fuel the growth of a2zgodaam.com, which also aggregates unorganized warehouses, and supercharge them with their own set of financiers and insurers and ways to allow farmers to sell directly through these warehouses if they need.
Powered by WPeMatico
Productivity software has been getting a major re-examination this year, and human resources platforms — used for hiring, firing, paying and managing employees — have been no exception. Today, one of the startups that’s built what it believes is the next generation of how HR should and will work is announcing a big fundraise, underscoring its own growth and the focus on the category.
Hibob, the startup behind the HR platform that goes by the name of “bob” (the company name is pronounced, “Hi, Bob!”), has picked up $70 million in funding at a valuation that reliable sources close to the company tell us is around $500 million.
“Our mission is to modernize HR technology,” said Ronni Zehavi, Hibob’s CEO, who co-founded the company with Israel David. “We are a people management platform for how people work today. Whether that’s remotely or physically collaborative, our customers face challenges with work. We believe that the HR platforms of the future will not be clunky systems, annoying, giant platforms. We believe it should be different. We are a system of engagement rather than record.”
The Series B is being led by SEEK and Israel Growth Partners, with participation also from Bessemer Venture Partners, Battery Ventures, Eight Roads Ventures, Arbor Ventures, Presidio Ventures, Entree Capital, Cerca Partners and Perpetual Partners, the same group that also backed Hibob in its last round (a Series A extension) in 2019. It has raised $124 million to date.
The company has its roots in Israel but these days describes its headquarters as London and New York, and the funding comes on the back of strong growth in multiple markets. In an interview, Zehavi said that Hibob specialises in the mid-market customers and says that it has more than 1,000 of them currently on its books across the U.S., Europe and Asia, including Monzo, Revolut, Happy Socks, ironSource, Receipt Bank, Fiverr, Gong and VaynerMedia. In the last year Hibob has had “triple-digit” year-on-year growth (it didn’t specify what those digits are).
Human resources has never been at the more glamorous end of how a company works, and it can sometimes even be looked on with some disdain. However, HR has found itself in a new spotlight in 2020, the year when every company — whether one based around people sitting at desks or in more interactive and active environments — had to change how it worked.
That might have involved sending everyone home to sign in from offices possibly made out of corners of bedrooms or kitchens, or that might have involved a vastly different set of practices in terms of when and where workers showed up and how they interacted with people once they did. But regardless of the implementations, they all involved a team of people who needed to be linked together, still feeling connected and managed; and sometimes hired, furloughed, or let go.
That focus has started to reveal the strains of how some legacy systems worked, with older systems built to consider little more than creating an employee identity number that could then be tracked for payroll and other purposes.
Hibob — Zehavi said they chose the name after the person who owned the bob.com domain wanted too much to sell it, but they liked “bob” for the actual product — takes an approach from the ground up that is in line with how many people work today, balancing different software and apps depending on what they are doing, and linking them up by way of integrations: its own includes Slack, Microsoft Teams and Mercer, and other packages that are popular with HR departments.
While it covers all of the necessary HR bases like payroll and further compensation, onboarding, managing time off and benefits, it further brings in a variety of other features that help build out bigger profiles of users, such as performance and culture, with the ability for peers, managers and workers themselves to provide feedback to enhance their own engagement with the company, and for the company to have a better idea of how they are fitting into the organization, and what might need more attention in the future.
That then links into a bigger organizational chart and conceptual charts that highlight strong performers, those who are possible flight risks, those who are leaders and so on. While there have been a number of others in the HR world that have built standalone apps that cover some of these features (for example, 15five was early to spot the value of a platform that made it much easier to set goals and provide feedback), what’s notable here is how they are all folded into one system together.
The end effect, as you can see here, looks less like word salad and more interactive, graphic interfaces that are presumably a lot more enjoyable and at least easier to use for HR people themselves.
The importance for investors has been that the product and the startup has identified the opportunity, but has delivered not just more engagement, but a strong piece of software that still provides the essentials.
“This is certainly not a Workday,” said Adam Fisher, a partner at Bessemer, in an interview. “Our overall thesis has been that HR is only growing in importance. And while engagement is super important, that opportunity is not enough to create the market.”
The end result is a platform that has a significant shot at building in even more over time. For example, another large area that has been seeing traction in the world of enterprise and B2B software is employee training. Specifically, enterprise learning systems are creating another way to help keep people not only up to speed on important aspects of how they work, but also engaged at a time when connections are under strain.
“Training, a SuccessFactors -style offering, is definitely in our road map,” said Zehavi, who noted they are adding new features all the time. The latest has been compensation, sometimes known as merit increase cycles. “That is a very complex issue and requires deeper integrations finance and the CFO’s office. We streamlined it and made it easy to use. We launched two months ago and it’s on fire. After learning and development there are other modules also down the road.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Demand for contactless payments and e-commerce has grown in South Korea during the COVID-19 pandemic. This is good news for payment service operators, but the market is very fragmented, so adding payment options is a time-consuming process for many merchants. CHAI wants to fix this with an API that enables companies to accept over 20 payment systems. The Seoul-based startup announced today it has raised a $60 million Series B.
The round was led by Hanhwa Investment & Securities, with participation from SoftBank Ventures Asia (the early-stage venture capital arm of SoftBank Group), SK Networks, Aarden Partners and other strategic partners. It brings CHAI’s total funding to $75 million, including a $15 million Series A in February.
Last month, the Bank of Korea, South Korea’s central bank, released a report showing that ()contactless payments increased 17% year-over-year since the start of COVID-19.
CHAI serves e-commerce companies with an API called I’mport, that allows them to accept payments from over twenty options, including debit and credit cards through local payment gateways, digital wallets, wire transfers, carrier billings and PayPal. It is now used by 2,200 merchants, including Nike Korea and Philip Morris Korea.
CHAI chief executive officer Daniel Shin told TechCrunch that businesses would usually have to integrate each kind of online payment type separately, so I’mport saves its clients a lot of time.
The company also offers its own digital wallet and debit card called the CHAI Card, which launched in June 2019 and now has 2.5 million users, a small number compared South Korea’s leading digital wallets, which include Samsung Pay, Naver Pay, Kakao Pay and Toss.
“CHAI is a late comer to Korea’s digital payments market, but we saw a unique opportunity to offer value,” said Shin. The CHAI Card offers merchants a lower transaction fee than other cards and users typically check its app about 20 times to see new cashback offers and other rewards based on how often they pay with their cards or digital wallet.
“We’ve digitized the plastic card experience, and this is the first step towards creating a robust online rewards platform,” Shin added.
In press statement, Hanhwa Investment & Securities director SeungYoung Oh director said, “I’mport has reduced what once took e-commerce businesses weeks to complete into a simple copy-and-paste task, radically reducing costs. It is a first-of-its-kind business model in Korea, and I have no doubt that CHAI will continue to grow this service into an essential infrastructure of the global fintech landscape.”
Powered by WPeMatico