Wait, you all haven’t been wiping down your smartphones this whole time?
A small consolation in the growing COVID-19 crisis is that some of our moderate germophobia has begun to feel like a minor super power. As I got settled for a cross-country flight last week, I took out my hand wipes and did a whole number on the screen, tray table and arm rests, and this time no one looked at me funny.
I go to a lot of conferences and trade shows and have to shake a lot of hands (though I’ve taken to the elbow bash in recent weeks) before handling my phone. Years ago, I switched from Purell bottles to hand wipes for two reasons:
- Hand sanitizer feels like lacquering the dirt on. This is probably another weird quirk, so do with that what you will.
- I touch my phone — and computer — a lot. I almost never leave the house without a product like Wet Ones in my bag. Hell, I included them in a travel gift guide last year. Merry Christmas, Billy, here’s the packet of antibacterial wipes you wanted but were too afraid to ask.
For those concerned about damage to your devices, fear not. Apple, which has never been prone to recklessness for such things, just gave disinfecting wipes a green light on its “How to clean your Apple products” that covers Mac, iPad, iPhone and iPod, among others.
Using a 70 percent isopropyl alcohol wipe or Clorox Disinfecting Wipes, you may gently wipe the hard, nonporous surfaces of your Apple product, such as the display, keyboard, or other exterior surfaces. Don’t use bleach. Avoid getting moisture in any opening, and don’t submerge your Apple product in any cleaning agents. Don’t use on fabric or leather surfaces.
iPhones these days sport IP67 or IP68 ratings. If it detects moisture in the Lightning port, it will throw up a “Charging not Available” warning. It’s best to avoid getting the port wet if you can, but that’s a nice fall back.
So, wipe, wipe away. Assuming, of course, you can still find them.
Powered by WPeMatico
Facebook Stories tests cross-posting to its pet, Instagram
Facebook’s latest colonization of Instagram has begun. Facebook is testing the option to cross-post Stories to Instagram, instead of just vice-versa. Hopefully, that means the two apps will finally sync up the “already viewed” status of cross-posted Stories so we don’t have to watch re-runs any more, as I harped about in January.
If fully launched, the cross-posting feature could save social media managers and average users time while letting them maximize the views on the content they create. It could also give a little boost to the total Stories available on Instagram so its algorithm has more to choose from when ranking what it shows first.

But the change could also been seen as the most invasive injection of parent company Facebook’s identity into Instagram — which has been steadily increasing since Instagram’s co-founders left the company in late 2018 as their autonomy dwindled. Facebook has already pasted an “Instagram – From Facebook” title screen into the photo-sharing app’s boot-up phase, and added an Open Facebook button to its settings menu. Instagram added cross-posting of its Stories to Facebook in October 2017, allowing its parent to piggyback on the popularity of its ephemeral content.
Facebook Stories, Instagram Stories and WhatsApp Status all had 500 million daily users as of a year ago, while Snapchat as a whole has just 218 million users.
The screenshot of the Facebook-to-Instagram cross-posting feature was generated from the Facebook for Android app code by Jane Manchun Wong. She’s the renowned reverse engineering expert who has furnished TechCrunch with tips on dozens of unreleased features that went on to officially launch. When you’ve shot a Facebook Story and are about to post it, you can tap Privacy to review who you’re sharing with. In addition to the Public, Friends, Custom and Hide From options, Facebook is testing a Share To Instagram toggle that appears to turn on continuous cross-posting of that post and future ones.
A Facebook spokesperson tells me that the company is now formally testing the cross-posting feature to make it easier to share moments with the people who matter to you, as people might have different audiences and followers on Facebook versus Instagram. Facebook will continue to explore options for simplifying and improving how Stories work across its apps. That means it’s out of the internal-only prototyping phase and is now being tested with users in the wild.
With any luck, Facebook and Instagram will eventually sync up data about which Stories you’ve watched on either app, and avoid showing you exact copies of ones you’ve already seen. I made my case for this to Instagram’s leadership at a recent press dinner, noting how reruns waste hundreds of millions of people’s time and lead them to close Stories or the app altogether. I asked Facebook about that specifically; they declined to comment.
