Apps
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
While companies might pay for a CEO coach, lower level employees often get stuck with lame skill-building worksheets or no mentorship at all. Not only does that limit their potential productivity, but it also makes them feel stagnated and undervalued, leading them to jump ship.
Therapy… err… executive coaching is finally becoming destigmatized as entrepreneurs and their teams realize that everyone can’t be crushing it all the time. Building a business is hard. It’s okay to cry sometimes. But the best thing you can do is be vulnerable and seek help.
Torch emerged from stealth last year with $18 million in funding to teach empathy to founders and C-suite execs. Since 2013, Everwise has raised $26 million from Sequoia and others for its peer-to-peer mentorship marketplace that makes workplace guidance accessible to rank-and-file staffers. Tomorrow they’ll official announce their merger under the Torch name to become a full-stack career coach for every level of employee.
“As human beings, we face huge existential challenges in the form of pandemics, climate change, the threats coming down the pipe from automation and AI” says Torch co-founder and CEO Cameron Yarbrough. “We need to create leaders at every single level of an organization and ignite these people with tools and human support in order to level up in the world.”
Startup acquisitions and mergers can often be train wrecks because companies with different values but overlapping products are jammed together. But apparently it’s gone quite smoothly since the products are so complementary, with all 70 employees across the two companies keeping their jobs. “Everwise is much more bottom up whereas Torch is about the upper levels, and it just sort of made sense” says Garry Tan, partner and co-founder of Initialized Capital that funded Torch’s Series A and is also a client of its coaching.
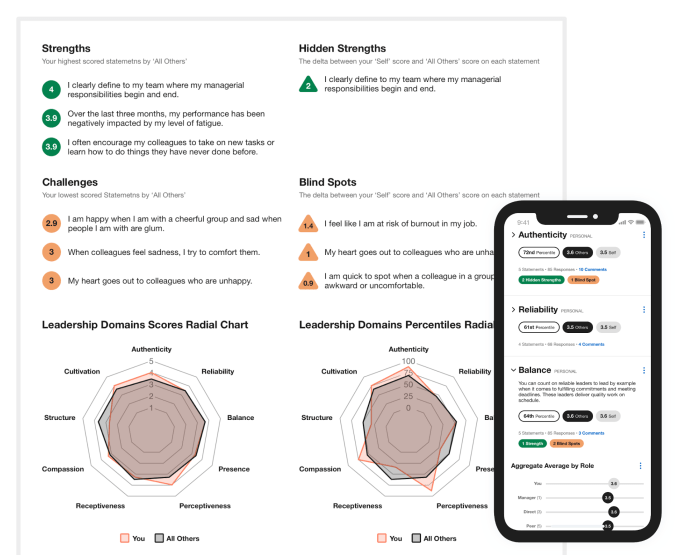
How does each work? Torch goes deep, conducting extensive 360-interviews with an executive as well as their reports, employees, and peers to assess their empathy, communication, vision, conflict resolution, and collaboration. Clients’ executives do extensive 360-interviews. It establishes quantifiable goals that executives work towards through video call sessions with Torch’s coaches. They learn about setting healthy workplace boundaries, staying calm amidst arguments, motivating staff without seeming preachy, and managing their own ego.
This coaching can be exceedingly valuable for the leaders setting a company’s strategy and tone. But the one-on-one sessions are typically too expensive to buy for all levels of employees. That’s where Everwise comes in.
Everwise goes wide, offering a marketplace with 6,000 mentors across different job levels and roles that can provide more affordable personal guidance or group sessions with 10 employees all learning from each other. It also provides a mentorship platform where bigger companies can let their more senior staffers teach junior employees exactly what it takes to succeed. That’s all stitched together with a curated and personalized curriculum of online learning materials. Meanwhile, a company’s HR team can track everyone’s progress and performance through its Academy Builder dashboard.
“We know Gen Z has grown up with mentors by their side from SAT prep” says Torch CMO Cari Jacobs. Everwise lets them stay mentored, even at early stages of their professional life. “As they advance through their career, they might notch up to more executive private coaching.” Post-merger, Torch can keep them sane and ambitious throughout the journey.
“It really allows us to move up market without sacrificing all the traction we’ve built working with startups and mid-market companies,” Yarbrough tells me. Clients have included Reddit and ZenDesk, but also giants like Best Buy, Genentech, and T-Mobile.

The question is whether Everwise’s materials are engaging enough to not become just another employee handbook buried on an HR site that no one ever reads. Otherwise, it could just feel like bloat tacked onto Torch. Meanwhile, scaling up to bigger clients pits Torch against long-standing pillars of the executive coaching industry like Aon and Korn Ferry that have been around for decades and have billions in revenue. Meanwhile, new mental health and coaching platforms are emerging like BetterUp and Sounding Board.
But the market is massive since so few people get great coaching right now. “No one goes to work and is like, ‘Man, I wish my boss was less mindful,’” Tan jokes. When Yarbrough was his coach, the Torch CEO taught the investor that while many startup employees might think they thrive on flexibility, “people really want high love and high structure.” In essence, that’s what Torch is trying to deliver — a sense of emotional camaraderie mixed with a prod in the direction of fulfilling their destiny.
Powered by WPeMatico
We need to go hands-off in the age of coronavirus. That means touching fewer doors, elevators, and sign-in iPads. But once a building is using phone-based identity for security, there’s opportunities to speed up access to WIFI networks and printers, or personalize conference rooms and video call set-ups. Keyless office entry startup Proxy wants to deliver all of this while keeping your phone in your pocket.
“The door is just a starting point” Proxy co-founder and CEO Denis Mars tells me. “We’re . . . empowering a movement to take back control of our privacy, our sense of self, our humanity, our individuality.”
