Thought Machine nabs $83M for a cloud-based platform that powers banking services
The world of consumer banking has seen a massive shift in the last ten years. Gone are the days where you could open an account, take out a loan, or discuss changing the terms of your banking only by visiting a physical branch. Now, you can do all this and more with a few quick taps on your phone screen — a shift that has accelerated with customers expecting and demanding even faster and more responsive banking services.
As one mark of that switch, today a startup called Thought Machine, which has built cloud-based technology that powers this new generation of services on behalf of both old and new banks, is announcing some significant funding — $83 million — a Series B that the company plans to use to continue investing in its platform and growing its customer base.
To date, Thought Machine’s customers are primarily in Europe and Asia — they include large, legacy outfits like Standard Chartered, Lloyds Banking Group, and Sweden’s SEB through to “challenger” (AKA neo-) banks like Atom Bank. Some of this financing will go towards boosting the startup’s activities in the US, including opening an office in the country later this year and moving ahead with commercial deals.
The funding is being led by Draper Esprit, with participation also from existing investors Lloyds Banking Group, IQ Capital, Backed and Playfair.
Thought Machine, which started in 2014 and now employs 300, is not disclosing its valuation but Paul Taylor, the CEO and founder, noted that the market cap is currently “increasing healthily.” In its last round, according to PitchBook estimates, the company was valued at around $143 million, which, at this stage of funding, puts this latest round potentially in the range of between $220 million and $320 million.
Thought Machine is not yet profitable, mainly because it is in growth mode, said Taylor. Of note, the startup has been through one major bankruptcy restructuring, although it appears that this was mainly for organisational purposes: all assets, employees and customers from one business controlled by Taylor were acquired by another.
Thought Machine’s primary product and technology is called Vault, a platform that contains a range of banking services: checking accounts, savings accounts, loans, credit cards and mortgages. Thought Machine does not sell directly to consumers, but sells by way of a B2B2C model.
The services are provisioned by way of smart contracts, which allows Thought Machine and its banking customers to personalise, vary and segment the terms for each bank — and potentially for each customer of the bank.
Food for Thought (Machine)
It’s a little odd to think that there is an active market for banking services that are not built and owned by the banks themselves. After all, aren’t these the core of what banks are supposed to do?
But one way to think about it is in the context of eating out. Restaurants’ kitchens will often make in-house what they sell and serve. But in some cases, when it makes sense, even the best places will buy in (and subsequently sell) food that was crafted elsewhere. For example, a restaurant will re-sell cheese or charcuterie, and the wine is likely to come from somewhere else, too.
The same is the case for banks, whose “Crown Jewels” are in fact not the mechanics of their banking services, but their customer service, their customer lists, and their deposits. Better banking services (which may not have been built “in-house”) are key to growing these other three.
“There are all sorts of banks, and they are all trying to find niches,” said Taylor. Indeed, the startup is not the only one chasing that business. Others include Mambu, Temenos and Italy’s Edera.
In the case of the legacy banks that work with the startup, the idea is that these behemoths can migrate into the next generation of consumer banking services and banking infrastructure by cherry-picking services from the VaultOS platform.
“Banks have not kept up and are marooned on their own tech, and as each year goes by, it comes more problematic,” noted Taylor.
In the case of neobanks, Thought Machine’s pitch is that it has already built the rails to run a banking service, so a startup — “new challengers like Monzo and Revolut that are creating quite a lot of disruption in the market” (and are growing very quickly as a result) — can integrate into these to get off the ground more quickly and handle scaling with less complexity (and lower costs).
Money talks
Taylor was new to fintech when he founded Thought Machine, but he has a notable track record in the world of tech that you could argue played a big role in his subsequent foray into banking.
Formerly an academic specialising in linguistics and engineering, his first startup, Rhetorical Systems, commercialised some of his early speech-to-text research and was later sold to Nuance in 2004.
His second entrepreneurial effort, Phonetic Arts, was another speech startup, aimed at tech that could be used in gaming interactions. In 2010, Google approached the startup to see if it wanted to work on a new speech-to-text service it was building. It ended up acquiring Phonetic Arts, and Taylor took on the role of building and launching Google Now, with that voice tech eventually making its way to Google Maps, accessibility services, the Google Assistant and other places where you speech-based interaction makes an appearance in Google products.
While he was working for years in the field, the step changes that really accelerated voice recognition and speech technology, Taylor said, were the rapid increases in computing power and data networks that “took us over the edge” in terms of what a machine could do, specifically in the cloud.
And those are the same forces, in fact, that led to consumers being able to run our banking services from smartphone apps, and for us to want and expect more personalised services overall. Taylor’s move into building and offering a platform-based service to address the need for multiple third-party banking services follows from that, and also is the natural heir to the platform model you could argue Google and other tech companies have perfected over the years.
