Apps
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Following my report from yesterday, Apple has removed many of the apps I pointed out. When you try to find them on the App Store, they are no longer available.
App Store Review Guidelines are very clear when it comes to app duplicates. According to rule 4.3, you can’t release the same app multiple times on the App Store as it is considered as spamming.
But that rule has been poorly enforced, and some companies have taken advantage of that. In my original report, I focused on one category in particular — VoIP apps that let you get a second phone number and send and receive calls and texts from that new number.
Developers release multiple versions of the same app so they can use different names, different keywords and different categories. This way, they can cover a wide range of keywords when you’re searching for an app in the App Store.
So let’s look at the developers I called out yesterday. It’s still unclear if some of these apps will reappear after some changes.
TextMe, Inc.
BinaryPattern and Flexible Numbers LLC
Appverse Inc.
Dingtone Inc.
This case illustrates once again that Apple holds the keys to the App Store kingdom. The company acts as a judge and can make or break some companies.
Some of those companies have released clones of their apps and benefited from that strategy for many years. The main issue here is that App Store rules aren’t enforced consistently.
The clone plague is far from over. Many categories also use this App Store optimization strategy.
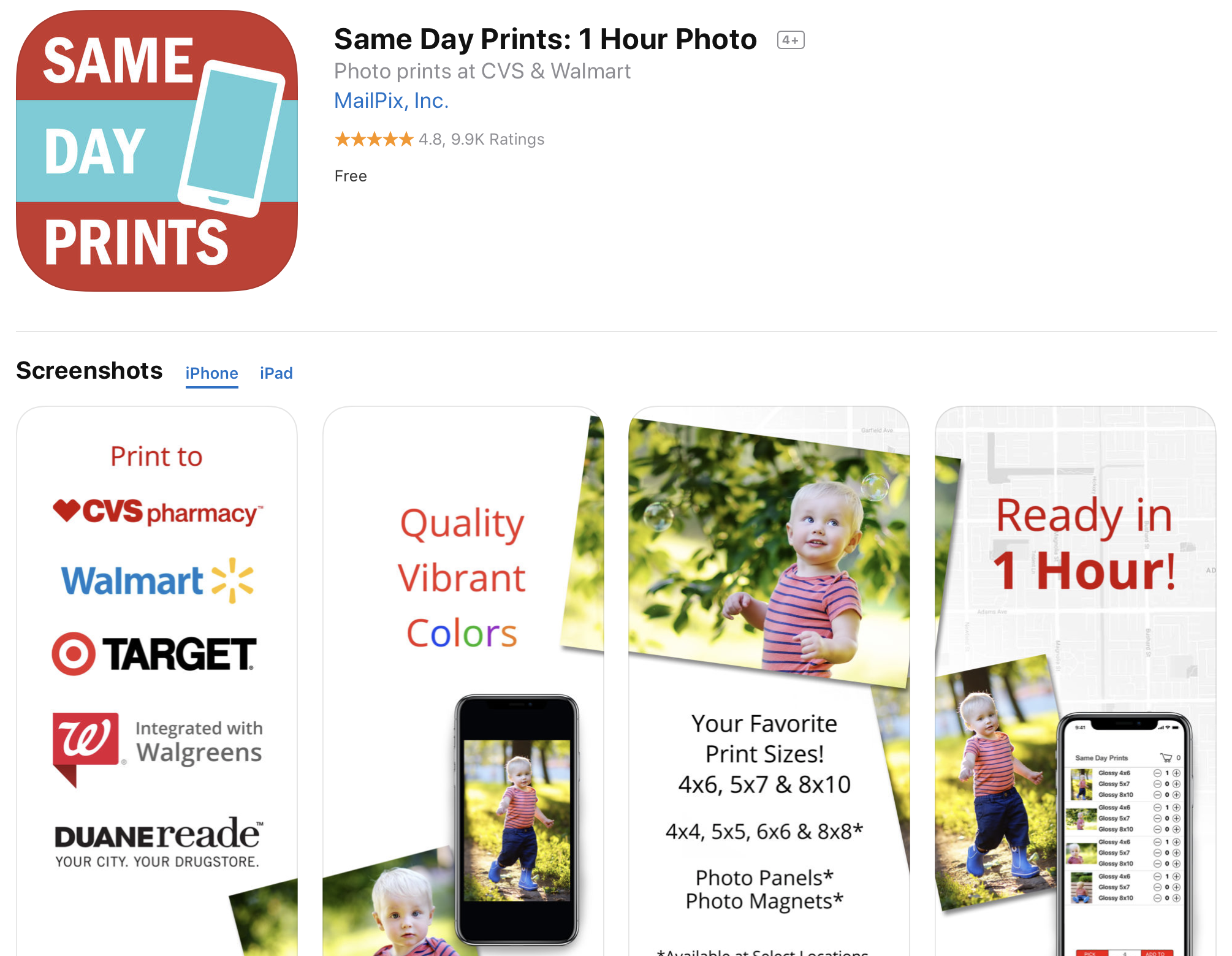
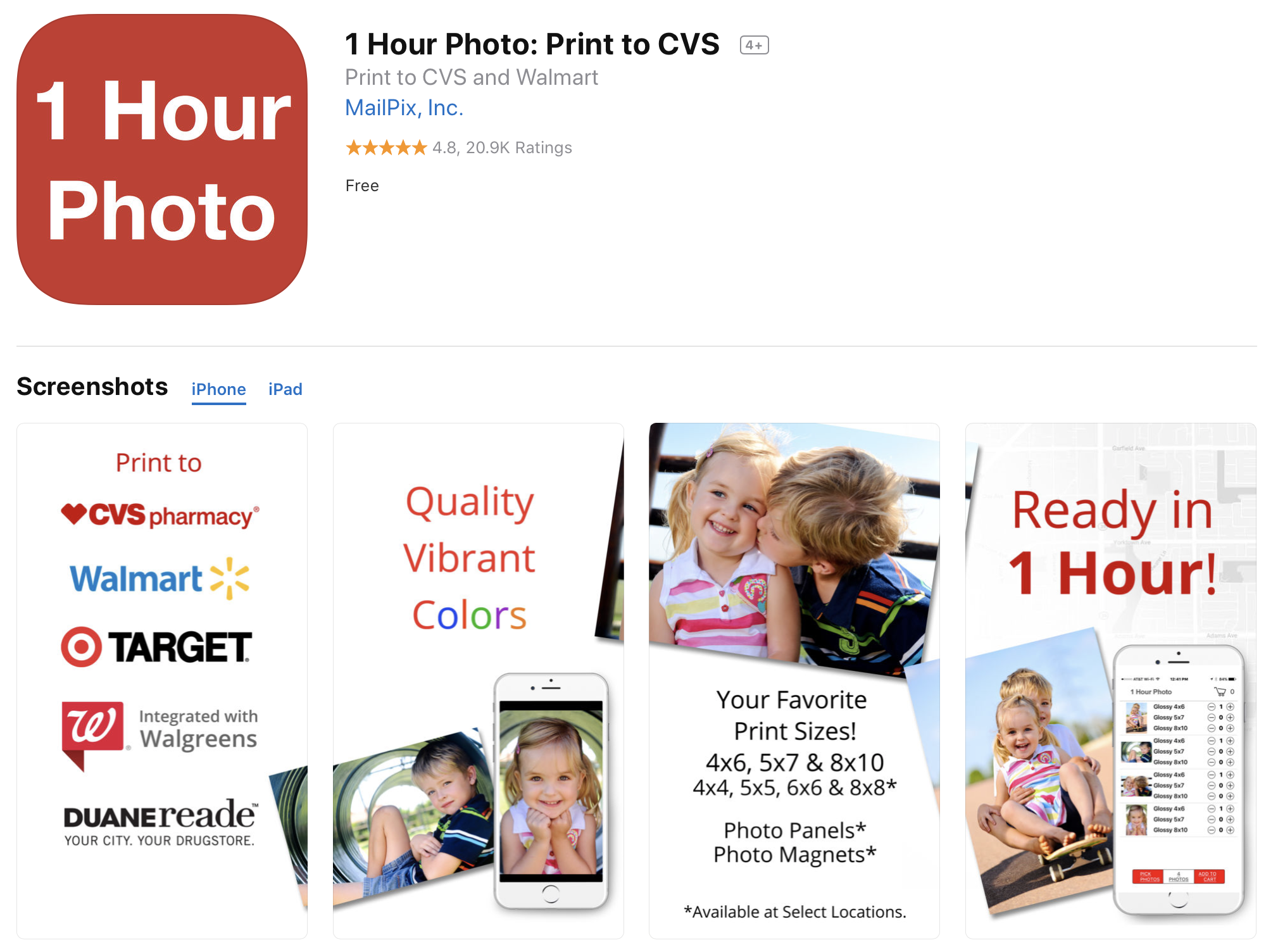
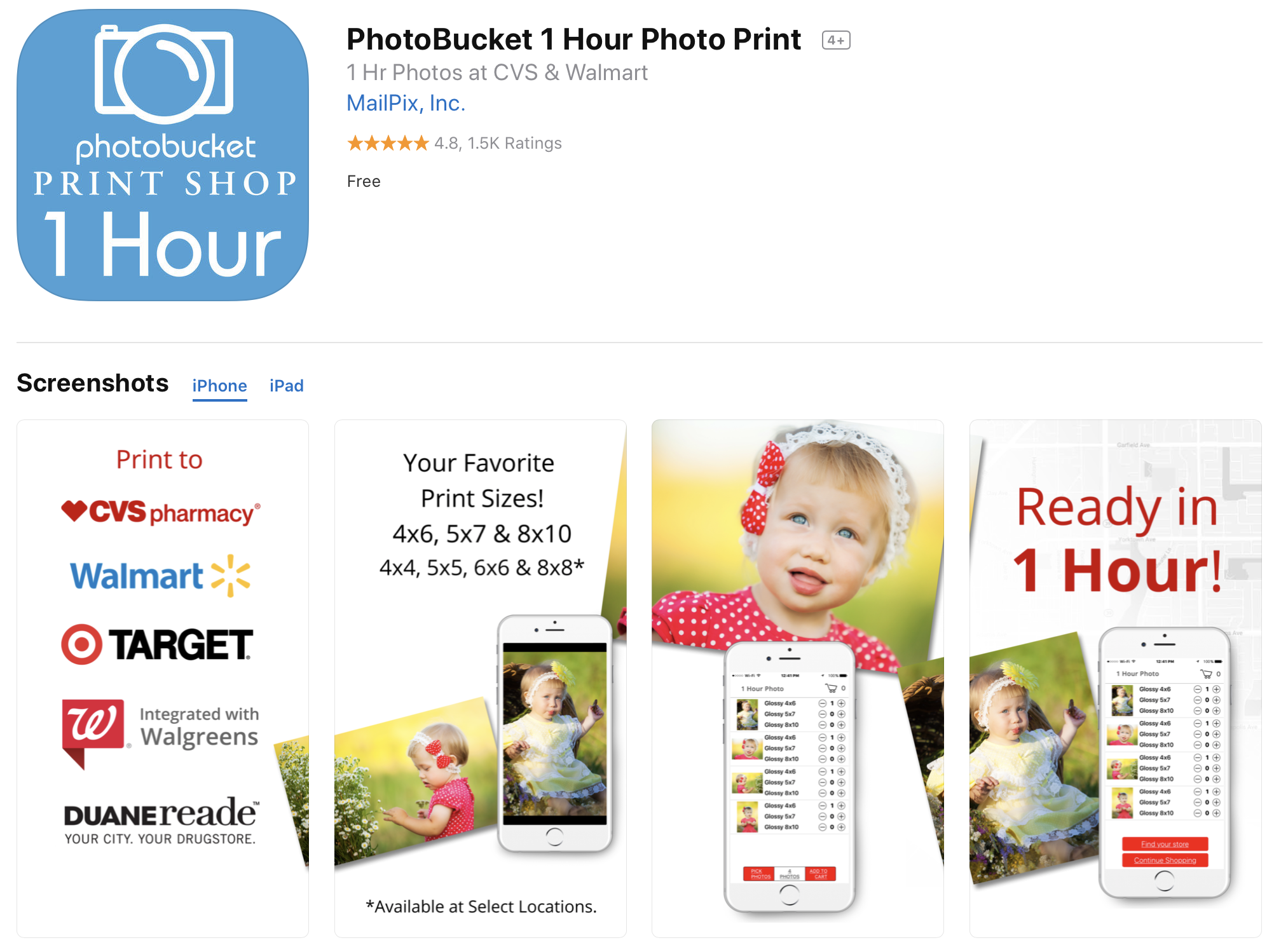
JPEG Labs has released four different apps that let you print photos in Walgreens or CVS stores around you. They all do the same thing but have different names and keywords. (They also tell you to leave a review right after opening the app.)