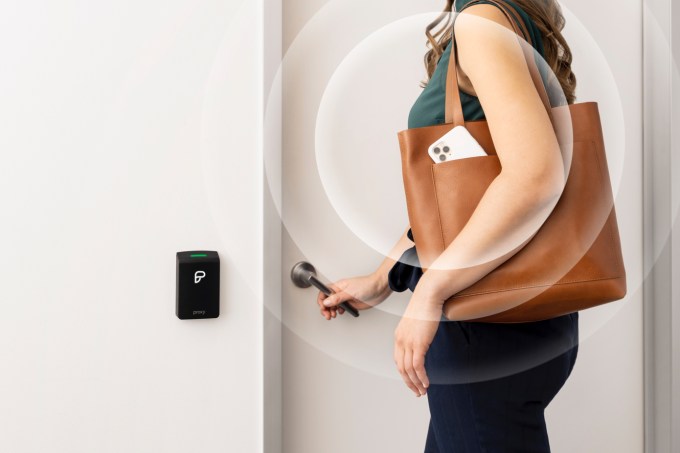

With the contagion concerns and security risks of people rubbing dirty, cloneable, stealable key cards against their office doors, investors see big potential in Proxy. Today it’s announcing here a $42 million Series B led by Scale Venture Partners with participation from former funders Kleiner Perkins and Y Combinator plus new additions Silicon Valley Bank and West Ventures.
The raise brings Proxy to $58.8 million in funding so it can staff up at offices across the world and speed up deployments of its door sensor hardware and access control software. “We’re spread thin” says Mars. “Part of this funding is to try to grow up as quickly as possible and not grow for growth sake. We’re making sure we’re secure, meeting all the privacy requirements.”
How does Proxy work? Employers get their staff to install an app that knows their identity within the company, including when and where they’re allowed entry. Buildings install Proxy’s signal readers, which can either integrate with existing access control software or the startup’s own management dashboard.
Employees can then open doors, elevators, turnstiles, and garages with a Bluetooth low-energy signal without having to even take their phone out. Bosses can also opt to require a facial scan or fingerprint or a wave of the phone near the sensor. Existing keycards and fobs still work with Proxy’s Pro readers. Proxy costs about $300 to $350 per reader, plus installation and a $30 per month per reader subscription to its management software.
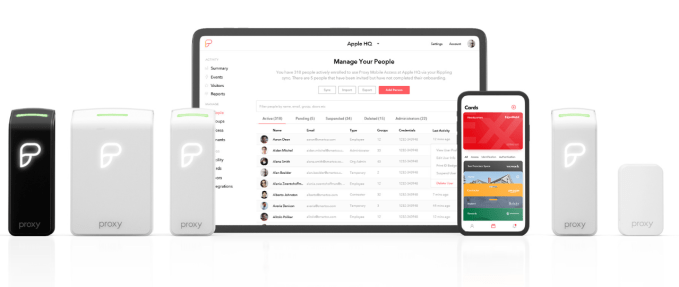
Now the company is expanding access to devices once you’re already in the building thanks to its SDK and APIs. Wifi router-makers are starting to pre-provision their hardware to automatically connect the phones of employees or temporarily allow registered guests with Proxy installed — no need for passwords written on whiteboards. Its new Nano sensors can also be hooked up to printers and vending machines to verify access or charge expense accounts. And food delivery companies can add the Proxy SDK so couriers can be granted the momentary ability to open doors when they arrive with lunch.
Rather than just indiscriminately beaming your identity out into the world, Proxy uses tokenized credentials so only its sensors know who you are. Users have to approve of new networks’ ability to read their tokens, Proxy has SOC-2 security audit certification, and complies with GDPR. “We feel very strongly about where the biometrics are stored . . . they should stay on your phone” says Mars.
Yet despite integrating with the technology for two-factor entry unlocks, Mars says “We’re not big fans of facial recognition. You don’t want every random company having your face in their database. The face becomes the password you were supposed to change every 30 days.”

Keeping your data and identity safe as we see an explosion of Internet Of Things devices was actually the impetus for starting Proxy. Mars had sold his teleconferencing startup Bitplay to Jive Software where he met his eventually co-founder Simon Ratner, who’d joined after his video annotation startup Omnisio was acquired by YouTube. Mars was frustrated about every IoT lightbulb and appliance wanting him to download an app, set up a profile, and give it his data.
The duo founded Proxy in 2016 as a universal identity signal. Today it has over 60 customers. While other apps want you to constantly open them, Proxy’s purpose is to work silently in the background and make people more productive. “We believe the most important technologies in the world don’t seek your attention. They work for you, they empower you, and they get out of the way so you can focus your attention on what matters most — living your life.”
Now Proxy could actually help save lives. “The nature of our product is contactless interactions in commercial buildings and workplaces so there’s a bit of an unintended benefit that helps prevent the spread of the virus” Mars explains. “We have seen an uptick in customers starting to set doors and other experiences in longer-range hands-free mode so that users can walk up to an automated door and not have to touch the handles or badge/reader every time.”

The big challenge facing Proxy is maintaining security and dependability since it’s a mission-critical business. A bug or outage could potentially lock employees out of their workplace (when they eventually return from quarantine). It will have to keep hackers out of employee files. Proxy needs to stay ahead of access control incumbents like ADT and HID as well as smaller direct competitors like $10 million-funded Nexkey and $28 million-funded Openpath.
Luckily, Proxy has found a powerful growth flywheel. First an office in a big building gets set up, then they convince the real estate manager to equip the lobby’s turnstiles and elevators with Proxy. Other tenants in the building start to use it, so they buy Proxy for their office. Then they get their offices in other cities on board…starting the flywheel again. That’s why Proxy is doubling down on sales to commercial real estate owners.
