ZmURL customizes Zoom link previews with images & event sites
Sick of sharing those generic Zoom video call invites that all look the same? Wish your Zoom link preview’s headline and image actually described your meeting? Want to protect your Zoom calls from trolls by making attendees RSVP to get your link? ZmURL.com has you covered.
Launching today, ZmURL is a free tool that lets you customize your Zoom video call invite URL with a title, explanation and image that will show up when you share the link on Twitter, Facebook or elsewhere. ZmURL also lets you require that attendees RSVP by entering their email address so you can decide who to approve and provide with the actual entry link. That could stop Zoombombers from harassing your call with offensive screenshared imagery, profanity or worse.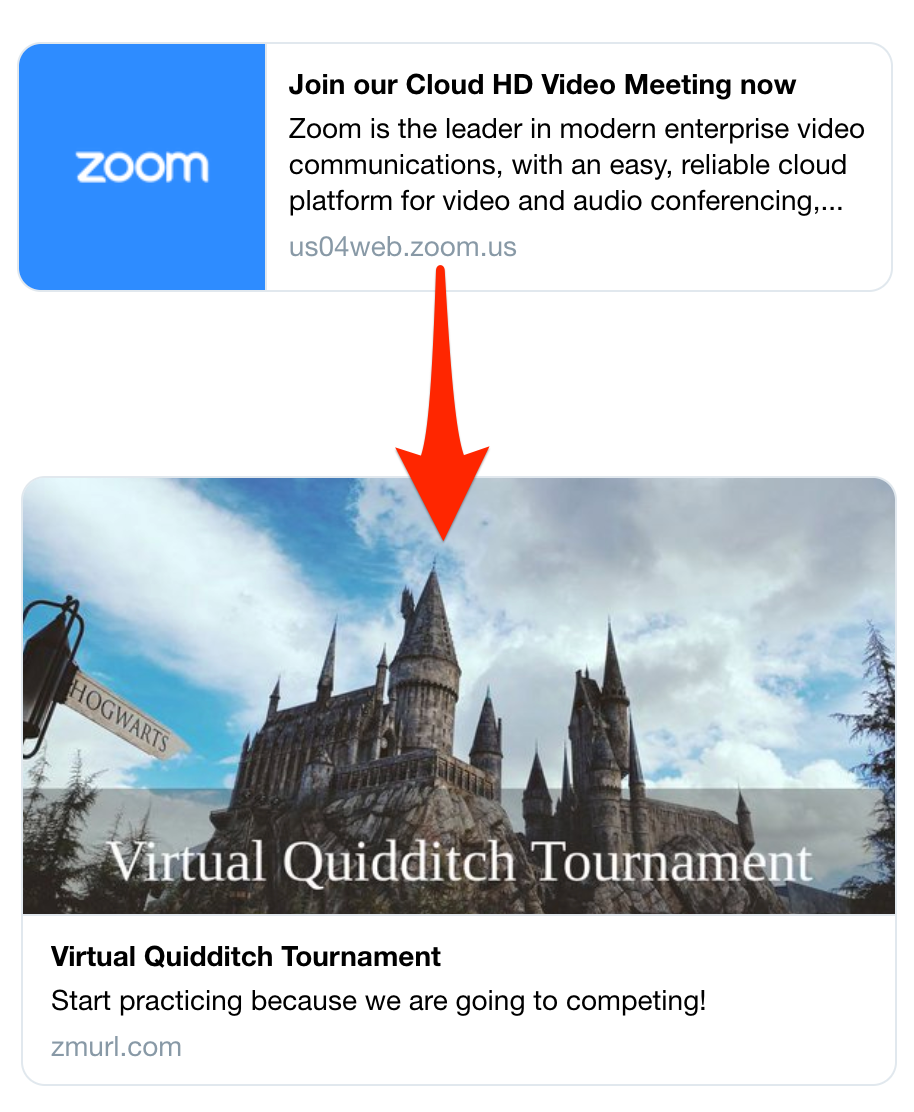
“We built zmurl.com to make it easier for people to stay physically distant but socially close,” co-founder Victor Pontis tells me. “We’re hoping to give event organizers the tools to preserve in-person communities while we are all under quarantine.”
Zoom wasn’t built for open public discussions. But with people trapped inside by coronavirus, its daily user count has spiked from 10 million to 200 million. That’s led to new use cases, from cocktail parties to roundtable discussions to AA meetings to school classes.
That’s unfortunately spawned new problems, like “Zoombombing,” a term I coined two weeks ago to describe malicious actors tracking down public Zoom calls and bombarding them with abuse. Since then, the FBI has issued a warning about Zoombombing, The New York Times has written multiple articles about the issue and Zoom’s CEO Eric Yuan has apologized.
Yet Zoom has been slow to adapt it features as it struggles not to buckle under its sudden scale. While it has turned on waiting rooms and host-only screensharing by default for usage in schools, most people are still vulnerable due to Zoom’s permissive settings and reused URLs that were designed for only trusted enterprise meetings. Only today did Zoom concede to shifting the balance further from convenience to safety, turning on waiting rooms by default and requiring passwords for entry by Meeting ID.
Meanwhile, social networks have become a sea of indistinguishable Zoom links that all show the same blue and white logo in the preview, with no information on what the call is about. That makes it a lot tougher to promote calls, which many musicians, fitness instructors and event producers are relying on to drive donations or payments while their work is disrupted by quarantines.

ZmURL’s founders during their only in-person meeting ever
Luckily, Pontis and his co-founder Danqing Liu are here to help with ZmURL. The two software engineers fittingly met over Zoom a year ago and have only met once in person. Pontis, now in San Francisco, had started bike and scooter rental software companies Spring and Scooter Map. Liu, from Beijing but now holed up in New York, had spent five years at Google, Uber and PlanGrid before selling his machine learning tool TinyMind.
The idea for ZmURL stemmed from Liu missing multiple Zoom events he’d wanted to attend. Then a friend of Pontis’ was laid off from their yoga instructor job, and they and their colleagues were scrambling to market and earn money from hosting their own classes over Zoom. The duo quickly built a beta, with zero money raised, and tested it with some yoga gurus who found it simplified promoting events and gathering RSVPs. “We’re all going through a tough time right now. We see ZmURL as our opportunity to help,” Pontis tells me.
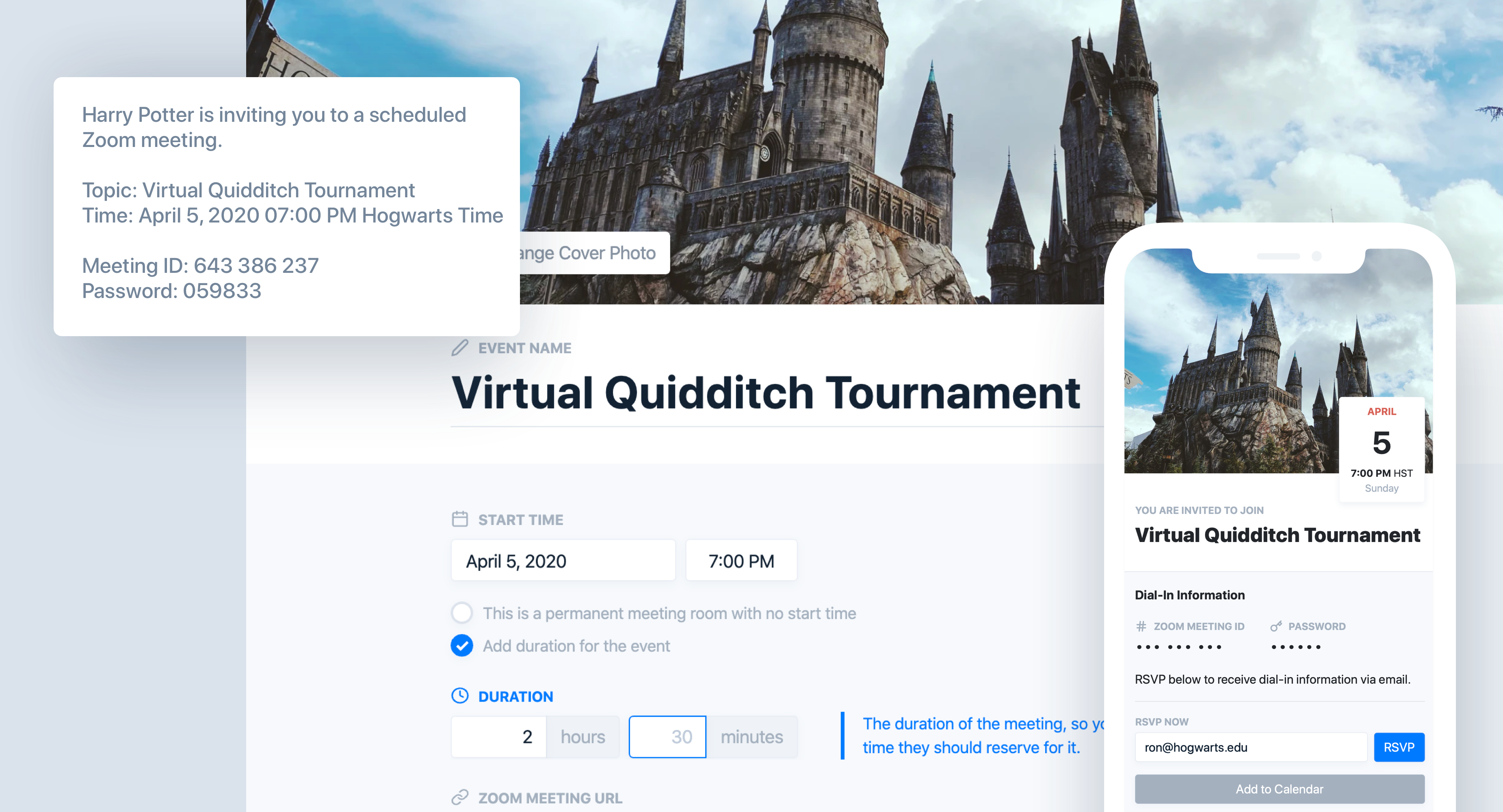
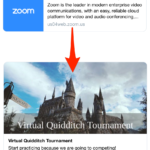
To use the tool, you generate a generic meeting link from Zoom like zoom.us/ji/1231231232 and then punch it into ZmURL. You can upload an image or choose from stock photos and color gradients. Then you name your event, give it a description and set the time and date. You’ll get a shorter URL like https://zmurl.com/smy5m or you can give it a custom one like zmurl.com/quidditch.
