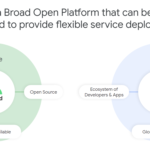
Google Cloud goes after the telco business with Anthos for Telecom and its Global Mobile Edge Cloud
Google Cloud today announced a new solution for its telecom customers: Anthos for Telecom. You can think of this as a specialized edition of Google’s container-based Anthos multi-cloud platform for both modernizing existing applications and building new ones on top of Kubernetes. The announcement, which was originally slated for MWC, doesn’t come as a major surprise, given Google Cloud’s focus on offering very targeted services to its enterprise customers in a number of different verticals.
Given the rise of edge computing and, in the telco business, 5G, Anthos for Telecom makes for an interesting play in what could potentially be a very lucrative market for Google. This is also the market where the open-source OpenStack project has remained the strongest.
What’s maybe even more important here is that Google is also launching a new service called the Global Mobile Edge Cloud (GMEC). With this, telco companies will be able to run their applications not just in Google’s 20+ data center regions, but also in Google’s more than 130 edge locations around the world.
“We’re basically giving you compute power on our edge, where previously it was only for Google use, through the Anthos platform,” explained Eyal Manor, the VP of Engineering for Anthos. “The edge is very powerful and I think we will now see substantially more innovation happening for applications that are latency-sensitive. We’ve been investing in edge compute and edge networking for a long time in Google over the years for the internal services. And we think it’s a fairly unique capability now to open it up for third-party customers.”
For now, Google is only making this available to its teleco partners, with AT&T being the launch customers, but over time, Manor said, it’ll likely open its edge cloud to other verticals, as well. Google also expects to be able to announce other partners in the near future.
As for Anthos for Telecom, Manor notes that this is very much what its customers are asking for, especially now that so many of their new applications are containerized.
“[Anthos] brings the best of cloud-as-a-service to our customers, wherever they are, in multiple environments and provide the lock-in free environment with the latest cloud tools,” explained Manor. “The goal is really to empower developers and operators to move faster in a consistent way, so regardless of where you are, you don’t have to train your technical staff. It works on-premise, it works on GCP and on other clouds. And that’s what we hear from customers — customers really like choice.”
In the telecom industry, those customers also want to get higher up the stack and get consistency between their data centers and the edge — and all of that, of course, is meant to bring down the cost of running these networks and services.
“We don’t want to manage the [technology] we previously invested in for many years because the upgrades were terribly expensive and slow for that. I hear that consistently. And please Google, make this seem like a service in the cloud for us,” Manor said.
For developers, Anthos also promises to provide the same development experience, no matter where the application is deployed — and Google now has an established network of partners that provides both solutions to developers as well as operators around Anthos. To this effect, Google is also launching new partnerships with the Amdocs customer experience platform and Netcracker today.
“We’re excited to unveil a new strategy today to help telecommunications companies innovate and accelerate their digital transformation through Google Cloud,” said Thomas Kurian, CEO of Google Cloud, in today’s announcement. “By collaborating closely with leading telecoms, partners and customers, we can transform the industry together and create better overall experiences for our users globally.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Bluecrew launches a mobile app to help businesses manage a flexible workforce
Bluecrew, a flexible staffing business owned by holding company IAC, is launching a new mobile app called Bluecrew Manager.
Rather than relying on a network of independent contractors, Bluecrew hires its own W-2 employees, who in turn have the option to accept hourly jobs from Bluecrew customers.
The company already offered web-based management tools for those customers, but CEO Adam Roston said the mobile app is designed to help them accomplish “the stuff you need to do right now, while you’re on-the-go.”
For example, he said that a warehouse manager spends most of their day “running around the floor,” so if they’re visiting the pick-and-pack department and need to see who’s on the team that day, they can open the app and see pictures of everyone who’s supposed to be working. And if they see that someone forgot to check in, they can adjust their time clock directly from the app.
Other features include the ability to request more workers and to “favorite” a worker, making it more likely that they’ll be assigned to the same company for future jobs.
Bluecrew says it has been testing out the Manager app (which is available for free to all customers) for the past month. In the launch announcement, Eduardo Medrano, cafe manager at hospitality company Eurest, said the app “is completely changing how I approach staffing” because it allows him “to make adjustments and check who will be there right on my phone.”