Draper Esprit has to date built up a strong portfolio of fintech startups that includes Revolut, N26, TransferWise and Freetrade. Thought Machine’s platform approach is an obvious complement to that list. (Taylor did not disclose if any of those companies are already customers of Thought Machine’s, but if they are not, this investment could be a good way of building inroads.)
“We are delighted to be partnering with Thought Machine in this phase of their growth,” said Vinoth Jayakumar, Investment Director, Draper Esprit, in a statement. “Our investments in Revolut and N26 demonstrate how banking is undergoing a once in a generation transformation in the technology it uses and the benefit it confers to the customers of the bank. We continue to invest in our thesis of the technology layer that forms the backbone of banking. Thought Machine stands out by way of the strength of its engineering capability, and is unique in being the only company in the banking technology space that has developed a platform capable of hosting and migrating international Tier 1 banks. This allows innovative banks to expand beyond digital retail propositions to being able to run every function and type of financial transaction in the cloud.”
“We first backed Thought Machine at seed stage in 2016 and have seen it grow from a startup to a 300-person strong global scale-up with a global customer base and potential to become one of the most valuable European fintech companies,” said Max Bautin, Founding Partner of IQ Capital, in a statement. “I am delighted to continue to support Paul and the team on this journey, with an additional £15 million investment from our £100 million Growth Fund, aimed at our venture portfolio outperformers.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Making money from games: the future of virtual economies
Fictional portrayals of virtual worlds such as “Ready Player One” and “The Matrix” typically portray the physical and virtual worlds as distinct realms siloed from each other. Characters escape a dystopian, impoverished physical realm and enter a separate, utopian virtual realm in which they are wealthy and important.
Our non-fictional future won’t have that dichotomy. One main reason is money. Any virtual world has a virtual economy, and when that virtual economy gets really big, it integrates with our real-world economy. That is in equal parts due to market forces and government intervention.
This is part six of a seven-part series about “multiverse” virtual worlds. We will explore the dynamics of games’ virtual economies, the exchange of virtual assets for real money, challenges with money laundering and underage gambling, the compliance infrastructure needed for virtual economies, and the challenges in balancing a virtual economy’s monetary supply.
What separates virtual from “real” is the ability to make money
To many people, the idea of spending time in virtual worlds amassing in-game currency and trading goods still sounds like the geeky science fiction hobby of someone who needs to “get a real job.”
Our society gauges the worthiness of pursuits based on their social and economic productivity, and most people don’t view virtual worlds as productive places. As more people find enjoyment in virtual worlds and respect people with accomplishments in them, however, vying for accomplishment with those worlds will increasingly be viewed as socially productive. As more people start earning an income through work in virtual worlds, perception of economic productivity will quickly change, too.
Virtual worlds will be viewed as digital extensions of “the real world” and working a full-time job in a multiverse virtual world will become as normal as someone working in a social media marketing role today.
Powered by WPeMatico
Multiverse virtual worlds will be healthier for society than our current social networks
The basis of the classic James Bond film “Tomorrow Never Dies” is an evil media mogul who instigates war between the U.K. and China because it will be great for TV ratings. There’s been a wake-up call recently that our most popular social networks have been indirectly designed to divide populations into enemy camps and reward sensational content, but without the personal responsibility of Bond’s nemesis because they’re algorithmically driven.
(This is part five of a seven-part series about virtual worlds.)
The rise of “multiverse” virtual words as the next social frontier offers hope to one of the biggest crises facing democratic societies right now. Because the dominant social media platforms (in Western countries at least) monetize through advertising, these platforms reward sensational content that results in the most clicks and shares. Oversimplified, exaggerated claims intended to shock users scrolling past are best practices for individuals, media brands and marketing departments alike, and social platforms intentionally steer users toward more extreme content in order to captivate them for longer.
Our impending cultural shift to socializing equally as often through virtual worlds could help rescue us from this constant conflict of interest between what we recognize as healthy interactions with others and how these social apps incentivize us to behave.
Virtual worlds can have advertisements within them, but the dominant monetization strategies in MMOs are upfront purchase of games and in-game transactions. Any virtual world that gains enough adoption to compete as a social hub for mainstream society will need to be free-to-play and will earn more money through in-world transactions than from ads.
Powered by WPeMatico
This Week in Apps: Coronavirus impacts app stores, Facebook sues mobile SDK maker, Apple kicks out a cloud gaming app
Welcome back to This Week in Apps, the Extra Crunch series that recaps the latest OS news, the applications they support and the money that flows through it all.