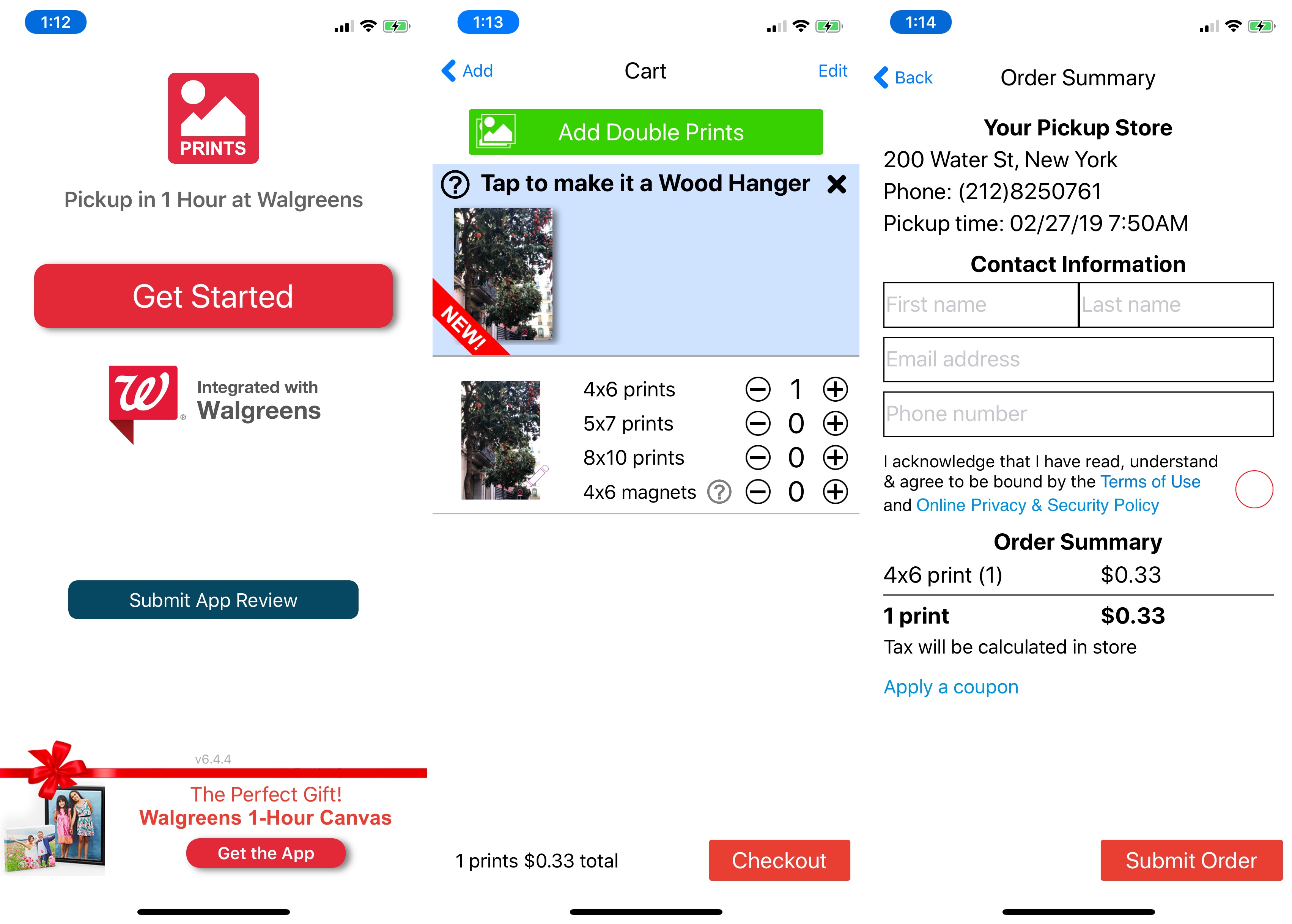
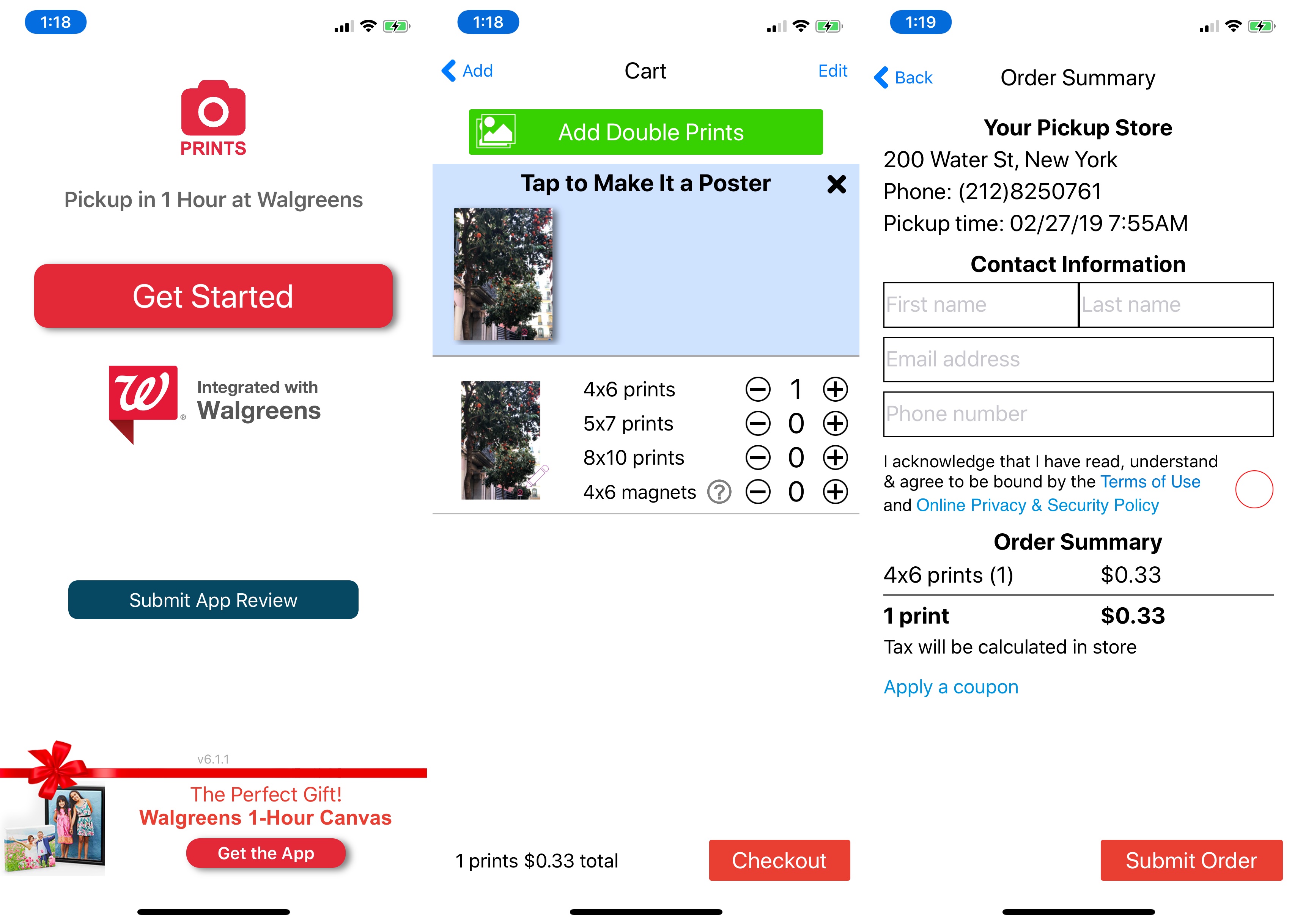
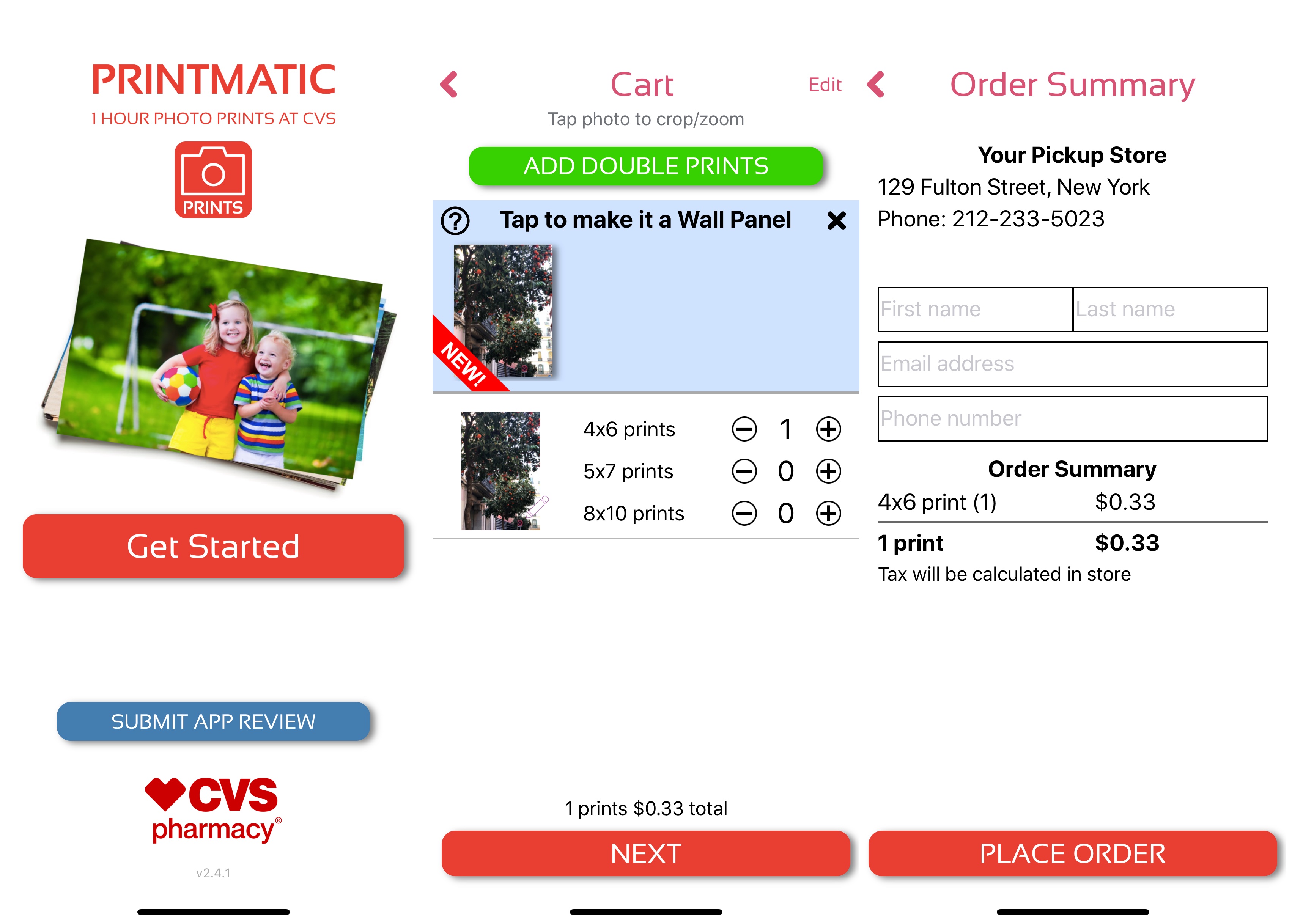
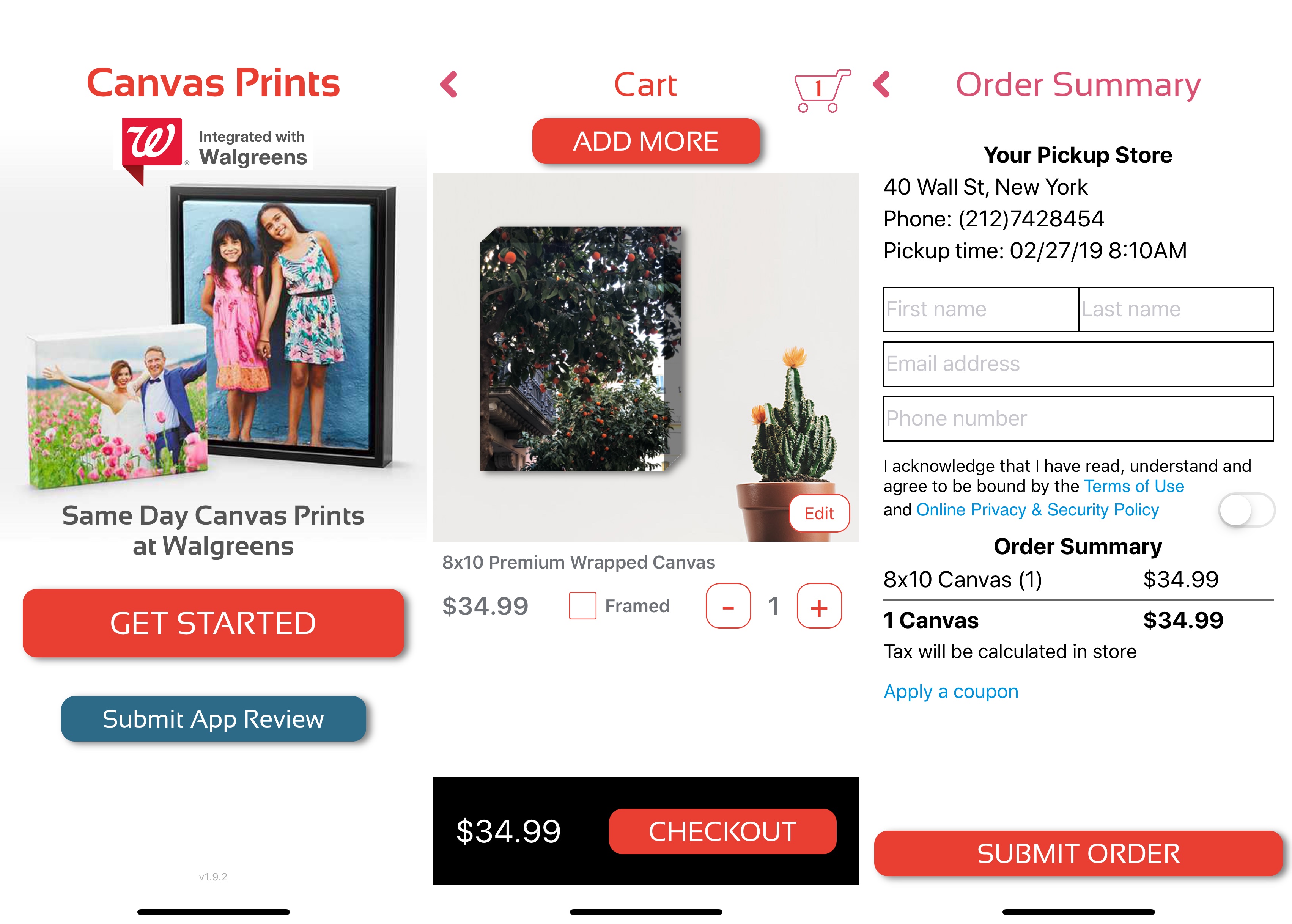
Another good example is MailPix, Inc. You can find multiple copies of the same app. The company is also slowly expanding its App Store footprint by acquiring competitors and changing those apps into duplicated versions of the main app.
MailPix acquired Photobucket’s printing app to turn it into a clone.
Powered by WPeMatico
Trust is a fundamental building block of any healthy relationship, whether that’s between individuals or companies and customers. If you can’t trust the company you are doing business with to do the right thing by you, it’s hard to continue the relationship. Too often, we have seen this trust broken when it comes to data sharing.
Last week, a Wall Street Journal article revealed a practice of apps sharing highly personal data with Facebook without user knowledge, whether the user had a Facebook account or not. In a follow-up article, the WSJ listed all 11 apps in its study (five of which stopped sharing data after being contacted by the publication). These included ovulation and heart-monitoring apps.
Whatever the reason, if your users aren’t aware that you are sharing their data in this fashion, and that would appear to be the case, then it’s a gross violation of trust between user and brand. Marc Benioff, co-CEO and co-founder at Salesforce, has often stated that trust is one of the primary components of a healthy brand-customer relationship. If you mess that up, it’s going to be very tough going for you as a business.
In an interview in September with Bloomberg’s Emily Chang, Benioff had this to say about trust. “Every CEO needs to ask themselves what is the most important thing to you. What is the most important thing to your company? What is your highest value? I know our highest value at Salesforce is trust. Nothing is more important than the trust that we have that we have with our customers or employees or partners or our top executives,” Benioff explained.
