“Happy to spend 10 minutes on our vision and the journey we’re on, but then, really, 15 minutes on what we’ve got today, what it is we’ve achieved, what it is our AI does,” says Tractable co-founder and CEO Alexandre Dalyac when I video called him a couple of weeks ago. “You can probably speed up all of that,” I quip back.
The resulting conversation, lasting well over an hour, spanned all of the above and more, including what is required to build a successful AI business and why he and his team think they can help prevent another “AI winter.”
Founded in 2014 by Dalyac, Adrien Cohen and Razvan Ranca after going through company builder Entrepreneur First, London-based Tractable is applying artificial intelligence to accident and disaster recovery. Specifically, through the use of deep learning to automate visual damage appraisal, and therefore help speed up insurance payouts and access to other types of financial aid.
Our AI has already been trained on tens of millions of these cases, so that’s a perfect case of us already having distilled thousands of people’s work experience Alexandre Dalyac
Dalyac launches into what is clearly a well-rehearsed and evidently polished pitch. “We are on a journey to help the world recover faster from accidents and disasters. Our belief is that when accidents and disasters hit, the response could be 10 times faster thanks to AI. So what we mean there is, everything from road accidents, burst piping to large-scale floods and hurricane. Whenever any of these things happen, things get damaged.”
Those things, he says, broadly break down into cars, homes and crops, roughly equating to $1 trillion in damage each year. But, perhaps more importantly, livelihoods get impacted.
“If a car gets damaged, mobility is reduced. If a home gets damaged, shelter is reduced. And if crops get damaged, food is reduced. Across all of those accidents and disasters, we’re talking hundreds of millions of lives affected.”
It is here where a little lateral (and non-artificial) thinking is required. Accident and disaster recovery starts with visual damage appraisal: look at the damage, say how much it’s going to cost, unlock the funds and rebuild. The problem (and Tractable’s opportunity) is that having an appraiser look at a car, house or field can take days to weeks depending on availability — and therefore so can accessing funds to start rebuilding — whereas the claim is that computer vision and AI technology can potentially do the same job in minutes.
“When you assess, that is basically a very powerful but very narrow visual task, which is, look at the damage, how much is it gonna cost? Today, as you can imagine, these kind of assessments are manual. And they take days to weeks. And so you instantly know that with AI that can be 10 times faster,” says Dalyac.
“In some sense this is a perfect class of AI tasks, because it’s very heavy on image classification. And image classification is a task where AI can surpass human performance as of this decade. If you have instant appraisal, that means faster recovery. Hence the mission.”
Dalyac says that part of Tractable’s secret sauce is in the many millions of proprietary labels the company has produced. This has been aided by its patented “interactive machine learning technology,” which allows it to label images faster and cheaper than typical labeling services.
The team’s focus to date has been to train its AI to understand car damage, technology it has already deployed in six countries, seeing the startup work primarily with insurers.
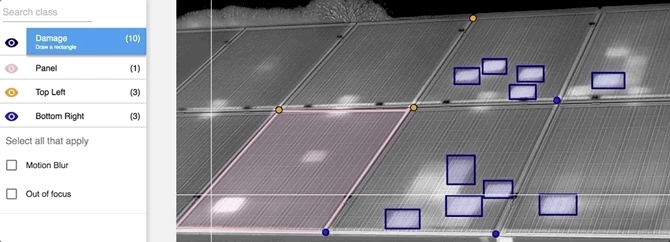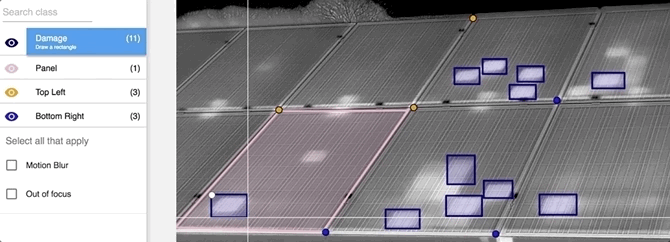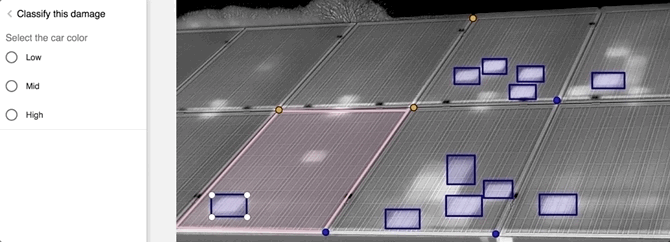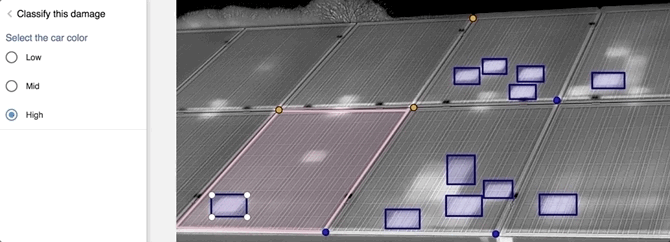
Related to this I’m shown a simple demo of Tractable’s car damage appraisal tool. Dalyac opens a folder of car images on his laptop and uploads them to the software. Within seconds, the AI has seemingly identified the different parts of the car and determined which parts can be repaired and which parts need to be entirely written-off and therefore replaced fully. Each has an AI-generated estimated cost.
It all happens within a matter of minutes, although I have no way of knowing how difficult the pre-determined and fully controlled task is. It’s also unclear how an AI can possibly do the full job of a human assessor based on a limited set of 2D images alone, and without the ability to peek under the hood or undertake further investigations.