The app industry is as hot as ever, with a record 204 billion downloads in 2019 and $120 billion in consumer spending in 2019, according to App Annie’s recently released “State of Mobile” annual report. People are now spending 3 hours and 40 minutes per day using apps, rivaling TV. Apps aren’t just a way to pass idle hours — they’re a big business. In 2019, mobile-first companies had a combined $544 billion valuation, 6.5x higher than those without a mobile focus.
In this Extra Crunch series, we help you keep up with the latest news from the world of apps, delivered on a weekly basis.
This week, we’ll look at the coronavirus outbreak’s impact on the App Store, China’s demand for App Store removals — and soon-to-be-removals, it seems. We’re also talking about Facebook’s lawsuit over a data-grabbing SDK, Tinder’s new video series, the TSA ban on TikTok, Instagram’s explanation for its lack of an iPad app and how Democratic presidential primary candidates are performing on mobile and social, among other things.
Headlines
Coronavirus concerns send Chinese ride-hailing apps crashing, games surging
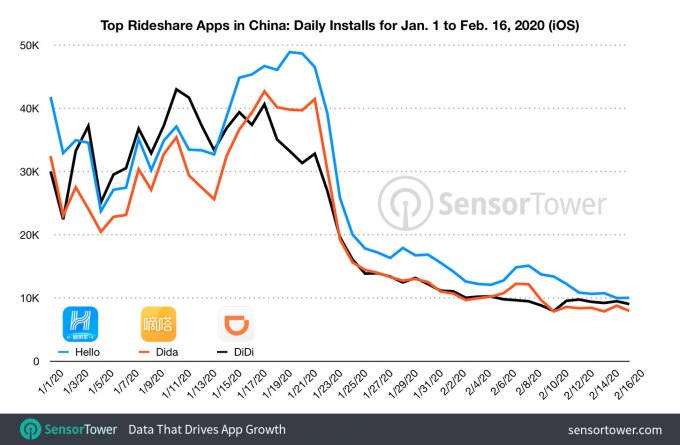
One of the many economic fallouts related to COVID-19 coronavirus concerns is a significant decline in the usage of Chinese ride-hailing applications. According to Sensor Tower data, downloads of the three most popular apps — Hello, Didi and Dida — were down 75% year-over-year during the week of February 10 compared with the same time frame in 2019. Meanwhile, people staying home have been ordering food and groceries more often. Overall downloads of the top 10 apps in the food-ordering category increased by 68% from January 13 to the week of February 3.
Also on the rise are mobile games. According to a recent report by the FT, users in China downloaded a record number of games and apps as the virus outbreak confined people to their homes. More than 22 million downloads were registered in Apple’s App Store in China during the week of February 2, according to App Annie, and average weekly downloads during the first two weeks of February were up 40% over the same time last year.
Meanwhile, Chinese tech giants, including Alibaba and Tencent, have been deploying health-rating systems to help authorities track the movements of millions of Chinese. Alibaba had been tapped to explore the rollout of a rating app to help the government control who can travel into and around the city. Along with Ant Financial, it worked to develop a smartphone-based rating system in conjunction with the government of Hangzhou. Tencent created a program for Shenzhen, reported The WSJ.
Top mobile game Plague Inc. pulled from China’s App Store amid coronavirus outbreak
Plague Inc., a simulation game with more than 130 million players, was pulled from the Chinese App Store this week, a move that appears to be linked to the coronavirus outbreak. The company behind the game, Ndemic, posted a statement announcing that the game’s content is now considered “illegal in China as determined by the Cyberspace Administration of China.” Ndemic says it’s trying to reach out to find out what, specifically, it could change in order to get the game back in China.
Powered by WPeMatico
Notivize makes it easier for non-technical teams to optimize app notifications
A new startup called Notivize aims to give product teams direct access to one of their most important tools for increasing user engagement — notifications.
The company has been testing the product with select customers since last year and says it has already sent hundreds of thousands of notifications. And this week, it announced that it has raised $500,000 in seed funding led by Heroic Ventures .
Notivize co-founder Matt Bornski has worked at a number of startups, including AppLovin and Wink, and he said he has “so many stories I can tell you about the time it takes to change a notification that’s deeply embedded in your stack.”
To be clear, Bornski isn’t talking about a simple marketing message that’s part of a scheduled campaign. Instead, he said that the “most valuable” notifications (e.g. the ones that users actually respond to) are usually driven by activity in an app.
For example, it might sound obvious to send an SMS message to a customer once the product they’ve purchased has shipped, but Bornski said that actually creating a notification like that would normally require an engineer to write new code.
