Apps
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
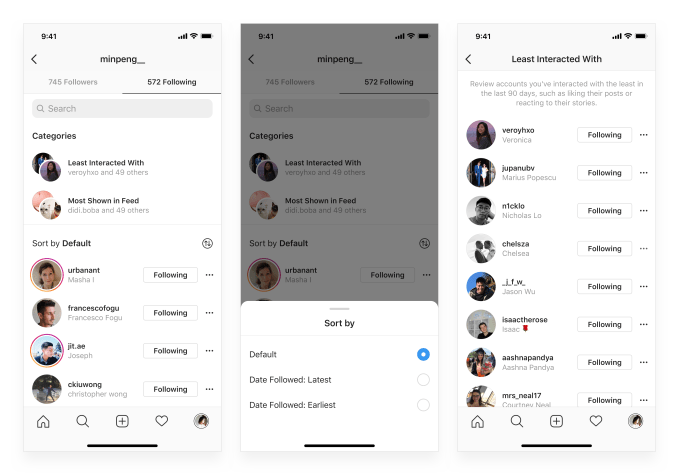
Instagram will now show you who you interact with least frequently in case you want to unfollow them. In an effort to help you keep your feed clean and relevant, today Instagram is launching “following categories” that divides the list of who you follow into batches, including “most seen in feed” and “least interacted with.” That way if someone annoying or boring is overwhelming your feed, or there’s someone whose content you’ve proven to not be interested in, you can easily remove them. Time to axe those courtesy and pity follows.
“Instagram is really about bringing you closer to the people and things you care about — but we know that over time, your interests and relationships can evolve and change,” a spokesperson tells me. “Whether you graduate, move to a new city, or become obsessed with a new interest and find a community, we want to make it easier to manage the accounts you follow on Instagram so that they best represent your current connections and interests.”
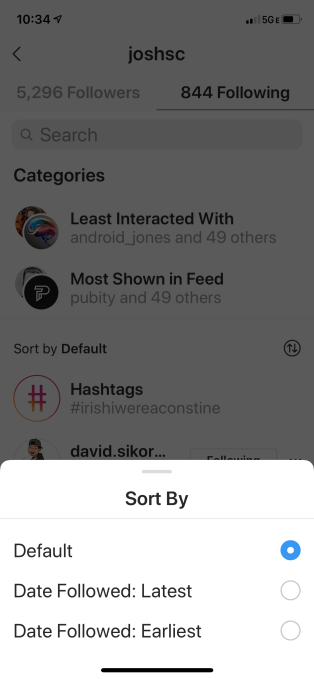
To access the feature, go to your profile, then “following,” then you’ll see the categories you can explore. You’re also able to sort who you follow by earliest to latest and vice versa, in case you want to clear out your earliest adds or make sure you actually care about the latest people you followed.
By increasing the density of high-quality posts in your feed and Stories by getting you to unfollow irrelevant accounts, Instagram could boost ad views. You’ll come across fewer lame posts that might make you close the app so you instead keep scrolling and fast-forwarding while racking up ad impressions. Instagram reportedly hit $20 billion in 2019 revenue according to Bloomberg.
I’ve been asking Twitter to build unfollow suggestions since 2013, but Instagram beat them to it. Even with filtered feeds, the algorithms can get things wrong and show too much of people you don’t care about.
Following back or adding someone who asks has become part of the modern-day social contract. It can be rude and cause drama to refuse, so people just bloat their following list. Manually sorting through, trying to remember who people are and if you see them too often or constantly ignore them can be a slow and emotionally draining chore. With Instagram now 10 years old, Twitter 14 and Facebook 16, we’ve had a long time to accidentally screw up our social graph.
Perhaps unfollow suggestions took this long because no app wants to overtly shame specific people. But Instagram’s approach via clear, quantifiable categories is just vague enough that you probably won’t screenshot them and show the friends it said to nix. With that sensitivity, Instagram has pulled off the rare feat of improving the user experience while simultaneously benefiting its revenue engine.
Powered by WPeMatico
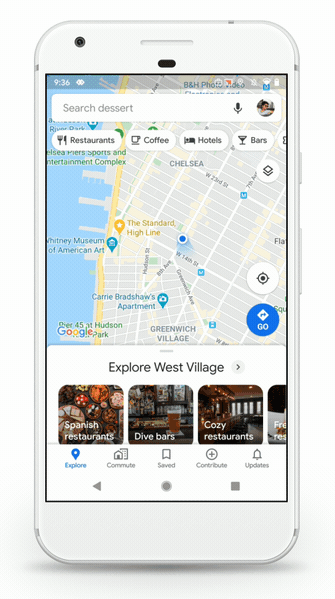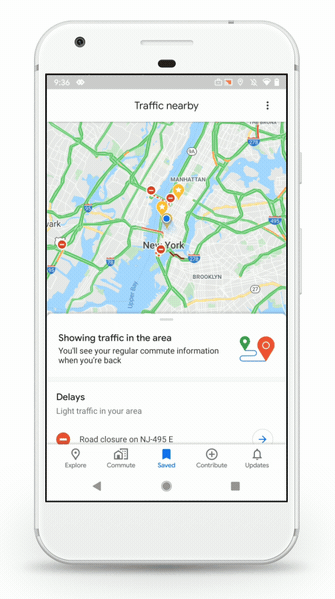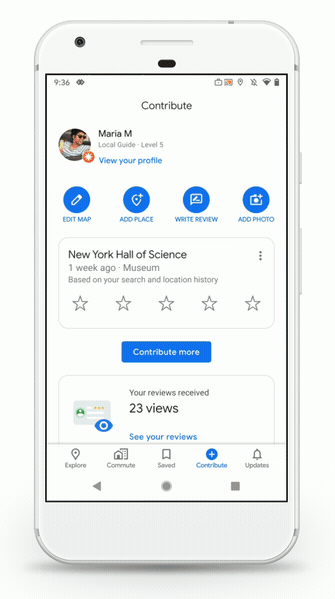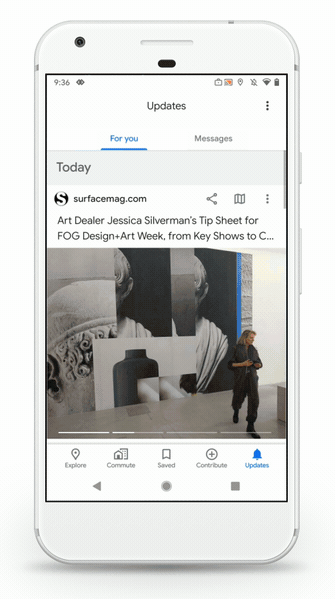
Google is updating Google Maps on Android and iOS with a revamped tab bar at the bottom, a new icon and a couple of new features. In particular, the company is putting more emphasis on user-generated content and recommendations.
At the bottom of the app, you now get five icons — Explore, Commute, Saved, Contribute and Updates. You could already save places and add more information to a Google Maps listing, but those features are now more visible. They’re no longer hidden in a side menu.
The Saved tab lets you easily access your saved places, lists and maps. You can also access the creepy timeline of all your past activity from the same menu now — you can disable location history in your Google account settings.
With the Contribute tab, you can see all your past contributions (reviews, photos, etc.) but also add content directly from that menu. In addition to reviews and photos, you can now directly suggest an edit and add a place from that menu instead of searching for a place and then adding or editing a place.
Finally, the Updates tab combines two existing features in a single view — a feed of recommendation (“For You”) as well messages from businesses. Google added the ability to message businesses in November 2018, but the inbox was a bit buried.
As for crowdsourced transit data, Google is expanding transit data beyond crowdedness reports. Google Maps prompts users to give more information about your bus or train ride at the end of the trip.
Users will now get prompts about the temperature, accessibility features and the presence of security cameras or security guards. In some regions, you’ll be able to say if there’s a women’s section. In Japan, Google Maps will offer you to pick a route with more carriages. Those features will roll out in March.
The company is also announcing some improvements to Live View, the feature that lets you see your route using augmented reality. For instance, you’ll be able to see a pin with your destination so that you get a better sense of where you should be headed.
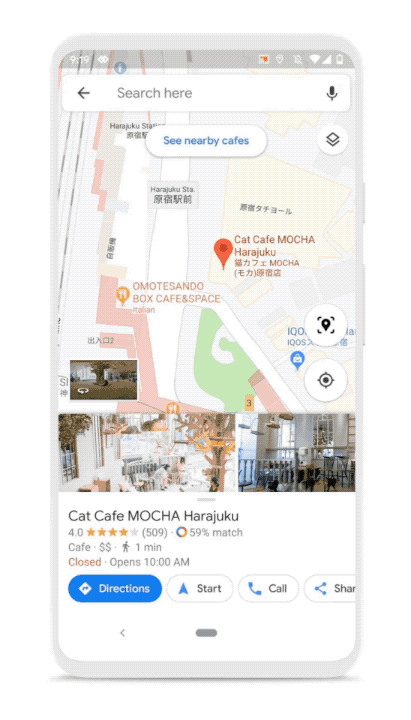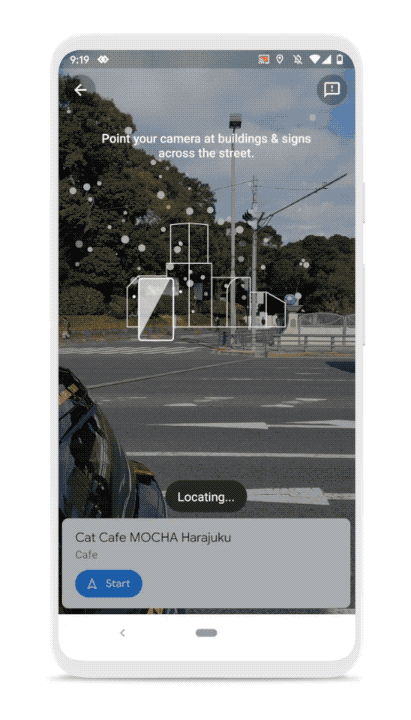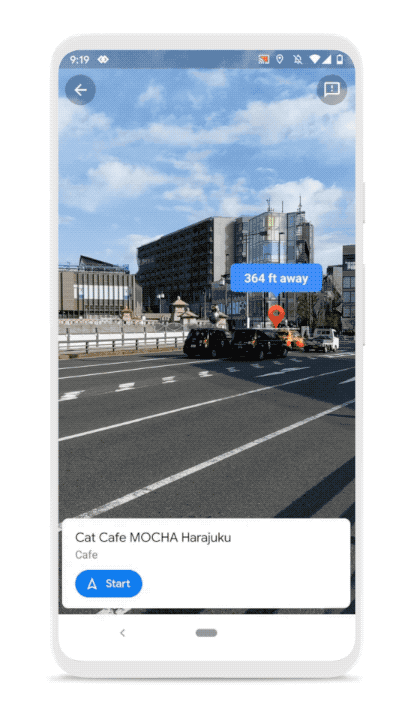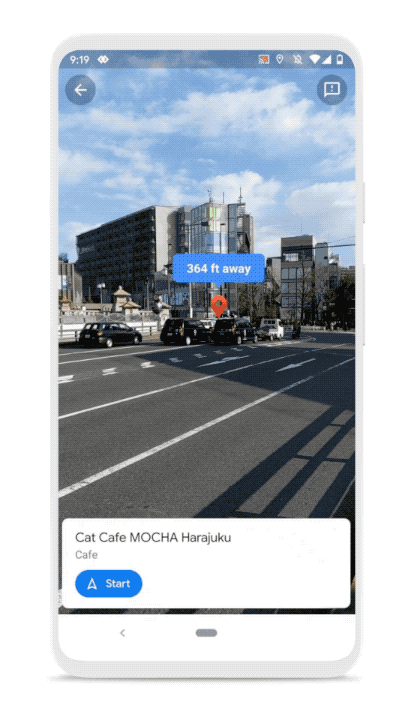
Finally, Google is updating the Google Maps logo. It’s a more minimalistic Google-colored pin.
Powered by WPeMatico
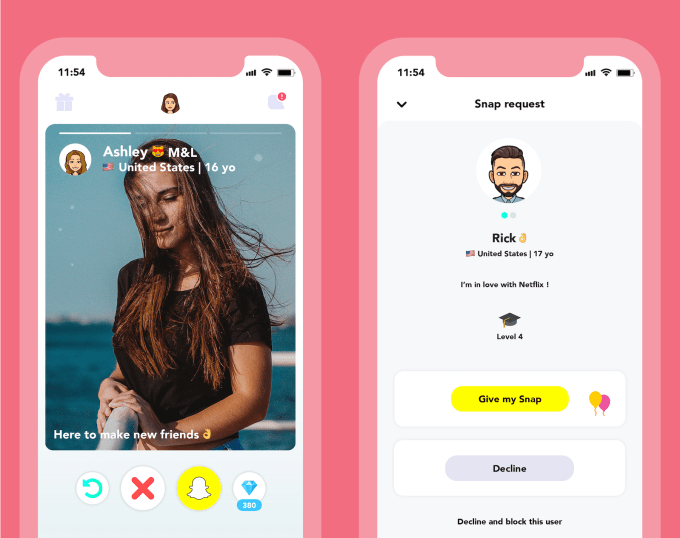
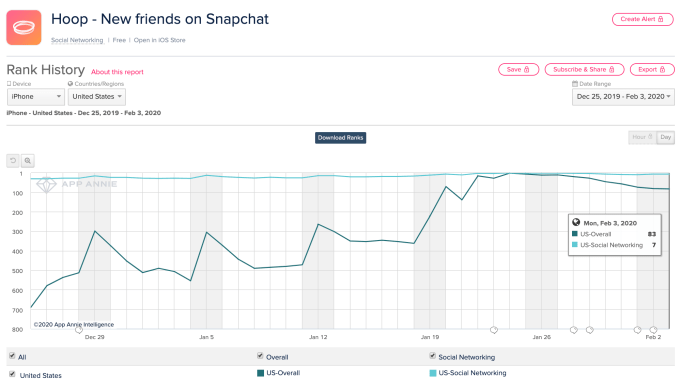
Snapchat’s developer platform is blowing up as a gateway to teen social app users. Hoop is the latest Snap Kit blockbuster, rocketing to No. 2 on the overall App Store charts this month with its Tinder -esque swiping interface for discovering people and asking to message with them over Snapchat. Within a week of going viral, unfunded French startup Dazz saw Hoop score 2.5 million downloads.