Creating two-way interoperability of Stories is a precursor to Facebook’s efforts to unify its Messenger, WhatsApp and Instagram Direct chat features. That could extend end-to-end encryption across the apps, protecting messages from prying eyes. But there’s been government grumbling about how encryption could hide the activity of criminals, and some see intertwining the chat features as a way to make it harder for regulators to break up Facebook.
Powered by WPeMatico
Apple could add mouse cursor support to the iPad
According to a report from 9to5mac, Apple could be working on full cursor support for the next major version of iOS and iPadOS. The report is based on code of an early version of iOS 14 and iPadOS 14.
If Apple ships that new feature, it means that you’ll be able to use a Bluetooth mouse or trackpad with your iPad to move a cursor around the screen. It would work pretty much like a mouse on a desktop computer.
Apple has already added basic support for an external mouse in the current version of iPadOS. It can be enabled in the Accessibility settings. But it basically mimics a finger on the screen.
With full cursor support, you can expect your cursor to change when you hover over a link, for instance. You could right click on some elements, as well.
According to this early version of iOS 14, the cursor will disappear after a few seconds if you don’t move the mouse. It reappears when you move the mouse again. On a Mac, the cursor disappears when you start typing text.
There are also multiple signs that seem to indicate that Apple is working on a new Smart Keyboard for the iPad and trackpad shortcuts — tap to click, tap with two fingers to right click, etc. It could mean that the next Smart Keyboard will feature a trackpad below the keyboard.
Although iOS and iPadOS share the same code base, I wouldn’t expect cursor support on the iPhone. Cursor support seems to be particularly useful on a bigger screen, such as the iPad. You can also connect the most recent iPad Pro models to an external monitor thanks to its USB-C port.
In 2017, with iOS 11, Apple brought many design metaphors from the Mac to the iPad. The company introduced a Dock at the bottom of the screen as well as a new Files app. iOS still feels like a completely different operating system from macOS. But it is interesting to see that some important desktop features also work quite well on an iPad.
Powered by WPeMatico
Calmer You fills in the gaps in meditation apps for anxiety sufferers
Meditation and mindfulness apps are booming. The top 10 apps pulled in $195 million in 2019, up 52% from the year before. Now, top meditation app Headspace’s former head of research, Nick Begley, is launching a new app that goes beyond mindfulness to specifically address the needs of those suffering from anxiety. The app, called Calmer You, offers a combination of activities, including not only guided meditation, but also journaling, cognitive behavioral therapy coursework and other health and wellness material.
The latter includes things like fitness videos, sleep stories and interviews with celebrities and inspirational people on their experiences with anxiety, among other things.
Begley worked for Headspace for two years, where he learned about the power of meditation apps to aid with self-development, he says.
 “I realized that it doesn’t have to be limited to just mindfulness,” explains Begley, as to how he got started with Calmer You. “There’s so much good advice out there, but just passively digesting it — watching videos or reading books — which is what most of us do when we want to improve, simply doesn’t deliver the changes that they promise,” Begley says.
“I realized that it doesn’t have to be limited to just mindfulness,” explains Begley, as to how he got started with Calmer You. “There’s so much good advice out there, but just passively digesting it — watching videos or reading books — which is what most of us do when we want to improve, simply doesn’t deliver the changes that they promise,” Begley says.
The problem isn’t that the advice isn’t good — it typically is. But people struggle with putting the advice into action, Begley says. That’s where Calmer You aims to help.
The app includes a few different components, including a 28-session course that helps guide you step-by-step to better understanding anxiety and helping to learn techniques to manage it. This includes cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness, compassion-focused therapy, analytic techniques and more. In addition, there’s a toolkit with more than 50 quicker practices that are recommended based on how you’re feeling in a given moment or whatever situation you may be in. A journal for tracking how you feel day-by-day is available, as well.
Customers subscribe to the app for $7.99 per month or $47.99 per year.
“We didn’t specifically aim to fill the gaps of Headspace, but this is what users have mentioned,” Begley says. “A lot of people find it hard to regularly meditate, and so we wanted to provide tools and practices — in addition to mindfulness — to help people with anxiety. We wanted to provide a premium quality app experience that provides a more comprehensive approach to specifically helping manage anxiety and the many ways in which it manifests,” he adds.
Calmer You was developed in collaboration with anxiety expert and author Chloe Brotheridge, whose book “The Anxiety Solution: A Quieter Mind, a Calmer You” contributes to the app’s name. The team was familiar with Brotheridge’s book and reached out to her to see if she would be open to building an app based on her actionable advice.