“There’s the traditional way that these things are built: The product team specs out that we need to send this email when this happens, or send this SMS or notification when this happens, then the engineering team will go in and find the part of the code where they detect that such a thing has happened,” he said. “What we really want to do is give [the product team] the toolkit, and I think we have.”
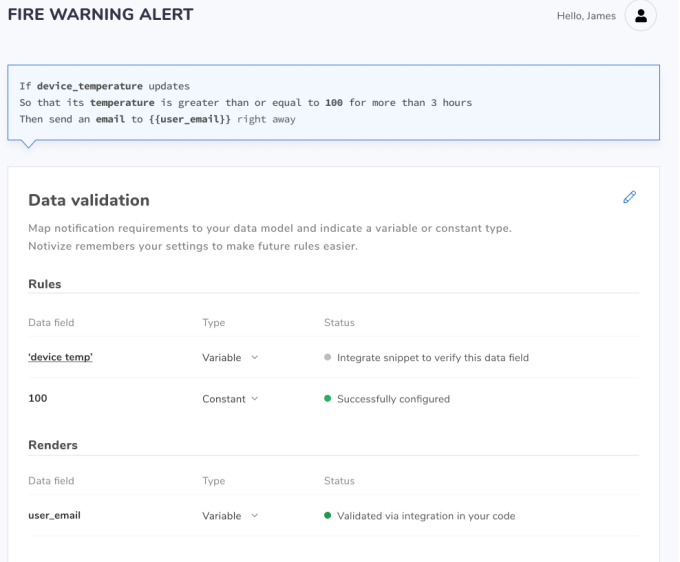
So with Notivize, non-coding members of the product and marketing team can write “if-then” rules that will trigger a notification. And this, Bornski said, also makes it easier to “A/B test and optimize your copy and your send times and your channels” to ensure that your notifications are as effective as possible.
He added that companies usually don’t build this for themselves, because when they’re first building an app, it’s “not a rational thing to invest your time and effort in when you’re just testing the market or you’re struggling for product market fit.” Later on, however, it can be challenging to “go in and rip out all the old stuff” — so instead, you can just take advantage of what Notivize has already built.
Bornski also emphasized that the company isn’t trying to replace services that provide the “plumbing” for notifications. Indeed, Notivize actually integrates with SendGrid and Twilio to send the notifications.
“The actual sending is not the core value [of what we do],” he said. “We’re improving the quality of what you’re paying for, of what you send.”
Notivize allows customers to send up to 100 messages per month for free. After that, pricing starts at $14.99 per month.
“The steady march of low-code and no-code solutions into the product management and marketing stack continues to unlock market velocity and product innovation,” said Heroic Ventures founder Michael Fertik in a statement. “Having been an early investor in several developer platforms, it is clear that Notivize has cracked the code on how to empower non-technical teams to manage critical yet complex product workflows.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Superhuman CEO Rahul Vohra on waitlists, freemium pricing and future products
The “Sent via Superhuman iOS” email signature has become one of the strangest flexes in the tech industry, but its influence is enduring, as the $30 per month invite-only email app continues to shape how a wave of personal productivity startups are building their business and product strategies.
I had a chance to chat with Superhuman CEO and founder Rahul Vohra earlier this month during an oddly busy time for him. He had just announced a dedicated $7 million angel fund with his friend Todd Goldberg (which I wrote up here) and we also noted that LinkedIn is killing off Sales Navigator, a feature driven by Rapportive, which Vohra founded and later sold in 2012. All the while, his buzzy email company is plugging along, amassing more interested users. Vohra tells me there are now more than 275,000 people on the waitlist for Superhuman.
Below is a chunk of my conversation with Vohra, which has been edited for length and clarity.
TechCrunch: When you go out to raise funding and a chunk of your theoretical user base is sitting on a waitlist, is it a little tougher to determine the total market for your product?
Rahul Vohra: That’s a good question. When we were doing our Series B, it was very easily answered because we’re one of a cohort of companies, that includes Notion and Airtable and Figma, where the addressable market — assuming you can build a product that’s good enough — is utterly enormous.
With my last company, Rapportive, there was a lot of conversation around, “oh, what’s the business model? What’s the market? How many people need this?” This almost never came up in any fundraising conversation. People were more like, “well, if this thing works, obviously the market is basically all of prosumer productivity and that is, no matter how you define it, absolutely huge.”
Powered by WPeMatico
FCC proposes $208M in fines for wireless carriers that sold your location for years
The FCC has officially and finally determined that the major wireless carriers in the U.S. broke the law by secretly selling subscribers’ location data for years with almost no constraints or disclosure. But its Commissioners decry the $208 million penalty proposed to be paid by these enormously rich corporations, calling it “not properly proportioned to the consumer harms suffered.”