He went on to say when companies misuse customer’s data, they are breaking that trust and that could involve losing key personnel or customers. “When you see top executives walking out. When you see customers questioning your privacy practices or how you’re using or misusing their data or how you’re misusing partnerships, you need to listen. You need to wake up. You need to [ask] what is going on. It’s very serious,” Benioff said
If Benioff is right, and trust is the basis of all business relationships, then you’re playing with fire when you abuse the trust by sharing data with third parties without your customer’s knowledge, and sooner or later that’s going to come back and bite you as a brand.
Let’s face it, people stop using apps for a variety of reasons that have nothing to do with something as fundamental as trust. It could just be buggy or slow, but when the app is sending data to another company without user knowledge, it’s easy enough to just remove it from the phone and find another one that doesn’t do that (or at least you hope it doesn’t).
For brands, perception is everything. If people begin to think you are not looking out for their best interests, or are putting profit over common sense protections, it becomes difficult to turn around those negative feelings once they begin to harden.
If the brand continues to abuse its users time and again, it will eventually have an impact on revenue and begin to hurt your relationship with your existing customer base, and your ability to attract new customers to your products and services.
It seems like a risk that would be too big to take, yet we see brands take these risks time and again. If you don’t want to go that route, it’s pretty easy to prevent. Do right by your customers and they’ll continue to believe in you — or don’t, and watch what happens.