The question is when Proxy will start knocking on consumers’ doors. While leveling up into the enterprise access control software business might be tough for home smartlock companies like August, Proxy could go down market if it built more physical lock hardware. Perhaps we’ll start to get smart homes that know who’s home, and stop having to carry pointy metal sticks in our pockets.
Powered by WPeMatico
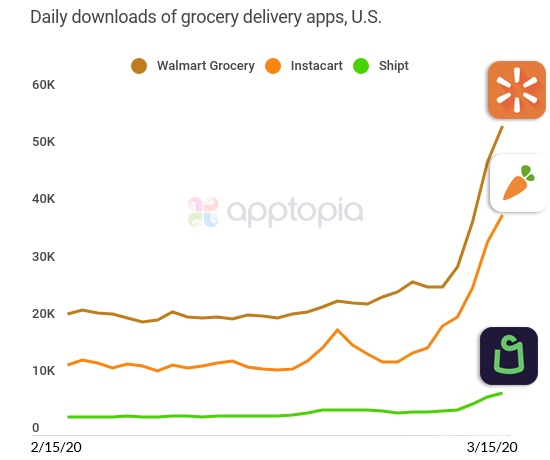
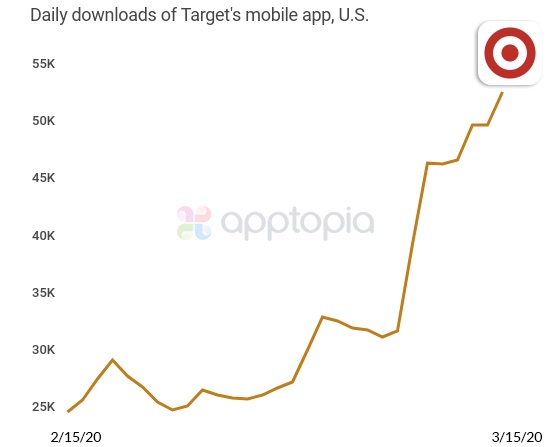
As the COVID-19 pandemic spreads across the U.S., grocery delivery apps have begun seeing record numbers of daily downloads, according to new data from app store intelligence firm Apptopia. On Sunday, online grocery apps, including Instacart, Walmart Grocery and Shipt, hit yet another new record for daily downloads for their respective apps, the firm says.
Comparing the average daily downloads in February to yesterday (Sunday, March 15), Instacart, Walmart Grocery and Shipt have seen their daily downloads surge by 218%, 160% and 124%, respectively.
Typically, these apps (except for Shipt) see tens of thousands to as many as 20,000+ downloads per day. But on Sunday, Instacart saw more than 38,500 downloads and Walmart Grocery saw nearly 54,000 downloads, the firm says. Shipt, though hitting record numbers, saw only 7,285 downloads on Sunday. To some extent, its lower figures could be due to Target’s move to integrate Shipt’s grocery delivery service, which it owns, into its main app.
In fact, the Target app has also broken records for daily downloads, the report found. On Sunday, Target’s app saw more than 53,100 daily downloads; a month ago, it was seeing 25,000+.
Walmart very recently announced it would merge its grocery delivery service into its main app, as Target has done. But for now, consumers are still seeking and downloading its standalone grocery app at record levels.
These grocery delivery apps are in demand more than ever during this health crisis.
With government mandates to practice “social distancing,” U.S. consumers have been stocking up for long weeks to be spent at home. Stores were cleared of key supplies, like toilet paper, and several also saw long lines and crowds as panic-buying set in. Grocery delivery and pickup, meanwhile, presents an easier option — as well as one where you could limit your exposure to other people. With grocery pickup, consumers only have to interact with a single store employee from their curbside parking space. And with grocery delivery, most orders can simply be left on the doorstep with no person-to-person contact required.
Several grocery delivery services, including Instacart and others, promoted the fact they would add a “contactless” delivery option, which helps contribute to the huge sales boost. On Thursday, Instacart said its sales growth rates for the week was 10 times higher than the week before, and had increased by as much as 20 times in areas like California, New York, Washington and Oregon.
Apptopia’s report didn’t analyze the impact of the coronavirus outbreak on Amazon’s grocery delivery business, which includes Amazon Fresh and Whole Foods deliveries. This is more difficult to do because Amazon grocery orders aren’t placed inside a dedicated app, as with Instacart. However, Amazon confirmed a technical glitch on Sunday affected online orders through both its grocery delivery services, which the company attributed to the increase in online shopping.
“As COVID-19 has spread, we’ve seen a significant increase in people shopping online for groceries,” an Amazon spokeswoman explained, in a statement shared with Bloomberg. “This resulted in a systems impact affecting our ability to deliver Amazon Fresh and Whole Foods Market orders [on Sunday night]. We’re contacting customers, issuing concessions, and are working around the clock to quickly to resolve the issue,” they added.
Amazon Prime is also expected to experience delays and shortages as consumers stock up on non-grocery household items, the company says.
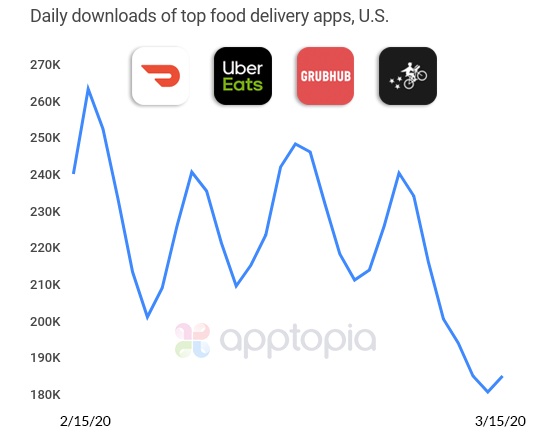
But even as grocery delivery booms, the market for food delivery apps has not seen the same results.