Under the proposed fines, T-Mobile would pay $91M; AT&T, $57M; Verizon, $48M; and Sprint, $12M. (Disclosure: TechCrunch is owned by Verizon Media. This does not affect our coverage in the slightest.)
The case has stretched on for more than a year and a half after initial reports that private companies were accessing and selling real-time subscriber location data to anyone willing to pay. Such a blatant abuse of consumers’ privacy caused an immediate outcry, and carriers responded with apparent chagrin — but often failed to terminate or even evaluate these programs in a timely fashion. It turns out they were run with almost no oversight at all, with responsibility delegated to the third party companies to ensure compliance.
Meanwhile the FCC was called on to investigate the nature of these offenses, and spent more than a year doing so in near-total silence, with even its own Commissioners calling out the agency’s lack of communication on such a serious issue.
Finally, in January, FCC Chairman Ajit Pai — who, it really must be noted here, formerly worked for one of the main companies implicated, Securus — announced that the investigation had found the carriers had indeed violated federal law and would soon be punished.
Today brings the official documentation of the fines, as well as commentary from the Commission. In the documents, the carriers are described as not only doing something bad, but doing it poorly — and especially in T-Mobile’s case, continuing to do it well after they said they’d stop:
We find that T-Mobile apparently disclosed its customers’ location information, without their consent, to third parties who were not authorized to receive it. In addition, even after highly publicized incidents put the Company on notice that its safeguards for protecting customer location information were inadequate, T-Mobile apparently continued to sell access to its customers’ location information for the better part of a year without putting in place reasonable safeguards—leaving its customers’ data at unreasonable risk of unauthorized disclosure
The general feeling seems to be that while it’s commendable to recognize this violation and propose what could be considered substantial fines, the whole thing is, as Commissioner Rosenworcel put it, “a day late and a dollar short.”
The scale of the fines, they say, has little to do with the scale of the offenses — and that’s because the investigation did not adequately investigate or attempt to investigate the scale of those offenses. As Commissioner Starks writes in a lengthy statement:
After all these months of investigation, the Commission still has no idea how many consumers’ data was mishandled by each of the carriers.
We had the power—and, given the length of this investigation, the time—to compel disclosures that would help us understand the true scope of the harm done to consumers. Instead, the Notices calculate the forfeiture based on the number of contracts between the carriers and location aggregators, as well as the number of contracts between those aggregators and third-party location-based service providers. That is a poor and unnecessary proxy for the privacy harm caused by each carrier, each of which has tens of millions of customers that likely had their personal data abused.
Essentially, the FCC didn’t even look at the number or nature of actual harm — it just asked the carriers to provide the number of contracts entered into. As Starks points out, one such contract can and did sometimes represent thousands of individual privacy invasions.
We know there are many—perhaps millions—of additional victims, each with their own harms. Unfortunately, based on the investigation the FCC conducted, we don’t even know how many there were, and the penalties we propose today do not reflect that impact.
And why not go after the individual companies? Securus, Starks says, “behaved outrageously.” But they’re not being fined at all. Even if the FCC lacked the authority to do so, it could have handed off the case to Justice or local authorities that could determine whether these companies violated other laws.
As Rosenworcel notes in her own statement, the fines are also extraordinarily generous even beyond this minimal method of calculating harm:
The agency proposes a $40,000 fine for the violation of our rules—but only on the first day. For every day after that, it reduces to $2,500 per violation. The FCC heavily discounts the fines the carriers potentially owe under the law and disregards the scope of the problem. On top of that, the agency gives each carrier a thirty-day pass from this calculation. This thirty day “get-out-of-jail-free” card is plucked from thin air.
Given that this investigation took place over such a long period, it’s strange that it did not seek to hear from the public or subpoena further details from the companies facilitating the violations. Meanwhile the carriers sought to declare a huge proportion of their responses to the FCC’s questions confidential, including publicly available information, and the agency didn’t question these assertions until Starks and Rosenworcel intervened.
$200M sounds like a lot, but divided among several billion-dollar communications organizations it’s peanuts, especially when you consider that these location-selling agreements may have netted far more than that in the years they were active. Only the carriers know exactly how many times their subscribers’ privacy was violated, and how much money they made from that abuse. And because the investigation has ended without the authority over these matters asking about it, we likely never will know.
The proposed fines, called a Notice of Apparent Liability, are only a tentative finding, and the carriers have 30 days to respond or ask for an extension — the latter of which is the more likely. Once they respond (perhaps challenging the amount or something else) the FCC can take as long as it wants to come up with a final fine amount. And once that is issued, there is no requirement that the fine actually be collected — and the FCC has in fact declined to collect before once the heat died down, though not with a penalty of this scale.