Powered by WPeMatico
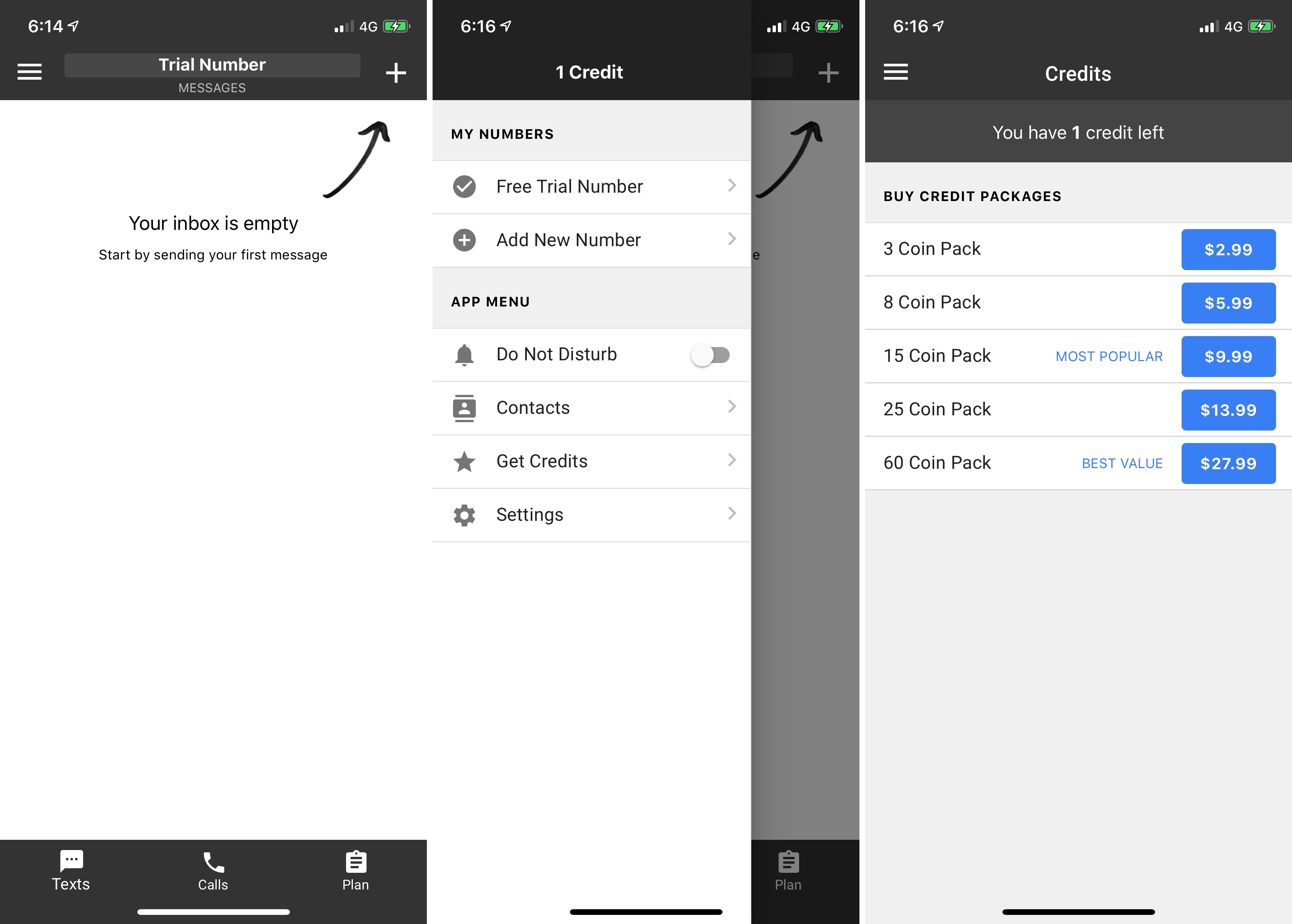
If you’ve searched the App Store for an app to get a second phone number, chances are you found dozens of apps with very little differences. A handful of companies are spamming the App Store with duplicated apps. This strategy is against Apple’s rules.
The App Store Review Guidelines are detailed rules that define what you can and cannot do on the App Store. As soon as you sign up for a developer account and submit an app to the App Store review team, you agree to comply with those rules. It’s a long document, but rule 4.3 titled “Spam” is straightforward:
Don’t create multiple Bundle IDs of the same app. If your app has different versions for specific locations, sports teams, universities, etc., consider submitting a single app and provide the variations using in-app purchase. Also avoid piling on to a category that is already saturated; the App Store has enough fart, burp, flashlight, and Kama Sutra apps already. Spamming the store may lead to your removal from the Developer Program.
A tipster looked at a specific category in the App Store — VoIP apps that let you get a second phone number and send and receive calls and texts from that new number. I looked at that category myself, and here are the results of my investigation.
Companies don’t even try to hide the fact that have submitted multiple versions of the same app with different names and icons. But core features remain the same. Apple hasn’t enforced its own guideline properly and developers took advantage of that grey area.
As you can see on the company’s website, TextMe currently operates three apps and is open about it — TextMe Up, TextMe and FreeTone. These three apps all have an average of 4.7 stars in the App Store with hundreds of thousands of reviews in total.
The wording is slightly different for each app. TextMe Up lets you “call & text anyone in the world from your mobile, tablet, and computer,” while TextMe lets you “get a new phone number and start texting and making calls for free” and FreeTone is all about “[enjoying] free calls & texts to the phone numbers in the US and Canada.”
But if you look at the App Store screenshots, the company doesn’t even bother changing the screenshots or marketing copy.
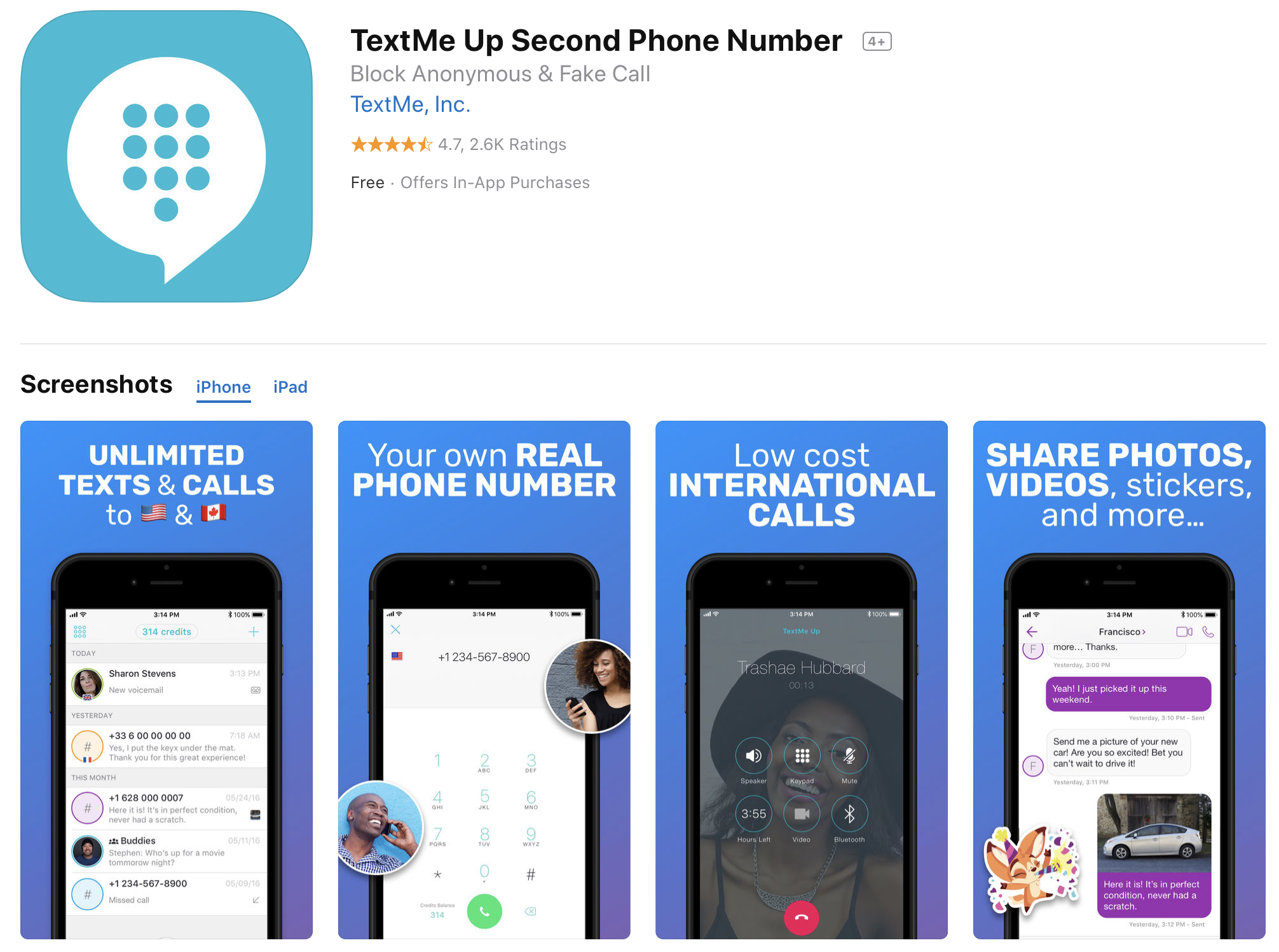


“Our apps have a different marketing target,” TextMe, Inc. co-founder and co-CEO Patrice Giami told me in a phone interview. “They share the same code base, but we can activate or deactivate some features in order to differentiate the apps. We manage that depending on the competitive environment and if we need to optimize distribution.”
Giami also believes that his company complies with the App Store guidelines. “Apple is doing a very systematic review — we’re constantly scrutinized because we release a lot of app updates. We’ve never been flagged or contacted by Apple — they’ve never said that we’re releasing complete clones of the same app,” he said.
TextMe uses the same developer account for its three apps, Text Me, Inc. Apple could easily compare those apps if it wanted to.
This case is a bit more sophisticated. The company behind these apps has two different developer accounts and tried to differentiate its App Store listings a bit. Similarly, buttons and colors vary slightly from one app to another, but it’s the same feature set.