When you share that URL, it’ll show your image, headline and description in the link preview on chat apps, social networks and more. Attendees who click will be shown a nicely rendered event page with the link to enter the Zoom call and the option to add it to their calendar. You can try it out here, zmurl.com/aloha, as the startup is hosting a happy hour today at 6pm Pacific.
Optionally, you can set your ZmURL calls to require an RSVP. In that case, people who click your link have to submit their email address. The host can then sift through the RSVPs and choose who to email back the link to join the call. If you see an RSVP from someone you don’t recognize, just ignore it to keep Zoombombers from slipping inside.
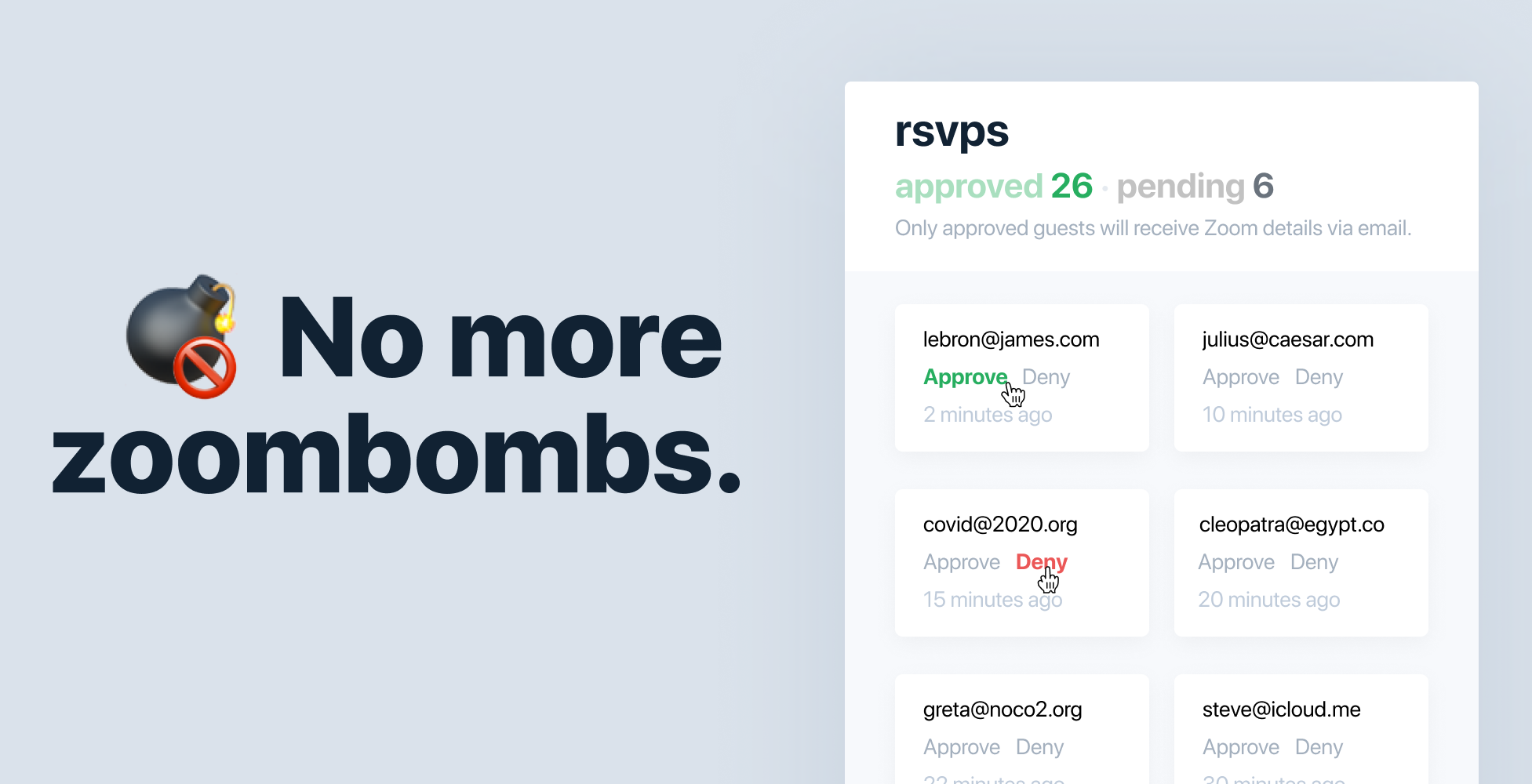
Surprisingly, there doesn’t seem to be any other tools for customizing Zoom call links. Zoom paid enterprise customers can only set up a image and logo-equipped landing page for their whole company’s Zoom account, not for specific calls. For now, ZmURL is completely free. But the co-founders are building out an option for hosting paid events that collect entry fees on the RSVP site while ZmURL takes a 5% cut.
Next, ZmURL wants to add the ability to link your Zoom account to its site so you can spawn call links without leaving. It’s also building out always-on call rooms, recurring events, organizer home pages for promoting all their calls, an option to add events to a public directory, email marketing tools and integrations with other video call platforms like Hangouts, Skype and FaceTime.
Pontis says the biggest challenge will be learning to translate more of the magic and business potential off offline events into the world of video calling. There’s also the risk that Zoom will try to intercede and force ZmURL to desist. But it shouldn’t, at least until Zoom builds all these features itself. Or it should just acquire ZmURL.
We’re dealing with an unprecedented behavior shift due to shelter-in-place orders that threaten to cripple the world economy and drive many of us crazy. Whether for fostering human connection or keeping event businesses afloat, Zoom has become a critical utility. It should accept all the help it can get.
Powered by WPeMatico
Want to survive the downturn? Better build a platform
When you look at the most successful companies in the world, they are almost never just one simple service. Instead, they offer a platform with a range of services and an ability to connect to it to allow external partners and developers to extend the base functionality that the company provides.
Aspiring to be a platform and actually succeeding at building one are not the same. While every startup probably sees themselves as becoming a platform play eventually, the fact is it’s hard to build one. But if you can succeed and your set of services become an integral part of a given business workflow, your company could become bigger and more successful than even the most optimistic founder ever imagined.
Look at the biggest tech companies in the world, from Microsoft to Oracle to Facebook to Google and Amazon. All of them offer a rich complex platform of services. All of them provide a way for third parties to plug in and take advantage of them in some way, even if it’s by using the company’s sheer popularity to advertise.