This is a part of Calmer You’s parent company PSYT’s agenda — turning self-help books into apps.
The Calmer You team, via PSYT, also includes psychologists. But the app itself isn’t yet validated through things like randomized control trials, for example. That’s something they’d like to do further down the road, however.
Calmer You is also more geared toward women, as much of Brotheridge’s own work was particularly focused on anxiety’s impact on young women.
“For as long as I can remember, I’ve struggled with anxiety and I had to work out what worked best for me,” said Brotheridge. “This is why as a therapist, I teach people many different techniques so they can find what works best for them, not just mindfulness. While it took a lot of work to include multiple approaches in the app, I think it’s essential to help empower people to find the practices that work best for them and their situation,” she says.
Since the app’s launch into beta testing in November 2019, the company has been adding tools to respond to what users said they needed help with, including two new “rebalancing” tools (one for calming social anxiety, another to help communicate confidently), a worry journal for evening use and several more guided meditations and sleep stories.
The app shouldn’t be used instead of visiting a doctor for severe cases of anxiety, but could be slotted into a user’s routine if they’re already using a meditation app, like Headspace, to aid with feelings of anxiety on a regular basis.
Calmer You is a free download on iOS with a subscription business model.
Powered by WPeMatico
Spotify rolls out a more personalized home screen to users worldwide
Spotify has been slowly rolling out a redesigned mobile app in small sections — first with an update to podcast pages, then to other parts of the experience. Today, the company is revamping the most critical part of the Spotify app: the home screen. Now, when Spotify users launch the app, they’ll notice the new home screen greets them depending on what time of day it is with a “Good Morning,” “Good Afternoon” or “Good Evening,” for example. But the screen’s content and recommendations will also change with the time of day, Spotify says, and the content has also been better organized so you more easily jump back in or browse recommendations from the main page.
Before, Spotify’s home screen emphasized your listening history by putting at the top of the page things like your “Recently Played,” “Your Top Podcasts” and “Your Heavy Rotation.”
Effectively, the update separates the app’s home screen into two main parts: familiar content on top and new or recommended content on the bottom half.
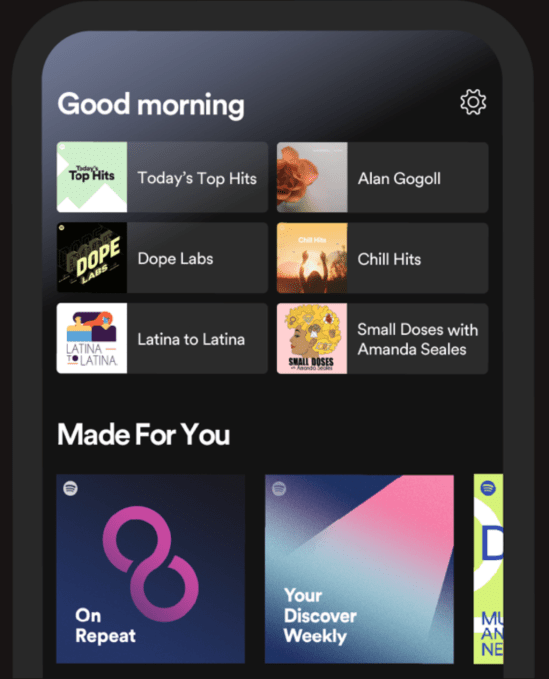 Now, the home screen reserves six spots underneath the daily greeting where you can continue with things like the podcast you stream every morning, your workout playlist or the album you’ve been listening to on heavy rotation this week. This content will update as your day progresses to better match your activities and interests, based on prior behavior.
Now, the home screen reserves six spots underneath the daily greeting where you can continue with things like the podcast you stream every morning, your workout playlist or the album you’ve been listening to on heavy rotation this week. This content will update as your day progresses to better match your activities and interests, based on prior behavior.
Beneath these six spots, the home page will display other things like your top podcasts, “made for you” playlists, recommendations for new discoveries based on your listening and more.
The concept for the new home screen is similar to what Pandora recently rolled out with its personalized “For You” tab late last year. Like Spotify, Pandora’s tab also customizes the content displayed based on the time of day, in addition to the day of the week and other predictions it can make about a customer’s mood or potential activity, based on prior listening data.