Here are a few screenshots I took:
Burner Phone Numbers SMS/Calls
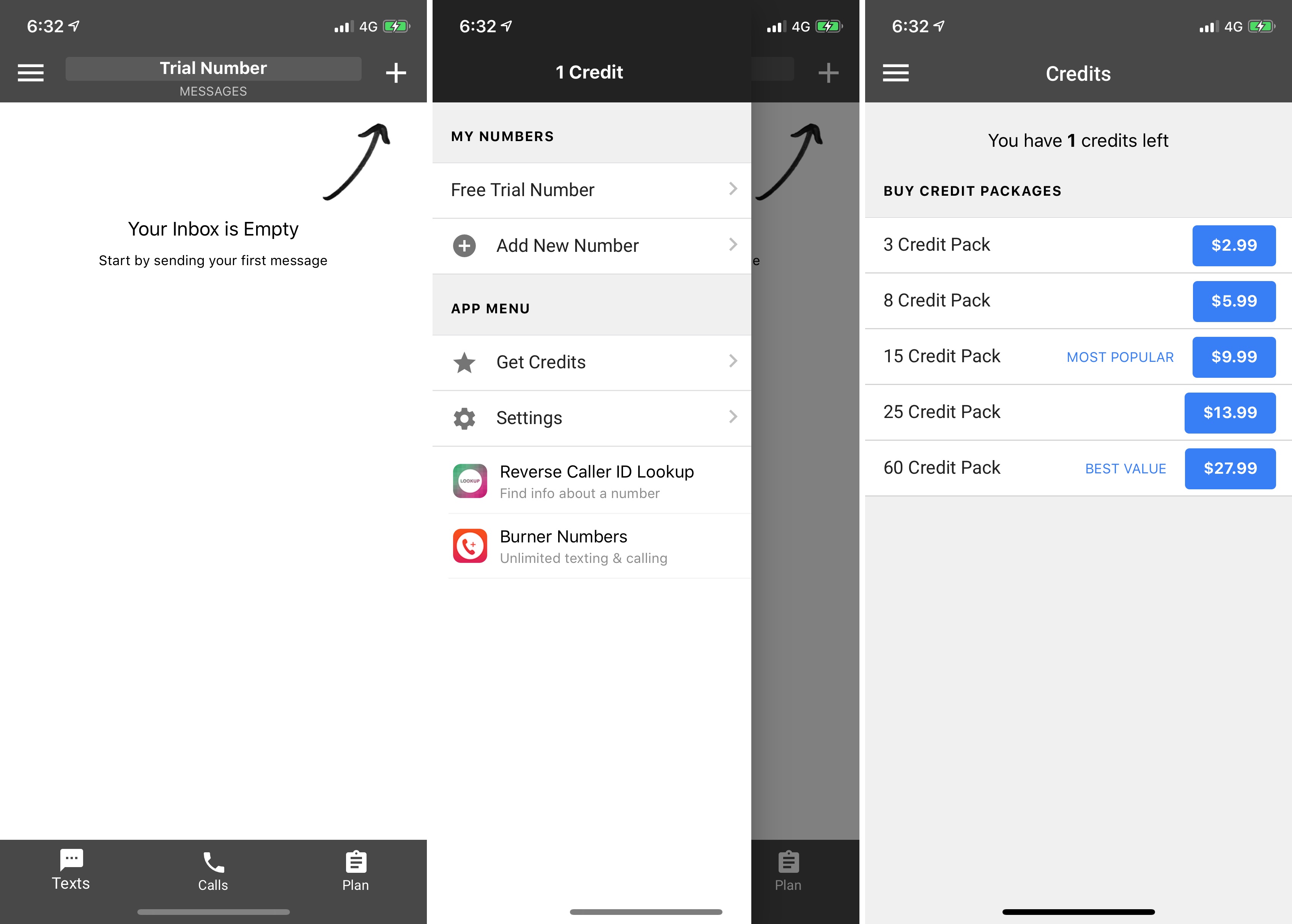
I’ve reached out to BinaryPattern/Flexible Numbers and haven’t heard back.
This time, Phoner, Second Line and Text Burner all share the same developer account. Even though these apps let you do the same thing, Appsverse has released its app in three different App Store categories — utilities, productivity and social networking.
By doing that, the company’s apps appear in multiple categories. Text Burner is No. 88 in social networking, Second Line is No. 74 in productivity and Phoner is No. 106 in utilities.
It seems a bit counterintuitive as Appsverse splits their downloads between multiple apps. But I believe the main reason the company is releasing multiple apps is for keyword optimization and App Store search results. It then picks a different category for each app, but it’s a side effect.
Appsverse sent me the following statement:
The guideline promotes a healthy App Store ecosystem that is good for both developers and users. It prevents proliferation of similar apps that does not have a differentiation in business model, features, use cases and demographic appeal.



On paper, Dingtone and Telos look like two different apps from two different companies. I downloaded the Dingtone app and signed up with my email address. I then downloaded the Telos app and signed up with the same email address. Here’s the message I got:
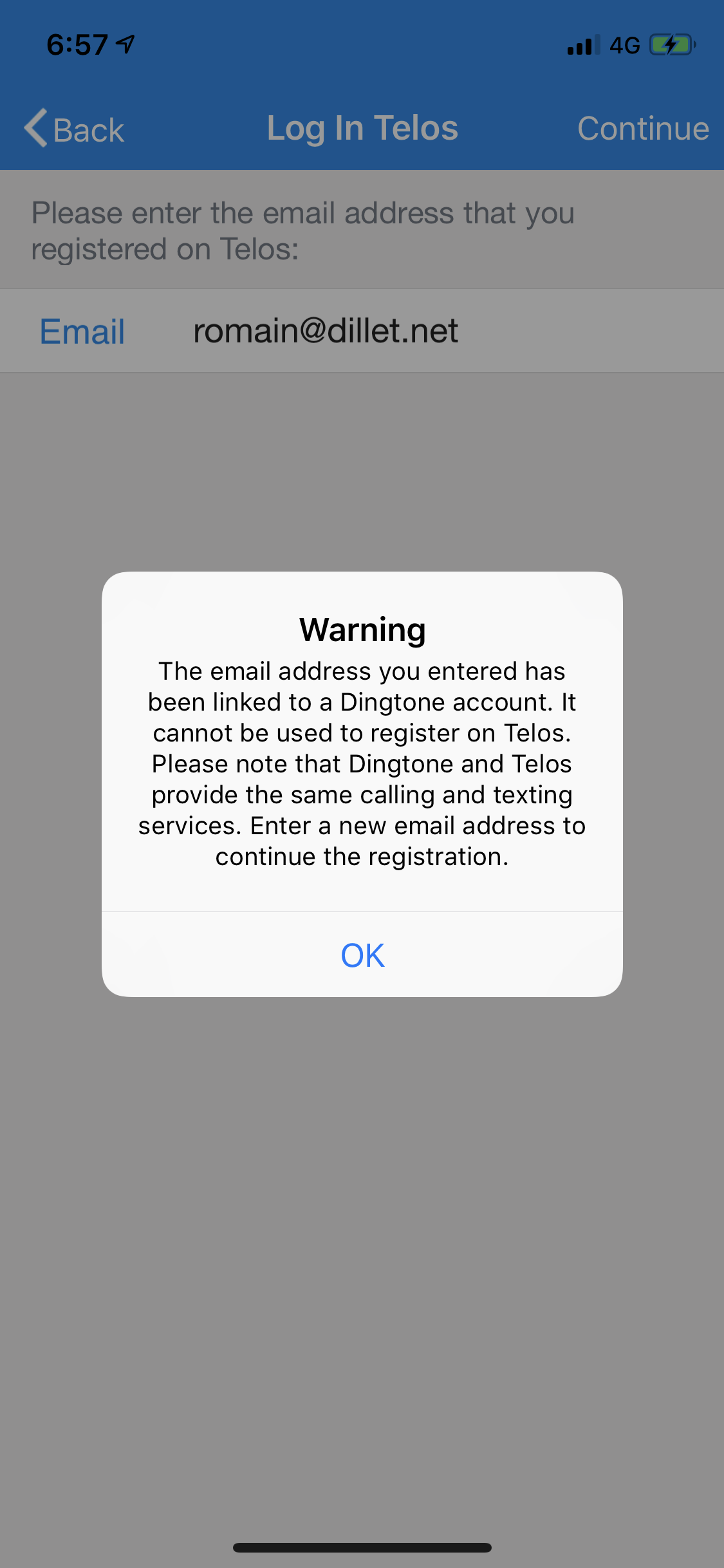
I’ve reached out to Telos/Dingtone and haven’t heard back.
These companies haven’t done anything illegal. They took advantage of Apple’s lack of oversight on an App Store rule. Releasing multiple versions of the same app is a great App Store optimization strategy. This way, you can pick a different name, different keywords and different categories. Chances are potential customers are going to see your app in their App Store search results.
While Apple is usually quite strict when it comes to App Store guidelines, it hasn’t enforced some of them. And this is unfair for app developers who play by the rules. They can’t compete as effectively with companies that know that they can ignore some rules.
Powered by WPeMatico
Google’s Gradient Ventures, the search giant’s dedicated AI fund, is casting its eye to Asia after it led a $7 million Series A round for Elsa, a startup that operates an app for English language learners.
The deal is Gradient’s first in Asia, and it includes participation from existing investors Monk’s Hill Ventures and SOSV. Elsa has now raised $12 million to date.
Elsa was founded in 2015 as a way to help non-English speakers improve their accent and general speaking ability. Vu Van, CEO and one half of the founding team, is a Vietnamese national who, despite being fluent in English, struggled to be understood after moving to the U.S. to study and then work. Together with speech recognition researcher Dr. Xavier Anguera — the startup’s CTO who leads its Portugal-based tech team — Van started Elsa to help people in the same predicament.
“I was very good at grammar, reading and writing but I realized people had a hard time understanding me because I had a very strong accent and my pronunciation wasn’t proper,” Van, who is based in San Francisco but travels extensively, told TechCrunch in an interview. “This impacts confidence when you apply for jobs or are even just meeting friends.”
“There are so many English learning solutions but they are mostly focused on expanding vocabulary or grammar, very few deal with pronunciation,” she added.
Elsa uses voice recognition and AI to grade a user’s speaking versus standard American English (and I thought us Brits were the global standard…) giving them a score at the end. That helps track their progress, while it focuses on pronunciation with a detailed review on how a user is speaking.
The service uses a freemium model that grants users full access to 1,000 courses for around $3-6 per month depending on the length of the package they select. That ranges from one month of access to 12 months. New content is added every week, Van said.

With this money in the bag, Elsa is going after growth in a number of its most promising markets.
The service has users in more than 100 countries, but Vietnam is its top market, with two million paying users. Partly because it is Van’s home market, Elsa has doubled down on Vietnam with a local sales team and localized payments, including the likes of bank transfers and local wallets.
That’s the blueprint for expansion in its next three target countries: Japan, Indonesia and India. Elsa has opened an office in Tokyo and is planning to introduce more localized content for Japanese users. Similar efforts will happen in Indonesia and India, where Van said the app sees strong engagement and downloads without any paid marketing efforts.
Elsa is also working on expanding its content from English to include other languages. Spanish is currently on the horizon and the company is already preparing the back-end technology to make it possible.
“We have to build the voice recognition technology to recognize those languages accurately. We have the infrastructure but now just need to collect voice data to train the model,” explained Van.

Vu Van started Elsa in 2015 with Dr. Xavier Anguera to help non-English speakers improve their accent and general speaking ability.
Beyond geographic expansion, Elsa is also going after schools and classrooms. Already, in Vietnam, it is working with a handful of schools that have added the app to their classroom work. The company allows schools to upload their specific content or curriculum to Elsa to make it part of a student’s homework or assessment. Teachers can see if a student has completed oral homework, and the app grades their efforts.
“We want to help these teachers help their students,” Van said. “Even with the best intentions, they simply can’t teach speaking.”
The model for the education push sees schools pay a licensing fee per student, which Van said is subsidized, while uploading their content is free.