Michael A. Cusumano, David B. Yoffie and Annabelle Gawer, who wrote the book The Business of Platforms, wrote an article recently in MIT Sloan Review on The Future of Platforms, saying that simply becoming a platform doesn’t guarantee success for a startup.
“Because, like all companies, platforms must ultimately perform better than their competitors. In addition, to survive long-term, platforms must also be politically and socially viable, or they risk being crushed by government regulation or social opposition, as well as potentially massive debt obligations,” they wrote.
In other words, it’s not cheap or easy to build a successful platform, but the rewards are vast. As Cusumano, Yoffie and Gawer point out their studies have found, “…Platform companies achieved their sales with half the number of employees [of successful non-platform companies]. Moreover, platform companies were twice as profitable, were growing twice as fast, and were more than twice as valuable as their conventional counterparts.”
From an enterprise perspective, look at a company like Salesforce . The company learned long ago that it couldn’t possibly build every permutation of customer requirements with a relatively small team of engineers (especially early on), so it started to build hooks into the platform it had built to allow customers and consultants to customize it to meet the needs of individual organizations.
Eventually Salesforce built APIs, then it built a whole set of development tools, and built a marketplace to share these add-ons. Some startups like FinancialForce, Vlocity and Veeva have built whole companies on top of Salesforce.
Rory O’Driscoll, a partner at Scale Venture Partners, speaking at a venture capitalist panel at BoxWorks in 2014, said that many startups aspire to be platforms, but it’s harder than it looks. “You don’t make a platform. Third-party developers only engage when you achieve a critical mass of users. You have to do something else and then become a platform. You don’t come fully formed as a platform,” he said at the time.
If you’re thinking, how you could possibly start a company like that in the middle of a massive economic crisis, consider that Microsoft launched in 1975 in the middle of recession. Google and Salesforce both launched in the late 1990s, just ahead of the dot-com crash, and Facebook launched in 2004, four years before the massive downturn in 2008. All went on to become tremendously successful companies
That success often requires massive spending and sales and marketing burn, but when it works, the rewards are enormous. Just don’t expect that it’s an easy path to success.
Powered by WPeMatico
Zoom will enable waiting rooms by default to stop Zoombombing
Zoom is making some drastic changes to prevent rampant abuse as trolls attack publicly-shared video calls. Starting April 5th, it will require passwords to enter calls via Meeting ID, since these may be guessed or reused. Meanwhile, it will change virtual waiting rooms to be on by default so hosts have to manually admit attendees.
The changes could prevent “Zoombombing”, a term I coined two weeks ago to describe malicious actors entering Zoom calls and disrupting them by screensharing offensive imagery. New Zoombombing tactics have since emerged, like spamming the chat thread with terrible GIFs, using virtual backgrounds to spread hateful messages, or just screaming profanities and slurs. Anonymous forums have now become breeding grounds for organized trolling efforts to raid calls.
Just imagine the most frightened look on all these people’s faces. That’s what happened when Zoombombers attacked the call.
The FBI has issued a warning about the Zoombombing problem after children’s online classes, alcoholics anonymous meetings, and private business calls were invaded by trolls. Security researchers have revealed many ways that attackers can infiltrate a call.
The problems stem from Zoom being designed for trusted enterprise use cases rather than cocktail hours, yoga classes, roundtable discussions, and classes. But with Zoom struggling to scale its infrastructure as its daily user count has shot up from 10 million to 200 million over the past month due to coronavirus shelter-in-place orders, it’s found itself caught off guard.
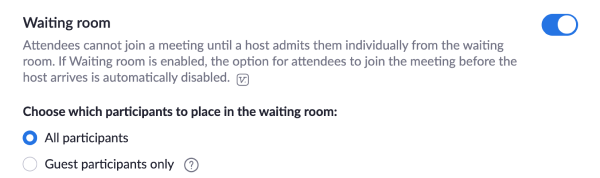
Zoom CEO Eric Yuan apologized for the security failures this week and vowed changes. But at the time, the company merely said it would default to making screensharing host-only and keeping waiting rooms on for its K-12 education users. Clearly it determined that wasn’t sufficient, so now waiting rooms are on by default for everyone.
Zoom communicated the changes to users via an email sent this afternoon that explains “we’ve chosen to enable passwords on your meetings and turn on Waiting Rooms by default as additional security enhancements to protect your privacy.”
The company also explained that “For meetings scheduled moving forward, the meeting password can be found in the invitation. For instant meetings, the password will be displayed in the Zoom client. The password can also be found in the meeting join URL.” Some other precautions users can take include disabling file transfer, screensharing, or rejoining by removed attendees.

NEW YORK, NY – APRIL 18: Zoom founder Eric Yuan reacts at the Nasdaq opening bell ceremony on April 18, 2019 in New York City. The video-conferencing software company announced it’s IPO priced at $36 per share, at an estimated value of $9.2 billion. (Photo by Kena Betancur/Getty Images)
The shift could cause some hassle for users. Hosts will be distracted by having to approve attendees out of the waiting room while they’re trying to lead calls. Zoom recommends users resend invites with passwords attached for Meeting ID-based calls scheduled for after April 5th. Scrambling to find passwords could make people late to calls.
But that’s a reasonable price to pay to keep people from being scarred by Zoombombing attacks. The rash of trolling threatened to sour many people’s early experiences with the video chat platform just as it’s been having its breakout moment. A single call marred by disturbing pornography can leave a stronger impression than 100 peaceful ones with friends and colleagues. The old settings made sense when it was merely an enterprise product, but it needed to embrace its own change of identity as it becomes a fundamental utility for everyone.
Technologists will need to grow better at anticipating worst-case scenarios as their products go mainstream and are adapted to new use cases. Assuming everyone will have the best intentions ignores the reality of human nature. There’s always someone looking to generate a profit, score power, or cause chaos from even the smallest opportunity. Building development teams that include skeptics and realists, rather than just visionary idealists, could keep ensure products get safeguarded from abuse before rather than after a scandal occurs.
Powered by WPeMatico
Google is now publishing coronavirus mobility reports, feeding off users’ location history
Google is giving the world a clearer glimpse of exactly how much it knows about people everywhere — using the coronavirus crisis as an opportunity to repackage its persistent tracking of where users go and what they do as a public good in the midst of a pandemic.
In a blog post today, the tech giant announced the publication of what it’s branding COVID-19 Community Mobility Reports, an in-house analysis of the much more granular location data it maps and tracks to fuel its ad-targeting, product development and wider commercial strategy to showcase aggregated changes in population movements around the world.
The coronavirus pandemic has generated a worldwide scramble for tools and data to inform government responses. In the EU, for example, the European Commission has been leaning on telcos to hand over anonymized and aggregated location data to model the spread of COVID-19.
Google’s data dump looks intended to dangle a similar idea of public policy utility while providing an eyeball-grabbing public snapshot of mobility shifts via data pulled off of its global user-base.
In terms of actual utility for policymakers, Google’s suggestions are pretty vague. The reports could help government and public health officials “understand changes in essential trips that can shape recommendations on business hours or inform delivery service offerings,” it writes.
“Similarly, persistent visits to transportation hubs might indicate the need to add additional buses or trains in order to allow people who need to travel room to spread out for social distancing,” it goes on. “Ultimately, understanding not only whether people are traveling, but also trends in destinations, can help officials design guidance to protect public health and essential needs of communities.”
The location data Google is making public is similarly fuzzy — to avoid inviting a privacy storm — with the company writing it’s using “the same world-class anonymization technology that we use in our products every day,” as it puts it.
“For these reports, we use differential privacy, which adds artificial noise to our datasets enabling high quality results without identifying any individual person,” Google writes. “The insights are created with aggregated, anonymized sets of data from users who have turned on the Location History setting, which is off by default.”
“In Google Maps, we use aggregated, anonymized data showing how busy certain types of places are—helping identify when a local business tends to be the most crowded. We have heard from public health officials that this same type of aggregated, anonymized data could be helpful as they make critical decisions to combat COVID-19,” it adds, tacitly linking an existing offering in Google Maps to a coronavirus-busting cause.
The reports consist of per country, or per state, downloads (with 131 countries covered initially), further broken down into regions/counties — with Google offering an analysis of how community mobility has changed vs a baseline average before COVID-19 arrived to change everything.
So, for example, a March 29 report for the whole of the U.S. shows a 47 percent drop in retail and recreation activity vs the pre-CV period; a 22% drop in grocery & pharmacy; and a 19% drop in visits to parks and beaches, per Google’s data.