The company says that since its acquisition by IAC in 2018, its client base has nearly quadrupled, with growth in industries like logistics and manufacturing, hospitality/culinary and warehousing.
Roston also pointed to California’s new AB-5 law (which limits the ways that companies can classify workers as independent contractors) as a sign that Bluecrew has taken the right approach to combining flexibility and worker protections.
“When [co-founder and CTO Gino Rooney] started the company five years ago, it seemed a little bit crazy to be doing this with W-2 employees,” Roston said. “Over the last year. the landscape has just shifted … The reality, is most companies in the country are already following labor laws and have been at W-2 for years. But we’ve seen some increased momentum from AB-5, and we would expect to see it elsewhere.”
Powered by WPeMatico
5G is now live in 24 markets, GSMA predicts it’ll be 20% of global connections by 2025 — and eyes a big tech break-up
The next-gen flavor of mobile connectivity, 5G, is now live in 24 markets globally, according to GSMA’s annual state of the global mobile economy report.
The cutting edge network tech is capable of supporting speeds up to 100x faster than LTE/4G and delivering latency of just a few milliseconds, as well as being able to connect many more devices per cell site. As it rolls out, it’s expected to underpin a new wave of “smarter” digital services which bake in real-time AI assistance and help drive the digitization of legacy industries.
In last year’s report the carrier association didn’t break out a firm figure for markets where 5G is live — but dubbed the tech “a reality” after commercial launches in the US and South Korea towards the end of 2018. It also said it was expecting 16 more “major countries” to have launched 5G networks by the end of 2019.
It’s now touting “significant traction” for 5G — saying 79 operators across a further 39 markets had announced plans to launch commercial 5G services as of January 20, 2020.
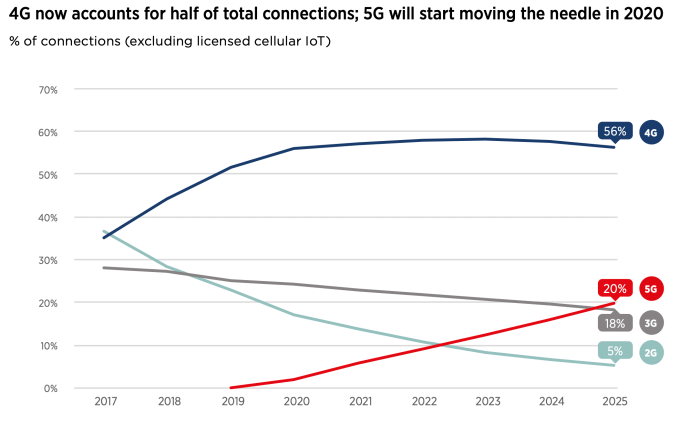
As it stands actual 5G connections remain a fraction of the connectivity pie vs current (4G) and previous gen cellular favors. Per the report, 4G became the dominant mobile tech globally in 2019 — with over 4BN connections, accounting for 52% of total connections (excluding licensed cellular IoT).
The GSMA expects 4G connections to continue to grow for the next few years, peaking at just under 60% of global connections by 2023.
For 5G its forecast is that it will account for a fifth (20%) of global connections by 2025, with the carrier association expecting “particularly strong” take-up across developed Asia, North America and Europe.
(For wider context, almost half of the global population (3.8BN people) are now users of the mobile internet as a whole (2G-5G), per the report — which is forecast to grow to 61% (5BN people) by 2025.)
It’s worth emphasizing that the presence of 5G in a market does not mean universal coverage.
On the contrary, 5G rollouts have tended to be targeted on urban centers. Which means 5G availability in the 24 markets that have launched commercial networks so far is likely highly limited vs population. There are also still relatively few 5G smartphones vs non-5G handsets (though since this time last year more are being unboxed; Sony, for example, just announced its first 5G handsets).
Perhaps, most importantly, consumer demand for the next-gen flavor of connectivity has yet to be robustly stood up. The GSMA’s report poses the (existential, for telcos) question of: “Will they pay for it?”
“The number of live 5G markets is increasing by the day and consumers’ awareness of the technology is also growing as hype makes way for reality. However, there is wide variation across the globe in terms of intentions to upgrade to 5G and the willingness to pay more for it,” it concedes.