Snagging investment from Gradient is a notable achievement for Elsa, but it will also allow the startup to tap into the company’s talent, too. That’s because Gradient operates a rotational program that allows Google employees to spend three to six months working at portfolio startups on secondment. That process hasn’t kicked off for Elsa just yet, but Van is hopeful of securing an engineer who might otherwise be prohibitively expensive for her company.
Gradient Ventures was founded in 2017 and this deal is the fund’s 18th, according to Crunchbase. Its previous investments include Canvass Analytics and Test.ai.

The Elsa team
Powered by WPeMatico
Tinder, the dating app company which, as of late, has been more fully embracing its status as the preferred hook-up app of choice for the younger generation, is today launching a new feature designed for its college-aged Tinder U users: Spring Break mode. The feature will allow students to swipe through potential matches before heading out to their Spring Break destination.
Here’s how it works.
From March 4 through March 31, 2019, Spring Break mode will go live in Tinder, offering 20 popular destinations, including Cabo, Lake Havasu, Las Vegas, Miami, New Orleans, Puerto Rico, Puerto Vallarta, San Diego and others. To opt in, Tinder U users will need to look for the Spring Break card while swiping.
When they see it, they can then select their Spring Break destination to see who’s going. This destination will then be shown to potential matches through a badge on their profiles.
The idea, says Tinder, was inspired by trends the company was already seeing in product usage during this March time frame, when there would be huge upticks in some cities and locations. For example, South Padre Island experienced a 100x increase in activity in March 2018 compared to the previous month; Panama City saw a 10x increase; Destin Beach a 6x increase; and both Cabo San Lucas and Lake Havasu saw a 2x increase.
In addition to using its own data from past spring breaks, Tinder also consulted with its Tinder U users about which destinations to include.
“Spring Break, like Tinder, is a staple for many college students across the country,” said Jenny Campbell, chief marketing officer at Tinder, in a statement. “We’ve historically seen huge upticks in Tinder usage during Spring Break in these destinations, and we are excited to give users the unique experience to connect before they pack their bags,” she said.
The new feature is one of several ways that Tinder is focusing on its more casual use case, as of late. Last November, the company told investors during its Q3 earnings that it would begin marketing the app as a way to enjoy the “single lifestyle” — that is, catering to a younger demographic’s demand for wanting to date around while in their 20s — before they’re ready to settle down.
Tinder had also begun an online publication, Swipe Life, and is running various advertising campaigns related to this initiative.
For years, Tinder had tried to downplay the app’s more casual nature, but it’s now able to change course due to its acquisition of dating app Hinge. Similarly aimed at younger users and millennials, Hinge is focused on creating relationships, not hook-ups. That frees up Tinder to refocus on what it does best: quick matches.
Tinder parent Match Group had hinted at its plans for Tinder U during its earnings call earlier this month.
“In 2019, we are planning to solidify our leadership position among college students by expanding Tinder U to cover even more schools throughout the U.S. while also launching Tinder U in select international markets,” said Match Group CEO Mandy Ginsberg, speaking to investors. “We’re also expanding marketing through our on campus brand ambassadors and social media influencers. Expect to see more events and marketing tied to the school social calendar such as Rivalry Week and Spring Break,” she noted.
However, by shifting focus more toward a younger, less established customer base, Tinder could be challenged on the revenue side, as college students are less likely to have disposable incomes for things like a paid Tinder Gold subscription. Instead, Tinder will need to generate revenue from these users through in-app purchases — like Boost and Super Like (the latter which is often used by mistake, turning it into a running joke on the dating app).
Tinder said it’s considering rolling out a wider range of à la carte features in the future, and plans to focus on this aspect of its service, as well, in 2019.
Powered by WPeMatico
As subscriptions continue to grow into a sizable revenue stream for mobile app developers, Apple has had to make adjustments to its guidelines, rules and even its tools for subscription management in recent weeks. It issued stricter guidelines around how subscriptions are to be presented to consumers, and it made the setting for canceling existing subscriptions more accessible. Now, Apple is rolling out new tools for developers that will help them retain their current customers and win back lapsed subscribers.
The company announced on Friday that apps with auto-renewable subscriptions will soon be able to offer their subscriptions at a discounted price for a specific period, as a means of growing and retaining their customer base. This will give the developers more control over their subscription pricing than was available before.
Until the change, developers could only make introductory offers to entice consumers to sign up for the first time. For example, developers could lure customers with a one-time introductory price, offer a free trial or offer a discounted rate for a specific period of time before the subscription converted to the full price.
But these offers could only be made to first-time customers. The new promotional offers will allow developers to cut similar deals for existing subscribers or to win back the business from those who used to pay for the subscription but had canceled.
While the new promotional offers allow for the same sort of discounts as introductory offers, they’re more flexible in terms of how they’re used.
With introductory offers, developers were allowed one offer per subscription, per territory. With promotional offers, developers can activate up to 10 offers per subscription. This allows them to test which ones work best for their customers, instead of having to pick just one.
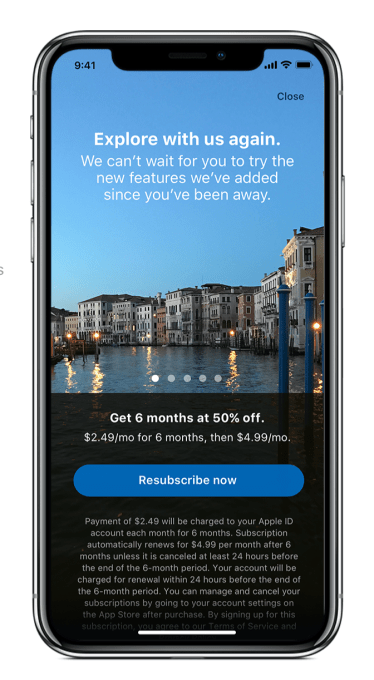 And developers are in control of when an offer displays to a customer, in which territories and how many offers a customer can redeem.
And developers are in control of when an offer displays to a customer, in which territories and how many offers a customer can redeem.
In addition, while introductory offers may display in the App Store when promoted, the promotional offers will not. That means developers can use business logic that targets winning back their most valuable customers with offers that may be better from those shown to others — and no one would be the wiser. It also means developers can offer different deals to lapsed customers — like maybe a discounted subscription — compared with promos meant to retain current subscribers.
Developers will also be able to use receipt validation tools to find subscribers who turned off auto-renewal, which allows them to target those customers with new offers before their subscription lapses. They may also decide to target those who cancel during the free trial with different offers than those who cancel after using a paid subscription for a time.
As an end-user looking to save money, these changes mean it may be worth toggling off your subscriptions from time to time to see if you’re offered a better deal to resubscribe.
Developers were alerted to the new features last week, but the offers themselves aren’t yet publicly available.
To create the offers, developers have to download the latest Xcode 10.2 beta and will need to implement the new StoreKit APIs. They can then test their offers on the latest beta version of iOS 12.2, macOS 10.14.4 and tvOS 12.2. Apple said the offers will be made available to the public “soon.”
Powered by WPeMatico
It’s only been a few weeks since Google brought the Assistant to Google Maps to help you reply to messages, play music and more. This feature first launched in English and will soon start rolling out to all Assistant phone languages. In addition, Google also today announced that the Assistant will come to Android Messages, the standard text messaging app on Google’s mobile operating system, in the coming months.
If you remember Allo, Google’s last failed messaging app, then a lot of this will sound familiar. For Allo, after all, Assistant support was one of the marquee features. The different, though, is that for the time being, Google is mostly using the Assistant as an additional layer of smarts in Messages while in Allo, you could have full conversations with a special Assistant bot.
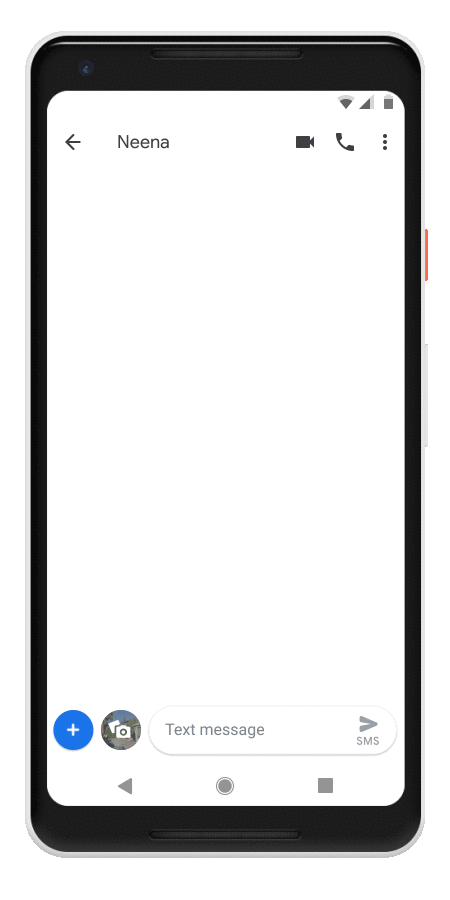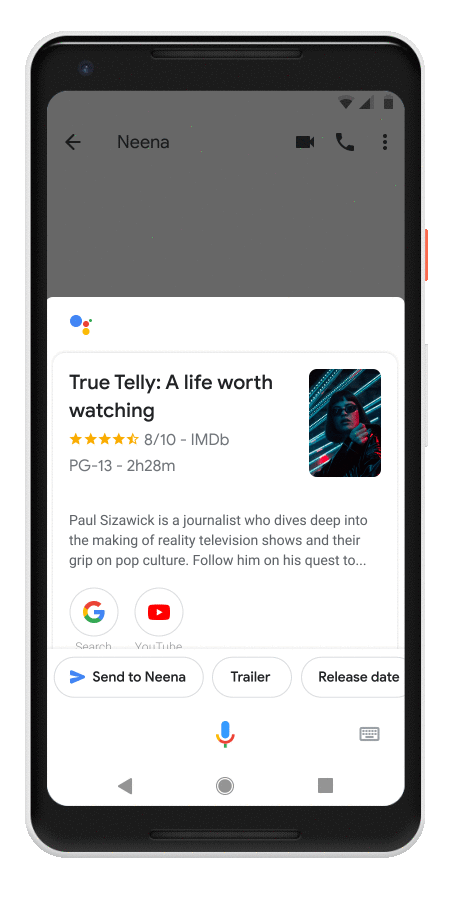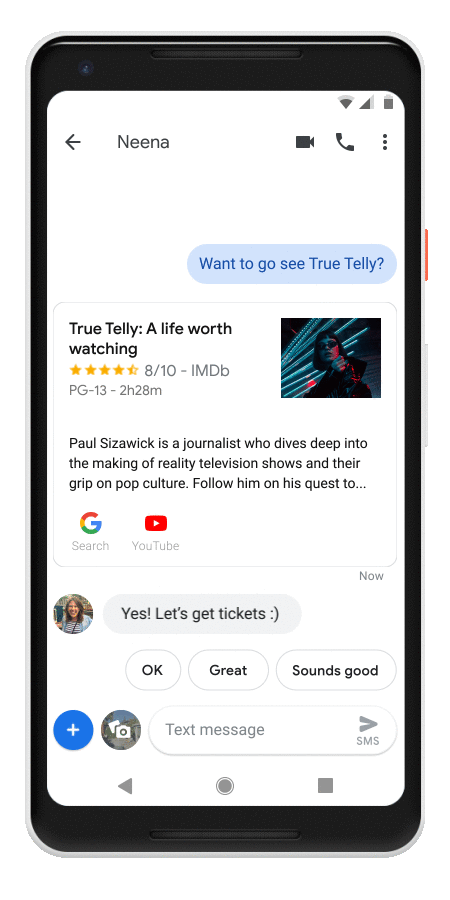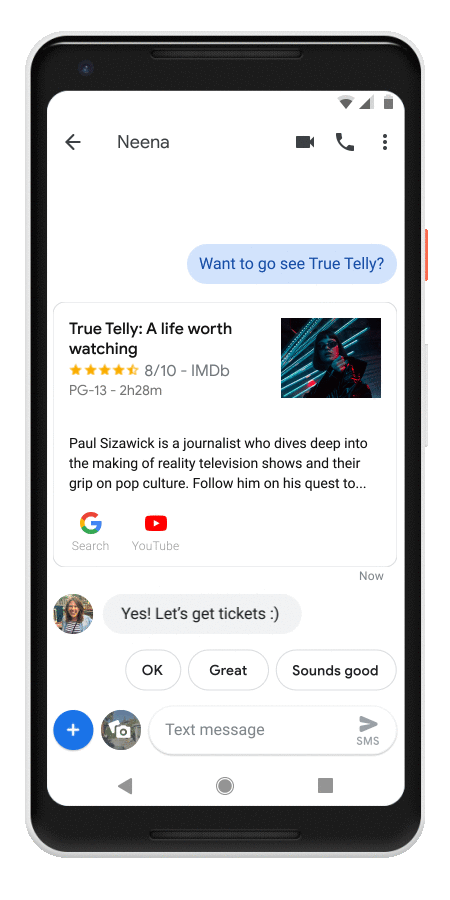
In Messages, the Assistant will automatically pop up suggestion chips when you are having conversations with somebody about movies, restaurants and the weather. That’s a pretty limited feature set for now, though Google tells us that it plans to expand it over time.