The fact that such a dumbfoundingly simple and already ubiquitous style of app was able to climb the charts so fast demonstrates the potential of Snap Kit to drive user lock-in for Snapchat. Because the developer platform lets other apps piggyback on its login system and Bitmoji avatars, it creates new reasons for users to set up a Snapchat account and keep using it. It’s the same strategy that made Facebook an entrenched part of the internet, but this time it’s for a younger crowd.
In the first-ever interview about Hoop, Dazz’s 26-year-old co-founders Lucas Gervais and Alexi Pourret reveal that the idea came from watching user patterns in their previous experiment on the Snap Kit platform. They built an app called Dazz in 2018 that let users create polls and get anonymous answers from friends, but they noticed their 250,000 users “always ended up adding each other on Snap. So we decided to create Hoop, the app to make new Snap friends,” Gervais tells me.
Gervais and Pourret have been friends since age two, growing up in small town in France. They met their two developers in high school, and are now marketing students at university. With Hoop, they say the goal was to “meet everyone’s needs, from connecting people from different cultures to helping lonely people to feel better to simply growing your Snapchat community.”

The Dazz / Hoop team (from left): Developers Julien Maire & Teddy Vallar, co-founders Alexi Pourret & Lucas Gervais
At first, Hoop for iOS or Android looks just like Tinder. You create an account with some photos and bio information, and start swiping through profiles. If you like someone, you tap a Snapchat button to request their Snap username so you can message them.
But then Hoop reveals its savvy virality and monetization strategy. Rather than being able to endlessly “swipe right” and approach people, Hoop limits your asks by making you spend its in-app “diamonds” currency to reach out. After about 10 requests to chat, you’ll have to earn more diamonds. You do that by sharing and getting friends to open your invite link to the app, adding people on Snapchat that you meet on Hoop, logging in each day, taking a survey, watching a video ad and completing offers by signing up for streaming services or car insurance providers. It also trades diamonds for rating Hoop in the App Store, though that might run afoul of Apple’s rules.
Those tactics helped Hoop climb as high as No. 2 on the overall iOS chart and No. #1 on the Social Apps chart on January 24th. It’s now at No. 83 overall and No. 7 in social, putting it above apps like Discord, LinkedIn, Skype and new Vine successor Byte. Hoop had more than 3 million installs as of a week ago.
There are certainly some concerns, though. Gervais claims that “We are not a meeting or dating app. We simply offer an easy way to make new Snap friends.” But because Tinder isn’t available for people under 18, they might be looking to Hoop instead. Thankfully, adults can’t see profiles of users under 18, and vice versa, and users only see potential matches in their age group. However, users can edit their age at any time.
Tools like Amazon’s AWS have made building a startup with a lean team and little money increasingly easy. Snap Kit’s ability to let developers skip the account creation and management process is another step in that direction. But the power to imbue overnight virality is something even Facebook never accomplished, though it helped build empires for developers like Zynga.
Another Snap Kit app called Yolo for receiving anonymous responses to questions shot up to No. 1 in May. Seven months later, it’s still at No. 51. That shows Snap Kit can offer longevity, not just flash-in-the-pan download spikes. Gervais calls the platform “a very powerful tool for developers.”
Three years ago I wrote that Snapchat’s anti-developer attitude was a liability. It needed to become a platform with a cadre of allies that could strengthen its role as an identity platform for teens, and insulate it against copycats like Facebook. That’s exactly what it did. By letting other apps launch themselves using its accounts, Stories and Bitmoji, they wouldn’t need to copy its social graph, sharing format or avatars, and instead would drive attention to the originals.
If Snap can keep building useful developer tools, perhaps by adding to its platform real-world object scanning, augmented reality filters and video calling, a Snapchat account could become a must-have for anyone who wants to use the next generation of apps. Then could come the crown jewel of a platform: discovery and virality. By building a section for promoting Snap Kit apps into Snapchat Discover, developers looking for shortcuts in both engineering and growth might join Evan Spiegel’s army.
Powered by WPeMatico
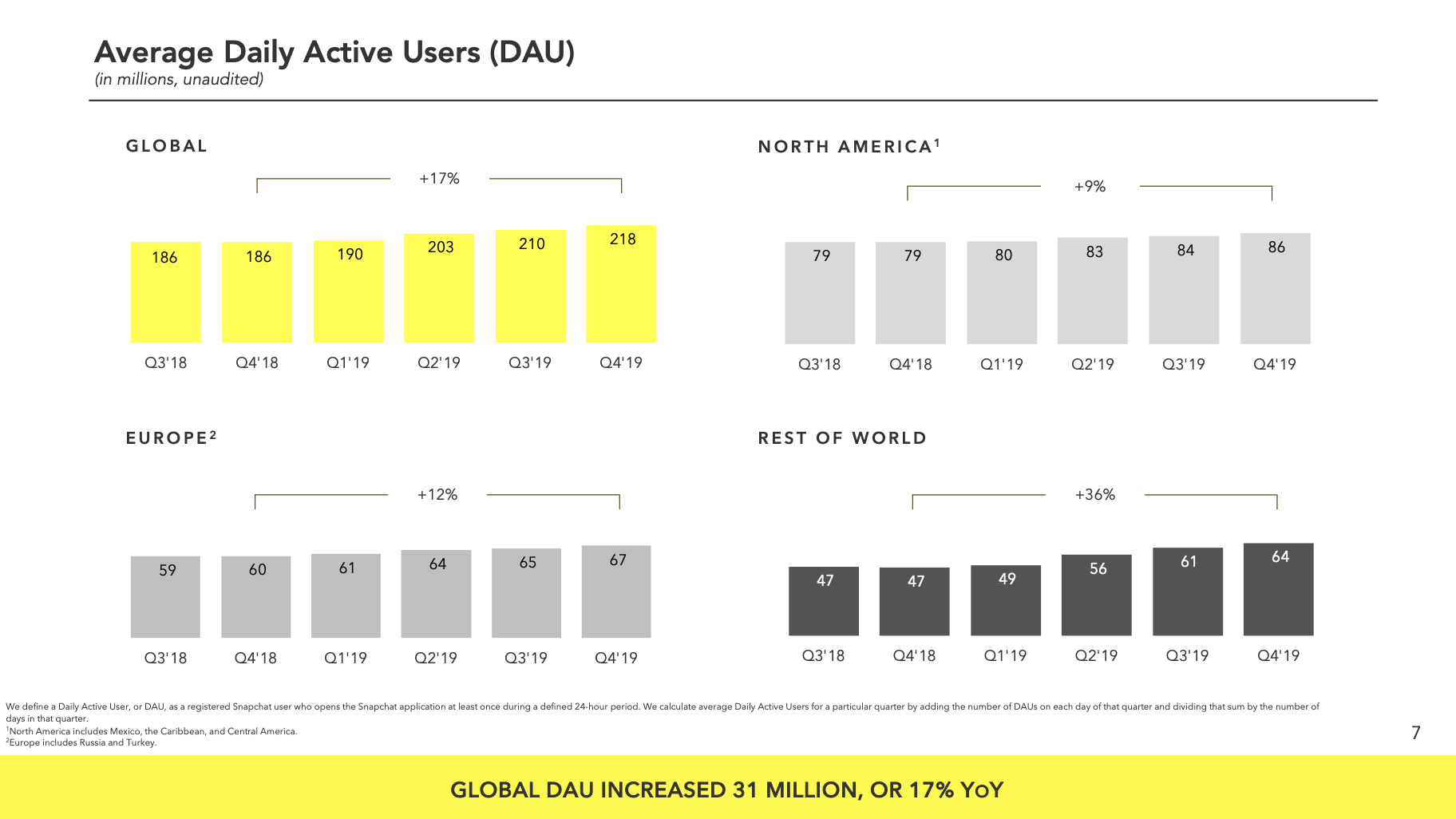
Snapchat still isn’t profitable nearly two years after its IPO. In Q4 2019, Snap lost $241 million on $560.8 million in revenue; that’s up 44% year-over-year and an EPS of $0.03. That comes from adding 8 million daily users to reach a total of 218 million up 3.8% this quarter from 210 million and 17% year-over-year.
The big problem was a one-time $100 million legal settlement that pushed it to lose $49 million more in Q4 2019 than Q4 2018. That comes from a shareholder lawsuit claiming Snap didn’t adequately disclose the impact of competition from Facebook on its business. The IPO was soured by weak user growth as people shifted from Snapchat Stories to Instagram Stories.
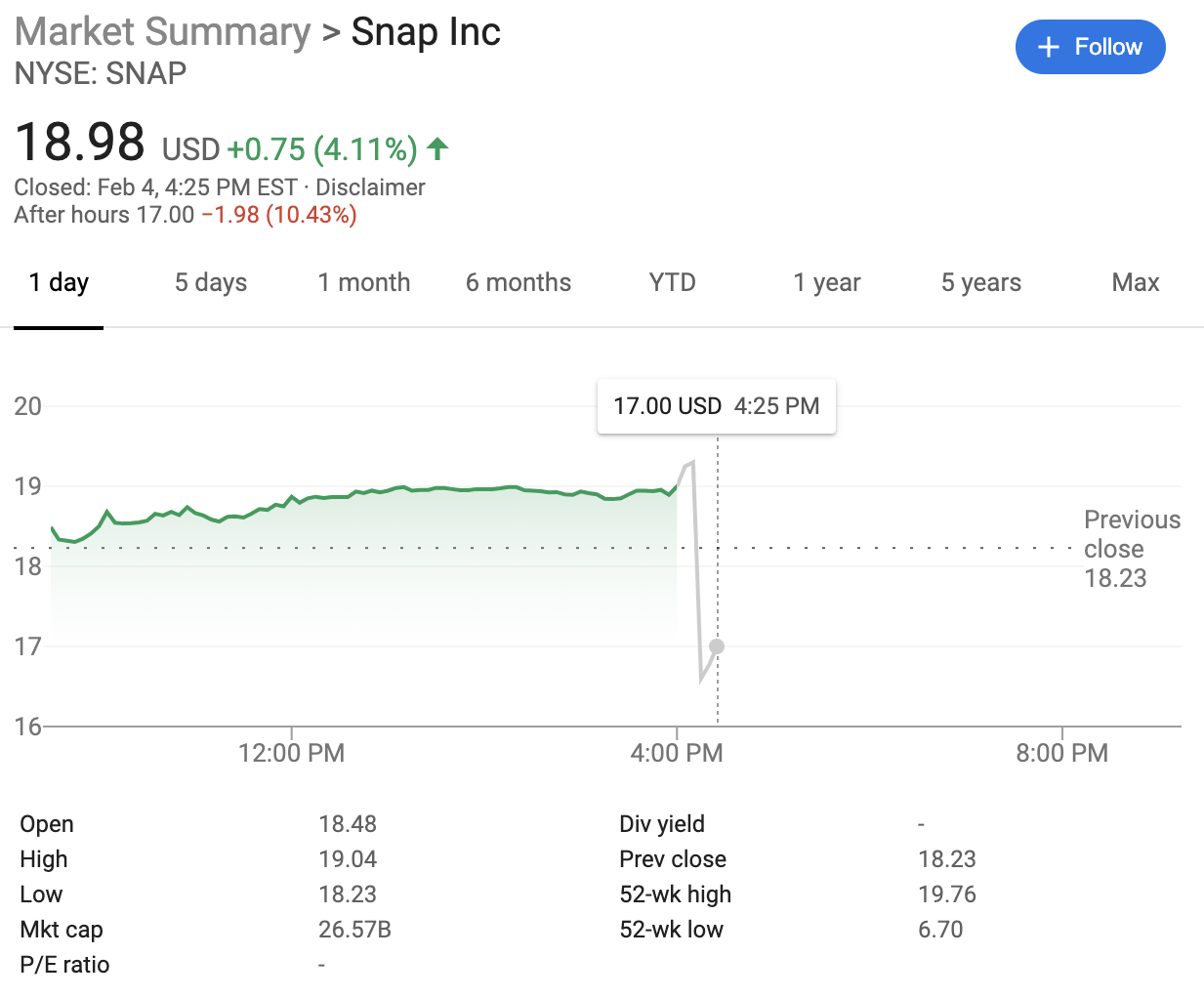
Snapchat had a mixed quarter compared to estimates, exceeding the EPS predictions but falling short on revenue. FactSet’s consensus predicted $563 million in revenue and a loss of $0.12 EPS. Estimize’s consensus came in at $568 million in revenue and an EPS gain of $0.02.