“In general, consumers in South Korea and China – having witnessed some of the earliest launches – appear to be the most excited by the prospect of upgrading to 5G, while those in the US, Europe and Japan seem more content with 4G for the time being,” the GSMA adds, before striking an upbeat note: “5G is still in its infancy though; as more tangible use cases are deployed, more consumers will appreciate the benefits of 5G.”
Aka, 5G needs a killer app. But one has yet to emerge. (Edit note: A global pandemic that triggers a mass transition to remote working and virtualized socializing could have potential though. After all, concerns about the corona virus did force the GSMA to cancel its own annual shindig, MWC, just last month.)
Despite the report’s prediction that consumers will, down the line, be sold on 5G’s “benefits” another graphic in the report maps out the current reality — that “awareness of 5G does not necessarily translate into an intention to upgrade”.
It shows adults in markets including the UK, Australia, Spain and Italy having high awareness of the tech but low intent to pay for 5G, with less than 35% saying they want to upgrade. The US market also has a similarly high level of awareness of 5G — and only a slightly higher intention to upgrade (~40%+).
The GSMA writes that more needs to be done by carriers to “raise awareness” of other “benefits” than just higher data speeds, touting claimed advantages such as “improved mobile service coverage”, “innovative new services” and “connectivity for previously unconnected devices” as having 5G marketing potential.
However, on the latter point at least, the report also chronicles variable and often low appetite — certainly outside China — for a range of ‘smart’ devices…
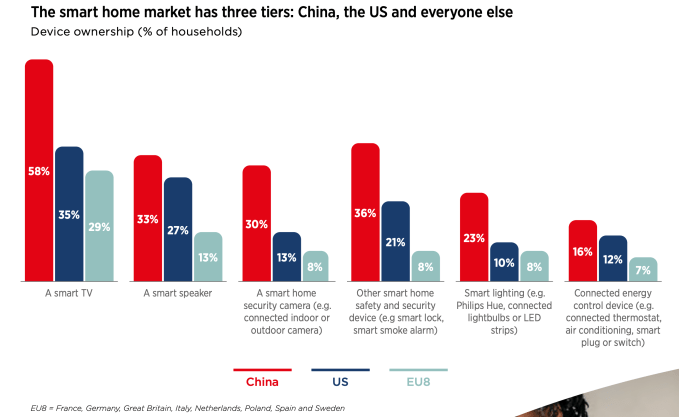
Still, the GSMA predicts billions more IoT devices will be coming on stream over the next five years — saying that between 2019 and 2025 the number of global IoT connections will more than double to almost 25 billion, while it expects global IoT revenue to more than triple to $1.1 trillion.
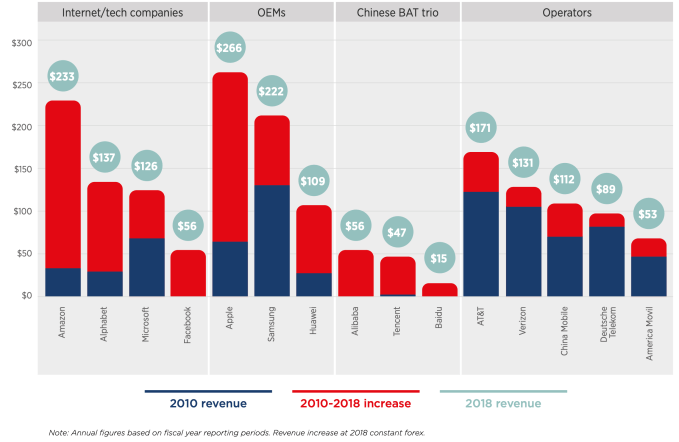
Another segment of the report deals with the perennial issue of stagnant operator revenue growth vs Internet companies, with the GSMA noting telcos continue to lag tech giants and major device makers.
“For many operators, revenue growth as a percentage is in the low single digits, if that,” it writes. “As core telecoms revenue stagnates, a common strategy now for major operator groups is to seek revenue growth from adjacent services. Pay TV, media, IoT, enterprise solutions and the broader array of digital services still only account for a minor share of operator revenues (10–20% for most), although there are a few notable exceptions, largely enabled by M&A activity.”
It’s perhaps no surprise, then, that top of the GSMA’s 2025 prediction/wish-list is a bold one that one of the GAFA companies (Google, Apple, Facebook and Amazon) will be broken up. (It makes not suggestion of which — though plenty of American eyes are now on Google.)