While the same date report for California shows a considerably greater drop in the latter (down 38% compared to the regional baseline); and slightly bigger decreases in both retail and recreation activity (down 50%) and grocery & pharmacy (-24%).
Google says it’s using “aggregated, anonymized data to chart movement trends over time by geography, across different high-level categories of places such as retail and recreation, groceries and pharmacies, parks, transit stations, workplaces, and residential.” The trends are displayed over several weeks, with the most recent information representing 48-to-72 hours prior, it adds.
The company says it’s not publishing the “absolute number of visits” as a privacy step, adding: “To protect people’s privacy, no personally identifiable information, like an individual’s location, contacts or movement, is made available at any point.”
Google’s location mobility report for Italy, which remains the European country hardest hit by the virus, illustrates the extent of the change from lockdown measures applied to the population — with retail & recreation dropping 94% vs Google’s baseline; grocery & pharmacy down 85%; and a 90% drop in trips to parks and beaches.
The same report shows an 87% drop in activity at transit stations; a 63% drop in activity at workplaces; and an increase of almost a quarter (24%) of activity in residential locations — as many Italians stay at home instead of commuting to work.
It’s a similar story in Spain — another country hard-hit by COVID-19. Though Google’s data for France suggests instructions to stay-at-home may not be being quite as keenly observed by its users there, with only an 18% increase in activity at residential locations and a 56% drop in activity at workplaces. (Perhaps because the pandemic has so far had a less severe impact on France, although numbers of confirmed cases and deaths continue to rise across the region.)
While policymakers have been scrambling for data and tools to inform their responses to COVID-19, privacy experts and civil liberties campaigners have rushed to voice concerns about the impacts of such data-fueled efforts on individual rights, while also querying the wider utility of some of this tracking.
And yes, the disclaimer is very broad. I’d say, this is largely a PR move.
Apart from this, Google must be held accountable for its many other secondary data uses. And Google/Alphabet is far too powerful, which must be addressed at several levels, soon. https://t.co/oksJgQAPAY
— Wolfie Christl (@WolfieChristl) April 3, 2020
Contacts tracing is another area where apps are fast being touted as a potential solution to get the West out of economically crushing population lockdowns — opening up the possibility of people’s mobile devices becoming a tool to enforce lockdowns, as has happened in China.
“Large-scale collection of personal data can quickly lead to mass surveillance,” is the succinct warning of a trio of academics from London’s Imperial College’s Computational Privacy Group, who have compiled their privacy concerns vis-a-vis COVID-19 contacts tracing apps into a set of eight questions app developers should be asking.
Discussing Google’s release of mobile location data for a COVID-19 cause, the head of the group, Yves-Alexandre de Montjoye, gave a general thumbs up to the steps it’s taken to shrink privacy risks. Although he also called for Google to provide more detail about the technical processes it’s using in order that external researchers can better assess the robustness of the claimed privacy protections. Such scrutiny is of pressing importance with so much coronavirus-related data grabbing going on right now, he argues.
“It is all aggregated; they normalize to a specific set of dates; they threshold when there are too few people and on top of this they add noise to make — according to them — the data differentially private. So from a pure anonymization perspective it’s good work,” de Montjoye told TechCrunch, discussing the technical side of Google’s release of location data. “Those are three of the big ‘levers’ that you can use to limit risk. And I think it’s well done.”
“But — especially in times like this when there’s a lot of people using data — I think what we would have liked is more details. There’s a lot of assumptions on thresholding, on how do you apply differential privacy, right?… What kind of assumptions are you making?” he added, querying how much noise Google is adding to the data, for example. “It would be good to have a bit more detail on how they applied [differential privacy]… Especially in times like this it is good to be… overly transparent.”
While Google’s mobility data release might appear to overlap in purpose with the Commission’s call for EU telco metadata for COVID-19 tracking, de Montjoye points out there are likely to be key differences based on the different data sources.
“It’s always a trade off between the two,” he says. “It’s basically telco data would probably be less fine-grained, because GPS is much more precise spatially and you might have more data points per person per day with GPS than what you get with mobile phone but on the other hand the carrier/telco data is much more representative — it’s not only smartphone, and it’s not only people who have latitude on, it’s everyone in the country, including non smartphone.”
There may be country specific questions that could be better addressed by working with a local carrier, he also suggested. (The Commission has said it’s intending to have one carrier per EU Member State providing anonymized and aggregated metadata.)
On the topical question of whether location data can ever be truly anonymized, de Montjoye — an expert in data reidentification — gave a “yes and no” response, arguing that original location data is “probably really, really hard to anonymize”.
“Can you process this data and make the aggregate results anonymous? Probably, probably, probably yes — it always depends. But then it also means that the original data exists… Then it’s mostly a question of the controls you have in place to ensure the process that leads to generating those aggregates does not contain privacy risks,” he added.
Perhaps a bigger question related to Google’s location data dump is around the issue of legal consent to be tracking people in the first place.
While the tech giant claims the data is based on opt-ins to location tracking the company was fined $57M by France’s data watchdog last year for a lack of transparency over how it uses people’s data.
Then, earlier this year, the Irish Data Protection Commission (DPC) — now the lead privacy regulator for Google in Europe — confirmed a formal probe of the company’s location tracking activity, following a 2018 complaint by EU consumers groups which accuses Google of using manipulative tactics in order to keep tracking web users’ locations for ad-targeting purposes.
“The issues raised within the concerns relate to the legality of Google’s processing of location data and the transparency surrounding that processing,” said the DPC in a statement in February, announcing the investigation.
The legal questions hanging over Google’s consent to track people likely explains the repeat references in its blog post to people choosing to opt in and having the ability to clear their Location History via settings. (“Users who have Location History turned on can choose to turn the setting off at any time from their Google Account, and can always delete Location History data directly from their Timeline,” it writes in one example.)
In addition to offering up coronavirus mobility porn reports — which Google specifies it will continue to do throughout the crisis — the company says it’s collaborating with “select epidemiologists working on COVID-19 with updates to an existing aggregate, anonymized dataset that can be used to better understand and forecast the pandemic.”
“Data of this type has helped researchers look into predicting epidemics, plan urban and transit infrastructure, and understand people’s mobility and responses to conflict and natural disasters,” it adds.
Powered by WPeMatico
Flagship Pioneering raises $1.1 billion to spend on sustainability and health-focused biotech
Flagship Pioneering, the Boston-based biotech incubator and holding company, said it has raised $1.1 billion for its Flagship Labs unit.
Flagship, which raised $1 billion back in 2019 for growth-stage investment vehicles, develops and operates startups that leverage biotechnology innovation to provide goods and services that improve human health and promote sustainable industries.
“We’re honored to have the strong support of our existing Limited Partners, as well as the interest from a select group of new Limited Partners, to support Flagship’s unique form of company origination during this time of unprecedented economic uncertainty,” said Noubar Afeyan, the founder and chief executive of Flagship Pioneering, in a statement.
In addition to its previous focus on health and sustainability, Flagship will use the new funds to focus on new medicines, artificial intelligence and “health security,” which the company says is “designed to create a range of products and therapies to improve societal health defenses by treating pre-disease states before they escalate,” according to Afeyan.
Flagship companies are already on the forefront of the healthcare industry’s efforts to stop the COVID-19 pandemic. Portfolio company Moderna is one of the companies leading efforts to develop a vaccine for the novel coronavirus which causes COVID-19.
In the 20 years since its launch, Flagship has 15 wholly owned companies and another 26 growth-stage companies among its portfolio of investments.
New companies include: Senda Biosciences, Generate Biomedicines, Tessera Therapeutics, Cellarity, Cygnal Therapeutics, Ring Therapeutics and Integral Health. Growth companies developed or backed by Flagship include Ohana Biosciences, Kintai Therapeutics and Repertoire Immune Medicines.
Two of the companies in the Flagship Labs portfolio have already had initial public offerings in the past two years, the company said. Kaleido Biosciences and Axcella Health raised public capital in 2019, and Moderna Therapeutics conducted a $575 million secondary offering earlier this year.
Powered by WPeMatico
Activity-monitoring startup Zensors repurposes its tech to help coronavirus response
Computer vision techniques used for commercial purposes are turning out to be valuable tools for monitoring people’s behavior during the present pandemic. Zensors, a startup that uses machine learning to track things like restaurant occupancy, lines and so on, is making its platform available for free to airports and other places desperate to take systematic measures against infection.