Despite promises for contactless delivery from several providers, including Uber Eats, food delivery apps are not experiencing a similar surge in daily downloads. According to Apptopia, the food delivery market earlier in March was starting to cool off. It later began to pick up but then cooled off again as consumers realized the expense of ordering food compared with home cooking, and because some consumers view restaurant delivery as not being as safe as cooking at home.
Powered by WPeMatico
Welcome back to This Week in Apps, the Extra Crunch series that recaps the latest OS news, the applications they support and the money that flows through it all.
The app industry is as hot as ever, with a record 204 billion downloads in 2019 and $120 billion in consumer spending in 2019, according to App Annie’s recently released “State of Mobile” annual report. People are now spending 3 hours and 40 minutes per day using apps, rivaling TV. Apps aren’t just a way to pass idle hours — they’re a big business. In 2019, mobile-first companies had a combined $544 billion valuation, 6.5x higher than those without a mobile focus.
In this Extra Crunch series, we help you keep up with the latest news from the world of apps, delivered on a weekly basis.
This week we’re taking a look at several stories related to the coronavirus outbreak, including the cancellation of WWDC in San Jose, as well as other app industry events that are going online. We’re also discussing the iOS 14 leak, the exposure of Sensor Tower’s app network, a potential ban on TikTok for government workers and more.
The impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic are continuing to play out on app stores and across the industry. This week, we’re leading with these stories followed by the other — and yes, still important — news.
Powered by WPeMatico
Y Combinator’s Demo Day is a key soirée on the startup calendar. This year, however, instead of a packed room replete with short pitches and lackluster catering, Demo Day has gone virtual. Even more, it was moved up by a week, pushing the public debut of a host of companies to this coming Monday.
TechCrunch will be covering it closely, so make sure to stick around the site for notes and interviews. But who wants to wait that long? I’ve gotten to know one of the pitching startups, FitnessAI, over the past few weeks. Let’s take a look at its business.
FitnessAI is a mobile application that helps users lift weights, helping them set new goals, gain strength over time and avoid frustration while dodging burnout.
The company was founded by Jake Mor in 2019, leveraging a workout data set that Mor had previously collected. Mor told TechCrunch that in college he built a tool called Lift Log (you can find it on the App Store here). That app was “just a very simple weightlifting tracking tool,” Mor said, but “over the course of three years over 40,000 users logged 6 million workouts.”
That huge set of workout data points helped Mor construct FitnessAI’s core weight-lifting algorithm.
Peering through his mountain of data, Mor said that he was able to discern “the perfect rate of progression for each exercise.” Regular progression isn’t a nice to have, according to Mor, but a key way to keep people in the gym (and using his service), saying that he’s found that breaking personal records “makes working out a little bit more addicting, and more motivating to keep going back to the gym.”
But data isn’t the full story to FitnessAI, despite it featuring “AI” in its name. During the life of his company, Mor found that a human touch was key to keeping users engaged. He told TechCrunch that lots of folks are self-conscious about going to the gym and working out in its environment, so while he was “so busy working on [the] algorithm” that powers the company’s service, “what users cared most about was tutorials.”
The helping hand of crafted guides and human outreach work together with the app’s code to keep people engaged. According to Mor, his team “will reach out to every single user if you don’t go to the gym,” adding that “half of fitness AI is the human touch.”
So from a data set to an algorithm to a mobile app to a guided weight-lifting experience, FitnessAI has gotten a lot done in the last year or so. And it has done so while largely self-funding.
To date, the company told TechCrunch that it has bootstrapped, apart from its standard Y Combinator check. That said, it’s looking to raise during the Demo Day cycle.
How has it gotten to where it is today on such little capital? By growing its revenues and paying for its own development. Indeed, the mobile app company is now north of $100,000 monthly recurring revenue (MRR), giving it annual recurring revenue (ARR) of more than $1.2 million. For a team of four today that was 1.5 not too long ago, that’s lots of cash.
But with more money comes more opportunities for product improvements, and go-to-market work. What FitnessAI has shown so far is that people need help lifting, and they are willing to pay for assistance. (FitnessAI has a number of price points, but costs a little less than $100 yearly, looking at its App Store listing today.)
More after Demo Day if FitnessAI raises the round it’s hunting for.
Powered by WPeMatico
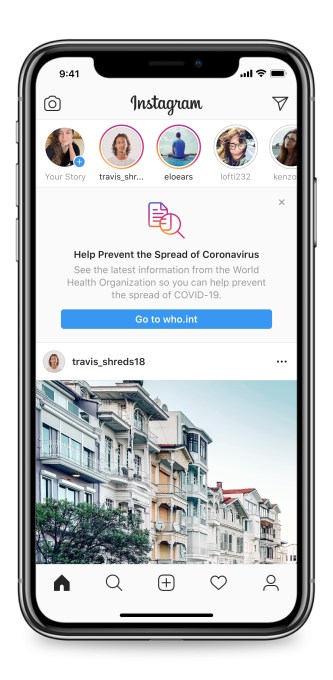
Instagram is embracing its potential as a news source, employing its ubiquity to distribute coronavirus prevention techniques through a new call-out at the top of its homescreen feed. In some countries, Instagram will show a link to information from the World Health Organization and local health ministries, along with a message like this: “Help Prevent the Spread of Coronavirus: See the latest information from the World Health Organization so you can help prevent the spread of COVID-19. — Go to who.int”.