“While I am glad the FCC is finally proposing fines for this egregious behavior, it represents little more than the cost of doing business for these carriers,” Congressman Frank Pallone (D-NJ) said in a statement. “Further, the Commission is still a long way from collecting these fines and holding the companies fully accountable.”
The only thing that led to this case being investigated at all was public attention, and apparently public attention is necessary to ensure the federal government follows through on its duties.
(This article has been substantially updated with new information, plus comments from Commissioner Starks and Rep. Pallone.)
Powered by WPeMatico
Facebook Messenger ditches Discover, demotes chat bots
Chat bots were central to Facebook Messenger’s strategy three years ago. Now they’re being hidden from view in the app along with games and businesses. Facebook Messenger is now removing the Discover tab as it focuses on speed and simplicity instead of broad utility like China’s WeChat.
The changes are part of a larger Messenger redesign that reorients the People tab around Stories as Facebook continues to try to dominate the ephemeral social media format it copied from Snapchat. The People tab now defaults to a full-screen sub-tab of friends’ Stories, and requires a tap over to the Active sub tab to see which friends are online now.
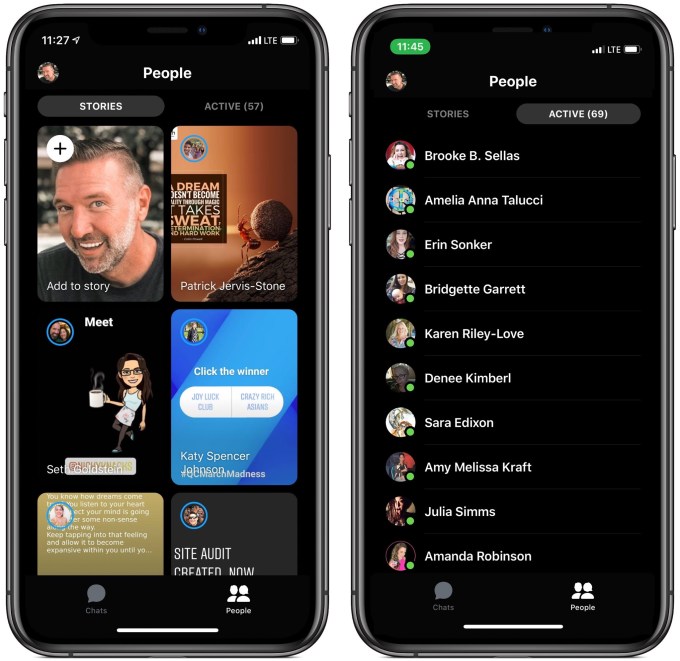
The changes could push users to spend more time visually communicating with friends and consuming content than exploring chat bots for shopping, connecting with businesses and playing games. That in turn could help Facebook earn more money from Messenger as it’s now showing Stories ads.
TechCrunch was tipped off to the redesign by social media director Jeff Higgins, who provided us with extensive screenshots of the update. These show the absence of Discover tab, the switch to just Chat and People tabs and the People sub-tabs for Stories and Active. We poked around some more and noticed the Instant Games and Transportation options missing from the chat composer’s utility tray. That formerly offered quick Uber and Lyft hailing. Messenger’s M Suggestions also no longer recommend the Transportation feature.
When we asked Messenger about the changes, a spokesperson confirmed that this redesign will soon start rolling out, removing Discover and splitting the People tab. Some users already have the update, and more will likely get it this week. They noted that Facebook had announced last August that it planned to eventually axe Discover, and that the added emphasis on Stories was motivated by users’ affinity for the ephemeral social media format. They also told us that Transportation was removed in late 2017, and Instant Games’ removal from the composer is part of the migration to Facebook Gaming announced last July.

A look at the old Messenger Discover tab that’s being removed
Chat bots, businesses and games are being hidden, but not completely banished from Messenger. They’ll still be accessible if users purposefully seek them through the Messenger search bar, Pages and ads on Facebook, buttons to start conversations on businesses’ websites, and m.me URL that create QR codes which open to business accounts in Messenger. The spokesperson diplomatically claimed that businesses are still an important part of Messenger.
But without promotion via Discover, businesses will have to rely on their owned or paid marketing channels to gain traction for their chat bots. That could discourage them from building on the Messenger platform.
The rise and fall of Facebook chat bots
The update feels like the end of a four-year era for Facebook. Back in 2016, it saw artificially intelligent chat bots as a way for businesses to scalably communicate with people, deliver customer service and push e-commerce. But when it launched the chat bot platform at its F8 conference that year, it arrived half-baked.