Snapchat shares plunged over 11% in after-hours trading following the announcement. Shares had closed up 4.17% at $18.99 today. That’s up from a low of $4.99 in December 2018 when its user count was shrinking under competition from Instagram Stories. It’s now hovering around its $17 IPO price, but it’s still under its post-IPO pop to $27.09.
Snap gave stronger than expected revenue guidance for Q1 2020 of $450 million to $470 million, and 224 million to 225 million users. The company’s CFO Derek Anderson says that “Q4 marked our first quarter of Adjusted EBITDA profitability at $42 million for the quarter, an improvement of $93 million over the prior year.” Still, he predicts an Adjusted EBITDA in Q1 of negative $90 million to negative $70 million. That’s manageable for Snap without raising more money, since it now has $2.1 billion in cash and marketable securities, down $148 million quarter-after-quarter.
“Throughout the course of 2019, we added 31 million daily active users, largely driven by investments in our core product and improvements to our Android application,” said Snapchat CEO Evan Spiegel . “We’ve recently completed our 2020 strategic planning process and have aligned our teams and resources around our goals of supporting real friendships on Snapchat, expanding our service to a broader global community, investing in our AR and content platforms, and scaling revenue while achieving profitability in order to self-fund our investments in the future.”
Some other highlights:
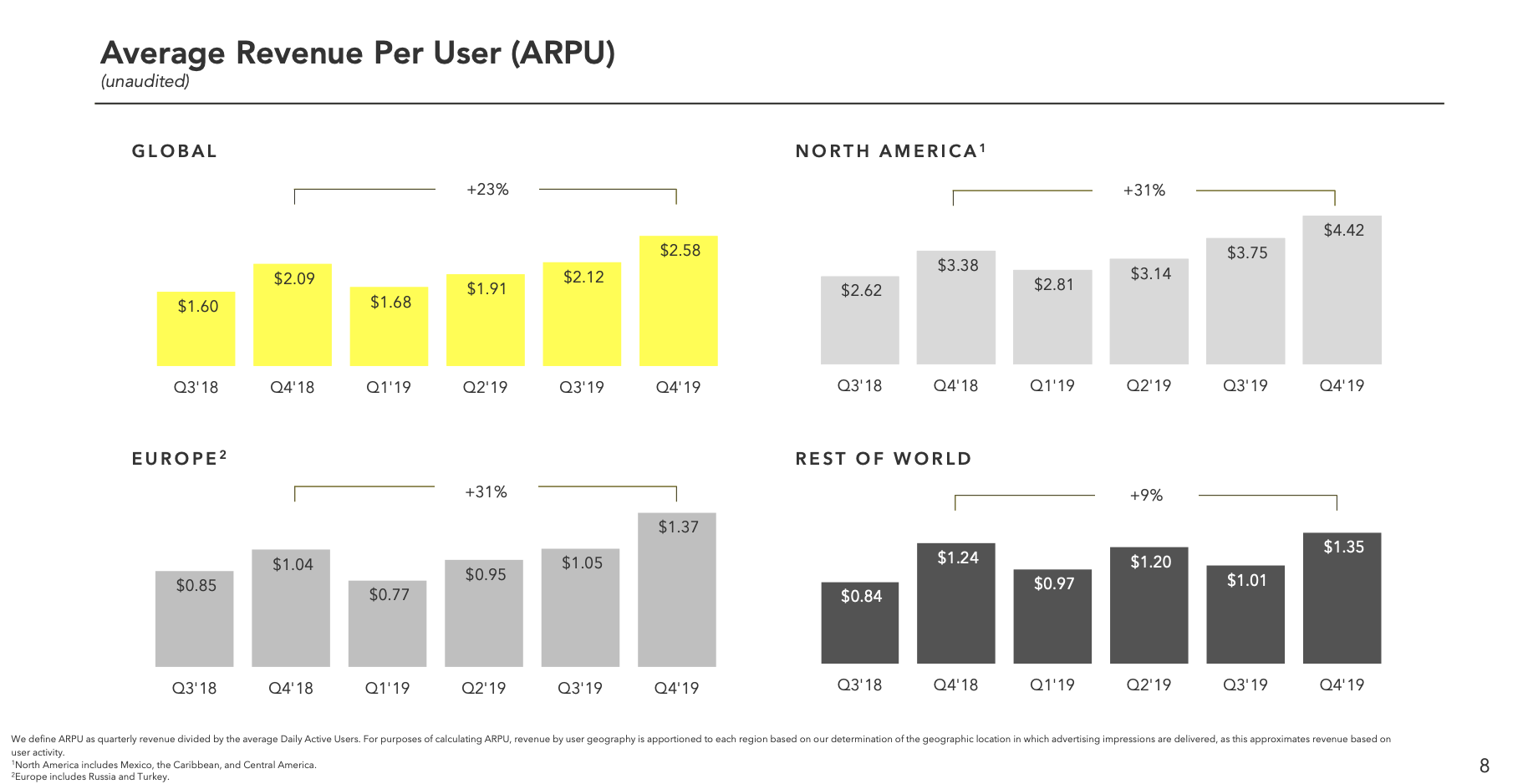
Snapchat’s user growth has been on a tear thanks to international penetration, especially in India, after it re-engineered its Android app for developing markets. It gained users in all markets. Crucially, it raised its average revenue per user 23% from $2.09 in Q4 2018 to $2.58, though only from $1.24 to $1.35 in the Rest of World region, where it’s growing user count the fastest. Snap will need to figure out how to squeeze more cash out of the international market to offset the costs of streaming tons of video to these users.
Q4 saw Snapchat readying several new products that could help boost engagement and therefore ad views. Cameos, first reported by TechCrunch, lets users graft their face onto an actor in an animated GIF like a lightweight deepfake. Bitmoji TV, which won’t run ads initially but could drive attention to Snapchat Discover, offers zany four-minute cartoons that star your Bitmoji avatar. We could see a bump to engagement from these starting in Q1 2020.
To retain its augmented reality filter creators, Snapchat has pledged $750,000 in payouts in 2020. It also expanded the use of product catalog ads, and now lets advertisers buy longer skippable ads.
Outside of the legal settlement, Snapchat is inching closer to profitability, but still has a ways to go. It has managed to develop a strong synergy between its popular chat feature that’s tougher to monetize, and the Stories and Discover content where it can inject ads. The big question is whether Facebook Messenger, Instagram and WhatsApp will get more serious about ephemeral messaging that’s at the core of Snapchat. If it can hold onto the market and maintain its place as where teens talk, it could ride out its costs and build revenue until it’s sustainable for the long-term.
Powered by WPeMatico
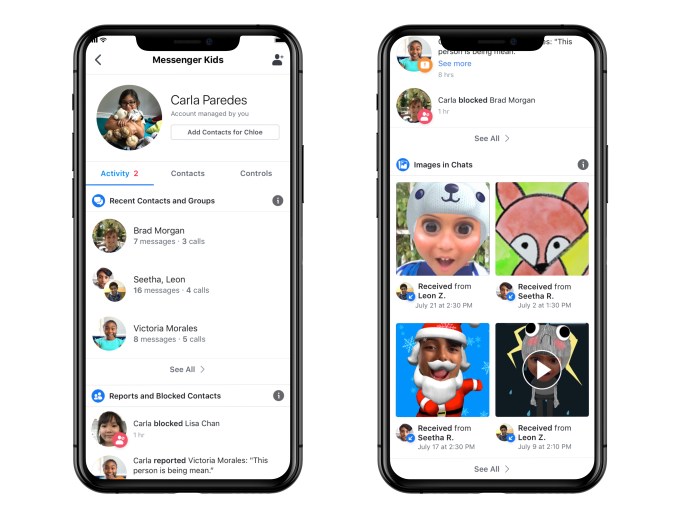
Facebook’s messaging app for families with children, Messenger Kids, is being updated today with new tools and features to give parents more oversight and control over their kids’ chats. Now, parents will be able to see who a child is chatting with and how often, view recent photos and videos sent through chat, access the child’s reported and block list, remotely log out of the app on other devices and download the child’s chats, images and videos, both sent and received. The company is also introducing a new blocking mechanism and has updated the app’s Privacy Policy to include additional information about data collection, use and deletion practices.
The Messenger Kids app was first introduced in late 2017 as a way to give kids a way to message friends and family with parental oversight. It arrived at a time when kids were already embracing messaging — but were often doing so on less controlled platforms, like Kik, which attracted predators. Messenger Kids instead allows the child’s parents to determine who the child can chat with and when, through built-in parental controls.
In our household, for example, it became a convenient tool for chatting with relatives, like grandparents, aunts, uncles and cousins, as well as a few trusted friends, whose parents I knew well.
But when it came time to review the chats, a lot of scrolling back was involved.
The new Messenger Kids features will help with the oversight aspects for those parents who allow their kids to online chat. That decision, of course, is a personal one. Some parents don’t want their kids to have smartphones and outright ban apps, particularly ones that allow interactions. Others, myself included, believe that teaching kids to navigate the online world is part of your parental responsibility. And despite Facebook’s reputation, there aren’t other chat apps offering these sort of parental controls — or the convenience of being able to add everyone in your family to a child’s chat list with ease. (After all, grandma and grandpa are already on Facebook and Messenger, but getting them to download new apps remains difficult.)
In the updated app, parents will be able to see who a child has been chatting with, and whether that’s text or video chat, over the past 30 days. This can save parents’ time, as they may not feel the need to review chat with trusted family members, for instance, so can redirect their focus and energy on reviewing the chats with friends. A log of images will help parents to see if all images and videos being sent and received are appropriate, and remove them or block them if not.
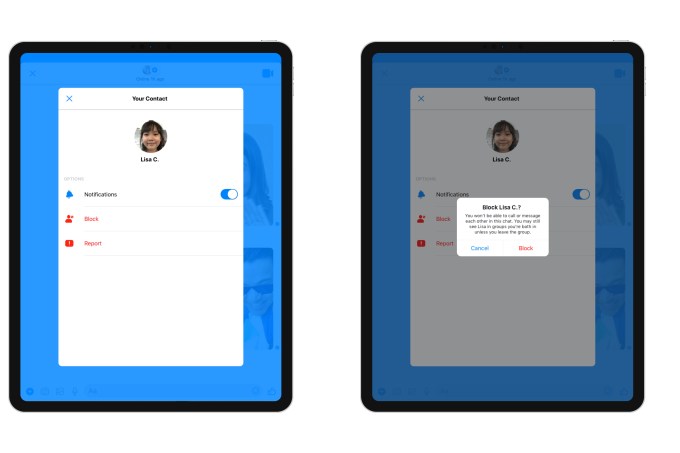
Parents also can now see if a child has blocked or reported a user in the app, or if they’ve unblocked them. This could be useful for identifying those problematic friends — the kind who sometimes cause trouble, but are later forgiven, then unblocked. (Anyone who’s dealt with tween-age drama can attest to the fact that there’s one in every group!) By gaining access to this information, parents can sit down with the child to talk about when to take that step and block someone, and when a disagreement with a friend can instead be worked out. These are decisions that a child will have to make on their own one day, so being able to use this as a teaching moment is useful.
With the update, unblocking is supported and parents are still able to review chats with blocked contacts. However, blocked contacts will remain visible to one another and will stay in shared group chats. They just aren’t able to message one-on-one. Kids are warned if they return to or are added to chats with blocked contacts. (If parents want a full block, they can just remove the blocked contact from the child’s contact list, as before.)
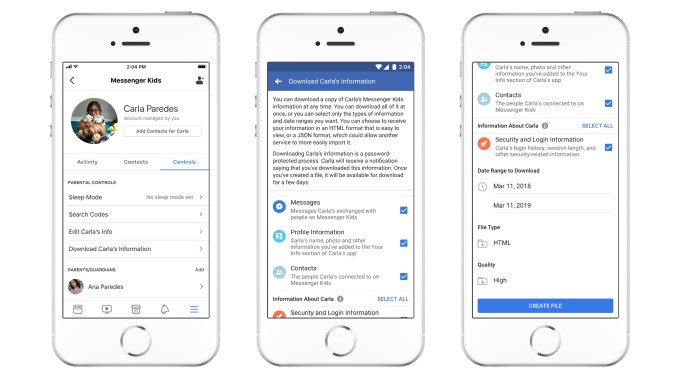
Remote device logout lets you make sure the child is logged out of Messenger Kids on devices you can’t physically access and control — like a misplaced phone. And the option to download the child’s information, similar to Facebook’s feature, lets you download a copy of everything — messages, images and videos. This could be a way to preserve their chat history when the child outgrows the app.