Pandora’s revamp led to double the number of users engaging with the personalized page, compared with the old Browse experience, it says. Spotify, too, is likely hoping to see a similar bump in usage and engagement, as users won’t have to dart around the app as much to find their favorite content or recommendations. That way, they’ll be able to start streaming more quickly after the app is launched, potentially leading to longer sessions and more discovery of new content.
Spotify to date has defined itself by its advanced personalization and recommendation technology, but its app hasn’t always been the easiest to use and navigate — especially in comparison to its top U.S. rival, Apple Music, which favors a simpler and cleaner look-and-feel. Its recent changes have tried to address this problem by making its various parts and pages easier to use.
Spotify says the updated home screen will roll out starting today to all global users with at least 30 days of listening history.
Powered by WPeMatico
TFLiving, with $4.8M in seed funding, wants to be the Uber for amenities
TFLiving, looking to bring amenities to residential and commercial spaces, has today announced the close of a $4.8 million seed financing led by Camber Creek. Courtside Ventures, and other strategic investors, also participated in the round.
TFLiving uses technology to connect service providers, like massage therapists, yoga instructors and dog walkers, with property managers and their residents. The service allows residents to sign up for classes or services, as well as request other community events or services, directly from an app.
The most popular use case of the service is fitness, both classes and individual trainings, but TFLiving offers a relatively broad variety of services and experiences to residents at its 300 partnered properties.
Here’s how it works.
TFLiving signs partnerships with property managers of buildings that don’t currently offer amenities, or want to complement existing amenity offerings. After checking out the building, TFLiving determines if there is any under-utliized space in the building, such as a rooftop or a vacant unit, that could be repurposed for community classes.
After evaluating the space, TFLiving surveys residents and determines what they’re interested in via the app, which then serves up options from actual service providers on the service within the guidelines of the property manager’s financial guidelines.
One of the strengths of the business, according to founder and CEO Devin Wirt, is that the cost structure of the platform is highly customizable. Who pays is a question that can be answered by the property manager. If the building has a huge budget for community engagement and the property manager sees value in offering five classes/month and unlimited on-demand massage, they can choose to do so. The property manager can also grant TFLiving access to the building without paying a dime, passing on the full cost of the service to residents.
In most cases, property managers will foot the bill for community events, while residents pay for their own individual services like massage and dog walking.
Because TFLiving’s pricing is based on service and not calculated by number of units, the product can be priced at an affordable cost within the budget of the property and based on demand from the residents.
TFLiving also allows property managers to mark up the class or service and keep a cut of the profit. For example, if a property manager doesn’t have the budget for community classes or services, but doesn’t mind letting residents book individual personal training in the on-site gym, that property manager can mark up the cost of fitness classes by 20% and generate some revenue that could eventually go toward community events.
“One of the things that we stay pretty stringent on is just how far they’re able to market the prices,” said Wirt. “As a core mission of staying affordable to all asset classes, we understand that because we’re not paying a lease, we’re able to charge below market pricing. We still want to stay true to our core mission that we want to provide affordable services.”
Unlike ClassPass, which also connects service providers to users in the fitness space, TFLiving does not dynamically price its various classes and services based on popularity or quality. Fitness classes, for example, are always between $50 and $80, with geography being the main determining factor on specific price.
The company declined to share the revenue breakdown between the company and service providers, but noted that it varies by vertical and that service providers receive a majority of the revenue.
TFLiving currently has agreements with properties across 29 states, with contracts at more than 800 properties, soon covering more than 200,000 units.
Wirt says that he sees the potential to implement TFLiving in commercial spaces as well, such as offices.
Moreover, TFLiving has worked on the tech side to be as useful, not necessarily as prominent, as possible. TFLiving integrates with a variety of property management platforms, from mobile doorman apps to platforms for paying rent to maintenance requests. Residents using those apps can request and book TFLiving amenities straight from those platforms.
Powered by WPeMatico
Box is now letting all staff work from home to reduce coronavirus risk
Box has joined a number of tech companies supporting employees to work remotely from home in response the outbreak of the novel coronavirus.
It’s applying the policy to all staff, regardless of location.