The company, founded two years ago but covered by TechCrunch in 2016, was among the early adopters of computer vision as a means to extract value from things like security camera feeds. It may seem obvious now that cameras covering a restaurant can and should count open tables and track that data over time, but a few years ago it wasn’t so easy to come up with or accomplish that.
Since then Zensors has built a suite of tools tailored to specific businesses and spaces, like airports, offices and retail environments. They can count open and occupied seats, spot trash, estimate lines and all that kind of thing. Coincidentally, this is exactly the kind of data that managers of these spaces are now very interested in watching closely given the present social distancing measures.
Zensors co-founder Anuraag Jain told Carnegie Mellon University — which the company was spun out of — that it had received a number of inquiries from the likes of airports regarding applying the technology to public health considerations.
Software that counts how many people are in line can be easily adapted to, for example, estimate how close people are standing and send an alert if too many people are congregating or passing through a small space.
“Rather than profiting off them, we thought we would give our help for free,” said Jain. And so, for the next two months at least, Zensors is providing its platform for free to “selected entities who are on the forefront of responding to this crisis, including our airport clients.”
The system has already been augmented to answer COVID-19-specific questions, like whether there are too many people in a given area, when a surface was last cleaned and whether cleaning should be expedited, and how many of a given group are wearing face masks.
Airports surely track some of this information already, but perhaps in a much less structured way. Using a system like this could be helpful for maintaining cleanliness and reducing risk, and no doubt Zensors hopes that having had a taste via what amounts to a free trial, some of these users will become paying clients. Interested parties should get in touch with Zensors via its usual contact page.
Powered by WPeMatico
Disney debuts its streaming service in India for $20 a year
Disney+ has arrived in the land of Bollywood. The company on Friday (local time) rolled out its eponymous streaming service in India through Hotstar, a popular on-demand video streamer it picked up as part of the Fox deal.
To court users in India, the largest open entertainment market in Asia, Disney is charging users 1,499 Indian rupees (about $19.5) for a year, the most affordable plan in any of the more than a dozen markets where Disney+ is currently available.
Subscribers of the revamped streaming service, now called Disney+ Hotstar, will get access to Disney Originals in English as well as several local languages, live sporting events, dozens of TV channels, and thousands of movies and shows, including some sourced from HBO, Showtime, ABC and Fox that maintain syndication partnerships with the Indian streaming service. It also maintains partnership with Hooq — at least for now.
Unlike Disney+’s offering in the U.S. and other markets, in India, the service does not support 4K and streams content at nearly a tenth of their bitrate.
Disney+ Hotstar is also offering a cheaper yearly premium tier, priced at Rs 399 (about $5.3), that will offer subscribers access to movies, shows (but not those sourced from aforementioned U.S. networks and studios) and live sporting events; it won’t include Disney Originals.
Access to streaming of sporting events, especially of cricket matches, has helped five-year-old Hotstar become the most popular on-demand video streaming in India. During the cricket tournament Indian Premier League (IPL) last year, the service amassed more than 300 million monthly active users and more than 100 million daily active users.
It also holds the global record for most simultaneous views on a live stream, about 25 million — more than thrice its nearest competitor.
Prior to today’s launch, Hotstar offered its premium plans at 999 Indian rupees, and 365 Indian rupees. Existing subscribers won’t be affected by the price revision for the duration of their current subscription.
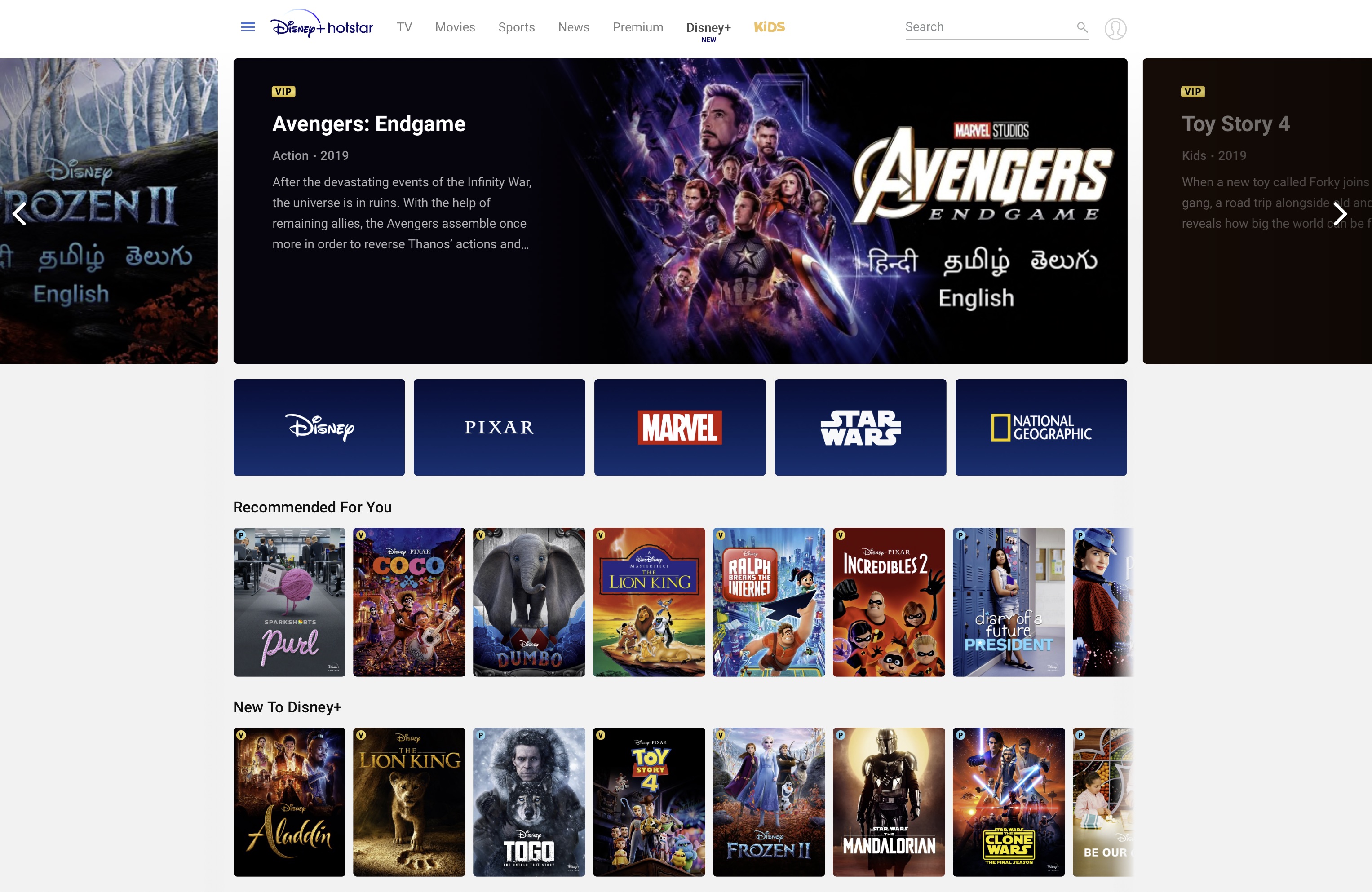
The service, run by Indian conglomerate Star India, offers access to about 80% of its catalog at no cost to users. The company monetizes these viewers through ads.
But in recent years, the company has begun to explore ways to turn its users into subscribers. Two years ago, Hotstar stopped offering cricket match streaming to non-paying users.
People familiar with the matter told TechCrunch that Hotstar has about 1.5 million paying subscribers, lower than what most industry firms estimate. But that figure is still higher than most of its competitors.
And there are many.
India’s on-demand video market
Disney+ will compete with more than three dozen international and local players in India, including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Times Internet’s MX Player (which has over 175 million monthly active users), Zee5, Apple TV+ and Alt Balaji, which has amassed over 27 million subscribers.
“The arrival of Disney+ in India is another case study in the globalization of entertainment in the digital era. For decades, the biggest companies in the world have expanded their reach into different markets. But it’s new, and actually quite profound, that everyone on earth receives the very same version of such a specific cultural product,” Matthew Ball, former head of strategic planning for Amazon Studios, told TechCrunch.
As in some other markets, including the U.S., streaming services have inked deals with telecom networks, TV vendors, cable TV operators and satellite TV players to extend their reach in India.
Most of these streaming services monetize their viewers by selling ads, and those who do charge have kept their premium plans below $3.