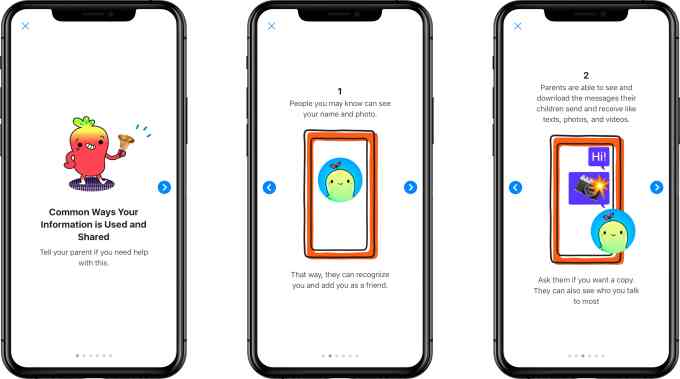
The Messenger Kids’ privacy policy was updated, as well, to better detail the information being collected. The app also attempts to explain this in plain language to the kids, using cute photos. In reality, parents should read the policy for themselves and make a decision, accordingly.
The app collects a lot of information — including names, profile photos, demographic details (gender and birthday), a child’s connection to parents, contacts’ information (like most frequent contacts), app usage information, device attributes and unique identifiers, data from device settings (like time zones or access to camera and photos), network information and information provided from things like bug reports or feedback/contact forms.
To some extent, this information is needed to help the app properly operate or to alert parents about a child’s activities. But the policy includes less transparent language about the collected information being used to “evaluate, troubleshoot, improve, create, and develop our products” or being shared with other Facebook Companies. There’s a lot of wiggle room there for extensive data collection on Facebook’s part. Service providers offering technical infrastructure and support, like a content delivery network or customer service, may also gain access to collected information, but must adhere to “strict data confidentiality and security obligations,” the policy claims, without offering further details on what those are.
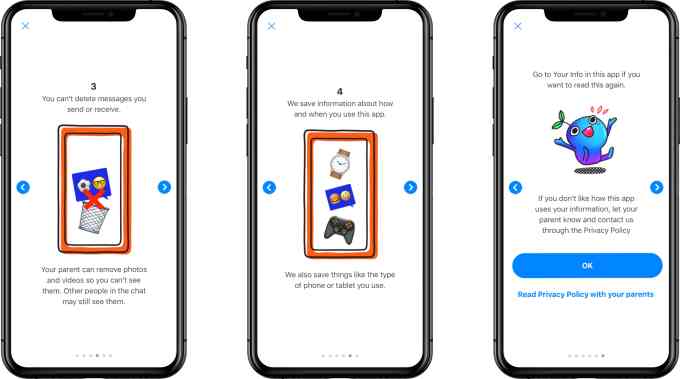
Despite its lengthiness, the policy leaves plenty of room for Facebook to collect private information and share it. If you have a Facebook account, you’ve already agreed to this sort of “deal with the devil” for yourself, in order to benefit from Facebook’s free service. But parents need to strongly consider if they’re comfortable making the same decision for their children.
The policy also describes things Facebook plans to roll out later, when Messenger Kids is updated to support older kids. As kids enter tween to teen years, parents may want to loosen the reigns a bit. The new policy will cover those changes, as well.
It’s unfortunate that the easiest tool, and the one with the best parental controls, is coming from Facebook. The market is ripe for a disruptor in the kids’ space, but there’s not enough money in that, apparently. Facebook, of course, sees the potential of getting kids hooked early and can invest in a product that isn’t directly monetized. Few companies can afford to do this, but Apple would be the best to take Facebook on in this area.
Apple’s iMessage is a large, secure and private platform — but it lacks these advanced parental controls, as well as the other bells and whistles (like built-in AR filters) that make the Messenger Kids app fun. Critically, it doesn’t work across non-Apple devices, which will always be a limiter when it comes to finding an app that the extended family can use together.
To be clear, there is no way to stop Facebook from vacuuming up the child’s information except to delete the child’s Messenger Kids Account through the Facebook Help Center. So consider your choices wisely.
Powered by WPeMatico
Lip-syncing app Dubsmash was on the brink of death. After a brief moment of virality in 2015 alongside Vine (R.I.P), Dubsmash was bleeding users faster than it could recruit them. The app let you choose an audio track like a rap song or movie quote and shoot a video of you pretending to say the words. But there was nowhere in the app to post the videos. It was a creation tool like Hipstamatic, not a network like Instagram. There’s a reason we’re only using one of those today.
So in 2017, Dubsmash‘s three executives burned down the 30-person company and rebuilt something social from the ashes with the rest of the $15.4 million it’d raised from Lowercase Capital, Index Ventures and Raine. They ditched its Berlin headquarters and resettled in Brooklyn, closer to the one demographic still pushing Dubsmashes to the Instagram Explore page: African-American teenagers posting dances and lip-syncs to indie hip-hop songs on the rise.
Dubsmash stretched its funding to rehire a whole new team of 15. They spent a year coding a new version of Dubsmash centered around Following and Trending feeds, desperately trying to match the core features of Musically, which by then had been bought by China’s ByteDance. It’s got chat but still lacks the augmented reality filters, cut transitions and photo slideshows of TikTok. But Dubsmash has the critical remix option for soundtracking your clip with the audio of any other video that sets it apart from Instagram and Snapchat.
Few social apps have ever pulled off a real comeback. Even Snapchat had only lost 5 million of its 191 million users before it started growing again. But in the case of Dubsmash, its biggest competitor was also its savior.

The pre-relaunch version of Dubsmash
In August 2018, ByteDance merged Musically into TikTok to form a micro-entertainment phenomenon. Instead of haphazardly sharing auto-biographical Stories shot with little forethought, people began storyboarding skits and practicing dances. The resulting videos were denser and more compelling than content on Snapchat and Instagram. The new Dubsmash, launched two months later, rode along with the surge of interest in short-form video like a Lilliputian in a giant’s shirt pocket. The momentum helped Dubsmash raise a secret round of funding last year to keep up the chase.
Now Dubsmash has 1 billion video views per month.
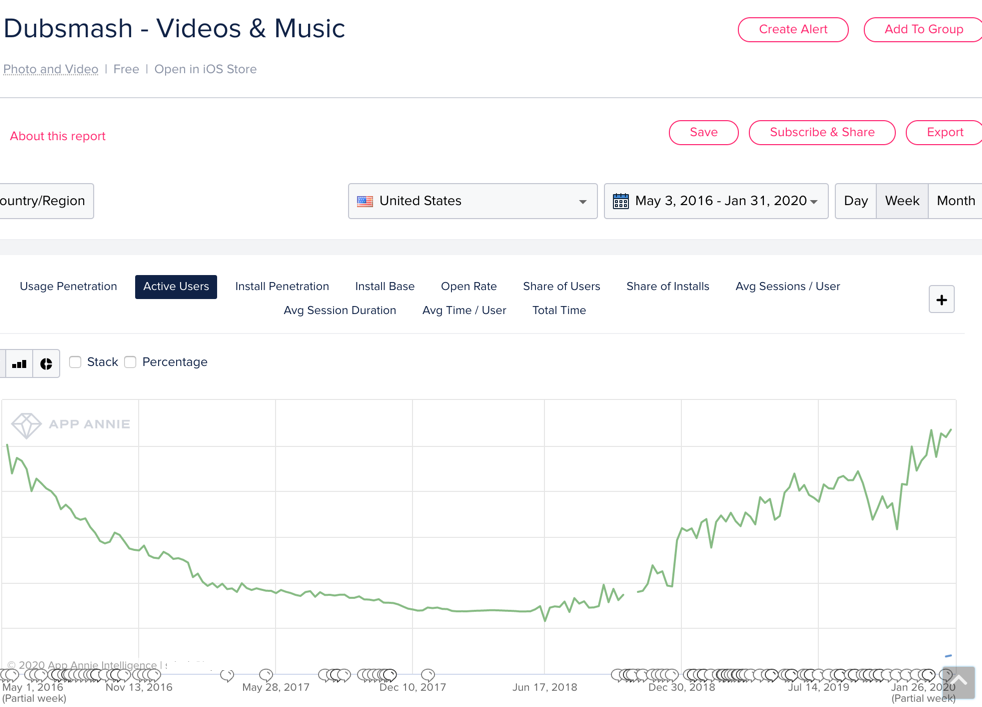
Dubsmash rebuilt its app and revived its usage
“The turnaround that we executed hasn’t been done in recent memory by a consumer app in such a competitive marketplace. Most of them fade to oblivion or shut down,” Dubsmash co-founder and president Suchit Dash tells me. “By moving the company to the United States, hiring a brand new all-star team and relaunching the product, we gave this company and product a second life. Through that journey, we obsessed only on one metric: retention.”
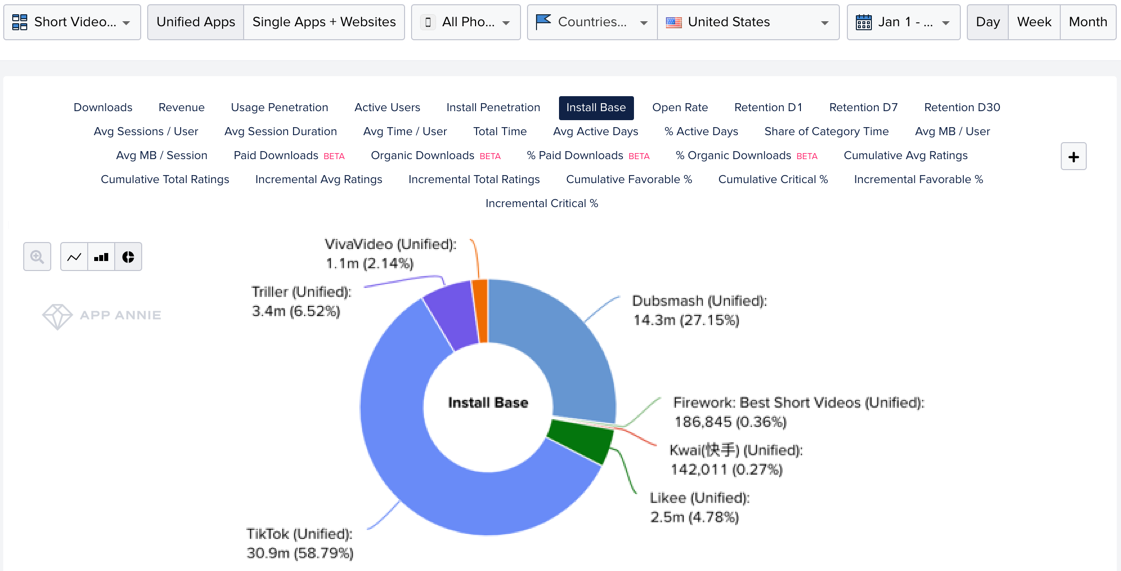
Now the app has pulled 27% of the U.S. short-form video market share by installs, second only to TikTok’s 59%, according to App Annie. Sensor Tower tells TechCrunch that TikTok has about 3X as many U.S. lifetime installs as Dubsmash, and 11X more between when Musically became TikTok in August 2018 and now. [Note: These statistics are based on polling methods and TechCrunch cannot confirm their exact accuracy.]
In terms of active users outside of TikTok, Dubsmash has 73% of the U.S. market, compared to just 23% on Triller, 3.6% on Firework and an embarrassing 0% on Facebook’s Lasso. And while Triller began surpassing Dubsmash in downloads per month in October, Dubsmash has 3X as many active users and saw 38% more first-time downloads in 2018 than 2019. Dubsmash now sees 30% retention after a month, and 30% of its daily users are creating content.
It’s that stellar rate of participation that’s brought Dubsmash back to life. It also attracted a previously unannounced round of $6.75 million in the spring of 2019, largely from existing investors. While TikTok’s superstars and huge visibility could be scaring some users away from shooting videos while a long-tail of recent downloaders watch passively, Dubsmash has managed to make people feel comfortable on camera.
“Dubsmash is ground zero for culture creation in America — it’s where the newest, most popular hip-hop and dance challenges on the internet originate,” Dash declares. “Members of the community are developing content that will make them the superstars of tomorrow.”
Being No. 2 might not be so bad, given how mobile video viewing is growing massively thanks to better cameras, bigger screens, faster networks and cheaper data. Right now, Dubsmash doesn’t make any money. It hopes to one day generate revenue while helping its creators earn a living too, perhaps through ad revenue shares, tipping, subscriptions, merchandise or offline meetups.

One advantage of not being TikTok is that the app feels less crowded by semi-pro creators and influencers. That gives users the vibe that they’re more likely to hit the Trending or Explore page on Dubsmash. The Trending page is dominated by hot new songs and flashy dances, even if they’re shot with a lower production quality that feels accessible.
Dubsmash tries to stoke that sense of opportunity by making Explore about discovering accounts and all the content they’ve made rather than specific videos. While popular clips might have tens of thousands of views rather than the hundred-thousand or multi-million counts on TikTok’s top content, there’s enough visibility to make shooting Dubsmashes worth it.
TikTok has already taken notice. Shown in a leak of its moderation guidelines from Netzpolitik, the company’s policy is to downrank the visibility of any video referencing or including a watermark from direct competitors, including Dubsmash, Triller, Lasso, Snapchat and WhatsApp. That keeps Dubsmash videos, which you can save to your camera roll, from going viral on TikTok and luring users away.