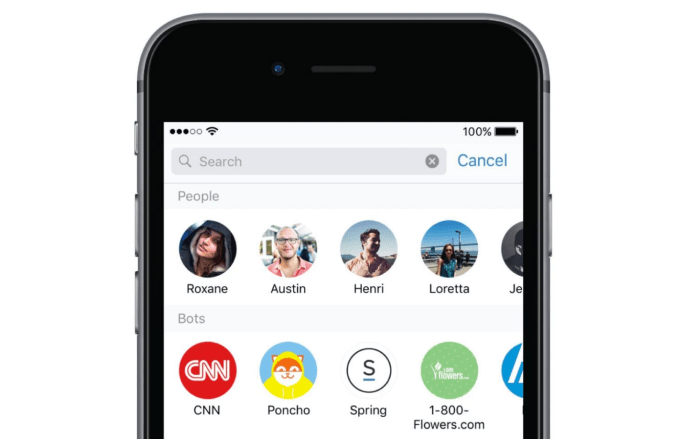
The typing-based semantic user interfaces were confusing, the AI necessary to make chat bots seem human (or at least reliably understand their human conversation partners hadn’t evolved yet) and several of the launch partner bots like Poncho The Weather Cat were laughably useless. The public soured on the idea of chat bots, and attempts to improve them felt insufficient.
Messenger launched Discover in 2017 in hopes that free promotion and visibility might convince developers to invest in building better chatbots. Yet by early 2018, even Facebook was backpedaling, shelving its plan to build out a full-service AI personal assistant called M that you could ask to do anything. Instead, it’d merely make AI suggestions of different Messenger features to use, like Stickers or reminders based on what you typed. Then it announced last year that it would move Instant Games out of Messenger and into Facebook’s dedicated Gaming tab.
There is still an opportunity to use chat bots for gathering initial info from people with sales or customer service inquiries. Everyone hates dealing with this stuff over the phone, waiting on hold and wading through touch-tone menus. Using asynchronous messaging makes communicating with businesses much more convenient. I’d bet Facebook will still be pushing this as an enterprise use case for Messenger. But this still usually requires a human in the loop at some point, and these are better structured as reactive utilities users search for than as experience proactively promoted by a Discover tab.

A laughably bad interaction with old Messenger chat bot Poncho The Weather Cat
Now with Discover disappearing, Messenger seems to be surrendering the fight to become a WeChat-style monolithic utility. In China, WeCat serves not just as a messaging app but as a way to make payments, hail a taxi, book flights, top up your mobile data, get a loan, find housing or shop at businesses via mini programs.
 But while that centralized all-in-one style fit Chinese culture, Western markets have experienced more of an unbundling with different apps emerging to handle each of these use cases. Facebook’s constant privacy scandals and increasing anti-trust scrutiny also inhibited this approach with Messenger. Users and the U.S. government weren’t ready to trust Facebook to handle so much of our daily lives. Facebook Messenger also has to jockey with competition like iMessage and Snapchat that could undercut it if it gets too bloated.
But while that centralized all-in-one style fit Chinese culture, Western markets have experienced more of an unbundling with different apps emerging to handle each of these use cases. Facebook’s constant privacy scandals and increasing anti-trust scrutiny also inhibited this approach with Messenger. Users and the U.S. government weren’t ready to trust Facebook to handle so much of our daily lives. Facebook Messenger also has to jockey with competition like iMessage and Snapchat that could undercut it if it gets too bloated.
So now Messenger is going in the opposite direction. It’s becoming more WhatsApp-like — simple, speedy and centered around peer-to-peer communication. Visual communication through Stories, with replies to them delivered as messages, feels like a natural extension of this focus while conveniently offering a path to monetization. If Messenger can be the best-in-class place to chat, unencumbered by promotion of chat bots and businesses, users might stay locked into the Facebook ecosystem.
Powered by WPeMatico
Facebook brings its 3D photos feature to users with single-camera phones
Facebook first showed off its 3D photos back in 2018, and shared the technical details behind it a month later. But unless you had one of a handful of phones with dual cameras back then (when they weren’t so common), you couldn’t make your own. Today an update brings 3D photos to those of us still rocking a single camera.
In case you don’t remember or haven’t seen one lately, the 3D photos work by analyzing a 2D picture and slicing it into a ton of layers that move separately when you tilt the phone or scroll. I’m not a big fan of 3D anything, and I don’t even use Facebook, but the simple fact is this feature is pretty cool.