Other near-term hopes on the GSMA’s list are that “AR eye glasses reach the mass market with a form factor from at least one global OEM”; health wearables become “part of the solution to overburdened public health systems”; and “private enterprise networks explode and become a battleground between telcos and cloud companies” (we don’t think they mean explode literally).
There’s also another 2025 prediction for 5G — that the technology becomes “the first generation in the history of mobile to have a bigger impact on enterprise than consumers”.
Which is certainly one way to silver-line a low-demand ‘cloud’ and hedge (hopefully) for business buy-in to make up for lacklustre consumer desire to pay more to do the same stuff slightly faster* (*depending on network conditions).
“Governments and regulators must play their part to help propel 5G into commercial use by implementing policies that encourage advanced technologies (e.g. AI and IoT) to be applied across all economic sectors,” the GSMA writes elsewhere in the report — a call to action that aligns exactly with policy priorities recently set out by the new European Commission, suggesting telco lobbying in Brussels has borne fruit.
Thierry Breton, the Commissioner for internal market — who’s now driving a pan-EU strategy to encourage the pooling and reuse of industrial data that leans heavily on the deployment of what’s he’s called “critical” 5G networks — is also a former chairman and CEO of France Telecom.
You can download the full GSMA report here.
Powered by WPeMatico
Boosted lays off ‘a significant portion’ of team as it looks for a buyer
Boosted, the startup behind the Boosted Boards and, more recently, the Boosted Rev electric scooter, has laid off “a significant portion” of its team, the company announced today. The company is now actively seeking a buyer.
Boosted attributes the layoffs to the costs of developing, producing and maintaining electric vehicles and the “unplanned challenge with the high expense of the US-China tariff war,” Boosted CEO Jeff Russakow and CTO John Ulmen wrote in a blog post.
“The Boosted brand will continue to pursue strategic options under new ownership,” they wrote.
Boosted, which got its start back in 2012, made its first foray outside of electric skateboards last year with the launch of an electric scooter. Boosted says more than 100,000 riders have traveled tens of millions of miles on the company’s vehicles.
“We are extremely proud of what our company has accomplished, and gratified to see so many happy customers riding their Boosted vehicles every day,” Russakow and Ulmen wrote.
This perhaps should not come as a surprise. For starters, micromobility is a hard business — one that no company can confidently say it has cracked. Meanwhile, The Verge reported earlier this month that the company was at risk of running out of money. On top of that, Boosted reportedly struggled to pay its vendors for the electric scooter.
“To Boosted’s customers and community, we’d like to thank you for your passionate support and encouragement over the last nine years,” Ulmen and Russakow wrote. “It’s been the thrill of our lives to spend time with you and help shape the future of mobility together. To the Boosted team, you made this company a special place, created multiple generations of incredibly innovative products, and created a compelling global brand; thank you so much for your hard work and dedication over the years.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Despite earnings beat and upbeat forecast, Zoom shares fall after reporting Q4 results
Today after the bell, Zoom reported its Q4 earnings. The company’s recorded revenue of $188.3 million and its adjusted per-share profit of $0.15 were ahead of expectations, including $176.55 million in revenue and earnings per share of $0.07, according to Yahoo Finance averages.
Down several points during a broad market rally, Zoom has been a hot company to track in recent months. Its profile was heightened due to its position as an incidental benefactor of the world’s grappling with the novel coronavirus — as more countries and companies stressed staying home and working remotely, respectively, Zoom’s video conferencing tool was expected to see rising usage and demand.
The company’s shares were down sharply after reporting its earnings.
What follows is a dive into Zoom’s Q4 earnings, its expectations for the coming period and what those figures may have to say about the infection and its impacts. We’ll wrap with notes from startups that are building remote-work friendly products, sharing what they are seeing on the ground regarding demand for their services during this bleakly fascinating period of history.
Q4 and the future
Powered by WPeMatico
Sustainable microgrids are the future of clean energy
Across the U.S., sustainable microgrids are emerging as a vital tool in the fight against climate change and increasingly common natural disasters. In the wake of hurricanes, earthquakes and wildfires, the traditional energy grid in many parts of the country is struggling to keep the power flowing, causing outages that slow local economies and ultimately put lives at risk.