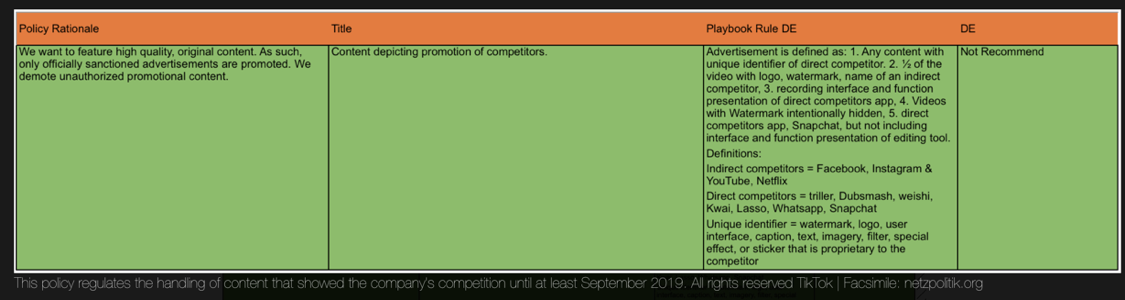
TikTok’s content moderation guidelines show it downranks content featuring the watermarks of competitors like Dubsmash
TikTok also continues to aggressively buy users via ads on competing apps like Facebook thanks to the billions in funding raked in by its parent ByteDance. In contrast, Dash says Dubsmash has never spent a dollar on user acquisition, influencer marketing or any other source of growth. That makes it achieving even half to a third of as many installs as TikTok in the U.S. an impressive fete.
Why would creators choose Dubsmash over TikTok? Dash clinically explains that it’s a “decoupled audio and video platform that enables producers and tastemakers to upload fresh, original tracks that are utilized by creators and influencers alike,” but that it’s also about “its role as a welcoming home for a community that’s underrepresented on social platforms.”
If Dubsmash keeps growing, though, it will encounter the inevitable content moderation problems that come with scale. It’s already doing a solid job of requiring users to sign up with their birth date to watch or post videos, and it blocks those under 13. Only users who follow each other can chat.
Any piece of content that’s flagged by users is hidden from the network until it passes a review by its human moderation team that works around the clock, and it does proactive takedowns too. However, brigading and malicious takedown reports could be used by trolls to silence their enemies. Dubsmash is working off of a common sense model of what’s allowed rather than firm guidelines, which will be tough to keep consistent at scale.
“Being a social media app in 2020 means you need to take greater responsibility for the well-being of the community,” says Dash. “We decided upon relaunch to take a strict perspective. Our goal is to be intentional and proactive early, and invest in safety and healthy growth rather than growth at all costs. This may not be the most popular approach amongst the market, but we believe this is the most effective way to build a social platform.”

Dubsmash proves that short-form video is so compelling to teens that the market can sustain multiple apps. That will have to be the case, given Instagram is preparing to release its TikTok clone, Reels, and Vine’s co-founder Dom Hofmann just launched his successor, Byte. The breakdown could look like:
Perhaps we’ll eventually see consolidation in the market, with giants like TikTok and Instagram acquiring smaller players to grow their content network effect with more fodder for remixes. But fragmentation could breed creativity. Different tools and audiences beg for different types of videos. Make something special, and there’s an app out there to enter you into pop culture cannon.
For more on the short-form video wars and the future of micro-entertainment, read:
Powered by WPeMatico
Medloop, which allows patients to manage healthcare needs and providers, has secured €6 million from Kamet Ventures and AXA.
The cash will be used to enhance its product offering and continue expansion across Germany and the U.K. Medloop is also developing an evidence-based medical rule engine embedded on the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) of patients.
Medloop offers patients what it calls “intuitive” self-service features in an app that enables them to navigate their own healthcare, including online appointment bookings, electronic medical results and prescription refills, as well as chatting in-app with healthcare providers.
Founded in 2018 by Berlin-based entrepreneur Shishir Singhee, some medical practices in Germany use the Medloop doctor system to run their entire practice, using it to give an overview of their patient population.
Singhee, said: “Healthcare today has become increasingly impersonalized as ever-growing patient registers have made it challenging for doctors to treat patients in a bespoke way. Medloop strives to bridge this critical gap, by employing technology to empower patients and help doctors deliver proactive and holistic care.“
Stephane Guinet, CEO of Kamet Ventures, said: “It is no secret how overstretched doctors are in terms of the time and care they can offer each patient. Medloop’s offering is a novel solution to this challenge and we are very excited to be part of Medloop’s growth story given how critical its offering is to the U.K. market and beyond.”
Medloop achieved compatibility with EMIS last summer, enabling its entry into the U.K. market.
In Germany, its main competitors are the incumbents that were built in the early 1990s, such as Medatix and Medistar. In the U.K. it is up against patient management tools such as QMasters.
Powered by WPeMatico
If you were the star of every show, would you watch more mobile television? Snapchat is betting that narcissism drives resonance for its new weekly videos that put you and your friends’ customizable Bitmoji avatars into a flurry of silly animated situations. Bitmoji TV premieres on Saturday morning, and it’s remarkably funny, exciting and addictive. Think cartoon SNL on fast-forward, with you playing a secret agent, a zombie president or a Moonlympics athlete.
It’s a style of content only Snapchat could pull off that relies on ubiquitous personalized avatars only Snapchat owns. The company says 70% of its daily active users, or 147 million of its 210 million, have made themselves a Bitmoji. Snapchat bought Bitmoji’s parent company Bitstrips in 2016 for a steal at $62.5 million, and it’s paying off. Amidst a sea of premium video and haphazard Stories that blur together across streaming services and social apps, Snapchat finally found something Facebook can’t copy.

“We really believe that we have invented a new category of entertainment. It’s scripted but it’s personalized. You could take that in a million directions,” says Bitmoji co-founder and CEO Ba Blackstock, who wrote and directed Bitmoji TV. “First and foremost, I hope that everyone who watches this has kind of a mind-blowing experience that they’ve never had before.”
Bitmoji TV, which TechCrunch was first to report Snapchat was building last month, will have its own Snapchat Show page where users can subscribe to get notifications and see new episodes on the Discover Page. Users can visit this page on mobile or tap and hold on the Snapcode below while pointing at it with the Snapchat camera to open Bitmoji TV.

The show is designed to be PG-13, with some bleeped out swearing and a little bloody violence. The shows are made out of Bitmoji’s Toronto office and are based on North American TV, film and advertising. Each episode cuts away and back to a main story, with the first two centered around an America’s Best Bitmoji game show and a Mime Cops hostage negotiation. Interspersed are “channel flips” between shorter single-gag clips that take your avatar into sit-coms, soap operas, action movies and infomercials.
The gags are ridiculous. At the basketball “Moonlympics,” a player jumps up for a dunk, but low gravity causes him to crash through the glass dome and suck all the other players into space. At Cannibal High, an school announcement says “Attention students, we’re all deeply saddened by the sudden passing of Vice Principal Schneider. To honor his legacy, today the cafeteria will be serving Vice Principal Schneider.”
You’re not alone it Bitmoji TV. There’ll be occasional celebrity guests like Randy Jackson, Andy Richter and Jon Lovitz. But your co-star in these segments is the Bitmoji of whichever person you last interacted with on Snapchat. That lets you control whether you want your best friend, your significant other or some rando alongside you. That decision will change the way you interpret the jokes and scenes. Your Bitmoji won’t talk, but their’s will.
Getting philosophical, Blackstock explains that “When you say words to me, it’s not just your words in a vacuum. They’re coming from you. You’re the medium . . . In any narrative fiction you learn about the characters, they have a back story, they have relationships that exist under the story that color it.” Who you make your supporting actor lends personal subtext that enriches each story. That’s one reason you can’t download or easily share clips of your version of Bitmoji TV, and Snap instead just lets you share a link to watch the real thing. Blackstock says it just doesn’t have the same effect if you’re not in the spotlight.
One thing you won’t find in Bitmoji TV, at least at first, are advertisements. The initial 10-episode season won’t have them. But that does seem to be the plan. When I asked Blackstock about monetizing the show, he said, “You can imagine. Discover has a business model of showing ads.” Since it make Bitmoji TV, Snapchat would get to keep that ad money rather than paying it out with revenue shares to partners or by buying content. Just as we’ve seen music and video streaming apps move to cut royalty expenses by creating content in-house, Snap seems to have the same idea.
Snapchat has yet to monetize Bitmoji directly beyond its merchandise store where you can get yours on t-shirts and mugs. Surprisingly, it doesn’t sell premium or branded clothes and looks for Bitmoji, nor does it allow brands to pay to have their apparel featured.
Snap did recently start letting people mix-and-match clothes for their Bitmoji, and when asked if that could foreshadow a revenue opportunity, Blackstock said, “You gotta build the store before you start selling the clothes . . . this was a foundational evolution designed to not only improve the experience for users but to set the stage for things to come.” You and your friends seeing your avatar’s fresh outfit on Bitmoji TV might make people care more about what their digital mini-mes wear.
![]()
Having watched the first three episodes, I’m pretty certain Bitmoji TV is going to be a hit. The show embodies the whimsy of Snapchat and the youth culture of the community who uses it. It’s rare to see something so premium but so unabashedly kooky. It’s reminiscent of the Rick and Morty “Interdimensional Cable” episodes that similarly feature rapid-fire snippets of fake and absurd TV shows.
Yet “the idea for Bitmoji TV actually precedes Bitmoji. It’s something I’ve been thinking about since those days [before Snapchat acquired it]. In a way it precedes Bitstrips. I’ve been making comics and cartoons since I was a little kid,” Blackstock tells me. “How I met two of the co-founders of Bitstrips was passing them comics in class. Even after school when we had jobs I would draw comics of my co-founder that were very compromising and I would fax them to his office to try to get him fired,” he recalls with a hearty laugh. Now he has the budget to make them TV-worthy, but just as crazy.
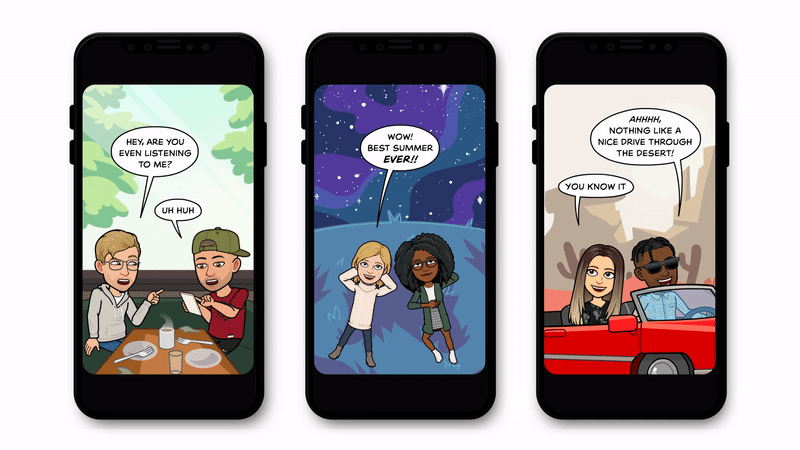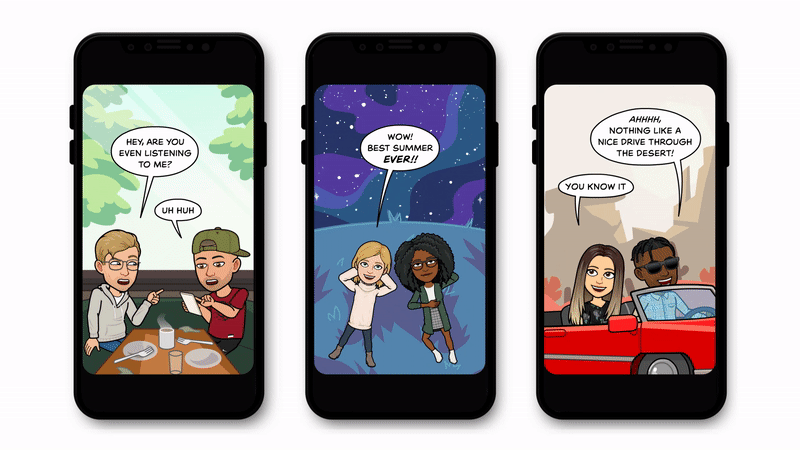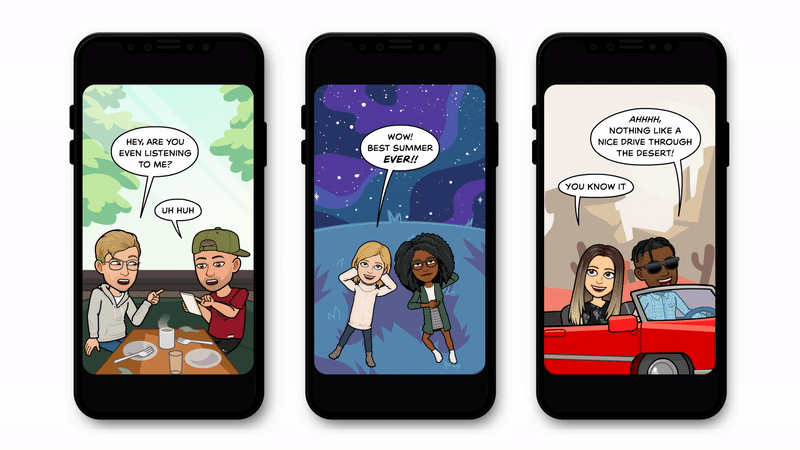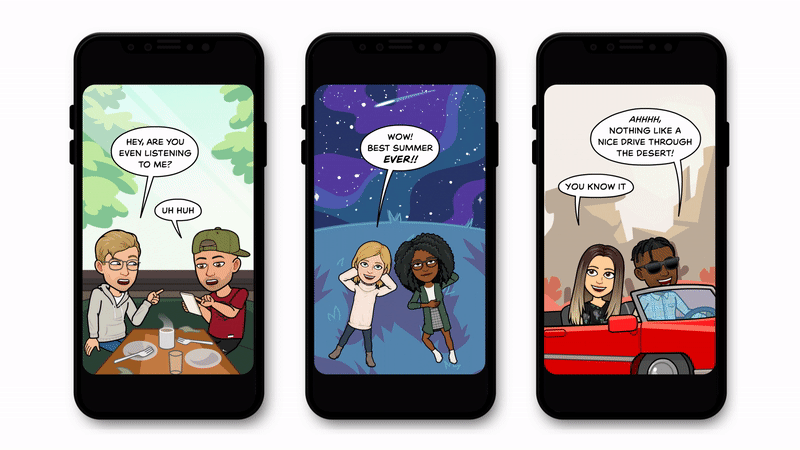
Snapchat has a good hunch it’s going to work because it’s been testing a comic-stripped down version called Bitmoji Stories. These still or lightly animated slideshows use the same idea of starring the avatars of you and your friends, but without full-motion video or constant audio. Indeed, 130 million people have watched Bitmoji Stories since they launched in late 2018.