“We’re trying to figure out how much damage there is to a vehicle based on photos,” explains Dalyac. “There’s some really tough correlations to pick out, which are: based on the photos of the outside, what’s the internal damage? When you’re a human you are going to have seen and torn down maybe about a thousand to two thousand cars in your whole life of 20 or 30 years of doing that. Our AI has already been trained on tens of millions of these cases, so that’s a perfect case of us already having distilled thousands of people’s work experience. That allows us to get hold of some very challenging correlations that humans just can’t do.”
You need to find real-world use cases that will make a difference, where you can surpass human performance Alexandre Dalyac
With that said, he does concede that a photo doesn’t always contain all of the necessary information, and that it might only have a certain level of accuracy. “You might need to then get a tear-down of the car and get photos of the internal damage. You might even want to get some data from the dashboard. And you can think that as cars get more sensors… the appraisal will be not just visual but also based on IoT data. But that doesn’t detract from the fact that we are convinced that it will be AI that will be doing this entirely.”
What is abundantly clear is Dalyac’s commitment to developing AI technology with real-world use that is commercially viable. If that doesn’t happen, he believes it won’t just be Tractable that will suffer, but the continued belief and investment in AI as a whole. Here, of course, he’s talking about the prospect of another so-called “AI winter,” citing a recent Crunchbase report that says funding for artificial intelligence companies in the U.S. has levelled off and even started to decline at seed stage.
“If you’re trying to make the $15 billion that has been invested into AI not fuck up and lead to something successful that will prevent an AI winter that will lead to continuous improvement, you need a really good return on that asset class. And for that you need those businesses to be successful.
“To make an AI company successful, really successful — not just an acqui-hire, not just an IP exit but a real commercial success that’s going to prevent an AI winter — you need to find real-world use cases that will make a difference, where you can surpass human performance, where you can change the way things work,” he says.
The reference to acqui-hire or IP exit takes on more meaning when you consider that Tractable was in the same cohort at Entrepreneur First as Magic Pony Technology, the AI startup acquired by Twitter for up to $150 million for its image enhancing technology. And most recently, the team behind Bloomsbury AI, another EF company, was acqui-hired by Facebook for $20-30 million.
To ensure that Tractable can continue its mission of applying AI to accident and disaster recovery — and presumably not sell too early — the startup has closed $20 million in Series B investment in a round led by U.S. venture capital firm Insight Venture Partners. Existing investors, including Ignition Partners, Zetta Venture Partners, Acequia Capital and Plug and Play Ventures, also participated. The new capital is to be spent on accelerating growth, expanding its research and development and entering new markets.
(The Series B also included an additional $5 million in secondary funding, seeing some investors at least partially exit. I understand Tractable’s founders sold a relatively small number of shares as they were permitted to take money off the table. Dalyac declined to comment.)
As we wrap up our call, I note that all of Tractable’s main investors, not including EF, are from the U.S. — something Dalyac says was a deliberate decision after he discovered the gulf between European and U.S. valuations.
“That’s a shame, isn’t it?” I say with my European tech ecosystem hat on.
“It isn’t; it’s enormous exports for the U.K.,” says the Tractable CEO who is French-born but raised in the U.K. “We have, as of today, the vast majority of our headcount in London. The entire product team is in London. The entire R&D team is in London. But most of the revenue comes from the United States. We are making AI an export industry of the U.K.”

Powered by WPeMatico




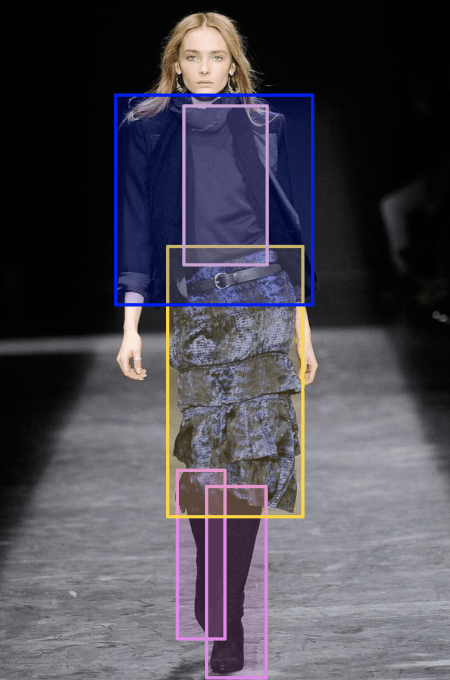 Long-term, the risk for Labelbox is that it’s arrived too early for the AI revolution. Most potential corporate customers are still in the R&D phase around AI, not at scaled deployment into real-world products. The big business isn’t selling the labeling software. That’s just the start. Labelbox wants to continuously manage the fine-tuning data to help optimize an algorithm through its entire life cycle. That requires AI being part of the actual engineering process. Right now it’s often stuck as an experiment in the lab. “We’re not concerned about our ability to build the tool to do that. Our concern is ‘will the industry get there fast enough?’” Ferreiras declares.
Long-term, the risk for Labelbox is that it’s arrived too early for the AI revolution. Most potential corporate customers are still in the R&D phase around AI, not at scaled deployment into real-world products. The big business isn’t selling the labeling software. That’s just the start. Labelbox wants to continuously manage the fine-tuning data to help optimize an algorithm through its entire life cycle. That requires AI being part of the actual engineering process. Right now it’s often stuck as an experiment in the lab. “We’re not concerned about our ability to build the tool to do that. Our concern is ‘will the industry get there fast enough?’” Ferreiras declares.