What’s important here is that the suggestions are generated on your phone (and that may be why the machine learning model is limited, too, since it has to run locally). Google is clearly aware that people don’t want the company to get any information about their private text chats. Once you tap on one of the Assistant suggestions, though, Google obviously knows that you were talking about a specific topic, even though the content of the conversation itself is never sent to Google’s servers. The person you are chatting with will only see the additional information when you push it to them.
Powered by WPeMatico
Facebook will end its unpaid market research programs and proactively take its Onavo VPN app off the Google Play store in the wake of backlash following TechCrunch’s investigation about Onavo code being used in a Facebook Research app the sucked up data about teens. The Onavo Protect app will eventually shut down, and will immediately cease pulling in data from users for market research, though it will continue operating as a Virtual Private Network in the short-term to allow users to find a replacement.
Facebook has also ceased to recruit new users for the Facebook Research app that still runs on Android but was forced off of iOS by Apple after we reported that it violated Apple’s Enterprise Certificate program for employee-only apps. Existing Facebook Research app studies will continue to run, though.
With the suspicions about tech giants and looming regulation leading to more intense scrutiny of privacy practices, Facebook has decided that giving users a utility like a VPN in exchange for quietly examining their app usage and mobile browsing data isn’t a wise strategy. Instead, it will focus on paid programs where users explicitly understand what privacy they’re giving up for direct financial compensation.
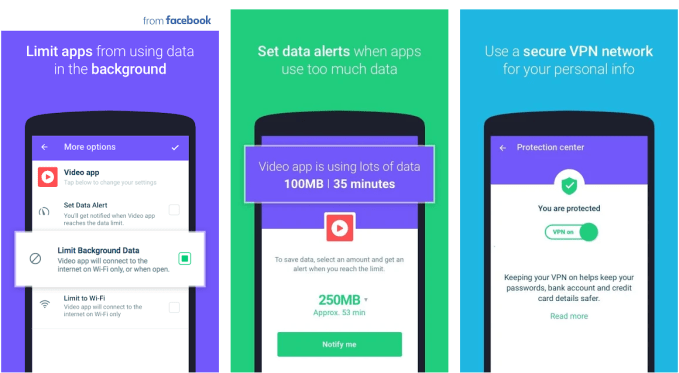
Onavo billed itself as a way to “limit apps from using background data” and “use a secure VPN network for your personal info” but also noted it would collect the “Time you spend using apps, mobile and Wi-Fi data you use per app, the websites you visit, and your country, device and network type.” A Facebook spokesperson confirmed the change and provided this statement: “Market research helps companies build better products for people. We are shifting our focus to reward-based market research which means we’re going to end the Onavo program.”
 Facebook acquired Onavo in 2013 for a reported $200 million to use its VPN app to gather data about what people were doing on their phones. That data revealed WhatsApp was sending over twice as many messages per day as Messenger, BuzzFeed’s Ryan Mac and Charlie Warzel reported, convincing Facebook to pay a steep sum of $19 billion to buy WhatsApp. Facebook went on to frame Onavo as a way for users to reduce their data usage, block dangerous websites, keep their traffic safe from snooping — while Facebook itself was analyzing that traffic. The insights helped it discover new trends in mobile usage, keep an eye on competitors and figure out what features or apps to copy. Cloning became core to Facebook’s product strategy over the past years, with Instagram’s version of Snapchat Stories growing larger than the original.
Facebook acquired Onavo in 2013 for a reported $200 million to use its VPN app to gather data about what people were doing on their phones. That data revealed WhatsApp was sending over twice as many messages per day as Messenger, BuzzFeed’s Ryan Mac and Charlie Warzel reported, convincing Facebook to pay a steep sum of $19 billion to buy WhatsApp. Facebook went on to frame Onavo as a way for users to reduce their data usage, block dangerous websites, keep their traffic safe from snooping — while Facebook itself was analyzing that traffic. The insights helped it discover new trends in mobile usage, keep an eye on competitors and figure out what features or apps to copy. Cloning became core to Facebook’s product strategy over the past years, with Instagram’s version of Snapchat Stories growing larger than the original.
But last year, privacy concerns led Apple to push Facebook to remove the Onavo VPN app from the App Store, though it continued running on Google Play. But Facebook quietly repurposed Onavo code for use in its Facebook Research app that TechCrunch found was paying users in the U.S. and India ages 13 to 35 up to $20 in gift cards per month to give it VPN and root network access to spy on all their mobile data.
Facebook ran the program in secret, obscured by intermediary beta testing services like Betabound and Applause. It only informed users it recruited with ads on Instagram, Snapchat and elsewhere that they were joining a Facebook Research program after they’d begun signup and signed non-disclosure agreements. A Facebook spokesperson claimed in a statement that “there was nothing ‘secret’ about this”, yet it had threatened legal action if users publicly discussed the Research program.
But the biggest problem for Facebook ended up being that its Research app abused Apple’s Enterprise Certificate program meant for employee-only apps to distribute the app outside the company. That led Apple to ban the Research app from iOS and invalidate Facebook’s certificate. This shut down Facebook’s internal iOS collaboration tools, pre-launch test versions of its popular apps and even its lunch menu and shuttle schedule to break for 30 hours, causing chaos at the company’s offices.
To preempt any more scandals around Onavo and the Facebook Research app and avoid Google stepping in to forcibly block the apps, Facebook is now taking Onavo off the Play Store and stopping recruitment of Research testers. That’s a surprising voluntary move that perhaps shows Facebook is finally getting in tune with the public perception of its shady actions. The company has repeatedly misread how users would react to its product launches and privacy invasions, leading to near constant gaffes and an unending news cycle chronicling its blunders.
Without Onavo, Facebook loses a powerful method of market research, and its future initiatives here will come at a higher price. Facebook has run tons of focus groups, surveys and other user feedback programs over the past decade to learn where it could improve or what innovations it could co-opt. And with more apps recently turning on encryption, Onavo likely started learning less about their usage. But given how cloning plus acquisitions like WhatsApp and Instagram have been vital to Facebook’s success, it’s likely worth paying out more gift cards and more tightly monitoring its research practices. Otherwise Facebook could miss the next big thing that might disrupt it.
Hopefully Facebook will be less clandestine with its future market research programs. It should be upfront about its involvement, make certain that users understand what data they’re giving up, stop researching teens or at the very least verify the consent of their parents and avoid slurping up sensitive information or data about a user’s unwitting friends. For a company that depends on people to trust it with their content, it has a long way to go win back our confidence.
Powered by WPeMatico
Instagram is threatening to attack Pinterest just as it files to go public the same way the Facebook-owned app did to Snapchat. Code buried in Instagram for Android shows the company has prototyped an option to create public “Collections” to which multiple users can contribute. Instagram launched private Collections two years ago to let you Save and organize your favorite feed posts. But by allowing users to make Collections public, Instagram would become a direct competitor to Pinterest.
Instagram public Collections could spark a new medium of content curation. People could use the feature to bundle together their favorite memes, travel destinations, fashion items or art. That could cut down on unconsented content stealing that’s caused backlash against meme “curators” like F*ckJerry by giving an alternative to screenshotting and reposting other people’s stuff. Instead of just representing yourself with your own content, you could express your identity through the things you love — even if you didn’t photograph them yourself. And if that sounds familiar, you’ll understand why this could be problematic for Pinterest’s upcoming $12 billion IPO.
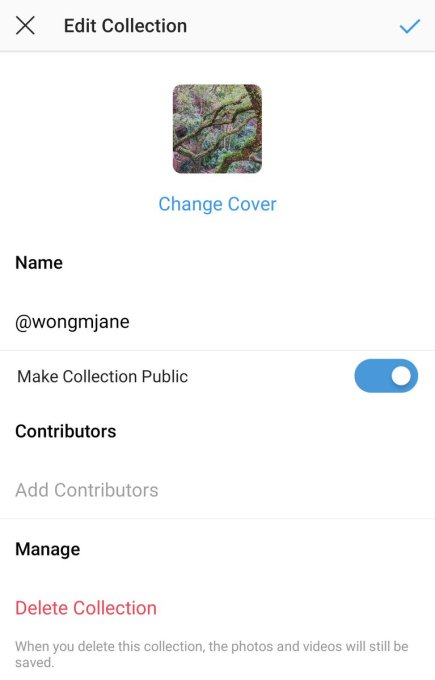
The “Make Collection Public” option was discovered by frequent TechCrunch tipster and reverse engineering specialist Jane Manchun Wong. It’s not available to the public, but from the Instagram for Android code, she was able to generate a screenshot of the prototype. It shows the ability to toggle on public visibility for a Collection, and tag contributors who can also add to the Collection. Previously, Collections was always a private, solo feature for organizing your bookmarks gathered through the Instagram Save feature Instagram launched in late 2016.