An Instagram spokesperson tells TechCrunch that the notice will start appearing in countries that have seen significant impact from the virus.
Additionally, Instagram is preventing users from searching for COVID-19-related augmented reality effects unless they were made in partnership with legitimate health organizations. This could limit the spread of disinformation or insensitive jokes about the virus. Instagram was already sending false information to fact checkers and listing official health sources atop the search results for coronavirus-related queries.
To help the company stay focused, Facebook is also shutting down the MSQRD app it acquired in 2016 to jumpstart is AR face filters feature. MSQRD will become unavailable on April 13th, though its tech is already fully integrated into Facebook and Instagram.
 Meanwhile, on Snapchat, the company prohibits partners from sharing misinformation, relying on its closed platform to prevent the false news hoaxes that have plagued open platforms like Facebook. Snapchat is also highlighting health information shared by its Discover partners, including NBC’s Stay Tuned, Sky News, The Wall Street Journal, The Washington Post, CNN and NowThis. Those include (these links may only open to content on mobile):
Meanwhile, on Snapchat, the company prohibits partners from sharing misinformation, relying on its closed platform to prevent the false news hoaxes that have plagued open platforms like Facebook. Snapchat is also highlighting health information shared by its Discover partners, including NBC’s Stay Tuned, Sky News, The Wall Street Journal, The Washington Post, CNN and NowThis. Those include (these links may only open to content on mobile):
These are smart efforts by social platforms that know they might get opened by more people more often than some traditional news sources. With over 1 billion monthly users on Instagram and over 200 million daily users on Snapchat, they have the power to spread vital information and act as a new form of the emergency broadcast system.
Powered by WPeMatico
In Asia, where I work as a partner at an early-stage VC firm, startups are regularly rolling out a minimum viable product (MVP) and then transacting on messaging apps.
Companies like shoe brand Portblue, AI e-commerce company Sorabel and Sama, an online recruitment platform for migrant workers, all started life using WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger to communicate with customers, onboard users and raise brand awareness.
For many years, WeChat has been the default app for daily life and business in China. It’s estimated that more than 30% of all internet traffic in China is through WeChat, and in 2017 they introduced “mini-programs,” where businesses could build apps inside WeChat. Now you never have to download any apps or go to a browser to access millions of services and businesses in WeChat.
We now see a similar trend in Southeast Asia. Here, WhatsApp is the dominant social platform and, while it has not built the same infrastructure for building apps, startups have found a way around that and now run many services on top of WhatsApp, validating with customers quickly and cheaply. These companies are not only mobile-first, but they are also WhatsApp-first.
Sampingan, an Antler portfolio company founded here in Singapore, provides an on-demand workforce to businesses in Indonesia. The first version of the product was on WhatsApp. The team sourced and managed more than 2,000 blue-collar workers in Indonesia who completed 25,000 jobs in the company’s first three months.

Lisa Enckell is a partner at Antler, an early-stage venture capital firm and startup generator.
Powered by WPeMatico
YC-backed Giveaway lets folks give away their unused or unnecessary items in a marketplace. Unlike other buy and sell or donation platforms, Giveaway uses a virtual currency on the platform to reward people for listing their products for free on the app.
Users earn Karma coins each time they list an item on the website. Folks can then use that Karma to claim items listed on the app.
The first person to try to claim an item offers zero Karma for the item. From there, a countdown begins, allowing others to offer more Karma for the item until the clock runs out. The user who offered the most Karma gets to claim the item. They are then connected to the giver via the app and can set a time and place to meet for the transaction. The person who claimed the item can inspect it and then approve the transaction, triggering the exchange of Karma coin.
Users can also rate and review each other on the platform for the quality of their items.
The app promotes giving items away to earn Karma but does offer a flow for purchasing the virtual currency. One Karma coin is equal to about $.30.
Giveaway was founded by Artem Artemiuk, Siarhei Lepchankou, and Siarhei Stasilovich. The idea came to them when traveling in Austria and coming across a store that allowed customers to choose one item for free.
After building the platform, the trio launched the app in their home market of Belarus and saw strong early growth. Since then, Giveaway has expanded to Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, and now the United States.
Artemiuk, Giveaway’s CMO, said the company is laser focused on pre-moderation, which uses a combination of machine learning and human input to ensure that inappropriate items don’t make it on the platform, including drugs, tobacco, alcohol, and weapons.
In terms of business model, Giveaway takes a percentage of all Karma coins purchased on the platform, which account for about 30 percent of all Karma. Giveaway also sees the opportunity to generate revenue through an enterprise product within the app, allowing big corporations to opt for Giveaway over sometimes costly recycling options, and pay for the opportunity to do so.
Giveaway has raised $150K from Y Combinator and will present at the accelerator’s upcoming demo day.
Powered by WPeMatico
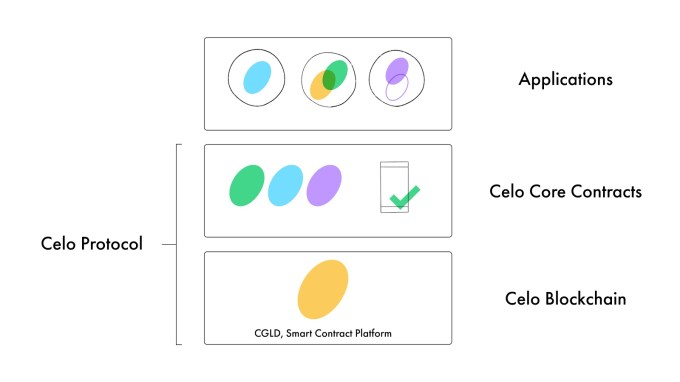
Some Libra Association members like Andreessen Horowitz and Coinbase Ventures are double-dipping, backing a competing cryptocurrency developer platform. Launching today with over 50 partners, non-profit The Celo Foundation’s ‘Alliance For Prosperity’ offers a way for developers to build decentralized mobile apps that are based on Celo’s blockchain platform and USD stablecoin.