Why that figure? That’s the number most industry executives think — by spending years in the Indian market — that people in the country are willing to pay for viewing content. The average of how much an individual pays for cable TV, for instance, in India is also about $3.
“I think everyone is still trying to sort out the right pricing. It’s true the average Indian consumer is used to far lower prices and can’t afford more. However, we need to focus on the consumers likely to buy this, who have the requisite broadband access and income, etc,” said Ball.

Commuters drive along a road past a billboard in Mumbai advertising the Amazon Prime Video online series “The Forgotten Army”. (Photo by INDRANIL MUKHERJEE / AFP via Getty Images)
At stake is India’s booming on-demand video streaming market that, according to Boston Consulting Group, is estimated to grow to $5 billion from half a billion two years ago.
Hotstar’s hold on India could make it easier for Disney+, which has launched in more than a dozen markets and has amassed over 28 million subscribers.
As the country spends about two more weeks in lockdown that New Delhi ordered last month to curtail the spread of coronavirus, this could also compel many to give Disney+ a try.
On the flip side, if the lockdown is extended, the current season of IPL, which has been postponed until mid-April, might be further delayed or cancelled altogether. Either of those scenarios could hurt the reach of Hotstar, which sees a massive drop in its user base after the conclusion of each cricket tournament.
Disney initially planned to launch its streaming service in India on March 28, the day IPL was supposed to commence. But the company later postponed the launch by six days.
Industry executives told TechCrunch that if IPL is cancelled, it could severely hurt the financials of Hotstar, which clocks more than 50% of its revenue during the 50-odd days of the cricket season.
Some said Disney+’s premier catalog might not be relevant for most of Hotstar’s user base, who seem to care about this streaming service only during the cricket season or to catch up on Indian soap operas.
Hotstar has also received criticism for censoring more content on its platform than any other streaming service in India. Last month, Hotstar blocked from streaming on its platform an episode of “Last Week Tonight with John Oliver” that was critical of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi. YouTube made that segment available without any edits.
John Oliver slammed Hotstar for censoring the episode and noted that the streaming service had additionally edited out parts from his older episodes where he made fun of Disney. In 2017, Hotstar also edited out a segment from Oliver’s show in which he mocked Samsung for the Galaxy Note 7 fiasco. Hotstar and Samsung had a commercial partnership.
Hotstar did not respond to multiple requests for comment in 2017. Hotstar did not respond to multiple requests for comment on the recent controversy.
Powered by WPeMatico
Estimote launches wearables for workplace-level contact tracing for COVID-19
Bluetooth location beacon startup Estimote has adapted its technological expertise to develop a new product designed specifically for curbing the spread of COVID-19. The company created a new range of wearable devices that co-founder Steve Cheney believes can enhance workplace safety for those who have to be co-located at a physical workplace even while social distancing and physical isolation measures are in place.
The devices, called simply the “Proof of Health” wearables, aim to provide contact tracing — in other words, monitoring the potential spread of the coronavirus from person-to-person — at the level of a local workplace facility. The intention is to give employers a way to hopefully maintain a pulse on any possible transmission among their workforces and provide them with the ability to hopefully curtail any local spread before it becomes an outsized risk.
The hardware includes passive GPS location tracking, as well as proximity sensors powered by Bluetooth and ultra-wide-band radio connectivity, a rechargeable battery and built-in LTE. It also includes a manual control to change a wearer’s health status, recording states like certified health, symptomatic and verified infected. When a user updates their state to indicate possible or verified infection, that updates others they’ve been in contact with based on proximity and location-data history. This information is also stored in a health dashboard that provides detailed logs of possible contacts for centralized management. That’s designed for internal use within an organization for now, but Cheney tells me he’s working now to see if there might be a way to collaborate with WHO or other external health organizations to potentially leverage the information for tracing across enterprises and populations, too.
These are intended to come in a number of different form factors: the pebble-like version that exists today, which can be clipped to a lanyard for wearing and displaying around a person’s neck; a wrist-worn version with an integrated adjustable strap; and a card format that’s more compact for carrying and could work alongside traditional security badges often used for facility access control. The pebble-like design is already in production and 2,000 will be deployed now, with a plan to ramp production for as many as 10,000 more in the near future using the company’s Poland-based manufacturing resources.
Estimote has been building programmable sensor tech for enterprises for nearly a decade and has worked with large global companies, including Apple and Amazon . Cheney tells me that he quickly recognized the need for the application of this technology to the unique problems presented by the pandemic, but Estimote was already 18 months into developing it for other uses, including in hospitality industries for employee safety/panic button deployment.
“This stack has been in full production for 18 months,” he said via message. “We can program all wearables remotely (they’re LTE connected). Say a factory deploys this — we write an app to the wearable remotely. This is programmable IoT.
“Who knew the virus would require proof of health vis-a-vis location diagnostics tech,” he added.
Many have proposed technology-based solutions for contact tracing, including leveraging existing data gathered by smartphones and consumer applications to chart transmission. But those efforts also have considerable privacy implications, and require use of a smartphone — something Cheney says isn’t really viable for accurate workplace tracking in high-traffic environments. By creating a dedicated wearable, Cheney says that Estimote can help employers avoid doing something “invasive” with their workforce, since it’s instead tied to a fit-for-purpose device with data shared only with their employers, and it’s in a form factor they can remove and have some control over. Mobile devices also can’t do nearly as fine-grained tracking with indoor environments as dedicated hardware can manage, he says.
And contact tracing at this hyperlocal level won’t necessarily just provide employers with early warning signs for curbing the spread earlier and more thoroughly than they would otherwise. In fact, larger-scale contact tracing fed by sensor data could inform new and improved strategies for COVID-19 response.
“Typically, contact tracing relies on the memory of individuals, or some high-level assumptions (for example, the shift someone worked),” said Brianna Vechhio-Pagán of John Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Lab via a statement. “New technologies can now track interactions within a transmissible, or ~6-foot range, thus reducing the error introduced by other methods. By combining very dense contact tracing data from Bluetooth and UWB signals with information about infection status and symptoms, we may discover new and improved ways to keep patients and staff safe.”
With the ultimate duration of measures like physical distancing essentially up-in-the-air, and some predictions indicating they’ll continue for many months, even if they vary in terms of severity, solutions like Estimote’s could become essential to keeping essential services and businesses operating while also doing the utmost to protect the health and safety of the workers incurring those risks. More far-reaching measures might be needed, too, including general-public-connected, contact-tracing programs, and efforts like this one should help inform the design and development of those.
Powered by WPeMatico
IRL pivots into virtual event calendar In Remote Life
What do you do if you’re an event discovery startup and suddenly it’s illegal to attend events? You lean into the cultural shift and pivot. Today, $11 million-funded calendar app IRL is morphing from In Real Life to In Remote Life. It will now focus on helping people find, RSVP for, plan, share and chat about virtual events, from live-streamed concerts to esports tournaments to Zoom cocktail parties.
Coronavirus could make IRL relevant to a wider audience because before an event “only mattered if it was around you. But now with In Remote Life, content has no geographical limitations,” says IRL co-founder and CEO Abe Shafi. “The need is exponentially greater because everyone’s routines have been shattered.” IRL ranked No. 138 in the U.S. App Store today, making it the top calendar app, even above Google’s (No. 168).
Robinhood’s Josh Elman joins IRL
IRL has some fresh product development talent to lead it through the transition. The startup has hired stock trading app Robinhood’s VP of Product Josh Elman . The former Greylock investor is well known for his product chops from jobs at Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn. Elman joined Robinhood in early 2018 but left late last year, notably before its rash of recent outages that enraged users.
 “I just realized more than anything that the company needed people who had 110% to give, and it wasn’t clear that was going to be me,” Elman said of Robinhood, now valued at $7.6 billion and struggling to scale. “My first passions and all the things I’ve talked about over the years have been social and media.”
“I just realized more than anything that the company needed people who had 110% to give, and it wasn’t clear that was going to be me,” Elman said of Robinhood, now valued at $7.6 billion and struggling to scale. “My first passions and all the things I’ve talked about over the years have been social and media.”
For now, IRL is a part-time gig, where he’ll be heading up a Secret Projects division. While most apps “try to suck more of our time,” he sees IRL as a chance to give this precious resource back to people. Though he insists “Robinhood’s great, I’m a very happy shareholder.”
Events without borders
“We were on a tear, hitting a stride with usaging and growth related to real life events,” says Shafi. “Then this happened,” motioning on our Zoom call to the COVID-19 reality we’re now stuck in. “We realized we had to pull all of our content because it wasn’t happening.”