Microgrids — power installations that are designed to run independently from the wider electricity grid in emergency situations — have been around for decades, but until the turn of the century, relied almost exclusively on fossil fuels to generate power. While it’s taken another 20 years for solar panels and battery storage costs to fall far enough to make truly sustainable microgrids an economic reality, a recent surge in interest and installations have shown that they’ve reached an inflection point and could very well be the future of clean energy.
Take Santa Barbara, where the Unified School District voted unanimously in November to allocate over $500,000 to study and design microgrid installations for schools around the county. A preliminary assessment by the Clean Coalition identified more than 15 megawatts of solar generation potential across 18 school sites.
These solar-plus-battery-storage microgrids would greatly enhance the ability of chosen schools to serve communities during natural disasters or power outages, like the ones induced by California’s PG&E electric utility that affected hundreds of thousands of residents last October. The sites will provide a place to coordinate essential emergency services, store perishable food and provide residents with light, power and connectivity in times of distress.
A completed feasibility study for the microgrid installations is expected in June, and while initial estimates put the final cost around $40 million, long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs) will allow the school district to have the sites set up for free and paid for over time via its normal electric bill — at a cost no greater than grid power. Agreements like these have only become economically viable in the last few years as renewable energy generation costs have continued to fall, and are a major driver of the microgrid boom.
At the end of January, Scale Microgrid Solutions received a commitment for $300 million in funding from investment firm Warburg Pincus. Microgrids today are typically designed and installed to the unique specifications of individual customers. Scale Microgrid Solutions instead provides modular microgrid infrastructure built using shipping containers that combine solar and battery storage with control equipment and backup gas generation.
These modules enable faster deployment and provide a viable option for customers or institutions seeking microgrid capabilities in the $15 million price range. The first modular microgrids were launched in May 2019 with financing provided by Generate Capital, a financing firm focused on advanced, clean-energy technology investments.
Meanwhile, on the opposite side of the country, successive disasters are already proving the value of solar-plus-storage microgrids in Puerto Rico. In 2017, Hurricane Maria catastrophically damaged the centralized electricity grid in the U.S. territory and left many without power for more than a year.
A project funded by the Rocky Mountain Institute, Save the Children and Kinesis Foundation installed solar-plus-battery-storage microgrids at 10 schools in the mountainous central regions of the island, designed to provide energy for on-site libraries, kitchens and water pumps indefinitely during power outages. The installations were completed in December 2019, just weeks before a series of earthquakes that began in January endangered the island’s already sluggish economic recovery. The RMI Island Energy Program told Microgrid Knowledge that while grid power around several of the sites had gone down, the microgrids had continued to operate successfully and provide critical services.
Microgrids go beyond schools though. Several communities are also linking solar-and-storage systems mounted on their homes, employing inverters and controllers that have only become efficient and affordable in the last few years to create “community microgrids” that share power among the participants to supplement or replace grid energy.
In January, Australian startup Relectrify closed $4.5 million in Series A funding to continue refining their inverter and battery-management technology that increases battery lifespan by as much as 30% while reducing operational costs. Relectrify tech also allows large batteries from electric cars — including Tesla’s wildly popular offerings — to be repurposed after they are no longer reliable enough for use in EVs, opening up an enormous pool of second-hand batteries to be repurposed for growing microgrid storage demand.
Programs like these are attractive not just because they offer resilience and independence from grid power often produced with fossil fuels, but because they are increasingly the cheaper option for energy consumers. Residential retail energy prices in Puerto Rico were as high as 27 cents per kilowatt hour (kWh) in 2019, while the calculated cost from home solar-plus-battery-storage systems fell as low as 24 cents in good conditions.
The cost of solar installations has plummeted 90% in the past decade according to the research firm Wood Mackenzie. At the same time, the early effects of a warming climate and associated natural disasters have started to take a toll on American energy infrastructure already struggling to keep pace with regular maintenance and demand growth. Impacted communities have already seen the value of microgrids and are racing to adopt them, even as many larger utility providers look to natural gas or other partial solutions that rely on the aging centralized power grid.