The open-source Celo platform is still in testing with plans to officially launch its mainnet in April. The non-profit founded in 2017 has raised $36.4 million, including its Series A where Andreessen Horowitz’s a16z Crypto bought $15 million worth of Celo Gold tokens.
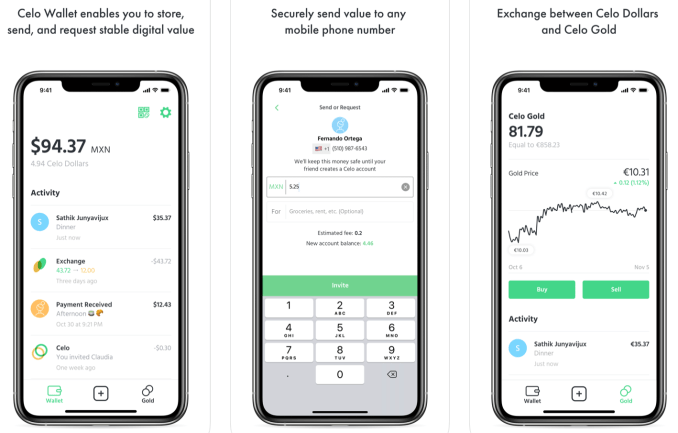
The biggest differentiator of Celo’s network versus other blockchains is that payments in the Celo Dollar stablecoin can be sent to people’s phone numbers rather than complicated addresses. The goal is to make delivering utility via blockchain easier by building a flexible network of applications that doesn’t scare regulators like Libra has.
The Alliance For Prosperity includes Andreessen Horowitz (which funded Celo), Coinbase (Ventures), Bison Trails, Anchorage, and Mercy Corps — all of which are also Libra Association members. That could potentially create a conflict of interest regarding which cryptocurrency and developer platform they promote to their portfolio companies, integrate into their products, or focus on for delivering financial services to the needy.
Other high-profile Alliance partners include Carbon, GiveDirectly, Grameen Foundation, Maple, and Polychain. Partners have made a somewhat vague commitment to “backing development efforts of the project, building infrastructure, implementing desired use cases on the platform, integrating Celo assets in their projects, or collaborating on education campaigns in their communities to further advance the use of blockchain technology” according to Chuck Kimble, Celo’s cLabs head of business development and head of the Alliance. Anyone can apply to join the open network, and there’s no minimum financial investment like Libra’s $10 million prerequisite.

Celo isn’t trying to replace the dollar with its own synthetic currency, and its reserve is backed with other cryptocurrencies rather than fiat cash. That might make it more acceptable to regulators who were worried that Libra’s token and fiat currency bundle-backed reserve could impact the global financial system. The first of the decentralized apps on the platform, the Celo Wallet, is already available for iOS and Android.

Like many blockchain projects, there are some lofty intentions for social impact with Celo. Use cases include “powering mobile and online work, enabling faster and affordable remittances, reducing the operational complexities of delivering humanitarian aid, facilitating payments, and enabling microlending” says Kimble. The real driver of this potential is Celo’s promise of much lower transaction fees than traditional middlemen charge.
When asked what the biggest threats to Celo’s success are, he told me “Banking infrastructure improving faster than we expect” and “Mobile adoption or LTE data not expanding on their current trajectory.” He did not mention the developer fatigue, regulatory scrutiny, technical complexity, or slow adoption of blockchain utilities that have plagued other crypto for good projects.
Here’s the full list of members working towards these goals:
Abra, Alice, AlphaWallet, Anchorage, Appen, Ayannah, Andreessen Horowitz, B12, BC4NB (Blockchain for the Next Billion), BeamAndGo, Bidali, Bison Trails, Blockchain Academy Mexico, Blockchain.com, Blockchain for Humanity (b4h), Blockchain for Social Impact (BSIC), Blockdaemon, Carbon, cLabs, CloudWalk Inc, Cobru, Coinbase, Coinplug, Cryptio, Cryptobuyer, CryptoSavannah, eSolidar, Fintech4Good, Flexa, Gitcoin, GiveDirectly, Grameen Foundation, GSMA, KeshoLabs, Laboratoria, Ledn, Maple, Mercy Corps, Metadium, Moon, MoonPay, Pipol, Pngme, Polychain, Project Wren, SaldoMX, Semicolon Africa, The Giving Block, Utrust, Upright, Yellow Card, and 88i. [Update: Ledger joined this morning.]
“Many of these organizations have on-the-ground operations that will begin to get Celo into the hands of those who have been underserved by the current global financial system” Andreessen Horowitz general partner Katie Haun told me. “Our hope is that this partnership will start unlocking the potential of internet money”. To spur adoption, the Alliance will distribute ‘Prosperity Gifts’ in the form of financial grants to developers proposing Celo products that would benefit society.
There are also some peculiar characteristics of Celo’s system. People exchange other cryptocurrencies for Celo Gold, then exchange that for Celo Dollars they can spend. The reserve is backed with other cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ethereum rather that fiat, and isn’t fully collateralized. That could make it vulnerable to a Celo bank run or crash in price of those currencies. Celo also lets arbitrageurs pocket the difference if Celo Gold and Celo Dollars get out of sync.