Instagram told TechCrunch “we’re not testing this,” which is its standard response to press inquiries about products that aren’t available to public users, but that are in internal development. It could be a while until Instagram does start experimenting publicly with the feature and longer before a launch, and the company could always scrap the option. But it’s a sensible way to give users more to do and share on Instagram, and the prototype gives insight into the app’s strategy. Facebook launched its own Pinterest -style shareable Sets in 2017 and launched sharable Collections in December.
Currently there’s nothing in the Instagram code about users being able to follow each other’s Collections, but that would seem like a logical and powerful next step. Instagrammers can already follow hashtags to see new posts with them routed to their feed. Offering a similar way to follow Collections could turn people into star curators rather than star creators without the need to rip off anyone’s content. Speaking of infuencers, Wong also spotted Instagram prototyping IGTV picture-in-picture, so you could keep watching a long-form video after closing the app and navigating the rest of your phone.
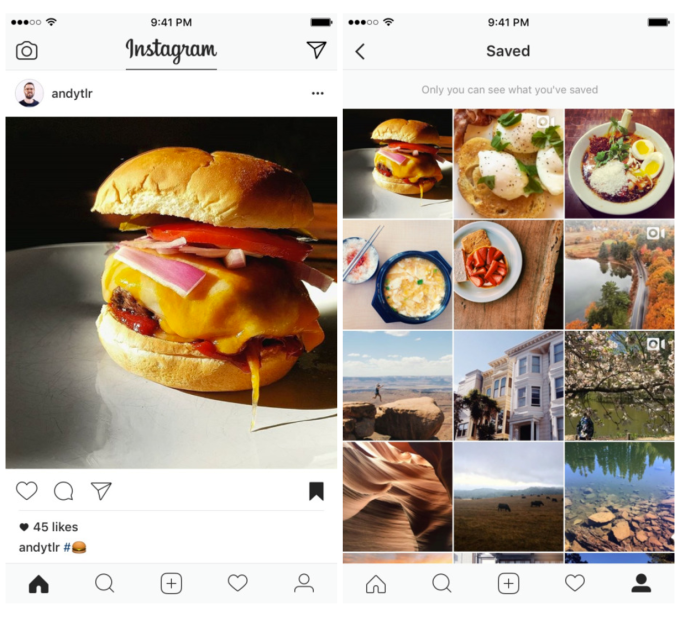
Instagram lets users Save posts, which can then be organized into Collections
Public Collections could fuel Instagram’s commerce strategy that Mark Zuckerberg recently said would be a big part of the road map. Instagram already has a personalized Shopping feed in Explore, and The Verge’s Casey Newton reported last year that Instagram was working on a dedicated shopping app. It’s easy to imagine fashionistas, magazines and brands sharing Collections of their favorite buyable items.
It’s worth remembering that Instagram launched its copycat of Snapchat Stories just six months before Snap went public. As we predicted, that reduced Snapchat’s growth rate by 88 percent. Two years later, Snapchat isn’t growing at all, and its share price is at just a third of its peak. With more than 1 billion monthly and 500 million daily users, Instagram is four times the size of Pinterest. Instagram loyalists might find it’s easier to use the “good enough” public Collections feature where they already have a social graph than try to build a following from scratch on Pinterest.
Powered by WPeMatico
Last fall, Opera introduced Opera Touch for iOS — a solid alternative to Safari on iPhone, optimized for one-handed use. Today, the company is rolling out a notable new feature to this app: cookie blocking. Yes, it can now block those annoying dialogs that ask you to accept the website’s cookies. These are particularly problematic on mobile, where they often entirely interrupt your ability to view the content, as opposed to on many desktop websites where you can (kind of) ignore the pop-up banner that appears at the bottom or the top of the page.
Cookie dialogs have become prevalent across the web as a result of Europe’s GDPR, but many people find them overly intrusive. Today, it takes an extra click to dismiss these prompts, which slows down web browsing — especially for those times you’re on the hunt for a particular piece of information and are visiting several websites in rapid succession.
The cookie blocking feature was first launched in November on Opera’s flagship app for Android, but hadn’t yet made its way to iOS — through any browser app, that is, not just one from Opera. The company says it uses a mix of CSS and JavaScript heuristics in order to block the prompts.
At the time of the launch, Opera noted it had tested the feature with some 15,000 sites.
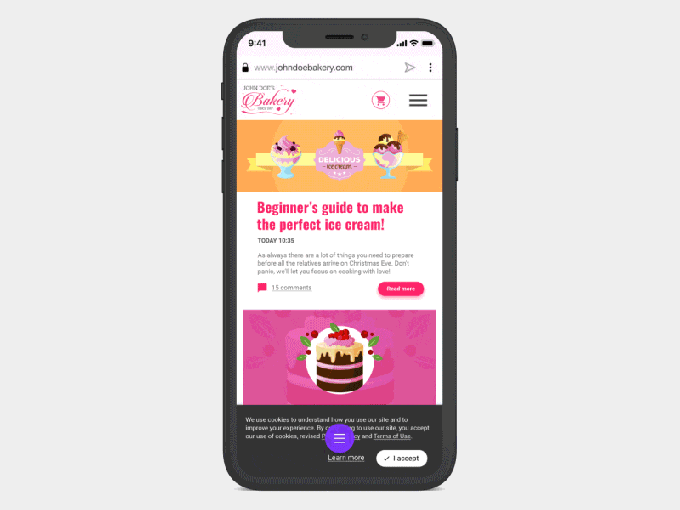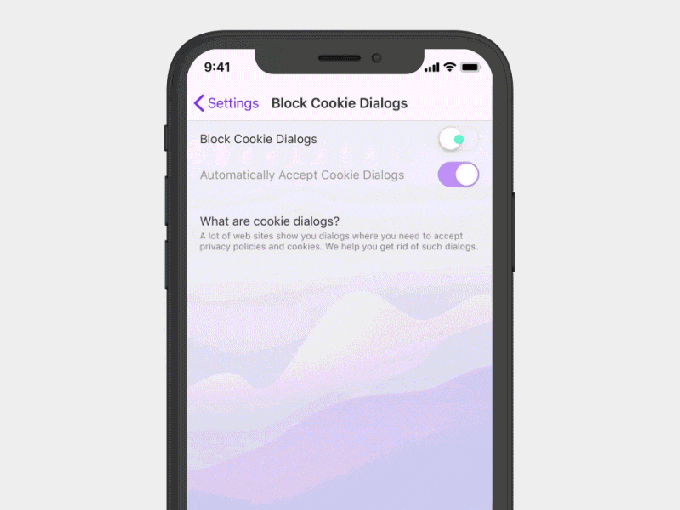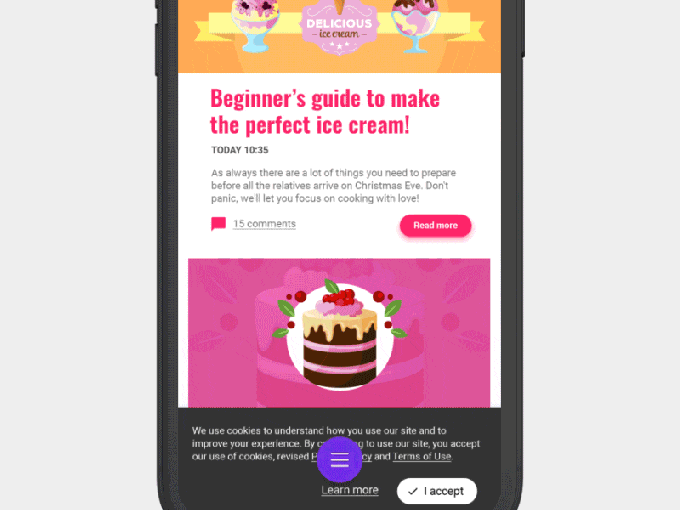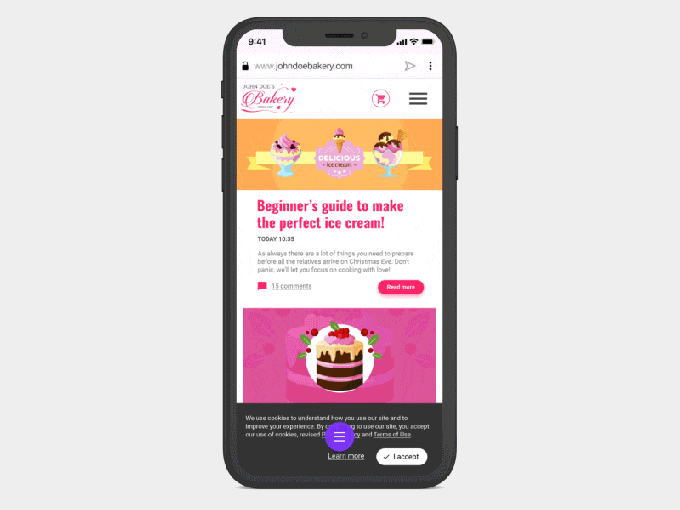
It’s important to note that the default setting for the cookie blocker on Opera Touch will allow the websites to set cookies.
Here’s how it works. When you enable the feature, it will hide the dialog boxes from appearing, allowing you to read a website without having to first close the prompt. However, when you turn on the Cookie Blocker option, another setting is also switched on: one that says “automatically accept cookie dialogs.”
That means, in practice, when you’re enabling the Cookie Blocker, you’re also enabling cookie acceptance if you don’t take further action.
But Opera says you can disable this checkbox, if you don’t want your browser to give websites your acceptance.
In addition to the new cookie blocking, the browser has a number of other options that make it an interesting alternative to Safari on iOS or Google Chrome.
For example, if offers built-in ad blocking, cryptocurrency mining protection (which prevents malicious sites from using your device’s resources to mine for cryptocurrencies), a way to send web content to your PC through Opera’s “Flow” technology and — most importantly — a design focused on using the app with just one hand.
Since the app’s launch in April, the company has rolled out 23 new features in total. This includes a new dark theme, as well as the addition of a private mode, plus search engine choice, which offers 11 options, including Qwant and DuckDuckGo, and other features.
The app is a free download on iOS.
Powered by WPeMatico