The greatest impact of these early sustainable microgrids may reach beyond the emergency power they provide to nearby residents. They offer a glimpse of a radically different way for communities and energy consumers to think about how power is produced and used. In community microgrid systems, residents have a concrete, practical connection to their source of energy and are asked to work together with their friends and neighbors to control their energy demand so there is enough to go around.
Such a system stands in stark contrast to the power grid of today, where peak demand facilities are routinely called upon to burn some of the most environmentally harmful fuels to accommodate demand with few if any social or technological limitations. Sustainable microgrids are finally becoming truly affordable, and in the process are beginning to change the way we think about energy consumption and resilience.
Powered by WPeMatico
Oyo layoffs, Airbnb’s delayed IPO and the long-term quandary of investing in travel startups
It’s the best and worst of times for travel startups.
Massive growth over the past few decades has made tourism one of the big global industries, covering everything from recreation to business conferences to shopping sprees.
But doubts about the future of the industry are growing — and not just because of the novel coronavirus and COVID-19. The rise of remote work and the increasing stresses from tourism on urban and environmental systems portends tougher times ahead.
Given the spate of bad news the past few weeks swirling around global tourism startups, I wanted to go over where we are and what the future holds — and why that’s going to be so challenging for startups in this space.
Powered by WPeMatico
Google Cloud announces four new regions as it expands its global footprint
Google Cloud today announced its plans to open four new data center regions. These regions will be in Delhi (India), Doha (Qatar), Melbourne (Australia) and Toronto (Canada) and bring Google Cloud’s total footprint to 26 regions. The company previously announced that it would open regions in Jakarta, Las Vegas, Salt Lake City, Seoul and Warsaw over the course of the next year. The announcement also comes only a few days after Google opened its Salt Lake City data center.
GCP already had a data center presence in India, Australia and Canada before this announcement, but with these newly announced regions, it now offers two geographically separate regions for in-country disaster recovery, for example.
Google notes that the region in Doha marks the company’s first strategic collaboration agreement to launch a region in the Middle East with the Qatar Free Zones Authority. One of the launch customers there is Bespin Global, a major managed services provider in Asia.
“We work with some of the largest Korean enterprises, helping to drive their digital transformation initiatives. One of the key requirements that we have is that we need to deliver the same quality of service to all of our customers around the globe,” said John Lee, CEO, Bespin Global. “Google Cloud’s continuous investments in expanding their own infrastructure to areas like the Middle East make it possible for us to meet our customers where they are.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Quibi closes on $750 million as its date with destiny approaches
With just over one month to go until its official launch date, the short-form, subscription streaming service Quibi has closed on $750 million in new financing, according to a report in the company’s private PR firm The Wall Street Journal.
The company declined to disclose exactly who invested in the new round (which is always a great sign) and didn’t comment on how the new investment would effect the company’s valuation.
Chief Executive Officer Meg Whitman told the Journal that the new financing was made to ensure that the company would have the financial flexibility and runway to build a long-term business, but it’s likely that companies as diverse as Brandless and WeWork said the same thing about their goals when raising capital, as well.
According to the story in the WSJ, the company’s new investment contains both existing investors, like the Alibaba Group and Hollywood Studios, along with WndrCo, the investment firm and holding company launched by Quibi’s co-founder and Hollywood mogul Jeffrey Katzenberg.
To date, Quibi has raised $1.75 billion.
While the company touts its original approach to storytelling, and its list of marquee talent developing series for the app, the emphasis on short-form has been tried before by other companies (notably TechCrunch’s own parent company)… and the results were less than promising.
The idea that people need to consume short-form stories instead of … maybe just hitting the pause button… is interesting as an experiment to see what kinds of narratives or reality show-style entertainment needs to live behind a paywall rather than on YouTube or TikTok.
Perhaps Quibi will win with its slate of reality and narrative shows (which, to be honest, look pretty fun). The big names that Katzenberg and co-founder Meg Whitman promised are certainly on offer in the roster that is helpfully synopsized in a recent Entertainment Weekly article about the company’s programming.
Quibi, unlike some of the streaming services that it’s going to compete with, doesn’t have a back catalog of titles to tap to pad out the service, so it’s coming to market with a whopping 175 shows in its first year with 8,500 episodes, which run no longer than 10 minutes.
When it launches, there will be 50 shows on offer from the service. A lot depends on the reception of those shows. While many of the titles seem compelling, there are only a couple that seem to have the appeal to break through to the audience that Quibi hopes it can reach, and that will be willing to shell out money for its subscriptions.