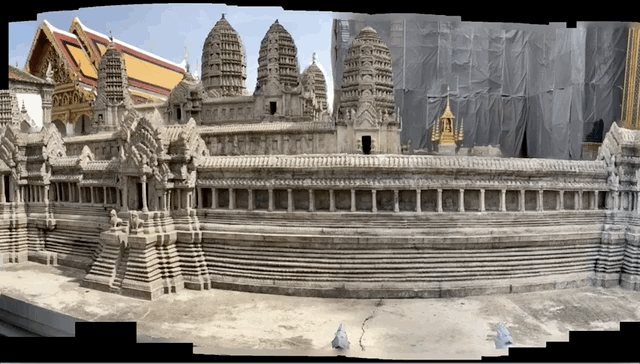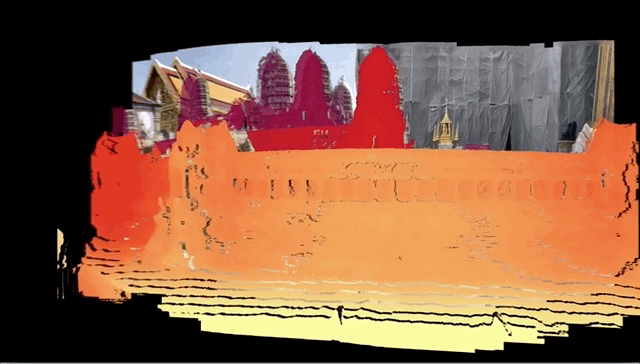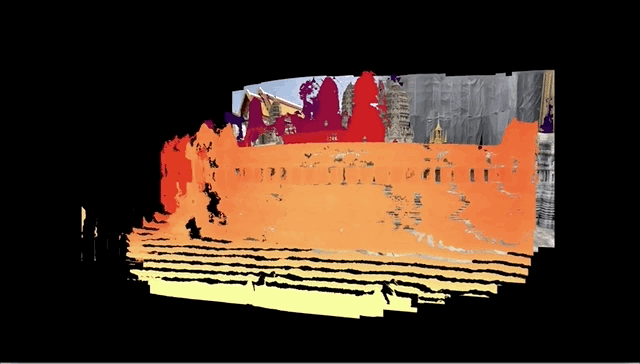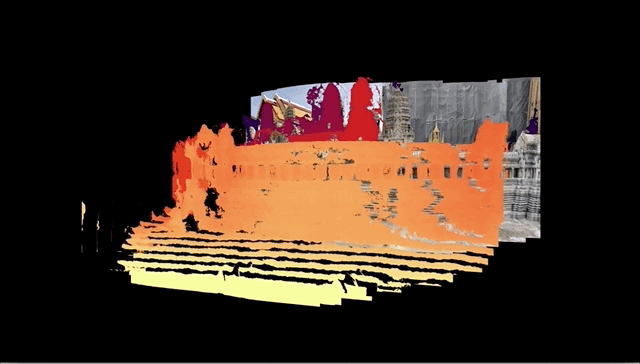
The problem is it used the dual-camera feature to help the system determine distance, which informed how the picture should be sliced. That meant I, with my beautiful iPhone SE, was out of the running — along with about a billion other people who hadn’t bought into the dual-camera thing yet.
But over the last few years the computer vision team over at Facebook has been working on making it possible to do this without dual-camera input. At last they succeeded, and this blog post explains, in terms technical enough that I’m not even going to attempt to summarize them here, just how they did it.
The advances mean that many — though not all — relatively modern single-camera phones should be able to use the feature. Google’s Pixel series is now supported, and single-camera iPhones from the 7 forward. The huge diversity of Android devices makes it hard to say which will and won’t be supported — it depends on a few things not usually listed on the spec sheet — but you’ll be able to tell once your Facebook app updates and you take a picture.
Powered by WPeMatico
Amazon is the latest to ditch GDC this year
GDC’s top sponsors continue to pull out of attending the San Francisco gaming conference. Today, Amazon announced it would no longer be sending employees to the event.
In an update, the team shared that they would instead be hosting a “global online event” to share news that they had been planning to detail at the conference.
Amazon Game Tech is a “diamond partner” at the Game Developers Conference this year, a designation that signifies sponsors “who play an integral role in the success of GDC,” the conference says on its website. At this point, the only diamond partners who have not officially withdrawn are Intel, Nvidia and Google.
Facebook, Sony, Microsoft, Unity and Epic Games have all pulled out of the conference over concerns surrounding the COVID-19 outbreak. Now, Amazon joins them.
TechCrunch has reached out to the other remaining sponsors at the event.
As pointed out by @beccahallstedt, the red companies have officially pulled out.
Wouldn’t be surprised if Google, Amazon, Intel, and Nvidia also pull out. pic.twitter.com/C81LomyM0L
— Xavier

GDC
(@XCK3D) February 27, 2020
Powered by WPeMatico