As Blackstock tells me, “They were easier to make at a high volume and release ongoingly, which we could put out as a prelude to get our audience ready for personalized content — but also for us to learn from and see how people responded and figure out our own processes in terms of production.” Snapchat had animators and engineers work hand in hand to build a rendering system for Bitmoji Stories and TV. That helps it rapidly produce the personalizable content that can flex to accommodate any shaped avatar without them clipping into their surroundings.
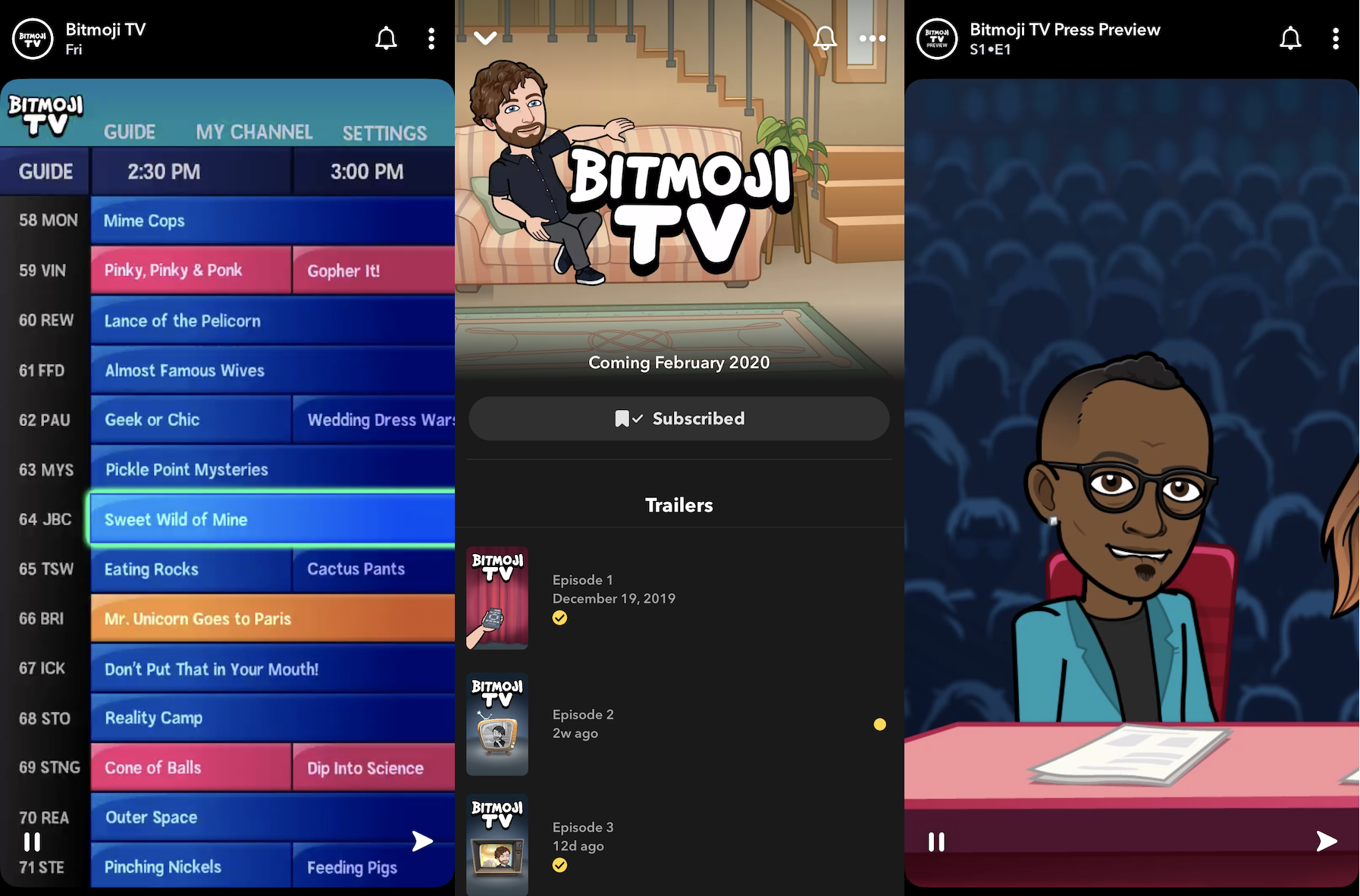
Tonight, Bitmoji TV will receive an in-person “silent disco-style” premiere at Los Angeles’ Soho House. Guests will scan a code on the big screen, don headphones and each watch on their own phone with themselves as the star.
Snapchat’s head of original content Sean Mills tells me that “New technology will unlock new kinds of storytelling,” citing “the power of bringing a user into the experience with their best friends.” Bitmoji TV has certainly found a way to turn vanity into engagement. It’s more compelling than the mediocre originals on Facebook Watch. And it’s technologically innovative, unlike the planned lineup for Quibi.
If the modern era of visual communication began with the selfie, Snap honed it into a messaging tool. A few words were more interesting with a friend’s face behind it. The original Bitmoji chat stickers let your face say whatever you wanted even without having to get on camera. Snapchat’s new Cameo feature grafts your face into GIFs to express even more complex feelings. And now with Bitmoji TV, an animated version of your face can live out your wildest fantasies or weirdest dreams. That’s something worth tuning into.
Powered by WPeMatico
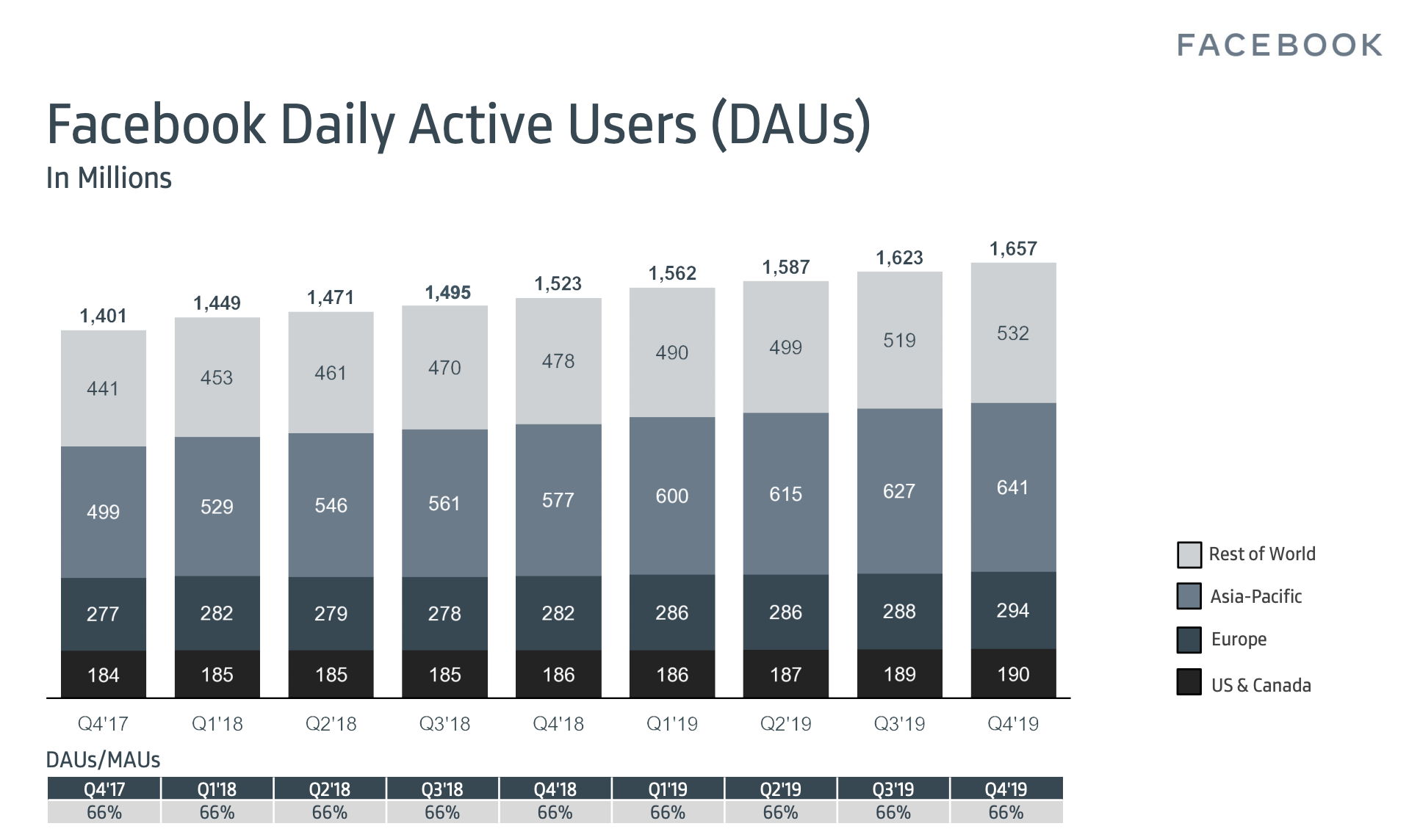
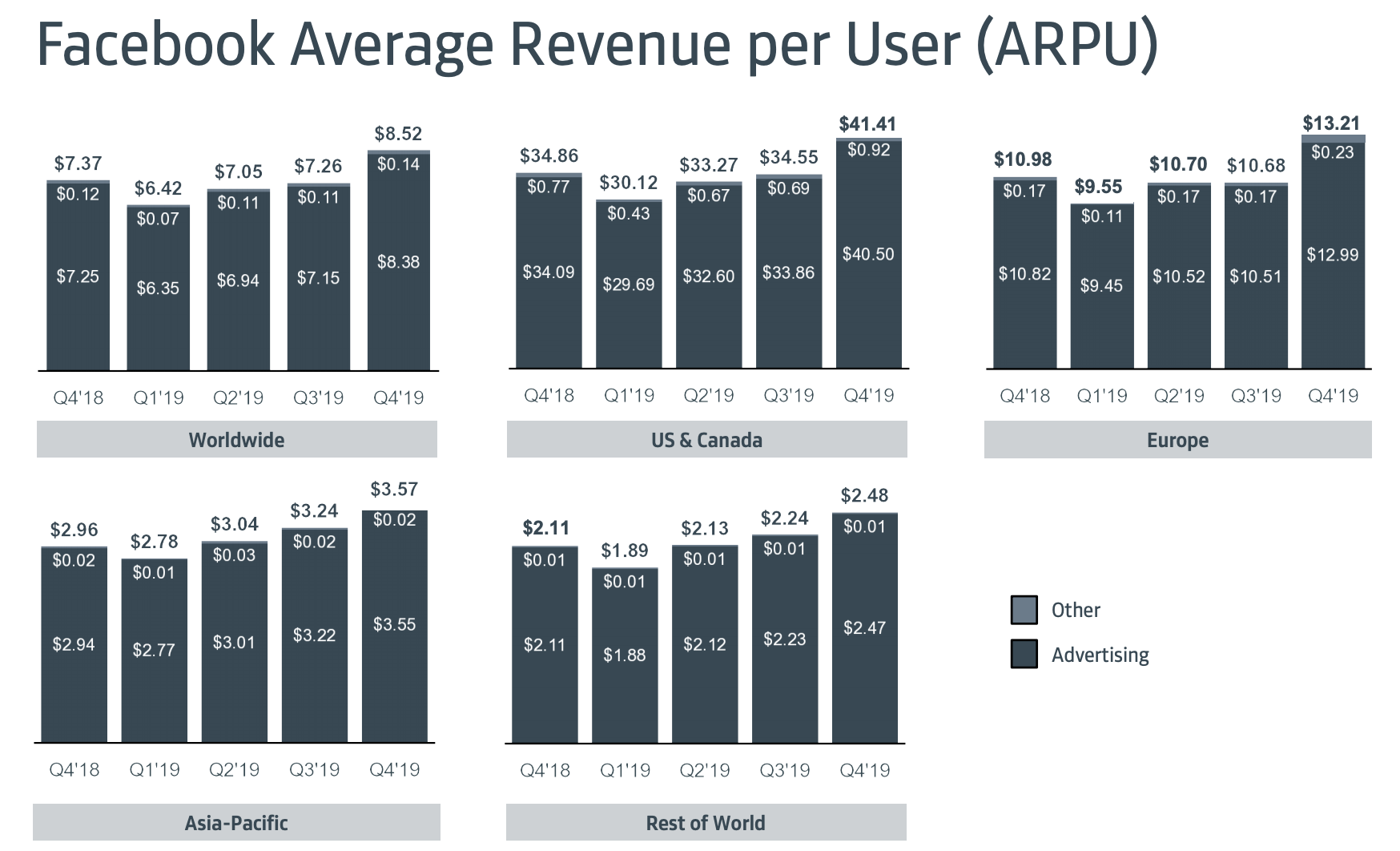
Facebook beat Wall Street estimates in Q4 but slowing profit growth beat up the share price. Facebook reached 2.5 billion monthly users, up 2%, from 2.45 billion in Q3 2019 when it grew 1.65%, and it now has 1.66 billion daily active users, up 2.4% from 1.62 billion last quarter when it grew 2%. Facebook brought in $21.08 billion in revenue, up 25% year-over-year, with $2.56 in earnings per share.