The service is also hoping to differentiate itself by dropping new episodes daily — rather than weekly releases common on network television or the season-long binges that Netflix encourages.
The app itself seems to be fairly undifferentiated from the services available from other streamers. As we wrote when the company launched pre-orders for its app in February:
Much has been made about Quibi’s potential to reimagine TV by taking advantage of mobile technology in new ways, but the app itself looks much like any other streaming service, save for its last app store screenshot showing off its TurnStyle technology.
The app appears to favor a dark theme common to streaming apps, like Netflix and Prime Video, with just four main navigation buttons at the bottom.
The first is a personalized For You page, where you’re presented a feed where you’ll discover new things Quibi thinks you’ll like.
A Search tab will point you toward trending shows and it will allow you to search by show titles, genre or even mood.
The Following tab helps you keep track of your favorite shows and a Downloads tab keeps track of those you’ve made available for offline viewing.
Otherwise, Quibi’s interface is fairly simple. Shows are displayed with big images that you flip through either vertically on your home feed or both horizontally and vertically as you move through the Browse section.
The company does promote its TurnStyle viewing technology in its app store description, though it doesn’t reference the technology by name. Instead, it describes it as a viewing experience that puts you in full control. “No matter how you hold your phone, everything is framed to fit your screen,” it says.
In vertical viewing mode, it also introduces controls that appear on either the left or right side the screen — you choose, based on whether you’re left or right-handed.
Quibi did not formally announce the app was open for pre-order.
The startup, founded by Jeffrey Katzenberg, is backed by more than a billion dollars — including a recently closed $400 million round.
Despite the doubt surrounding its success, Quibi managed to sell out of the initial $150 million in available advertising for the service’s first year.
Whether it’s as big of a hit with potential subscribers as with advertisers remains to be seen. The service could still become the Mike Bloomberg campaign of streaming media — a lot of money and no discernible result.
Powered by WPeMatico
Lunchr becomes Swile to expand beyond corporate lunch cards
Lunchr has rebranded to Swile in order to expand its product offering beyond meal vouchers. The company wants to focus on everything that happens at work but that isn’t technically work — money pots for a birthday, paying back your co-workers, creating team-building events and more.
At heart, Swile provides a payment card for your lunch. French companies of a certain size have to support employees in one way or another when it comes to their lunch break. Big companies usually build out a cafeteria, while small companies hand out meal vouchers.
Companies can sign up to Swile so their employees all get a payment card for their meal vouchers. The company tops up everyone’s card every month. Just like challenger banks, Swile wants to provide a better user experience. For instance, you can associate a debit card with your account so that your debit card is used if you pay for an expensive lunch above your daily limit.
Currently 200,000 employees across 7,500 companies use a Swile card to pay for lunch.
But paying for lunch is just one of the financial transaction types that you do at work. And Swile wants to capture a bigger chunk of that market.
It starts with two simple features. First, you can pay back your co-workers when they lend you some money. It isn’t limited to lunch money; you can basically associate a debit card with your account, send money and hold money.
Old habits die hard, so it’s going to be hard to convince people to switch from Lydia to Swile. People already use Lydia to send money to their friends, and the company has managed to attract millions of users in France.
Second, many companies need to collect money from the team. It could be for a gift when somebody is leaving the company, it could be in order to buy beers or grab a drink after work on a Friday evening.
Employees can create money pots and invite the team. Given that everybody in your company has already created a Swile account, you don’t need to manually add your co-workers to the app — you just have to find their name in the directory. Swile doesn’t charge any fee on those money pots when you transfer the money to a Swile account or a bank account.
In addition to payment, Swile wants to help you connect more easily with your team. You can create and join events in the app. It could be useful for a birthday party at work, a soccer match, etc.
In the future, Swile also wants to add the ability to message your friends directly in the app — at some point, all apps become messaging apps. Also coming soon, Swile will help you bookmark places and share with your co-workers a map of your favorite places around the office.
Starting in June, even if your company doesn’t use Swile’s meal vouchers, you’ll be able to create an account for your team in order to use events, money pots, etc. Basic features will be free and Swile will introduce a premium tier later this year.
Powered by WPeMatico