 While it might not be a danger to the world financial system like Libra, it could be a danger to itself. At least on the anti-money laundering front, cLabs — the team that’s kicking off development of the Celo platform — has hired former Capital One head of enterprise risk management Jai Ramaswamy. Plus, the Celo founders come well pedigreed, including Marek Olszewski and Rene Reinsberg who spun out machine learning startup Locu from MIT and sold it to GoDaddy, as well as EigenTrust inventor and former MIT Media Lab professor Sep Kamvar.
While it might not be a danger to the world financial system like Libra, it could be a danger to itself. At least on the anti-money laundering front, cLabs — the team that’s kicking off development of the Celo platform — has hired former Capital One head of enterprise risk management Jai Ramaswamy. Plus, the Celo founders come well pedigreed, including Marek Olszewski and Rene Reinsberg who spun out machine learning startup Locu from MIT and sold it to GoDaddy, as well as EigenTrust inventor and former MIT Media Lab professor Sep Kamvar.
So far, 130 teams have expressed interest in building on the Celo platform. For reference, Libra said 1,500 organizations had said they wanted to work on that project four months after its reveal. Celo Camp and Blockchain for Social Impact Incubator will also be fostering projects for the blockchain.
Celo could make banking cheaper and more accessible while power new fintech innovation. But for any of that to happen, it will need to get enough developers building truly useful products, make the blockchain and currency exchange simple enough for mainstream audiences in developing nations, and grow adoption to meaningful levels few cryptocurrency projects have yet achieved. The Alliance For Prosperity will have to throw their weight into this project, not just their names, if it’s going to succeed.
Powered by WPeMatico
Fitness, wallpaper, and lost item-finding startups could have a big new competitor baked into everyone’s iPhones. Leaks of the code from iOS 14 that Apple is expected to reveal in June signal several new features and devices are on the way. Startups could be at risk due to Apple’s ability to integrate these additions at the iOS level, instantly gain an enormous install base and offer them for free or cheap, as long as they boost sales of its main money maker, the iPhone.
It’s unclear if all of these fresh finds will actually get official unveiling in June versus further down the line. But here’s a breakdown of what the iOS 14 code obtained by 9To5Mac’s Chance Miller shows and which startups could be impacted by Apple barging into their businesses:
Apple appears to be preparing a workout guide app for iOS, WatchOS and Apple TV that would let users download instructional video clips for doing different exercises. The app could potentially be called Fit or Fitness, according to MacRumors‘ Juli Clover, and offer help with stretching, core training, strength training, running, cycling, rowing, outdoor walking, dance and yoga. The Apple Watch appears to help track your progress through the workout routines.

Icons for Apple’s fitness feature from the iOS 14 code
The iOS Health app is already a popular way to track steps and other fitness goals. By using Health to personalize or promote a new Fitness feature, Apple has an easy path to a huge user base. Many people are afraid of weight and strength training because there’s a lot to learn about having proper form to avoid injury or embarrassment. Visual guides with videos shot from multiple angles could make sure you’re doing those pushups or bicep curls correctly.
Apple’s entrance into fitness could endanger startups like Future, which offer customized workout routines with video clips demonstrating how to do each exercise. The $11.5 million-funded Future actually sends you an Apple Watch with its $150 per month service to track your progress while using visuals, sounds and vibrations to tell you when to switch exercises without having to look at your phone. By removing Future’s human personal trainers that text to nag you if you don’t work out, Apple could offer a simplified version of this startup’s app for free.
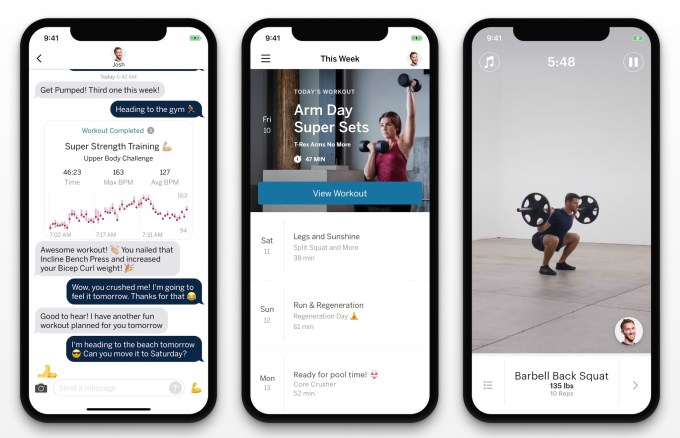
Apple Fitness could be even more trouble for less premium apps like Sweat and Sworkit that provide basic visual guidance for workouts, or Aaptiv that’s restricted to just audio cues. Hardware startups like Peloton, which offers off-bike Beyond the Ride workouts with live or on-demand class, and Tempo’s giant 3D-sensing in-home screen for weight lifting, could also find casual customers picked off by a free or cheap alternative from Apple.
There’s no code indicating a payment mechanism, so Apple Fitness could be free. But it’s also easy to imagine Apple layering on a premium feature like remote personal training assistance from human experts or a wider array of exercises for a fee, tying into its increasing focus on services revenue.