But net income was just $7.3 billion, up only 7% year-over-year compared to 61% growth over 2018. Meanwhile, operating margins fell from 45% over 2018 to 34% for 2019. Expenses grew to $12.2 billion for Q4 2019, up a whopping 34% from Q4 2018. For the year, Facebook’s $46 billion in expenses are up 51% vs 2018. One big source of those expenses? Headcount grew 26% year-over-year to 44,942, and Facebook now has over 1000 engineers working on privacy.
While Facebook’s user base keeps growing rather steadily, it’s having trouble squeezing more and more cash out of them with as much efficiency.
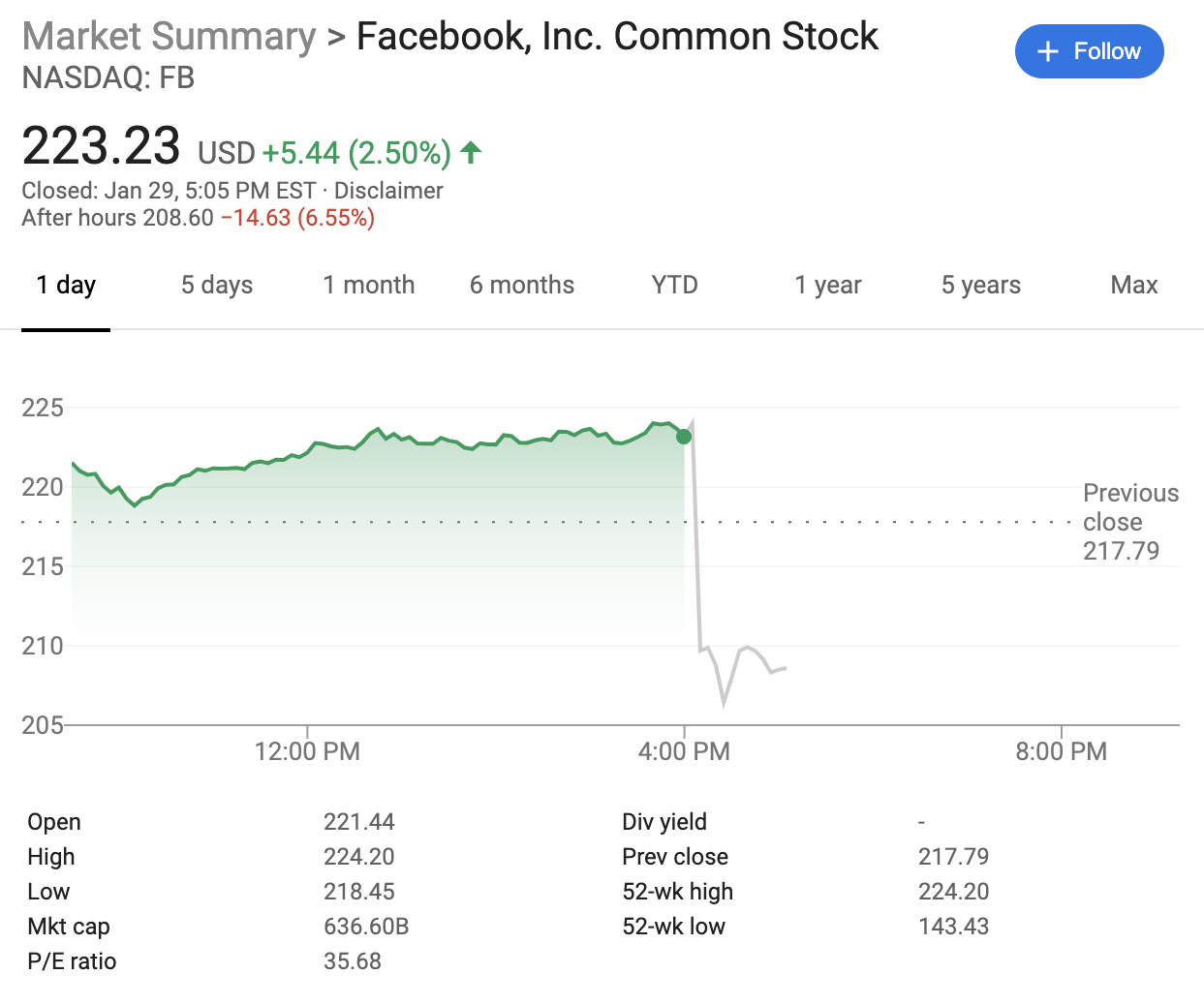
Facebook’s Q4 2019 earnings beat expectations compared to Zack’s consensus estimates of $20.87 billion in revenue and $2.51 earnings per share. Facebook shares fell over 7% in after-hours trading following the earnings announcement after closing up 2.5% at a peak $223.23 today. Still, Facebook remains near its previous share price high before this month.
Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg had previously warned that addressing hate speech, election interference, and other content moderation and safety issues would be costly. Still, expenses grew and profits shrunk faster than Wall Street seems to have expected. Facebook will have to hope its promise of using scalable AI to handle more of these jobs comes to fruition soon.
But some might see today as the proper reckoning for Facebook — penance for years of neglecting safety in favor of growth. Facebook’s CFO David Wehner confirms it has also just agreed to pay $550 million in a settlement over its violation of the Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act. The class action suit stems from Facebook collecting users’ facial recognition data to power its Tag Suggestions feature that recommends friends tag you in photos in which you appear. The record-breaking settlement still falls far short of the $35 billion in potential penalties Facebook could have received.
Facebook’s executives are apparently bullish on its value despite the share price being at a peak, as today Facebook announced plans to grow its share-repurchase program by $10 billion, adding to its previous authorization of buying back up to $24 billion worth.
Facebook managed to add 1 million daily users in the U.S. & Canada region where it earns the most money after returning to growth there last quarter following a year of slow or no growth. Facebook’s stickiness, or daily to monthly active user ratio remained at 66% amidst competition from apps like TikTok and a resurgent Snapchat.
Facebook notes that there are now 2.26 billion users that open either Facebook, Messenger, Instagram, or WhatsApp each day, up from 2.2 billion last quarter. The family of apps sees 2.89 billion total monthly users, up 9% year-over-year.
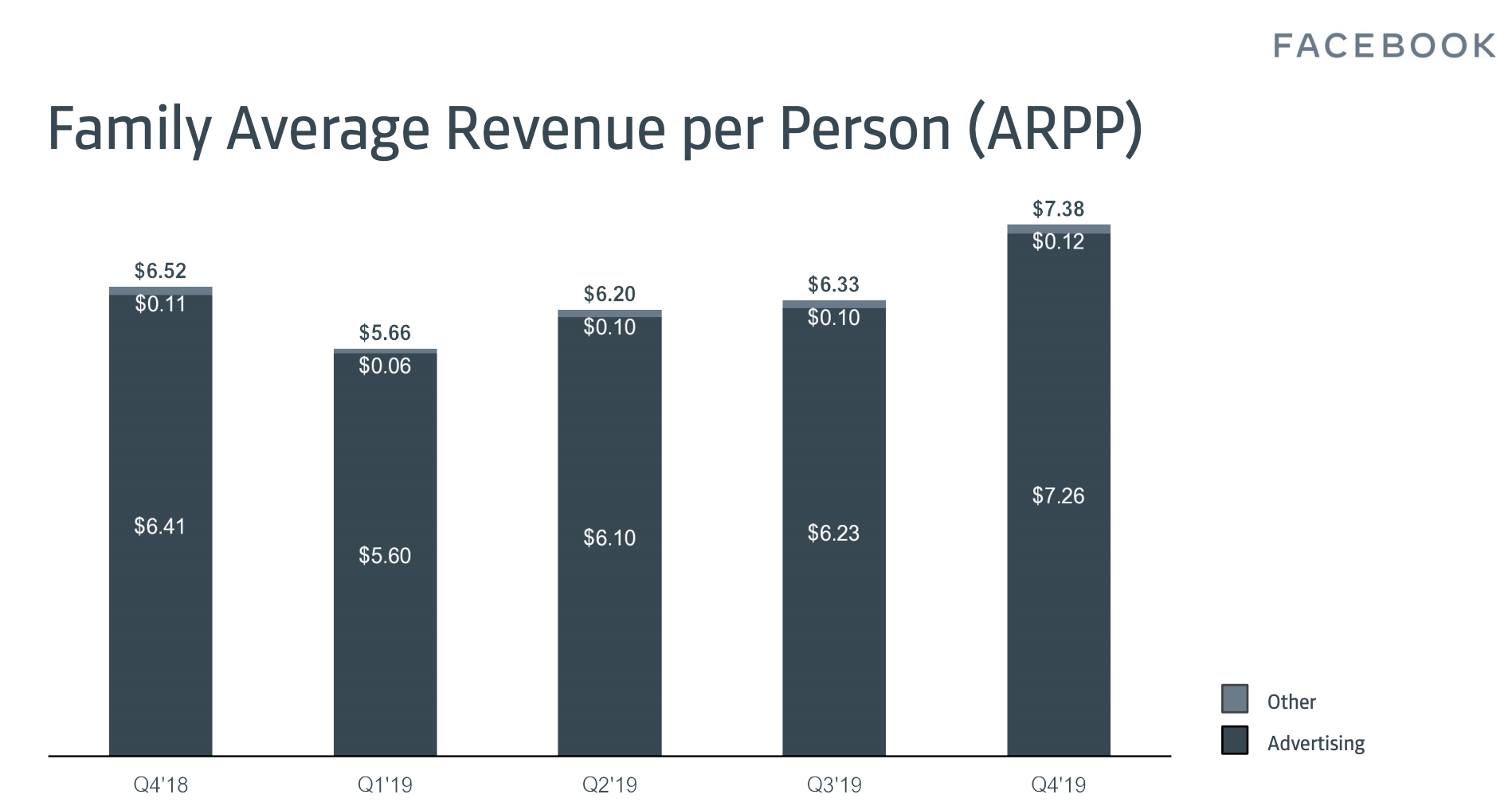
Facebook released a new stat with this earnings report: Family Average Revenue Per Person. That’s essentially the company’s total revenue divided by total users on Facebook, Messenger, Instagram, and WhatsApp. Clearly, the company is trying to use Instagram’s growing ad revenue to make the rest of the company look stronger. This might help mask changes in the Facebook app’s own revenue as teens look to more youthful content feeds. Wehner confirmed the company will cease sharing Facebook-only stats in favor of Family Of Apps stats in late 2020.
Sadly Facebook’s isn’t calling this metric FARPP
Zuckerberg stressed Facebook’s need to stay focused on addressing social issues and consequences of the company’s growth during the earnings call. He said Facebook will continue to make its apps more private and secure.
As for product updates, Zuckerberg seized on opportunities in commerce. Facebook is building out WhatsApp Pay, and he says “I expect this to start rolling out in a number of countries and for us to make a lot of progress here in the next six months.” 140 million small businesses now use its tools. People bought almost $5 million in content on the Oculus Store on Christmas Day, which Zuckerberg called a milestone. He says Facebook’s Spark AR platform is most used of its kind by developers, with hundreds of millions of people experiencing face filters built with it.
Regarding plans to integrate the family’s chat interfaces, Zuckerberg says Messenger, Instagram, and WhatsApp will retain their brands. He also noted they’re already quite integrated on the backend…which could be an attempt to persuade regulators it might be difficult to break up the company.
For guidance, Wehner said “we expect our year-over-year total reported revenue growth rate in Q1 to decelerate by low-to-mid single digit percentage points as compared to our Q4 growth rate. “Factors driving this deceleration include the maturity of our business, as well as the increasing impact from global privacy regulation and other ad targeting related headwinds.”