Late yesterday Box co-founder Aaron Levie tweeted a statement detailing the cloud computing company’s response to COVID-19, the name of the disease caused by the coronavirus — to, as he put it, “ensure the availability of our service and safety of our employees”.
We know how important secure collaboration and remote work is becoming for our customers right now. Here are a few of the measures we’re taking to ensure the availability of our service and safety of our employees: https://t.co/i65ONkIgNp
— Aaron Levie (@levie) March 8, 2020
In recent days Twitter has similarly encouraged all staff members to work from home. While companies including Amazon, Google, LinkedIn and Microsoft have also advised some staff to work remotely to reduce the risk of exposure to the virus.
In its response statement Box writes that it’s enacted its business continuity plans “to ensure core business functions and technology are operational in the event of any potential disruption”.
“We have long recognized the potential risks associated with service interruptions due to adverse events, such as an earthquake, power outage or a public health crisis like COVID-19, affecting our strategic, operational, stakeholder and customer obligations. This is why we have had a Business Continuity program in place to provide the policies and plans necessary for protecting Box’s operations and critical business functions,” the company writes.
In a section on “workforce resilience and business continuity” it notes that work from home practices are a normal part of its business operations but says it’s now extending the option to all its staff, regardless of the office or location they normally work out of — saying it’s doing so “out of an abundance of caution during COVID-19”.
Other measures the company says it’s taken to further reduce risk include suspending all international travel and limiting non-essential domestic travel; reducing large customer events and gatherings; and emphasizing health and hygiene across all office locations — “by maintaining sanitation supplies and encouraging an ‘if you are sick, stay home’ mindset”.
It also says it’s conducting all new hire orientation and candidate interviews virtually.
Box names a number of tools it says it routinely uses to support mobility and remote working, including its own service for secure content collaboration; Zoom’s video communication tool; the Slack messaging app; Okta for secure ID; plus additional unnamed “critical cloud tools” for ensuring “uninterrupted remote work for all employees”.
Clearly spying the opportunity to onboard new users, as more companies switch on remote working as a result of COVID-19 concerns, Box’s post also links to free training resources for its own cloud computing tools.
This report was updated with a correction to clarify that COVID-19 is the disease caused by the novel coronavirus; rather than another name for the virus
Powered by WPeMatico
China Roundup: Enterprise tech gets a lasting boost from coronavirus outbreak
Hello and welcome back to TechCrunch’s China Roundup, a digest of recent events shaping the Chinese tech landscape and what they mean to people in the rest of the world. This week, a post from Sequoia Capital sounding the alarm of the coronavirus’s impact on businesses is reaching far corners of tech communities around the world, including China.
Many echo Sequoia’s observation that the companies that are the “most adaptable” are the likeliest to survive. Others cling to the hope of “[turning] a challenging situation into an opportunity to set yourself up for enduring success.”
Two weeks ago I wrote about how the private sector and the government in China are working together to contain the epidemic, bringing a temporary boost to the technology industry. This week I asked a number of investors and founders which of these changes will stand to last, and why.
B2B on the rise
The business-to-business (B2B) space was rarely a hot topic in China until online consumer businesses became relatively saturated in recent times. And now, the COVID-19 epidemic has unexpectedly breathed life into the once-boring field, which stretches from virtual meetings, online education, digital healthcare, cybersecurity, telecommunications, logistics to smart cities, analysis from investment firm Yunqi Partners shows.
For one, there is an obvious opportunity for remote collaboration tools as people work from home. Downloads of indigenous work apps like Dingtalk, WeChat Work, TikTok’s sister Lark as well as America’s Zoom jumped exponentially amid the health crisis. While some argue that the boom is overblown and will dissipate as soon as businesses are back to normal, others suggest that the shift in behavior will endure.
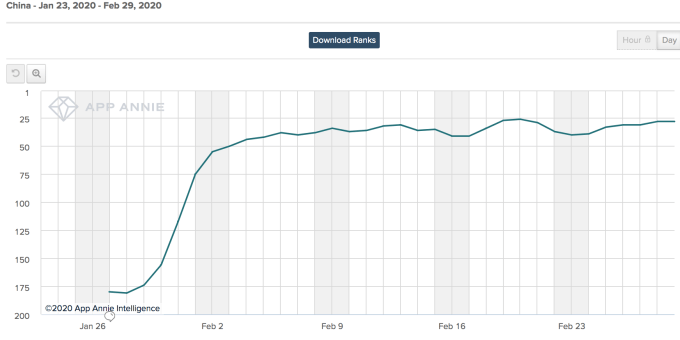
Like other work collaboration services, Zoom soared in China amid the coronavirus outbreak, jumping from No. 180 in late January to No. 28 as of late February in overall app installs. Data: App Annie
“People are reluctant to change once they form a new habit,” suggests Joe Chan, partner at Hong Kong-based Mindworks Ventures. The virus outbreak, he believes, has educated the Chinese masses to work remotely.