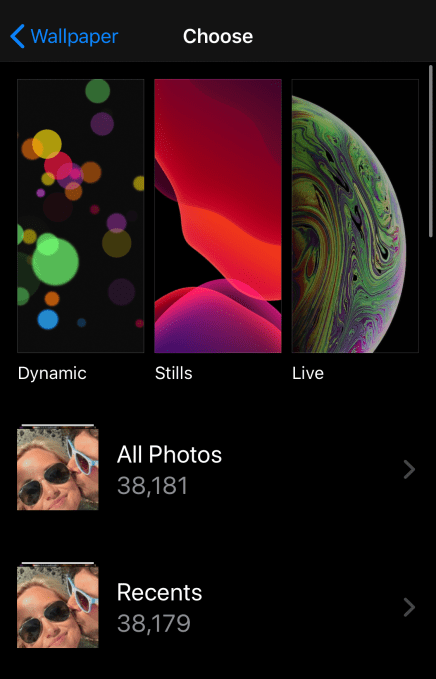
The iPhone’s current wallpaper selector
In iOS 14, it appears that Apple will offer new categorizations for wallpapers beyond the existing Dynamic (slowly shifting), Still and Live (move when touched) options. Apple’s always only offered a few native wallpapers plus the option to pull one from your camera roll. But the iOS 14 code suggests Apple may open this up to third-party providers.
A wallpaper “store” could be both a blessing and a curse for entrepreneurs in the space. It could endanger sites and apps like Vellum, Unsplash, Clarity, WLPPR and Walli that aggregate wallpapers for browsing, purchase or download. Instead, Apple could make itself the ultimate aggregator by being built directly into the wallpaper settings. But for creators of beautiful wallpaper images, iOS 14 could potentially offer a new distribution method where their collections could be available straight from where users install their phone backgrounds.
The big question will be whether Apple merely works with a few providers to add wallpaper packs for free, does financially backed deals to bring in providers or creates a full-blown marketplace for wallpapers where creators can sell their imagery like developers do apps. By turning this formerly free feature into a marketplace, Apple could also start earning a cut of sales to add to its services revenue.

Apple appears to be getting closer to launching its long-awaited AirTags, based on iOS 14 code snippets. These small tracking tags could be attached to your wallet, keys, gadgets or other important or easily lost items, and then located using the iOS Find My app. AirTags may be powered by removable coin-shaped batteries, according to MacRumors.

Native integration with iOS could make AirTags super-easy to set up. They also could benefit from the ubiquity of Apple devices, as the company could let the crowd help find your stuff by allowing AirTags to piggyback on the connectivity of any of its phones, tablets or laptops to send you the missing item’s coordinates.
Most obviously, AirTags could become a powerful competitor to the vertical’s long-standing frontrunner, Tile. The $104 million-funded startup sells $20 to $35 tracking tags that locate devices from 150 to 400 feet away. It also sells a $30 per year subscription for free battery replacements and 30-day location history. Other players in the space include Chipolo, Orbit and MYNT.
![]()
But as we saw with the launch of AirPods, Apple’s design expertise and native iOS integrations can allow its products to leapfrog what’s in the market. If AirTags get proprietary access to the iPhone’s Bluetooth and other connectivity hardware, and if they’re quicker to set up, Apple fans might jump from startups to these new devices. Apple also could develop a similar premium subscription for battery or full AirTag replacements, as well as bonus tracking features.
iOS 14 includes code for a new augmented reality feature that lets users scan places or potentially items in the real world to pull up helpful information. The code indicates Apple is testing the feature, codenamed Gobi, at Apple Stores and Starbucks to let users see product, pricing and comparison info, according to 9To5Mac’s Benjamin Mayo. Gobi can recognize QR-style codes for specific locations like a certain shop, triggering a companion augmented reality experience.

It appears that an SDK would allow partners to build their own AR offerings and generate the QR codes that initiate them. Eventually, these capabilities could be extended from Apple’s mobile devices to the AR headset it’s working on so you’d instantly get a heads-up display of information when you entered the right place.
Apple moving to power lighter-weight AR experiences rather than just offering the AR Kit infrastructure for developers to build full-fledged apps could create competition for a range of startups and other tech giants. The whole point of augmented reality is that it’s convenient to explore hidden experiences in the real world, which is defeated if users have to know to download and then wait to install a different app for every place or product. Creating a central AR app for simpler experiences that load instantly could speed up adoption.
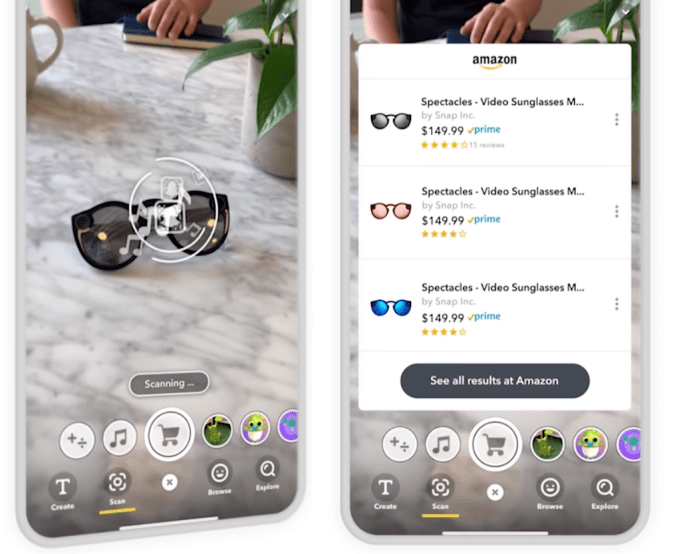
Snapchat’s Scan AR platform
Startups like Blippar have been working on AR scanning for years in hopes of making consumer packaged goods or retail locations come alive. But again, the need to download a separate app and remember to use it has kept these experiences out of the mainstream. Snapchat’s Scan platform can similarly trigger AR effects based on specific items from a more popular app. And teasers of Facebook and Google’s eventual augmented reality hardware and software hinge on adding utility to every day life.
If Apple can build this technology into everyone’s iPhone cameras, it could surmount one of AR’s biggest distribution challenges. That might help it build out a developer ecosystem and train customers to seek out AR so they’re all ready when its AR glasses finally arrive.
Powered by WPeMatico