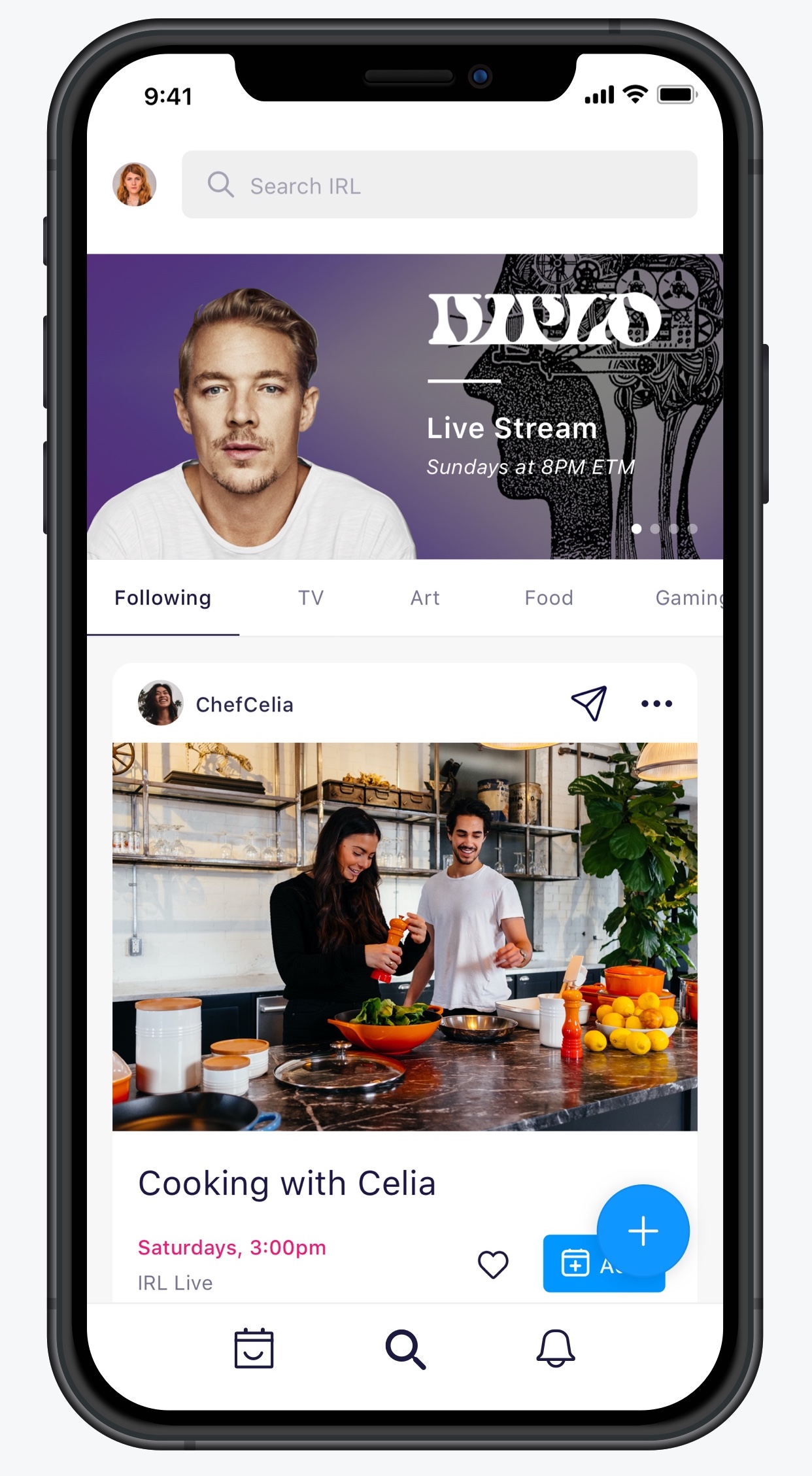 Today IRL’s iOS app launches a redesign of its Discover home screen content to center on virtual events people can attend from home. There’s now tabs for gaming, podcasts, TV and EDU, as well as music, food, lifestyle and a catch-all “fun” section. Each event can be added to your calendar that syncs with Google Cal, or Liked to add it to your profile that friends and fans can follow. You also can instantly launch a group chat about the event in IRL, or share it to Instagram Stories or another messaging app.
Today IRL’s iOS app launches a redesign of its Discover home screen content to center on virtual events people can attend from home. There’s now tabs for gaming, podcasts, TV and EDU, as well as music, food, lifestyle and a catch-all “fun” section. Each event can be added to your calendar that syncs with Google Cal, or Liked to add it to your profile that friends and fans can follow. You also can instantly launch a group chat about the event in IRL, or share it to Instagram Stories or another messaging app.
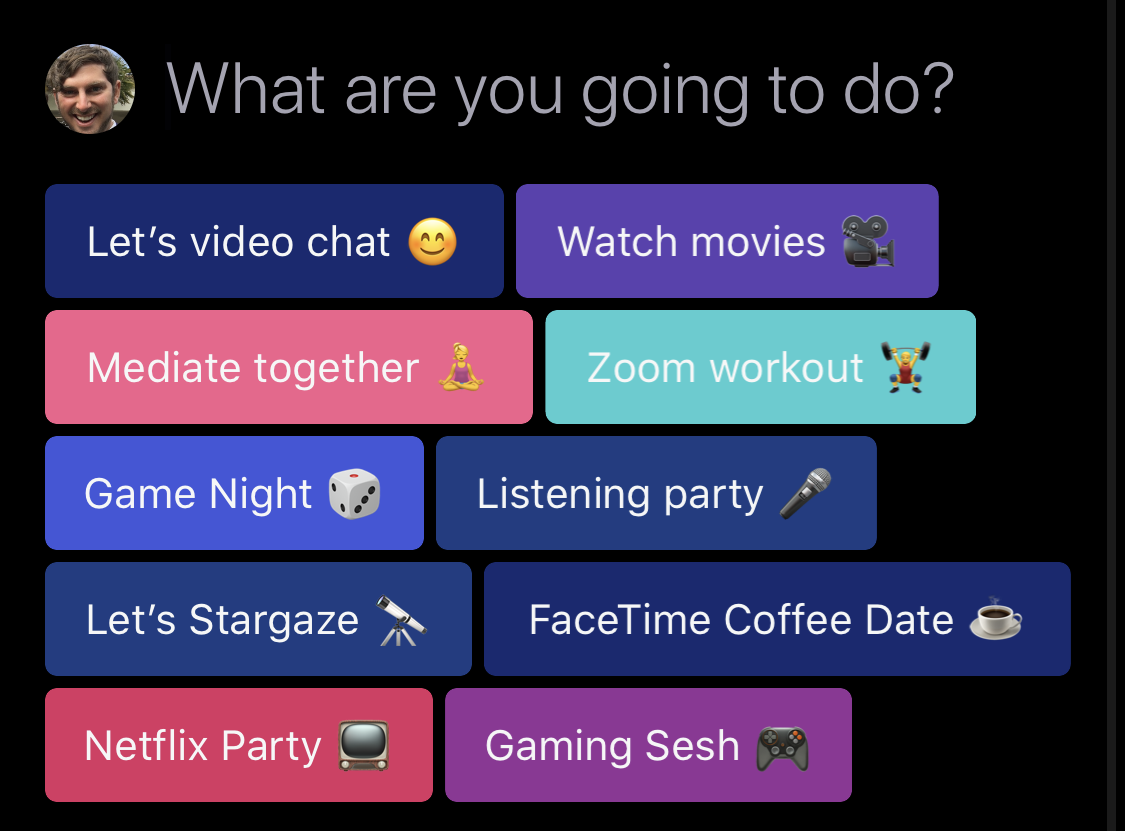
If you can’t find something public to do, you can make plans with friends using the composer with suggestions like “Let’s video chat,” “Zoom workout,” “gaming sesh” or “Netflix party.” That instantly sets up a calendar event you can invite people to. And if you’re not sure when you want to host, IRL’s “Soon” option lets you keep the schedule vague so you and friends can figure out when everyone’s available. Indeed, 50% of IRL plans start out as “Soon,” Shafi reveals, identifying a gap in rigid time/date calendars.
Beyond individual events, IRL also wants to make it easier to develop habits by letting you subscribe to workout, meditation and other schedules. With sports seasons suspended, IRL lets people sync with calendars of hip-hop album releases and more instead. Or you can subscribe to an influencer’s life and digitally accompany them to events. The goal is that IRL will be able to merge offline events back into its content recommendations as social distancing subsides.