“Meeting in person and through Zoom both have their own merits, depending on the social norm. Some people are used to thinking that relationships need to be established through face-to-face encounters, but those who don’t hold that view will have fewer meetings. [The epidemic] presents a chance for a paradigm shift.”
But changes are slow
Growth in enterprise businesses might be less visible than what China witnessed over the SARS epidemic that fueled internet consumer verticals such as ecommerce. That’s because software-as-a-services (SaaS), cloud computing, health tech, logistics and other enterprise-facing services are intangible for most consumers.
“Compared to changes in consumer behavior, the adoption of new technologies by enterprises happen at a slower pace, so the impact of coronavirus on new-generation innovations [B2B] won’t come as rapidly and thoroughly as what happened during SARS,” contended Jake Xie, vice president of investment at China Growth Capital.
Xie further suggested that the opportunities presented by the outbreak are reserved for companies that have been steadily investing in the field, in part because enterprise services have a longer life cycle and require more capital-intensive infrastructure. “Opportunists don’t stand a chance,” he concluded.
As for changing consumer behavior, such as the uptick in grocery delivery usage by seniors trapped indoors, the impact might be short-lived. “The only benefit that the epidemic brings to these apps is getting more people to try their services. But how many of them will stay? The argument that people will keep using these apps over concerns of getting sick in offline markets is unsubstantiated. The strength of a business lies in its ability to solve user problems in the long term, for example, providing affordability and convenience,” suggested Derek Shen, chairman of Danke Apartment, the Chinese co-living startup slated to list on NYSE.
Summoned by Beijing
The adjacent sector of enterprise services — at-scale technologies tailored to energizing government functions — has also seen traction over the course of the epidemic. Private firms in China have teamed up with regional authorities to better track people’s movements, ramp up facial recognition capacities aimed at a mask-wearing public, develop contact-free consumer experience, among other measures.
Tech firms touting services to the government are no stranger to criticisms concerning the lack of transparency in how user data is used. But the appeal to private firms is huge, not only because state contracts tend to provide a steady stream of long-term revenue, but also that certain public-facing projects can be billed as a fulfillment of corporate social responsibilities. Following the virus outbreak, Chinese tech companies of all sizes hastened to offer contributions, with efforts ranging from making monetary donations to building tools that keep the public informed.
On the flip side, the government also needs private help in emergency management. As prominent Chinese historian Luo Xin poignantly pointed out in podcast SurplusValue’s recent episode [1:00:00], some of the most efficient and effective responses to the public health crisis came not from the government but the private sector, whether it is online retailer JD.com or logistics firm SF Express delivering relief supplies to the epicenter of the outbreak.
That said, Luo argued there are signs that some local authorities’ tendency to centralize control is getting in the way of private efforts. For example, some government offices have stumbled in their attempts to develop crisis management systems from scratch, overlooking a pool of readily available and proven infrastructure powered by the country’s tech giants.
Powered by WPeMatico
How the information system industry became enterprise software
If you were a software company employee or venture capitalist in Silicon Valley before 1993, chances are you were talking about “Information Systems Software” and not “Enterprise Software.” How and why did the industry change its name?
The obvious, but perplexing answer is simple — “Star Trek: The Next Generation.”
As befuddling and mind-numbingly satisfying as it is to your local office Trekkie, the industry rebranded itself thanks to a marketing campaign from the original venture-backed system software company, Boole & Babbage (now BMC software).
While the term “Enterprise” was used to describe complex systems for years before 1993, everything changed when Boole & Babbage signed a two-year licensing agreement with the then-highest-rated show in syndication history to produce an infomercial.