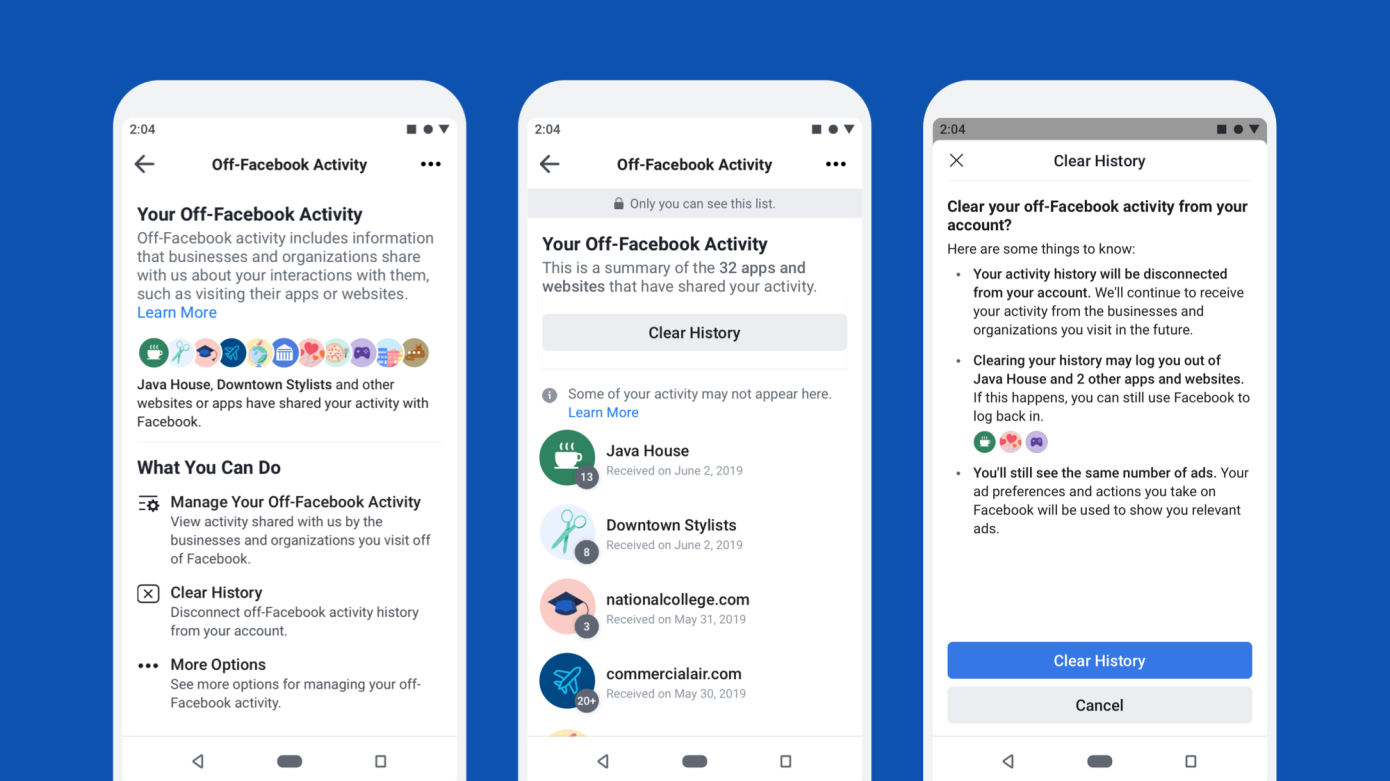
Wehner says to expect that the worst of these privacy headwinds are still to come due to regulatory initiatives like GDPR and CCPA, mobile operating systems and browser providers like Apple and Google limiting access to ad targeting singals, and Facebook’s own product changes like the new way to disconnect off-Facebook data from your acccount.
On Facebook’s perception issues, Zuckerberg said “We’re also focused on communicating more clearly what we stand for. One critique of our approach for much of the last decade was that, because we wanted to be liked, we didn’t always communicate our views as clearly because we were worried about offending people. So this led to some positive but shallow sentiments towards us and towards the company. And my goal for this next decade isn’t to be liked, but to be understood, because in order to be trusted, people need to know what you stand for.”
The business aside, Facebook had another tough quarter under the scrutiny of journalists and regulators. Democratic presidential candidates have railed against Zuckerberg’s decision to continuing allowing misinformation in political ads. The company dropped out of the top 10 places to work, and pledged $130 million to fund an Oversight Board for its content policies.
The CEO was grilled on Capitol Hill about Facebook’s cryptocurrency Libra that seems stuck in its tracks as major partners like Visa and Stripe dropped out. Facebook took heat for how its treats content moderators and how it tried to cut off competitors from its developer platform. The FTC continued its anti-trust investigation and weighed an injunction that would halt Facebook intermingling its messaging app infrastructure.

But those headwinds didn’t stop Facebook’s march forward. Its four main apps took the top four spots amongst the most downloaded apps of the 2010s. It moved deeper into hardware sales with its new Portal TV attachable camera. It acquired gaming companies like Playgiga and the studio behind VR hit Beat Saber, while signing exclusive game streaming deals with influencers like Disguised Toast. It launched Facebook News, Facebook Pay, its dating feature in the US, and it tested a meme-making app called Whale.
Facebook’s share price remains near an all-time high despite today’s tumble. While the world may be increasingly uncomfortable with Facebook’s access to private data, there’s no debate about how incredibly valuable that data is.
Powered by WPeMatico
Fifty iPads were stolen from Verkada co-founder Hans Robertson’s old company. Only when they checked the security system did they realize the video cameras hadn’t been working for months. He was pissed. “The market lagged behind the progress seen in the consumer space, where someone could buy high-end cameras with cloud-based software to protect their home,” Verkada’s CEO and co-founder Filip Kaliszan tells me of his own attempt to buy enterprise-grade security hardware.
Usually, startups ascend on the backs of fresh technologies and developer platforms. But Kaliszan and Robertson realized that commercial security was so backward that just implementing the established principles of machine vision and the cloud could create a huge company. The plan was to keep data secure yet accessible and train its cameras to take clearer photos when AI detects suspicious situations instead of just grainy video.
At first, few could see the vision through the slow upgrade cycles and basement security rooms common with most potential clients. “The seed and the A were extremely difficult rounds to raise compared to the later rounds because people didn’t believe we could execute what were are proposing,” Kaliszan glumly recalls.
But today Verkada receives a huge vote of confidence. It just raised an $80 million Series C at a stunning $1.6 billion post-money valuation thanks to lead investor Felicis Ventures writing Verkada its biggest check to date. The cash brings Verkada to $139 million in funding to sell dome cameras, fisheye lenses, footage viewing stations and the software to monitor it all from anywhere.
Why sink in so much cash at a valuation triple that of Verkada’s $540 million price tag after its April 2019 Series B? Because Verkada wants to bring two-factor authentication to doors with its new access control system that it’s announcing is now in beta testing ahead of a Spring launch. Instead of just allowing a stealable key fob or badge to open your office entryway, it could ask you to look into a Verkada camera too so it can match your face to your permissions.

“Our mission is to be the essential physical security software layer for every building, and the foundation of a larger enterprise IoT infrastructure,” Kaliszan tells me. By uniting security cameras and door locks in one system, it could keep banks, schools, hospitals, government buildings and businesses safe while offering new insights on how their spaces are used.
The founders’ pedigrees don’t hurt its efforts to sell that future to investors like Next47, Sequoia Capital and Meritech Capital, which joined the round. Robertson co-founded IT startup Meraki and sold it to Cisco for $1.2 billion. Kaliszan and his other co-founders Benjamin Bercovitz and James Ren started CourseRank for education software while at Stanford before selling it to Chegg.

Making a better product than what’s out there isn’t rocket science, though. Many building security systems only let footage be accessed from a control room in the building… which doesn’t help much if everyone’s trying to escape due to emergency or if a manager elsewhere simply wants to take a look. Verkada’s cloud lets the right employees keep watch from mobile, and data is also stored locally on the cameras so they keep recording even if the internet cuts out. “Our competitors stream unencrypted video and it’s on you to protect it. We’re responsible for handling that data,” Kaliszan says.
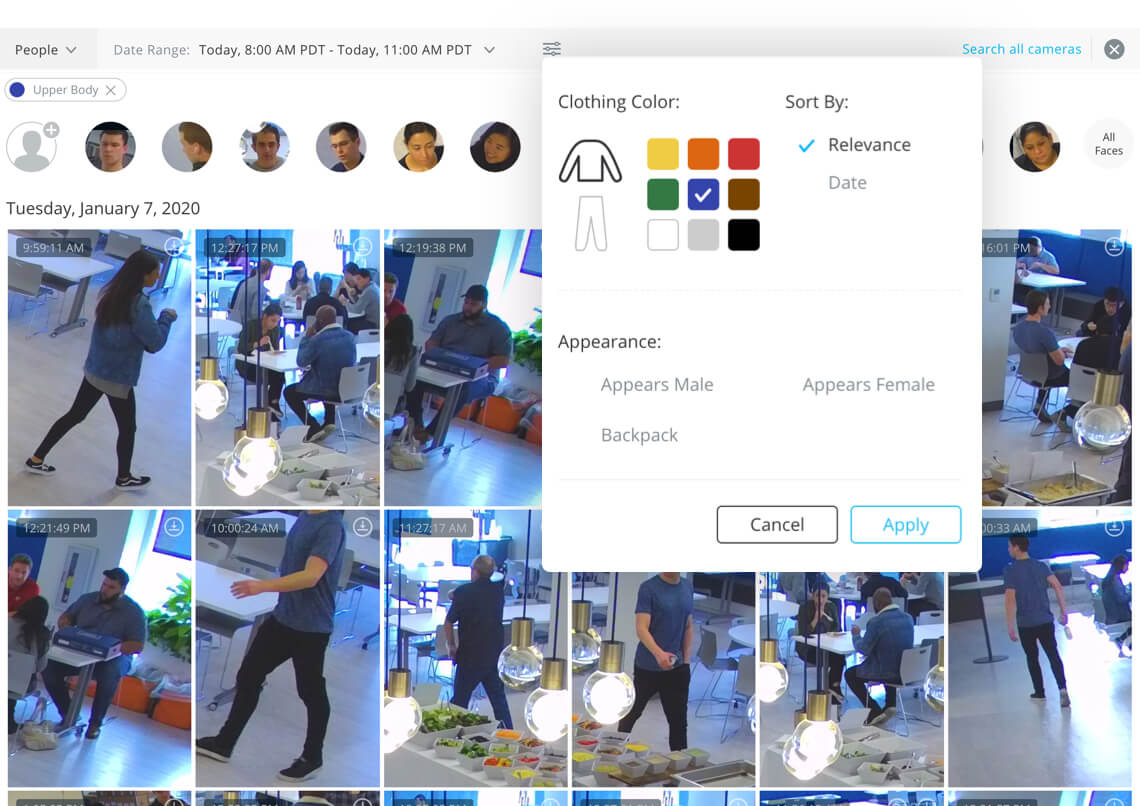
Verkada’s machine vision software can make sense of all the footage its cameras collect. “We can immediately show them all the video containing a particular person of interest rather than manually searching through hours of footage,” Kaliszan insists. “Our platform can use AI/machine learning to recognize patterns and behaviors that are out of the norm in real time.”
For example, a hostage negotiator was able to use Verkada’s system to assess whether a SWAT team needed to invade a building. Verkada can group all spottings of an individual together for review, or scan all the footage for people wearing a certain color or with other search filters.

Indeed, 2,500 clients, including 25 Fortune 500 companies, are already using Verkada. In the last year it has tripled revenue, partnered with 1,100 resellers, launched nine new camera models, added people and vehicle analytics, opened its first London office and is on track to grow from 300 to 800 employees by the end of 2020.
“We call this reinvention,” says Felicis Ventures founder and managing director Aydin Senkut. “One thing people underestimate is how big this market is. Honeywell is valued at $110 billion-plus. There’s a Chinese company that’s over $50 billion. The opportunity to be the operating system for all buildings in the world? Sounds like that market couldn’t be better.” Senkut knows Verkada works because he had it installed in all his homes and offices.
Most enterprise software companies don’t have to worry about the complexities of hardware supply chains. There’s always a risk that its sales process stumbles, leaving it stuck with too many cameras. “We’re still burning money. We’re not there yet or we wouldn’t be raising venture. Because we’re going after a mature market, you can’t come at it with a model that doesn’t make sense. Investors come at it from a hard-nosed approach,” Robertson admits.

“People have a tendency to write off Verkada as a boring camera company. They don’t realize how access control as the second product is going to supercharge the company’s potential,” Senkut declares.
One bullet Verkada dodged is the one firmly lodged in Amazon’s chest. Ring security cameras have received stern criticism over Amazon’s cooperation with law enforcement that some see as a violation of privacy and expansion of a police state. “We don’t have any arrangements with law enforcement like Ring,” Kaliszan tells me. “We view ourselves as providing great physical security tools to the people that run schools, hospitals and businesses. The data that those organizations gather is their own.”
Powered by WPeMatico