The biggest challenge for IRL will be tuning its event recommendation algorithm. It has lost a lot of the traditional relevance signals about events, like how close they are to your home, how much they cost or if they’re even in your city. Transitioning to In Remote Life means a global range of happenings is now available to everyone, and because they’re often free to host, many lonely low-quality events have sprung up. That makes it much tougher for IRL to determine what to show.

For now, it’s basing recommendations on what you engage with most on its home screen, but I found that can make the initial experience very hit-or-miss. The top events in each category were rarely exciting. But IRL is planning to beef up its onboarding process to ask about your interests, and integrate with Spotify so it knows which musicians’ online concerts you’d want to attend.
Still, Shafi thinks IRL is already better than asocial alternatives. “Our main age range is 13 to 25, college and post-college metropolitan areas and across college campuses. Our average user has never used a calendar before, or they’ve just used a default calendar like Gcal or iCal.
A cure for loneliness
Hopefully, IRL will take a more serious swing at helping friends realize they’re free at the same time and can hang out. While Down To Lunch failed in this space, now Facebook Messenger and Instagram are exploring it with their auto-status feature, and location apps like Snap Map and Zenly could adapt to share not just where you are, but if you have the intention to hang out.
“How can we use just a little bit of nudging, transparency or suggestion to get people to just do one more thing per month?,” Shafi asks. IRL is trying to figure out how to let you passively share that “I have 2 hours free” in a way that “never makes you feel rejected if they don’t respond.”
Facebook did launch a standalone Events calendar app back in 2016, but later paired down the calendaring features, folded it in with restaurant recommendations and renamed it Local. “As big as Facebook is, it can only do so many things insanely well,” Elman says of his old employer. “They could do more [on Events], but it’s never been the juggernaut like photos.”
Shafi is happy to have the opportunity in such a foundational space. He describes the concept of the calendar as one he’s sure will outlive him, so it’s worth the effort to make it social no matter how long it takes — though I’m sure his investors like Goodwater Capital, Founders Fund, Kleiner Perkins and Floodgate hope it’ll find a way to monetize eventually.
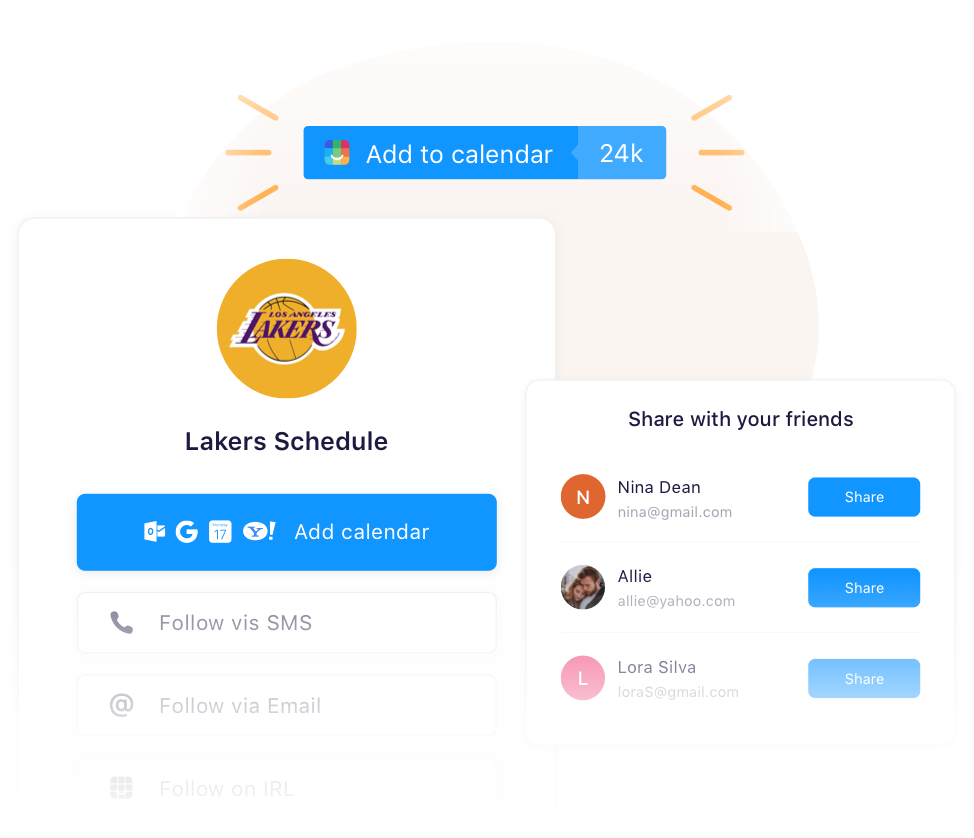
Revenue could come in the form of selling access to events through the app, or letting promoters and local businesses pay for enhanced discovery. For now, though, IRL is building a deeper connection with event and content publishers with the upcoming launch of its free Add To Calendar button they can build into their sites and emails. Elman says several services charge for these buttons that integrate with Apple and Google’s calendars, but IRL hopes giving them away will help fill its app with things to do, whatever that might be.
“Our tagline is ‘live your best life.’ It’s not judgmental. If your best life is playing video games on your couch with your homies, we don’t judge you for that.”
Powered by WPeMatico
T-Mobile customers on unlimited wireless family plans get a free year of Quibi
T-Mobile this morning officially announced its exclusive partnership with the new streaming service, Quibi, set to launch on April 6. The service will be made available for free for a year to T-Mobile customers on its unlimited wireless family plans.
The streaming service, founded by Hollywood media mogul Jeffrey Katzenberg, has been specifically built for on-the-go viewing on mobile devices. Its “shows” can be watched in 10 minutes or less and take advantage of the mobile device’s ability to be held different ways to enable seamless switching between portrait and landscape modes.
Thanks to Katzenberg’s industry connections, Quibi original content will feature A-Listers and other big names, including Jennifer Lopez, Chrissy Teigen, Chance the Rapper, Liam Hemsworth, Sophie Turner, Lena Waithe, Nicole Richie, Reese Witherspoon and others.
Typically, Quibi subscriptions are offered at $4.99 per month for its ad-supported plan or $7.99 per month for its ad-free option.
Quibi had confirmed last October that a deal with T-Mobile was in place, in statements made to various news outlets. But the details of the deal itself were not yet announced nor confirmed by T-Mobile at that time.
According to T-Mobile’s release, Magenta and ONE plans with taxes and fees included will be eligible for the free Quibi add-on, as will discounted First Responder, Military and Magenta Plus 55 plans, and small business customers with up to 12 lines.
T-Mobile customers can go to mytmobile.com now through July 7 to sign up, or they can use the T-Mobile Android or iOS app beginning on April 6 to add Quibi.
In addition, until April 3, T-Mobile customers who use the T-Mobile Tuesdays app for Android or iOS can get early access to three bonus episodes of the new Jennifer Lopez series “Thanks a Million” when it launches on April 6. That means customers will have a total of six episodes to watch at launch. And on April 7, five people who enter the T-Mobile Tuesdays sweepstakes will win a free Google Pixel 4 XL.
“T-Mobile customers have always been ahead of the curve – streaming more data, watching more mobile video – so when we first heard about Quibi, we knew our customers would love it,” said Mike Sievert, president and CEO of T-Mobile, in a statement. “And, with more of us staying home right now, Quibi’s never been more needed. It comes on the scene with a totally different experience, made for mobile, quick to watch and as entertaining as anything you’ve ever seen!”
Teaming up with a mobile carrier to gain traction among customers for a streaming service is a viable strategy. Disney+ did it with Verizon, which ultimately accounted for 20% of its early customers.
However, Quibi isn’t Disney — it’s not a known brand with pent-up consumer demand for a streaming service. What’s more, its initial marketing no longer makes sense in the post-COVID-19 era.
Quibi has had to reposition its service in the wake of the coronavirus outbreak as something that works for at-home viewing. But in reality, the service had been intended to fill those empty moments in your on-the-go lifestyle — like riding the subway, standing in line, sitting in a waiting room before an appointment and more. Now, with people stuck at home in government lockdowns and home quarantines, the minutes stretch out endlessly. There’s plenty of time to watch long-form content and the living room TV has more draw over the small phone screen.
But ultimately, Quibi’s success may not come down to its technology, tricks or episode length. It will come down the quality of its shows and their ability to capture an audience.
Powered by WPeMatico