Star Trek fans have been talking about this crazy marketing agreement for years, and you can read the full details about how it was executed in TrekCore. But even Trekkies don’t appreciate its long-term impacts on our industry. In this license agreement with Paramount, Boole & Babbage had unlimited rights to create and distribute as much Star Trek content as they could. They physically mailed VHS cassettes to customers, ran magazine ads and even dressed their employees as members of Starfleet at trade shows. Boole & Babbage used this push to market itself as the “Enterprise Automation Company.”
Commander Riker says in the infomercial, “just as the bridge centralizes the functions necessary to control the USS Enterprise, Boole’s products centralize data processing information to allow centralized control of today’s complex information systems.” This seemed to scratch an itch that other systems companies didn’t realize needed scratching.
Not to be outdone, IBM in 1994 rebranded their OS/2 operating system “OS/2 Warp,” referring to Star Trek’s “warp drive.” They also tried to replicate Babbage’s licensing agreement with Paramount by hiring the Enterprise’s Captain Picard (played by actor Patrick Stewart) to emcee the product launch. Unfortunately, Paramount wouldn’t play ball, and IBM hired Captain Janeway (played by actress Kate Mulgrew) from Star Trek: Voyager instead. The licensing issues didn’t stop IBM from also hiring Star Trek’s Mr. Spock (played by actor Leonard Nimoy) to tape a five-minute intro to the event:
Outside of OS/2, IBM’s 1994 announcement list included 13 other “enterprise” initiatives. Soon, leading software companies began to rebrand themselves and release products using the term “enterprise software” as a valuable identifier. MRP software makers like SAP and Baan began embracing the new “Enterprise” moniker after 1993 and in 1995, Lotus rebranded itself as an “Enterprise Software Company.”
“Enterprise” was officially the coolest new vernacular and after industry behemoth IBM bought Lotus in 1996, they incorporated “Enterprise” across all of their products. And while Gartner’s 1990 paper “ERP: A Vision of the Next-Generation MRP II” by Wylie is the technical birth of ERP software, no one cared until Commander Riker told Harold to “monitor your entire Enterprise from a single point of control.” The ngram numbers don’t lie:
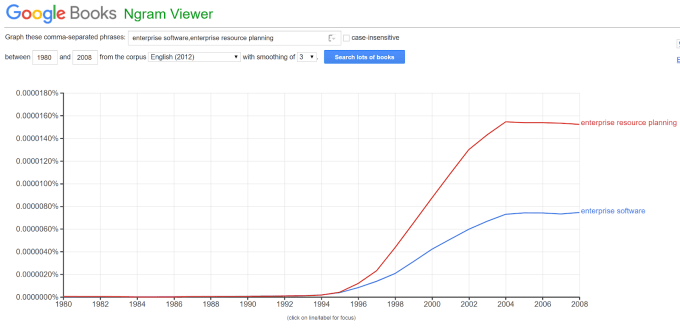
Almost 30 years later, we live in a world in which business is run on enterprise software and the use of the term is ubiquitous. Whenever I see a software business plan come across my desk or read an article on enterprise software, I can’t help but give Commander Riker a little due credit.
Powered by WPeMatico
Crypto wallet app ZenGo launches savings mode
ZenGo is expanding beyond the basic features of a cryptocurrency wallet — letting you hold, send and receive crypto assets. You can now set aside some of your crypto assets to earn interests. In other words, ZenGo now also acts like a savings account.
The company has partnered with two DeFi projects for the new feature. DeFi means “decentralized finance”, and it has been a hot trend in the cryptocurrency space. DeFi projects are the blockchain equivalent of traditional financial products. For instance, you can lend and borrow money, invest in derivative assets and more.
If you want to learn more about DeFi, here’s an article I wrote on the subject:
But let’s come back to ZenGo. When you have crypto assets in your ZenGo wallet, you can now open the savings tab, pick an asset, such as Dai, and select what percentage of your holdings you want to set aside.
After that, all you have to do is wait. You get an overview of your savings “accounts” at any time. This way, you can see your total earned interests. Interests are automatically reinvested over time. You can move your money from those DeFi projects back to your wallet whenever you want.
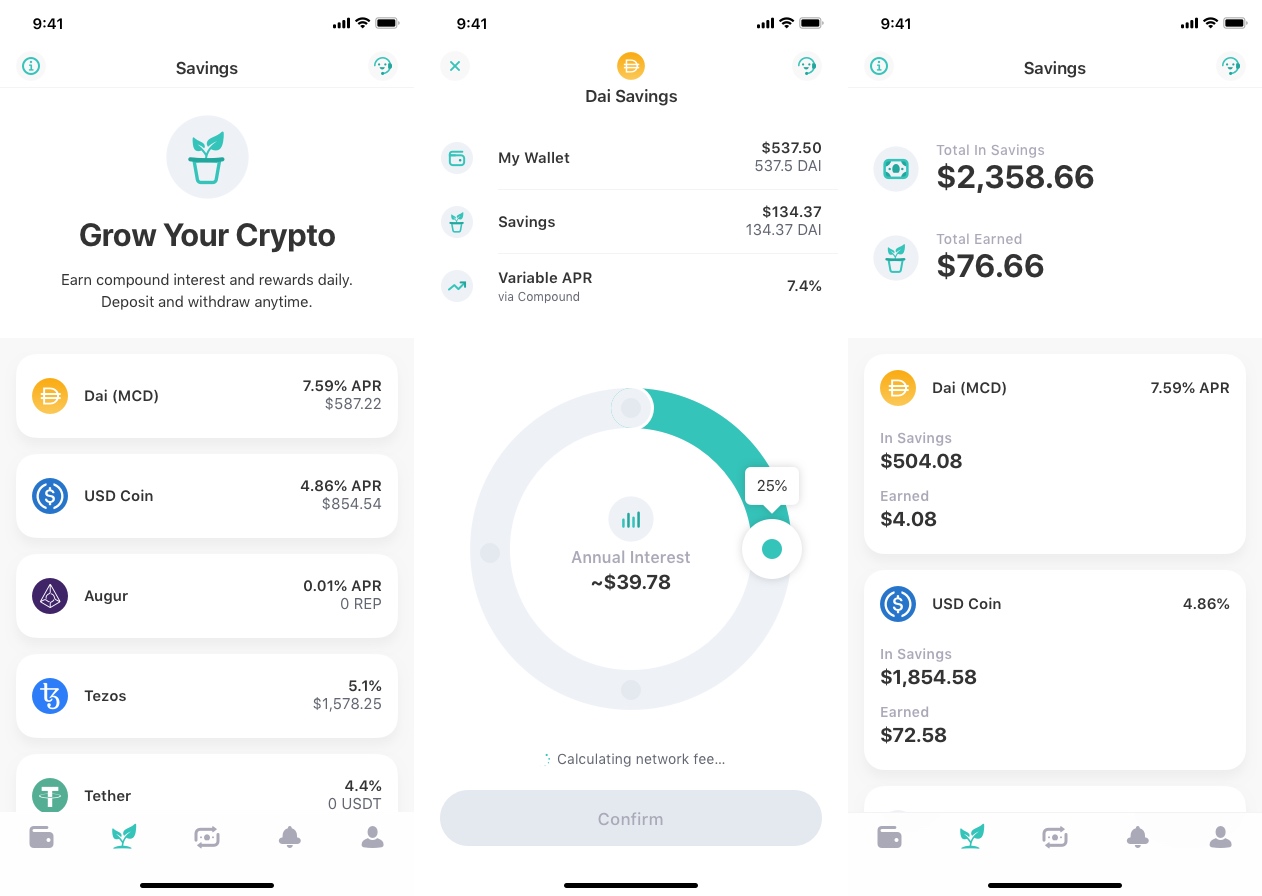
Behind the scene, ZenGo uses the Compound protocol, a lending DeFi project. It works a bit like LendingClub, but on the blockchain. Some users send money to Compound to contribute to liquidity pools. Other users borrow money from that pool.
Interest rates go up and down depending on supply and demand. That’s why you currently earn more interests when you inject DAI or USD Coin in Compound. But that could change over time.
ZenGo also uses Figment in order to stake Tezos. This time, it isn’t a lending marketplace. When you lock some money in a staking project, it means that you support the operations of a particular blockchain. Few blockchains support staking as they need to be based on proof-of-stake.
For the end user, it looks like a savings account whether you’re relying on Compound or Figment. There are other wallet apps that let you access DeFi projects, such as Coinbase Wallet and Argent. But ZenGo thinks they’re still too complicated for regular users.
Powered by WPeMatico